Abstract
As the predominant modification in RNA, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) has attracted increasing attention in the past few years since it plays vital roles in many biological processes. This chemical modification is dynamic, reversible and regulated by several methyltransferases, demethylases and proteins that recognize m6A modification. M6A modification exists in messenger RNA and affects their splicing, nuclear export, stability, decay, and translation, thereby modulating gene expression. Besides, the existence of m6A in noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) could also directly or indirectly regulated gene expression. Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common cancer around the world and of high mortality. Increasing evidence have shown that the changes of m6A level and the dysregulation of m6A regulatory proteins have been implicated in CRC carcinogenesis and progression. However, the underlying regulation laws of m6A modification to CRC remain elusive and better understanding of these mechanisms will benefit the diagnosis and therapy. In the present review, the latest studies about the dysregulation of m6A and its regulators in CRC have been summarized. We will focus on the crucial roles of m6A modification in the carcinogenesis and development of CRC. Moreover, we will also discuss the potential applications of m6A modification in CRC diagnosis and therapeutics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common malignant tumor in the world and it is of the second highest mortality [1]. Although the survival time of CRC patients has increased in recent years by improving basic diagnosis and treatment strategies, the mortality of CRC is still at a relatively high level. Due to the lack of reliable early diagnosis biomarkers and the asymptomatic disease progression, some of the diagnosed CRC patients are in advanced clinical stages, which results in death of approximately 900,000 patients every year [2]. Surgical resection is a possible cure strategy, but only for a few patients with advanced CRC, and postoperative tumor recurrence is very common. Due to the difficulties in early diagnosis and limited treatment options, CRC remains a challenging disease. It is generally believed that, genomic instability (e.g., chromosomal instability, DNA-repair defects and aberrant DNA/RNA methylation), mutational inactivation of tumor suppressor genes (e.g., APC, TP53 and TGF-β), and activation of oncogenes (e.g., RAS, BRAF and PI3K) are all involved in the occurrence and development of CRC [3], but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain largely unexplored. Thus, understanding the molecular mechanisms of CRC occurrence and progression more clearly is essential for advancing the diagnosis and treatment in the future.
Epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation and histone modification have participated in many biological processes, and epigenetic dysregulation is involved in a variety of diseases including cancer. Recently, chemical modifications of RNA have drawn increasing attention since these modifications could fine-tune the structure and function of RNA, and this has leaded to the proposal of RNA epigenetics/epitranscriptomics [4]. As a typical form of RNA modification, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) was found both in coding RNA and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). The level of m6A modification is dynamic and reversible, and this is mainly mediated by the m6A methyltransferases and demethylases. The m6A modification is recognized by different reader proteins and exerts its unique biological function. Specifically, through targeted regulation of RNA fate, deregulation of m6A modulators is related to immunomodulation [5], cancer stemness [6], epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [7] and cancer metabolism [8]. Multiple m6A regulatory proteins are recently reported to be abnormally regulated and act either as oncogenes or tumor suppressors in CRC. In this review, we summarized the latest findings about the impacts of m6A modification located on different types of RNA on CRC initiation and progression. Moreover, we discussed the potential implications of m6A modification in CRC diagnosis and therapeutics.
N6-methyladenosine
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification refers to the addition of a methyl group at the N6 position of adenosine. This is an evolutionarily conservative RNA modification that can be found in most organisms, from bacteria to mammals [9]. M6A modification is considered to be the most common chemical modification in eukaryotic mRNA and lncRNA [10], and 0.1–0.4% of all adenosines in total cellular RNAs with an average of 3–5 m6A modifications per mRNA [11]. The action-sites of m6A modification are not random, and they have a typical consensus sequence RRACH (R = G, A or U; H = A, C or U). Moreover, m6A modification highly occurs in 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR), near the stop codon region, and long internal exons [10, 12].
Reversible m 6 A modification
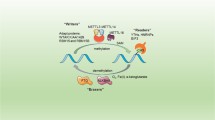
Similar to DNA, RNA can also be methylated and demethylated by specific methyltransferases and demethylases, respectively. RNA m6A modification was previously considered to be static, discrete, and used to fine-tune RNA structure and function. However, with the discovery of METTL3/METTL14/WTAP methyltransferase complex [13] and demethylase FTO [14] and ALKBH5 [15], investigations on m6A modification have returned to the forefront because these findings indicate that m6A modification is reversible and can be dynamically adjusted, implying the potential of these regulatory proteins in regulating biological processes.
Writers, erasers and readers of m 6 A
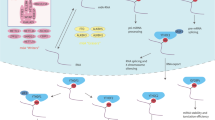
The biological effects of m6A are mainly mediated by the proteins of writer, eraser and reader (Fig. 1). As mentioned above, m6A modification is dynamic and reversible, and this indicates RNA can be methylated by methyltransferases (writers) and demethylated by demethylases (erasers). Writers mainly consist of METTL3 and METTL14 and their cofactors WTAP. Both of METTL3 and METTL14 contain an S-adenosylmethionine-binding (SAM-binding) motif to play the role of transferring methyl group to adenosine at N6 position [16]. METTL3 is the major catalytic enzyme and the main function of METTL14 is to stabilize METTL3 and recognize target RNA [17, 18]. WTAP can regulate m6A methylation complex which helps METTL3 and METTL14 to be located in nuclear spots [19]. Besides, METTL16 [20], KIAA1429 [21] and RBM15 [22] were also identified as m6A writers.
