Abstract
In this paper, the dynamical behaviors for multiple delayed latent virus model with virus-to-cell infection and cell-to-cell transmissions and humoral immunity are investigated. The virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell incidence rates are modeled by general nonlinear functions. The basic reproduction number \(R_{0}\) and the humoral immune response number \(R_{1}\) are calculated and proved to be threshold conditions determining the local and global properties of the virus model. The existence of Hopf bifurcation with immune delay as a bifurcation parameter is presented, and the effects of some key parameters on viral dynamics are revealed by numerical simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
The role of immune response in controlling within-host dynamics of human viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and hepatitis B virus (HBV) is important. Mathematical modeling and analysis have been essential tools to get a better systematic understanding of within-host viral infection. Nowak et al. [1] designed a mathematical model including uninfected cells, infected cells, and virus to describe HIV-1 infection. Several virus dynamics models have been further constructed and analyzed [2–19]. In different virus infections, immunity system protects us against pathogens. In cell-mediated immune response, activated effector T cells can detect peptide antigens and destroy infected cells. As for humoral immunity, matured B cells migrate from bone marrow to other lymphatic organs, where they begin to generate antibodies to remove the viruses [20]. In some diseases such as malaria, humoral immune response is more powerful than cell-mediated immune response [21]. Murase et al. [22] have extended the basic viral infection model presented in [1] by integrating the basic dynamics of the interaction between uninfected cells, infected cells, viruses, and immune cells.
It is mentioned in [2, 3] that cell-to-cell transmission seems to be a more potent and efficient means of virus propagation than the virus-to-cell transmission. Various models of viral infection with two ways of transmission have been developed by many researchers [4–11, 16, 17, 19]. A recent review on modeling viral spread can be found in [8]. Li and Wang in [9] dealt with the global dynamics of an HIV infection model which incorporated direct cell-to-cell transmission. Meanwhile, Lai and Zou [10] studied the effect of cell-to-cell transfer of HIV-1 on the virus dynamics. Lin et al. [11] have proposed a delayed viral infection model with humoral immunity and both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions, but the latently infected cells has been ignored. Miao et al. [12] have proposed a virus dynamics model with humoral impairment. The model presented in [12] has neglected the latently infected cells and cell-to-cell transmission. In a very recent work, Elaiw et al. [13] have studied the global stability of an HIV infection model with impairment of B-cell functions, but the cell-to-cell transmission has been ignored.
In case of HIV infection, current treatment consisting of several antiretroviral drugs can suppress viral replication to a low level but cannot eradicate the virus. An important reason is that HIV provirus can reside in latently infected cells [14, 15]. Latently infected cells live long, are not affected by antiretroviral drugs or immune responses, but can be activated to produce HIV by relevant antigens [16]. Motivated by the works in [6, 10, 11, 13, 16], in this paper we investigate the effects of combining both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions in delayed latent virus infection model with humoral immunity
where \(T(t)\), \(L(t)\), \(I(t)\), \(V(t)\), and \(Z(t)\) denote the concentration of uninfected cells, latently infected cells, productively infected cells, viruses, and B cells at time t. The terms s and \(d_{1}T\) represent the production and death rates of the uninfected cells. The death rates of latently infected cells, productively infected cells, viruses, and B cells are given by \(d_{2}L\), \(d_{3}I\), \(d_{4}V\), and \(d_{5}Z\), respectively. The viruses are produced at rate kI, and removed by the B cells at rate \(qVZ\). The B cells are proliferated at rate \(cVZ\). Latently infected cells can be activated by their relevant antigens to become productively infected cells at a rate α, The fractions \(1-\eta \) and η with \(0 < \eta < 1 \) are the probabilities that an uninfected cell will turn into either latently infected cell or productively infected cell. The functions \(f_{1}(T,V)\) and \(f_{2}(T,I)\) are the virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell incidence rates, respectively; \(\tau _{1}\) and \(\tau _{2}\) represent the times between virus particle touches an uninfected cell and the cell becomes latently infected and actively infected cell, respectively; \(e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{i}}\), \(i = 1, 2\), represents the damage of uninfected cells during the interval \([t -\tau _{i},t]\). Antigenic stimulation generating antibody response involves a sequence of processes and needs a period of time \(\tau _{3}\).
