Abstract
Background
The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses are a group of neurodegenerative, lysosomal storage disorders. They are inherited as an autosomal recessive pattern with the exception of adult neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, which can be inherited in either an autosomal recessive or an autosomal dominant manner. The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses are characterized by accumulation of autofluorescent lipopigments in the cells and one of the most important pathological manifestations is ceroid accumulation in the lysosomes. Various types of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses are categorized based on the clinical manifestations and the genes involved. Accumulatively, 15 different genes have been found so far to be implicated in the pathogenesis of at least nine different types of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses, which result in similar pathological and clinical manifestations.
Case presentation
A 5-year-old Iranian boy affected by a neurodegenerative disorder with speech problems, lack of concentration, walking disability at age of 4 years leading to quadriplegia, spontaneous laughing, hidden seizure, clumsiness, psychomotor delay, and vision deterioration at age of 5 years, which could be the consequence of macular dystrophy, was referred to us for genetic testing. Trio whole exome sequencing, Sanger validation, and segregation analysis discovered a novel in-frame small deletion c.325_339del (p.Val109_Ile113del) in MFSD8 gene associated with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 7.
Conclusions
The deletion found in this patient affects the exon 5 of this gene which is the region encoding transmembrane domain. Sequencing analysis in this family has shown that the index is homozygous for 15 base pairs in-frame deletion, his uncle has normal homozygous, and his parents are heterozygous. This pattern of mutation inheritance and the signs and symptoms observed in the affected male of this family are compatible with what is described in the literature for neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 7 and, therefore, suggest that the MFSD8 gene deletion found in this study is most probably the cause of disease in this family.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs or CLNs), also called Batten disease, are a set of neurodegenerative genetic disorders with an overall frequency of 1 in 100,000 individuals around the world [1, 2]. This condition conforms to an autosomal recessive (AR) pattern of inheritance and is mainly caused by consanguineous marriage [3]. Babies affected with these lysosomal storage diseases do not manifest any clinical symptoms at birth; however, signs and symptoms mostly begin before 7 years of age depending on the gene involved [3, 4]. These conditions are genetically heterogeneous and consist of a wide spectrum of phenotypical and clinical manifestations. NCLs are characterized by the accumulation of autofluorescent lipopigments in cells [5] and one of the most important pathological manifestations is ceroid accumulation in lysosomes [1, 6]. The accumulation of storage material in nerve cells results in massive neuronal loss and subsequent apoptosis, as has been shown in an autopsy of the brain [7]. The categorization of various types of NCLs is based on the phenotype and the genes that are mutated. Accumulatively, mutation in at least 15 different genes has been shown to be implicated in the pathogenesis of at least nine different types of NCLs which result in a similar pathological and clinical manifestation; Table 1 [8,9,10]. Genes involved in the pathogenesis of NCLs are mainly affected by loss-of-function mutations [11, 12].
Phenotypically, there are three common different forms of NCLs; the categorization of these three forms of NCLs is mainly based on the age of onset: infantile NCL (INCL) that begins between 6 and 18 months of age; late INCL (LINCL) which begins at 2–4 years of age; and juvenile NCL (JNCL) which begins at the age of 6–10 years or sometimes in adulthood [13,14,15]. All types show overlapping sign and symptoms, mainly cognitive impairment, progressive neuronal degeneration, motor deficits, seizures, progressive visual deterioration, and blindness [16]. Motor dysfunction could lead to subsequent quadriplegia [17, 18]. The genes involved in NCLs present similar clinical manifestations; so, the finding of genetic mutations may explain unclear clinical findings and distinguish between them [19, 20].