Erasers, which can achieve the function of demethylation, mainly include FTO and ALKBH5. FTO was identified as the first m6A demethylase, and this major breakthrough leads to great prosperity in the realm of RNA epigenetics. FTO can sequentially oxidize m6A to N6-hydroxymethyladenosine and N6-formyladenosine, and then N6-formyladenosine can be hydrolyzed to adenosine easily [14]. ALKBH5, an FTO homologue, can directly oxidize m6A to adenosine [15].
Apart from writers and erasers, another group is readers, which can recognize m6A modification and exert different biological functions. One type of readers with the YT521B homology (YTH) domain contains YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3, YTHDC1 and YTHDC2. They all have specific m6A binding domains and preferentially bind to m6A modification sites in RNA with RRm6ACH sequence [23]. Among these, YTHDF2 was firstly identified and it can influence mRNA stability. YTHDF2 accelerates the degradation of mRNA by sending m6A-mediated mRNAs to mRNA decay sites (such as P-bodies) [24], and it can also recruit the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex to promote mRNA degradation [25]. YTHDF1 has shown the ability to promote mRNA translation efficiency by interacting with translation initiation factor eIF3 [26]. YTHDF3 can be fine-tuned to balance the different effects of YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 on mRNA [27, 28]. YTHDC1 can mediate RNA splicing and control the nuclear export of its targets by interacting with SRSF3 [29]. YTHDC2 can interact with RNA helicase to promote the extension of the translation process [30]. Moreover, readers also contain IGF2BP1/2/3 and three heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs), including hnRNPC, hnRNPG and hnRNPA2B1. IGF2BP proteins specifically recognize m6A-containing transcripts and stabilize them. For hnRNPs, it has been reported that hnRNPC/G can influence mRNA localization and alternative splicing [31], and hnRNPA2B1 can promote microRNA maturation with the help of DGCR8, which is an RNA-binding protein that recognizes pri-miRNA hairpin [32].
Function of m6A on coding and noncoding RNAs
Function of m 6 A on mRNA
Gene expression is strictly controlled at four levels, i.e., transcription, post-transcription, translation and post-translation. M6A modification deposits on natural RNA transcripts during transcription and affects gene expression after transcription by altering RNA structure or through specific recognition by m6A binding proteins [33] (Fig. 2).
Functions of m6A modification on mRNA. M6A modification undergo alternative splicing with the recruitment of splicing factors to m6A sites or flanking sequences. After splicing, m6A-containing mRNAs are recognized by YTHDC1 and exported into cytoplasm. M6A on mature mRNAs affects mRNA stability, translation initiation, and translation elongation
The m6A writers and erasers are located in nuclear speckles, where they are related to mRNA splicing factors, suggesting that m6A is functionally related to mRNA splicing [14, 15, 34]. Specifically, m6A on the pre-mRNA can exert mRNA splicing function by recruiting hnRNPB2A1 or changing the local structure to increase the accessibility to the splicing factor hnRNPC/hnRNPG [35, 36]. In addition, m6A can also recruit the splicing factor SRSF3 by binding to YTHDC1 to complete the splicing of exons [37]. YTHDC1 can also affect the exportation of m6A modified mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm and thus affects its transcription process [29].
Mature mRNA in the cytoplasm can be loaded onto ribosomes for active translation, or sorted onto messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) foci for degradation or storage. The YTH domain-containing family proteins (YTHDFs) tend to accelerate metabolism of m6A-modified mRNAs. YTHDF1 selectively recognizes m6A and interacts with initiation factor eIF3 to promote translation initiation and protein synthesis [26]. On the contrary, YTHDF2 brings m6A modified translatable mRNA to the site of mRNA decay and recruits CCR4-NOT complex to trigger mRNA degradation [25, 38]. YTHDF3 cooperates with YTHDF1 to promote mRNA translation and promotes the degradation of m6A-containing mRNA by interacting with YTHDF2 [27, 28]. In contrast to the promoting degradation function of YTHDF2, proteins of the IGF2BP family interact with ELAVL1 (also known as HuR), MATR3, and PABPC1 to protect m6A-modified mRNA in P-body and stress granules from degradation and promote their translation [39]. Since m6A is usually enriched near the stop codon, the role of m6A in promoting translation initiation is achieved through a closed-loop model, in which the cyclization of mRNA is accomplished via the interaction between the elFs and METTL3 or YTHDF1 bound to the m6A site near the stop codon [26, 40]. It is also reported that the m6A modification in 5′UTR can promote cap-independent translation by recruiting eIF3a to a nearby translation start site [41]. In the translation extension stage, the m6A modification on mRNA can hinder tRNA accommodation, thereby disturbs the translation extension dynamics [42]. Besides, m6A modification on mRNA can bind to YTHDC2 to positively regulate translation elongation [30].
Function of m 6 A on ncRNAs
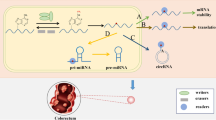
Although ncRNAs cannot be directly translated into protein, they have special functions in regulating gene expression, and can be divided into long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and small non-coding RNA according to whether the length exceeds 200 nt. Previous studies indicated that m6A modification also played important roles in the expression and functions of ncRNAs, including lncRNA, miRNA and circRNA [43,44,45,46] (Fig. 3).
