Abstract
Two stratigraphically well constrained (by ammonites and conodonts) coleoid remains have been recorded from the Triassic (Anisian) dark-grey organodetritic limestones (Ráztoka Limestone) of Western Carpathians (Hronic Nappe). The limestones deposited at the periphery of a former carbonate platform. It yields a highly diverse cephalopod fauna including nautiloids (2 taxa), ammonoids (7 taxa) and indetermined aulacoceratids. Two unusual coleoid specimens are referred to genus Mojsisovicsteuthis (M. boeckhi) and probably to a new taxon (described as Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus herein) possessing similar morphological features of genus Breviconoteuthis (Phragmoteuthida) and/or Zugmontites. Based on index ammonites and conodonts, both records are of the uppermost Trinodosus through the lowermost Reitzi zones (Anisian—lower Illyrian). While the genus Mojsisovicsteuthis has been widely dispersed (however its records are rare), the occurrence of Breviconoteuthis and Zugmontites is strictly limited to the Alpine-Carpathian region. Comparing with the holotype and additional specimens stored in the Hungarian Natural History Museum, the overal shell of Mojsisovicsteuthis and its size has been reconstructed. Its relationship to aulacoceratids and phragmoteuthids is briefly discussed. Geochemical record (n-alkanes from the bulk rock) provided a relevant signal of the existence of algal meadows.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Triassic coleoids are rare compared to the uncountable records from the Jurassic and Cretaceous (Fuchs, 2012; Schweigert & Fuchs, 2012). Aulacoceratid rostra (Aulacoceratida Stolley, 1919) are more abundant, but mostly without further information on their phragmocone and soft tissue morphology. Records of gladius-bearing coleoids are very rare and not beyond any doubts (Fuchs, 2020; Lukeneder & Lukeneder, 2022; Reitner, 1978). Belemnitid belemnoids probably arose during the Triassic, but so far only a handful of rostra are described (Iba et al., 2012).
The order Phragmoteuthida Mojsisovics, 1882, a Triassic—Jurassic group that links aulacoceratids with a long tubular body chamber and Mesozoic belemnitids with a slender spatulate proostracum are comparatively well known (Doguzhaeva et al., 2007; Fuchs & Donovan, 2018; Lukeneder & Lukeneder, 2022). Earliest records of phragmoteuthids are known with question marks from the Upper Permian, but phragmocones with their characteristic broad three-lobed proostracum certainly appear in the Middle Triassic (Anisian). Upper Anisian Breviconoteuthis Rieber, 1973 represents the first unambiguous record of a phragmoteuthid and its diagnosis builds the morphological framework of the order- together with the genus Phragmoteuthis Mojsisovics, 1882 (lower Carnian—upper Sinemurian). The type species Breviconoteuthis breviconus comes from Grenzbitumenzone of Monte San Giorgio (Switzerland—Italian boundary), Polymorphus Zone (Rieber, 1973). Additional records of genus Breviconoteuthis are known from Wettersteinkalk of Zugspitzmassivs (Austria; Rieber, 1973) and from Balaton area (Azsófő village, Hungary; Vörös, 1987). One goal of this contribution is to introduce a new specimen very similar to Breviconoteuthis breviconus, coming from Western Carpathians (locality Podhradie, Slovakia). The second coleoid record, which resembles a poorly defined species complex is united within the genus Mojsisovicsteuthis (Anisian—Hettangian). Our second goal is to better define this aberrant genus, which is currently used as a waste bin for phragmocones that are untypical for both aulacoceratid and phragmoteuthid coleoids.
Comparisons with equivalent coleoid cephalopods from Hungary, Austria and Switzerland provide new insights into their morphology, systematics and habitat. Stratigraphical age of specimens is based on ammonoids and conodonts and microfacies (based on thin sections) and geochemical analysis (n-alkanes from the bulk rock) enabled reconstruction of habitat. We highlight an unusual diversity and disparity of cephalopods in time and space within Ráztoka Limestone of Western Carpathians (Hronic Nappe).
Geology and geography
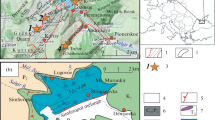
Studied macro and microfossil fauna was collected from two localities (Fig. 1). First one, Podhradie, is situated in the eastern part of the Považský Inovec Mts, SSW of the cemetery in the village Podhradie (GPS 48° 39′ 27.2″ N 18° 03′ 11.2″ E). It is represented by approx. 3 m thick outcrop in the road cut, made of variously bedded (2–30 cm of individual bed thickness) dark-grey to black limestones, some beds show indistinctly nodular pattern, belonging to Ráztoka Limestone Member (Kochanová & Michalík, 1986). Total thickness of this member here is around 5 m. The lower part of the unit is composed of dark-grey organodetritic limestones rich in thin-shelled bivalves and crinoids. From the microfacies point of view, these are biomicrites to biosparites with filament to filament-crinoidal microfacies, containing also benthic foraminifers, ostracods, juvenile gastropods, echinoid spines, fragments of thick-shelled bivalves and globochaetes. In the upper part, this facies makes only “nodules” in crinoid rich grey to pinkish more clayey matrix. This part also contains thin-bedded (7–9 cm) grey microcrystalline slightly clayey limestones with accumulations of bioclasts on the bases of the beds and with parallel lamination in their upper part (Havrila in Ivanička & Kohút et al., 2011). Apart from ceratitic ammonoids and rare nautiloids, coleoid cephalopod remains were collected from Bed 3 (Fig. 1). The second locality, Harmanecká Cave—Kozelník, is situated on the boundary between Starohorské vrchy Mts and Veľká Fatra Mts, above the Harmanecká Cave (GPS 48°48,582′ N 19°02,265′ E). The natural rocky wall outcrop is built (in stratigraphical order) of 3.3 m thick Jasenie Limestone Member (Kochanová & Michalík, 1986), 1.7 m thick Ráztoka Limestone Member and more than 5 m (only the basal part of the formation is exposed) of Reifling Formation (Havrila et al., 2016). It is noteworthy, another 0.4 m thick body of the Ráztoka Limestone Member was documented about 3.5 m above the base of the Reifling Fm. In this locality, the Ráztoka Limestone is bedded, grey to dark-grey, or brown-grey limestone with bed thickness between 5 and 30 cm, with slightly undulated bedding planes (Havrila et al., 2016). It contains various amounth of fine to coarse biodetritus, mainly crinoids. Limestones are intrabiopelmicrosparites to intrabiopelmicrites, wackestones to packstones with filament, filament-crinoidal, crinoid-bivalve-gastropod to crinoidal microfacies, other allochems are represented by echinoid spines, benthic foraminifers, ostracods, globochaetes and reefal and shallow-water bioclasts such as incertae sedis Plexoramea and Tubiphytes and algae Thaumatoporella (Havrila et al., 2016). Cephalopod fauna comes from the uppermost part of the 1.7 m thick biodetritic limestone. Apart of cephalopods, numerous brachiopods were collected as well.
Geographical position of the areas of interest (A, B) and close-up views of the satellite photo with precise localization of the studied outcrops in the village Podhradie (C), and near Dolný Harmanec (D). E Outcrop in the roadcut in the village Podhradie. The fossiliferous Bed 3 is outlined. Orange circles with acronyms TO represent the sampling points for the organic geochemistry
From the tectonic point of view both localities belong to the Hronic Nappe (Kováč & Havrila, 1998). Paleogeographically, they were situated on subsiding blocks at the periphery of Mojtín-Harmanec Carbonate Platform. This platform was bordered by Dobrá Voda Basin on the west and Biely Váh Basin on the east. For these subsiding blocks, the names Mojtín Block (or Basin) for the western part, and the Harmanec Block (or Basin) for the eastern part, are commonly used (e.g. Havrila, 2011; Havrila et al., 2016). Middle Triassic deposition in these subsiding areas were typical of biodetritic Ráztoka Limestone, rich in macro and microfauna. Both localities show similar lithostratigraphic successions. Ráztoka Limestone Member (Illyrian) together with Jasenie Limestone Member (Upper Pelsonian) are lithostratigraphic members of the Zámostie Limestone Formation (Kochanová & Michalík, 1986), which deposited above shallow-water limestones of the Steinalm Formation (Pelsonian). Jasenie Limestone Member directly underlies the Ráztoka Limestone Member in Harmanecká Cave section. Ráztoka Limestone is partly composed of the resedimented shallow-water detritus from the bordering platfom. It is overlain by bedded to nodular pelagic cherty limestones of the Reifling Formation.