We need the following assumptions on the function \(f_{i}(T, \theta )\), \(i=1,2\):
Define
- \((H_{1})\):
-
\(f_{i}(T, \theta )\) is continuously differentiable; \(f_{i}(T, \theta )>0\) for \(T\in (0,\infty )\), \(\theta \in (0,\infty )\); \(f_{i}(T, \theta )=0\) if and only if \(T=0\) or \(\theta =0\).
- \((H_{2})\):
-
\(\frac{\partial f_{i}(T, \theta )}{\partial T}>0\) and \(\frac{\partial f_{i}(T, \theta )}{\partial \theta }>0\), for all \(T>0\) and \(\theta >0\), \(i=1,2\).
- \((H_{3})\):
-
\(f_{i1}(T)>0\) and \(f_{i1}'(T)>0 \) for all \(T>0\), \(i=1,2\).
- \((H_{4})\):
-
\(\frac{f_{i}(T, \theta )}{\theta }\) is nonincreasing with respect to θ for all \(\theta >0\), \(i=1,2\).
In this paper, the aim is to investigate a virus dynamics model which includes: (i) B-cell functions, (ii) both latently and productively infected cells, (iii) both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions, (iv) three time delays, (v) general virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell incidence rates. Our purpose is to investigate the dynamical properties of model (1), expressing the stability of equilibria and the existence of Hopf bifurcation. The reproduction numbers for viral infection and antibody response are calculated. By using Lyapunov functionals and LaSalle’s invariance principle, the threshold conditions for the global asymptotic stability of infection-free equilibrium \(E_{0}\), immune-free equilibrium \(E_{1}\), and infection equilibrium \(E_{2}\) with antibody response when the delay \(\tau _{3}=0\) are established. By using the linearization method, the instability of equilibria \(E_{0}\) and \(E_{1}\), respectively, are also established. Furthermore, by using the numerical simulation method, we will discuss the existence of the Hopf bifurcation and stability switches at equilibrium \(E_{2}\) when \(\tau _{3}>0\).
The organization of our paper is as follows. In Sect. 2, the basic properties of model (1) for the boundedness of solutions, the threshold values and the existence of equilibria are discussed. In Sect. 3, the threshold conditions on the global stability and instability for equilibria \(E_{0}\), \(E_{1}\), and \(E_{2}\) are stated. In Sect. 4, the numerical simulations are presented to further illustrate the dynamical behavior of the model and study the effects of cell-to-cell transmission, viral production rate, death rate of infected cells, and viral removal rate on viral dynamics, respectively. Besides, we perform a sensitivity analysis of reproduction ratios. Finally, we will give a conclusion.
2 Boundedness and equilibrium
Let \(\tau =\max \{{\tau _{1},\tau _{2},\tau _{3}}\}\) and \(R^{5}_{+}=\{(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3},x_{4},x_{5}): x_{i}\geq 0, i=1,2,3,4,5 \}\). By \(C([-\tau ,0], R^{5}_{+})\) we denote the space of continuous functions mapping interval \([-\tau ,0]\) into \(R^{5}_{+}\) with norm \(\|\phi \|=\sup_{-\tau \leq t\leq 0}\{|\phi (t)|\}\) for any \(\phi \in C([-\tau ,0],R^{5}_{+})\).
The initial conditions for model (1) are given as follows:
where \((\phi _{1}(\theta ), \phi _{2}(\theta ), \phi _{3}(\theta ), \phi _{4}( \theta ), \phi _{5}(\theta ))\in C([-\tau ,0],R^{5}_{+})\). By the fundamental theory of functional differential equations [23, 24], it is easy to see that model (1) admits a unique solution \((T(t),L(t),I(t),V(t),Z(t))\) satisfying the initial conditions (2). We have the following basic result of model (1).
Theorem 2.1
Let \((T(t),L(t),I(t),V(t),Z(t))\) be the solution of model (1) satisfying initial conditions (2), then \(T(t)\), \(L(t)\), \(I(t)\), \(V(t)\), and \(Z(t)\) are positive and ultimately bounded.