The most prevalent types of NCLs are NCL1, which is considered an infantile form, NCL2, which is considered a late infantile form, and NCL3, which is considered a juvenile form [21]. NCL1 is the most common form of INCLs. At birth, a baby with NCL1 has normal development, but this process is lost and motor dysfunction leads to hypotonia [22]. There is evident vision loss and seizure at approximately 1 year of age [23]. Profound microcephaly is a usual finding and patients will usually die before they reach the age of 7 years. Mutation in the palmitoyl-protein thioesterase (PPT) gene which encodes a fatty acid cleavage lysosomal protein is the cause of NCL1. R122W (c.364A>T) and R151X (c.451C>T) are the most common mutations of the PTT gene and accounted for approximately 20% of mutations [2]. NCL2, also called Jansky–Bielschowsky disease, in which almost the majority of affected patients’ manifestations begin at late infantile period of life, is caused by mutations in the CLN2 gene which encodes tripeptidyl-peptidase 1 (TPP1) [24]. NCL3 is the juvenile form of this disease and often diagnosed with retinitis pigmentosa and late onset seizures at the second decade of life [25]. There are other various types of NCLs; some of these conform to an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance (types of NCL4 which are caused by mutation in the DNAJC5 gene). NCL10 is the most malignant form and the only type of NCL which affect newborns [26,27,28]. NCL7 is caused by mutations in the MFSD8/CLN7 gene and is a LINCL type [27, 28].
Case presentation
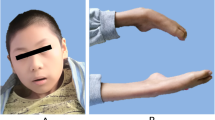
A 5-year-old Iranian boy with a neurodegenerative disorder was referred for genetic testing. His clinical symptoms were speech problems, lack of concentration, walking disability at age of 4 years leading to quadriplegia, spontaneous laughing and crying because of hidden seizure, clumsiness, psychomotor delay, and vision deterioration at age of 5 years which could be the consequence of macular dystrophy. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and electroencephalogram (EEG) showed bilateral white matter signal change with preservation of white matter (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2). There are no available histopathological studies or skin biopsy for this patient.
The organic acids in his urine were determined using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) of the trimethylsilyl ethers and esters of the ethyl acetate extract from acidified urine after preparation of the ethoxime derivatives. The organic acid in the urine of this patient showed a normal pattern with no evidence for metabolic disorders. There is no evidence for tyrosinemia, glutaric aciduria, methylmalonic aciduria, Canavan disease, propionic aciduria, isovaleric aciduria, and other organic aciduria known in Iran. Neonatal screening, clinical chemistry, and metabolism assays showed a normal pattern and these analyses were unremarkable (Table 2 and Table 3).
Our patient’s parents are first cousins and had experienced three gestations, the first one aborted spontaneously before 4 weeks of pregnancy. The second one is the male reported here and the third one is a 2-year-old girl who does not manifest any signs and symptoms yet and seems to be normal. The pedigree is shown in Fig. 3.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was extracted from peripheral blood of our patient and his healthy parents. Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed on all three samples as following. Approximately 37 mega base pairs (Mb; 214,405 exons) of the Consensus Coding Sequences (CCS) were enriched from fragmented genomic DNA by > 340,000 probes designed against the human genome (Nextera Rapid Capture Exome, Illumina) and the generated library sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq 4000 platform (Illumina) to an average coverage depth of more than 100 × (Table 4). An end-to-end bioinformatics pipeline including base calling, primary filtering of low quality reads and probable artifacts, and annotation of variants was applied. All disease-causing variants reported in HGMD® or ClinVar (class 1) as well as all variants with minor allele frequency (MAF) of less than 1% in Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC) database were considered. The evaluation focused on exons and intron boundaries +/− 20. All relevant inheritance patterns were considered and clinical information was used to evaluate eventually identified variants. Relevant variants identified by WES were validated by Sanger sequencing in forward and reverse direction. By applying different filtering steps mentioned in the method part we ended up with only two novel variants in MFSD8 and AFF2 genes (Table 5).
The c.325_339del (p.Val109_Ile113del) variant in the MFSD8 gene was a previously unreported variant and found to be homozygous in our patient whereas his parents were heterozygote carriers (Table 5). Segregation analysis of this variant was done in the affected index, his parents, and relatives. It is a deletion of 15 base pairs (bp), which causes the loss of five residues. The evolutionary conservation of amino acid residues in the region of deletion estimated by ConSurf tool [29] is shown in Fig. 4.
The conservation scale adapted from the ConSurf Service. http://consurf.tau.ac.il/2016/. Mutated domain highlighted in box
The c.259A>G (p.Asn87Asp) variant found in AFF2 was a hemizygous change in our patient; his mother was also heterozygous whereas his father was negative for this variant. This variant had not been reported in the public databases at the time of this publication (Table 5).
