Abstract
Background and aims
There is a link between genetics with metabolic balance and adiposity homeostasis on metabolic syndrome (MetS). Polymorphism in adipokine genes such as leptin and adiponectin may play an important role in its development. This study aimed to determine the association of the individual and general components of MetS with genetic alterations in LEP (rs7799039 and rs2167270) and ADIPOQ (rs1501299 and rs2241766) genes in the Mexican population.
Methods and results
The polymorphisms of the LEP gene rs7799039 and rs2167270, together with rs1501299 and rs2241766 polymorphisms of the ADIPOQ gene were genotyped using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) on 328 individuals (n = 131 MetS). The rs7799039 under the recessive inheritance model was found to be associated with increased risk of MetS (OR = 2.16, 95% CI = 1.06–4.37), dyslipidemia (OR = 7.97, 95% CI = 2.17–29.36), low HDL (OR = 7.01, 95% CI = 1.65–29.71) and hypertension (OR = 13.02, 95% CI = 1.76–96.44); the heterozygote demonstrate a protective effect on MetS (OR = 0.48, 95% CI = 0.28–0.88) and diabetes (OR = 0.09, 95% CI = 0.02–0.53) under the over the dominant model. Haplotype analysis showed linkage disequilibrium between the SNPs of ADIPOQ rs1501299/rs2241766, and their association as risk factors for low HDL and hypertension.
Conclusion
The association of rs7799039 with the presence of MetS, suggests a risk factor for the development of dyslipidemia, as well as its heterozygous as a protective factor for DM. There is a linkage disequilibrium between the SNPs of ADIPOQ.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) is an increasing public health problem worldwide. It is a cluster of disorders that together lead to progressive disease with five times more vulnerable to developing diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2) and 2.5 times more likely to die from cardiovascular diseases [1, 2]. Among the indicators of MetS are abdominal obesity, atherogenic dyslipidemia, elevated blood pressure, and hyperglycemia [3], considering central obesity as a starting point in most cases [4].
The development of obesity is usually the result of a chronic imbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure [5], however, this does not evaluate the metabolic alterations that regulate energy balance, such as the peptide hormone leptin, secreted primarily from white adipose tissue into the bloodstream to bind its receptors in peripheral tissues, inducing gluconeogenesis in the liver and inhibits the release of insulin from pancreatic β cells; it has been proved that insufficient leptin action leads not only to the development of obesity but also increases insulin resistance [6, 7]. Several single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) found in the LEP (Leptin) gene may be associated with serum leptin concentration related to the pathophysiology of obesity and its complications among specific ethnic groups [8].
Another relevant protein secreted exclusively by adipocytes to regulate metabolic processes is adiponectin (encoded by the ADIPOQ gene) [9]. Adiponectin is recognized as having anti-inflammatory, insulin-sensitizing, and anti-atherogenic properties and plays a critical role in the development of insulin resistance [10]. Numerous SNPs are associated with the pathophysiology of MetS, obesity, and associated complications [2, 11]. The polymorphisms rs1501299 and rs2241766 may act through decreased adiponectin expression, which may in turn cause increased body weight and insulin resistance [10, 11].
The SNPs in this study were chosen on the basis that previous studies have shown varying contrasting associations with MetS and their components [8,9,10, 12]. The conflicting results point to potential inter-ethnic differences in genetic predisposition to the diseases [9]. The highest prevalence of MetS among Hispanic/Latino adults [3], aimed to evaluate the association of the individual and general components of MetS with genetic alterations in LEP (rs7799039 and rs2167270) and ADIPOQ (rs1501299 and rs2241766) genes in Mexican population.
Methods
Study population
A blood sample was taken by venipuncture from 328 fasting individuals submitted to Regional General Hospital #1 and Family Medicine Unit #36, belonging to the Mexican Institute of Social Security (IMSS). MetS group was classified according to the criteria of the Latin American Diabetes Association with its working group Latin American Group for the Study of MetS (ALAD/GLESMO), with an adjustment for the parameters of abdominal diameter for the diagnosis of obesity for the Latin American population suggested by the International Diabetes Federation (waist circumference (WC) men above 94 cm and 88 cm in the case of women); controls were determined to be clinically healthy, with no indicators of MetS. Clinicopathological characteristics such as age, gender, weight, blood pressure, and biochemical parameters were collected through direct questionnaires and serological tests. All patients were approved by signing an informed consent review and approved by the Local Committee for Research and Ethics in Health Research of the IMSS.
