Abstract
Background
Chronic stress exposure increases the risk of mental health problems such as anxiety and depression. The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) is a hub for controlling stress responses through communicating with multiple limbic structures, including the basolateral amygdala (BLA) and nucleus accumbens (NAc). However, considering the complex topographical organization of the mPFC neurons in different subregions (dmPFC vs. vmPFC) and across multiple layers (Layer II/III vs. Layer V), the exact effects of chronic stress on these distinct mPFC output neurons remain largely unknown.
Results
We first characterized the topographical organization of mPFC neurons projecting to BLA and NAc. Then, by using a typical mouse model of chronic restraint stress (CRS), we investigated the effects of chronic stress on the synaptic activity and intrinsic properties of the two mPFC neuronal populations. Our results showed that there was limited collateralization of the BLA- and NAc-projecting pyramidal neurons, regardless of the subregion or layer they were situated in. CRS significantly reduced the inhibitory synaptic transmission onto the BLA-projecting neurons in dmPFC layer V without any effect on the excitatory synaptic transmission, thus leading to a shift of the excitation-inhibition (E-I) balance toward excitation. However, CRS did not affect the E-I balance in NAc-projecting neurons in any subregions or layers of mPFC. Moreover, CRS also preferentially increased the intrinsic excitability of the BLA-projecting neurons in dmPFC layer V. By contrast, it even caused a decreasing tendency in the excitability of NAc-projecting neurons in vmPFC layer II/III.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that chronic stress exposure preferentially modulates the activity of the mPFC-BLA circuit in a subregion (dmPFC) and laminar (layer V) -dependent manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Exposure to extreme or prolonged environmental stress is widely recognized as a major risk in the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric disorders, including anxiety and major depressive disorder [1,2,3]. Previous studies have consistently shown that the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) acts as a critical node in regulating stress-related anxiety behavior through its top-down control over the subcortical structures [4,5,6]. For instance, stress enhances the excitatory synaptic transmission from the mPFC to the amygdala and facilitates the expression of anxiety-like behavior in mice [7, 8].
The topographical and functional organization of the mPFC are complicated. mPFC is classically divided into dorsal mPFC (dmPFC) and ventral mPFC (vmPFC) in rodents based on cytoarchitectural differences [9]. It has been reported that dmPFC and vmPFC have opposing roles in stress reactivity and alcohol drinking [10, 11]. There is also evidence showing that dmPFC and vmPFC exhibit distinct roles in tuning the anxiety-like behavior, with dmPFC activation producing anxiety-like behavior, whereas vmPFC activation has no effect [12, 13]. Moreover, the rodent mPFC displays laminar organization and can be divided into multiple layers (layer I, II/III, V). Previous studies have also highlighted layer-specific responses of mPFC neurons to stress [14,15,16,17]. For example, chronic stress decreased the dendritic branching of the projection neurons in layer II/III, but increased it in layer V [18]. Another study also revealed that chronic stress produced synapse loss only in deeper layers [19]. Moreover, evidence shows layer-specific changes undergoing chronic pain, with enhanced activity in layer II/III neurons and decreased activity in layer V neurons [20].
The mPFC neurons send their projections to multiple cortical and subcortical regions. Among them, the basolateral amygdala (BLA) and nucleus accumbens (NAc), two regions critically involved in the regulation of stress response, receive relatively dense inputs from mPFC [21,22,23,24]. The mPFC-BLA circuit has been shown to play a crucial role in the pathophysiology of stress-related diseases [7, 8, 25, 26]. For instance, in stressed mice, the excitatory synaptic transmission in mPFC-BLA circuit is markedly increased, and this change is tightly correlated with the increased anxiety-like behavior [8]. The projection from mPFC to NAc, on the other hand, is generally thought as a reward circuit, and optogenetic activation of this circuit increases resilience against stress [27, 28]. Notably, while most of the previous work studied these two mPFC circuits as a whole, little is known about how the subcircuits established by the mPFC neurons in different subregions or layers respond in face of chronic stress.
To address this issue, we first characterized the topographical organization of mPFC neurons projecting to BLA and NAc. We then investigated the influence of chronic restraint stress on the synaptic and neuronal activity of the BLA- versus NAc-projecting neurons in different layers of dmPFC and vmPFC. Our results showed that CRS preferentially shifted the E-I balance toward excitation in BLA-projecting neurons in dmPFC layer V without any noticeable effect on NAc-projecting neurons, regardless of the subregions or layers. Moreover, CRS markedly increased the intrinsic excitability in BLA-projecting dmPFC neurons in layer V, but instead caused a tendency of decrease in NAc-projecting neurons in vmPFC layer II/III. Our findings thus suggest that the mPFC-BLA circuit is more vulnerable to chronic stress than its mPFC-NAc counterpart.
Results
Anatomical characterization of the BLA and NAc-projecting mPFC neurons
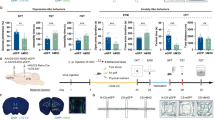
To characterize the topographical organization and collateralization of the mPFC neurons projecting to BLA or NAc (Fig. 1A), we used a retrograde adeno-associated viral (AAV) tracing strategy by injecting retrogradely traveling AAV vector carrying mCherry (AAV-mCherry) and EGFP (AAV-EGFP) under the control of hSyn promoter into BLA and NAc, respectively (Fig. 1B). We found a similar proportion of neurons projecting to BLA (dmPFC→BLA PNs) and NAc (dmPFC→NAc PNs) in layer II/III, whereas in layer V, a higher proportion of dmPFC→NAc PNs than dmPFC→BLA PNs. Among the fluorescently labelled neurons, there were only few projecting to both regions in layer II/III and V (Fig. 1C–E). Similarly, the two neuronal populations were also found to be intermingled but seldom overlapped in layers II/III and V of vmPFC (Fig. 1F–H). These results indicate minimal collateralization of BLA- and NAc- projecting neurons in mPFC. We then determined the identity of the two long-range projection neuronal populations. Quantitative analysis revealed the presence of CaMKIIα (a pyramidal neuronal marker) in 96% of mCherry+ and 98% of EGFP+ cells, indicating most of the BLA- and NAc- projecting neurons in mPFC are glutamatergic cells (Additional file 1: Fig. S1).