Proof
We first show that \(T(t)>0\) for all \(t >0\). Assume that there exists a \(t_{1} > 0\) such that \(T(t_{1}) = 0\), \(T(t)>0\), \(t\in [0, t_{1})\). Thus, \(T'(t_{1})\leq 0\). From the first equation of (1), we have \(T'(t_{1}) = s > 0\), which is a contradiction. This implies that \(T(t) > 0\) for all \(t >0\). By the last three equations of model (1), we have
which shows that \(L(t) > 0\), \(I(t) > 0\), \(V(t) > 0\), and \(Z(t)>0\) for a small \(t >0\). Now, we prove that \(L(t) > 0\), \(I(t) > 0\), \(V(t) > 0\), and \(Z(t)>0\) for all \(t >0\). Assume that \(t_{2} > 0\) is the first time such that
If \(L(t_{2}) = 0\), \(L(t) > 0\) for \(t\in [0, t_{2})\) and \(I(t) > 0\), \(V(t) > 0\), \(Z(t) > 0\), \(t \in [0, t_{2}]\), then we have \(L'(t_{2})\leq 0\). On the other hand, from the second equation of (1), we have
This leads to a contradiction.
If \(I(t_{2}) = 0\), \(I(t) > 0\) for \(t\in [0, t_{2})\) and \(L(t) > 0\), \(V(t) > 0\), and \(Z(t) > 0\), \(t\in [0, t_{2}] \), we also have \(\dot{I(t_{2})} \leq 0\). However, from the third equation, we have
This also leads to a contradiction.
Similarly, we know that \(V(t_{2}) = 0\) and \(Z(t_{2}) = 0 \) are impossible. Thus, \(T(t) > 0\), \(L(t) > 0\), \(I(t) > 0\), \(V(t) > 0\), and \(Z(t) > 0\) for all \(t >0\).
Next, we prove the boundedness of the solution of model (1) with the initial condition (2). From the positivity of the solution and the first equation of (1), we obtain
which yields
Let
Calculating the derivative of \(N_{1}(t)\) along solutions of model (1), we have
where \(\sigma _{1}= \min \{d_{1},\alpha +d_{2}\}\). This yields
Denote
Calculating the derivative of \(N_{2}(t)\) along solutions of model (1), we have
where
This implies that \(\limsup_{t\rightarrow \infty }N_{2}(t)\leq \frac{a}{\sigma _{2}}\), and hence, \(I(t)\), \(V(t)\), and \(Z(t)\) are bounded.
Next, we discuss the existence of equilibria of model (1). It always has an infection-free equilibrium \(E_{0}=(T_{0},0,0,0,0)\), where \(T_{0}=\frac{s}{d_{1}}\). Inspired by the method in [25, 26], we consider the infection and viral production, and define matrices \(\mathbb{F}\) and \(\mathbb{V}\) as
and
Thus, the basic reproductive number, \(R_{0}\), can be defined as the spectral radius of the next generation operator \(\mathbb{F}\mathbb{V}^{-1}\), where
where
Therefore,
which biologically describes the average number of secondary infections produced by one infected cell at the beginning of infection. In the above expression of \(R_{0}\), divided into parts as \(R_{0}=R_{01}+R_{02}\), where \(R_{01}=(\eta e^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}\frac{\alpha }{\alpha +d_{2}}+(1- \eta ) e^{-m_{1}\tau _{2}})\cdot \frac{k}{d_{3}d_{4}}\cdot \frac{\partial f_{1}(\frac{s}{d_{1}},0)}{\partial V}\) is the basic reproduction number via the virus-to-cell infection and \(R_{02}=(\eta e^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}\frac{\alpha }{\alpha +d_{2}}+(1- \eta ) e^{-m_{1}\tau _{2}})\cdot \frac{1}{d_{3}}\cdot \frac{\partial f_{2}(\frac{s}{d_{1}},0)}{\partial I}\) is the basic reproduction number via the cell-to-cell transmission, respectively.