Material and methods
The new cephalopods from Slovakia (collected by MH, JH, MK and JS) are stored in the collections of the Department of Geology and Palaeontology, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Comenius University in Bratislava, Slovakia (KGP-KO signatures). Besides this new material, we reinvestigated the holotype of Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875) from the Anisian of Hungary, which is registered as specimen T.829 in the collections of Mining and Geological Survey of Hungary in Budapest. In the same collection (material with signature T), we found additional specimens from the type locality labelled as Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi. Other holotypes of the Mojsisovicsteuthis species complex were unfortunately not available for comparative examinations. In these cases, we had to rely on their original descriptions. For specific delimitations, we also consulted type specimens of Breviconoteuthis breviconus (Reis, 1907 (stored in the Paläontologisches Institut und Museum der Universität Zürich, Switzerland) and Zugmontites mojsisovicsi Reis, 1907 (stored in the Bayerische Staatssammlung für Paläontologie und Historische Geologie München, Germany).
Microstructural analyses follows classifications of Folk (1962), Dunham (1962) and Embry and Klovan (1971). Microfacies were correlated with the standard microfacies types for the rimmed tropical carbonate platform of Wilson (1975), emended by Flügel and Munnecke (2010).
For the conodont microfauna, an analyses of the fossiliferous Bed 3 (Fig. 1) from Podhradie locality was carried out. The rock samples were collected by one of us (MH), laboratory processing was done in the Geological Survey of Slovenia with a standard preparation technique and application of acetic acid. The microfossil material is currently housed in the micropaleontologic collection of the Geological Survey of Slovenia and is labeled SL 264 A/80. The illustrated conodont elements presented in this paper were photographed by the JEOL JSM 6490LV Scanning Electron Microscope at the Geological Survey of Slovenia.
Micro-computed tomography (μ-CT) imaging was performed with phoenix v|tome|× L 240 device, developed by GE Sensing & Inspection Technologies at the Earth Science Institute of the Slovak Academy of Sciences in Banská Bystrica. Investigated samples were analyzed by using 240 kV/320W microfocus tube. Scanning parameters were set as follows: voltage 200 kV, current 150 μA, projections 1600, fastscan mode, timing 750 ms, voxel size 42.5 μm, detector sensitivity 1, and 0.1Cu filter.
Organic geochemistry: Samples were crushed to a grain size of < 0.2 mm and extracted using an Accelerated Solvent Extractor (ASE-150, Dionex) at 100 °C with dichloromethane: MeOH (93:7, v/v). All extracts were analysed using a GC/MS system a Trace 1310 GC with ISQ single quadrupole (ThermoScientific) equipped with a CP5 capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm × 25 μm). After a split-less injection, a temperature program was started from 40 to 300 °C, with helium as a carrier gas. Mass spectra were recorded in the electron impact mode (70 eV) in the 45–650 m/z range. The identification of compounds was based on a comparison of the spectra with the NIST mass spectral library.
Systematics, morphology, terminology, measurements, and size categories follow Fuchs and Donovan (2018), Fuchs (2020) and Mariotti et al. (2021).
Results
Ammonoid biostratigraphy
The ammonoid fauna (Figs. 2, 3) collected from the Podhradie section is rather common but poorly preserved. The identifiable part of the material consists of 19 specimens—7 taxa as listed below (specimen numbers in parentheses): Lardaroceras ? sp. (5 specimens, Fig. 2F–G), Ronconites ? sp. (2), Paraceratites trinodosus (Mojsisovics, 1882) (7, Fig. 2A–D), Paraceratites cf. rothi (Mojsisovics, 1882) (1), Semiornites ? sp. (2), Kellnerites cf. bispinosus (Hauer, 1896) (1, Fig. 2H–I), Ptychites cf. oppeli Mojsisovics, 1882 (1, Fig. 2E). In addition, single specimens of Pleuronautilus ? sp. and Nautilida indet. were also recognized.
Associated ammonoid fauna recorded at the locality Podhradie. A Paraceratites trinodosus (Mojsisovics, 1882), Bed 3, lower part. B Paraceratites trinodosus (Mojsisovics, 1882), Bed 3, lower part. C Paraceratites trinodosus (Mojsisovics, 1882), Bed 3. D Paraceratites trinodosus (Mojsisovics, 1882), Bed 3, lower part. E Ptychites cf. oppeli Mojsisovics, 1882, Bed 3. F, G Lardaroceras ? sp., Bed 3, lower part. H, I Kellnerites cf. bispinosus (Hauer, 1896), Bed 3, upper part
Associated ammonoid fauna recorded at the locality Harmanecká Cave—Kozelník. A–C Lardaroceras sp. aff. krystyni Balini, 1992a
The ammonoid fauna collected from the Harmanecká Cave—Kozelník locality contains rather large specimens of a relatively good manner of preservation. One large specimen portrays suture lines. The identifiable part of the ammonoid material consists of 11 specimens—4 taxa, as listed below (number of specimens in parentheses): Lardaroceras sp. aff. krystyni Balini, 1992a (3 specimens, Fig. 3A–C), Lardaroceras sp. indet. (5), Kellnerites sp. indet. (1), Flexoptychites ? sp. indet. (2). In addition, a single specimen of Nautilida indet was also recognized.
The specimens of Lardaroceras sp. aff. krystyni morphologically stand between Lardaroceras krystyni and Lardaroceras pseudohungaricum Balini, 1992a. Their rather coarse ribbing reminds the latter species, but the almost total absence of strong lateral nodes brings them closer to L. krystyni. The subammonitic suture line, recorded in one of the specimens from Harmanecká Cave—Kozelnik, is a shared feature of the Lardaroceras species.
The stratigraphical evaluation of the identified ammonoid taxa is based on the data in Balini (1992a, 1992b) and Vörös (2018). All ammonoid taxa, collected from the “lower part” of Bed 3 at Podhradie section, were recorded by the mentioned authors from the Illyrian Trinodosus Zone. The genus Lardaroceras characterizes the uppermost part of the Trinodosus Zone, namely the Pseudohungaricum Subzone. Kellnerites cf. bispinosus, indicating the lowermost part of the Reitzi Zone, came from the “upper part” of Bed 3. This may suggest some degree of condensation in Bed 3; alternatively, the base of the Reitzi Zone lies somewhere within this layer.
Similarly in Harmanecká Cave—Kozelník locality, all species of the genus Lardaroceras characterize the uppermost part of the Trinodosus Zone, namely the Pseudohungaricum Subzone. Kellnerites sp. may indicate a somewhat higher horizon, the lowermost part of the Reitzi Zone (Felsoeoersensis Subzone?).
Conodonts biostratigraphy
The recovered microfauna (Fig. 4) comes from a single sample collected from the 15 cm thick Bed 3 of the Podhradie section. The ammonoid fauna reveals a condensation within this bed 3, indicating the Illyrian Trinodosus Zone in its lower part (Pseudohungaricum Subzone) and the Reitzi Zone in its upper part. The studied microfauna is relatively well preserved and the conodont elements are very pale gray and dark gray (Epstein et al., 1977). In addition, ostracods, foraminifers, echinoid and crinoid ossicles and fish remains e.g., various dermal scales Nurrella sp. and teeth Acodina sp. have been recorded. The determined conodont taxa are: Neogondolella constricta (Mosher & Clark, 1965), Neogondolella ex gr. constricta (Mosher & Clark, 1965), Neogondolella sp., Paragondolella cf. alpina (Kozur & Mostler, 1982), Paragondolella bifurcata Budurov & Stefanov, 1972, Paragondolella praeszaboi (Kovács et al., 1996), Paragondolella cf. praeszaboi (Kovács et al., 1996), Paragondolella slugovensis (Ramovš, 1996), Paragondolella trammeri (Kozur, 1972), Paragondolella ex gr. trammeri (Kozur, 1972).
