Abstract
Background
Placental mesenchymal dysplasia (PMD) is a morphological abnormality resembling partial hydatidiform moles. It is often associated with androgenetic/biparental mosaicism (ABM) and complicated by Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), an imprinting disorder. These phenomena suggest an association between PMD and aberrant genomic imprinting, particularly of CDKN1C and IGF2. The existence of another type of PMD containing the biparental genome has been reported. However, the frequency and etiology of biparental PMD are not yet fully understood.
Results
We examined 44 placental specimens from 26 patients with PMD: 19 of these were macroscopically normal and 25 exhibited macroscopic PMD. Genotyping by DNA microarray or short tandem repeat analysis revealed that approximately 35% of the macroscopic PMD specimens could be classified as biparental, while the remainder were ABM. We performed a DNA methylation analysis using bisulfite pyrosequencing of 15 placenta-specific imprinted differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and 36 ubiquitous imprinted DMRs. As expected, most DMRs in the macroscopic PMD specimens with ABM exhibited the paternal epigenotype. Importantly, the biparental macroscopic PMD specimens exhibited frequent aberrant hypomethylation at seven of the placenta-specific DMRs. Allelic expression analysis using single-nucleotide polymorphisms revealed that five imprinted genes associated with these aberrantly hypomethylated DMRs were biallelically expressed. Frequent aberrant hypomethylation was observed at five ubiquitous DMRs, including GRB10 but not ICR2 or ICR1, which regulate the expression of CDKN1C and IGF2, respectively. Whole-exome sequencing performed on four biparental macroscopic PMD specimens did not reveal any pathological genetic abnormalities. Clinical and molecular analyses of babies born from pregnancies with PMD revealed four cases with BWS, each exhibiting different molecular characteristics, and those between BWS and PMD specimens were not always the same.
Conclusion
These data clarify the prevalence of biparental PMD and ABM-PMD and strongly implicate hypomethylation of DMRs in the pathogenesis of biparental PMD, particularly placenta-specific DMRs and the ubiquitous GRB10, but not ICR2 or ICR1. Aberrant hypomethylation of DMRs was partial, indicating that it occurs after fertilization. PMD is an imprinting disorder, and it may be a missing link between imprinting disorders and placental disorders incompatible with life, such as complete hydatidiform moles and partial hydatidiform moles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Placental mesenchymal dysplasia (PMD) is a morphological abnormality that resembles partial hydatidiform moles but presents as placentomegaly and hydropic changes with vascularized edematous villi in the absence of abnormal trophoblastic proliferation. The condition can manifest as multiple thrombosis within the chorionic villi because of the tortuous vessels’ vulnerability to mesenchymal hyperplasia [1,2,3,4]. PMD is estimated to occur in 0.02% of all pregnancies [5], and roughly 80% of affected fetuses are female [3, 6]. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include high rates of fetal growth restriction, preterm delivery, and intrauterine fetal demise; neonatal outcomes include complications such as hematologic disorders (anemia and thrombocytopenia), liver tumors, and Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) [2, 3, 6].
With respect to the etiology of PMD, several studies have reported androgenetic/biparental mosaicism (ABM) in PMD specimens [7,8,9,10]. ABM can be caused by failed replication of the maternal genome after fertilization or by dispermy, which occurs when two haploid sperm cells fertilize one oocyte [10]. In PMD, androgenetic cells are distributed throughout the chorionic membrane, chorionic mesenchyme, stroma, and enlarged chorionic vessels [8, 11]. However, androgenetic cells are not distributed to the trophoblast, which contains only the biparental genome, leading to normal proliferation [8, 11].
The presence of ABM implies that disruption of genomic imprinting is involved in the etiology of PMD. Several findings have implicated the imprinted genes at 11p15.5, CDKN1C and IGF2, in the etiology of PMD. For example, BWS, which is caused by the disruption of CDKN1C or IGF2 imprinting, has been found to occur in approximately 20% of PMD cases [6]; mosaicism of maternal deletion of 11p15.5 has been found in placentas with PMD [12]; and partial trisomy of 11p15.5 (two paternal copies and one maternal copy) has been found in an enlarged placenta with edematous villi [13]. Furthermore, mice with a null mutation of Cdkn1c and loss of Igf2 imprinting have been reported to display placentomegaly and dysplasia, although human and mouse placentas have substantially different architecture [14].
In contrast to cases with ABM, several PMD cases have been found to be composed entirely of biparental cells and stromal cells positive for p57KIP2, which is encoded by CDKN1C [11, 15,16,17,18]. Therefore, there are two subsets of PMD: one involves ABM, in which imprinting disruption of CDKN1C or IGF2 may be involved in the etiology; the other is biparental PMD, whose etiology is unknown. The frequency of biparental PMD among all PMD cases is also unknown.
In this study, we screened the genotypes of placental specimens obtained from 26 patients with PMD to investigate the frequency of biparental PMD. We also performed DNA methylation analysis of 51 imprinted differentially methylated regions (DMRs), including placenta-specific and ubiquitous DMRs. Further, we analyzed the allelic expression of several imprinted genes associated with aberrantly methylated DMRs. We also performed clinical and molecular analyses of babies born from pregnancies with PMD. Our results strongly suggest that imprinting disruption of several DMRs other than those for CDKN1C and IGF2 is implicated in the pathogenesis of biparental PMD and may be a molecular link between PMD and other imprinting disorders.