Functions of m6A modification on non-coding RNA. M6A on lncRNA plays roles in RNA structural switch, lncRNA-mediated ceRNA model and XIST-mediated gene silencing. Presence of m6A on pri-miRNA facilitates or inhibits miRNA processing. In circRNA, m6A could promote circRNA translation, circRNA cytoplasmic export and circRNA degradation
The m6A methylation on lncRNA was usually located on the poly (A) region. Due to the lack of coding ability, lncRNA regulates gene expression by acting as an RNA structural switch, participating in the lncRNA-mediated competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) model or promoting X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) mediated gene silencing. lncRNA-mediated ceRNA model means that lncRNA acts as a competitive RNA of miRNA to affect its function. It was reported that m6A modification acted as a structural switch to affect RNA–protein interactions by modulating the structure of several RNAs, including metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript (MALAT1) [47], which is a lncRNA and has been consistently associated with the progression of various cancers. Several studies have proposed lncRNA-mediated ceRNA model, in which lncRNA LINC01234 and SNHG6-003 act as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate the activity and biological function of miRNAs [48, 49]. In addition, WTAP and RBM15B have been identified as XIST-associated protein and both of them are necessary for XIST-mediated transcriptional repression [22, 50].
MiRNA is a highly abundant small noncoding RNA and its functions mainly include gene silencing and post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. The primary transcript of miRNA (pri-miRNA) transcribed from DNA undergoes a series of cleavage processes to generate hairpin precursors, precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) and mature miRNA successively. The pri-miRNAs are rich in canonical m6A motif (GGAC), and most of them can be methylated by METTL3 [51]. The pri-miRNAs labeled with m6A can be recognized by hnRNPA2B1, which can interact with DGCR8 and promote miRNA processing [32]. Interestingly, no changes were observed in the primary transcription products. After FTO knockdown, several mature miRNAs were down-regulated [52], indicating that m6A has a negative impact on the stability of miRNAs. Therefore, the amount of mature miRNA can be altered by knocking down or overexpressing m6A regulatory proteins to affect the level of m6A.
CircRNA is a new type of ncRNA, which can form a covalently closed continuous loop structure by back splicing. Recently, it has been found that m6A modification is also prevalent in circRNA and shares the readers and writers with that in mRNA [53]. Alike in mRNA, recognition of m6A-modified circRNA by YTHDF2 can also promote circRNA degradation. Park et al. reported that a subset of m6A-modified circRNAs combined with YTHDF2 was selectively downregulated by RNase P/MRP [54]. Besides, m6A promotes cytoplasmic export of circRNAs, Chen et al. found that YTHDC1 could export circNSUN2 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to stabilize HMGA2 mRNA [55]. M6A can also drive circRNA-related protein synthesis by recruiting YTHDF3 and initiation factor eIF4G2 [56].
Interestingly, several studies reported that ncRNAs can affect m6A regulators reversely. Wang et al. [57] found that lncRNA LINRIS (Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 Stability) blocks K139 ubiquitination of IGF2BP2 to maintain its stability so as to promote the aerobic glycolysis in CRC. As for miRNA, it was reported that FTO is negatively regulated by miR-1266 and lowly expressed miR-1266 promotes the occurrence and progression of CRC by directly targeting FTO [58]. Moreover, Yue et al. [59] found that miR-96 could enhance the expression of FTO indirectly by down-regulating AMPKα2 to promote occurrence and progression of CRC.
The implications of m6A modification in CRC
In recent years, continuous efforts have been devoted to revealing the important roles of the imbalance of m6A modification and m6A regulatory protein in CRC. Considering the key role of m6A regulatory protein in mediating the occurrence and development of CRC, we reviewed the tumor-promoting and anti-tumor effects of several important m6A regulatory proteins on CRC (Table 1). Interestingly, we also found that m6A modifications could play similar roles by targeting different types of RNA molecules. And we summarized these mechanisms in Fig. 4.
The molecular mechanism of m6A on different types of RNA involved in CRC. METTL3, METTL14, FTO and YTHDC2 regulate m6A modification on mRNA to affect CRC initiation and progression. METTL3, METTL14, ALKBH5 and YTHDF3 regulate m6A modification on lncRNA to affect CRC. METTL3, METTL14 and hnRNPCL2 regulate m6A modification on miRNA to affect CRC. YTHDC1 regulates m6A modification on circRNA to affect CRC
METTL3 promotes CRC occurrence and progression
METTL3, as the most common m6A methyltransferase, has been found to play oncogenic function in a variety of cancers, including CRC. Li et al. [60] found that METTL3, as an oncogene, can extend the half-life of sex determining region Y-box 2 (SOX2) mRNA relied on IGF2BP2 to maintain the expression of SOX2 and SOX2 target genes (CCND1, MYC and so on), which further promotes CRC progression. Similarly, another study suggested that METTL3 promotes CRC progression through enhancing c-myc proto-oncogene (MYC) expression in an m6A-IGF2BP1-dependent manner [61]. METTL3 could methylate 3′UTR of CCNE1 mRNA to stabilize it and make it translated to form more cyclin E1 protein, which promotes CRC cell proliferation [62]. Additionally, METTL3 was reported to be directly interacted with the 5′/3′UTR regions of Hexokinase 2 (HK2) mRNA relied on IGF2BP2/3, the 3′UTR region of Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) mRNA relied on IGF2BP2, stabilized them and then further activated the glycolysis pathway to induce CRC tumorigenesis [63]. As mentioned above, METTL3-mediated different m6A-modified mRNA molecules were recognized by IGF2BP1/2/3, and ultimately played the same role in promoting the translation of mRNA molecules, although they used different mechanisms to protect the stability of mRNA molecules. Further, a recent study reported that METTL3 directly induced m6A-GLUT1-mTORC1 axis to promote CRC development [64]. Zhang et al. [65] found that METTL3 relied on IGF2BP1 to stabilize chromo box 8 (CBX8) mRNA which can inhibit the chemosensitivity and maintain the stemness of colon cancer (CC) by promoting the expression of leucine rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5). Similarly, Xu and colleagues [66] found that the up-regulation of METTL3 leads to a decrease in the expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2), and further promotes CC cell proliferation by inducing LGR5. Besides, METTL3 that favored by β-catenin could bind and activate Heat shock transcription factor1 (HSF1) mRNA translation initiation to promote CRC development [67].