Discussion
The identified variant is a 15 bp in-frame deletion in MFSD8 gene. Pathogenic variants in the MFSD8 gene have been shown to be associated with AR NCL type 7. Visual loss and seizures may be the initial signs and symptoms. Epilepsy, ataxia, and myoclonus may be the initial features [28] in children with age of onset after 4 years (Tables 6 and 7). Segregation analysis in this family found 15 bp in-frame deletion in MFSD8 gene which is compatible with disease (Fig. 3).
MFSD8 is located on chromosome 4q28.1-q28.2; it has 55,180 bp and 13 exons, encoding a 4562 bp transcript and a protein with 518 amino acids. Major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 8 which encoded by MFSD8 is a transmembrane ubiquitous protein that consists of a major facilitator superfamily (MFS) and transporter domains [27]. This protein locates into lysosomal membrane and acts as a multi-pass membrane protein using chemiosmotic ion gradients [30]. Figure 5 shows topological structure of MFSD8 wild type and mutant protein. The deletion found in this patient affects the exon 5 of this gene which is the region encoding transmembrane domain. According to IRANOME database (http://www.iranome.ir/), the mean allele frequency of this variant is unknown.
Based on the NCL mutation database held at the University College London, at the time of writing this manuscript, there were 38 reported mutations in MFSD8 gene in different populations [9]. The most common mutations are missense and nonsense mutations; however, other types of mutations such as splice site, single bp deletion, frameshift, and one case of 17 bp deletion are also reported [28].
Rare pathogenic variants in the AFF2 gene have been identified in patients with autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders as well as with X-linked intellectual disability and developmental and speech delay [31, 32]. In addition, this gene has been associated with syndromic autism, where a subpopulation of individuals with a given syndrome develops autism. A rare pathogenic variant in the AFF2 gene has been identified in patients with fragile X syndrome [32]. Mondal et al. suggested that rare variants in AFF2 may be the cause for previously unrecognized autism spectrum disorder (ASD) susceptibility locus and may help to explain some of the male excess of ASD [33]. The other related phenotypes to AFF2 gene are abnormality of metabolism/homeostasis [34], aggressive behavior [35], epicanthic fold, and delayed speech and development of language [36].
AFF2 is a protein coding gene and member of the AF4\FMR2 gene family which is located on chromosome Xq28. This ribonucleic acid (RNA)-binding protein is implicated in the splicing process. The trinucleotide repeat expansion of CCG at 5′ untranslated region (UTR) of AFF2 causes fragile XE syndrome (FRAXE) [37]. More details of this gene are included in Tables 6 and 7. Although the hemizygous variant found in the affected male of this family segregates in the tested samples, based on the clinical symptoms of the affected male, this variant cannot explain the hallmark and pathognomonic characteristics observed in the affected male. So, based on the clinical findings, correlation of the AFF2 variant with the disease in this family is very unlikely. Tables 6 and 7 summarize the expected and observed phenotypic symptoms.
Conclusions
Sequencing analysis in this family has shown that the index is homozygous for 15 bp in-frame deletion, his uncle has normal homozygous, and his parents are heterozygous (Fig. 6).
This pattern of mutation inheritance and the signs and symptoms observed in the affected male of this family are compatible with what is described in the literature for NCL type 7 and, therefore, suggest that the MFSD8 deletion found in this study is most probably the cause of disease in this family.
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Autosomal recessive
- ASD:
-
Autism spectrum disorder
- bp:
-
Base pair
- CCS:
-
Consensus Coding Sequences
- CLNs or NCLs:
-
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- FRAXE:
-
Fragile XE syndrome
- GC-MS:
-
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
- INCL:
-
Infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis
- JNCL:
-
Juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis
- LINCL:
-
Late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis
- MAF:
-
Minor allele frequency
- Mb:
-
Mega base pairs
- MFS:
-
Major facilitator superfamily
- NCLs or CLNs:
-
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses
- PPT :
-
Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase
- TPP1:
-
Tripeptidyl-peptidase 1
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- WES:
-
Whole exome sequencing
References
Geraets RD, Koh SY, Hastings ML, Kielian T, Pearce DA, Weimer JM. Moving towards effective therapeutic strategies for Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2016;11(1):40.
Bennett MJ, Rakheja D. The neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2013;17(3):254–9.
Jadav RH, Sinha S, Yasha TC, Aravinda H, Gayathri N, Rao S, Bindu PS, Satishchandra P. Clinical, electrophysiological, imaging, and ultrastructural description in 68 patients with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses and its subtypes. Pediatr Neurol. 2014;50(1):85–95.