Results
Approximately one-third of macroscopic PMD specimens show biparental genotype
Most of the placentas with PMD had two distinct areas: one with a macroscopically normal appearance and the other exhibiting macroscopic PMD characteristics (Additional file 3: Fig. S1). We tested 19 macroscopically normal specimens and 25 macroscopic PMD specimens for ABM via microarray or short tandem repeat analysis (Table 1; Additional file 3: Fig. S2). We found ABM in 64.0% (n = 16/25) of the macroscopic PMD specimens, which we denoted ABM-PMD, while the remaining 36.0% (n = 9/25) displayed normal biparental genotypes, which we denoted biparental-PMD (Table 1; Additional file 3: Figs. S2 and S3). Of the macroscopically normal placentas, just 21.1% (n = 4/19) exhibited ABM, which we denoted ABM-normal, while the other 78.9% (n = 15/19) displayed normal biparental genotypes, which we denoted biparental-normal (Table 1; Additional file 3: Figs. S2 and S3). The difference in ABM frequency between the macroscopic PMD (16/25, 64.0%) and macroscopically normal placentas (4/19, 21.1%) was significant (p = 0.005; chi-squared test). Further, ABM was more frequently isodisomic than heterodisomic (Table 1). We identified numerous copy number variations (CNVs) via microarray analysis, but none were obviously pathological (Additional file 3: Fig. S4). These findings support a link between aberrant imprinting due to ABM and the pathogenesis of PMD [7,8,9,10].
Aberrantly hypomethylated imprinted DMRs in biparental-PMD specimens
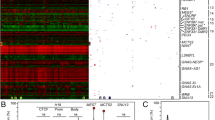
The existence of biparental-PMD specimens prompted us to analyze the DNA methylation status of imprinted DMRs (Additional file 3: Fig. S2). We analyzed biparental-normal (n = 11), biparental-PMD (n = 8), and ABM-PMD (n = 6) specimens, using quantitative bisulfite pyrosequencing, at 15 placenta-specific DMRs, which have been verified as gametic maternally methylated DMRs in several previous studies [19,20,21]. We also analyzed 36 ubiquitous DMRs and compared the results with those for normal placenta specimens. We defined aberrant hypomethylation as less than the mean for normal placentas minus two standard deviations (SDs), and aberrant hypermethylation as more than the mean for normal placentas plus two SDs.
In the ABM-PMD specimens, most of the DMRs were aberrantly methylated: The maternally methylated DMRs were aberrantly hypomethylated, while the paternally methylated DMRs were aberrantly hypermethylated (Table 2, Additional file 1: Table S1). These results were consistent with ABM. In the biparental-PMD and biparental-normal specimens, we focused on identifying the DMRs that were most frequently affected. For this purpose, we counted the number of aberrantly hypomethylated DMRs, which we defined as DMRs that were aberrantly hypomethylated but not aberrantly hypermethylated in more than half of the specimens (i.e., four or more of the biparental-PMD specimens, or six or more of the biparental-normal specimens). In the biparental-PMD specimens, seven of 15 (46.7%) placenta-specific DMRs (MCCC1, AIM1, AGBL3, GLIS3, FAM196A, N4BP2L1, and FAM20A) were aberrantly hypomethylated in more than half of the specimens, whereas five of 25 (20.0%) gametic maternally methylated ubiquitous DMRs (PPIEL, NAP1L5, GRB10, NESPAS-GNASXL, and WRB) were aberrantly hypomethylated in more than half of the specimens (Tables 2 and 3, Additional file 1: Table S1). In the biparental-normal specimens, there were no placenta-specific DMRs showing aberrant hypomethylation in more than half of the specimens, whereas one ubiquitous DMR, WRB, showed aberrant hypomethylation in 10 of 11 specimens. These results indicated that the gametic maternally methylated DMRs were aberrantly hypomethylated according to the progress of the macroscopic and genetic changes in the PMD specimens, and that placenta-specific DMRs were more affected in the PMD specimens.