Except METTL3 targeting downstream mRNA has been reported, METTL3 could also affect the progress of CRC by regulating the m6A modifications targeted ncRNAs. Wu et al. [68] found that RP11 as lncRNA was highly expressed in CRC tissues and was positively correlated with the tumor stage of patients. METTL3 can induce the formation of m6A modification in RP11 to increase the nuclear accumulation of RP11 which plays a role in preventing Zeb1 degradation. Zeb1 is an EMT-related transcription factor, and upregulation of Zeb1 is essential for RP11-induced cell invasion and metastasis. In addition, Peng and co-workers [69] reported that upregulated METTL3 could promote the maturation of pri-miR-1246 relied on DGCR8. Mature miR-1246 could decrease the expression of anti-oncogene SPRED2 to exert the effect of promoting CRC cells migration by interacting with the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway.
Overwhelming majority of studies believed that MELLT3 targeting mRNA and ncRNAs to play a role in promoting cancer in the occurrence and development of CRC. However, Deng et al. proposed that METTL3 acted as a tumor suppressor in the proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells through the p38/ERK pathway [70].
METTL14 suppresses CRC occurrence and progression
Unlike METTL3, METTL14 has an opposite effect on the occurrence and development of CRC relied on the function of m6A reader YTHDF2. METTL14-mediated m6A modified RNA molecules are selectively recognized and bound by YTHDF2, thereby promoting the degradation of these RNA molecules. A recent study reported by Wang group shows that METTL14 promotes SOX4 mRNA degradation by relying on YTHDF2-dependent pathway, and this can inhibit CRC progression partly through SOX4-mediated EMT process and PI3K/Akt signals [71]. Similarly, Yang and colleagues [72] reported that METTL14 down-regulated the expression of XIST lncRNA through the m6A-YTHDF2-dependent pathway to exert tumor suppressive effect. Consistently, XIST expression was negatively correlated with the content of METTL14 and YTHDF2 in CRC tissue, and the reduction of METTL14 was related to the poor prognosis of CRC patients in clinical. Besides, Chen et al. [73] found the expression of METTL14 in CRC tissue was down-regulated and closely related to the overall survival of CRC patients. METTL14 knockdown would weaken the binding of DGCR8 to the primary miR-375 and thus reduce the expression level of miR-375. Specifically, they verified that METTL14 suppressed CRC cell growth via the miR-375/Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) pathway, and inhibited CRC cell migration and invasion through the miR-375/SP1 pathway.
YTH family proteins promote CRC occurrence and progression
A study reported that knocking down the expression of YTHDF1 can significantly inhibit the tumorigenicity of CRC cells in vitro and the growth of mouse xenografts in vivo [74]. Moreover, Ni et al. [75] found that YTHDF3 was not only a new target of YAP, but also could promote the degradation of m6A modified lncRNA GAS5. GAS5 can promote the nuclear export of endogenous YAP and further promote its phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitin-mediated YAP degradation, and thus the expression of lncRNA GAS5 in tissue of CRC patients is negatively correlated with the level of YAP protein. In summary, this study revealed the negative functional loop of the GAS5-YAP-YTHDF3 axis to explain the role of m6A modified GAS5 in the progression of CRC. In addition, Chen et al. [55] found that m6A modified circNSUN2 was often upregulated in tumor tissues and serum samples from CRC patients with liver metastasis, and could be used to predict poor survival of CRC patients. Besides, they clarified that m6A modification of circNSUN2 regulated cytoplasmic output through YTHDC1-dependent manner. It is worth noting that by forming the circNSUN2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 RNA–protein ternary complex, increased cytoplasmic expression of circNSUN2 can enhance the stability of HMGA2 mRNA, which further leads to liver metastasis of CRC. Tanabe and colleagues [76] revealed that YTHDC2 can facilitate transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein express, thereby playing an important role in the metastasis of CRC by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Other m 6 A regulatory proteins affect CRC occurrence and progression
Zhang et al. [77] reported that WTAP could serve as a novel oncogene in CRC by forming WTAP-WT1-TBL1 axis to mediate Wnt signaling pathway. Besides, Yue et al. [59] found that FTO could upregulate MYC via blocking its m6A modification, further promote CRC occurrence and progression. ALKBH5 was found to have the opposite function to METTL3, it could serve as a tumor suppressor gene in CRC by reducing the nuclear accumulation of RP11 and thus inhibiting the function of EMT [35]. In addition, Sun et al. [78] reported a novel RNA-binding protein, RALY (also known as hnRNPCL2) could mediate mitochondrial metabolism to promote CRC development. RALY could bind to m6A-modified pri-miRNAs to promote the post-transcriptional processing of a specific subset of miRNAs (miR-483, miR-676 and miR-877), which downregulate the expression of the metabolism-associated genes (ATP5l, ATP5G1, ATP5G3 and CYC1) to reprogramme mitochondrial metabolism in the cancer cell.
