Abstract
Backgrounds
The t(8;22)(q24.13;q11.2) has been identified as one of several recurrent constitutional translocations mediated by palindromic AT-rich repeats (PATRRs). Although the breakage on 22q11 utilizes the same PATRR as that of the more prevalent constitutional t(11;22)(q23;q11.2), the breakpoint region on 8q24 has not been elucidated in detail since the analysis of palindromic sequence is technically challenging.
Results
In this study, the entire 8q24 breakpoint region has been resolved by next generation sequencing. Eight polymorphic alleles were identified and compared with the junction sequences of previous and two recently identified t(8;22) cases . All of the breakpoints were found to be within the PATRRs on chromosomes 8 and 22 (PATRR8 and PATRR22), but the locations were different among cases at the level of nucleotide resolution. The translocations were always found to arise on symmetric PATRR8 alleles with breakpoints at the center of symmetry. The translocation junction is often accompanied by symmetric deletions at the center of both PATRRs. Rejoining occurs with minimal homology between the translocation partners. Remarkably, comparison of der (8) to der(22) sequences shows identical breakpoint junctions between them, which likely represent products of two independent events on the basis of a classical model.
Conclusions
Our data suggest the hypothesis that interactions between the two PATRRs prior to the translocation event might trigger illegitimate recombination resulting in the recurrent palindrome-mediated translocation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The constitutional t(8;22)(q24.13;q11.2) is recognized as a one of several recurrent translocations in humans [1]. The most prevalent recurrent constitutional translocation is the t(11;22)(q23;q11) [2]. Although t(11;22) balanced-translocation carriers are phenotypically normal, they often manifest problems with reproduction such as infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, or the birth of unbalanced offspring with the supernumerary der(22)t(11;22) syndrome (Emanuel syndrome [MIM 609029]) [3]. Among the small supernumerary marker chromosomes seen clinically, +der(22)t(11;22) is the most frequent, while + der(22)t(8;22) is the second most prevalent [4]. Similar to the t(11;22), balanced carriers of the t(8;22) are often identified after the birth of an unbalanced offspring with the supernumerary der(22) t(8;22), the phenotype of which includes extremity anomalies, mild dysmorphism and intellectual disability.
The mechanism that leads to the constitutional t(11;22)(q23;q11) has been extensively studied. The breakpoints of both chromosomes are consistently located within palindromic AT-rich repeats (PATRRs) [5]-[9]. Palindromic regions, i.e. inverted repeats, have a potential for the formation of hairpin/cruciform structures by intrastrand annealing and palindrome induced genomic instability has been demonstrated in many experimental model organisms [10]-[12]. In humans, a considerable number of de novo t(11;22)s arise during spermatogenesis, but de novo occurrences have not been detected in tissues other than sperm [13]. It has been proposed that the secondary structure of the palindromic DNA during spermatogenesis induces genomic instability leading to the recurrent chromosomal translocation [14],[15]. Taking advantage of breakpoint co-localization on 22q11, the translocation junction fragments of the t(8;22) have been isolated, the breakpoints on 8q24 were assessed, and a similar mechanism of translocation was suggested [1],[16]. Although PATRR-like sequence (PATRR8) was compiled from the junction sequences, detailed analysis of the breakpoint region have not been performed since the analysis of the palindromic region is technically challenging [17]. Further, since the database of human reference sequence does not include the complete sequence of PATRR8, details of the t(8;22) translocation mechanism are incomplete.
In this study, we first obtained the complete sequence of several polymorphic PATRR8 alleles from normal individuals using next generation sequencing. Using translocation-specific PCR, we also determined the translocation junctions in two unrelated Japanese families with the t(8;22)(q24.13;q11.2). We performed an investigation to examine the breakpoint within PATRR8 and PATRR22 by comparing the junction sequences with the normal PATRR8 and PATRR22. These data further confirm that the t(8;22) translocation is a recurrent rearrangement with a mechanism consistent with that proposed for the t(11;22) and the t(8;22) in previous studies. These findings provide additional support for the role of palindromic sequences in genomic instability. Further, our new finding, the similarity of the der(8) and the der(22) sequences, might elicit a new feature of palindrome-mediated translocations.