It was intriguing that among the ubiquitous DMRs, GRB10 was aberrantly hypomethylated in all eight biparental-PMD specimens, and NAP1L5 and WRB were in seven of them (Table 2). On the other hand, two DMRs critical for BWS pathogenesis, ICR1 and ICR2, were not frequently affected in the biparental-PMD specimens: ICR1 was hypermethylated and hypomethylated in two specimens each, and ICR2 was hypermethylated and hypomethylated in one and two specimens, respectively (Table 2). Furthermore, ICR1-related somatic DMRs, such as H19-promoter, IGF2-DMR0, and IGF2-DMR2, were barely affected in the biparental-PMD specimens (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Biallelic expression of imprinted genes associated with placenta-specific DMRs in biparental-PMD specimens
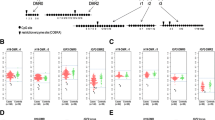
Next, we analyzed whether the aberrant hypomethylation at placenta-specific DMRs influenced the allelic expression of the imprinted genes associated with each DMR. Using single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based genotype screening, we identified four specimens—three biparental-PMD (PMD-002, PMD-020, and PMD-024) and one biparental-normal (PMD-028)—as informative (heterozygous) for at least two of five genes: MCCC1, AIM1, AGBL3, GLIS3, and DNMT1 (Fig. 1). PMD-002 was informative for MCCC1 and DNMT1; PMD-020 was informative for AIM1, AGBL3, and GLIS3; PMD-024 was informative for MCCC1, AIM1, and DNMT1; and PMD-028 was informative for MCCC1, AIM1, AGBL3, and DNMT1. The cystic region in specimens PMD-002 and PMD-020 continued to term, as often occurs, but in PMD-024 and PMD-028 it shrank during pregnancy, indicating that the phenotypes of these cases were milder than those of PMD-002 and PMD-020. We confirmed that all five genes were preferentially expressed from the paternal allele in normal placentas (Additional file 3: Fig. S5). However, we observed biallelic expression of all five genes associated with aberrant hypomethylation in specimens PMD-002 and PMD-020, both of which were biparental-PMD. In PMD-024, we found biallelic expression of one gene associated with aberrant hypomethylation and monoallelic expression of two genes associated with methylation within the normal range. In PMD-028, a biparental-normal specimen, there was biallelic expression of one gene associated with aberrant hypomethylation and monoallelic expression of two genes, one of which was associated with aberrant hypomethylation and the other with normal-range methylation. The allelic expression of DNMT1 in PMD-028 was indeterminate because of very low expression levels of the maternal alleles in some of the normal placenta samples we used as controls (Additional file 3: Fig. S5). Although we could not evaluate the total expression levels of these genes because of the instability of the quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis due to poor RNA quality, these data strongly suggest that biallelic expression of placenta-specific imprinted genes is correlated with aberrant hypomethylation and with the typical phenotype (PMD-002 and PMD-020) rather than milder phenotype (PMD-024 and PMD-028). Therefore, disruption of imprinting, especially placenta-specific imprinted genes, may be involved in the pathogenesis of PMD.
Biallelic expression of placenta-specific imprinted genes in specimens of biparental placental mesenchymal dysplasia (PMD). Using single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), we screened the genotypes of imprinted genes via polymerase chain reaction with genomic DNAs (gPCR) and examined their allelic expression via reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR). Two biparental-PMD specimens (PMD-002 and PMD-020) showed biallelic expression. Specimen PMD-024 was a biparental-PMD specimen in which the cystic region had shrunk during pregnancy; this specimen showed biallelic expression of one gene and monoallelic expression of two genes. Specimen PMD-028 was a biparental-normal specimen in which the cystic region had also shrunk during pregnancy; in this specimen, one gene exhibited biallelic expression, two exhibited monoallelic expression, and one was indeterminate (*) because of very low expression of the maternal allele in some of the normal placental samples we used as controls (Additional file 3: Fig. S5). Arrows indicate the positions of the SNPs. bi: biallelic expression; mono: monoallelic expression. Differences in DNA methylation levels between the normal specimens and the PMD specimens are indicated in parentheses. Since the analyses were performed on additional specimens excised from placental tissues, the methylation levels differ from those shown in Table 2, which refer to the original specimens
Putative pathogenic variants not detected in biparental-PMD specimens
Pathological variants of zinc finger protein genes such as ZFP57 and ZNF445 and of genes related to the subcortical maternal complex such as NLRP2, NLRP5, NLRP7, and KHDC3L have been identified in cases of multilocus imprinting disturbances (MLIDs) and recurrent hydatidiform moles (RHMs) [22]. Whole-exome sequencing (WES) of four biparental-PMD specimens (PMD-001, PMD-002, PMD-003, and PMD-bws022) and one biparental-normal specimen (PMD-008) failed to reveal any pathological variants of the above genes or any others, irrespective of zygosity (data not shown).
Molecular investigation reveals babies with Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome born following PMD-complicated pregnancies
Twenty-two babies were born from 26 patients with PMD (Table 1 and 4). Seventeen were female and five were male, one of which (PMD-bws027) exhibited mosaicism of the sex chromosomes (Table 1). The male–female ratio was consistent with that of previous reports [3, 6]. We examined the clinical features of these babies and scored them according to the Beckwith–Wiedemann spectrum (BWSp) scoring system [23]. We then examined 12 of these babies for the main known causative alterations characteristic of BWS, including gain of methylation at ICR1, loss of methylation at ICR2 (ICR2-LOM), paternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 11 (patUPD), CDKN1C pathogenic variant, and CNVs of chromosome 11p. Of the 12 babies from ABM-PMD pregnancies, we found that two (PMD-022 and PMD-bws027) could be diagnosed with classic BWS (BWSp score ≥ 4). One of these showed no alterations, while the other exhibited ABM, indicating paternal uniparental diploidy (Table 4). We also found that one case (PMD-042), who had a BWSp score of 3, showed no alterations and was not diagnosed with BWS. However, of nine babies from pregnancies exhibiting biparental-PMD, two could be diagnosed with classic BWS. One of these displayed ICR2-LOM (PMD-020) and the other exhibited patUPD limited to 11p (PMD-bws022). The frequency of BWS in babies born from pregnancies with PMD (18.2%, 4/22) was similar to that reported previously [6].
Discussion
Our study is the first to assess the incidence of ABM-PMD and biparental PMD by splitting the affected placental specimens into macroscopically normal and macroscopic PMD tissue samples. The presence of ABM even in macroscopically normal tissue from placentas with PMD, along with its significantly greater prevalence in macroscopic PMD tissue than in macroscopically normal tissue, supports the existence of an association between aberrant imprinting and PMD. The fact that ABM was more frequently isodisomic than heterodisomic is consistent with the established evidence indicating that it is more often caused by failed replication of the maternal genome following normal fertilization than by dispermy [24].