Discussion
The diagnosis potential of m 6 A for CRC
Deregulation of m6A writer, eraser and reader proteins has been recently reported to be associated with increased probability of CRC occurrence and increased aggressiveness. Liu et al. [79] found that most genes related to m6A were significantly up-regulated in tumor tissues from CRC patients compared with normal tissues, but METTL14, YTHDF3 and ALKBH5 were down-regulated. Survival analysis showed that the expression levels of METTL14, METTL16 and FTO were positively related to the clinical prognosis of CRC patients but the expression levels of METTL3 and ALKBH5 were negatively related to it. In addition, Ji et al. [80] reported that the dysregulation of WTAP and FTO are significantly related to the progression of CRC, and YTHDC2 and ALKBH5 can predict the prognosis of CRC patients independently. Taken together, the expression of m6A and its regulators (writers, erasers, readers) may be a potential biomarker for molecular typing and prognosis prediction of CRC patients. A recent study demonstrated that m6A could be detected in the circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from lung cancer patients by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and the level of m6A was higher than that in whole blood [81]. This study indicates that analysis of m6A levels in CTC may become a new non-invasive cancer diagnostic method. Further studies to confirm whether the differences of m6A and m6A regulators can be observed in precancerous lesions are desirable, which will be helpful to evaluate the potential of these molecules as indictors for early detection of CRC.
The therapeutic potential of m 6 A for CRC
Previous studies have shown that dysregulation of m6A regulatory factors may be related to the development of chemotherapy resistance. For instance, Nishizawa et al. [82] reported that c-Myc promoted YTHDF1 expression to increase chemotherapy sensitivity for CRC. It was also reported that METTL3 participated in the upregulation of CBX8 which could promote stemness and suppress chemosensitivity through LGR5 [65]. These studies highlighted the important therapeutic value of targeted m6A modulators in drug-resistant tumors. In addition, targeting m6A and m6A regulators could also be a potential therapeutic strategy for radiotherapy and immunotherapy. A recent study found that the inhibition of METTL3/14 methylation modifications to STAT1 and IRF1 can enhance the sensitivity of anti-PD-1 therapy in pMMR/MSI-L CRC [83]. So far, no studies have explained the relationship between m6A modification and CRC radiotherapy sensitivity. Chemotherapy is commonly used in CRC and radiotherapy is an indispensable treatment for patients with low- and middle-level rectal cancer. PD-1/PD-L1-related immunotherapy has proven to be effective in many cancers including CRC [84]. It is important to identify the different therapeutic sensitivity of each patient via certain indicators, and m6A regulators could be such indicators. Therefore, more novel researches on m6A regulators and CRC treatment responses are urgently needed.
With further understanding of m6A modulators, it is more and more necessary to develop effective and specific m6A modulators inhibitors [85]. Although Rhein was found not to be an FTO-specific inhibitor, Huang et al. [86] revealed that meclofenamic acid (MA) showed high selectivity in inhibiting FTO over ALKBH5. Besides, it was reported that the proliferation and progression of acute myeloid leukemia in vivo was significantly reduced by treatment with FB23-2, a derivative of MA [87]. In another study, Shen et al. [63] found that 3-deazaadenosine (DAA), a chemical inhibitor of m6A, could more effectively inhibit the proliferation of CRC cells with high expression of METTL3. Sincerely, further molecular structure studies and large-scale chemical screening experiments are needed to develop specific inhibitors against dysregulated m6A regulatory proteins. Novel specific m6A regulatory protein inhibitors will not only enhance our understanding of the function of m6A modulators acted on carcinogenesis and progression of CRC, but also provide new and more favorable treatment strategies for CRC.
Conclusion
RNA m6A modification plays vital roles in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression, and it is involved in the occurrence and development of CRC. Dysregulation of m6A regulators can regulate the expression of downstream targets by mediating different RNA fate. In this review, we summarized recent studies on elucidation of the important roles of m6A modification played in the occurrence and development of CRC. Further investigations are desirable to elucidate the heterogeneity and complexity of m6A modification and m6A modulators in CRC carcinogenesis and progression. With the rapid development of m6A localization methods and m6A editing tools, the studies of m6A at the level of single nucleotide will be greatly promoted, and this will help researchers to better understand the roles of m6A in CRC tumorigenesis and development. Additionally, more efforts are required to identify new specific m6A modification for early diagnosis of CRC, and develop specific inhibitors of m6A modulators for better therapeutic purposes in future.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ALKBH5:
-
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase alkB homolog 5
- CBX8:
-
Chromo box 8
- ceRNA:
-
Competitive endogenous RNA
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- DGCR8:
-
DiGeorge syndrome crisis area gene 8
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- FTO:
-
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein
- GLUT1:
-
Glucose transporter 1
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- HK2:
-
Hexokinase 2
- hnRNP:
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins
- HSF1:
-
Heat shock transcription factor1
- IGF2BP1–3:
-
Insulin like growth factor 2 binding protein 1–3
- lncRNA:
-
Long noncoding RNA
- METTL14:
-
Methyltransferase like 14
- METTL3:
-
Methyltransferase like 3
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- MYC:
-
C-myc proto-oncogene
- m6A:
-
N6-methyladenosine
- SOCS2:
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2
- SOX2:
-
Sex determining region Y-box 2
- SOX4:
-
Sex determining region Y-box 4
- WTAP:
-
WT1 associated protein
- XIST:
-
X-inactive specific transcript
- YTH:
-
YT521-B homology
- YTHDC1–2:
-
YTH domain containing protein 1–2
- YTHDF1–3:
-
YTH domain containing protein family
- YAP:
-
Yes-associated protein
References
Keum N, Giovannucci E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:713–32.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Markowitz SD, Bertagnolli MM. Molecular origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2449–60.