To find the equilibria of model (1), we need to solve
When \(Z(t)=0\), the fourth equation of (3) leads to \(I=\frac{d_{4}V}{k}\). From the second and third equations of (3), we obtain \(L= \frac{d_{3}\eta e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}}{\alpha \eta e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}+(\alpha +d_{2})(1-\eta )e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{2}}} \cdot \frac{d_{4}V}{k}\). Solving T from (3), we get \(T=\frac{s}{d_{1}}- \frac{(\alpha +d_{2})d_{3}d_{4}V}{d_{1}k(\alpha \eta e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}+(\alpha +d_{2})(1-\eta )e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{2}})} \triangleq h(V)\). We get from the second equation that
Define
then \(F(0)=0\), the positive solution of \(h(V)=0\) is given by
We can see that
Moreover,
Assumption \((H_{1})\) implies that \(\frac{\partial f_{1}(T_{0},V)}{\partial T}=0\) and \(\frac{\partial f_{2}(T_{0},I)}{\partial T}=0\), then
Therefore, if \(R_{0}>1\), then \(F'(0)>0\) and \(\exists V_{1}\in (0,\bar{V})\) such that \(F(V_{1})=0\). Hence, model (1) has a unique immune-free equilibrium \(E_{1}=(T_{1},L_{1},I_{1},V_{1},0)\), where
When \(Z(t)\neq 0\), the fourth equation of (3) leads to \(V=\frac{d_{5}}{c}\). From the second and third equations of (3), we obtain \(L= \frac{d_{3}\eta e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}I}{\alpha \eta e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}+(\alpha +d_{2})(1-\eta )e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{2}}}\). Solving T from (3), we get \(T=\frac{s}{d_{1}}- \frac{(\alpha +d_{2})d_{3}I}{d_{1}(\alpha \eta e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{1}}+(\alpha +d_{2})(1-\eta )e ^{-m_{1}\tau _{2}})} \triangleq h(I)\). We get from the second equation that
Define
then \(F(0)=f_{1}(\frac{s}{d_{1}},\frac{d_{5}}{c})>0 \) and the positive solution of \(h(I)=0\) is given by
We can see that
Moreover,
then we have
Therefore, if \(R_{02}>1\), then \(F'(0)>0\) and \(\exists I_{2}\in (0,\bar{I})\) such that \(F(I_{2})=0\).
Define
From the fourth equation of (3), we obtain that \(Z_{2}=\frac{kI_{2}-d_{4}V_{2}}{qV_{2}}= \frac{d_{4}(\frac{kcI_{2}}{d_{4}d_{5}}-1)}{q}= \frac{d_{4}(R_{1}-1)}{q}\). Hence, when \(R_{1}>1 \), model (1) has a unique infection equilibrium \(E_{2}=(T_{2},L_{2},I_{2},V_{2},Z_{2})\) with antibody response, where
□
3 Stability analysis
To state the global stability on \(E_{0}\), we need an additional assumption:
- \((H_{5})\):
-
The supremum of \(\frac{f_{21}(T)}{f_{11}(T)}\) on \((0,T_{0}]\) is achieved at \(T = T_{0}\).
Theorem 3.1
(a) If \(R_{0} \leq 1\), then the infection-free equilibrium \(E_{0}\) is globally asymptotically stable.
(b) If \(R_{0}>1\), then the equilibrium \(E_{0}\) is unstable.
Proof
Consider claim (a). Define a Lyapunov functional
Calculating the derivative of \(U_{1}(t) \) along positive solution of model (1) and noting that \(T_{0}=\frac{s}{d_{1}}\), we obtain
where
and
From Assumption \((H_{3})\), we have
Moreover, by utilizing Assumptions \((H_{4})\)–\((H_{5})\), we obtain
Therefore, we obtain
Note that \(\frac{dU_{1}(t)}{dt}= 0\) if and only if \(T=T_{0}\), \(L=0\), \(V=0\), and \(Z=0\). So, the maximal compact invariant set in \(\{(T,L,I,V,Z)\in R^{5}_{+}:\frac{dU_{1}(t)}{dt}=0\}\) is the singleton \(\{E_{0}\}\). By the LaSalle’s invariance principle [23], \(E_{0}\) is globally asymptotically stable when \(R_{0}\leq 1\).