Albert D, De Los RE, Vidaurre J. A case of neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis masquerading as Panayiotopoulos syndrome. J Pediatr Epilepsy. 2016;5(01):047–52.
Stogmann E, El Tawil S, Wagenstaller J, Gaber A, Edris S, Abdelhady A, Assem-Hilger E, Leutmezer F, Bonelli S, Baumgartner C, Zimprich F. A novel mutation in the MFSD8 gene in late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Neurogenetics. 2009;10(1):73–7.
Mink JW, Augustine EF, Adams HR, Marshall FJ, Kwon JM. Classification and natural history of the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. J Child Neurol. 2013;9:0883073813494268.
Haltia M, Goebel HH. The neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses: a historical introduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832(11):1795–800.
Goebel HH, Mole SE, Lake BD. The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (Batten disease). Amsterdam: IOS Press; 1999.
NCL mutation database. Available at: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/ncl/SummaryTableMay2015.htm.
Warrier V, Vieira M, Mole SE. Genetic basis and phenotypic correlations of the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832(11):1827–30.
Sleat DE, Gin RM, Sohar I, Wisniewski K, Sklower-Brooks S, Pullarkat RK, Palmer DN, Lerner TJ, Boustany RM, Uldall P, Siakotos AN. Mutational analysis of the defective protease in classic late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, a neurodegenerative lysosomal storage disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;64(6):1511–23.
Mole SE, Williams RE, Goebel HH. Correlations between genotype, ultrastructural morphology and clinical phenotype in the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Neurogenetics. 2005;6(3):107–26.
Jalanko A, Braulke T. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1793(4):697–709.
Sleat DE, Donnelly RJ, Lackland H, Liu CG, Sohar I, Pullarkat RK, Lobel P. Association of mutations in a lysosomal protein with classical late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Science. 1997;277(5333):1802–5.
Nita DA, Mole SE, Minassian BA. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Epileptic Disord. 2016;18(s2):73–88.
Götzl JK, Mori K, Damme M, Fellerer K, Tahirovic S, Kleinberger G, Janssens J, van der Zee J, Lang CM, Kremmer E, Martin JJ. Common pathobiochemical hallmarks of progranulin-associated frontotemporal lobar degeneration and neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;127(6):845–60.
Karaa A, Simas AM, John S, Glykys J, Xin W, Cotman SL, Sims KB. Expanding the clinical spectrum of the lysosomal disorders with whole exome sequencing. Abstracts/Mol. Genet. Metab. 2015;114:S11–30.
Patel J, Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S. Epileptic encephalopathy in childhood: a stepwise approach for identification of underlying genetic causes. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016;83(10):1164–74.
García-Cazorla A, Wolf NI, Mochel F, Hoffmann GF. Neurological disease. In: Hoffman GF, Zschocke J, Nyhan WL, editors. Inherited metabolic diseases: A clinical approach. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer; 2017. p. 251–92.
Langereis EJ, Wijburg FA. Lysosomal diseases and therapeutic options: an overview. In: Boelens JJ, Wynn R, editors. Stem cell therapy in Lysosomal storage diseases. New York: Springer; 2013. p. 1–20.
Cooper JD, Williams RE. Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinoses. In: Mehta A, Winchester B, editors. Lysosomal Storage Disorders: A Practical Guide, vol. 4; 2012. p. 137–41.
Järvelä I, Schleutker J, Haataja L, Santavuori P, Puhakka L, Manninen T, Palotie A, Sandkuijl LA, Renlund M, White R, Aula P. Infantile form of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (CLN1) maps to the short arm of chromosome 1. Genomics. 1991;9(1):170–3.
Grisolia M, Sestito S, Ceravolo F, Invernizzi F, Salpietro V, Polizzi A, Ruggieri M, Garavaglia B, Concolino D. The neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinoses: a case-based overview. J Pediatr Biochemistry. 2016;6(01):060–5.
Mahmood F, Fu S, Cooke J, Wilson SW, Cooper JD, Russell C. A zebrafish model of CLN2 disease is deficient in tripeptidyl peptidase 1 and displays progressive neurodegeneration accompanied by a reduction in proliferation. Brain. 2013;136:1488–507.
