Abstract
Background
Tumoral calcinosis is rarely located in spine. A 55-year-old Japanese woman with cervical tumoral calcinosis is presented, along with a review of the literature relating to tumoral calcinosis in the spine. We discussed the etiology, diagnosis, and management of this condition.
Case presentation
We report a case of a patient with cervical tumoral calcinosis with end-stage renal disease. A computed tomography scan showed a lobulated, calcified mass around the right facet joint at the fourth-fifth cervical spine and calcifications were also observed in the right intervertebral foramens at fourth-fifth cervical spine and fifth-sixth cervical spine levels and the anterior wall of the spinal canal. By performing a cervical decompression and stabilization, the patient recovered from her neurological symptoms.
Conclusions
Although tumoral calcinosis is rarely located in the spine, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of spinal lesions. If a calcified mass causes acute neurological symptoms, resection of the mass is still the most important treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Tumoral calcinosis (TC) was first presented by Inclan et al. in 1943 as a disease with large juxta-articular lobular calcified masses [1]. TC is a pathologic entity characterized by the presence of large calcified masses in periarticular soft tissue [2]. It is usually located at large joints. The most common locations of TC in descending order are the hip, elbow, shoulder, foot, and wrist [3].
TC involving the spine is rare and only 31 cases of spinal TC have been reported in the English literature [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. In this case report, a very rare patient with TC located in the cervical spine was presented and previous case reports with TC in spine summarized.
Case presentation
A 55-year-old Japanese woman presented with a 3-week history of gradually progressing symptoms of numbness, dull pain, and limited range of motion (ROM) in the right upper extremity. Her medical history included chronic renal failure, treated with peritoneal dialysis for the past approximately 5 years.
A physical examination at the initial visit revealed limited ROM of her right shoulder and neck due to pain. The muscle strength of her right upper extremity on the manual muscle testing was one out of five for the deltoid, one out of five for the biceps brachii, and approximately four out of five for other muscle.
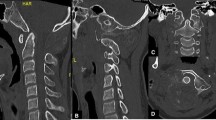
Cervical X-rays (anteroposterior view and lateral view) showed no apparent abnormalities (Fig. 1a, b). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed slight compression of the dura mater from the right anterior direction of the spinal canal at the fourth-fifth cervical spine (C4-C5) intervertebral level. Her cervical spinal cord was not compressed. Computed tomography (CT) showed a vague calcified lesion around the right facet joint at the C4-C5 level; calcifications were also observed in the right intervertebral foramens at the C4-C5 and C5-C6 levels and the anterior wall of the spinal canal. Calcifications were extraosseous, lobulated, and well-demarcated. There were no destructive changes of cervical vertebrae (Fig. 1c, d). Hematological tests showed renal anemia, increased blood urea nitrogen, creatinine and parathyroid hormone, as well as, slightly increased calcium and phosphorus.
X-ray images show no remarkable change in anteroposterior view (a) and slight kyphosis in lateral view (b). Axial computed tomography scan image demonstrates lobulated and extraosseous calcified mass in the intervertebral foramen of fourth-fifth cervical spine (c). Coronal computed tomography scan image also demonstrates lobulated and extraosseous calcified mass at right side of spine (d)
These findings suggested C5 or C6 radiculopathy due to TC. Surgery was thus performed, with right hemilaminectomy at C4-C5 and C3-6 fusion and internal fixation. When the right C4-C5 facet joint was partly resected, milky white fluid came out (Fig. 2). Around the right-sided nerve root at C5, there was a cyst containing white powder and milky white fluid, with adhesion to the C5 nerve root. Under microscopic observation, this cyst was detached from the nerve root and resected.
Histopathological examination of the resected tissue around the white powder showed unstructured (somewhat sand-like granular) materials, which were bluish purple on hematoxylin and eosin staining, along with calcification and supporting tissue including fibroblasts, with few cell components (Fig. 3). The crystals were not composed of calcium pyrophosphate or uric acid.
Her numbness and dull pain in the right upper extremity gradually disappeared postoperatively. The muscle strength of the right upper extremity on the manual muscle testing was full recovered. Postoperative X-rays (anteroposterior view and lateral view) and CT performed 2 years after surgery demonstrated the disappearance of the residual calcified masses (Fig. 4a, b, c, d).