Associated conodont fauna recorded at the locality Podhradie. All specimens come from the Bed 3. A Paragondolella trammeri (Kozur, 1972). B Paragondolella cf. alpina (Kozur & Mostler, 1982). C Paragondolella slugovensis (Ramovš, 1996). D Paragondolella ex gr. praeszaboi (Kovács et al., 1996). E, F Neogondolella constricta (Mosher & Clark, 1965). G Paragondolella praeszaboi (Kovácset al., 1996). H Paragondolella cf. praeszaboi (Kovács et al., 1996). I–K Paragondolella bifurcata Budurov & Stefanov, 1972. Scale bar 200 μm (A) and 200 μm (B–K)
Among these species, P. bifurcata and P. praeszaboi are typical only for the Anisian. The first species is a marker of the Bifurcata Zone that is present also in the following Constricta Zone and the species entire stratigraphic range is from the upper Pelsonian to the middle Illyrian (Kolar-Jurkovšek & Jurkovšek, 2019). Species P. bifurcata has been reported from different parts of the Dinarides (Kolar-Jurkovšek, 1983, 1991; Smirčić et al., 2018). In the Internal Dinarides, P. bifurcata has been documented in the Zvornik Limestone of the Drinjača section and in the Bulog Limestone of the Sarajevo area (localities: Studenkovići, Blizanac, Han Bulog, Prodvorica), in the Uvac Canyon, as well as in the surroundings of Gradac at Plevlja (Sudar, 1986). This species is represented in the upper Pelsonian and lower Illyrian faunas of the Zlatibor Mountain, Serbia in the Bulog Formation that is interpreted to be deposited in a more offshore position, further to the east and nearer to the Neotethys Ocean (Sudar et al., 2013).
P. praeszaboi is characterized by the elements with very high carina composed of numerous and closely spaced denticles and a narrow platform. It was originally described as two subspecies. Stratigraphic range of P. praeszaboi is upper Pelsonian and Illyrian, i.e. uppermost Bulgarica, Bifurcata and lowermost Constricta Zones (Kovács et al., 1996).
Other four recognized taxa, N. constricta, P. cf. alpina, P. slugovensis and P. trammeri are Anisian-Ladinian taxa and all of them appear already in the Illyrian, except P. slugovensis that has been hitherto known to occur only from the Fassanian. N. constricta was first described from the upper Anisian of Nevada in North America (Mosher & Clark, 1965) but is well represented in many Illyrian and lower Fassanian faunas in the Tethys; in the standard conodont zonation it designates the Illyrian Constricta Zone (Kozur, 2003). In the studied material, the elements of N. constricta are found in different growth stages. P. slugovensis is marked by asymmetric posterior part as well as prolongation of the keel and has been so far documented only from the type locality in Slovenia (Ramovš, 1996). In the Global boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) of the Ladinian Stage at Bagolino section, P. alpina first appears in the Reitzi Zone, whereas P. trammeri in the following Secedensis Zone (Brack et al., 2005). According to Chen et al. (2015), P. alpina ranges up to the lower Fassanian, whereas P. trammeri up to the middle Longobardian.
The conodont fauna of the Bed 3 confirms a presence of mixed association, the uppermost Pelsonian to middle Illyrian fauna is marked with P. bifurcata and P. praeszaboi, whereas the upper Illyrian-lower Fassanian fauna is characterized by N. constricta, P. cf. alpina, P. slugovensis and P. trammeri. Recovery of a small but diagnostic well preserved conodont fauna is excellent starting point for further and more precise sampling across the Anisian-Fassanian sequence that will enable (at least partly) to solve a stratigraphic issue in terms of the degree of condensation.
Systematics
Subclass Coleoidea Bather, 1888
stem Neocoleoidea Haas, 1997 (proostracum-less coleoids)
Order and family uncertain
Genus Mojsisovicsteuthis Jeletzky, 1966
Type species: Orthoceras convergens von Hauer, 1847; p. 259, Tab. 7, figs. 1–2.
Diagnosis: Phragmocone longi- to orthoconic, medium-sized (up to 40 cm), laterally compressed, apical angle 10–20°, chamber length-to-diameter ratio 0.16–0.30, final chamber tubular (= proostracum absent), its relative length uncertain; sutures simple or with lateral lobes, septal necks short, prochoanitic?, connecting rings swollen; siphuncle at the ventral narrow side; sheath investment-like, smooth, rostrum solidum apparently absent.
Remarks: Despite an unusual set of characters, Jeletzky (1966) originally (and later authors such as Rieber, 1973 as well) placed the genus Mojsisovicsteuthis along with aulacoceratid belemnoids (see also Rieber, 1973). Prochoanitic septal neck as well as “conothecal growth lines” led them to this conclusion. Doyle (1990) placed Mojsisovicsteuthis to the family Xiphoteuthididae (Naef, 1922) within Aulacoceratida Stolley, 1919. By contrast, Mariotti and Pignatti (1992) and Mariotti et al. (2021) excluded Mojsisovicsteuthis from the Aulacoceratida mainly owing to the absence of a rostrum proper and untypically dense (short) chambers. Pohle & Klug (2024) recently revisited the affinities of Mojsisovicsteuthis and concluded that the systematic affiliation are still puzzling. We follow this open nomenclature, because a tubular (ventrally closed) final chamber excludes this taxon from the Phragmoteuthida, whose members are typified by a ventrally opened final chamber. The overall mantle length in aulacoceratids and Mojsisovicsteuthis is difficult to estimate for the following reasons: (1) we do not know the proostracum in both taxa (if it was originally present) or its length. (2) large aulacoceratids s.l. are more than 50 cm long (Mariotti & Pignatti, 1992)—but this length represents mainly the phragmocone. The largest size of the phragmocone within Mojsisovicsteuthis is estimated to be about 35 cm (see below).
Other species previously assumed to be close to Mojsisovicsteuthis convergens (von Hauer, 1847) are M. elliptica (Mojsisovics, 1871), M. meneghinii (Salomon, 1895), M. subrotundus (Salomon, 1895), M. boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875) and Mojsisovicsteuthis? n. sp. (Jeletzky, 1966, Pl. 5, Fig. 1).
Stratigraphic and geographic occurrences: So far known from the Anisian (Middle Triassic) through the Hettangian (Lower Jurassic).
According to previous workers and their ambiguous samples, representatives of this rare genus are known from the Middle Triassic (Anisian to Ladinian) through the Lower Jurassic (Hettangian) of the Alpine region, Hungary, Indo-Pacific Region (Timor), with question mark also from British Columbia (Jeletzky, 1966) and also other regions (see below—M. boeckhi). In Slovakia (this report), it comes from dark-grey to black biodetritic limestones of the Ráztoka Limestone Member of Zámostie Limestone Formation, dated to lower Illyrian (upper Anisian), uppermost part of the Trinodosus Zone (Pseudohungaricum Subzone)—probably lowermost part of the Reitzi Zone (Felsoeoersensis Subzone?).
Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875)
(Fig. 5, A–Q; 6; 7 A–D)
Synonymy:
*1875Atractites böckhi Stürzenbaum, p. 254, Tab. V, fig. 1.
1882Atractites boeckhi (Stürzenbaum). Mojsisovics, p. 302, pl. XCIII, figs. 12–13.
? 1914Atractites böckhi Stürzenbaum. Smith, p. 138, pl. XCIV, figs. 20–21.
1915Atractites Boeckhi Stürzenbaum, Diener, p. 18 (with additional/full synonymy).
1920Atractites Boeckhi Stürzenbaum; Büllow-Trummer, p. 65 (with additional synonymy).
1973Mojsisovicsteuthis cf. M. ? boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875); Rieber, p. 73–74, fig. 20, a–g.
? 1973Mojsisovicsteuthis meneghinii (Salomon, 1895); Rieber, p. 74, fig. 20, n–o.
? 1975Ausseites bilhynicus Arthaber, 1915; Özdemir, p. 137, pl. 4, figs. 1–4.
2024 Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi. Pohle & Klug, XXXX
Studied material: A single specimen (Fig. 5A–D) from Harmanecká Cave—Kozelník (GPS 48°48,582′ N 19°02,265′ E, Slovakia, No. KGP-KO-001; stored at Comenius University in Bratislava). Five specimens from the type locality (Additional file 1: Table S1) stored in the Mining and Geological Survey of Hungary in Budapest: including the holotype No. T.829 (Fig. 5J–P); specimens Nos T.3593, T.3206, T.3137 and two fragments referred to the taxon (T.81, and T.371).
Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875). A–D Specimen No. KGP-KO-001, upper Anisian, lower Illyrian, Harmanecká Cave—Kozelník, Slovakia. A Dorso-ventral view; B lateral view; C cross-section; D position of the siphuncle (s). E–H Specimen No. T.3593. E Dorso-ventral view; F lateral view; G, H Cross-section with position of the siphuncle (H. enlarged); I Cross-section of the apical part. J–P. Holotype No. T.829. Bakony (Hungary), Anisian, Reitzi Zone. J Original figure of Stürzenbaum (1875), lateral view; K lateral view; L dorso-ventral view; M cross-section; N original figure of Stürzenbaum (1875) with missinterpreted position of the siphuncle; O, P longitudinal section of the phragmocone with septa arrangement (partly seen). Q The largest specimen No. T.3137 in the lateral view. Scale bar equals 1 cm
Description: The steinkern of the phragmocone fragment is 42 mm long and includes 7–8 chambers. Apical and apertural chambers are missing. The width (dimension of the flattened phragmocone) of the largest chambers measures 19 mm. The straight phragmocone appears longi- to orthoconic (apical angle 11–12°, Fig. 6). Thanks to a circular structure in the periphery of the smallest chamber determinable as the former position of the siphuncle, one can define the anatomical orientation. The phragmocone diameter is accordingly laterally compressed. Poorly defined remains of sutures, which are visible only on one side of the steinkern, are c. 4 mm apart implicating a ratio chamber length to chamber diameter of about 0.19. This suggests comparatively low chambers. Lateral lobes are perceptible. There is no evidence of preserved shell material. As mentioned above, the siphuncle is only slightly indicated in Slovakian specimen.
Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875)—the size reconstruction based on the phragmocone angle and size extrapolation. The largest specimen does not possess a “body chamber”, therefore, the approximated size may exceed 35 cm
The material stored in the collections of Mining and Geological Survey of Hungary in Budapest provided unambiguous evidence of the siphuncle position (Fig. 5G, H) which lies in the narrow ventral side. The diameter of the siphuncle is ~ 1.3 mm (specimen No. T.3593, Fig. 5G, H).
In specimens Nos T.3206 (Fig. 7A) and T.81 (Fig. 7B), the tubular final chamber is partly preserved. The preserved length measures 25 and 30 mm (Additional file 1: Table S1). In these specimens, a marked constriction of the last septum prior the final chamber is seen.
A–D, Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875), Bakony (Hungary), Anisian, Reitzi Zone. A Specimen No. T.3206 with preserved final chamber in lateral view. B Specimen No. T.81 with preserved final chamber in lateral view. The constriction of the last septum prior the final chamber is well seen in both specimens. C–D Specimen No. T.255. C lateral view; D detail of the septum attachment to the phragmocone wall. E–L Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus, upper Anisian, lower Illyrian, Podhradie, Slovakia. E Ventral view; F, G lateral views demonstrating backwards inclined septa; H dorsal view; I, J cross section at the apical part; J position of the siphuncle; K, L micro-CT imaginations; K longitudinal section in lateral view; L longitudinal section in dorso-ventral view. Specimen No. KGP-PO-001. M Breviconoteuthis breviconus (Reis, 1907), original of Rieber (1974: Fig. 3), upper Anisian, Besano Formation, Monte San Giorgio, Switzerland. N, O. Zugmontites mojsisovicsi Reis, 1907, holotype, No. 1901-II-508, upper Anisian, Wettersteinkalk, Austria. N Lateral view; O dorso-ventral view. Scale bar equals 1 cm
Comparing the specimen No. KGP-PO-0001 with the Hungarian material including the holotype, we observed stability in the phragmocone angle reaching 11–12°.
With the phragmocone diameter and the apical angle of 12°, one can calculate the maximum phragmocone length by the help of trigonometric laws [diameter/2 × sin (84)/sin (12/2)]. Accordingly, specimen T.3206 with a maximum phragmocone diameter of 37 mm had a phragmocone length of approx 180 mm (length of the final chamber is not known). Assuming a final chamber that reaches a similar length (in specimens with this part preserved, Fig. 6), the total shell length of this specimen was about 350 mm, which classifies it as a medium-sized coleoid.
Comparison: We exclude affinities to the order Phragmoteuthida, owing to the absence of a three-lobed proostracum and the presence of a longiconic (rather than brevi—or cyrtoconic) phragmocone. Despite our observation of an aulacoceratid-like final chamber, the overall phragmocone characteristics (dense chambers, apical angle, lateral lobus) also prevent a placement within the order Aulacoceratida.
Regarding chamber distance, the specimen from Slovakia resembles the holotype of M. convergens, the type species of Mojsisovicsteuthis. However, in M. convergens, the cross section is more circular or even almost circular, as figured in von Hauer (1847, pl. VII, fig. 2), later corrected by Mojsisovics (1902, Pl. XVI, fig. 1). The apical angle of the phragmocone in the dorso-ventral view is moreover significantly higher in M. convergens (20°).
The Slovakian specimen and the holotypes of M. boeckhi (Stürzenbaum, 1875) and M. meneghinii (Salomon, 1895, p. 195) share a laterally compressed phragmocone, but M. meneghinii differs from our specimen in a higher apical angle (16–19° according to Salomon, 1895) and more densely spaced chambers (0.13–0.17).
In terms of apical angle, our specimen is almost identical with the holotype of M. boeckhi (Fig. 6). In addition, the Slovakian and the Hungarian specimens share a compressed phragmocone, a well developed lateral lobus, and a chamber distance ranging from 4 to 12 mm. The chamber distances just prior the final chanber are significantly constricted (in specimen T.81 ~ 3 mm).
Recently, Vörös et al. (2022) published record of cephalopod fauna from the Middle Anisian locality Akol Hill at Barnag (Hungary) including specimen described as Mosjsisovicsteuthis sp. The specimen clearly differs from our material by having significantly more densely spaced septa.
Specimens similar to Slovakian specimen and referred to genus Ausseites (Flower, 1944; rejected as nomen dubius by Mariotti et al., 2021) were figured by Özdemir (1975) from Ladinian/Carnian transition of Koaceli (Turkey). A. bilhynicus (Arthaber, 1915) resembles our specimen in shape, but the apical angle is higher in A. bilhynicus (~ 20–21°).
Remarks: The relatively large size (up to 30 cm) of the phragmocone (Fig. 6) is comparable to larger specimens of aulacoceratids. The reconstruction of the length is based on the stability in the phragmocone angle in all ontogenetical stages studied.
Stratigraphy and palaeogeography: M. boeckhi is known from the Anisian—Ladinian strata of the Alpine-Carpathian-Dinaridic region (Trinodosus—Lomelli zones; Alma, 1926). Apart of the here described material, it is reported from Wettersteinkalk in Germany (Reis, 1901), Austria (Alma, 1926—Schreyeralmkalke, Marmolatkalke; Schnetzer, 1934—Muschelkalk), Italy (Marmolada—Salomon, 1895; Monte Clapsavon—Canavari, 1890), Montenegro (Martelli, 1904), ?Romania (Braşov, Ladinian, see on-line report: https://formatiunigeologice.igr.ro/formatiune/42), Hungary (Stürzenbaum, 1875; Vörös, 1987, 2018), Bosnia and Herzegovina (Kraus, 1916; von Hauer, 1888), Greece (Renz, 1909), Bulgarian/Romanian borders (Dobrudzha; Büllow-Trummer, 1920) and ?Turkey (Koaceli—Ladinian/Carnian transition; Özdemir, 1975). Smith (1914) reported M. boeckhi from the Trinodosus Zone of North America. However, these old records (predominantly attributed to “Atractites boeckhi” or ?Ausseites in the latter case) were not studied/verified by the authors of this article.
Crown Neocoleoidea Haas, 1997 (proostracum-bearing coleoids)
Order Phragmoteuthida Mojsisovics, 1882
Genus Breviconoteuthis Rieber, 1973
Type species: Atractites breviconus Reis, 1907; p. 148, pl. 3. fig. 3 by monotypy.
Diagnosis (after Fuchs & Donovan, 2018): Phragmocone very small to small, brevi- to slightly cyrtoconic, circular in cross section, apical angle 38°–40°; ratio of chamber length to diameter about 0.15; pro-ostracum three-lobed, longer than phragmocone, anterior median field rounded; siphuncle marginal; rostrum unknown.
Diagnosis (emended): Phragmocone very small to small sized, brevi- to slightly cyrtoconic, circular in cross section, apical angle 30–40°; ratio of chamber length to diameter between 0.15–0.25; pro-ostracum three-lobed, longer than phragmocone, anterior median field rounded; siphuncle marginal; rostrum unknown.
Stratigraphic and geographic occurrences: So far known only from the upper Anisian (Wettersteinkalk) of Austria (Tyrol), Switzerland (Fuchs & Donovan, 2018) and Slovakia (Anisian—lower Illyrian; this paper).
