Abstract
Background
In developing countries like Ethiopia, infections with antibiotic resistant bacteria become a real threat. Hence, monitoring of local level antimicrobial resistance profile is indispensable to contain the spread of drug resistant bacteria and intervene poor awareness on antimicrobial resistance. Therefore, this study aimed at determining bacterial and antibiotic resistance profiles of infections from different sites that occurred among patients.
Methods
Retrospective data recorded were analyzed on culture and drug susceptibility test results at Debre Markos Referral Hospital which were performed from 2011 to 2014. Drug susceptibility tests were performed using disk-diffusion technique. Chi square test was computed to compare the proportion of bacterial isolates with patients’ age and sex.
Results
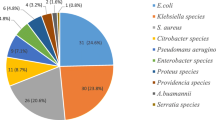
Out of 575 clinical samples processed, 280 (48.7%) were culture positive for aerobic bacteria pathogens. Wound 238 (41.4%) and urine 108 (18.8%) were the most frequent samples processed. Overall, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was the predominant isolate 100 (31.5%) followed by Escherichia coli (E. coli) 39 (13.8%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) 30 (10.3%) and Salmonella spp. 25 (8.9%). P. aeruginosa was the most frequent isolate followed by S. aureus from ear infection. E. coli was the leading isolate followed by Klebsiella spp. from urinary tract infection. Salmonella and Shigella spp. were the most frequent isolates in stool in children below 5 years of age. Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae) 16 (76.2%) was the most common isolate from urethral discharge. The overall multidrug-resistant Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria isolates were 113 (84.6%) and 96 (72.2%), respectively. Gram positive bacteria revealed resistance to cotrimoxazole (80%), gentamicin (83.1%), amoxicillin (85.1%), ampicillin (85.8%), penicillin (89.7%), clindamycin (93.2%) and erythromycin (90.9%). Gram negative bacteria showed resistance to cotrimoxazole (53.1%), amoxicillin (58.8%), ampicillin (70.4%), tetracycline (75.9%) and gentamicin (76.9%).
Conclusions
Various bacterial infections linked with high levels of MDR bacteria pathogens are major health problems in the study area. Therefore, treatment of common bacterial infections in the study area needs to be guided by drug-susceptibility testing of isolates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Bacterial infections caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria are a growing threat worldwide [1]. They are major cause of morbidity and mortality in developing countries including Ethiopia. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major problem in both hospital and community acquired infections [2, 3].
The term MDR refers to a bacterium that is simultaneously resistant to a number of antimicrobial drugs belonging to different chemical classes or subclasses through various mechanisms [4]. Many bacteria species isolated from different clinical specimens have showed one or more resistance mechanisms to each of the major classes of antimicrobial agents [5, 6]. MDR bacteria acquire resistance by mutation or gene transfer through conjugation, transformation or transduction. These resistance mechanisms are widespread among common pathogens and cause considerable concern in several clinical situations in which treatment options have become very limited [5, 6].
AMR problem is challenging in low income countries due to high prevalence of infections, irrational uses of antimicrobials, over the counter availability of drugs and lack of clinical microbiology laboratories for antimicrobial susceptibility testing [3]. Infections caused by resistant bacteria adversely affect treatment outcomes, costs, disease spread and duration of illnesses, posing a serious challenge to the future chemotherapies [2, 7]. In addition to this, the battle between bacteria and their susceptibility to drugs is yet problematic among public, researchers, clinicians and drug companies who are looking for effective drugs [7].
The ongoing spread of resistant bacteria is partly due to the indiscriminate use of antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance emerges commonly when patients are treated with empiric antimicrobial drugs. This is critical in developing countries where the available antibiotics are misused [3, 6, 8]. To overcome these difficulties, monitoring of resistance profiles in the health institutions is needed [2, 6, 8, 9].