He C. Grand challenge commentary: RNA epigenetics? Nat Chem Biol. 2010;6:863–5.
Zheng Q, Hou J, Zhou Y, Li Z, Cao X. The RNA helicase DDX46 inhibits innate immunity by entrapping m(6)A-demethylated antiviral transcripts in the nucleus. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:1094–103.
Zhong X, Yu J, Frazier K, Weng X, Li Y, Cham CM, Dolan K, Zhu X, Hubert N, Tao Y, et al. Circadian clock regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism by modulation of m(6)A mRNA methylation. Cell Rep. 2018;25(1816–28):e4.
He Y, Hu H, Wang Y, Yuan H, Lu Z, Wu P, Liu D, Tian L, Yin J, Jiang K, et al. ALKBH5 inhibits pancreatic cancer motility by decreasing long non-coding RNA KCNK15-AS1 methylation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48:838–46.
Minton K. RNA decay: stabilizing stemness through m6A. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:76–7.
Fu Y, Dominissini D, Rechavi G, He C. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m6A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:293–306.
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–46.
Rottman F, Shatkin AJ, Perry RP. Sequences containing methylated nucleotides at the 5’ termini of messenger RNAs: possible implications for processing. Cell. 1974;3:197–9.
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–6.
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X, et al. A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:93–5.
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:885–7.
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li CJ, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 2013;49:18–29.
Wang P, Doxtader KA, Nam Y. Structural basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 methyltransferases. Mol Cell. 2016;63:306–17.
Barbieri I, Tzelepis K, Pandolfini L, Shi J, Millán-Zambrano G, Robson SC, Aspris D, Migliori V, Bannister AJ, Han N, et al. Promoter-bound METTL3 maintains myeloid leukaemia by m(6)A-dependent translation control. Nature. 2017;552:126–31.
Weng H, Huang H, Wu H, Qin X, Zhao BS, Dong L, Shi H, Skibbe J, Shen C, Hu C, et al. METTL14 inhibits hematopoietic stem/progenitor differentiation and promotes leukemogenesis via mRNA m(6)A modification. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(191–205):e9.
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X, Wang WJ, Adhikari S, Shi Y, Lv Y, Chen YS, et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014;24:177–89.
Pendleton KE, Chen B, Liu K, Hunter OV, Xie Y, Tu BP, Conrad NK. The U6 snRNA m(6)A methyltransferase METTL16 regulates SAM synthetase intron retention. Cell. 2017;169(824–35):e14.
Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Wang T, Maciag K, Bushkin GG, Mertins P, Ter-Ovanesyan D, Habib N, Cacchiarelli D, et al. Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5’ sites. Cell Rep. 2014;8:284–96.
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A, Jackson C, Guttman M, Jaffrey SR. m(6)A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 2016;537:369–73.
Roundtree IA, Evans ME, Pan T, He C. Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell. 2017;169:1187–200.
Zhou J, Wan J, Gao X, Zhang X, Jaffrey SR, Qian SB. Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response. Nature. 2015;526:591–4.
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M, Ma J, Wu L. YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12626.
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H, He C. N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell. 2015;161:1388–99.
Li A, Chen YS, Ping XL, Yang X, Xiao W, Yang Y, Sun HY, Zhu Q, Baidya P, Wang X, et al. Cytoplasmic m(6)A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res. 2017;27:444–7.
Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhao BS, Ma H, Hsu PJ, Liu C, He C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N(6)-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017;27:315–28.
Roundtree IA, Luo GZ, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhou T, Cui Y, Sha J, Huang X, Guerrero L, Xie P, et al. YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N(6)-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. Elife. 2017;6:e31311.
Mao Y, Dong L, Liu XM, Guo J, Ma H, Shen B, Qian SB. m(6)A in mRNA coding regions promotes translation via the RNA helicase-containing YTHDC2. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5332.
Guichard C, Amaddeo G, Imbeaud S, Ladeiro Y, Pelletier L, Maad IB, Calderaro J, Bioulac-Sage P, Letexier M, Degos F, et al. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2012;44:694–8.
Alarcón CR, Goodarzi H, Lee H, Liu X, Tavazoie S, Tavazoie SF. HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of m(6)A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell. 2015;162:1299–308.
Huang H, Weng H, Chen J. m(6)A modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: roles and therapeutic implications in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2020;37:270–88.
Bartosovic M, Molares HC, Gregorova P, Hrossova D, Kudla G, Vanacova S. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO targets pre-mRNAs and regulates alternative splicing and 3’-end processing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:11356–70.
Aguilo F, Zhang F, Sancho A, Fidalgo M, Di Cecilia S, Vashisht A, Lee DF, Chen CH, Rengasamy M, Andino B, et al. Coordination of m(6)A mRNA methylation and gene transcription by ZFP217 regulates pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17:689–704.
Zhou KI, Shi H, Lyu R, Wylder AC, Matuszek Ż, Pan JN, He C, Parisien M, Pan T. Regulation of Co-transcriptional Pre-mRNA splicing by m(6)A through the low-complexity protein hnRNPG. Mol Cell. 2019;76(70–81):e9.
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY, et al. Nuclear m(6)A reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2016;61:507–19.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature. 2014;505:117–20.