Remarks: Breviconoteuthis and the slightly younger genus Phragmoteuthis Mojsisovics, 1882 (Carnian), the eponym of the order Phragmoteuthida, share a three-lobed proostracum morphology. Therefore, both genera can presently be distinguished only by phragmocone characters. The phragmocone of Breviconoteuthis displays a ventral curvature that is so far unknown in Phragmoteuthis.
The genus Zugmontites Reis, 1907 (upper Anisian) is based on a single specimen whose phragmocone parameters are close to those of Breviconoteuthis. Fuchs and Donovan (2018) interpreted Zugmontites as a putative phragmoteuthid owing to the absence of a proostracum. Due to the lack of available specimens, it can be presently not excluded that Zugmontites mojsisovicsi Reis, 1907, the type spieces of Zugmontites, is identical to Breviconoteuthis breviconus. One feature delimiting the two type species might be the ventral curvature that seems to be more distinct in Breviconoteuthis than in Zugmontites.
Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus (Reis, 1907)
(Fig. 7E–L).
Studied material: A single specimen from the locality Podhradie (Slovakia, No. KGP-PO-001; stored at Comenius University in Bratislava). The specimen was compared to the type material—e.g. B. breviconus (No. PIMUZ M12; Fig. 7M) stored in the Paläontologisches Institut und Museum der Universität Zürich, Switzerland; and Zugmontites mojsisovicsi Reis, 1907 (No. 1901-II-508; Fig. 7N–O) stored in the Bayerische Staatssammlung für Paläontologie und Historische Geologie München, Germany.
Locality: Podhradie (GPS 48° 39′ 27.2″ N 18° 03′ 11.2″ E), eastern part of the Považský Inovec Mts.
Description: The specimen represents a steinkern of a brevi- to slightly endogastric cyrtoconic phragmocone. Its apical angle measures 34° in dorsoventral and 32° in lateral views. Neither mineralized (e.g., conotheca, septa, sheath) nor nonmineralized shell material (e.g., proostracum) is preserved. Also, the ontogenetically oldest chambers are missing. The preserved part is up to 65 mm long and 45 mm wide and includes 11 chambers. Therefore, the phragmocones diameter seems to be dorsoventrally flattened; at least in the ontogentically youngest chambers. Annular constrictions on the outer surface, which correspond to former mural ridges, suggest a septal distance that gradually increases from 4 mm (apical part) to 8 mm at the anterior part. The ratio chamber length to chamber diameter varies from 0.19 to 0.23 (average 0.22). The sutures are unusually inclined towards the venter (backwards inclined). They appear to be simple without lobes or saddles. In ventral view, one can recognize a longitudinal depression that likely correlates with the former position of the siphuncle. This observation implicates that the septal necks were in contact with the inner surface of the conotheca, which in turn suggests a marginal rather than a submarginal siphuncle. There is no evidence of a longitudinal keel along the dorsum.
Comparisons: In having a brevi- to slightly cyrtoconic phragmocone (Fig. 7M herein), the here reported Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus is similar especially to the holotype of Breviconoteuthis breviconus Rieber, 1973. Taking into consideration that our specimen might have suffered a faint compaction, their apical angles do not differ significantly. Major differences between our Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus and Breviconoteuthis breviconus concern the chamber distance (longer in our specimen ~ 4–8 mm vs. 2–3 mm in the holotype) and in the siphuncle characteristics (its wider cross-section in our specimen). The inclination of the septa, which is backward in our specimen, might represent the main difference, but this character is unfortunately poorly known in the type specimens.
Mojsisovics (1871, tab 2, fig. 9) described a similar taxon Aulacoceras ellipticum. The figured specimen resembles Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus in the septal and cameral arrangement (cf. Fig. 7E, F). However, the chamber distances are visibly larger in B. aff. breviconus. Furthermore, A. ellipticum is laterally compressed (in this respect, it more resembles genus Mosisovicsteuthis, see above), whereas B. aff. breviconus is dorsolaterally flattened. Regarding this aspect, A. ellipticum may represent another and younger Breviconoteuthis species (Austriacum Zone, Carnian; Mojsisovics, 1871), although the lateral compression also links this specimen to Zugmontites (Fig. 7N, O, herein).
The slight phragmocone compaction may have resulted in different compressions of phragmocones in several phragmoteuthid taxa. We assume our specimen might be slightly dorso-ventrally flattened, therefore, the original cross-section should actually be more circular. However, the compression is very slight as it is seen in septal shapes, showing no significant deformation (Fig. 7 K, L).
Stratigraphy and palaeogeography: The species is known from the Middle Triassic (upper Anisian) of Switzerland, Austria (Fuchs & Donovan, 2018) and Slovakia (this report). Here, it comes from dark-grey to black biodetritic limestones of the Ráztoka Limestone Member of Zámostie Limestone Formation, dated to lower Illyrian (upper Anisian), uppermost part of the Trinodosus Zone (Pseudohungaricum Subzone)—lowermost part of the Reitzi Zone.
Palaeobiogeographic distribution of recorded coleoids is shown on the Fig. 8.
Palaeobiogeographic distribution of genera Mojsisovicsteuthis and Breviconoteuthis (Anisian–Carnian). While Mojsisovicsteuthis (larger straight phragmocone) shows large geographic distribution, the genus Breviconoteuthis (smaller phragmocone) is known only from few sites in the Alpine-Carpathian system
Overall cephalopod diversity
Cephalopod diversity at locality Podhradie consists of: Coleoids—aulacoceratids (probably 1 taxon—too fragmentarily preserved), Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus, 2 nautiloid species (indetermined), and 7 ammonoid species (see above). Taxonomically (at species levels), coleoids represent 18% of the cephalopod fauna.
Cephalopod diversity at locality Harmanecká Cave—Kozelník (same lithostratigraphical unit): Coleoids—Mojsisovicsteuthis boeckhi, 1 indetermined aulacoceratid specimen, 1 nautiloid species (indetermined), 4 ammonoid species (see above). Coleoids taxonomically (at species levels) represent 29% of the cephalopod fauna.
Rather scarce fossil record of coleoids, however, supports overall high Anisian cephalopod diversity including ammonoids, nautiloids and coleoids at equal time and space.
Palaeoenvironment
The limestones of the Ráztoka Limestone Member are represented by filament, filament-crinoidal, crinoid-bivalve-gastropod to crinoidal microfacies. Part of the bioclasts was produced on a shallow-water carbonate platform, from where it was redeposited to the sedimentation area of these limestones at the platform periphery, probably situated on subsiding tectonic blocks (Havrila et al., 2016). Relatively shallow-water neritic environment probably at the margin of neritic carbonate platform for the Ráztoka Limestone was also proposed in the type area of this member in Nízke Tatry Mts by Kochanová and Michalík (1986), however here the limestones bear a frequent distinct lamination possibly revealing cross and ripple mark (?)-bedding, the features unknown in the studied localities.
The geochemical record unambigenously provided organic mater linked to a rich algae cover. The samples contained about 0.005% of extractable matter that corresponded with the low total organic carbon contents (Additional file 1: Table S2). In the extracts, n-alkanes ranging from n-C14 to n-C19, isoprenoid coumpounds including pristane (Pr) and phytane (Ph), fatty acids and their esters were identified. n-Alkanes in sediments can generally come from multiple sources and are considered important biomarkers for terrestrial higher plants, algae and bacteria (Peters & Moldowan, 1993). For short-chain n-alkanes in the C15–C21 range, that were identified, aquatic algae and/or bacteria can be considered as primary input sources. However, they generally produce n-alkanes with an odd number of carbons, such as n-C15, n-C17, and n-C19 (Cranwell et al., 1987), and such obvious odd–even carbon predominance was not observed in the studied sediments. A likely explanation for this anomalous distribution could be diagenetic reduction of n-fatty acids under reducing conditions (Simoneit, 1977) or a highly saline carbonate environment (Pearson & Obaje, 1999).
Next to the n-alkanes, also the saturated (14:0, 16:0, and 18:0), monounsaturated (16:1 and 18:1), and the polyunsaturated (18:2) fatty acids were identified. The shorter-chain fatty acids are produced by all plants, but they are the dominant lipid components of algae and bacteria (Ervin, 1973; Simoneit et al., 1979; Wang & Liu, 2012).
These isoprenoids are used to estimate redox conditions (Didyk et al., 1978), since pristane is believed to be generated by an oxidative pathway, while phytane is generated by reductive pathways. The graph of the dependence of Ph/n-C18 on Pr/n-C17 is used to provide information on the depositional environment, relative maturity and possible diagenetic processes. For the studied samples, the graph shows that the starting material was seaweed, which was preserved in a reducing environment (Fig. 9).
