Abstract
Background
As compared to other regions of the world, Sub Saharan Africa (SSA) is the region with the highest neonatal mortality and is the region showing the least progress in the reduction of newborn death. Despite better progress made in reducing neonatal mortality, Ethiopia contributes the highest rate of neonatal death in Africa. In Ethiopia, findings from few studies were inconsistent and there is a need to systematically pool existing data to determine the impact of antenatal care on neonatal mortality among mother-neonate pairs in Ethiopia.
Methods
Published articles from various electronic databases such as Medline, Hinari, Pub Med, Cochrane library, the Web of Science, and Google Scholar were accessed. Also, unpublished studies from library catalogs were identified. All observational studies that were conducted on the association between antenatal care follow-up and neonatal mortality among neonates in Ethiopia were included. Data were extracted on the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet and analyzed using STATA 14.1 version. A random-effects model was used to estimate the pooled estimate with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Forest plots were used to visualize the presence of heterogeneity and estimate the pooled impact on antenatal care on neonatal mortality. The presence of publication bias was assessed by funnel plots and Egger’s statistical tests.
Results
Initially, a total of 345 studies were accessed. Finally, 28 full-text studies were reviewed and fourteen studies fulfilled inclusion criteria and included in the final meta-analysis. The overall pooled estimate indicates the odds of neonatal death among neonates from women with antenatal care were 65% lower than those neonates from women who had no antenatal care follow-up (OR: 0.35, 95% CI: 0.24, 0.51).
Conclusions
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, lack of ANC follow-up increase the probability of neonatal mortality as compared to having ANC follow-up. Thus, we will recommend for more coverages of appropriate antenatal care where risk groups can best be identified and managed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Globally in 2017, under-five mortality accounted 5.4 million deaths and an estimated 2.5 million deaths of under-five occur among newborns [1, 2]. Neonatal death contributes nearly 45% of under-five mortality, and the rate of death among newborn is higher than that of under-five death [3]. Worldwide in 2017, the neonatal mortality rate (NMRs) was 18 deaths per 1000 live births [4], with an estimated 1 million death happen on the first day and close to 1 million death within the first week of birth. Moreover, each year, around 1 million newborns develop long-term disability, including cerebral palsy and cognitive delays [2].
Neonatal period is the first 28 days of life, and is the time in which the child is most vulnerable to death, at a global rate of 19 deaths per 1000 live births. The NMR is an indicator of newborn care and directly reflects prenatal, intrapartum, and neonatal care [5]. The highest number of NMRs death occurred in Southern Asia and SSA with 39 and 38%, respectively [6]. From the top 10 countries contributing to NMRs, eight countries are from SSA and this region is the region with the highest child mortality rate in the world [2, 7]. In SSA, NMR ranges from 24 to 31 deaths per 1000 live births which is higher as compared to other regions of the world [2].
Reducing neonatal mortality is an essential part of the third Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) and is targeted to reduce the neonatal mortality rate to 12 or less per 1000 live births by 2030 [4]. Congruent to this, the government of Ethiopia aimed to end all preventable newborn diseases and developed a roadmap to drop under-five mortality rate to less than 20/1000 live births by 2035 [8]. In spite of all these plans and activities, neonatal mortality is still one of the great problems of this globe, with 18,000 under five and 7000 newborns dying every day, most of them from preventable causes [2].
Ethiopia is one of the top five countries contributes for half of neonatal mortality worldwide [6]. According to UNICEF 2018 report, NMRs in Ethiopia were 28 deaths per 1000 live births and are one of the top ten countries affected by NMR globally [2]. Mortality rates among under five children are a key output indicator for child health and survival, and, more broadly, for social and economic development. The neonatal mortality is a public health indicator that reflects the access of children and communities to basic health interventions such as vaccination, medical treatment of infectious diseases and adequate nutrition. The government of Ethiopia developed a National Newborn and Child Survival Strategy in 2014 which aimed to decrease NMR from 28/1000 live births in 2013 to 11/ 1000 live births in 2020 [8]. Even though the government of Ethiopia planned to decrease NMR by greater than half in 2020, still the NMR is at an alarming stage. According to mini EDHS 2019, the NMR in Ethiopia is 30 per 1000 live births [9] and preterm birth complications 26%, Intrapartum related events 30%, Sepsis/tetanus 18%, congenital abnormalities 11%, and pneumonia 8% are the leading causes for neonatal mortality [10]. In addition, factors such as lack of ANC follow-up [11, 12], Cesarian section [11], premature rupture of membrane [11, 13], Induced labor [13, 14], prolonged labor [14], lack of early initiation of EBF [14], being rural residence [13, 15, 16], poor wealth index [15, 16] and multiple birth [13, 16]. Despite lack ANC follow-up increase the occurrence of neonatal mortality, finding from developing countries presented inconclusive findings [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30], which need meta-analysis Assessing the impact of ANC follow-up on neonatal mortality is important for addressing neonatal related problems and designing appropriate intervention which used to reduce neonatal mortality, particularly in resource-limited settings such as Ethiopia. Therefore, the objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to estimates the pooled impact of ANC on neonatal mortality among neonates in Ethiopia. The implications of the findings of our study are for national policymakers, program managers, and non-governmental organizations to reduce mortality among newborns in low-resource settings.