Results
Genomic structure of the PATRR8
Based on the putative PATRR8 sequences compiled by analysis of translocation junctions, the majority of PATRR8 is deleted and only a portion of the proximal arm appears in the human genome database [1]. To determine the complete sequence of PATRR8, we first attempted conventional PCR followed by standard Sanger sequencing. The sizes of the PCR products that include PATRR8 vary among individuals. We previously classified them into four categories: long (L), medium (M), short (S) and super-short (SS) [1]. The M and S alleles were the major alleles, while L and SS alleles were less frequent. Despite the fact that we could generate the complete sequence of the SS allele, their AT-rich and palindromic nature prevented us from sequencing the central region of the PATRR in other allele types [17].
Next, we attempted to sequence the PCR product by massively parallel sequencing using a next generation sequencer. Although the central region was under-represented (~50 reads out of ~30,000 reads per PCR product), we finally obtained the sequence of the entire PATRR8 in 11 out of 24 PCR products. Indeed, the sequence data obtained by next generation sequencing demonstrated that size polymorphisms of the PCR products result from size polymorphisms of PATRR8 itself as well as size variation in the flanking AT-rich repeat region (Figure 1A, Additional file 1: Figure S1).
The M allele (~350 bp), one of the most frequent variants, manifests a nearly perfect palindrome (Table 1). AT-richness is as high as 98%. Identity between the proximal and distal arms is >98%, showing a nearly perfect palindromic structure. Subtle nucleotide alterations produce three subtypes, M1, M2 and M3 (Figure 1B). The S allele (~310 bp), the other most frequent variant, also manifests a high AT-content (97%) and a perfect palindrome (identity 100%). The L allele (423 bp) and the SS allele (98 bp) are less frequent. The SS allele appears to be an asymmetrically deleted version of the S allele, whereas the L allele appears to have an asymmetric insertion of AT-rich sequence of unknown origin. The PATRR8 sequence appearing in the human genome database was not found to be a subtype of PATRR8 polymorphism. The deletion in the database carries a 16 bp homology at the junction (Additional file 1: Figure S1), suggesting that the sequence is an artifact generated during bacterial culture for clone preparation for sequencing.
Unlike other translocation-related PATRRs, PATRR8 has another AT-rich flanking region both at its proximal and distal side. Both of these AT-rich regions manifest size polymorphisms. The proximal flanking region carries a 35 bp direct repeat, whose copy number is increased in M alleles (Additional file 1: Figure S1). The distal region also carries a similar 28 bp direct repeat, copy number variation of which produces size polymorphism. Since we could not distinguish between M and S alleles simply by gel electrophoresis due to these size polymorphisms in the flanking regions, we could not determine the exact frequency of polymorphic PATRR8 alleles in the general population.
Analysis of the breakpoints of the der(8) and der(22)
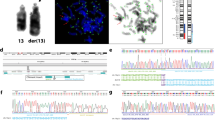
Using primers flanking PATRR8 and PATRR22 (Figure 2A), genomic DNAs from all of the t(8;22) cases yielded translocation specific PCR products (Figure 2B). Approximately 850 bp of the der(8) and 650 bp of the der(22) harboring the translocation junction were amplified by PCR from balanced translocation carriers in family 1 (FHU13-033) and family 2 (FHU13-027) as well as from the unrelated balanced translocation carriers published previously [1]. Only the der(22) PCR product was amplified from the proband in family 1 (FHU13-031) with the typical supernumerary der(22)t(8;22). Now that we have the complete sequence of PATRR8, we can compare the junction sequences with the putative original sequences. Based on sequence polymorphisms at the center and on the arm regions of PATRR8, we can deduce the original allele types. We suggest that FHU13-033 (family 1) as well as case 13 originated from PATRR8M, while FHU13-027 (family 2) as well as cases 8, 9, 12 and 16 originated from PATRR8S1 (Table 2). Regarding the PATRR22, FHU13-033 (family 1) and FHU13-027 (family 2) originated from PATRR22C, while cases 12 and 13 originated from PATRR22A. PATRR22 sequence in case 16 was so diverged from known PATRR22 variants that we could not determine the origin. Virtually all of the translocations occurred on symmetrical alleles of PATRR8 and PATRR22.
