Abstract
Background
The American Diabetes Association proposed two subcategories for type 1 diabetes mellitus: type 1A or immune-mediated diabetes (IDM) and type 1B or idiopathic diabetes. The absence of β-cell autoimmune markers, permanent insulinopenia and prone to ketoacidosis define the second category, whose pathogenesis remains unclear. Only a minority of patients fall into this category, also designated non-immune-mediated (NIDM), which is considered by several authors similar to type 2 diabetes. The aim of this study is to evaluate differences at the diagnosis and 10 years later of two categories.
Methods
Retrospective cohort study of patients with β-cell autoimmune markers performed at diagnosis and undetectable c-peptide. Were excluded patients with suspicion of another specific type of diabetes. We obtained two groups: IDM (≥ 1 positive antibody) and NIDM (negative antibodies). Age, family history, anthropometry, duration of symptoms, clinical presentation, blood glucose at admission, A1C, lipid profile, arterial hypertension, total diary insulin dose (TDID), microvascular and macrovascular complications were evaluated. Results were considered statistically significant with p < 0.05.
Results
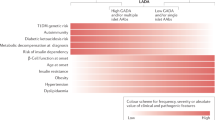
37 patients, 29 with IDM and 8 patients with NIDM. The age of diagnosis of IDM group (23 years) was significantly different (p = 0.004) from the NIDM group (38.1). The body mass index (BMI) at the diagnosis did not differ significantly (p = 0.435). The duration of symptoms was longer in the NIDM (p = 0.003). The disease presentation (p = 0.744), blood glucose (p = 0.482) and HbA1c (p = 0.794) at admission and TDID at discharge (p = 0.301) did not differ significantly. Total and LDL cholesterol levels were higher in NIDM group but did not differ significantly (p = 0.585 and p = 0.579, respectively). After 10 years BMI did not differ between groups (p = 0.079). Patients with IDM showed a significantly higher HbA1c (p = 0.008) and TDID (p = 0.017). Relative to the lipid profile, there was no significant difference, however the LDL cholesterol and triglycerides were higher on the NIDM group, as the percentage of hypertension. Microvascular complications were higher in the IDM group, but no significant difference was found.
Conclusion
Patients with IDM had a poor metabolic control and higher insulin requirement. Patients with NIDM were older and showed higher cardiovascular risk, resembling a clinical phenotype of type 2 diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In 1997, the American Diabetes Association proposed two subcategories for type 1 diabetes mellitus: type 1A or immune-mediated diabetes and type 1B or idiopathic diabetes [1, 2].
The immune-mediated diabetes (IDM) results from a cellular autoimmune destruction of the β-cells of the pancreas, mediated by T-cells [3, 4]. Markers of the immune destruction of the β-cell include islet cell autoantibodies, insulin autoantibodies, GAD (GAD65) autoantibodies and tyrosine phosphatase (IA2) autoantibodies. There is little or no insulin secretion, manifested by low or undetectable levels of plasma C-peptide [4], and exogenous insulin is necessary to preserve life. Insulin resistance does not play a major role in its pathogenesis [3]. The disease has strong HLA (human leukocyte antigen) haplotypes associations, with linkage to the DQA and DQB genes. The IDM commonly occurs in childhood and adolescence, but it can occur at any age and patients are rarely obese at the diagnosis [4].
The idiopathic diabetes is characterized by absence of β-cell autoimmune markers, with permanent insulinopenia and prone to ketoacidosis [1, 2, 4]. The authors of this paper evoked this type of diabetes by non-immune-mediated diabetes mellitus (NIDM).
Only a minority of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus fall into this subcategory, however it is being recognized as an important clinical entity [5].
NIDM has been mostly described in African-American and Asian patients, even though it has also been described in native Americans and in European Mediterranean individuals [1,2,3].
Although patients with NIDM have generally an onset similar to that of patients with IDM, some differences are frequently found.