Next, we consider conclusion (b). The characteristic equation of the linearized system of model (1) at the equilibrium \(E_{0}\) is
where
with
When \(R_{0}>1\), we have \(F(0)=d_{3}d_{4}(\alpha +d_{2})(1-R_{0})<0\) and \(\lim_{\lambda \to \infty }F(\lambda )=+\infty \). Hence, there is a \(\lambda ^{*}>0\) such that \(F(\lambda ^{*})=0\). Therefore, when \(R_{0}>1\), \(E_{0}\) is unstable. This completes the proof. □
We establish a set of conditions which are sufficient for the global stability of equilibria for \(E_{1}\) and \(E_{2}\). Here, we assume that the functions \(f_{1}(T,V)\) and \(f_{2}(T,I)\) satisfy the following:
- \((H_{6})\):
-
$$\begin{aligned}& f_{1}(T_{i},V_{i})f_{2}(T,I)I_{i}-f_{1}(T,V_{i})f_{2}(T_{i},I_{i})I< 0, \\& f_{1}(T,V)V_{i}-f_{1}(T,V_{i})V< 0, \quad i=1,2. \end{aligned}$$
Theorem 3.2
Let \(R_{0}>1\). (a) If \(R_{1}\leq 1\), then the immune-free equilibrium \(E_{1}\) is globally asymptotically stable.
(b) If \(R_{1}>1\), then the equilibrium \(E_{1}\) is unstable.
Proof
Letting \(H(\xi )=\xi -1-\ln \xi \), we have that \(H(\xi )\geq 0\) for all \(\xi >0\) and \(H(\xi )=0\) if and only if \(\xi =1\). Consider claim \((a)\). Define a Lyapunov functional
Calculating the derivative of \(U_{2}(t) \) along positive solution of model (1), it follows that
From \((H_{2})\), \((H_{4})\), and \((H_{6})\), we have
Hence, \(\frac{dU_{2}(t)}{dt}\leq 0\) and \(\frac{dU_{2}(t)}{dt}=0\) if and only if \(T(t)=T_{1}\), \(L(t)=L_{1}\), \(I(t)=I_{1}\), \(V(t)=V_{1}\), and \(Z(t)=0\). From the LaSalle’s invariance principle [23], we have that \(E_{1}\) is globally asymptotically stable when \(R_{0}>1\) and \(R_{1}\leq 1\).
Next, we consider conclusion (b). The characteristic equation of the linearized system of model (1) at the equilibrium \(E_{1}\) is
where
and
with
When \(R_{1}>1\), we have \(h_{1}(0)=d_{5}-cV_{1}<0\). Since \(\lim_{\lambda \to \infty }h_{1}(\lambda )=+\infty \), there is also a positive root \(\lambda ^{*}\) such that \(h_{1}(\lambda ^{*})=0\). Therefore, when \(R_{1}>1\), \(E_{1}\) is unstable. This completes the proof. □
Theorem 3.3
If \(R_{1}>1\) and \(\tau _{3}=0\), then the infection equilibrium \(E_{2}\) with antibody response is globally asymptotically stable.
Proof
Define a Lyapunov functional
Calculating the derivative of \(U_{3}(t) \) along positive solution of model (1), it follows that
From \((H_{2})\), \((H_{4})\), and \((H_{6})\), we have
Hence, \(\frac{dU_{3}(t)}{dt}\leq 0\) and \(\frac{dU_{3}(t)}{dt}=0\) if and only if \(T(t)=T_{2}\), \(L(t)=L_{2}\), \(I(t)=I_{2}\), \(V(t)=V_{2}\), and \(Z(t)=Z_{2}\). From the LaSalle’s invariance principle [23], we have that \(E_{2}\) is globally asymptotically stable when \(R_{1}>1\). This completes the proof. □
4 Numerical simulations
In the above sections, we established the global asymptotic stability of equilibrium \(E_{2}\) when \(\tau _{1}\geq 0\), \(\tau _{2}\geq 0\), and \(\tau _{3}=0\). However, considering the case \(\tau _{1}\geq 0\), \(\tau _{2}\geq 0\), and \(\tau _{3}\geq 0\), by using the numerical simulation, it is shown that stability switches occur at \(E_{2}\) as \(\tau _{3}\) increases. In model (1), we have \(f_{1}(T,V)= \frac{\beta _{1} T(t)V(t)}{1+\alpha _{1} T(t)+\alpha _{2} V(t)}\), \(f_{2}(T,I)= \beta _{2} T(t)I(t)\). Take \(s=10\), \(d_{1}=0.01\), \(d_{2}=0.8\), \(\beta _{1}=0.25\), \(\beta _{2}=0.001\), \(\alpha _{1}=0.01\), \(\alpha _{2}=0.01\), \(d_{3}=0.5\), \(\alpha =0.01\), \(\eta =0.49\), \(k=0.4\), \(d_{4}=3\), \(q=1\), \(c=1.5\), \(m_{1}=0.01\), \(m_{2}=0.01\), \(d_{5}=1\), \(\tau _{1}=2\), and \(\tau _{2}=5\), and choose \(\tau _{3}\) as a free parameter. Computing we obtain \(R_{0}=3.0743>1\), \(R_{1}=1.7440>1\), and \(E_{2}(112,5.2649,8.72,0.6667,2.2321)\).