The most important findings in this study were aberrant hypomethylation at imprinted DMRs in biparental-PMD specimens, especially at placenta-specific DMRs, along with altered biallelic expression of associated imprinted genes. We found that the frequency of aberrant hypomethylation in placenta-specific DMRs was higher than that in ubiquitous DMRs. Biallelic expression of five associated imprinted genes occurred in biparental-PMD with the typical phenotype more commonly than in the milder phenotype. These results strongly suggest that aberrant imprinting is involved in PMD pathogenesis. While polymorphic imprinting of placenta-specific DMRs has been reported previously [20, 21, 25], our results suggest a relatively minor contribution of polymorphic imprinting and a greater contribution of aberrant hypomethylation to PMD pathogenesis. We also detected frequently aberrant methylation in several gametic maternally methylated ubiquitous DMRs in our biparental-PMD specimens. Notably, ICR2 and ICR1 were not included in this group, and GRB10 was aberrantly hypomethylated in all biparental-PMD specimens. The DMR associated with GRB10, which is an imprinted gene that encodes a growth inhibitor, is maternally methylated in the human placenta, and the maternal allele is expressed [26]. Since DMR methylation and expression levels are positively correlated [27], reduced expression is assumed in biparental-PMD specimens. In addition, maternal deletion of GRB10 has been reported in the enlarged cystic villi of placentas with biparental PMD and the enlarged placentas of maternal knockout mice [28, 29]. These results suggest that hypomethylation at GRB10 is involved in the pathogenesis of biparental PMD. NAP1L5 and WRB were also frequently aberrantly hypomethylated in biparental-PMD specimens, but these genes may not be involved in the pathogenesis of biparental PMD for the following reasons. Mice with two paternal copies of the chromosomal region including NAP1L5 and other imprinted genes showed normal-sized placentas [30]. WRB is biallelically expressed in 10 human tissues [31], and the methylation status of several CpGs in and around the DMR analyzed in this study is not correlated with gene expression levels in human placentas [32]. Together, our results lead us to surmise that a switch from the paternal to the maternal epigenotype at certain DMRs, including placenta-specific DMRs and at least one ubiquitous DMR (GRB10), is strongly linked to PMD pathogenesis.
In contrast to the aberrant hypomethylation of a subset of DMRs in biparental-PMD specimens, the majority of maternally methylated ubiquitous DMRs and placenta-specific DMRs were severely hypomethylated in RHMs from females with NLRP7 or KHDC3L mutations [33, 34]. This suggests that the difference in the incidence and degree of aberrant hypomethylation of DMRs is critical for the pathogenesis of either PMD or RHMs.
Nearly all the aberrantly hypomethylated DMRs we identified were at maternally methylated DMRs. Hypomethylation is thought to occur after fertilization, because the DMR methylation does not reach the minimum level of 0%, suggesting mosaicism of hypomethylated and normally methylated cells. Maternal methylation of ubiquitous DMRs is protected from demethylation between fertilization and implantation and preserved post-implantation by DNMT1, which is recruited via ZFP57, ZFP445, and TRIM28 [35]. In the case of human placenta-specific DMRs, however, the mechanism that maintains maternal methylation remains poorly understood. It has been suggested that site-specific exclusion of DNA methyltransferases or selective recruitment of demethylation-related factors is critical to the mechanisms of methylation maintenance [21]. DMR hypomethylation in placentas with biparental PMD seems to be caused by a disruption of these mechanisms, although the etiology of this disruption is unknown.
We detected several CNVs in our analyses, but none of them were pathological or affected any of the DMRs analyzed in this study. Further, our WES analysis did not identify any pathological variants of maternal effect genes, including those linked to MLIDs and RHMs. Recently, missense variants of three genes—NLRP2 (p.Thr516Ala), NLRP7 (p.Val319Ile), and ATRX (p.Arg808Gln)—in a single case of biparental PMD were reported [17]. However, given the interpretation of these variants as benign or likely benign on ClinVar (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/), the pathogenicity of these variants is probably minimal. Therefore, PMD seems to be primarily caused by epigenetic rather than genetic factors, although because our WES sample size was small and we did not conduct a WES analysis of mothers with pregnancies complicated by PMD, we cannot completely rule out the involvement of the maternal effect genes mentioned above or of other genetic factors.
Similar to a previous report [6], 18% of the babies in our study that were born from pregnancies with PMD had BWS. The molecular characteristics of babies with BWS and of PMD specimens were not always the same, suggesting that the cells of origin in BWS and PMD also differ. In ABM-PMD and biparental PMD, androgenetic cells and aberrantly hypomethylated cells may arise at the first cleavage of the zygote [8,9,10] and during the preimplantation period, respectively. The molecular defects that are causative of BWS, such as patUPD and ICR2-LOM, also arise during the preimplantation period. It is possible that differences in the extent of the uniparental disomic (UPD) region or aberrant hypomethylation of DMRs is one of the critical factors determining cell fate, differentiation into extraembryonic tissue or embryonic tissue, or later retention or elimination in either tissue type.