Methods
Search strategy
This systemic review and meta-analysis were conducted to assess the impact of antenatal care on neonatal mortality in Ethiopia. The existence of similar systematic reviews and meta-analysis which have been published on this topic was checked to prevent repetitions. Both published and unpublished studies were searched thoroughly using electronic databases such as Medline, Hinari, PubMed, Cochrane library, the Web of Science and Google Scholar using the key terms “ Antenatal care, Neonatal mortality, Neonatal outcomes, Obstetric care, Ethiopia”.
To find unpublished papers, some research centers, such as Addis Ababa University Digital Library and African digital library were searched. The search was conducted from November 1 to December 15, 2019. Pre-defined search terms were used to enable a comprehensive search strategy that included all the relevant studies. All fields within records and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) were used to expand the search in advanced Pub Med search. The search strategy was prepared and modified for the various databases using important Boolean operators with initial keywords (“Neonatal mortality” OR “neonatal death” OR “neonatal outcomes” AND “antenatal care” OR “obstetric care” AND “Ethiopia”). The meta-analysis was reported using Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.
Selection and eligibility criteria
This systematic review included studies that were conducted on neonatal mortality and its association with antenatal care in Ethiopia. Study participants were all mother-neonates and cross sectional-studies, case-control, and cohort studies (both prospective and retrospective) which reported the association between ANC and neonatal mortality in Ethiopia was considered in this review. The included studies were written in the English language which was published in different journals and master’s thesis. We excluded articles that were found as abstract only since it was difficult to access all essential information required for the analysis. We tried to contact the primary authors of the articles with incomplete information and we excluded articles that were not accessible after contacting the principal investigator two times by email.
Outcome measurement
The outcome of this systematic review and meta-analysis was the association between ANC follow-up and neonatal mortality. Neonatal mortality is death of the infant before 28 completed days. For the outcome variable, data were extracted in a format of two by two tables, and then the log OR was calculated based on the findings of the original studies. The systematic review and meta-analysis used the PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcomes) framework to assess the eligibility of the articles included. The study population (P) was all neonates in Ethiopia, the Intervention (I) was lack of ANC follow-up, the Comparison (C) was having greater than one ANC and the Outcomes (O) of the interest was neonatal death.
Quality assessment and data extraction
The Joanna Briggs Institute Meta-Analysis of Statistics Assessment and Review Instrument (JBI-MAStARI) was used for critical appraisal. Initially, the reference management software (Endnote version X7) was used to combine database search results and to remove duplicate articles manually. Data were extracted by two data extractors using a standardized data extraction checklist. Then, studies excluded after a thorough assessment of their titles and abstracts. Full-text articles were evaluated for the remaining literature. Based on the pre-stated inclusion and exclusion criteria, eligibility of the studies was assessed. The checklist for data extraction contains the name of authors, publication year, region (the area where the study was conducted), study design, sample size, response rate and participants with the outcome (Table 1). Two reviewers (TT and BM) extracted the data using a standardized data extraction checklist on Microsoft excel. Discrepancies between two independent reviewers were reached on consensus by involving a third reviewer (DB).