Anatomical characterization of the mPFC neurons projecting to the BLA and NAc. A Schematic structure of different regions and layers of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). B Schematic showing injection of AAV2/retro-hSyn-eGFP into NAc and AAV2/retro-hSyn-mCherry into BLA (left) and representative images showing the injection site in BLA and NAc (right). Scale bar: 500 μm. C Representative images showing the labeled dmPFC→BLA and dmPFC→NAc PNs. Scale bar: 100 μm. D Pie charts illustrating the abundance of the BLA-and NAc-projecting neurons in dmPFC. E Bar graph illustrating the percentage of the BLA- and NAc-projecting neurons in dmPFC. F Representative images showing the labeled vmPFC→BLA and vmPFC→NAc PNs. Scale bar: 100 μm. G Pie charts illustrating the abundance of the BLA- and NAc-projecting neurons in vmPFC. H Bar graph illustrating the percentage of the BLA- and NAc-projecting neurons in vmPFC
CRS selectively disrupts the excitation-inhibition balance of dmPFC→BLA PNs in layer V
We next asked how the two neuronal populations responded to stress. We utilized chronic restraint stress (CRS) paradigm to induce anxiety-like behavior. Consistent with previous findings [8, 29, 30], the mice subjected to CRS displayed a typical anxiogenic phenotype as evidenced by less time in and entries into open arms during elevated plus maze test (EPMT) (Fig. 2A–D), as well as shorter time in the center area during open field test (OFT) than the non-stressed ones (Fig. 2E, F). However, there were no significant between-group changes in the total distance traveled and averaged speed, indicating that CRS does not alter locomotor activity (Fig. 2G, H).
CRS significantly induces anxiety-like behavior in mice. A Experimental procedures. B Representative activity tracking in EPMT. C, D Summary plots of time in open arms (C) and open-arm entries (D) during EPMT. E Representative activity tracking in center area OFT. F Summary plots of time in center area during OFT. G Summary plots of total distance travelled during OFT. H Summary plots of mean speed during OFT
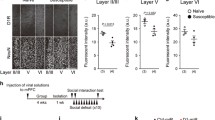
We then investigated the impact of CRS on the electrophysiological properties of these two mPFC neuronal populations using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in acutely isolated ex vivo brain slices (Fig. 3A–C). Since the imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory synaptic neurotransmission is thought as a main factor causing stress-related anxiety [8], we first measured the effects of CRS on the miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) and miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) in dmPFC layer II/III and V neurons. As shown in Fig. 3D–F, in layer II/III, the frequency of mEPSCs remained unaltered in both dmPFC→BLA and dmPFC→NAc PNs, while the amplitude was increased only in the former population. Notably, neither the frequency nor the amplitude of mIPSCs in the two populations was altered by CRS (Fig. 3G–I). Similarly, the ratios of IPSCs/EPSCs frequency and amplitude were comparable between the two groups after CRS (Fig. 3J, K). In layer V, mEPSCs changes were observed in neither population (Fig. 3L–N). By contrast, CRS significantly decreased the frequency and amplitude of mIPSCs in dmPFC→BLA but not dmPFC→NAc PNs (Fig. 3O–Q). As a consequence, the frequency and amplitude of the I/EPSCs ratio were markedly decreased in dmPFC→BLA PNs (Fig. 3R, S), suggesting that CRS selectively shifts the excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) balance toward excitation in the former but not the latter population.
CRS markedly decreases inhibitory synaptic transmission onto dmPFC→BLA PNs in layer V. A Experimental procedures. B Schematic showing injection of AAV2/retro-hSyn-eGFP into NAc and AAV2/retro-hSyn-mCherry into BLA. C Schematic showing recording in dmPFC→BLA or dmPFC→NAc PNs. D Representative traces showing miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) in dmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 1 s, 15 pA). E, F Summary plots of averaged mEPSC frequency (E) and amplitude (F). G Representative traces showing mIPSCs in dmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 1 s, 20 pA). H, I Summary plots of averaged mIPSC frequency (H) and amplitude (I). J Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in dmPFC layer II/III. K Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio in dmPFC layer II/III. L Representative traces showing mEPSCs in dmPFC layer V (scale bar: 1 s, 15 pA). M, N Summary plots of averaged mEPSC frequency (M) and amplitude (N). O Representative traces showing mIPSCs in dmPFC layer V (scale bar: 1 s, 20 pA). P, Q Summary plots of averaged mIPSC frequency (P) and amplitude (Q). R Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in dmPFC layer V. S Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio dmPFC layer V
To further test whether the shift of E/I balance in the dmPFC→BLA PNs in layer V also occurred in other stress paradigms, we repeated the experiments in mice experiencing chronic unpredictable stress (CUS). As expected, CUS markedly increased the anxiety-like behavior as measured by EPMT and OFT (Additional file 1: Fig. S2). Similarly, CUS decreased the frequency and amplitude of mIPSCs in dmPFC→BLA PNs without any effects in dmPFC→NAc PNs in layer V. By contrast, mEPSCs changes were observed in neither PN population irrespective of the layers (Additional file 1: Fig. S3A–L). Not surprisingly, in the dmPFC→BLA PNs in layer V, CUS caused a marked reduction of the I/EPSCs frequency ratio and a decreasing tendency in their amplitude ratio (Additional file 1: Fig. S3M–P).
Altogether, these results consistently suggest that chronic stress preferentially disrupts the E/I balance in the dmPFC→BLA PNs in layer V, supporting the notion that chronic stress dysregulates the synaptic transmission in the dmPFC neurons in a layer- and projection-specific manner.