Two cases of PMD occurred in pregnancies that resulted from assisted reproductive technology (ART). It is known that the risk of imprinting disorders increases in babies conceived via ART [36, 37]. However, thus far, only one ABM-PMD pregnancy with twins resulting from in vitro fertilization has been reported [38]. Therefore, specimens from more PMD cases should be collected and analyzed to improve our understanding of the relationship between PMD and ART.
Conclusions
The data obtained in this study strongly implicate DMR hypomethylation in the pathogenesis of biparental PMD, particularly hypomethylation of placenta-specific DMRs and the ubiquitous GRB10, but not of ICR2 and ICR1. Therefore, both ABM-PMD and biparental PMD are imprinting disorders, which may constitute a missing link between imprinting disorders in liveborn children and placental disorders that are incompatible with life, such as partial and complete hydatidiform moles (including RHMs). Since the functions of placenta-specific imprinted genes have not yet been resolved [20, 21], functional analysis of these genes should be conducted to elucidate their relationship to PMD pathogenesis. In addition, whole-genome methylation analysis beyond imprinted DMRs, exploration of the genetic origins of PMD by conducting WES of more placental samples and mothers, and whole-genome sequencing analyses are important for further clarifying the pathogenesis of PMD. In the future, it may become possible to diagnose PMD via noninvasive prenatal testing, based on specific epigenomic or genomic abnormalities, which should usefully inform clinical diagnostics and pregnancy care.
Methods
Placental tissue
We collected data on 49 cases of PMD from across Japan [39]. Of these, 26 placentas from patients with PMD (fetal sex: 19 female, 5 male, 2 unspecified; average gestation: 33 weeks 6 days ± 28 days, except for four abortions) were available for nucleic acid extraction and molecular analyses (Table 1). All PMD cases were diagnosed by at least two experts in placental pathology, according to the specific pathological features specified by Lokan et al. [1]. Most of the placentas with PMD displayed two distinct areas: an area with a macroscopically normal appearance and an area exhibiting characteristic macroscopic PMD (Additional file 3: Figure S1). In four of the specimens (PMD-024, PMD-028, PMD-029, and PMD-033), the cystic PMD region shrank during the pregnancy, but a macroscopic PMD region was still present at birth for all specimens except PMD-028. In this specimen, only a macroscopically normal sample was available for the analyses. Twenty normal placentas were used as controls (fetal sex: 10 female, 10 male; average gestation: 36 weeks 5 days ± 14 days).
Nucleic acid extraction
We extracted genomic DNA from 19 macroscopically normal specimens, 25 macroscopic PMD specimens, and 20 control placentas using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit, following the manufacturer’s instructions (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). Total RNA was extracted from placental tissue using ISOGEN II according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Nippon Gene, Tokyo, Japan).
DNA microarray analysis
We used the Genome-Wide Human SNP Array 6.0 (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and the CytoScan HD Array (Affymetrix) to investigate ABM and CNVs. The genotypes generated by the SNP array were subjected to Genotyping Console 4.0 analysis (Affymetrix), and the copy number state and allele ratios were analyzed using Nexus Copy Number software 6.0 (BioDiscovery, Hawthorne, CA, USA). The genotypes, CNVs, and allele ratios from the CytoScan array were analyzed using the CytoScan Chromosome Analysis Suite, version 2.1 (Affymetrix). The genomic positions of the SNPs from the SNP Array and CytoScan corresponded to NCBI36/hg18 and GRCh37/hg19, respectively.
Short tandem repeat marker analysis
For the quantitative analyses, we used 12 short tandem repeat markers (tetranucleotide repeat markers) on chromosomes 11, 14, 15, and 16 to investigate ABM as previously described [40, 41]. These markers were amplified and separated via electrophoresis using an Applied Biosystems 3130 genetic analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). We then quantitatively analyzed the data using the Peak Scanner 2 software (Applied Biosystems).
Methylation analysis of imprinted DMRs via bisulfite pyrosequencing
Genomic DNA (500 ng) was subjected to bisulfite conversion using the EZ DNA Methylation Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). We analyzed the methylation status of imprinted DMRs via bisulfite pyrosequencing using the PyroMark Q24 pyrosequencing instrument (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. To validate the quantitative capability of bisulfite pyrosequencing methylation analysis, we evaluated all the primer sets we designed using varying mixtures of unmethylated and fully methylated control DNA (0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, or 100% methylated DNA), as previously described [42, 43]. All primers used for the methylation analyses are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2.
Genotyping and expression analysis of MCCC1, AIM1, AGBL3, GLIS3, and DNMT1
We used additional excised specimens from placental tissues with PMD for our genotyping and expression analysis. We used SNPs to screen informative samples and analyze allelic expression of the following genes: rs937652 in exon 1 of MCCC1; rs4945755 in exon 1 of AIM1; rs1159148 in exon 2 of AIM1; rs2348049 in exon 4 of AGBL3; rs7852293 in exon 1 of GLIS3; and rs2228611 in exon 17 of DNMT1. We performed the genotyping and allelic expression analysis via PCR followed by Sanger sequencing using the Applied Biosystems 3130 genetic analyzer. We treated the RNA with RNase-free DNase I (TAKARA, Tokyo, Japan) and performed reverse transcription using random primers and ReverTra Ace (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan). All primers used for the genotyping and allelic expression analysis are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2.