NIDM is characterized by acute onset of severe hyperglycemia with ketoacidosis, requiring hospital admission and treatment with insulin and fluid and electrolyte replacement [5]. Insulin therapy is generally necessary for a period going from 6 to 18 months, with subsequent good control of disease just with oral agents and diet [2]. Recurrent ketoacidosis is unusual [5].
NIDM shows a different phenotype, are more often male, middle aged, overweight, or modestly obese (obesity class I). They have a family history of type 2 diabetes [2, 3, 5, 6]. Due to the presence of some metabolic features of type 2 diabetes, the NIDM has also been referred in the literature as atypical diabetes, type 1.5 diabetes, Flatbush diabetes and ketosis-prone diabetes [5, 7,8,9].
Its pathogenesis is unknown, and the information about this is scare, but is likely related to insulin resistance and transient β-cell dysfunction, perhaps due to glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity mechanisms [2, 3, 10]. HLA-related genes are not believed to be involved in its pathogenesis, even though mutations in different genes from HLA have been reported, suggesting that NIDM may have a specific genetic background.
Recently, at the Classification of diabetes mellitus 2019 of the World Health Organization, the NIDM was reclassified as ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes [11].
Methods
This study was approved by the local ethics review boards (Coimbra Hospital and University Center). All Patients signed an informed consent for the scientific use of their data.
Retrospective cohort study, from January 2003 to December 2008, based on clinical records of patients with low C-peptide (< 0.5 ng/mL) and in which diabetes mellitus-related autoimmune markers (anti GAD-65, anti-islets, anti-insulin, anti IA2) were measured. Only patients whose assays were performed at the time of diagnosis of diabetes mellitus were considered to ensure the inclusion of patients with type 1 DM. Of these, we obtained two groups: one with positive autoimmunity—IDM group (≥ 1 positive antibody) and another with negative autoimmunity—NIDM group. Differences between groups at diagnosis were evaluated with regard to age of diagnosis, family history, anthropometry, duration of symptoms, clinical presentation of disease, plasma glucose at hospital admission, HbA1c, lipid profile, arterial hypertension and total daily insulin dose (TDID).
The authors also analyzed differences between the groups at long term follow-up-ten years—with regard to anthropometry, HbA1c, lipid profile, arterial hypertension, TDID, microvascular and macrovascular complications.
C-peptide measurement was performed after correction of ketosis or ketoacidosis and stabilization of plasma glucose levels. The lipid profile was obtained in the first medical evaluation after discharge.
In this study, all patients included were treated with conventional basal-bolus therapy.
All patients were Caucasian.
Categorical variables are presented as frequencies and percentages, and continuous variables as means and standard deviations, or medians and interquartile ranges for variables with skewed distributions. Normal distribution was checked using skewness and kurtosis. All reported p values are two-tailed, with a p value of 0.05 indicating statistical significance.
The differences between groups were detected by the Student’s t test for continuous variables with normal distribution, by the Mann–Whitney test and Wilcoxon test for continuous variables without normal distribution and by the χ2 test for categorical variables.
Analyses were performed with the use of SPSS v.25.
Results
Differences at diagnosis
At diagnosis, 29 patients (78.4%) had positive autoimmune markers and 8 had negative autoimmune markers. In the group with positive autoimmunity, 15 patients were female (48.3%), while in the group with negative autoimmunity they were all male.
In the IDM group, the median age of patients at diagnosis was 23.0 (9) years, and in the NIDM group the mean age at diagnosis was 38.1 ± 12.8 years, with a statistically significant difference (p = 0.004).
BMI at diagnosis did not differ significantly (p = 0.435) between the two groups (20.97 kg/m2 in IDM vs 20.37 kg/m2 in NIDM). There was no statistically significant association between groups and family history of type 1 DM (p = 0.999) or type 2 DM (p = 0.999).
Symptoms duration in both patient groups was statistically different (p = 0.003), with a duration of 21.8 ± 8.8 days in the IDM group vs 45.0 (60) days in the NIDM group, but there was no statistically significant association between the groups and the clinical presentation of the disease (p = 0.744).