Majority of physicians and nurses in Ethiopia lack up to-date information on AMR [3]. Culture and drug susceptibility tests have been started since 2011 at Debre Markos Referral Hospital hence there was no documented comprehensive data on pathogenic bacteria and their drug susceptibility profiles from different sites of infections. Furthermore, ministry of health in its strategy includes monitoring of local antimicrobial resistance trends using standardized microbiological methods to intervene empirical therapy, poor awareness on AMR and to contain drug resistance. Therefore, the present study was conducted to determine bacteria and antibiotic resistance profiles of infections from different sites that occurred among patients at Debre Markos Referral Hospital, Ethiopia.
Methods
Study design, period and area
A Retrospective data review was made in January, 2015 on culture results of clinical specimens taken from different infection sites performed from September 2011 to December 2014 at Debre Markos Referral Hospital (DMRH). DMRH has more than 147 beds offering different specialized services. It receives patients from its catchment area and referrals from different areas of East Gojjam Zone. The hospital has four major wards namely, Internal Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics and Gynecology and Obstetrics used for diagnosis and treatment of infected patients. Culture and drug susceptibility tests were conducted at DMRH microbiology laboratory for both out and inpatients. However, there is no laboratory facility for isolation of anaerobic bacteria from clinical specimens.
Data collection
The age and sex of patients, the bacteria isolated and the drug susceptibility profiles were retrieved from DMRH microbiology, laboratory unit registration records using a standard data collection form. Laboratory records which had incomplete information of either age, sex or culture and drug susceptibility test results were excluded.
Isolation and identification of bacteria
For the detection of pathogenic bacteria, all clinical samples were collected by standard microbiological technique [10]. The sources of specimens were pus/swab from wound, urine, ear discharge, blood, stool, urethral or cervical discharge, nasal or throat swab and CSF. Depending on the source of samples, each specimen were platted onto MacConkey agar, Blood agar, Mannitol Salt agar, Xylose lysine deoxycholate agar, Chocolate agar and Thayer–Martin agar (Oxoid, UK) and then incubated aerobically at 37 °C for 24 h. Bacterial species were identified as per the standard microbiological methods [10].
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was done on Mueller–Hinton agar (Oxoid, England) using disk diffusion technique according to Kirby–Bauer method [11]. The antimicrobial agents tested were: ampicillin (10 µg), penicillin (10 IU), Oxacillin (1 µg), clindamycin (30 µg) amoxicillin (10 µg), ceftriaxone (30 µg), ciprofloxacin (5 µg), cloxacillin (5 µg), cotrimoxazole (25 µg), doxycycline (10 µg), tetracycline (30 µg), erythromycin (15 µg), chloramphenicol (30 µg), gentamicin (10 µg) (Oxoid, England). The antibiotic susceptibility profiles were interpreted based on Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI, 2006) guidelines [12]. Moreover, MDR profile was determined against different classes of antimicrobials: cephalosporin class (ceftriaxone), Aminoglycosides class (gentamycin); Fluoroquinolones class (ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin), Tetracycline class (doxycycline); Folate pathway inhibitors (cotrimoxazole); phenicols class (chloramphenicol); penicillin class (oxacillin, ampicillin, penicillin), Macrolides class (erythromycin) and Lincosamides class (clindamycin). Due to the varied definitions that are being used and differences in the antimicrobial agents that are used for routine antimicrobial susceptibility testing in clinical, referral and public health microbiology laboratories, no standard definitions for MDR have been agreed up on yet by the medical community. Therefore, we authors of this manuscript determined the MDR profiles by taking the literal definition of MDR as resistant to more than one antimicrobial agent [13].
Quality control
A standard bacteriological procedure was followed to maintain correct laboratory test results. American Type Culture collection (ATCC) standard reference strains Escherichia coli (E. coli) ATCC-25922, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) ATCC 25923 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) ATCC 25853 were used to control quality of culture and drug susceptibility testing.