Whole-exome sequencing
We performed WES on four biparental-PMD specimens (PMD-001, PMD-002, PMD-003, and PMD-bws022) and one biparental-normal specimen (PMD-008). We sequenced enriched libraries prepared using SureSelect Human All Exon V4 + UTRs (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) using the SOLiD 5500xl 50 bp + 25 bp paired-end procedure (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). We processed the read data we obtained using an in-house workflow [44] to align them to the hg19 human reference genome with NovoAlignCSMPI version 1.02.03 (Novocraft Technologies, Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia). We also used the read data to call single-nucleotide variations and small insertions and deletions of bases using the UnifiedGenotyper program in the Genome Analysis Toolkit version 2.3 [45]. We omitted common variations by filtering out variants that had alternative allele frequencies (AAF) greater than the threshold in any of the following databases: the October 2014 release of the 1000 Genomes Project (AAF > 0.5%), the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Exome Sequencing Project ESP6500SI-V2 (AAF > 0.5%), the Human Genetic Variation Database [46] version 1.42 (AAF > 0.5%), and the Complete Genomics 46 genomes database (AAF > 2%). We used GENCODE version 19 to classify deleterious variants that were nonsynonymous, had gained or lost stop codons, were within 2 bp of exon–intron boundaries, or contained in-frame or frameshift insertions and deletions. We also omitted variations within regions tagged as genomic segmental duplications in the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser.
Statistical analysis
We used chi-squared tests to compare the frequency of ABM between macroscopically normal and macroscopic PMD specimens. We considered p values less than 0.05 to be statistically significant.
Availability of data and materials
Data generated or analyzed during this study, except for the WES data, are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. The CNV and WES datasets are not publicly available because no positive data were obtained, but they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AAF:
-
Alternative allele frequencies
- ABM:
-
Androgenetic/biparental mosaicism
- ART:
-
Assisted reproductive technology
- BWS:
-
Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome
- BWSp:
-
Beckwith–Wiedemann spectrum
- CNV:
-
Copy number variation
- DMR:
-
Differentially methylated region
- ICR2-LOM:
-
Loss of methylation at ICR2
- MLID:
-
Multilocus imprinting disturbance
- patUPD:
-
Paternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 11
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PMD:
-
Placental mesenchymal dysplasia
- RHMs:
-
Recurrent hydatidiform moles
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- UPD:
-
Uniparental disomy
- WES:
-
Whole-exome sequencing
References
Lokan J, Chan YF, Agnesta F. Placental mesenchymal dysplasia. Pathology. 2002;34(4):375–8.
Nayeri UA, West AB, Grossetta Nardini HK, Copel JA, Sfakianaki AK. Systematic review of sonographic findings of placental mesenchymal dysplasia and subsequent pregnancy outcome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013;41(4):366–74.
Colpaert RM, Ramseyer AM, Luu T, Quick CM, Frye LT, Magann EF. Diagnosis and Management of Placental Mesenchymal Disease. A Review of the Literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2019;74(10):611–22.
Soejima H, Ohba T. Genomic Imprinting Disorders (Including Mesenchymal Placental Dysplasia). In: Masuzaki H, editor. Fetal Morph Functional Diagnosis: Springer Singapore; 2021. p. 149–68.
Arizawa M, Nakayama M. Suspected involvement of the X chromosome in placental mesenchymal dysplasia. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2002;42(4):309–17.
Pham T, Steele J, Stayboldt C, Chan L, Benirschke K. Placental mesenchymal dysplasia is associated with high rates of intrauterine growth restriction and fetal demise: A report of 11 new cases and a review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;126(1):67–78.
Surti U, Hill LM, Dunn J, Prosen T, Hoffner L. Twin pregnancy with a chimeric androgenetic and biparental placenta in one twin displaying placental mesenchymal dysplasia phenotype. Prenat Diagn. 2005;25(11):1048–56.
Kaiser-Rogers KA, McFadden DE, Livasy CA, Dansereau J, Jiang R, Knops JF, et al. Androgenetic/biparental mosaicism causes placental mesenchymal dysplasia. J Med Genet. 2006;43(2):187–92.
Robinson WP, Lauzon JL, Innes AM, Lim K, Arsovska S, McFadden DE. Origin and outcome of pregnancies affected by androgenetic/biparental chimerism. Hum Reprod. 2007;22(4):1114–22.
Morales C, Soler A, Badenas C, Rodriguez-Revenga L, Nadal A, Martinez JM, et al. Reproductive consequences of genome-wide paternal uniparental disomy mosaicism: description of two cases with different mechanisms of origin and pregnancy outcomes. Fertil Steril. 2009;92(1):393 e5–9.
Armes JE, McGown I, Williams M, Broomfield A, Gough K, Lehane F, et al. The placenta in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: genotype-phenotype associations, excessive extravillous trophoblast and placental mesenchymal dysplasia. Pathology. 2012;44(6):519–27.
Robinson WP, Slee J, Smith N, Murch A, Watson SK, Lam WL, et al. Placental mesenchymal dysplasia associated with fetal overgrowth and mosaic deletion of the maternal copy of 11p15.5. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A(15):1752–9.
Drut RM, Drut R. Nonimmune fetal hydrops and placentomegaly: diagnosis of familial Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome with trisomy 11p15 using FISH. Am J Med Genet. 1996;62(2):145–9.