Statistical analysis and synthesis
Data were extracted in Microsoft Excel format and imported to STATA version 14 statistical software for analysis. The logarithm and standard error of the odds ratio (OR) for each included study were generated using the “generate” command. Cochran’s Q test (reported as p-value) and inverse variance index (I2) were used to check the presence of heterogeneity among the included studies. A high degree of heterogeneity was observed hence a random effect model was used for analysis to estimate the pooled impact of ANC on neonatal mortality. In addition, we conducted Meta-regression to identify the source of heterogeneity by using sample size and year of publication. A funnel plot of asymmetry was used to check the presence of publication bias. Furthermore, Egger and Begg’s statistical test was used to check the statistical significance of publication bias. Subgroup analyses by region (Addis Ababa (AA), Somali, Oromia, Ethiopia demographic health survey (EDHS), Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples’ (SNNP), Amhara, Benishangul Gumuz) and study setting (community, facility based) of the included studies were carried out. The odds ratio of the association between ANC and neonatal mortality in the form of forest plot was reported.
Results
Search result
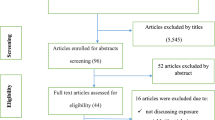
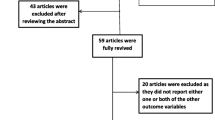
In the first step of our search, 345 studies were identified on neonatal mortality in Ethiopia through various electronic databases and library catalogs. Of these, 92 studies were excluded due to duplicates. From the remaining 253 studies, 225 articles were screened after reviewing their titles and abstracts based on the assessment as non-relevance to this study. The remaining 28 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility and 14 articles were excluded due to pre-determined eligibility criteria. Finally, 14 articles fulfilled the eligibility criteria and included in systematic review and meta-analysis (Fig. 1).
Features of included studies
As shown below in Table 1, in the present meta-analysis 23,932 neonates were involved in the studies to estimates the pooled impact of antenatal care on neonatal mortality. All of the 14 articles included in this study were published from 1997 to 2019. Thirteen of the included studies were published in peer-reviewed journals and one study was an unpublished as a master’s thesis at Addis Ababa University [24]. Regarding study design, five of the studies are retrospective cohort study design [17, 18, 21, 24, 25], three are case-control [22, 26, 29], three cross-sectional study design [20, 28, 30] and one study is prospective cohort study design [23]. The sample size of the studies ranging from 219 to 8651. Of the fourteen studies, four studies were conducted in Oromia region [18, 25,26,27], Three from Addis Ababa [17, 24, 30], three from SNNP [20, 21, 29], One from Amhara region [22], One from Somali region [23], one from Benishangul region [19], and one study from EDHS data [28]. However, there were no studies reported from Gambella, Afar and Tigrai region (Table 1).
Impact of ANC follow-up on neonatal mortality
The findings of single studies were inconsistent and inconclusive with the association between neonatal mortality and antenatal care which found to be significant in some studies and insignificant other. Of those studies that found a significant association between ANC and neonatal mortality, the strongest negative association was observed in the study conducted in the SNNP region, with an odds ratio of 0.05 (95% CI, 0.02, 0.11) [29].
In this study, the pooled odds ratio indicated that antenatal care was negatively associated with neonatal mortality (OR: 0.35, 95% CI: 0.24, 0.51). High heterogeneity (I2 = 90.9% and p-value < 0.001) was observed across the included studies; hence, a random-effects meta-analysis model was used to examine the association between ANC and neonatal care (Fig. 2). To identify the possible sources of heterogeneity, meta-regression was computed by busing sample size and year of publication but none of these variables were found to be statistically significant (Table 2). To see for the presence of publication bias, the graphical funnel plot (Fig. 3) and Egger’s test at 5% significance level were executed. The traditional funnel plot showed it to be asymmetric for publication bias. In addition, Egger’s test showed statistically significant for the presence of publication bias (p = 0.033).
To reduce and adjust the publication bias in the studies, the trim and fill analysis was performed for estimation of the number of missing studies that might exist (Supplementary material 1). Trim and fill analysis is a nonparametric methods for estimating the number of missing studies that might exist and it helps in reducing and adjusting publication bias in meta-analysis. In trim and fill analysis, there was no studies imputed for missing studies and after adjustment for publication bias, the estimated pooled impact of ANC on neonatal mortality was the same with the main result of meta-analysis 0.35 (95% CI, 0.24, 0.51) (Fig. 4).
Subgroup analysis
We performed subgroup analysis based on the regions where the studies were conducted and study setting. Accordingly, subgroup analysis conducted by the region where the studies were conducted to reduce the possible random disparity between studies. The finding showed the strongest association between ANC and neonatal mortality was found in the study conducted in the SNNP region than other regions. The odds of neonatal mortality among women who had ANC follow-up was 89% lower compared to women who had no ANC follow-up in study conducted in the SNNP region (OR: 0.11, 95% CI: 0.06–0.19) (Fig. 5).