Biochemical parameters
Overnight fasting blood samples were collected from each participant to measure serum lipids, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), Low-density lipoprotein (LDL), total cholesterol (TC), fasting blood glucose (FBG) and leptin levels.
Genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leukocyte pellets using the alt precipitation method [13] and diluted to a working concentration of 20 ng/ml for further use and stored at -20°C until use for genotyping. The genotyping of polymorphism LEP G2548A (rs7799039) LEP G19A (rs2167270), ADIPOQ T45G (rs2241766), and ADIPOQ G276T (rs1501299) were performed by polymerase chain reaction-based Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) methods. Amplification of DNA sample was done by using the following flanking primers for LEP: F: 5′- CTCTGGAGGGACATCAAGGA-3’and R: 5′- GCCAAGAAAGACCAGCAGAG-3’ and for ADIPOQ, F: 5′- TCTCTCCATGGCTGACAGTG-3’ and R: 5′- AGATGCAGCAAAGCCAAAGT-3’.
The PCR procedure was performed with 50µL reaction mixture (200ng of template DNA, 20µM of each primer, 0.2MM of dNTPs, 1 U/ml of Taq Polymerase, and 1X PCR buffer, consisting of an initial melting step of 10 min at 94° C followed by 30 cycles of 45 s at 94° C, 45 s at 60° C and final elongation step of 10 min at 72 °C.
PCR products (468 bp for ADIPOQ and 353 bp for LEP) were detected on 1.5% agarose gel stained with gel red; amplified PCR products were digested with 20U of restriction enzymes SmaI (ADIPOQ T45G), BsmI (ADIPOQ 5276T), MspA1I (LEP G19A) and HhaI (LEP G2548A) according to manufacturer instructions (BioLabs, New England). The restriction products were resolved by 7.5% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis against 100 bp ladder as standard at 100 V for 1 h and stained with silver nitrate to visualize the products. For each reaction, a negative control (without a DNA template) was added to monitor PCR contamination. For ADIPOQ, the digestion resulted in fragments of 86 and 382 bp for the G allele (T45G), and 320 bp and 148 bp for the T allele (G27T); the homozygous wild allele and mutant, respectively, remain undigested. In LEP digestion products, the G allele (G19A) resulted in fragments of 59 and 294 bp, also 182 bp and 60 bp for the G allele (G2548A); the homozygous mutant allele, remains undigested in both SNPs.
Statistical analysis
Statistical tests were performed using SPSS 20.0 (IBM corporation, Chicago, IL, USA). The quantitative data were represented as means ± SD and compared by independent sample t-test. Variables without normal distribution were compared through the Mann-Whitney U test.
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) and linkage disequilibrium (LD) for the polymorphisms were calculated with the use of SNPStats software (https://www.snpstats.net/start.htm)(14) and HaploView software. Multiple inheritance models were used to assess statistically significant associations between genotypes and MetS: codominant, dominant, recessive, and over-dominant. The qualitative data were expressed in percentages, which were further analyzed using the Chi-square test. Associations of clinical variables with polymorphisms were evaluated by logistic regression to obtain odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). To account for covariate effects on genotypes and haplotypes, statistics were adjusted for age, sex, and WC. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The anthropometric and clinical parameters of all the participants are presented in Table 1. The 36.6% of the study population were women, 32.5% of them with MetS. Individuals with MetS had higher age, WC, SBP, DBP, FBG, TG, TC, LDL, and leptin levels compared to levels in those without MetS (p < 0.05). Of those with WC above limits (94 cm and 88 cm in the case of women), 61.5% were MetS patients and 38.5% were controlled. 72.8% of patients with FBG > 100 mg/dL were classified with MetS. Of those with a serum TG level of ≥ 150 mg/dL, 82.5% were MetS patients. Low HDL was identified in 62% of MetS and 32% of control groups.
In both MetS and control groups, genotype distribution and allele frequencies for LEP and ADIPOQ polymorphism have been presented in Table 2. The LEP G2548A and G19A polymorphisms were common among the MetS group; allele frequencies were similar between groups. In ADIPOQ T45G and G276T, the normal genotype had a higher frequency. There was no significant difference between the two groups according to genotype and allele frequencies of any SNP. The distribution of genotypes observed in both the control and case samples was in HWE.