Caspary T, Cleary MA, Perlman EJ, Zhang P, Elledge SJ, Tilghman SM. Oppositely imprinted genes p57(Kip2) and igf2 interact in a mouse model for Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Genes Dev. 1999;13(23):3115–24.
Højberg KE, Aagaard J, Henriques U, Sunde L. Placental vascular malformation with mesenchymal hyperplasia and a localized chorioangioma. A rarity simulating partial mole. Pathol Res Pract. 1994;190(8):808–13; discussion 14.
Chen CP, Chern SR, Wang TY, Huang ZD, Huang MC, Chuang CY. Pregnancy with concomitant chorangioma and placental vascular malformation with mesenchymal hyperplasia. Hum Reprod. 1997;12(11):2553–6.
Huang TC, Chang KC, Chang JY, Tsai YS, Yang YJ, Chang WC, et al. Variants in Maternal Effect Genes and Relaxed Imprinting Control in a Special Placental Mesenchymal Dysplasia Case with Mild Trophoblast Hyperplasia. Biomedicines. 2021;9(5).
Hoffner L, Dunn J, Esposito N, Macpherson T, Surti U. P57KIP2 immunostaining and molecular cytogenetics: combined approach aids in diagnosis of morphologically challenging cases with molar phenotype and in detecting androgenetic cell lines in mosaic/chimeric conceptions. Hum Pathol. 2008;39(1):63–72.
Court F, Tayama C, Romanelli V, Martin-Trujillo A, Iglesias-Platas I, Okamura K, et al. Genome-wide parent-of-origin DNA methylation analysis reveals the intricacies of human imprinting and suggests a germline methylation-independent mechanism of establishment. Genome Res. 2014;24(4):554–69.
Hanna CW, Penaherrera MS, Saadeh H, Andrews S, McFadden DE, Kelsey G, et al. Pervasive polymorphic imprinted methylation in the human placenta. Genome Res. 2016;26(6):756–67.
Hamada H, Okae H, Toh H, Chiba H, Hiura H, Shirane K, et al. Allele-Specific Methylome and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Widespread Imprinting in the Human Placenta. Am J Hum Genet. 2016;99(5):1045–58.
Elbracht M, Mackay D, Begemann M, Kagan KO, Eggermann T. Disturbed genomic imprinting and its relevance for human reproduction: causes and clinical consequences. Hum Reprod Update. 2020;26(2):197–213.
Brioude F, Kalish JM, Mussa A, Foster AC, Bliek J, Ferrero GB, et al. Expert consensus document: Clinical and molecular diagnosis, screening and management of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: an international consensus statement. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(4):229–49.
Lawler SD, Fisher RA, Dent J. A prospective genetic study of complete and partial hydatidiform moles. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991;164(5 Pt 1):1270–7.
Sanchez-Delgado M, Court F, Vidal E, Medrano J, Monteagudo-Sanchez A, Martin-Trujillo A, et al. Human Oocyte-Derived Methylation Differences Persist in the Placenta Revealing Widespread Transient Imprinting. PLoS Genet. 2016;12(11): e1006427.
Monk D, Arnaud P, Frost J, Hills FA, Stanier P, Feil R, et al. Reciprocal imprinting of human GRB10 in placental trophoblast and brain: evolutionary conservation of reversed allelic expression. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18(16):3066–74.
Turan N, Ghalwash MF, Katari S, Coutifaris C, Obradovic Z, Sapienza C. DNA methylation differences at growth related genes correlate with birth weight: a molecular signature linked to developmental origins of adult disease? BMC Med Genomics. 2012;5:10.
Surti U, Yatsenko S, Hu J, Bellissimo D, Parks WT, Hoffner L. Maternal GRB10 microdeletion is a novel cause of cystic placenta: Spectrum of genomic changes in the etiology of enlarged cystic placenta. Placenta. 2017;57:33–41.
Charalambous M, Cowley M, Geoghegan F, Smith FM, Radford EJ, Marlow BP, et al. Maternally-inherited Grb10 reduces placental size and efficiency. Dev Biol. 2010;337(1):1–8.
Beechey CV. A reassessment of imprinting regions and phenotypes on mouse chromosome 6: Nap1l5 locates within the currently defined sub-proximal imprinting region. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;107(1–2):108–14.
Alves da Silva AF, Machado FB, Pavarino É C, Biselli-Périco JM, Zampieri BL, da Silva Francisco Junior R, et al. Trisomy 21 Alters DNA Methylation in Parent-of-Origin-Dependent and -Independent Manners. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0154108.
Litzky JF, Deyssenroth MA, Everson TM, Armstrong DA, Lambertini L, Chen J, et al. Placental imprinting variation associated with assisted reproductive technologies and subfertility. Epigenetics. 2017;12(8):653–61.
Sanchez-Delgado M, Martin-Trujillo A, Tayama C, Vidal E, Esteller M, Iglesias-Platas I, et al. Absence of Maternal Methylation in Biparental Hydatidiform Moles from Women with NLRP7 Maternal-Effect Mutations Reveals Widespread Placenta-Specific Imprinting. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(11): e1005644.
Demond H, Anvar Z, Jahromi BN, Sparago A, Verma A, Davari M, et al. A KHDC3L mutation resulting in recurrent hydatidiform mole causes genome-wide DNA methylation loss in oocytes and persistent imprinting defects post-fertilisation. Genome Med. 2019;11(1):84.