The der(8) and the der(22) junction fragments of the t(8;22). A. Diagram for the translocation-specific PCR system. Chromosome 8 is indicated in white, while chromosome 22 is depicted in grey. Hatched boxes indicate PATRR arms. Translocation-specific PCR was performed with one primer designed at the flanking region of PATRR8 (grey primers) and with the other primer at the flanking region of PATRR22 (black primers). B. Results of family 1. Upper panel indicates results for the der(8), while lower panel indicates those of the der(22). Lane M, size markers; lane 1, FHU13-031 (proband); lane 2, FHU13-032 (father); lane 3, FHU13-033 (mother); lanes 4 and 5, normal healthy controls; lane 6, water control; lanes 7 and 8, balanced t(8;22) translocation carriers unrelated to the family. C. Results of family 2. Lane M, size markers; lane 1, FHU13-027 (proband); lanes 2 and 3, normal healthy controls; lane 4, water control; lanes 5 and 6, balanced t(8;22) translocation carriers unrelated to the family.
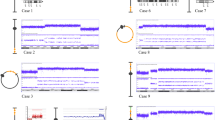
When the chromosome 8 portions of the der(8) and der(22) were aligned with PATRR8, the central region often appeared to be deleted (Figure 3A). Although the extent of deletion differs amongst cases, the sequence derived from the proximal and the distal arms shows loss of the same number of nucleotides from PATRR8. Likewise, the deletion is symmetrically located at the center of PATRR22 (Figure 3B). This suggests that the breakage always occurred at the center of the palindrome followed by a progression of bidirectional deletion.
Sequence comparison between the der(8) and the der(22) junction fragments with the putative original PATRRs. A. Compilation of the chromosome 8 side of the der(8) and der(22) with the PATRR8. B. Compilation of the chromosome 22 side of the der(8) and der(22) with the PATRR22. Triangles indicate the center of the PATRRs. Nucleotides participating in microhomology are underlined.
Analyses of the junctions of the der(8) and der(22)
We analyzed the junctions of PATRR8 and PATRR22 both for the der(8) and der(22). No substantial homology could be observed between PATRR8 and PATRR22 (35-50% similarity). We only observed a few identical nucleotides at the point where the original PATRR8 and PATRR22 sequences were joined (2-11 bp) (Figure 3A, B). Both PATRR8 and PATRR22 are so highly AT-rich that even homology-independent rejoining could manifest some microhomology at the junction by chance [9]. Therefore, the molecular pathways that are assumed to drive generation of this translocation might include microhomology-mediated end joining, classical non-homologous end joining, or alternative non-homologous end joining.
Comparison between the der(8) and der(22) sequences
We further compared the junction sequences of the der(8) and the der(22). Strikingly, the der(8) and the der(22) sequences were identical at the junctions in all cases (Figure 4), although subtle nucleotide differences were identified in the arm region that reflected nucleotide differences between the proximal and distal arms. On the basis of a standard mechanism of translocation formation based on double-strand DNA repair, formation of the der(8) and the der(22) occur independently [18]. If there were a long stretch of homologous sequence at the junction, there would be a chance to produce the same junction fragments independently. However, even at the junction with microhomology of only a few nucleotides, the der(8) and the der(22) sequences were identical.