The whole combination in the samples of identified compounds: n-alkanes, isoprenoids and fatty acids, along with their specific distribution, is indicative of organic matter coming from an algal source. No traces of any other source of organic material were found.
Based on palaeontological, sedimentological and geochemical records, we have reconstructed depositional environment and cephalopod diversity during the sedimentation of dark-grey organodetritic crinoidal limestones (Figs. 10, 11). Additional geochemical records showed the presence of organic matter linked to abundant algae. We suppose the algal cover played an important role on the former shallow carbonate platform and its subdiding peripheries, where the studied localities were situated in that time. Observed redeposits from the adjacent shallow-water carbonate platform document a continuous connection of the sedimentation area of Ráztoka Limestone with this high productivity environment. The algae vegetation in the Anisian may, with question mark, resemble significantly shallower-water sea-grasses which occurred at the end of Cretaceous Period (Forsey, 2019; van der Ham et al., 2007). These conditions were probably suitable spots of cephalopod diversity and disparity, as we can see in Carpathian localities.
A Reconstruction of cephalopod habitat within Western Carpathian Ráztoka Limestone, Illyrian Trinodosus—Reitzi Zones. Reconstruction: Petr Modlitba, with courtesy of author. B 1. Nautiloids. 2. Diverse ammonoids. 3. Aulacoceratids. 4. Mojsisovicsteuthis. 5. Breviconoteuthis. The benthic fauna is composed by abundant crinoids, echinoids, bivalves and brachiopods. Algae meadows are supposed based on geochemical data. C Fragment of partly tectonically deformed phragmocone of undetermined aulacoceratid; scale bar equals 1 cm
Conclusions
We report the first records of Triassic (non-aulacoceratid) coleoid cephalopods in the Western Carpathians, which are precisely biostratigraphically calibrated. Based on ammonites and conodonts, we confirmed the Middle Triassic—upper Anisian (Illyrian age): lower Illyrian (upper Anisian), uppermost part of the Trinodosus Zone (Pseudohungaricum Subzone)—lowermost part of the Reitzi Zone (Felsoeoersensis Subzone?).
Breviconoteuthis shows endemic character linked exclusivelly to the Alpine region and is firstly described from Carpathian system. The rare and enigmatic genus Mosjsisovicsteuthis has been recorded in the same strata and environment, its anatomy has been specified based on comparable material from Hungary (the type material, including the holotype) and the overal size of species M. boeckhi was reconstructed.
We concluded that Mojsisovicsteuthis resembles aulacoceratids in some aspects (size, “body chamber), however, differences are also obvious (see above). The similar size of the phragmocone within two distinct taxa living in the same time and occupying same habitat suggests parallel and/or convergent evolution.
The occurrence of Breviconoteuthis, Mojsisovicsteuthis and aulacoceratids in the same strata and environment is typical for the Middle Triassic of the Alpine region (Rieber, 1973; Pohle & Klug, 2024) and demonstrates the co-existence of (at that time) highly, moderately, and merely advanced coleoids. Especially the intermediate morphology of Mojsisovicsteuthis is of particular interest. This taxon may represent an evolutionary experiment (?or a transitional stage) in the Middle Triassic and may be rised to higher systematic rank in the future).
Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus probably represents a new species of genus Breviconoteuthis. We here refrain from erecting a new taxon until new and better preserved specimens are available.
The field research revealed diverse cephalopod fauna including ammonoids, nautiloids and coleoids. This quite unusual diversity seems to be linked to the suitable habitats including crinoid/algae meadows rich in benthic fauna. The source apportionment on the basis of n-alkanes, isoprenoids and fatty acids suggests that the soluble organic matter was originated from a source rich in marine algae. The sea-bottom palaeoenvironment is interpreted herein like a tectonically induced subsiding periphery of a shallow-water carbonate platform with rich algae vegetation probably resembling later sea-grasses, however, formed by different plants at shallower depth. In this point we assume that at least some coleoids were linked to this type of environment already in the Triassic. However, this assumption needs to be tested in the future.
Availability of data and materials
All studied or figured specimens are available for study at their respective institutions and museums: Department of Geology and Palaeontology, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Comenius University in Bratislava, Slovakia and of the Mining and Geological Survey of Hungary in Budapest, Paläontologisches Institut und Museum der Universität Zürich, Switzerland; and the Bayerische Staatssammlung für Paläontologie und Historische Geologie München, Germany. The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the repository at the Faculty of Science, Charles Unversity, Prague. Permanent link: https://web.natur.cuni.cz/ugp/main/paleodata/brevicono1https://web.natur.cuni.cz/ugp/main/paleodata/brevicono2
References
Alma, F. H. (1926). Eine Fauna des Wettersteinkalkes bei Innsbruck. Annalen des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien, 40, 111–129.
Arthaber, G. (1915). Die Entwicklung der Trias in Anatolien. Mitteilungen der Geologischen Gesellschaft in Wien, 8(1–2), 47–61.
Balini, M. (1992a). Lardaroceras gen. n., a new Late Anisian ammonoid genus from the Prezzo Limestone Southern Alps. Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia, 98(1), 3–28.
Balini, M. (1992b). New genera of Anisian ammonoids from the Prezzo Limestone Southern Alps. Atti Ticinensi di Scienze Della Terra, 35, 179–198.
Bather, F. A. (1888). Shell-growth in Cephalopoda (Siphonopoda). Journal of Natural History, 1, 298–309.
Brack, P., Rieber, H., Nicora, A., & Mundil, R. (2005). The global boundary stratotype section and point (GSSP) of the Ladinian Stage (Middle Triassic) at Bagolino (Southern Alps, Northern Italy) and its implications for the Triassic time scale. Episodes, 28(4), 233–244.
Budurov, K., & Stefanov, S. (1972). Plattform Conodonten und ihre Zonen inder Mittleren Trias Bulgariens. Mitteilungen der Gesellschaft der Geologie und Bergbaustudenten in Österreich, 21, 829–852.
Bülow-Trummer, E.V. 1920. Cephalopoda dibranchiata. In Fossilium Catalogus, Animalia. Pars 11 (pp. 1–271). W. Junker.
Canavari, M. (1890). Note di malacologia fossile. Bollettino Societd Malacologica Italiano, 15, 214–219.
Chen, Y. L., Krystyn, L., Orchard, M. J., Lai, X. L., & Richoz, S. (2015). A review of the evolution, biostratigraphy, provincialism and diversity of Middle and early Late Triassic conodonts. Papers in Palaeontology, 2, 235–263.
Cranwell, P. A., Eglinton, G., & Robinson, N. (1987). Lipids of aquatic organisms as potential contributions to lacustrine sediments II. Organic Geochemistry, 11, 513–527.
Didyk, B. M., Simoneit, B. R. T., Brassell, S. C., & Eglinton, G. (1978). Organic geochemical indicators of palaeoenvironmental conditions of sedimentation. Nature, 272, 216–222.
Diener, C. (1915). Cephalopoda Triadica, 8. In F. Frech (Ed.), Fossilium Catalogus I, Animalia. W. Junk.
Doguzhaeva, L. A., Summesberger, H., Mutvei, H., & Brandstaetter, F. (2007). The mantle, ink sac, ink, arm hooks and soft body debris associated with the shells in Late Triassic coleoid cephalopod Phragmoteuthis from the Austrian Alps. Palaeoworld, 16, 272–284.
Doyle, P. (1990). The biogeography of the Aulacocerida (Coleoidea). In: G. Pallini, F. Cecca, S. Cresta, and M. Santantonia (Eds.), Atti del secondo convegno internazionale, Fossili, Evoluzione, Ambiente, Pergola. Editore Comitato Centenario Raffaele Piccinini. Pergola. pp. 267–271.
Dunham, R.J. (1962). Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture. In: W.E. Ham (Eds.), Classification of carbonate rocks, a Symposium, AAPG, Tulsano, pp 108–121.
Embry, A. F., & Klovan, J. E. (1971). A Late Devonian reef tract on northeastern Banks Island, Northwest Territories. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 19, 730–781.
Epstein, A. G., Epstein, J. B., & Harris, L. D. (1977). Conodont color alteration— an index to organic metamorphism. U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 995, 1–27.