Hanna CW. Placental imprinting: Emerging mechanisms and functions. PLoS Genet. 2020;16(4): e1008709.
Hattori H, Hiura H, Kitamura A, Miyauchi N, Kobayashi N, Takahashi S, et al. Association of four imprinting disorders and ART. Clin Epigenetics. 2019;11(1):21.
Cortessis VK, Azadian M, Buxbaum J, Sanogo F, Song AY, Sriprasert I, et al. Comprehensive meta-analysis reveals association between multiple imprinting disorders and conception by assisted reproductive technology. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018;35(6):943–52.
Linn RL, Minturn L, Yee LM, Maniar K, Zhang Y, Fritsch MK, et al. Placental mesenchymal dysplasia without fetal development in a twin gestation: a case report and review of the spectrum of androgenetic biparental mosaicism. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2015;18(2):146–54.
Kodera C, Aoki S, Ohba T, Higashimoto K, Mikami Y, Fukunaga M, et al. Clinical manifestations of placental mesenchymal dysplasia in Japan: A multicenter case series. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021;47(3):1118–25.
Higashimoto K, Watanabe H, Tanoue Y, Tonoki H, Tokutomi T, Hara S, et al. Hypomethylation of a centromeric block of ICR1 is sufficient to cause Silver-Russell syndrome. J Med Genet. 2021;58(6):422–5.
Sun F, Hara S, Tomita C, Tanoue Y, Yatsuki H, Higashimoto K, et al. Phenotypically concordant but epigenetically discordant monozygotic dichorionic diamniotic twins with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185(10):3062–7.
Hidaka H, Higashimoto K, Aoki S, Mishima H, Hayashida C, Maeda T, et al. Comprehensive methylation analysis of imprinting-associated differentially methylated regions in colorectal cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 2018;10(1):150.
Watanabe H, Higashimoto K, Miyake N, Morita S, Horii T, Kimura M, et al. DNA methylation analysis of multiple imprinted DMRs in Sotos syndrome reveals IGF2-DMR0 as a DNA methylation-dependent, P0 promoter-specific enhancer. FASEB J. 2020;34(1):960–73.
Mishima H, Sasaki K, Tanaka M, Tatebe O, Yoshiura K-i. Agile parallel bioinformatics workflow management using Pwrake. BMC Research Notes. 2011;4(1):331.
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20(9):1297–303.
Higasa K, Miyake N, Yoshimura J, Okamura K, Niihori T, Saitsu H, et al. Human genetic variation database, a reference database of genetic variations in the Japanese population. J Hum Genet. 2016;61(6):547–53.
Acknowledgements
The authors are deeply grateful to the following researchers for providing PMD samples: Seiichi Hayakawa (Department of Pediatrics, Hiroshima University Graduate School of Biomedical and Health Sciences), Satoshi Ishikawa and Takahiro Yamada (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Hokkaido University Hospital), Tomoka Jimbo (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University), Atsushi Kasamatsu (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kansai Medical University), Tomomi Kotani (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine), Takao Matsuda (Department of Reproduction and Genetics, National Hospital Organization Nishi Beppu Hospital), Kazuya Mimura (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Osaka University Hospital), Sachiko Minamiguchi (Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kyoto University Hospital), Kiyonori Miura (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Nagasaki University Hospital), Makoto Nomiyama (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, National Hospital Organization Saga Hospital), Yoko Okamoto and Keiko Matsuoka (Osaka Women’s and Children’s Hospital), Rituko K. Pooh (Clinical Research Institute of Fetal Medicine Prenatal Medical Clinic), Shigeru Saito (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Toyama), Shunji Suzuki (Japanese Red Cross Tokyo Katsushika Prenatal Center), Hironori Takahashi (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Jichi Medical University), Akiko Tanuma-Takahashi (Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Jikei University School of Medicine), Yuto Yamamoto (Department of Medical Genetics, Seto Hospital), and Hajime Yasuhara (Department of Neonatal Intensive Care, Nara Prefecture General Medical Center). We also would like to thank the Analytical Research Center for Experimental Sciences at Saga University for experimental support.
Funding
This study was supported in part by the following grants: the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (KAKENHI), under Grant Numbers JP21K19451 (HS), JP20H03643 (HS), JP20K08183 (KH), and JP19K06451 (SH); the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, under Grant Numbers JP20ek0109486 and JP20ek0109489 (HS); and the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare Program, under Grant Number JP20FC1046 (HS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS designed and supervised the study. SaA, KH, HH, YO, HY, HM, and KiY performed the experiments. ShA performed the histological examinations. TO, HK, KN, and KiH provided the samples and clinical information. SaA and HS interpreted the data and performed the statistical analyses. SaA and HS drafted the manuscript. KH, SH, TO, and HK reviewed the manuscript and provided comments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee for Human Genome and Gene Analyses of the Faculty of Medicine at Saga University and Kumamoto University. Written informed consent was obtained from the participants and the parents or guardians of the babies.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
. Supplementary Table S1.
Additional file 2
. Supplementary Table S2.
Additional file 3
. Supplementary Figures.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki, S., Higashimoto, K., Hidaka, H. et al. Aberrant hypomethylation at imprinted differentially methylated regions is involved in biparental placental mesenchymal dysplasia. Clin Epigenet 14, 64 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-022-01280-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-022-01280-0