However, a significant difference was not observed in the allele frequency analysis, multiple inheritance models were used to assess associations between genotypes and MetS. The LEP G2548A showed statistically significant associations in three inheritance models after adjustments for age, gender, and WC: codominant (p = 0.037), recessive (p = 0.032), and overdominant (p = 0.017). However, in the codominant inheritance model, the A allele did not confer the risk of MetS. The rs2167270, rs2241766, and rs1501299 did not show statistically significant associations with MetS in all the inheritance models (Supplementary Table 1).
In the recessive model (Table 3), the − 2548AA homozygous genotype of LEP carriers had an increased risk for the development of dyslipidemia (OR = 7.97, 95% CI = 2.17–29.36; p = 0.008). The heterozygous shows a protective effect over DM (OR = 0.09, 95% CI = 0.02–0.53; p = 0.085) in the overdominant model.
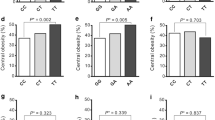
Based on the measures LD, it could be inferred that the two studied SNPs of ADIPOQ (rs2241766 and rs1501299) were in moderate LD (D´0.6741, r2 0.044, p < 0.001) among MetS risk (Fig. 1). The global frequencies of haplotypes with different combinations of polymorphisms (ADIPOQ T45G/G276T) between MetS and control groups are shown in Table 4. Association of the haplotypes with covariates indicates a higher susceptibility to low HDL (OR = 4.37, 95% CI = 1.10-17.33) and hypertension (OR = 8.73, 95% CI = 1.12–67.84) in the carriers of GG haplotype; thus, the GT haplotype consisting of two mutated alleles-45G and − 276T, confer a protective effect towards the obesity (Table 5).
Discussion
The prevalence of MetS varies, greatly depending on the definition used, gender, age, socioeconomic status, and ethnic background [15]. Thus, the present study aimed to estimate the prevalence of the individual and general components of metabolic syndrome, considering sex-related differences, and assess the impact of age, sex, BMI, education level, and physical activity on the likelihood that participants present the metabolic syndrome. Genetic predisposition can have a great impact on the development of this syndrome, a higher prevalence of MetS has been demonstrated among Hispanic/Latino adults [3].
LEP G2548A and G19A polymorphisms are common genetic variants in people with MetS. These polymorphisms are found in the LEP gene, which encodes a protein that controls appetite and weight regulation. The presence of these polymorphisms may contribute to leptin resistance and, therefore, to obesity and metabolic syndrome [8, 16, 17]. Based on the analysis of genotypic frequencies in the Mexican population, the most common genotype for LEP G2548A was the GA genotype in both study groups, which differs from the frequencies reported in other populations [8]. An interesting observation after adjustment for age, sex, and WC is that the G2548A variant was shown to be associated with MetS in three inheritance models (codominant, recessive, and overdominant) reported in this study in the Mexican population. This is in contradiction with the results of the previous study, in which a relationship between this LEP polymorphism and the risk of MetS was determined [8, 16]. Nevertheless, it is consistent with reports from other populations such as Taiwan and Brazil [18, 19]. The − 2548AA homozygous genotype of LEP carriers had an increased risk for the development of dyslipidemia and − 2548GA shows a protective effect on DM, the biological causes of this are unknown, however, it is known that overdominant models occur when individuals heterozygous for a locus show a higher biological efficacy than individuals homozygous for that same locus, where the most severe manifestation for the disease or health status is when a double dose is received, either normal homozygous or mutated homozygous.
On the other hand, the GA genotype of the LEP G19A polymorphism was also frequently observed in both study groups which agrees with the report in the North Indian Punjabi population [20] and differs from the previous report we found in the literature performed in Egyptian population. In this report conducted in 2020, they describe that this polymorphism is highly associated with obesity and theorize that although it is located in a non-coding region, the association is attributed to its critical position in the 5’UTR regulatory region [20].