Erwin, J. (1973). Comparative biochemistry of fatty acids in eukaryotic microorganisms. In J. A. Erwin (Ed.), Lipids and biomembranes of eukaryotic microorganisms (pp. 41–143). Academic Press.
Flower, R. H. (1944). Atractites and related coleoid cephalopods. American Midland Naturalist, 32(3), 756–770.
Flügel, E., & Munnecke, A. (2010). Microfacies of carbonate rocks: Analysis, interpretation and application (p. 984). Springer Verlag.
Folk, R. L. (1962). Spectral subdivision of limestone types. In W. E. Ham (Ed.), Classification of carbonate rocks (Vol. 1, pp. 62–84). American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Memoirs.
Forsey, G. F. (2019). Seagrass and cuttlefish - an historic association. Palaeontologia Electronica, 118592, 1–24.
Fuchs, D. (2012). The evolution of coleoid cephalopods— what happened during the Triassic?. In Jahrestagung der Paläontologische Gesellschaft, Berlin Terra Nostra, 3, p. 60.
Fuchs, D. (2020). Systematic Descriptions: Octobrachia. Treatise Online 138: Part M, Chapter 23G. https://doi.org/10.17161/to.vi.14661.
Fuchs, D., & Donovan, D.T. (2018). Systematic descriptions: Phragmoteuthida. Treatise Online 111: Part M, Chapter 23C, 1–7.
Haas, W. (1997). Der Ablauf der Entwicklungsgeschichte der Decabrachia (Cephalopoda, Coleoidea). Palaeontographica, Abteilung A, 245, 63–81.
Havrila, J., Boorová, D., & Havrila, M. (2016). Ráztoka Limestone of the Šturec Facies Area in the Hronicum. Geologické Práce, Správy, 129, 35–54.
Havrila, M. (2011). Hronikum: paleogeografia a stratigrafia (vrchný pelsón–tuval), štrukturalizácia a stavba. Geologické Práce, Správy, 117, 5–103.
Iba, Y., Sano, S. I., Mutterlose, J., & Kondo, Y. (2012). Belemnites originated in the Triassic-a new look at an old group. Geology, 40, 911–914.
Ivanička, J., Kohút, M., Havrila, M., Olšavský, M., Hók, J., Kováčik, M., Madarás, J., Polák, M., Rakús, M., Filo, I., Elečko, M., Fordinál, K., Maglay, J., Pristaš, J., Buček, S., Šimon, L., Kubeš, P., Scherer, S., Zuberec, J., … Klukanová, A. (2011). Explanation of geological map of Považský Inovec and SE part of Trenčín lowland 1: 50 000. In J. Ivanička & M. Kohút (Eds.), Explanations of regional geological maps of Slovakia (p. 389). Štátny geologický ústav Dionýza Štúra.
Jeletzky, J. A. (1966). Comparative morphology, phylogeny, and classification of fossil Coleoidea (Mollusca 7). The University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions, 42, 1–162.
Kochanová, M., & Michalík, J. (1986). Stratigraphy and macrofauna of the Zámostie Limestones (Upper Palsonian–Lower Illyrian) of the Choč Nappe at the southern slopes of the nízke Tatry Mts. (west Carpathians). Geologická Zborník, Geologica Carpathica, 37(4), 501–531.
Kolar-Jurkovšek, T. (1983). Srednjetriasni konodonti Slovenije (Middle Triassic Conodonts from Slovenia (NW Yugoslavia)). Rudarsko-Metalurški Zbornik, 30(4), 323–364.
Kolar-Jurkovšek, T. (1991). Mikrofavna srednjega in zgornjega triasa Slovenije in njen biostratigrafski pomen (Microfauna of Middle and Upper Triassic in Slovenia and its biostratigraphic significance). Geologija, 33(1990), 21–170.
Kolar-Jurkovšek, T., & Jurkovšek, B. (2019). Konodonti Slovenije/Conodonts of Slovenia (p. 265). Geološki zavod Slovenije/Geological Survey of Slovenia.
Kováč, P., & Havrila, M. (1998). Inner structure of Hronicum. Slovak Geological Magazine, 4(1998), 275–280.
Kovács, S., Papšová, J., & Perri, M. C. (1996). New Middle Triassic conodonts of the Gondolella szaboi-G. trammeri lineage from the West Carpathian Mts and from the Southern Alps. Acta Geologica Hungarica, 39(1), 103–128.
Kozur, H. (1972). Die Conodontengattung Metapolygnathus Hayashi, 1968 und ihr stratigraphischer Wert. Geologisch-Paläontologische Mitteilungen Innsbruck, 2, 1–37.
Kozur, H. (2003). Integrated ammonoid, conodont and radiolarian zonation of the Triassic. Hallesches Jahrbuch für Geowissenschaften, 25, 49–79.
Kozur, H., & Mostler, H. (1982). Neue Conodonten aus dem Illyr und Fassan der Profile Fellbach und Karalm (Gailtaler Alpen, Kärnten, Österreich). Geologisch-Paläontologische Mitteilungen Innsbruck, 11(8), 291–298.
Kraus, R. (1916). Die Cephalopodenfauna des Muschelkalkes der Volujak-Alpe bei Gacka in der Herzegowina. Wissenschaftliche Mitteilungen aus Bosnien und der Herzegowina, 13, 1–102.
Lukeneder, P., & Lukeneder, A. (2022). Mineralized belemnoid cephalic car-tilage from the late Triassic Polzberg Konservat-Lagerstätte (Austria). PLoS ONE, 17(4), e0264595.
Mariotti, N., & Pignatti, J. S. (1992). Systematic remarks on Atractites-like coleoid cephalopods: Crassiatractites gen. nov., Breviatractites gen. nov. Paleopelagos, 2, 109–141.
Mariotti, N., Pignatti, J., & Riegraf, W. (2021). Treatise online no. 148: Part M, Chapter 23B: Systematic descriptions: Aulacoceratida. Treatise Online. https://doi.org/10.17161/to.vi.15255
Martelli, A. (1904). Cefalopodi triasici di Boljevici presso Vir rel Montenegro. Palaeontographica Italica, 10, 75–140.
Mosher, L. C., & Clark, D. L. (1965). Middle Triassic conodonts from the Prida Formation of northwestern Nevada. Journal of Paleontology, 39, 551–565.
Naef, A. (1922). Die fossilen Tintenfische: Eine Paläozoologische Monographie (p. 322). Gustav Fischer.
Özdemir, Ü. (1975). Über die typischen belemniten der Trias von Koaceli. Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration, 85, 129–141.
Pearson, M. J., & Obaje, N. G. (1999). Onocerane and other triterpenoids in Late Cretaceous sediments from the Upper Benue Trough, Nigeria: Tectonic and palaeoenvironmental implications. Organic Geochemistry, 30, 583–592.
Peters, K. E., & Moldowan, J. M. (1993). The biomarker guide: Biomarkers and isotopes in petroleum exploration and earth history (2nd ed., p. 1155). Cambridge University Press.
Pohle, A., & Klug, C. (2024). Orthoceratoid and coleoid cephalopods from the Middle Triassic of Switzerland with an updated taxonomic framework for Triassic Orthoceratoidea. Swiss J Palaeontol, 143, 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13358-024-00307-8
Ramovš, A. (1996). Oberfassanische (mitteltriassiche) Conodonten aus Kalken südlich von Slugovo, Südslovenien. Geologija, 37–38(1994/1995), 141–151. https://doi.org/10.5474/geologija.1995.005
Reis, O. M. (1901). Die Fauna des Wettersteinkalkes 1. Teil. Cephalopoden. Geognostiche Jahreshefte, 13, 71–105.
Reis, O. M. (1907). Eine Fauna des Wettersteinkalkes. Teil 2: Nachtrag zu den Cephalopoden. Geognostische Jahreshefte, 18, 113–152.
Reitner, J. (1978). Ein Teuthiden-Rest aus dem Obernor(Kössener-Schichten) der Lahnewies-Neidernachmuldebei Garmisch-Partenkirchen (Bayern). Paläontologische Zeitschrift, 52, 205–212.
Renz, O. (1909). Zur Entdeckung der Trias in der Argolis. Zentralblatt für Mineralogie, Geologie und Paläontologie, 3, 79–83.
Rieber, H. (1973). Cephalopoden aus der Grenzbitumenzone (Mittlere Trias) des Monte San Giorgio (Kanton Tessin, Schweiz). Schweizerische Paläontologische Abhandlungen, 93, 1–95.