CRS does not affect the excitation-inhibition balance of vmPFC→BLA and vmPFC→NAc PNs
Next, we explored how CRS would affect the E/I balance in vmPFC-BLA and vmPFC-NAc circuits (Fig. 4A–C). We found that neither the frequency nor the amplitude of mEPSCs was altered in the two PN populations in layer II/III and V (Fig. 4D–I). Similarly, the mIPSCs changes were observed in neither PN population (Fig. 4J–O), yielding unaltered I/EPSCs frequency or amplitude ratio in both populations (Fig. 4P–S). We repeated the above tests in CUS models and also found no mEPSCs and mIPSCs changes in both populations (Additional file 1: Fig. S4). Altogether, unlike its selective regulation of the E/I balance in BLA-projecting PNs in the layer V of dmPFC, chronic stress has a negligible effect on the vmPFC neurons disregarding whether they project to BLA or NAc.
CRS does not affect the synaptic transmission onto both vmPFC→BLA or vmPFC→NAc PNs. A Experimental procedures. B Schematic showing injection of AAV2/retro-hSyn-eGFP into NAc and AAV2/retro-hSyn-mCherry into BLA. C Schematic showing recording in vmPFC→BLA or vmPFC→NAc PNs. D Representative traces showing mEPSCs in vmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 1 s, 15 pA). E, F Summary plots of averaged mEPSC frequency (E) and amplitude (F). G Representative traces showing mEPSCs in vmPFC layer V (scale bar: 1 s, 15 pA). H, I Summary plots of averaged mEPSC frequency (H) and amplitude (I). J Representative traces showing mIPSCs in vmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 1 s, 20 pA). K, L Summary plots of averaged mIPSC frequency (K) and amplitude (L). M Representative traces showing mIPSCs in vmPFC layer V (scale bar: 1 s, 20 pA). N, O Summary plots of averaged mIPSC frequency (N) and amplitude (O). P Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in vmPFC layer II/III. Q Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio in vmPFC layer II/III. R Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in vmPFC layer V. S Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio vmPFC layer V
CRS selectively increases intrinsic excitability of dmPFC→BLA PNs in layer V
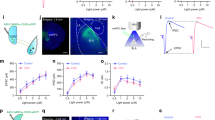
In addition to causing changes in synaptic activity, the external stimuli also regulate the neuronal activity through altering their intrinsic excitability [22]. We then examined the effect of CRS on the intrinsic excitability of the two PN populations in dmPFC by evoking the action potentials (AP) in these neurons (Fig. 5A). In layer II/III, CRS altered neither the number of AP in dmPFC→BLA and dmPFC→NAc PNs nor the parameters depicting AP including the threshold, amplitude, and half-width. Moreover, CRS failed to affect the input resistance, sag ratio, and rheobase in these neurons (Fig. 5B–K). However, in layer V, CRS selectively increased the number of APs in dmPFC→BLA PNs but not dmPFC→NAc PNs (Fig. 5L–N). We also analyzed the AP parameters, which have been widely proved to contribute to altering intrinsic excitability. CRS had no obvious effect on the threshold, amplitude, and half-width of AP of two PN populations (Fig. 5O–Q) but selectively increased the input resistance of the dmPFC→BLA PNs (Fig. 5R). In contrast, the sag ratio and rheobase in the dmPFC→BLA PNs were decreased following chronic stress (Fig. 5S–V).
CRS markedly increases intrinsic excitability of dmPFC→BLA PNs in layer V. A Schematic showing recording in dmPFC→BLA or dmPFC→NAc PNs in layer II/III. B Representative traces showing APs in dmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 200 ms, 30 mV). C Summary plots of APs. D Summary plots of AP threshold. E Summary plots of AP amplitude. F Summary plots of AP half-width. G Summary plots of input resistance. H Representative traces showing sag in dmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 200 ms, 10 mV). I Summary plots of sag ratio. J Representative traces showing rheobase in dmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 200 ms, 30 mV). K Summary plots of rheobase. L Schematic showing recording in dmPFC→BLA or dmPFC→NAc PNs in layer V. M Representative traces showing APs in dmPFC layer V (scale bar: 200 ms, 30 mV). N Summary plots of APs. O Summary plots of AP threshold. P Summary plots of AP amplitude. Q Summary plots of AP half-width. R Summary plots of input resistance. S Representative traces showing sag in dmPFC layer V (scale bar: 200 ms, 10 mV). T Summary plots of sag ratio. U Representative traces showing rheobase in dmPFC layer V (scale bar: 200 ms, 30 mV). V Summary plots of rheobase
Taken together, these results demonstrate that CRS preferentially increases the intrinsic excitability of the dmPFC→BLA neurons but not their dmPFC→NAc neighbors, and this effect appears to only emerge in layer V but not layer II/III. Thus, in line with its layer and projection-specific influence on the synaptic activity of dmPFC neurons, the effect of chronic stress on the intrinsic excitability of dmPFC neurons also varies with their projection targets and the layer they are located in. Relative to the dmPFC-NAc circuit, the dmPFC-BLA circuit appears more vulnerable to stress exposure.
CRS does not alter intrinsic excitability of vmPFC→BLA and vmPFC→NAc PNs
Having found that CRS had little influence on the synaptic activity of the two PN populations in vmPFC (Fig. 4), we next tested whether CRS would change their intrinsic excitability. The results showed that in layer II/III, the number of AP in vmPFC→BLA PNs was not altered by CRS; however, there was a decreasing tendency in the vmPFC→NAc PNs (Fig. 6A–C). The AP parameters, including the threshold, amplitude and half-width, and the input resistance of the two PN populations were unaffected by CRS (Fig. 6D–G). Additionally, CRS unaltered the sag ratio in both populations but preferentially increased the rheobase of vmPFC→NAc PNs (Fig. 6H–K). In contrast, in layer V, neither the AP number nor the AP parameters were changed by CRS (Fig. 6L–V).
