Abstract
Background
Corticosteroids are widely used in medicine. Few cases of central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) have been reported following topical corticosteroid administration. We describe the first case of pediatric CSC related to topical corticosteroid administration.
Case presentation
A 14-year-old boy presented with decreased vision, pigment epithelial detachments, and serous retinal detachments in the right eye after starting treatment for atopic dermatitis with Betamethasone Valerate 0.1% topical ointment. His condition resolved 2 weeks after discontinuing the steroid and administering Bromfenac 0.9 mg/ml eyedrops.
Conclusions
Although the pathogenesis of CSC is poorly understood, ophthalmologists should be informed about the potential link between CSC and topical corticosteroid treatment, and they should be aware that CSC might, albeit infrequently, affect children.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) is an ocular disease that causes an idiopathic serous detachment of the retina and a fluid leakage from the choroid through a defect in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) outer blood-retina barrier [1]. CSC is a common cause of visual impairment in the working-age population and has been estimated as the fourth most frequent non-surgical retinopathy after age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusion [2]. Patients often experience loss of central vision, central scotoma, micropsia or metamorphopsia. Visual acuity may only be moderately decreased, and there may be a hyperopic shift [2]. Although many cases resolve spontaneously with minimal sequelae, 30-45% of patients have recurrence and a poorer visual prognosis [3]. CSC typically affects men aged 25 to 50 years, but it may occur in women or older individuals [3]. Although the pathogenesis remains unknown, risk factors include type A personality, Cushing disease, pregnancy, and corticosteroid use [1]. Actually, there are only five reported pediatric CSC cases [4,5,6,7,8]. To the best of our knowledge, we report the first pediatric CSC case associated with topical corticosteroid use.
Case presentation
A 14-year-old boy presented with a 2-week history of decreased visual acuity in the right eye.
The boy suffered from atopic dermatitis (AD) with facial and scalp involvement and had been treated by a dermatologist since he was 5 years old. The disease had been well controlled for several years by skin hydration with soaking baths and use of topical ointments.
However, skin lesions had worsened in the past 2 years and the patient was prescribed Betamethasone Valerate 0.1% topical ointment 3 times a day. Although the patient was instructed to stop the therapy after 5 weeks, he continued using the ointment 3 times a day for about 6 months, after noticing significant improvement.
He presented at our attention complaining decreased visual acuity in the right eye. On ocular examination, his best corrected visual acuity measured 20/25 in his right eye and 20/20 in his left eye. Intraocular pressure was normal and anterior segment examination in each eye was unremarkable. Posterior segment examination of the right eye showed a large serous retinal detachment involving the posterior pole. Posterior segment examination of the left eye was normal.
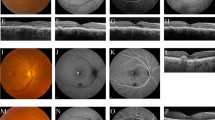
Therefore, we decided to perform a macular optical coherence tomography (OCT) examination (Spectralis HRA; Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany). OCT examination in the right eye (Fig. 1) revealed the presence of a detachment of the neurosensory retina in macular region, associated with elongated photoreceptor segments and irregular RPE. Multiple associated pigment epithelial detachments were located inferonasally and inferotemporally to the fovea. In the left eye OCT examination showed normal finds.
Right eye, Baseline. Infrared funduscopic image (left) and macular OCT B-scan (right). Presence of subretinal fluid causing a circumscribed area of serous retinal detachment in the macular region (white arrow), associated with elongated photoreceptor segments and irregular retinal pigment epithelium layer
Lastly, the blood pressure values were within normal ranges and the patient claimed to have a peaceful mind.
Structural retinal findings associated to clinical signs and history addressed the diagnosis to the CSC, probably linked to the persistent topical steroid treatment.
We decided to treat the patients with Bromfenac 0.9 mg/ml eye drops 3 times a day and to discontinue Betamethasone Valerate ointment. The therapy was well-tolerated by the patient and no side effects were reported.
At 2 weeks follow-up, OCT examination showed a complete resolution of neuroepithelium detachment (Fig. 2), associated to a restoration of normal visual acuity.
Discussion and conclusions
This atypical case of CSC in a pediatric patient resolved promptly on cessation of the topical steroid and administration of Bromfenac eye drops.
The pathophysiology of CSC is poorly understood. Guyer and colleagues suggested that the pathogenesis of CSC may be choroidal vascular hyperpermeability. They noted diffuse hyperpermeability around active leakage sites seen with indocyanine green videoangiography (ICG-V) but not with fluorescein angiography (FA). Therefore, they concluded that hyperpermeability was at the level of the choroid rather than the RPE [9]. An alternative theory suggests that CSC results from dysfunction of the RPE which causes a reverse in fluid movement in a chorioretinal direction [10].
CSC induced by the systemic use of steroids was first reported in 1984 in two patients that developed serous macular detachment upon initiation of systemic Betamethasone therapy for retrobulbar neuritis [11]. However, the best evidence for an association between corticosteroid use and CSC comes from two large, retrospective case-control studies [12, 13]. Tittl and colleagues conducted the first of these, studying systemic factors associated with CSC [12]. This study included a total of 230 CSC cases and 230 age and sex-matched controls. They found that 21 CSC subjects were using corticosteroid medications, whereas 7 control subjects were using corticosteroids. This difference yielded an odds ratio of 3.2 (95% CI 1.3 to 7.70, P = 0.0063). Carvalho-Recchia et al. published the first report of a consecutive series of patients with acute CSC studied prospectively for an association with corticosteroids [13]. They found a statistically significant difference in corticosteroid exposure between study patients and controls.