Because ADIPOQ regulates metabolism and lipid levels, the potential associations between ADIPOQ SNPs and MetS were also investigated. The ADIPOQ gene provides instructions for making a protein called adiponectin, which regulates glucose levels and fatty acid breakdown in the body. T45G and G276T have been associated with various health outcomes, including obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes [21]. Concerning the ADIPOQ T45G and G276T variants in our study, the normal genotype had a higher prevalence among patients in both study groups, and no statistically significant evidence was found that the distribution of genotype frequency was different between the two study groups. This is not to the reports in the Asian population published by Kaur et al., where the most common genotype for the G276T variant was the mutated TT [11]. In the case of the T45G variant, no conclusive information was found on the distribution of genotypes in populations. However, some studies report that the mutated T allele was the most frequent concerning the G allele, which supports our results, where the T allele was the most common in our study populations in both groups [22]. In the ADIPOQ polymorphic variants we are reporting, they were not observed to be associated with MetS, despite adjustment for age, sex, and WC. However, when performing the haplotype analysis, we identified a moderate probability of LD, which is why it was interesting to analyze further detail. The combination in the “ADIPOQ T45G/G276T” haplotype could influence the production, secretion, and function of adiponectin, which in turn could have implications for the risk of developing metabolic syndrome by association with its indicators [23]. In our results, despite differences in the CI for the covariates of hypertension, obesity, and low HDL, such a statistical association was not verified. However, reported ADIPOQ haplotypes that include the T45G and G276T variations, associated with indicators of the MetS, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity, also link their findings with risk factors associated with the disease such as FBG, BMI, and lipid parameters, which suggests its crucial role in susceptibility to metabolic disease [24]. Further research is needed to understand the clinical aspects of genetic variants regulating adiponectin levels in other cohorts.
The frequency distributions of these polymorphisms differ between populations and, therefore, the susceptibility of the individual to the diseases related to these variations. These divergent results could be due to interactions of the polymorphisms with environmental factors, as well as with other polymorphisms present in the LEP and/or ADIPOQ genes, the sample size of a population, or the model used in the statistical analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the present work demonstrated the association of the LEP G2548A variant with the presence of MetS, suggesting a risk factor as part of the development and implications of MetS. Likewise, the homozygous LEP − 2548AA genotype was observed as a risk factor for the development of dyslipidemia, as well as the heterozygous LEP − 2548GA genotype as a protective factor for DM in the Mexican population. Our findings suggest that variants in LEP are of utmost relevance for the understanding of MetS development.
Data Availability
Clinicopathological data presented in this work was the only information available in the hospital database. Raw data supporting our findings were generated at the Universidad Autonoma de Sinaloa and the Universidad Politecnica de Sinaloa. Raw data is available if requested from the corresponding author.
References
Gouveia ÉR, Gouveia BR, Marques A, Peralta M, França C, Lima A, et al. Predictors of metabolic syndrome in adults and older adults from Amazonas, Brazil. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(3):1303.
Wang Q, Ren D, Bi Y, Yuan R, Li D, Wang J, et al. Association and functional study between ADIPOQ and metabolic syndrome in elderly Chinese Han population. Aging. 2020;12(24):25819–27.
Reina SA, Llabre MM, Vidot DC, Isasi CR, Perreira K, Carnethon M, et al. Metabolic syndrome in hispanic youth: results from the Hispanic Community Children’s Health Study/Study of latino youth. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2017;15(8):400–6.
Hopkins JL, Hopkins PN, Brinton EA, Adams TD, Davidson LE, Nanjee MN, et al. Expression of metabolic syndrome in women with severe obesity. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2017;15(6):283–90.
Löffler MC, Betz MJ, Blondin DP, Augustin R, Sharma AK, Tseng YH, et al. Challenges in tackling energy expenditure as obesity therapy: from preclinical models to clinical application. Mol Metab. 2021;51:101237.
D’souza AM, Neumann UH, Glavas MM, Kieffer TJ. The glucoregulatory actions of leptin. Mol Metab. 2017;6(9):1052–65.
Tucholski K, Otto-Buczkowska E. The role of leptin in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. Endokrynol Pol. 2011;62(3):258–62.
Dagdan B, Chuluun-Erdene A, Sengeragchaa O, Malchinkhuu M, Janlav M. Leptin gene G2548A polymorphism among mongolians with metabolic syndrome. Med Sci. 2018;7(1):3.
Truong S, Tran NQ, Ma PT, Hoang CK, Le BH, Dinh T, et al. Association of ADIPOQ single-nucleotide polymorphisms with the two clinical phenotypes type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and metabolic syndrome in a Kinh Vietnamese Population. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022;15:307–19.