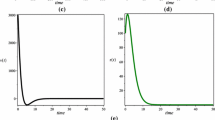
In the following Figs. 1–4, panels (a), (b), (c), (d), and (e) show the time evolution of \(T(t)\), \(L(t)\), \(I(t)\), \(V(t)\), and \(Z(t)\).
4.1 Effect of cell-to-cell transmission
In order to investigate the effect of cell-to-cell transmission, we carry out some numerical simulations to show the contribution of cell-to-cell transmission during the whole infection. Figure 5 (\(\beta _{2}=0\), \(\beta _{2}=0.001\), \(\beta _{2}=0.0025\), \(\beta _{2}=0.005\)) shows that latently infected cells, productively infected cells, and virus reach the peak levels quicker and they become larger as \(\beta _{2}\) increases. Therefore, cell-to-cell transmission plays an important role in the whole virus infection.
The effect of \(\beta _{2}\) on the dynamical behavior of model (1)
4.2 Effect of viral production rate
Viral production rate also has a great influence on the dynamical behavior of the model. We set the viral production rate k as 0.4, 4, and 40. In Fig. 6, we observe that the time to reach the peak levels of latently infected cells, productively infected cells, and virus becomes shorter as k increases, which means that a larger viral production rate contributes to the viral infection. In terms of the prevention and treatment of virus infection, decreasing k contributes to inhibiting virus reproduction.
The effect of k on the dynamical behavior of model (1)
4.3 Effect of death rate of infected cells and viral removal rate
Usually, the death rate of infected cells is larger than the death rate of uninfected cells due to the fact that virus infection can kill more host cells. From Fig. 7, we can observe that latently infected cells, productively infected cells, and virus increase more slowly as \(d_{3}\) increases, which indicates that increasing the death rate of infected cells can slow down the virus infection. Humoral immunity is used to clear virus in our body, so the viral remove rate \(d_{4}\) has an effect on viral infection as well. Figure 8 implies that as \(d_{4}\) increases, latently infected cells, productively infected cells, and virus increase more slowly, which has similar results to \(d_{3}\). Therefore, promoting body’s immunity helps increase the mortality of infected cells and viral removal rate.
The effect of \(d_{3}\) on the dynamical behavior of model (1)
The effect of \(d_{4}\) on the dynamical behavior of model (1)
4.4 Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis is used to quantify the range of variables in reproduction ratios and to identify the key factors giving rise to reproduction ratios. In [27, 28], Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) is found to be a more efficient statistical sampling technique which has been introduced to the field of disease modeling. In [28], Marino et al. mentioned that partial rank correlation coefficients (PRCCs) provide a measure of the strength of a linear association between the parameters and the reproduction ratios. We perform sensitivity analysis by using the Latin hypercube sampling method to generate 5000 parameter combinations with each parameter. In Fig. 9, we obtain the PRCCs of \(R_{0}\) and \(R_{1}\). Specially, we show that \(\beta _{1}\), \(\beta _{2}\), and k are positively correlative variables with \(R_{0}\) and \(R_{1}\), while others are negatively correlated variables.