Moreover, subgroup analysis was conducted by study setting to minimize potential random variation between studies. Accordingly, the association between ANC and neonatal mortality were stronger in studies conducted at institutional setting than community-based study, in which the odds of neonatal mortality among women who had ANC follow-up was 72% lower compared to women who had no ANC follow-up in study conducted at institutions (OR: 0.28, 95% CI: 0.17, 0.48) (Fig. 6).
Discussion
Obstetric care is a single most important determinant for the outcome of pregnancy of which antenatal care is recognized as an effective method of preventing adverse outcomes in mothers as well as their neonates. The current systematic review and meta-analysis, therefore, was conducted to assess the pooled association between antenatal care and neonatal mortality in Ethiopia. This systematic review and meta-analysis indicated the impact of ANC follow-up on neonatal mortality has a statistically significant negative association. Having ANC follow-up decrease the odds of neonatal mortality as compared to lack of ANC follow-up. Therefore, frequent and timely ANC follow-up is very important obstetric care to reduce neonatal mortality particularly, in low and middle-income countries.
The finding this systematic review and meta-analysis were similar to a study conducted in Kenya [31] where having ANC follow-up was found to have a significant (negative) effect on the likelihood of neonatal mortality. The finding is also in line with the study conducted in Sub-Saharan Africa countries [32] which indicated that prenatal care with skilled providers decreases the risk of neonatal mortality. Similarly, studies conducted in Nigeria [33], Zimbabwe [34] India [35] Afghanistan [36] and Brazil [37] also reported that ANC has a significant effect on the reduction of neonatal mortality. A previously conducted meta-analysis [38] reported a strong negative association of perinatal mortality with a lack of antenatal care.
This is because women who received ANC services which include a pregnancy checkup, provision health promotion, and disease prevention activities such as supplementation of iron/folic acid, tetanus toxoid vaccination, health education and counseling by a skilled health care provider. These services are crucial for the survival of the newborn and neonates as well.
Moreover, studies conducted in Bangladesh [39], Indonesia [40] and United Kingdom [41] revealed that the number of ANC visits determines perinatal and/ or outcomes which mean that as the number of visit increases, the probability of perinatal/ neonatal mortality decreases significantly. This is because as pregnant women come to health facilities frequently, they can access quality obstetric care in each visit. This is important to detect any deviation from normality so that problems are detected early and appropriate measures could be taken promptly.
The current review also performed subgroup analysis to identify the heterogenic characteristics of the included studies. A subgroup analysis was conducted by regions of the country. Accordingly, a higher association between ANC and neonatal mortality was observed among studies conducted in SNNP than in other regions. This could be because of social, economic, and cultural differences between regions where studies were conducted. A subgroup analysis by study setting indicated a strong association was observed in institutional studies than community-based studies which are probably the difference in the characteristics of study participants of the included studies.
This study has its own implication for future researchers. It guides researchers to conduct large scale and follow-up study from primary data to see the relationship between ANC follow-up and neonatal mortality by including other potential factors which contribute for neonatal mortality.
Strengths and limitations of the study
This review has several strengths including; this review focus on the most important determinant of neonatal mortality which is ANC, essential care during pregnancy. Moreover, we used comprehensive search strategies and PRISMA checklist to improve the quality of the review. Whereas, this review has limitations such as the review included studies that were published only in the English language. Also, the other limitation of this review is that the protocol of this manuscript was not registered prospectively.
Conclusions
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, the absence of antenatal care booking positive impact on neonatal mortality which might be due to a lack of prevention of most other preventable factors during pregnancy. Intervention that focus on educating mothers on the importance of antenatal visits, as well as ensuring screening, detection, monitoring, and management of maternal conditions during the pregnancy, could help to reduce NMR. Provision of the continuum of care from pregnancy through delivery to the post neonatal period should be provided so as to decrease neonatal mortality. In addition, since the finding is heterogeneous across the regions of the country, culture- and context-specific maternal health education needs to be encouraged.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ANC:
-
Antenatal care
- CI:
-
Confidence Interval
- SSA:
-
Sub Saharan Africa
- SDG:
-
Sustainable Development Goals
- OR:
-
Odd Ratio
- SNNP:
-
Southern Nation Nationalities and People
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
WHO and UNICEF. Levels & trends in child mortality: Report 2017. UNICEF, WHO, the World Bank, United Nations population division. New York: UNICEF on behalf of the UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation; 2017.