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, et al. Recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:285–95.
Choe J, Lin S, Zhang W, Liu Q, Wang L, Ramirez-Moya J, Du P, Kim W, Tang S, Sliz P, et al. mRNA circularization by METTL3-eIF3h enhances translation and promotes oncogenesis. Nature. 2018;561:556–60.
Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J, Zinoviev A, Skabkin MA, Elemento O, Pestova TV, Qian SB, Jaffrey SR. 5’ UTR m(6)A promotes cap-independent translation. Cell. 2015;163:999–1010.
Choi J, Ieong KW, Demirci H, Chen J, Petrov A, Prabhakar A, O’Leary SE, Dominissini D, Rechavi G, Soltis SM, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine in mRNA disrupts tRNA selection and translation-elongation dynamics. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23:110–5.
Brown JA, Kinzig CG, DeGregorio SJ, Steitz JA. Methyltransferase-like protein 16 binds the 3’-terminal triple helix of MALAT1 long noncoding RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:14013–8.
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO, Meydan C, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods. 2015;12:767–72.
Liu N, Parisien M, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Pan T. Probing N6-methyladenosine RNA modification status at single nucleotide resolution in mRNA and long noncoding RNA. RNA. 2013;19:1848–56.
Warda AS, Kretschmer J, Hackert P, Lenz C, Urlaub H, Höbartner C, Sloan KE, Bohnsack MT. Human METTL16 is a N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) methyltransferase that targets pre-mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep. 2017;18:2004–14.
Liu N, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Parisien M, Pan T. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature. 2015;518:560–4.
Chen X, Chen Z, Yu S, Nie F, Yan S, Ma P, Chen Q, Wei C, Fu H, Xu T, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate CBFB expression by sponging miR-204-5p in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:2002–14.
Cao C, Zhang T, Zhang D, Xie L, Zou X, Lei L, Wu D, Liu L. The long non-coding RNA, SNHG6-003, functions as a competing endogenous RNA to promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2017;36:1112–22.
Chu C, Zhang QC, da Rocha ST, Flynn RA, Bharadwaj M, Calabrese JM, Magnuson T, Heard E, Chang HY. Systematic discovery of Xist RNA binding proteins. Cell. 2015;161:404–16.
Alarcón CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N, Tavazoie SF. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature. 2015;519:482–5.
Berulava T, Rahmann S, Rademacher K, Klein-Hitpass L, Horsthemke B. N6-adenosine methylation in MiRNAs. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0118438.
Zhou C, Molinie B, Daneshvar K, Pondick JV, Wang J, Van Wittenberghe N, Xing Y, Giallourakis CC, Mullen AC. Genome-wide maps of m6A circRNAs identify widespread and cell-type-specific methylation patterns that are distinct from mRNAs. Cell Rep. 2017;20:2262–76.
Park OH, Ha H, Lee Y, Boo SH, Kwon DH, Song HK, Kim YK. Endoribonucleolytic cleavage of m(6)A-containing RNAs by RNase P/MRP complex. Mol Cell. 2019;74(494–507):e8.
Chen RX, Chen X, Xia LP, Zhang JX, Pan ZZ, Ma XD, Han K, Chen JW, Judde JG, Deas O, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4695.
Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang Y, Jin Y, Yang Y, Chen LL, Wang Y, et al. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017;27:626–41.
Wang Y, Lu JH, Wu QN, Jin Y, Wang DS, Chen YX, Liu J, Luo XJ, Meng Q, Pu HY, et al. LncRNA LINRIS stabilizes IGF2BP2 and promotes the aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:174.
Shen XP, Ling X, Lu H, Zhou CX, Zhang JK, Yu Q. Low expression of microRNA-1266 promotes colorectal cancer progression via targeting FTO. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:8220–6.
Yue C, Chen J, Li Z, Li L, Chen J, Guo Y. microRNA-96 promotes occurrence and progression of colorectal cancer via regulation of the AMPKα2-FTO-m6A/MYC axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:240.
Li T, Hu PS, Zuo Z, Lin JF, Li X, Wu QN, Chen ZH, Zeng ZL, Wang F, Zheng J, et al. METTL3 facilitates tumor progression via an m(6)A-IGF2BP2-dependent mechanism in colorectal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:112.
Xiang S, Liang X, Yin S, Liu J, Xiang Z. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation through enhancing MYC expression. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:1789–806.
Zhu W, Si Y, Xu J, Lin Y, Wang JZ, Cao M, Sun S, Ding Q, Zhu L, Wei JF. Methyltransferase like 3 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by stabilizing CCNE1 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:3521–33.
Shen C, Xuan B, Yan T, Ma Y, Xu P, Tian X, Zhang X, Cao Y, Ma D, Zhu X, et al. m(6)A-dependent glycolysis enhances colorectal cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:72.
Chen H, Gao S, Liu W, Wong CC, Wu J, Wu J, Liu D, Gou H, Kang W, Zhai J, et al. RNA m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 facilitates colorectal cancer by activating m(6)A-GLUT1-mTORC1 axis and is a therapeutic target. Gastroenterology. 2020;160(4):1284-1300.e16.
Zhang Y, Kang M, Zhang B, Meng F, Song J, Kaneko H, Shimamoto F, Tang B. m(6)A modification-mediated CBX8 induction regulates stemness and chemosensitivity of colon cancer via upregulation of LGR5. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:185.