Statistical analysis
Data were entered and analyzed using SPSS Statistical software Package (IBM Corp. Released 2011 IBM SPSS statistics for windows, version 20. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp). Chi square tests were computed to compare the proportion of bacterial isolates with patients’ age and sex. P value of <0.05 was considered to indicate statistically significant differences.
Results
A total of 575 patients specimens were collected and submitted for culture and drug susceptibility tests from patients with clinical evidence of infections from different sites. The subjects included 349 (60.7%) females and 226 (39.3%) males. One hundred fifty-three (26.6%) were in the age group of ≤18 years. Overall, 280 (48.7%) of infections had aerobic bacterial isolates. The proportion of bacterial infection was 116 (51.3%) in males and 164 (47.6%) in females (Table 1). Wound 238 (41.4%) and urine 108 (18.8%) samples were the most frequent specimens processed (Table 2).
Bacteria profile
From 280 aerobic bacteria isolates, 270 (96.4%) had single isolates while 10 (3.6%) had mixed ones (data not shown). Two (6.9%) Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae) were isolated from patients aged 15–18 years (P = 0.04). On the other hand, Salmonella spp. (P < 0.001) and Shigella spp. (P = 0.001) were the most common isolates in stools in children less than 5 years of age (Table 1). Gram negative bacteria accounted for 146 (52.1%) of the isolates. As shown in Table 2, S. aureus 100 (35.4%) was the predominant isolate, followed by E. coli 39 (13.9%), P. aeruginosa 30 (10.7%) and Salmonella spp. 25 (8.9%). Furthermore: S. aureus 71 (78%) was the leading isolate followed by P. aeruginosa 6 (6.6%) and E. coli 5 (5.5%) in wound infection. P. aeruginosa 19 (34.5%) was the predominant isolate followed by S. aureus 18 (32.7%) in ear infection. E. coli 27 (60%) was the leading isolate followed by Klebsiella spp. 7 (14.6%) in urinary tract infection. S. pneumoniae 7 (36.8%) was the most frequent isolate followed by E. coli 4 (21.1%) in blood stream infection.
Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of bacterial isolates
Gram positive bacteria
Overall Gram positive isolates were resistant to cotrimoxazole (80%), penicillin (89.7%), clindamycin (93.2%), and erythromycin (90.9%). Moreover, higher (>83%) resistance was exhibited to gentamicin, ampicillin and amoxicillin (Table 3). S. aureus isolates were resistant to cotrimoxazole (81.3%), ampicillin (85.4%), gentamicin (86.8%), amoxicillin (87.5%), erythromycin (96.8%), penicillin (93.8%) and clindamycin (93.2%). However, S. aureus isolates were susceptible to ceftriaxone and norfloxacin with resistance rates of 13.5–22.2% (Table 3).
Gram negative bacteria
Majority of Gram negative isolates were resistant to cotrimoxazole (53.1%), amoxicillin (58.8%), ampicillin (70.4%) and gentamicin (76.9%). Salmonella spp. was resistant to cotrimoxazole (72.7%), amoxicillin (88.9%) and ampicillin (100%). Shigella isolates were 100% resistant to cotrimoxazole, norfloxacin and chloramphenicol. N. gonorrhoeae isolates were 100% resistant to norfloxacin, chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin and tetracycline. Conversely, these isolates were susceptible to ceftriaxone (38.5%) (Table 4). E. coli isolates were resistant to gentamicin (69.6%) and tetracycline (75%). Moreover, P. aeruginosa isolates were resistant to tetracycline (57.1%) and gentamicin (87.5%). Details of drug resistance profiles of Gram negative bacteria are presented in Table 4.
Multidrug- resistance profiles of the isolates
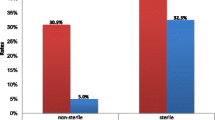
Overall, 24 (8.6%) of the isolates were susceptible to drugs tested, whereas 256 (91.4%) were resistant to one and more antimicrobials tested. Multidrug-resistance to two and more drugs were found in 213 (76.1%) of the isolates at a time (Table 5). The overall MDR rate among Gram positive (2–7 antimicrobial types) and Gram negative bacteria (2–6 antimicrobial types) isolates were 113 (84.6%) and 96 (72.2%), respectively (Table 5). Species specific MDR rate is depicted in Table 5.