CRS does not alter the intrinsic excitability of both vmPFC→BLA or vmPFC→NAc PNs. A Schematic showing recording in vmPFC→BLA or vmPFC→NAc PNs in layer II/III. B Representative traces showing APs in vmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 150 ms, 40 mV). C Summary plots of APs. D Summary plots of AP threshold. E Summary plots of AP amplitude. F Summary plots of AP half-width. G Summary plots of input resistance. H Representative traces showing sag in vmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 200 ms, 10 mV). I Summary plots of sag ratio. J Representative traces showing rheobase in vmPFC layer II/III (scale bar: 200 ms, 30 mV). K Summary plots of rheobase. L Schematic showing recording in vmPFC→BLA or vmPFC→NAc PNs in layer V. M Representative traces showing APs in vmPFC layer V (scale bar: 150 ms, 40 mV). N Summary plots of APs. O Summary plots of AP threshold. P Summary plots of AP amplitude. Q Summary plots of AP half-width. R Summary plots of input resistance. S Representative traces showing sag in vmPFC layer V (scale bar: 200 ms, 10 mV). T Summary plots of sag ratio. U Representative traces showing rheobase in vmPFC layer V (scale bar: 200 ms, 30 mV). V Summary plots of rheobase
Discussion
In the present study, we provide new evidence that chronic stress exposure dysregulates the synaptic activity and intrinsic excitability in distinct mPFC PN populations in a laminar- and subregion-dependent manner. For the mPFC→BLA PNs, CRS caused a shift of the E-I balance of synaptic transmission toward excitation and an increase of neuronal intrinsic excitability, but only in those situated in layer V of dmPFC. Neither the vmPFC→BLA PNs nor the d/vmPFC→NAc PNs were affected following CRS exposure, suggesting that among the complex neuronal populations in mPFC, the dmPFC→BLA PNs, particularly for those in layer V of dmPFC, represent a group vulnerable to chronic stress exposure.
As a critical hub for brain to cope with stress, mPFC is highly heterogenous in terms of the responses made by the neurons in different subregions or even different layers [4, 31, 32]. Mounting evidence indicates that the dmPFC and vmPFC neurons have distinct roles in stress coping and regulating anxiety and fear expression [12]. For instance, while the dmPFC neurons were shown to mainly participate in anxiety and fear expression, those in vmPFC are more engaged in fear extinction and have little effect on anxiety-like behavior [12, 33]. At a more microscopic level, chronic stress was observed to alter the spine density and increase the expression of c-fos, an indicator of neuronal activity, in dmPFC but not vmPFC neurons [11, 34]. Adding complexity to these, we found that CRS also preferentially decreased the inhibitory transmission and increased intrinsic excitability in dmPFC but not vmPFC neurons. Although the exact reasons for the subregion-specific changes are not yet known, there are finding showing that the GABAergic transmission and neuronal intrinsic excitability differ between dmPFC and vmPFC. For the dmPFC neurons, they receive relatively stronger GABAergic inputs but have weaker intrinsic excitability than their vmPFC neighbors[35, 36]. These differences may be related to the different influences of CRS on these two mPFC PN populations. In addition to this, we further found that these CRS influences only occurred in the dmPFC layer V but not layer II/III neurons. It may not be surprising, given that increasing evidence has been accumulated to show that the superficial and deeper layers of mPFC neurons are differently affected by acute versus chronic stress. For instance, chronic stress was shown to alter the excitability and synaptic transmission in the mPFC layer V but not layer II/III neurons [16, 37]. By contrast, acute stress selectively altered the synaptic transmission onto mPFC neurons in layer II/III but not layer V neurons [17].
Recent studies have begun to show that individual mPFC neurons exhibit markedly different responses to stress, which is likely associated with their molecular profiles and structural connectivity with other brain regions. For instance, chronic unpredictable stress increases excitability and excitatory synaptic transmission of dopamine D1-type receptor-expressing pyramidal neurons in the dmPFC, but reduces that in dopamine D2-type receptor-expressing neurons [37]. In terms of structural connectivity, evidence shows that chronic variable stress (CVS) increases the activity of ventral tegmental area (VTA)-projecting mPFC neurons and induces anxiety-like behavior [38]. Optogenetic inhibition of the dorsal raphe nucleus projecting mPFC neurons reduces social behaviors after chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) [39]. In supporting the view that stress causes specific regulation of activity of mPFC neurons in a circuit-dependent manner, we here found that CRS selectively decreased the inhibitory synaptic transmission and increased the intrinsic excitability in dmPFC→BLA neurons in layer V, which added new evidence to previous literature highlighting the importance of mPFC-BLA circuit in the pathology of stress-related disorders [7, 8, 40,41,42]. Notably, for the NAc-projecting mPFC neurons, we did not observe any changes in the synaptic transmission, except for a tendency of decrease in intrinsic excitability. We speculate that dmPFC→BLA neurons may be more vulnerable to chronic stress than its dmPFC-NAc counterpart. It should be noted that we only used male mice in this study. A previous study showed that CVS causes sex-specific modifications in the morphology of NAc- projecting mPFC neurons, since CVS decreased the dendritic arborization in NAc-projecting neurons in female mice but not male mice [38]. Considering females are more sensitive to stress exposure and are more likely to develop anxiety and depression, it would be interesting to determine whether CRS has any effect on the NAc-projecting mPFC neurons in female in future studies.
Chronic stress-induced disruption of excitatory-inhibitory (E-I) balance in mPFC plays a critical role in the pathological of anxiety- and depression-like behavior [43, 44]. For example, a study showed that chronic stress reduces the inhibitory transmission in the mPFC [45]; interestingly, we found that the reduced inhibitory transmission mainly occurred in the dmPFC-BLA neurons but not in their proximal dmPFC-NAc ones. Since the excitatory synaptic transmission remained unaffected, a net shift of the E-I balance of synaptic transmission toward excitation emerged in dmPFC-BLA neurons. Although the exact molecular mechanisms underlie the CRS-induced decrease in the inhibitory signal in dmPFC-BLA neurons remains unknown, one possible explanation is that CRS may inhibit the probability of GABA release from presynaptic terminals of GABAergic interneurons. It has been showed that chronic stress decreases the release probability of GABA from GABAergic interneurons, leading to a decrease in the frequency of mIPSCs in mPFC [45]. On the other hand, as generally known, the GABAergic interneurons are composed of multiple populations which express relatively specific markers such as the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin (PV), the neuropeptide somatostatin (SST) and the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) respectively with each providing distinct inhibition onto the pyramidal neurons [46,47,48]. Accumulating evidence suggests a causal relationship between the deficit of interneurons in mPFC and stress-related psychiatric disorders. For example, chronic stress reduces the cell density of PV interneurons in mPFC [49,50,51], and causes deficit of SST cell function [52]. It is worthwhile to identify which interneuron subtype contributes to the chronic stress-induced deficit of GABAergic signal in the BLA-projecting dmPFC neurons.