Darroch JE, Sully E, Biddlecom A. Adding it up: investing in contraception and maternal and newborn health, 2017—supplementary tables. New York: The Guttmacher Institute; 2017.
World Health Organization. “Survive and thrive: transforming care for every small and sick newborn.” (2019).
Tekelab T, Akibu M, Tagesse N, Tilhaun T, Yohanes Y, Nepal S. Neonatal mortality in Ethiopia: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-019-1012-x.
Rosati F, Faria LG. Addressing the SDGs in sustainability reports: the relationship with institutional factors. J Clean Prod. 2019;215:1312–26.
Wright S. Ending newborn deaths: ensuring every baby survives. Save the Children; 2014.
Hug L, Alexander M, You D, Alkema L, for Child UI. National, regional, and global levels and trends in neonatal mortality between 1990 and 2017, with scenario-based projections to 2030: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(6):e710–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30163-9.
Federal Ministry of Health (FMoH). National Strategy for Newborn and Child Survival in Ethiopia: 2015/16–2019/20. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia; 2015. Available at: https://www.healthynewbornnetwork.org/hnn-content/uploads/nationalstrategy-for-newborn-and-child-survival-inethiopia-201516-201920.pdf. Accessed on 20 Dec 2019.
Ethiopian Public Health Institute. Ethiopia mini demographic and health survey 2019: key indicators. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia; 2019. Available at: https://www.ephi.gov.et/images/Mini-Demographic-and-Health-Survey-Key-Indicators-2019.pdf. (Accessed on 15 Dec 2019).
(WHO), W.H.O., Estimates generated by the WHO and Maternal and Child Epidemiology Estimation Group (MCEE) 2018 and downloaded from http://data.unicef.org. 2018.
Mersha A, Bante A, Shibiru S. Factors associated with neonatal near-miss in selected hospitals of Gamo and Gofa zones, southern Ethiopia: nested case-control study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-019-2684-x.
Bayou G, Berhan Y. Perinatal mortality and associated risk factors: a case control study. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2012;22(3):153–62 PMCID: PMC3511893. PMID: 23209349.
Adhena T, Haftu A, Gebre G, Dimtsu B. Assessment of magnitude and associated factors of adverse birth outcomes among deliveries at Suhul hospital Shire Tigray, Ethiopia from September, 2015 to February, 2016. Res Rev. 2019;6(1):1.
Samuel D, Zinabu D, Alemu B. Magnitude of neonatal mortality and associated factors among neonates at Arba Minch general hospital. Asploro J Pediatr Child Health. 2019;2019(1):20.
Mekonnen Y, Tensou B, Telake DS, Degefie T, Bekele A. Neonatal mortality in Ethiopia: trends and determinants. BMC Public Health. 2013;13(1):483. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-483.
Hibstu DT, Ayele TA, Mengesha ZB. Determinants of neonatal mortality in Ethiopia: a case control study, 2013. Open Access Library J. 2014;1(06):1. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1100880.
Worku B, Kassie A, Mekasha A, Tilahun B, Worku A. Predictors of early neonatal mortality at a neonatal intensive care unit of a specialized referral teaching hospital in Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2012;26(3):200–7.
Debelew GT, Afework MF, Yalew AW. Determinants and causes of neonatal mortality in Jimma zone, southwest Ethiopia: a multilevel analysis of prospective follow-up study. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e107184. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107184.
Kidus F, Woldemichael K, Hiko D. Predictors of neonatal mortality in Assosa zone, Western Ethiopia: a matched case control study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):108.
Mihiretu A, Negash T, Elazar T. Perinatal death and associated factors in Wolaita Sodo referral hospital, southern Ethiopia: a facility based cross-sectional study. Primary Health Care. 2017;7(2):1–5.
Orsido TT, Asseffa NA, Berheto TM. Predictors of neonatal mortality in neonatal intensive care unit at referral Hospital in Southern Ethiopia: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19(1):83.
Kolola T, Ekubay M, Tesfa E, Morka W. Determinants of neonatal mortality in north Shoa zone, Amhara regional state, Ethiopia. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0164472. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164472.
Elmi Farah A, Abbas AH, Tahir AA. Trends of admission and predictors of neonatal mortality: A hospital based retrospective cohort study in Somali region of Ethiopia. PLoS One. 2018;13(9):e0203314. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203314.