Discussion
Multidrug-resistant bacterial infection becomes a real threat in developing countries including Ethiopia. In the study area the majority of pathogenic bacteria isolated from various clinical specimens such as wound, urine, stool, ear and urethral discharge were drug resistant.
In the present study, Gram negative bacteria were the dominant isolates similar to previous studies in other areas of Ethiopia [14,15,16,17] and elsewhere [18]. However, S. aureus was the most frequent isolate followed by E. coli, P. aeruginosa and Salmonella spp. This trend agrees with reports of other studies in Ethiopia [14,15,16,17]. The possible reason for the high frequency is that majority of these isolates are normal flora on skin and gut of healthy individuals. When they get breach on skins and soft tissues and displaced from their resident to other sterile sites they can easily disseminate. Moreover, most of these bacteria are commonly found in the hospital environment which might increase the proportion of wound, ear and urinary tract infection and cross contamination among admitted patients.
The high proportion of S. aureus followed by P. aeruginosa in wound infection in this study might be because of endogenous source of infection or contamination from the environment such as contamination of surgical instruments with the disruption of natural skin barrier as these bacteria are a common bacterium on surfaces, easily finds their way into wounds [16]. Moreover, the high frequency of P. aeruginosa in ear infection could be related to the ability of P. aeruginosa to survive in competition with other organisms and resist antibiotics.
In this study N. gonorrhoeae was most frequently isolated in patients with the age groups of 15–18 years compared to other age groups. This is in agreement with a study done in other part of Ethiopia [19]. This might be because individuals at this age are key populations of higher risk for sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea acquisition or transmission. Hence between these ages young individuals undergo transition in life style, maturity and legal rights which will place them at different vulnerabilities at different time points.
Salmonella and Shigella spp. were the most common isolates in stool in children less than 5 years of age, which is in line with studies conducted in Ethiopia [20] and China [21]. It is true that children with in this age group are more susceptible to shigellosis and salmonellosis primarily because of lack of resistance, previous exposure to infections, poor personal hygiene and higher exposure to contaminated environments.
In this study, overall high levels of resistance were demonstrated against amoxicillin, clindamycin, erythromycin and penicillin. These were consistent with resistance rates obtained from previous studies in Ethiopia [6, 16] and India [22]. However, majority of bacteria isolates revealed lower levels of resistance against ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone, norfloxacin and chloramphenicol. Moreover, Gram positive bacteria showed high levels of resistance (82.1–98.5%) to ampicillin, gentamicin, cotrimoxazole, amoxicillin, penicillin and clindamycin. This finding is similar with studies carried out in Ethiopia [23] and India [22] where 75–100% resistance to the above antibiotics reported. Similarly, S. aureus isolates revealed high levels of resistance (81.3–96.8%) to the above mentioned antibiotics. These results are in agreement with the reports from Ethiopia and other countries [6,7,8,9, 17, 22].
In the present study, N. gonorrhoeae isolates revealed 100% resistant to ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and tetracycline. This agrees with studies carried out in Ethiopia [19, 24], Uganda [25], Port Elizabeth [26] and Iran [27]. This might be because of easy availability, over and indiscriminate use of these drugs outside the hospitals. In contrast, N. gonorrhoeae exhibited low level of resistance to ceftriaxone. This was coherent with reports of other studies elsewhere [19, 24, 28, 29].
In the present study Salmonella spp. showed high levels of resistance (85.7–100%) against amoxicillin and ampicillin. These were consistent with previous studies done in Ethiopia [6, 20, 30] and Madagascar [31]. In the current study, it was found that Shigella spp. revealed high level of resistance to cotrimoxazole (100%). This was in agreement with reports from other studies [6, 31,32,33,34]. This might be due to the indiscriminate drug prescription by clinicians in the study area since culture and susceptibility testing were not employed in the previous years.