Plasma glucose at hospital admission was not statistically different (25.47 mmol/L in the IDM group vs 23.92 mmol/L in the NIDM group) (p = 0.482), such as HbA1c at diagnosis (11.3% vs 11.8%, respectively) (p = 0.794).
With regard to lipid profile, total-cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C and triglycerides levels, they did not differ significantly between the two groups (p = 0.585, p = 0.579, p = 0.833 and p = 0.555, respectively), although total-cholesterol and LDL-C levels were higher in the NIDM group. The percentage of patients with dyslipidemia was higher in the NIDM group (25% vs 24.1%), however the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.999). With regard to arterial hypertension, there was no significant difference between the groups (p = 0.999).
The TDID at discharge was not statistically different (46.4 units vs. 40.1 units) (p = 0.301) (Table 1).
Differences at 10 years of follow-up
At ten years evaluation, BMI was not statistically different (p = 0.079) between the two groups (25.14 kg/m2 in IDM group vs 22.58 kg/m2 in NIDM).
Relative to HbA1c there was statistically significant difference between the groups (p = 0.008), with 8.7% for IDM group and 7.4% for NIDM group.
The insulin requirement was also statistically different. The TDID of the IDM group was 52.35 units and the NIDM group was 33.5 units (p = 0.017).
The percentage of patients with dyslipidemia was higher in the NIDM group (62.5% vs 44.8%), however the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.999).
With regard to lipid profile, total-cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C and triglycerides levels there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.728, p = 0.571, p = 0.338, p = 0.648, respectively), however the LDL-C and triglycerides levels were higher in the NIDM group.
The percentage of patients with hypertension was higher in the NIDM group (25% vs 17.2%), although there was no significant difference between the groups (p = 0.999).
With regard to microvascular complications, there was no statistically significant difference at the percentage of retinopathy, neuropathy and nephropathy between the two groups (p = 0.550, p = 0.550, p = 0.550, respectively) but the percentage was higher in the IDM group. At 10 years follow-up, the NIDM group had not microvascular complications.
There was no significant difference on the macrovascular disease too (Table 2).
Discussion and conclusions
Our study suggests that the NIDM may be detected among subjects of Caucasian ethnicity and in spite of initial clinical presentation compatible with IDM, they differ at diagnosis in terms of autoimmune markers, sex, age of patients and symptoms duration.
All patients in the NIDM group included in our study were men, reporting a male predominance consistent with other studies [1,2,3, 12] So far, the cause of this male predominance is unknown, however it is thought that hormonal factors may be involved.
In the IDM group, the median age of patients at diagnosis was higher, in agreement with other studies [1, 7, 13].
Symptoms duration in both patient groups was statistically different, with a longer duration in the NIDM group, unlike other studies, in which there were no differences between the two groups [1].
BMI at diagnosis did not differ significantly between the two groups. In most previous studies, patients in the NIDM group have a higher BMI with visceral obesity, resembling patients with type 2 diabetes [1, 2].
There was no statistically significant association in the clinical presentation of the disease, as in previous studies [3, 7, 12], making sometimes difficult to differentiate it with the IDM group.
HbA1c at diagnosis and the TDID at discharge were not statistically different between the two groups, which is in agreement with other works [1, 2]. Total-cholesterol and LDL-C levels were higher in the NIDM group, as previously reported in other studies, where patients from this group have a more atherogenic lipid profile, as patients with type 2 diabetes [2].
At a long-term evaluation, our study shows that patients with IDM had a poor metabolic control, with higher HbA1c and higher insulin requirement, consistent with previous studies [2]. On the other hand, in the NIDM group there was a higher HbA1c reduction with lower insulin requirement.
In fact, other studies reported a severe insulin secretory deficiency only during the acute ketotic phase in patients with NIDM with a clinical remission phase correlated to an insulin secretion recovery [2].
Patients with NIDM showed a lower tendency to microvascular complications, like type 2 diabetes. Microvascular complications were more frequent in the IDM group.