Xu J, Chen Q, Tian K, Liang R, Chen T, Gong A, Mathy NW, Yu T, Chen X. m6A methyltransferase METTL3 maintains colon cancer tumorigenicity by suppressing SOCS2 to promote cell proliferation. Oncol Rep. 2020;44:973–86.
Song P, Feng L, Li J, Dai D, Zhu L, Wang C, Li J, Li L, Zhou Q, Shi R, et al. β-catenin represses miR455-3p to stimulate m6A modification of HSF1 mRNA and promote its translation in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:129.
Wu Y, Yang X, Chen Z, Tian L, Jiang G, Chen F, Li J, An P, Lu L, Luo N, et al. m(6)A-induced lncRNA RP11 triggers the dissemination of colorectal cancer cells via upregulation of Zeb1. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:87.
Peng W, Li J, Chen R, Gu Q, Yang P, Qian W, Ji D, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Tang J, et al. Upregulated METTL3 promotes metastasis of colorectal Cancer via miR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:393.
Deng R, Cheng Y, Ye S, Zhang J, Huang R, Li P, Liu H, Deng Q, Wu X, Lan P, et al. m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 suppresses colorectal cancer proliferation and migration through p38/ERK pathways. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:4391–402.
Chen X, Xu M, Xu X, Zeng K, Liu X, Pan B, Li C, Sun L, Qin J, Xu T, et al. METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of SOX4 mRNA inhibits tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:106.
Yang X, Zhang S, He C, Xue P, Zhang L, He Z, Zang L, Feng B, Sun J, Zheng M. METTL14 suppresses proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by down-regulating oncogenic long non-coding RNA XIST. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:46.
Chen X, Xu M, Xu X, Zeng K, Liu X, Sun L, Pan B, He B, Pan Y, Sun H, et al. METTL14 suppresses CRC progression via regulating N6-methyladenosine-dependent primary miR-375 processing. Mol Ther. 2020;28:599–612.
Bai Y, Yang C, Wu R, Huang L, Song S, Li W, Yan P, Lin C, Li D, Zhang Y. YTHDF1 regulates tumorigenicity and cancer stem cell-like activity in human colorectal carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2019;9:332.
Ni W, Yao S, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Huang P, Zhou A, Liu J, Che L, Li J. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by interacting with and triggering YAP phosphorylation and degradation and is negatively regulated by the m(6)A reader YTHDF3. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:143.
Tanabe A, Tanikawa K, Tsunetomi M, Takai K, Ikeda H, Konno J, Torigoe T, Maeda H, Kutomi G, Okita K, et al. RNA helicase YTHDC2 promotes cancer metastasis via the enhancement of the efficiency by which HIF-1α mRNA is translated. Cancer Lett. 2016;376:34–42.
Zhang J, Tsoi H, Li X, Wang H, Gao J, Wang K, Go MY, Ng SC, Chan FK, Sung JJ, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IV inhibits colon cancer development by inhibiting the Wnt signalling pathway through targeting the WTAP-WT1-TBL1 axis. Gut. 2016;65:1482–93.
Sun L, Wan A, Zhou Z, Chen D, Liang H, Liu C, Yan S, Niu Y, Lin Z, Zhan S, et al. RNA-binding protein RALY reprogrammes mitochondrial metabolism via mediating miRNA processing in colorectal cancer. Gut. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320652.
Liu X, Liu L, Dong Z, Li J, Yu Y, Chen X, Ren F, Cui G, Sun R. Expression patterns and prognostic value of m(6)A-related genes in colorectal cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:3972–91.
Ji L, Chen S, Gu L, Zhang X. Exploration of potential roles of m6A regulators in colorectal cancer prognosis. Front Oncol. 2020;10:768.
Huang W, Qi CB, Lv SW, Xie M, Feng YQ, Huang WH, Yuan BF. Determination of DNA and RNA methylation in circulating tumor cells by mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2016;88:1378–84.
Nishizawa Y, Konno M, Asai A, Koseki J, Kawamoto K, Miyoshi N, Takahashi H, Nishida N, Haraguchi N, Sakai D, et al. Oncogene c-Myc promotes epitranscriptome m(6)A reader YTHDF1 expression in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2018;9:7476–86.
Wang L, Hui H, Agrawal K, Kang Y, Li N, Tang R, Yuan J, Rana TM. m(6) A RNA methyltransferases METTL3/14 regulate immune responses to anti-PD-1 therapy. EMBO J. 2020;39:e104514.
Chen DS, Mellman I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature. 2017;541:321–30.
Chen B, Ye F, Yu L, Jia G, Huang X, Zhang X, Peng S, Chen K, Wang M, Gong S, et al. Development of cell-active N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylase FTO inhibitor. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:17963–71.
Huang Y, Yan J, Li Q, Li J, Gong S, Zhou H, Gan J, Jiang H, Jia GF, Luo C, et al. Meclofenamic acid selectively inhibits FTO demethylation of m6A over ALKBH5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:373–84.
Huang Y, Su R, Sheng Y, Dong L, Dong Z, Xu H, Ni T, Zhang ZS, Zhang T, Li C, et al. Small-Molecule targeting of oncogenic FTO demethylase in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2019;35(677–91):e10.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC1302803), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY19B050007) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (21402172).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CG and SZ designed the study. ZHF and CG drafted the manuscript. YQH, JHH and YQH revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Z., Hu, Y., Hu, J. et al. The crucial roles of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in the carcinogenesis and progression of colorectal cancer. Cell Biosci 11, 72 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00583-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00583-8