Minye HM, Fabritius AL, Vesa J, Peltonen L. Data on characterizing the gene expression patterns of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis genes: CLN1, CLN2, CLN3, CLN5 and their association to interneuron and neurotransmission markers: Parvalbumin and Somatostatin. Data in Brief. 2016;8:741–9.
Mole SE, Goyal S, Williams RE. The neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinoses. In: Panayiotopoulos CP, editor. Atlas of epilepsies. London: Springer; 2010. p. 1235–41.
Kashyap SS, Johnson JR, McCue HV, Chen X, Edmonds MJ, Ayala M, Graham ME, Jenn RC, Barclay JW, Burgoyne RD, Morgan A. Caenorhabditis elegans dnj-14, the orthologue of the DNAJC5 gene mutated in adult onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, provides a new platform for neuroprotective drug screening and identifies a SIR-2.1-independent action of resveratrol. Human Molecular Genetics. 2014;23:5916–27.
Craiu D, Dragostin O, Dica A, Hoffman-Zacharska D, Gos M, Bastian AE, Gherghiceanu M, Rolfs A, Nahavandi N, Craiu M, Iliescu C. Rett-like onset in late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (CLN7) caused by compound heterozygous mutation in the MFSD8 gene and review of the literature data on clinical onset signs. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2015;19(1):78–86.
Ashkenazy H, Erez E, Martz E, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N. ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:W529–33.
Aiello C, Terracciano A, Simonati A, Discepoli G, Cannelli N, Claps D, Crow YJ, Bianchi M, Kitzmuller C, Longo D, Tavoni A. Mutations in MFSD8/CLN7 are a frequent cause of variant-late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Hum Mutat. 2009;30(3):E530–40.
Abrams MT, Doheny KF, Mazzocco MM, Knight SJ, Baumgardner TL, Freund LS, Davies KE, Reiss AL. Cognitive, behavioral, and neuroanatomical assessment of two unrelated male children expressing FRAXE. Am J Med Genet. 1997;74(1):73–81.
Bensaid M, Melko M, Bechara EG, Davidovic L, Berretta A, Catania MV, Gecz J, Lalli E, Bardoni B. FRAXE-associated mental retardation protein (FMR2) is an RNA-binding protein with high affinity for G-quartet RNA forming structure. Nucleic Acids Research. 2009;37:1269–79.
Mondal K, Ramachandran D, Patel VC, Hagen KR, Bose P, Cutler DJ, Zwick ME. Excess variants in AFF2 detected by massively parallel sequencing of males with autism spectrum disorder. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(19):4356–64.
Weinstein E, Cui X, Simmons P, Sigma-Aldrich Co. Genomic editing of genes involved in autism spectrum disorders. United States patent application US 12/842,678. 2010.
Todorova A, Litvinenko I, Todorov T, Tincheva R, Avdjieva D, Tincheva S, Mitev V. A family with fragile X syndrome, Duchenne muscular dystrophy and ichthyosis transmitted by an asymptomatic carrier. Clin Genet. 2014;85(3):286–9.
Sahoo T, Theisen A, Marble M, Tervo R, Rosenfeld JA, Torchia BS, Shaffer LG. Microdeletion of Xq28 involving the AFF2 (FMR2) gene in two unrelated males with developmental delay. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155(12):3110–5.
Santos CB, Lima C, Pimentel MM. A new PCR assay useful for screening of FRAXE/FMR2 mental impairment among males. Hum Mutat. 2001;18(2):157–62.
Acknowledgements
The Authors would like to give special thanks to the involved family who tightly collaborated with this report.
We are also grateful to Dr Ahmad Reza Salehi and Mr Ehsan Razmara for their assistance and valuable comments.
Availability of data and materials
Results of genetic analysis are included in this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG conducted the experiments. MG and AHB analysed the data. AHB contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. MG and AHB wrote the paper. MG and AHB read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The involved family was informed about the benefits and consequence of genetics testing and a written consent letter was also obtained for their participation.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s legal guardian(s) for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini Bereshneh, A., Garshasbi, M. Novel in-frame deletion in MFSD8 gene revealed by trio whole exome sequencing in an Iranian affected with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 7: a case report. J Med Case Reports 12, 281 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1788-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1788-7