5 Discussion
In this paper, we developed a delayed latent virus model with both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions and humoral immunity. We see that intracellular delay \(\tau _{1}\) and virus replication delay \(\tau _{2}\) do not affect the stability of the equilibria. However, immune response delay \(\tau _{3}\) strongly impacts the stability of infection equilibrium with antibody response \(E_{2}\). Under certain assumptions \((H_{1})\)–\((H_{6})\), we have shown that, when \(R_{0}<1\), \(E_{0}\) is globally asymptotically stable for any delays \(\tau _{1}\geq 0\), \(\tau _{2}\geq 0\), and \(\tau _{3}\geq 0\), which means that the virus is eradicated. When \(R_{0}>1\) and \(R_{1}\leq 1\), \(E_{1}\) is globally asymptotically stable for any delays \(\tau _{1}\geq 0\), \(\tau _{2}\geq 0\), and \(\tau _{3}\geq 0\), which means that the antibody response would not be activated and the viral infection vanishes. When \(R_{1}>1\) and \(\tau _{3}=0\), \(E_{2}\) is globally asymptotically stable for any delays \(\tau _{1}\geq 0\) and \(\tau _{2}\geq 0\), that is, uninfected cells, latently infected cells, productively infected cells, virus and antibodies coexist in vivo.
When \(\tau _{3}\geq 0\), by numerical simulations, it is shown that the Hopf bifurcation and stability switches occur at \(E_{2}\) as \(\tau _{3}\) increases. From Figs. 1–4, we see when \(\tau _{3}\) is small enough, \(E_{2}\) is asymptotically stable and, when \(\tau _{3}\) is increasing, the stability switch occurs at \(E_{2}\), while, when \(E_{2}\) is unstable, Hopf bifurcation occurs. Finally, when \(\tau _{3}\) is large enough, \(E_{2}\) is always unstable. This illustrates that \(\tau _{3}\) plays a negative role in disease prevalence and control. Besides, we can see in Figs. 5–8 the effects of cell-to-cell transmission \(\beta _{2}\), viral production rate k, death rate of infected cells \(d_{3}\), and viral remove rate \(d_{4}\) on viral dynamics. Figure 9 shows a sensitivity analysis of reproduction ratios, which implies some useful consequences on the prevention and treatment of the viral infection.
It is easy to see that basic reproduction ratios \(R_{0}\) is the sum of the reproduction ratio determined by virus-to-cell infection \(R_{01}\) and cell-to-cell transmission \(R_{02}\). Therefore, neglecting the cell-to-cell transmission will lead to an underevaluated basic reproduction number. Observing all obtained results in this paper, we can directly put forward the following open questions which need to be further studied in the future. First, based on the model in [29, 30], we wonder whether the results obtained in this paper can be extended to control the dynamic process. Second, this model can be extended to incorporate a stochastic perturbation. Meanwhile, model (1) can be extended to describe the HIV dynamics with two classes of target cells and more stages. We leave these problems as possible future works.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Nowak, M.A., Bangham, C.R.M.: Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent viruses. Science 272, 74–79 (1996)
Portillo, A.D., et al.: Multiploid inheritance of HIV-1 during cell-to-cell infection. J. Virol. 85, 7169–7176 (2011)
Komarova, N.L., Wodarz, D.: Virus dynamics in the presence of synaptic transmission. Math. Biosci. 242, 161–171 (2013)
Wang, J., Guo, M., Liu, X., Zhao, Z.: Threshold dynamics of HIV-1 virus model with cell-to-cell transmission, cell-mediated immune responses and distributed delay. Appl. Math. Comput. 291, 149–161 (2016)
Elaiw, A.M., AlShamrani, N.H.: Stability of a general adaptive immunity virus dynamics model with multi-stages of infected cells and two routes of infection. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.5923
Elaiw, A.M., AlShamrani, N.H.: Global stability of humoral immunity virus dynamics models with nonlinear infection rate and removal. Nonlinear Anal., Real World Appl. 26, 161–190 (2015)
Yang, Y., Zou, L., Ruan, S.: Global dynamics of a delayed within-host viral infection model with both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions. Math. Biosci. 270, 183–191 (2015)
Graw, F., Perelson, A.S.: Modeling viral spread. Annu. Rev. Virol. 3, 555–572 (2016)
Li, F., Wang, J.: Analysis of an HIV infection model with logistic target-cell growth and cell-to-cell transmission. Chaos Solitons Fractals 81, 136–145 (2015)