Except for the reduced inhibitory synaptic transmission, another important observation in the present study was that CRS also caused strengthened intrinsic excitability of BLA-projecting dmPFC neurons in layer V. This may provide an explanation for why CRS enhances the glutamatergic transmission from dmPFC projection to BLA neurons in our recent study [8]. One limitation of the study is that the potential factors contributing to the regulation of intrinsic excitability are not investigated. However, our further analysis of the AP parameters revealed that CRS increased the input resistance while decreased the rheobase and sag ratio in BLA-projecting dmPFC neurons, hinting a potential involvement of HCN channels, which have been widely reported in regulating the input resistance and sag ratio, and subsequently modulates neuronal excitability [36, 53,54,55], and are considered as a potential target for treating stress-related disorders, such as anxiety and depression [56, 57]. For instance, knockdown of HCN channels in the dorsal hippocampal increased neuronal excitability that is sufficient to produce anxiolytic-like and antidepressant effects [57]. In addition, chronic stress increases neuron firing through HCN channel impairments in BLA and induces anxiety-like behavior [58]. In line with our results that CRS enhanced the excitability of BLA-projecting neurons in dmPFC layer V but not in layer II/III, a previous finding shows that the HCN channel expression is higher in Layer V neurons than layer II/III [36], it is plausible that the different expression and function of HCN channels may provide a physiological basis for layer-specific response to chronic stress.
While our study showed for the first time that chronic stress differentially regulates the GABAergic transmission and intrinsic excitability of mPFC neurons projecting to BLA and NAc in a laminar- and subregion-dependent manner, some questions are still open. For example, although we have observed that CRS decreased inhibitory synaptic transmission and increased intrinsic excitability in BLA- but not NAc-projecting dmPFC neurons, what are the molecular mechanisms driving such changes? Second, the causal link between the CRS-induced dysregulation of functional neuroplasticity in dmPFC neurons projecting to BLA and anxiety-like behavior remains unknown. Answering these important questions will expand our understanding of the pathological mechanism of stress-related disorders.
Materials and methods
Animals
C57BL/6J mice were bred in the animal facility of Nanchang University. 4–5 mice were housed in a cage in a temperature-controlled (25 ℃) vivarium and food and water were provided ad libitum under a 12-h light/dark cycle with lights on at 07:00 am. Only male C57BL/6J mice were used in all experiment. All experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanchang University (approval No.: ncdxsydwll-2018-26).
Stereotaxic surgery
Four-week-old mice were anaesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of 2% pentobarbital sodium and placed in a stereotaxic frame (RWD, Shenzhen, China). For labelling the BLA- and NAc-projecting mPFC neurons, the retrogradely AAV2/retro-hSyn-mCherry and AAV2/retro- hSyn-EGFP virus were bilaterally injected (0.2 μL per hemisphere) into the BLA (posterior to bregma, AP = − 1.28 mm; lateral to the midline, ML = ± 3.2 mm; below the bregma, DV = − 5.05 mm) and NAc (AP = + 1.42 mm; ML = ± 0.85 mm; DV = − 4.7 mm) with a glass micropipette at a rate of 80 nl/min using a stereotactic injector (QSI, Stoelting, Wood Dale, IL, USA), respectively.
Confocal imaging
Mice were deeply anesthetized with 2% pentobarbital sodium and transcardially perfused with PBS and of 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA). Brains were quickly removed from the skull and then post-fixed overnight at 4 ℃ in PFA. 40 μm thick coronal slices including the dmPFC or vmPFC were cut using VT1200S Vibratome (Leica Microsystems). Slices were washed in PBS 3 for 5 min and incubated with DAPI solution (Beyotime, China) for nuclear labeling and then mounted onto slides with Fluoromount aqueous mounting medium (Sigma-Aldrich, Sant Louis, Missouri, MO, USA). Images were taken using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Olympus FV1000, Tokyo, Japan). The number of virus-labeled neurons in dmPFC or vmPFC was calculated using ImageJ software (version 1.50, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, USA) with the Cell Counter plug-in for assessing the overlay of BLA-projecting and NAc-projecting dmPFC or vmPFC neurons.
Chronic restraint stress
Fifty-day-old mice were subjected to a restraint cylinder fitted closely to body size for 2 h per day at 10:00 am, for 10 consecutive days. For non-stressed control mice, they were transferred to the experimental room from their home cages and gently handled for 5 min before being returned to the holding room 2 h later.
Chronic unpredictable stress
Fifty-day-old mice were subjected to a variety of stressors at different times of the day for 10 days. The stressors included 2-h restraint, 15-min tail pinch, 24-h constant light, 24-h wet bedding with 45° cage tilt, 10-min inescapable foot shocks, and social isolation. Stress exposure was conducted in a procedure room.
Open field test
Each mouse was habituated to test room for 30 min prior to experimentation and placed in the center of a chamber, made of transparent plastic (50 × 50 cm), for 10 min with monitored by overhead video-tracking system (Med Associates Inc., Farifax, VT, USA). The maze was cleaned with 75% ethanol between each trial. ANY-maze software (Stoelting Co., USA) was used to analyze the time mice spent in center area and total distance they traveled during each test.
Elevated plus maze test
Mice placed in the center of a plus-shaped maze with a pair of closed and open arms followed 30-min habituation in testing room. During behavioral test, a video-tracking system (Med Associates Inc., Farifax, VT, USA) was used to monitored their behavior for 10 min. The maze was cleaned with 75% ethanol between each trial. The ANY-maze software (Stoelting Co., USA) was used to analyze the time spent in open arms and entries into the open or closed arms.