In the present study, E. coli was the most frequently isolated bacteria in urinary tract infection and a common isolate in bacteremia. This shows that urosepsis is a major cause of infection. Majority of E. coli resisted the antimicrobials gentamicin and tetracycline. A similar result was documented from other studies [16, 35].
In the case of P. aeruginosa, high level of resistance (87.5%) to gentamicin and considerable level of resistance (57%) to tetracycline were recorded. This was consistent with studies conducted in other parts of Ethiopia [7, 15]. However, the rate of resistance of P. aeruginosa against gentamicin is different from other studies [9, 15, 16]. On the other hand, P. aeruginosa was 100% susceptible to ceftriaxone and norfloxacin. A similar result was documented from other studies [8, 14].
The overall MDR (two and above drugs tested) of the isolates in this study was 76.1% which was coherent with studies conducted in other parts of Ethiopia [3, 14] where 63.3–85% MDR rate was reported. In this study, 85% of Gram positive bacteria (S. aureus, S. pyogenes and S. pneumoniae) demonstrated MDR. This was similar with the 77 and 65.2% MDR rate documented for these bacteria in Ethiopia [23, 35]. However, it was lower than 98.6 and 100% MDR reported in other places of Ethiopia [7, 36]. The possible explanation for such disparity might be difference in type of organism isolated, study population, antimicrobial prescription pattern, study area in terms of laboratory infrastructure, infection prevention practices and up to-date knowledge of clinicians on AMR [3]. About 90% of S. aureus also became MDR of which 12% were resisted to seven drugs tested.
The overall MDR rate of Gram negative bacteria tested for seven types of drugs was 68.5% in this study. This finding is higher than studies conducted in other parts of Ethiopia where 51–59.3% MDR Gram negative bacterial isolates from different types of infections were reported [23, 32]. This might be due to the drugs having been in use for much longer time.
Concerning species specific MDR profiles, Salmonella and Shigella spp. showed MDR, 88 and 60%, respectively. This was consistent with previous studies done in Ethiopia [6, 20, 30, 32, 33] and Madagascar [31]. It was also found that 61.5% of E. coli was MDR. A similar result was documented from other studies [16, 35]. However, Godebu et al. documented 23.3% rate of MDR E. coli in Ethiopia. In the case of P. aeruginosa, 75.9% was MDR. This was consistent with studies conducted in Ethiopia [7, 15] where 100% MDR rate reported. Lastly, 62.5% of gonococci isolates in the present study revealed multidrug-resistance that needs further large scale study on antibiogram of N. gonorrhoeae to control the alarming spread of N. gonorrhoeae and other pathogenic species.
Because of retrospective nature of the study, detail information on patient profiles could not be obtained. For some of the pathogen and antibiotic combination, numbers tested were small and this limits the interpretation of the data. Furthermore, anaerobic bacteria were not isolated due to limited laboratory infrastructure.
Conclusions
This study revealed that S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, Salmonella spp. and N. gonorrhoeae were the most common isolates in clinical samples. Isolates showed high levels of resistance to ampicillin, gentamicin, cotrimoxazole, amoxicillin, penicillin and clindamycin. However, lower levels of resistance were showed for ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone, norfloxacin and chloramphenicol. Majority of Gram positive and Gram negative isolates showed MDR. Therefore, treatment of common bacterial infections in the study area needs to be guided by antibiotic susceptibility testings.
Abbreviations
- AMR:
-
antimicrobial resistance
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- CLBI:
-
Clinical and Laboratory standards Institute
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- DMRH:
-
Debre Markos Referral Hospital
- MDR:
-
multidrug-resistant
References
Roca I, Akova M, Baquero F, Carlet J, Caveleri M, Coenen S. Corrigendum to ‘‘the global threat of antimicrobial resistance: science for intervention’’. New Microbes New Infect. 2015;6:22–9.