Rieber, H. (1974). Breviconoteuthis breviconis (Reis), ein Phragmoteuthide aus der mittleren Trias des Monte San Georgio (Kanton Tessin, Schweiz). Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Monatshefte, 7, 415–421.
Salomon, W. (1895). Geologische und paläontologische studien über die Marmolata. Palaeontographica, 42, 1–210.
Schnetzer, R. (1934). Die Muschelkalkfauna des Öfenbachgrabens bei Saalfelden. Palaeontographica A, 81(1–3), 1–160.
Schweigert, G., & Fuchs, D. (2012). First record of a true coleoid cephalopod from the Germanic Triassic (Ladinian). Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen, 266, 19–30.
Simoneit, B. R. T. (1977). Diterpenoid compounds and other lipids in deep-sea sediments and their geochemical significance. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41, 463–476.
Simoneit, B. R. T., Mazurek, M. A., Brenner, S., Crisp, P. T., & Kaplan, I. R. (1979). Organic geochemistry of recent sediments from Guaymas Basin, Gulf of California: Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 26, 879–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/0198-0149(79)90102-X
Smirčić, D., Kolar-Jurkovšek, T., Aljinović, D., Barudžija, U., Jurkovšek, B., & Hrvatović, H. (2018). Stratigraphic definition and correlation of Middle Triassic volcaniclastic facies in the External Dinarides (Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina). Journal of Earth Science, 29(4), 864–878.
Smith, J. P. (1914). The middle Triassic marine vertebrate faunas of North America. United States Geological Survey, Professional Paper, 83, 1–254.
Stolley, E. (1919). Die Systematik der Belemniten. Jahresbericht des Niedersächsischen Geologischen Vereins zu Hannover, 11, 1–59.
Stürzenbaum, J. (1875). Adatok a Bakony Ceratites Reitzi-szint faunájának ismeretéhez (Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Fauna des Ceratites Reitzi-Horizontes des Bakony Gebirges). Földtani Közlöny, 5(11–12), 253–262.
Sudar, M. (1986). Mikrofosili i biostratigrafija trijasa unutrašnjih Dinarida Jugoslavije između Gučeva i Ljubišnje (Triassic microfossils and biostratigraphy of the Inner Dinarides between Gučevo and Ljubišnja Mts., Yugoslavia). Geološki Anali Balkanskoga Poluostrva, 50, 151–394.
Sudar, M. N., Gawlick, H. J., Lein, R., Missoni, S., Kovács, S., & Jovanović, D. (2013). Depositional environment, age and facies of the Middle Triassic Bulog and Rid formations in the Inner Dinarides (Zlatibor Mountain, SW Serbia): Evidence for the Anisian break-up of the Neotethys Ocean. Neues Jahrbuch Für Geologie Und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen, 269(3), 292–320.
van der Ham, R. W. J. M., van Konijnenburg-van Cittert, J. H. A., & Indeherberge, L. (2007). Seagrass foliage from the Maastrichtian type area (Maastrichtian, Danian, NE Belgium, SE Netherlands). Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 44, 301–321.
von Hauer, F. (1847). Neue Cephalopoden aus dem rothen Marmor von Aussee. Haidingers Naturwissenschaften Abhandlungen, 1, 1–21.
von Hauer, F. (1888). Die Cephalopodcn des Bosnischen Muschelkalker von Han Bulog bei Sarajevo. Denkschriften der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften/ Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Klasse, 54, 1–50.
von Hauer, F. (1896). Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Cephalopoden aus der Trias von Bosnien. II. Nautileen und Ammoniten mit ceratitischen Loben aus dem Muschelkalk von Haliluci bei Sarajevo. Denkschriften der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften/Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Klasse, 62, 237–276.
von Mojsisovics, E. (1871). Über das Belemnitiden-Geschlecht Aulacoceras Fr. v. Hauer. Jahrbuch der Kaiserlich Königlichen Geologischen Reichsanstalt, 21, 41–57.
von Mojsisovics, E. (1882). Die Cephalopodon der Mediteranen Triazprovinz: 3 Dibranchiata. Abhandlungen der Kaiserlich-Königlichen Geologischen Reichsanstalt, 10, 295–307.
von Mojsisovics, E. (1902). Die Cephalopoden der Hallstätter Kalke. Abhandlungen der Kaiserlich-Königlichen Geologischen Reichsanstalt, 6(1), 177–356.
Vörös, A. (1987). Preliminary results from the Aszófő section (Middle Triassic, Balaton area, Hungary): A proposal for a new Anisian ammonoid subzonal scheme. Fragmeta Mineralogica et Palaeontologica, 13, 53–64.
Vörös, A. (2018). The Upper Anisian ammonoids of the Balaton Highland (Middle Triassic, Hungary). Geologica Hungarica Series Palaeontologica, 60, 1–241.
Vörös, A., Budai, T., Makádi, L., Bercsényi, M., Földvári, G., Pintér, Z., & Szabó, M. (2022). Rediscovery of a classic Middle Triassic fossil site of the Balaton Highland (Transdanubian Range, Hungary): cephalopods, brachiopods and vertebrate remains from the Akol Hill at Barnag. Földtani Közlöny, 152, 233–257. https://doi.org/10.23928/foldt.kozl.2022.152.3.233
Wang, Z., & Liu, W. (2012). Carbon chain length distribution in n-alkyl lipids: A process for evaluating source inputs to Lake Qinghai. Organic Geochemistry, 50, 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2012.06.015
Wilson, J. L. (1975). Carbonate facies in geologic history (p. 471). Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Czech Science Foundation (GAČR), project No. 23-05217S, by Slovak grant agencies APVV 22-0523 and VEGA 2/0106/23, and by the Slovenian Research and Innovation Agency (program P1-0011). We thank Marija Petrović for technical work and Miloš Miler for his assistance in SEM imaging. We are indebted to Petr Modlitba who kindly performed and provided reconstructions of palaeoenvironment. We thank Christian Klug (Zurich), Alexander Nützel (Munich) for providing comparative material. We thank the Editor Daniel Marty and reviewers René Hoffmann (Bochum) and Kenneth De Baets (Warsaw) for valuable comments and corrections which significantly rised quality of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding Open Access funding enabled and organised by Project of the Czech Science Foundation No. 23-05217S Granted to KH. The research was also supported by Slovak grant agencies APVV 22-0523 and VEGA 2/0106/23 Garanted by JS, the Slovenian Research and Innovation Agency (program P1-0011) Garanted to TKJ and project Cooperatio (Faculty of Science) garanted by MK and KH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: MK, JS, DF. Methodology: MK, JS, DF, TK-J, AV, MH, JŠ, KH. Investigation: MK, JS, DF, TK-J, AV, MH, MHa, JŠ, KH. Visualization: MK, JS, TK-J, AV, JŠ. Field work-sampling: MHa, JS, MK, KH. Writing—original draft: MK, JS, DF, TK-J, AV, MH, JŠ, KH. Writing—review and editing: MK, JS, DF, TK-J, AV, MH, JŠ, KH.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All authors read the paper and declare no ethic conflicts.
Consent for publication
All authors declare the consent to publications.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Editorial Handling: Rakhi Dutta
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Table S1:
Specimens of M. boeckhi with measured parameters. L – length of preserved part of the phragmocone; HF (A) – height of the phragmocone at the apical part of preserved phragmocone; HF (LPCh) - height of the phragmocone at the last preserved chamber. W – maximum width of the phragmocone; NPCh – number of preserved chambers; HCh (A-LPCh) – height of chambers, from apical part to the last preserved chamber. All measured data are in (mm), angle in degrees. *estimated; ** height of the preserved “body chamber”. Table S2: SOM = soluble organic matter; TOC = total organic carbon. Additional file Fig/movie 1A: Micro-CT visualisation (movie) of longitudinal sections of specimen Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus documenting character of the septa and their attachment to the wall of the phragmocone. Additional file Fig/movie 1B: The 3D micro-CT visualisation (movie) of the specimen Breviconoteuthis aff. breviconus from locality Podhradie. Fig S2: Total ion chromatograms. All peaks represent an organic compound and the peak area corresponds to the concentration of the compound. As it is well seen, all three chromatograms from three Beds (1-3, samples TO 7-9) are almost identical indicating a very similar content of organic matter produced by algae.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Košťák, M., Schlögl, J., Fuchs, D. et al. Rare Middle Triassic coleoids from the Alpine-Carpathian system: new records from Slovakia and their significance. Swiss J Palaeontol 143, 19 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13358-024-00316-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13358-024-00316-7