Electrophysiological slice recording
Mice were anesthetized with ether and decapitated, then their brains were rapidly removed and chilled in well-oxygenated (95% O2 and 5% CO2) ice-cold dissection buffer containing (in mM): 80 NaCl, 3.5 KCl, 4.5 MgSO4, 0.5 CaCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 25 NaHCO3, 90 sucrose, and 10 glucose. Coronal brain slices (320 μm) containing dmPFC or vmPFC were cut using VT1200S microtome (Leica Microsystems) and were subsequently transferred to oxygenated ACSF containing (in mM): 124 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2 MgSO4, 2.5 CaCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 22 NaHCO3, and 10 glucose, for 30 min recovery at 34 ℃. Then the brain slices were maintained at RT for at least 1 h and a single slice was transferred to the recording chamber and continuously perfused with oxygenated ACSF during all electrophysiological studies. Automatic temperature controller (TC-324B, Warner Instrument Co. Hamden, CT, USA) was used to maintain the temperature of ACSF in the chamber at 29 ± 1 ℃. Recording patch pipettes were made from filamented borosilicate glass capillary tubes (inner diameter, 0.84 μm) by using a horizontal pipette puller (P-97; Sutter Instrument Co., Novato, CA, USA). The recording of mEPSCs and mIPSCs was performed as previous study [37]. Briefly, tetrodotoxin (1 μM) was added in the bath solution and the patch pipettes were filled with an intracellular solution containing (in mM): 130 Cs-methanesulfonate, 5 NaCl, 1 MgCl2, 10 HEPES, 0.2 EGTA, 2 MgATP, 5 QX314, and 0.1 NaGTP, pH was adjusted to 7.30 with CsOH. To evoke action potentials, picrotoxin (100 μM) and CNQX (20 μM) were added in the bath solution. The virus-labelled neurons were injected with the depolarizing current pulses with their strength ranging from 0 to 250 pA and increased at a 50-pA step. The AP amplitude was measured as the voltage difference between the threshold and peak of the AP. The AP Half-width was determined as the duration of half-height between the threshold and the peak of the AP. The voltage sag ratio was calculated using the following equation: sag ratio = Vmax/Vss = (Vbaseline − Vmin)/(Vbaseline − Vsteady), in which Vsteady is the voltage averaged within 50 ms before the end of current injection, Vbaseline is the resting membrane potential, and Vmin is the hyperpolarizing current that induced minimum voltage. The AP rheobase was defined as the smallest current that produce the first spike. The patch pipettes were filled with 130 mmol/L k-gluconate. Data were collected with the PATCHMASTER software (version 2.53) using the patch-clamp amplifier (EPC 10 USB, HEKA Instrument, Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Germany).
Statistical analyses
The statistical analyses were performed by GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Data were analyzed using Student t test or two-way analysis of variance with or without repeated measures, followed by post hoc test with Bonferroni correction. Data are presented as means ± SEM. The threshold for statistical significance was p < 0.05.
References
Moghaddam B, Javitt D. From revolution to evolution: the glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia and its implication for treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37:4–15.
Bale TL. Sensitivity to stress: dysregulation of CRF pathways and disease development. Horm Behav. 2005;48:1–10.
Sharma S, Powers A, Bradley B, Ressler KJ. Gene × environment determinants of stress- and anxiety-related disorders. Annu Rev Psychol. 2016;67:239–61.
Belleau EL, Treadway MT, Pizzagalli DA. The impact of stress and major depressive disorder on hippocampal and medial prefrontal cortex morphology. Biol Psychiatry. 2019;85:443–53.
Cerqueira JJ, Mailliet F, Almeida OF, Jay TM, Sousa N. The prefrontal cortex as a key target of the maladaptive response to stress. J Neurosci. 2007;27:2781–7.
Wellmana CL, Bollinger JL, Moench KM. Effects of stress on the structure and function of the medial prefrontal cortex: insights from animal models. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2020;150:129–53.
Liu WZ, Huang SH, Wang Y, Wang CY, Zhao PHQ, K, et al. Medial prefrontal cortex input to basolateral amygdala controls acute stress-induced short-term anxiety-like behavior in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;48:734.
Liu WZ, Zhang WH, Zheng ZH, Zou JX, Liu XX, Huaug SH, et al. Identification of a prefrontal cortex-to-amygdala pathway for chronic stress-induced anxiety. Nat Commu. 2020;11:2221.
Heidbreder CA, Groenewegen HJ. The medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: evidence for a dorso-ventral distinction based upon functional and anatomical characteristics. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003;27:555–79.
McGinnis MM, Parrish BC, Alexander CAM, NJ, McCool BA,. Chronic ethanol differentially modulates glutamate release from dorsal and ventral prefrontal cortical inputs onto rat basolateral amygdala principal neurons. eNeuro. 2019;7:0132–1119.
Qu Y, Yang C, Ren Q, Ma M, Dong C, Hashimoto K. Regional differences in dendritic spine density confer resilience to chronic social defeat stress. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2018;30:117–22.
Suzuki S, Saitoha A, Ohashi M, Yamadaa M, Oka JI, Yamadaa M. The infralimbic and prelimbic medial prefrontal cortices have differential functions in the expression of anxiety-like behaviors in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2016;304:120–4.
Saitoh A, Ohashi M, Suzuki S, Tsukagoshi M, Sugiyama A, Yamada M, et al. Activation of the prelimbic medial prefrontal cortex induces anxiety-like behaviors via N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated glutamatergic neurotransmission in mice. J Neurosci Res. 2014;92:1044–53.
Xu P, Chen A, Li YP, Xing XZ, Lu H. Medial prefrontal cortex in neurological disease. Physiol Genomics. 2019;51:432–42.
Van De Werd HJ, Rajkowska G, Evers P, Uylings HB. Cytoarchitectonic and chemoarchitectonic characterization of the prefrontal cortical areas in the mouse. Brain Struct Funct. 2010;214:339–53.