Javeed I, Hafeez R, Anwar AS. Patients admitted to a tertiary care hospital in Lahore. Biomedical. 2011;27:19–23.
Abera B, Kibret M, Mulu W. Knowledge and beliefs on antimicrobial resistance among physicians and nurses in hospitals in Amhara Region, Ethiopia. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;15:26.
Tanwar J, Das S, Fatima Z, Hameed S. Multidrug resistance: an emerging crisis. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/541340.
Shahidullah MS, Yusuf MA, Khatun Z, Ara U, Mitul MT. Antibiotic sensitivity pattern of bacterial isolates from different clinical specimens: experience at NICVD, Dhaka. Cardiovasc J. 2012;5:67–72.
Moges F, Endris M, Mulu A, Tessema B, Belyhun Y, Shiferaw Y, et al. The growing challenges of antibacterial drug resistance in Ethiopia. JGAR. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2014.02.004.
Mulu W, Kibru G, Beyene G, Damtie M. Postoperative nosocomial infections and antimicrobial resistance pattern of bacteria isolates among patients admitted at Felege Hiwot Referral Hospital, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2012;22:7–17.
Tenover FC. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Am J Med. 2006;119(1):S3–10.
Kibret M, Abera B. Antimicrobial resistance trend of bacteria from clinical isolates: an 8-year retrospective study at Dessie Regional Laboratory, Northeast Ethiopia. Ethiop Pharm J. 2010;28:39–46.
Cheesbourgh M. District laboratory practice in tropical countries Part II. 2nd ed. NewYork: Cambridge University Press; 2006.
Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by standard single disc method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966;45:493–6.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Seventeenth Information Supplement. CLSI document M100-S17, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Wayne Pennsylvania. 2006.
Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:268–81.
Muluye D, Wondimeneh Y, Ferede G, Nega T, Adane K, Biadgo B, et al. Bacterial isolates and their antibiotic susceptibility patterns among patients with pus and/or wound discharge at Gondar University Hospital. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:619.
Abera B, Kibret M. Bacteriology and antimicrobial susceptibility of Otitis Media at Dessie Regional Health Research Laboratory, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2011;25(2):161–7.
Mama M, Abdissa A, Sewunet T. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of bacterial isolates from wound infection and their sensitivity to alternative topical agents at Jimma University specialized Hospital, South-West Ethiopia. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2014;13:14.
Demilie T, Beyene G, Melaku S, Tsegaye W. Urinary bacterial profile and antibiotic susceptibility pattern among pregnant women in Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2012;22:121–8.
Turhan V, Mutluoglu M, Acar A. Increasing incidence of Gram-negative organisms in bacterial agents isolated from diabetic foot ulcers. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2013;7(10):707–12. doi:10.3855/jidc.2967.
Hailemariam M, Abebe T, Mihret A, Lambiyo T. Prevalence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and their antimicrobial susceptibility patterns among symptomatic women attending gynecology outpatient department in Hawassa Referral Hospital, Hawassa, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2013;23(1):10–4.
Debas G, Kibret M, Biadglegne F, Abera B. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Shigella species at Felege Hiwot Referral Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop Med J. 2011;49(3):249–56.
Xia S, Xu B, Huang L, Zhao J, Ran L, Zhang J, et al. Prevalence and characterization of human Shigella infections in Henan Province, China in 2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;40(1):232–42.
Prakash D, Saxena RS. Distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of bacterial pathogens causing urinary tract infection in urban community of Meerut City, India. ISRN Microbiol. 2013. doi:10.1155/2013/749629.
Godebo G, Kibru G, Tassew H. Multidrug-resistant bacteria isolates in infected wounds at Jimma University specialized Hospital, Ethiopia. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2013;12:17.
Tibebu M, Shibabaw A, Medhin G, Kassu A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae non-susceptible to cephalosporins and quinolones in Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:415.