Two-year follow-up images. X-ray images show third-sixth cervical spine C3-C6 fusion and internal fixation: anteroposterior view (a), lateral view (b). Axial computed tomography scan image demonstrates disappearance of calcified mass in the intervertebral foramen of fourth-fifth cervical spine (c). Coronal computed tomography scan image also demonstrates disappearance of calcified mass at right side of spine (d)
Discussion
Most cases of TC are located in the shoulder, hip, and metatarsophalangeal joints; they are rarely located in the spine [23]. The common symptoms are local pain, limited ROM of the joint, headache, and numbness and weakness of the extremities. A thorough search of the PubMed database was completed on June 29, 2016. Twenty-eight potentially relevant references, including 48 cases, were identified on the basis of the keywords “tumoral calcinosis” and “spine”. The diagnosis of TC was based on characteristic radiographic features: a calcified, multilobulated, and peripherally corticated mass in the spine. Seventeen cases were excluded, because seven cases with a medical history of scleroderma or rheumatoid arthritis belonged to dystrophic TC, three cases had a final diagnosis of idiopathic TC, and seven cases had no detailed information on treatment. Finally, 32 cases including the present patient were collected. In regard to these patients’ background characteristics, there were 13 males and 19 females, and their mean age was 55.4 years (range 1.4 to 90 years). Overall, 15 cases involved the cervical spine, three involved the thoracic spine, and 14 involved the lumbar spine. The summary of 32 cases is shown in Table 1.
Smack et al. [24] reviewed the literature on TC and proposed a pathogenesis-based classification: primary normophosphatemic TC, primary hyperphosphatemic TC and secondary TC. In our research, 14 cases had no particular causes. One case was related to hyperphosphatemia; 17 cases were secondary TC; four cases had a history of trauma or surgeries to the involved area; nine cases including the present one were related to dialysis; three cases were related to osteoarthritis; and one was related to seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
One of common causes of secondary TC is renal failure. While the etiology of uremic tumoral calcinosis (UTC) is poorly understood, a necessary condition is an elevated serum calcium-phosphate product [25, 26].
Currently, surgical interventions including resection of focal lesions, parathyroidectomy (PTX), and renal transplantation have been performed. Resection is the most important treatment for TC, and it is generally undertaken for lesions causing acute, progressive, or refractory neurological dysfunction. Overall, 21 of 32 cases underwent surgical resections. Chang et al. [6] reported a case of UTC causing atlantoaxial subluxation, and they noted that resection and fusion surgery resulted in satisfactory pain relief and functional improvement.
PTX usually achieves remarkable resolution in dialysis patients with severe hyperparathyroidism and elevated serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) [25]. Chu et al. [25] reported three patients who were administered PTX because of co-existing UTC and secondary hyperparathyroidism, but only one case was successfully cured by PTX. The other two patients, who did not have a marked increase in serum ALP preoperatively, had unsatisfactory improvement. Renal transplantation provides complete resolution of UTC [23, 25, 27]. Of the 32 cases, two underwent renal transplantation.
Medical therapy is also used for TC patients, especially for UTC patients using aggressive phosphate binders, calcimimetics, using low-calcium dialysate solutions, and increased length and frequency of hemodialysis treatments [28]. Fatehi et al. [8] reported a case that keeping on hemodialysis improved the symptoms and reduced the mass of the lesion.
In this case, a hemilaminectomy of the cervical spine and resection of the calcified masses were performed. CT performed 2 years after surgery demonstrated the disappearance of the residual calcified masses. We report a rare patient with TC located in the cervical spine who was fully recovered neurologically after right hemilaminectomy at C4-C5 and C3-C6 fusion.
Conclusions
Although TC is rarely located in the spine, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of spinal lesions. If a calcified mass causes acute neurological symptoms, resection of the mass is still the most important treatment.
References
Inclan A, Leon PP, Camejo M. Tumoral calcinosis. J Am Med Ass. 1943;121:490–5.
Durant DM, 3rd Riley LH, Burger PC, McCarthy EF. Tumoral calcinosis of the spine a study of 21 cases. Spine. 2001;26(15):1673–9.
Olsen KM, Chew FS. Tumoral calcinosis: pearls, polemics, and alternative possibilities. Radiographics. 2006;26:871–85.
Blay P, Fernandez-Martinez JM, Diaz-Lopez B. Vertebral involvement in hyperphosphatemic tumoral calcinosis. Bone. 2001;28(3):316–8.
Carlson AP, Yonas HM, Turner PT. Disorders of tumoral calcification of the spine illustrative case study and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord. 2007;20(1):97–103.
Chang CC, Sung CC, Hsia CC, Lin SH. Uremic tumoral calcinosis causing atlantoaxial subluxation and spinal cord compression in a patient on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2013;45(5):1511–6. doi:10.1007/s11255-012-0215-z.
Emon ST, Bozkurt SU, Gercek A, Ozgen S. Tumoral calcinosis and epidural lipomatosis of the lumbar spine. Turk Neurosurg. 2011;21(1):110–2.
Fatehi M, Ahuja CS, Wang S, Ginsberg HJ. Uremic tumoral calcinosis in the cervical spine:case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(1):26–30. doi:10.3171/2015.12.SPINE151085.