Liu RJ, Aghajanian GK. Stress blunts serotonin- and hypocretin-evoked EPSCs in prefrontal cortex: role of corticosterone-mediated apical dendritic atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:359–64.
Hwa LS, Neira S, Pina MM, Pati D, Calloway R, Kash TL, et al. Predator odor increases avoidance and glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the prelimbic cortex via corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 signaling. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019;44:766–75.
Urban KR, Geng E, Bhatnagar S, Valentino RJ. Age- and sex-dependent impact of repeated social stress on morphology of rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. Neurobiol Stress. 2019;10: 100165.
Csabai D, Wiborg O, Czeh B. Reduced synapse and axon numbers in the prefrontal cortex of rats subjected to a chronic stress model for depression. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:24.
Mitric M, Seewald A, Moschetti G, Sacerdote P, Ferraguti F, Kummer KK, et al. Layer- and subregion-specific electrophysiological and morphological changes of the medial prefrontal cortex in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9479.
Zhang WH, Zhang JY, Holmes A, Pan BX. Amygdala circuit substrates for stress adaptation and adversity. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;89:847–56.
Zhang WH, Liu WZ, He Y, You WJ, Zhang JY, Xu H, et al. Chronic stress causes projection-specific adaptation of amygdala neurons via small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel downregulation. Biol Psychiatry. 2019;85:812–28.
Francis TC, Chandra R, Friend DM, Finkel E, Dayrit G, Miranda J, et al. Nucleus accumbens medium spiny neuron subtypes mediate depression-related outcomes to social defeat stress. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:212–22.
Anastasiades PG, Carter AG. Circuit organization of the rodent medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Neurosci. 2021;44:550–63.
Maeng LY, Waddell J, Shors TJ. The prefrontal cortex communicates with the amygdala to impair learning after acute stress in females but not in males. J Neurosci. 2010;30:16188–96.
Zheng ZH, Tu JL, Li XH, Hua Q, Liu WZ, Liu Y, et al. Neuroinflammation induces anxiety- and depressive-like behavior by modulating neuronal plasticity in the basolateral amygdala. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;91:505–18.
Eagle AL, Manning CE, Williams ES, Bastle RM, Gajewski PA, Garrison A, et al. Circuit-specific hippocampal DeltaFosB underlies resilience to stress-induced social avoidance. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4484.
Chang X, Ma M, Wu H. Animal models of stress and stress-related neurocircuits: a comprehensive review. Stress Brain. 2021;1:108–27.
Moreno-Martinez S, Tendilla-Beltran H, Sandoval V, Flores G, Terron JA. Chronic restraint stress induces anxiety-like behavior and remodeling of dendritic spines in the central nucleus of the amygdala. Behav Brain Res. 2022;416: 113523.
Wood GE, Norris EH, Waters E, Stoldt JT, McEwen BS. Chronic immobilization stress alters aspects of emotionality and associative learning in the rat. Behav Neurosci. 2008;122:282–92.
Musaelyan K, Yildizoglu S, Bozeman J, Du Preez, A, Egeland M, Zunszain P, et al. Chronic stress induces significant gene expression changes in the prefrontal cortex alongside alterations in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain Commun. 2020; 2.
McKlveen JM, Myers B, Herman JP. The medial prefrontal cortex: coordinator of autonomic, neuroendocrine and behavioural responses to stress. J Neuroendocrinol. 2015;27:446–56.
Sierra-Mercado D, Padilla-Coreano N, Quirk GJ. Dissociable roles of prelimbic and infralimbic cortices, ventral hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala in the expression and extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:529–38.
Jing XY, Wang Y, Zou HW, Li ZL, Liu YJ, Li LF. mGlu2/3 receptor in the prelimbic cortex is implicated in stress resilience and vulnerability in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;906:174231.
Kim H II, Kim N, Kim S, Toda K, Catavero CM, Courtland JL, et al. Dysregulation of the synaptic cytoskeleton in the PFC drives neural circuit pathology, Leading to social dysfunction. Cell Rep. 2020;32: 107965.
Song CG, Moyer JR Jr. Layer- and subregion-specific differences in the neurophysiological properties of rat medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2018;119:177–91.
Anderson EM, Gomez D, Caccamise A, McPhail D, Hearing M. Chronic unpredictable stress promotes cell-specific plasticity in prefrontal cortex D1 and D2 pyramidal neurons. Neurobiol Stress. 2019;10: 100152.
Bittar TP, Pelaez MC, Hernandez Silva JC, Quessy F, Lavigne AA, Morency D, et al. Chronic stress induces sex-specific functional and morphological alterations in corticoaccumbal and corticotegmental pathways. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;90:194–205.
Challis C, Beck SG, Berton O. Optogenetic modulation of descending prefrontocortical inputs to the dorsal raphe bidirectionally bias socioaffective choices after social defeat. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014;8:43.
Yu H, Chen L, Lei H, Pi G, Xiong R, Jiang T, et al. Infralimbic medial prefrontal cortex signalling to calbindin 1 positive neurons in posterior basolateral amygdala suppresses anxiety- and depression-like behaviours. Nat Commun. 2022;13:5462.
LeClair KB, Russo SJ. Using social rank as the lens to focus on the neural circuitry driving stress coping styles. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021;68:167–80.
Gao F, Huang J, Huang GB, You QL, Yao S, Zhao ST, et al. Elevated prelimbic cortex-to-basolateral amygdala circuit activity mediates comorbid anxiety-like behaviors in chronic pain. J Clin Invest. 2023;133:e166356.
Lener MS, Niciu MJ, Ballard ED, Park M, Park LT, Nugent AC, et al. Glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid systems in the pathophysiology of major depression and antidepressant response to ketamine. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;81:886–97.
Page CE, Coutellier L. Prefrontal excitatory/inhibitory balance in stress and emotional disorders: evidence for over-inhibition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019;105:39–51.
Czeh B, Vardya I, Varga Z, Febbraro F, Csabai D, Martis LS, et al. Long-term stress disrupts the structural and functional integrity of GABAergic neuronal networks in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:148.