Florence PA, Otim F, Okongo F, Ogwang M, Greco D. The prevalence and antibiotics susceptibility pattern of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in patients attending OPD clinics at St. Mary’s Hospital Lacor Uganda. J Prev Med Hyg. 2012;53:186–9.
Govender S, Lebani T, Nell R. Antibiotic susceptibility patterns of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in Port Elizabeth. S Afr Med J. 2006;96:225–6.
Bokacin M, Qureshi MI, Dabire S, Fard AHH. An investigation on antibiotic resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from gonorrheal patients in Zahedan, Iran from 2007 to 2010. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2011;5(17):2455–9.
Bhatta DR, Gokhale S, Ansari MT, Tiwari HK, Gaur A, Mathuria JP, Ghosh AN. Gonococcal infections: the trends of antimicrobial susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Western Nepal. NJMS. 2012;1(2):74–8.
Medeiros MI, Silva JO, Carneiro AMM, Recha SHC, Rocha LSD, Silva PD. Antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from Ribecrpreto, Sao Paulo, Brazil. DSP-Jras Doencas Sex Transm. 2013;25(1):31–5.
Aklilu A, Kahase D, Dessalegn M, Tarekegn N, Gebremichael S, Zenebe S. Prevalence of intestinal parasites, Salmonella and Shigella among apparently health food handlers of Addis Ababa University student’s cafeteria, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:17.
Randrianirina F, Ratsima EH, Ramparany L. Antimicrobial resistance of bacterial enteropathogens isolated from stools in Madagascar. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:104.
Abera B, Biadglegne F. Antimicrobial resistance of fecal isolates of Salmonella and Shigella spp. at Bahir Dar regional health research laboratory, northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop Pharm J 2009;27(1). doi:10.4314/epj.v27i1.51119
Yismaw G, Negeri C, Kassu A. A five year antimicrobial resistance pattern observed in Shigella species isolated from stool samples in Gondar University Hospital, northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2006;20(3):194–8.
Mukhtar AM, Saeed HA. Profile of antibiotic sensitivity and resistance of some pathogenic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens in Sudan. J Sci Technol. 2011;12:14–9.
Yishak A, Biruk LW. Microbial susceptibility of bacteria isolated from open fracture wounds presenting to the Black-Lion Hospital, Addis Ababa University. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2009;3:939–51.
Biadglegne F, Abera B, Alem A, Anagaw B. Bacterial isolates from wound infection and their antimicrobial susceptibility pattern in Felege Hiwot Referral Hospital, North West Ethiopia. Ethiop J health Sci. 2009;19:173–7.
Authors’ contributions
WM designed the study, performed the statistical analysis and interpret and wrote the manuscript. HA and DA performed the culture and antimicrobial susceptibility test, collected the data and revised the manuscript. TH and MY, involved in data analysis and interpretation and critically revised the manuscript. BA involved in data analysis and interpretation and critically revised and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We authors grateful to acknowledge, DMRH for giving permission to conduct the study. We would like also to thank Mr. Belachew Mulu, Medical laboratory technician at Debre Markos referral Hospital for his contribution in assisting the data collection process.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The finding of this study is generated from the data collected and analyzed based on the stated methods and materials. All the data are already found in the manuscript and there are no supplementary files. The original data supporting this finding will be available at any time upon request.
Consent for publication
Consent to publish is not applicable for this manuscript because there is no individual data details like images or videos.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the research ethics committee of Debre Markos Referral Hospital. To access the data permission letter was obtained from Debre Markos Referral Hospital. We followed all chains of command to get support letter from legally authorized representatives for data collection. Confidentiality of the result was maintained anonymously and not communicated for other purposes.
Funding
Funding is not applicable for this study because the research project was not funded by any organization.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Mulu, W., Abera, B., Yimer, M. et al. Bacterial agents and antibiotic resistance profiles of infections from different sites that occurred among patients at Debre Markos Referral Hospital, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Res Notes 10, 254 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2584-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2584-y