Iglesias A, Arias M, Brasa J, Gonzalez A, Conde C. Tumoral calcinosis presenting as an extradural mass: MR findings and pathological correlation. Eur Radiol. 2002;12(9):2377–80. doi:10.1007/s00330-001-1215-z.
Jackson W, Sethi A, Carp J, Talpos G, Vaidya R. Unusual spinal manifestation in secondary hyperparathyroidism: a case report. Spine. 2007;32(19):E557–60.
Kokubun S, Ozawa H, Sakurai M, Tanaka Y. Tumoral calcinosis in the upper cervical spine: a case report. Spine. 1996;21(2):249–52.
Matsukado K, Amano T, Itou O, Yuhi F, Nagata S. Tumoral calcinosis in the upper cervical spine causing progressive radiculomyelopathy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2001;41(8):411–4.
Mooney 3rd JF, Glazier SS. Tumoral calcinosis of the cervical spine in an infant. J Neurosrug. 1997;86(1):162.
Rafaelsen S, Johansson S, Ræder H, Bjerknes R. Long-term clinical outcome and phenotypic variability in hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis and hyperphosphatemic hyperostosis syndrome caused by a novel GALNT3 mutation; case report and review of the literature. BMC Genet. 2014;15:98. doi:10.1186/s12863-014-0098-3.
Riemenschneider PA, Ecker A. Sciatica caused by tumoral calcinosis: a case report. J Neurosurg. 1952;9(3):304–7.
Sasaki O, Nakamura K, Nashimoto T, Shibuya H. Tumoral calcinosis involving the cervical spine. Surg Neurol Int. 2015;6:109. doi:10.4103/2152-7806.159074.
Shah A, Miller CJ, Nast CC, Adams MD, Truitt B, Tayek JA, Tong L, Mehtani P, Monteon F, Sedor JR, Clinkenbeard EL, White K, Mehrotra R, LaPage J, Dickson P, Adler SG, Iyengar SK. Severe vascular calcification and tumoral calcinosis in a family with hyperphosphatemia: a fibroblast growth factor 23 mutation identified by exome sequencing. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29(12):2235–43. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfu324. Epub 2014 Nov 5.
Sharma M, Sinha R, Hussey K, Fouyas IP. Tumoral calcinosis of the filum terminale. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(3):E596. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000170987.14821.6F.
Slavin RE, Wen J, Kumar D, Evans EB. Familial tumoral calcinosis. A clinical, histopathologic, and ultrastructural study with an analysis of its calcifying process and pathogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17(8):788–802.
Tuy BE, John TK, Uglialoro AD, Beebe KS, Vives MJ, Patterson FR. Tumoral calcinosis presenting as neck pain and mass lesion of the cervical spine. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead, NJ). 2008;37(11):E191–5.
Watanabe A, Isoe S, Kaneko M, Nukui H. Tumoral calcinosis of the lumbar meninges: case report. Neurosurgery. 2000;47(1):230–2.
Wong RH, Bhansali AP, Doppenberg EM. Cervical spine instability from tumoral calcinosis. Acta Neurochir. 2013;155(7):1245–6. doi:10.1007/s00701-013-1709-x.
Cofan F, Garcia S, Combalia A, Campistol JM, Oppenheimer F, Ramón R. Uremic tumoral calcinosis in patients receiving longterm hemodialysis therapy. J Rheumatol. 1999;26(2):379–85.
Smack D, Norton SA, Fitzpatrick SE. Proposal for pathogenesis-based classification of tumoral calcinosis. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:265–71.
Chu HY, Chu P, Lin YF, Chou HK, Lin SH. Uremic tumoral calcinosis in patients on peritoneal dialysis: clinical, radiologic, and laboratory features. Perit Dial Int. 2011;31:430–9.
Lebl DR, Girardi FP. Isolated cervical spine facet joint tumoral calcinosis. Spine J. 2013;13:208–9.
Remy-Leroux V, Reguiaï Z, Labrousse AL, Zakine EM, Clavel P, Bernard P. Tumoral calcinosis at an unusual site in a haemodialysis patient. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009;136(4):350–4. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2008.10.035.
Sunder S, Verma H, Venkataramanan K. Cervical tumoral calcinosis with secondary hyperparathyroidism in a chronic hemodialysis patient. Hemodial Int. 2013;17:441–62.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RG drafted the manuscript, did the first selection of articles, and assessed the quality of the papers. TKu, TKo, and TI gave important input for the case report. TM and TS assessed the quality of the manuscript, and critically revised the manuscript content. YK helped to draft and correct the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This publication was conducted with the approval of our university’s ethics committee (approval number 1681).
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, R., Kurata, T., Kondo, T. et al. Tumoral calcinosis in the cervical spine: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Reports 11, 304 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-017-1474-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-017-1474-1