The mainstay of Atopic Dermatitis treatment is represented by topical corticosteroids, while several routes of steroid administration have been discussed in the literature. These medications reduce inflammation and pruritus primarily by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of various proinflammatory genes. Topical corticosteroids are available in a wide range of potencies, from the least potent Group 1 preparations (e.g. Hydrocortisone 1% ointment), to the most potent Group 7 preparations (e.g. Clobetasol Propionate 0.05% ointment). The greater the potency of topical corticosteroid used, the greater the risk of systemic and local side effects [14]. Betamethasone Valerate 0.1% is in group 3 (high potency topical corticosteroids).
Despite that, it was suggested that steroid-induced CSC may be related to an idiosyncratic response in selected vulnerable individuals rather than to a dose-dependent effect, since very low doses can induce CSC episodes [15].
CSC has been associated with topical steroid use in several case reports. In 2004, Karadimas and colleagues reported two cases of presumed topical steroid-associated CSC [16]. Fernandez and colleagues reported a suspected case of topical steroid-associated CSC, in which a 43-year-old female developed CSC after 1 month of topical steroid use for lichen planus [17]. Ezra and colleagues also reported a case of a 25-year-old male with psoriasis and 15 years of topical steroid use. He experienced a single episode of CSC with resolution upon steroid cessation [18].
While CSC has previously been linked to systemic corticosteroid use, it is rarely linked to topical administration.
Idiopathic CSC in children has been reported in a few case reports [5,6,7,8], however this condition has never been linked to topical corticosteroid therapy in young patients.
In light of this, we assume that this may be the first pediatric case of CSC related to transdermal steroid treatment.
Poor imaging is a limitation of this case report, because CSC diagnosis is typically based on a serous retinal detachment described on OCT examination and confirmed by FA, which reveals early-phase localized dye leakage and late-phase dye pooling under the sensory retina. However, we chose not to perform FA on our young patient because OCT scans clearly revealed the diagnosis.
In conclusion, it should be kept in mind that CSC can affect children as well as adults, and this case outlines the importance for ophthalmologists to carefully assess CSC patients for local and systemic corticosteroid use.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Atopic dermatitis
- CSC:
-
Central serous chorioretinopathy
- FA:
-
Fluorescein angiography
- ICG-V:
-
Indocyanine green videoangiography
- OCT:
-
Optical coherence tomography
- RPE:
-
Retinal pigment epithelium
References
Mudvari SS, Goff MJ, Fu AD, McDonald HR, Johnson RN, Ai E, et al. The natural history of pigment epithelial detachment associated with central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina. 2007;27:1168–73.
Wang M, Munch IC, Hasler PW, Prünte C, Larsen M. Central serous chorioretinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008;86:126–45.
Gilbert CM, Owens SL, Smith PD, Fine SL. Long-term follow-up of central serous chorioretinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984;68:815–20.
Fine SL, Owens SL. Central serous retinopathy in a 7-year-old girl. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980;90:871–3.
Velazquez-Martin JP, Fulda E, Domville D, Graue-Wiechers F, Krema H. Presumed idiopathic central serous chorioretinopathy in a 12-year-old girl. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2012;3:5–10.
Kim YC, Kim SD, Kim KS. A case of idiopathic central serous chorioretinopathy in a 12-year-old male treated with bevacizumab. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2012;26:391–3.
Katta M, Kwok T. Bilateral idiopathic central serous Chorioretinopathy in a twelve year old girl. Ann Clin Case Rep. 2018;3:1508.
Abdullah OO. Presumed idiopathic central serous Chorioretinopathy in 9 years old boy. Health Sci J. 2020;4:732.
Guyer DR, Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS, Sorenson JA, Allen H, Orlock D. Digital indocyanine green videoangiography of central serous chorioretinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994;112:1057–62.
Ciardella AP, Guyer DR, Spitznas M. Central serous chorioretinopathy. In: Retina, vol. 2. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: The C. V. Mosby Co; 2001. p. 1153–81.
Wakakura MA, Ishikawa SA. Central serous chorioretinopathy complicating systemic corticosteroid treatment. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984;68:329–31.
Tittl MK, Spaide RF, Wong D, et al. Systemic findings associated with central serous chorioretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999;128:63–8.
Carvalho-Recchia C, Yannuzzi L, Negrao S, et al. Corticosteroids and central serous chorioretinopathy. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:1834–7.
Lyons JJ, Milner JD, Stone KD. Atopic dermatitis in children: clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am. 2015;35:161–83.
Daruich A, Matet A, Dirani A, et al. Central serous chorioretinopathy: recent findings and new physiopathology hypothesis. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015;48:82–118.
Karadimas P, Kapetanios A, Bouzas EA. Central serous chorioretinopathy after local application of glucocorticoids for skin disorders. Arch Ophthalmology. 2004;122:784–6.
Fernandez CF, Mendoza AJ, Arevalo JF. Central serous chorioretinopathy associated with topical dermal corticosteroids. Retina. 2004;24:471–4.
Ezra N, Taban M, Behroozan D. Central serous chorioretinopathy associated with topical corticosteroids in a patient with psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:918–21.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This manuscript was supported by University of Insubria Funds for research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR and ER collected data; SR, LF and ER drafted the work; PN and SD substantively revised it; PN, SD and PR supervised the redaction and the discussion of the clinical case. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors agreed both to be personally accountable for the author’s own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods were performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Written informed consent to discuss and publish this case was obtained from the parents of the patient.
Authors confirm they have obtained ethical approval and consent for this case report.
This case report has been granted an exemption from requiring ethics approval from the Ethics Committee of Insubria University, Varese.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of clinical details and clinical images was obtained from the parents of the patient. A copy of the consent form is available for review by the Editor of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ranno, S., Fontanel, L., Ruggiero, E. et al. Central Serous Chorioretinopathy in a 14-year-old atopic boy: a case report. Ital J Pediatr 49, 1 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-022-01386-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-022-01386-4