Han LY, Wu QH, Jiao ML, Hao YH, Liang LB, Gao LJ, et al. Associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (+ 45T > G, + 276G > T, – 11377 C > G, – 11391G > A) of adiponectin gene and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2011;54(9):2303–14.
Kaur H, Badaruddoza B, Bains V, Kaur A. Genetic association of ADIPOQ gene variants (-3971A > G and + 276G > T) with obesity and metabolic syndrome in north Indian Punjabi population. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(9):e0204502.
Aljanabi M, Alfaqih M, Khanfar M, Amarin Z, Elsalem L, Saadeh R, et al. Leptin and the GA genotype of rs2167270 of the LEP gene increase the risk of prediabetes. Biomed Rep. 2021;14(5):44.
Gustincich S, Manfioletti G, Del Sal G, Schneider C, Carninci P. A fast method for high-quality genomic DNA extraction from whole human blood. Biotechniques. 1991;11(3):298–300.
Solé X, Guinó E, Valls J, Iniesta R, Moreno V. SNPStats: a web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics. 2006;22(15):1928–9.
Wang HH, Lee DK, Liu M, Portincasa P, Wang DQH. Novel insights into the Pathogenesis and management of the metabolic syndrome. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2020;23(3):189.
Boumaiza I, Omezzine A, Rejeb J, Rebhi L, Ouedrani A, Ben Rejeb N, et al. Relationship between leptin G2548A and leptin receptor Q223R gene polymorphisms and obesity and metabolic syndrome risk in Tunisian volunteers. Genet Test Mol Biomark. 2012;16(7):726–33.
Erem C, Hacıhasanoglu A, Deger O, Topbaş M, Hosver I, Ersoz HO, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and associated risk factors among Turkish adults: Trabzon MetS study. Endocrine. 2008;33(1):9–20.
de Oliveira R, Cerda A, Genvigir FDV, Sampaio MF, Armaganijan D, Bernik MMS, et al. Leptin receptor gene polymorphisms are associated with adiposity and metabolic alterations in Brazilian individuals. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2013;57:677–84.
Suriyaprom K, Tungtrongchitr R, Thawnasom K. Measurement of the levels of leptin, BDNF associated with polymorphisms LEP G2548A, LEPR Gln223Arg and BDNF Val66Met in Thai with metabolic syndrome. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014;6(1):6.
Bains V, Kaur H, Badaruddoza B. Association analysis of polymorphisms in LEP (rs7799039 and rs2167270) and LEPR (rs1137101) gene towards the development of type 2 Diabetes in north Indian Punjabi population. Gene. 2020;754:144846.
Tangjittipokin W, Narkdontri T, Teerawattanapong N, Thanatummatis B, Wardati F, Sunsaneevithayakul P, et al. The variants in ADIPOQ are Associated with maternal circulating Adipokine Profile in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023;16:309–19.
Leu HB, Chung CM, Lin SJ, Jong YS, Pan WH, Chen JW. Adiponectin Gene Polymorphism is selectively Associated with the Concomitant Presence of metabolic syndrome and Essential Hypertension. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(5):e19999.
Kyriakou T, Collins LJ, Spencer-Jones NJ, Malcolm C, Wang X, Snieder H, et al. Adiponectin gene ADIPOQ SNP associations with serum adiponectin in two female populations and effects of SNPs on promoter activity. J Hum Genet. 2008;53(8):718–27.
Palit SP, Patel R, Jadeja SD, Rathwa N, Mahajan A, Ramachandran AV, et al. A genetic analysis identifies a haplotype at adiponectin locus: Association with obesity and type 2 Diabetes. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):2904.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge all the healthcare professionals who participated in the study.
Funding
This work was not financially supported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FLO carried out all the experiments, data analyses, FLO, EAM and AMC: wrote the manuscript. FLO, NGM and MIA: carried out statistics analysis and supported the analysis and interpretation of the data. EAM and NGM: revised the manuscript. All authors participated in the writing of the manuscript and approved the final version and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patients were approved by signing an informed consent review and approved by the Local Committee for Research and Ethics in Health Research of the IMSS.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ortega, F.L., Camberos, A.M., Arredondo, M.I. et al. LEP (G2548A-G19A) and ADIPOQ (T45G-G276T) gene polymorphisms are associated with markers for metabolic syndrome. Diabetol Metab Syndr 15, 237 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-023-01215-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-023-01215-6