Rudy B, Fishell G, Lee S, Hjerling-Leffler J. Three groups of interneurons account for nearly 100% of neocortical GABAergic neurons. Dev Neurobiol. 2011;71:45–61.
Tremblay R, Lee S, Rudy B. GABAergic interneurons in the neocortex: from cellular properties to circuits. Neuron. 2016;91:260–92.
Markram H, Toledo-Rodriguez M, Wang Y, Gupta A, Silberberg G, Wu CZ. Interneurons of the neocortical inhibitory system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:793–807.
Todorovic N, Micic B, Schwirtlich M, Stevanovic M, Filipovic D. Subregion-specific protective effects of fluoxetine and clozapine on parvalbumin expression in medial prefrontal cortex of chronically isolated rats. Neuroscience. 2019;396:24–35.
Ganguly P, Holland FH, Brenhouse HC. Functional uncoupling NMDAR NR2A subunit from PSD-95 in the prefrontal cortex: effects on behavioral dysfunction and parvalbumin loss after early-life stress. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:2666–75.
Page CE, Coutellier L. Adolescent stress disrupts the maturation of anxiety-related behaviors and alters the developmental trajectory of the prefrontal cortex in a sex- and age-specific manner. Neuroscience. 2018;390:265–77.
Lin LC, Sibille E. Somatostatin, neuronal vulnerability and behavioral emotionality. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20:377–87.
Bean BP, Yamada-Hanff J. Activation of Ih and TTX-sensitive sodium current at subthreshold voltages during CA1 pyramidal neuron firing. J Neurophysiol. 2015;114:2376–89.
Sun Z, Williams DJ, Xu B, Gogos JA. Altered function and maturation of primary cortical neurons from a 22q11.2 deletion mouse model of schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8:85.
Yi F, Danko T, Botelho SC, Patzke C, Pal C, Wernig M, et al. Autism-associated SHANK3 haploinsufficiency causes Ih channelopathy in human neurons. Science. 2016;352:aaf2669.
Sanghee Y, Reynolds PR, Petrof I, White A, Rivera PD, Segev A, et al. Stimulation of entorhinal cortex–dentate gyrus circuitry is antidepressive. Nat Med. 2018;24:658–66.
Kim CS, Chang PY, Johnston D. Enhancement of dorsal hippocampal activity by knockdown of HCN1 channels leads to anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like behaviors. Neuron. 2012;75:503–16.
Shao LX, Jiang Q, Liu XX, Gong DM, Yin YX, Wu G, et al. Functional coupling of Tmem74 and HCN1 channels regulates anxiety-like behavior in BLA neurons. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:1461–77.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Key R&D Program of China (2021ZD0202704 to PB), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 82101589 to LW, 81930032 and 82125010 to PB, 32222034 and 31970953 to ZW, 32160193 to PH), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20212ACB206038 to ZW), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2021TQ0138 and 2021M701545 to LW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W-ZL, W-HZ, and B-XP conceived the study. C-YW, YW, M-TC, W-XZ and TL performed the experiments. Z-HW, and H-QP analyzed the data. W-ZL, W-HZ and B-XP wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Use of animal was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanchang University (approval No.: ncdxsydwll-2018-26) and no human participants and human tissue were included in our studies.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional
file 1: Figure S1. Characterizations of the specificity of BLA- and NAc- projecting neurons in mPFC. A Representative images showing the co-labeling of mPFC→BLA PNsand pyramidal neuronal marker-CaMKIIα. Scale bar: 100 μm. B Summary plots showing the ratio of CaMKIIα expressing cells in mPFC→BLA PNs. C Representative images showing the colabeling of mPFC→NAc PNsand CaMKIIα. Scale bar: 100 μm. D Summary plots showing the ratio of CaMKIIα expressing cells in mPFC→NAc PNs. Figure S2. CUS significantly induces anxiety-like behavior in mice. A Experimental procedures. B Representative activity tracking in EPMT. C, D Summary plots of time in open arms and open-arm entries during EPMT. E Representative activity tracking in center area OFT. F Summary plots of time in center area during OFT. G Summary plots of total distance travelled during OFT. H Summary plots of mean speed during OFT. Figure S3. CUS markedly decreases inhibitory synaptic transmission onto dmPFC→BLA PN in layer V. A Representative traces showing mEPSCs in dmPFC layer II/III. B, C Summary plots of averaged mEPSCs frequency and amplitude . D Representative traces showing mEPSCs in dmPFC layer V. E,F Summary plots of averaged mEPSCs frequency and amplitude . G Representative traces showing mIPSCs in dmPFC layer II/III. H, I Summary plots of averaged mIPSCs frequency and amplitude. J Representative traces showing mIPSCs in dmPFC layer V. K, L Summary plots of averaged mIPSCs frequency and amplitude. M Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in dmPFC layer II/III. N Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio in dmPFC layer II/III. O Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in dmPFC layer V. P Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio dmPFC layer V. Figure S4. CUS does not changes synaptic transmission onto both vmPFC→BLA or vmPFC→NAc PN. A Representative traces showing mEPSCs in vmPFC layer II/III. B, C Summary plots of averaged mEPSCs frequency and amplitude. D Representative traces showing mEPSCs in vmPFC layer V. E,F Summary plots of averaged mEPSCs frequency and amplitude. G Representative traces showing mIPSCs in vmPFC layer II/III. H, I Summary plots of averaged mIPSCs frequency and amplitude. J Representative traces showing mIPSCs in vmPFC layer V. K, L Summary plots of averaged mIPSCs frequency and amplitude. M Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in vmPFC layer II/III. N Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio in vmPFC layer II/III. O Summary plots of I/E frequency ratio in vmPFC layer V. P Summary plots of I/E amplitude ratio in vmPFC layer V.
Additional
file 2: Statistical detail informationfor figures.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, WZ., Wang, CY., Wang, Y. et al. Circuit- and laminar-specific regulation of medial prefrontal neurons by chronic stress. Cell Biosci 13, 90 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-023-01050-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-023-01050-2