Patients with NIDM showed, as at the diagnosis, a typical atherogenic lipid profile, characterized at 10 years by high LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides levels. This group also showed a higher proportion of arterial hypertension patients. So, the authors concluded that NIDM is associated with higher cardiovascular risk than IDM since the diagnosis.
There are some limitations of this study, that should be mentioned, such as the sample size that was conditioned by the retrospective nature of the study. The authors were limited to patients whose assays were made at diagnosis to avoid misdiagnosis.
In conclusion, recognition of the NIDM category is critical in clinical practice because it may modify the therapeutic approach of these patients, in the mid and long term. This entity was initially diagnosed in Asian and African American populations, however, individuals from other ethnic groups, namely Caucasian, have been increasingly identified. The initial clinical presentation is similar to the IDM group, requiring intensive initial insulin therapy and fluid and electrolyte replacement. However, behind the glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity phase, there is functional recovery of the β cell after several weeks, which allows in most patients an approach with diet alone or diet plus oral medications.
The pathophysiological mechanisms leading to the acute onset of severe hyperglycemia, with or without ketosis and ketoacidosis in susceptible patients are unknown; hence further investigation in this area is needed.
The recognition of NIDM patients is also crucial because they are exposed to a higher cardiovascular risk needing adequated treatment to reduce the long-term cardiovascular complications.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- NIDM:
-
Non-immune-mediated diabetes mellitus
- IDM:
-
Immune-mediated diabetes mellitus
- TDID:
-
Total daily insulin dose
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- GAD:
-
Glutamic acid decarboxylase
References
Aguilera E, Casamitjana R, Ercilla G, et al. Adult-onset atypical (type 1) diabetes: additional insights and differences with type 1A diabetes in a European Mediterranean population. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1108–14.
Guarnotta V, Vigneri E, Pillitteri G, et al. Higher cardiometabolic risk in idiopathic versus autoimmune type 1 diabetes: a retrospective analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2018;10:40.
Piñero-Piloña A, Avilés-Santa L, Lintonjua P, et al. Idiopathic type 1 diabetes in Dallas, Texas. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1014–8.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:S64–71.
Lebovitz HE, Banerjy MA. Ketosis—prone diabetes (Flatbush Diabetes): an emerging world wide clinically important entity. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18:1–8.
Winer WE, Maclaren N, Riley W, Clarke DW, Kappy MS, et al. Maturity on-set diabetes of youth in black Americans. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:285–91.
Umpierrez GE. Ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes: time to revise the classification. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2755–7.
Juneja R, Palmer JP. Type 1 1/2 diabetes: myth or reality? Autoimmunity. 1999;29:65–83.
Palmer JP, Hampe CS, Chiu H, Goel A, Brooks-Worrell BM. Is latent autoimmune diabetes in adults distinct from type 1 diabetes or just type 1 diabetes at an older age? Diabetes. 2005;54(2):S62–7.
Umpierrez GE, Casals MMC, Gebhart SSP, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis in obese African-Americans. Diabetes. 1995;44:790–5.
World Health Organization. Classification of diabetes mellitus. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
Mauvais-Jarvis F, Sobngwi E, Porcher R, et al. Ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes in patients of Sub-Saharan African origin: clinical pathophysiology and natural history of beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2004;53(3):645–53.
Gupta R, Ramachandran R, Gangadhara P, et al. Clinical characteristics, beta-cell dysfunction and treatment outcomes in patients with A-ß + ketosis-Prone Diabetes (KPD): the first identified cohort amongst Asian Indians. J Diabetes Complicat. 2017;31:1401–7.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DC and DS has produced the report and literature review. CR, JG and LR assisted in the production of the article and the literature review. IP and LC oversaw the creation of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the local ethics review boards (Coimbra Hospital and University) and all participants signed the consent to use their data for scientific purpose.
Consent for publication
It was obtained from all the participants included.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Catarino, D., Silva, D., Guiomar, J. et al. Non-immune-mediated versus immune-mediated type 1 diabetes: diagnosis and long-term differences—retrospective analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr 12, 56 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-020-00563-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-020-00563-x