Lai, X., Zou, X.: Modelling HIV-1 virus dynamics with both virus-to-cell infection and cell-to-cell transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 74, 898–917 (2014)
Lin, J., Xu, R., Tian, X.: Threshold dynamics of an HIV-1 virus model with both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions, intracellular delay, and humoral immunity. Appl. Math. Comput. 315, 516–530 (2017)
Miao, H., Abdurahman, X., Teng, Z., Zhang, L.: Dynamical analysis of a delayed reaction-diffusion virus infection model with logistic growth and humoral immune impairment. Chaos Solitons Fractals 110, 280–291 (2018)
Elaiw, A.M., Alshehaiween, S.F., Hobiny, A.D.: Global properties of delay-distributed HIV dynamics model including impairment of B-cell functions. Mathematics 7, 837–864 (2019)
Chun, T.W., Stuyver, L., Mizell, S.B., Ehler, L.A., Mican, J.A.M., Baseler, M., Lloyd, A.L., Nowak, M.A., Fauci, A.S.: Presence of an inducible HIV-1 latent reservoir during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94, 13193–13197 (1997)
Wong, J.K., Hezareh, M., Gunthard, H.F., Havlir, D.V., Ignacio, C.C., Spina, C.A., Richman, D.D.: Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science 278, 1291–1295 (1997)
Wang, X., Tang, S., Song, X., Rong, L.: Mathematical analysis of an HIV latent infection model including both virus-to-cell infection and cell-to-cell transmission. J. Biol. Dyn. 11, 455–483 (2017)
Shu, H., Chen, Y., Wang, L.: Impacts of the cell-free and cell-to-cell infection modes on viral dynamics. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 30, 1817–1836 (2018)
Elaiw, A.M., AlShamrani, N.H.: Stability of an adaptive immunity pathogen dynamics model with latency and multiple delays. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 36, 125–142 (2018)
Sun, H., Wang, J.: Dynamics of a diffusive virus model with general incidence function, cell-to-cell transmission and time delay. Comput. Math. Appl. 77, 284–301 (2019)
Charles, J., Paul, T., Mark, W.: Immunobiology, 5nd edn. Garland, New York (2001)
Deans, J.A., Cohen, S.: Immunology of malaria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 37, 25–49 (1983)
Murase, A., Sasaki, T., Kajiwara, T.: Stability analysis of pathogen-immune interaction dynamics. J. Math. Biol. 51, 247–267 (2005)
Kuang, Y.: Delay Differential Equations with Applications in Population Dynamics. Academic Press, San Diego (1993)
Hale, J.K., Lunel, S.V.: Introduction to Functional Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1993)
Diekmann, O., Heesterbeek, J.A., Metz, J.A.: On the definition and the computation of the basic reproduction ratio \(R_{0}\) in models for infectious diseases in heterogeneous populations. J. Math. Biol. 28, 365–382 (1990)
van den Driessche, P., Watmough, J.: Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180, 29–48 (2002)
Hoare, A., Regan, D.G., Wilson, D.P.: Sampling and sensitivity analyses tools (SaSAT) for computational modelling. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 5, 4–21 (2008)
Marino, S., Hogue, I.B., Ray, C.J.: A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology. J. Theor. Biol. 254, 178–196 (2008)
Wang, X., Qi, Y., Tao, C., Xiao, Y.: A class of delay differential variational inequalities. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 172, 56–69 (2017)
Wang, X., Teo, K.L.: Generalized Nash equilibrium problem over a fuzzy strategy set. In: Fuzzy Sets and Systems (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2021.06.006
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the referees for valuable comments and suggestions that helped them improve this article.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 11901363, 11771373, 12001341, and 12001340), Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (Grant no. 2019L0489), the Youth Research Fund for the Shanxi basic research project (Grant no. 2015021025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author contributed to every part of the work equally; all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, H., Liu, R. & Jiao, M. Global dynamics of a delayed latent virus model with both virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions and humoral immunity. J Inequal Appl 2021, 156 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13660-021-02691-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13660-021-02691-y