Asmare Y. Survival status and predictor of mortality among premature neonate admitted to neonatal intensive care unit from 2013–2017 in Tikur Anbesa specialized hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2018, in Nursing. Addis Ababa: Addis Ababa University; 2018. p. 70.
Roro EM, Tumtu MI, Gebre DS. Predictors, causes, and trends of neonatal mortality at Nekemte Referral Hospital, east Wollega Zone, western Ethiopia (2010–2014). Retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0221513. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221513.
Roro EM, Sisay MM, Sibley LM. Determinants of perinatal mortality among cohorts of pregnant women in three districts of North Showa zone, Oromia Region, Ethiopia: Community based nested case control study. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):888. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5757-2.
Kolobo HA, Chaka TE, Kassa RT. Determinants of neonatal mortality among newborns admitted to neonatal intensive care unit Adama, Ethiopia: a case–control study. J Clin Neonatol. 2019;8(4):232.
Wakgari N, Wencheko E. Risk factors of neonatal mortality in Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2013;27(3):192–9.
Tesfaye S, Gebru Z, Mamo M, Getahun F, Boti N. Determinants of Perinatal Mortality in Arba Minch General Hospital, Gamo Zone, Southern Ethiopia. Ethiopian J Reprod Health. 2019;11(4):7.
Sahle-Mariam Y, Berhane Y. Neonatal mortality among hospital delivered babies in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiopian J Health Dev (EJHD). 1997;11(3).
Arunda M, Emmelin A, Asamoah BO. Effectiveness of antenatal care services in reducing neonatal mortality in Kenya: analysis of national survey data. Glob Health Action. 2017;10(1):1328796. https://doi.org/10.1080/16549716.2017.1328796.
McCURDY RJ, Kjerulff KH, Zhu J. Prenatal care associated with reduction of neonatal mortality in sub-Saharan Africa: evidence from demographic and health surveys. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011;90(7):779–90.
Owolabi AT, Fatusi AO, Kuti O, Adeyemi A, Faturoti SO, Obiajuwa PO. Maternal complications and perinatal outcomes in booked and unbooked Nigerian mothers. Singap Med J. 2008;49(7):526.
Tachiweyika E, Gombe N, Shambira G, Chadambuka A, Tshimamga M, Zizhou S. Determinants of perinatal mortality in Marondera district, Mashonaland East Province of Zimbabwe, 2009: a case control study. Pan Afr Med J. 2011;8(1). https://doi.org/10.4314/pamj.v8i1.710.
Singh A, Pallikadavath S, Ram F, Alagarajan M. Do antenatal care interventions improve neonatal survival in India? Health Policy Plan. 2014;29(7):842–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czt066.
Al Kibria GM, Burrowes V, Choudhury A, Sharmeen A, Ghosh S, Mahmud A, Angela KC. Determinants of early neonatal mortality in Afghanistan: an analysis of the demographic and health survey 2015. Glob Health. 2018;14(1):47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-018-0363-8.
Kassar SB, Melo AM, Coutinho SB, Lima MC, Lira PI. Determinants of neonatal death with emphasis on health care during pregnancy, childbirth and reproductive history. J Pediatr. 2013;89(3):269–77.
Berhan Y, Berhan A. Meta-analysis of selected maternal and fetal factors for perinatal mortality. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2014;24:55–68. https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v24i0.6s.
Pervin J, Moran A, Rahman M, Razzaque A, Sibley L, Streatfield PK, Reichenbach LJ, Koblinsky M, Hruschka D, Rahman A. Association of antenatal care with facility delivery and perinatal survival–a population-based study in Bangladesh. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2012;12(1):111.
Ibrahim J, Yorifuji T, Tsuda T, Kashima S, Doi H. Frequency of antenatal care visits and neonatal mortality in Indonesia. J Trop Pediatr. 2012;58(3):184–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmr067.
Petrou S, Kupek E, Vause S, Maresh M. Antenatal visits and adverse perinatal outcomes: results from a British population-based study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2003;106(1):40–9.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all authors of the studies included in this systematic review and meta-analysis.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TT, BM, and GF involved in design, selection of articles, data extraction. GF, TT and DB participated in statistical analysis and manuscript writing. All authors involved in developing the initial drafts of the manuscript, revising subsequent drafts and prepared the final draft of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tolossa, T., Fekadu, G., Mengist, B. et al. Impact of antenatal care on neonatal mortality among neonates in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Public Health 78, 114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-020-00499-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-020-00499-8