Discussion
Characterization of the PATRR8
In this study, we determined the entire PATRR8 sequence in humans for the first time. All of the translocation-related PATRRs identified to date have three common features. 1) They comprise nearly perfect palindromes, whose lengths are several hundred base pairs. 2) An AT-rich region is located at the center, while there are relatively non-AT-rich regions at both ends. 3) Another AT-rich region exists flanking the PATRR [9]. Although non-AT-rich regions were absent within PATRR8, it possesses all three common features of translocation related PATRRs. It is proposed that all of these features foster the propensity for forming secondary structure at palindromic regions. Indeed, PATRR8 contributes to generation of not only the t(8;22), but also the constitutional t(3;8) that is associated with hereditary renal cell carcinoma predisposition, suggesting that the PATRR8 is a hotspot for palindrome-mediated translocations [19]. It is likely that for the t(8;22), as for other PATRR-related recurrent translocations such as the t(11;22) and t(17;22), DNA secondary structure might contribute to the generation of the translocation.
Similar to other translocation-related PATRRs, PATRR8 manifests size polymorphisms due to those within the PATRR itself as well as those in the flanking AT-rich region. Although minor variations are present at the nucleotide level, size variations of PATRR8 were found to be of only four types; two symmetric types and two asymmetric types. This might imply that PATRR8 is generally transmitted stably and is not predisposed to insertion or deletion. Alternatively, it is possible that PATRR8 might have emerged recently during evolution. Similar to other recurrent PATRR-mediated translocations, the t(8;22) was found to arise from symmetric variants [20],[21]. This indirectly but strongly suggests that PATRR8 adopts secondary structures in vivo.
Clinical significance for translocation-specific PCR
In all cases, both translocation breakpoints are located within several hundred base pair intervals on each chromosome, which could be identified with primers flanking PATRR8 and PATRR22. Similar to the t(11;22), this translocation-specific PCR is diagnostic since it can detect all of the t(8;22) translocations [22]. For example, in examination of a case like FHU13-027 with a balanced t(8;22) with intellectual disability and mild dysmorphic features, it might be difficult to know if the t(8;22) translocation is responsible for the phenotype as a result of breakpoint variation. On the basis of positive t(8;22)-specific PCR for both derivatives, we could conclude that the case is a standard t(8;22) balanced carrier and the t(8;22) translocation itself was unlikely to be the cause of the phenotype. Such translocation-specific PCR can also be useful in determining the origin of a small supernumerary marker chromosome of unknown origin. Since the t(8;22) is the second most frequent amongst small supernumerary marker chromosomes [4], t(8;22)-specific PCR is a simple and cost-effective method for marker identification as compared to multicolor spectral karyotyping for example.
Among the conceptions with unbalanced translocation products from a balanced t(8;22) translocation carrier that might result in early pregnancy loss, only a fetus with + der(22) karyotype through meiotic 3:1 segregation might be viable. Prenatal diagnosis for supernumerary der(22)t(8;22) syndrome could be performed via chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis. Non-invasive prenatal testing might also be possible, particularly if the male partner is a balanced translocation carrier. Further, translocation-specific PCR can also be applied for pre-implantation diagnosis using DNA amplified by whole genome amplification methods using the genomic DNA from a blastomere or blastocyst biopsy.
Possible mechanism for palindrome-mediated translocation
PATRR-mediated genomic instability is likely to occur via two distinct mechanisms; replication-dependent and replication-independent [23],[24]. The replication-dependent route is induced by replication fork stalling as a result of a hairpin structure within the lagging-strand template during DNA replication [25]. This is followed by template switching via microhomology leading to gross chromosomal rearrangements like translocations [26] Indeed, this kind of somatic rearrangement is often identified in cancer cells [27]. However, translocation-specific PCR only detects the t(8;22) as well as the t(11;22) in sperm, suggesting that PATRR-mediated translocations arise in gametogenesis, most notably spermatogenesis [13],[28]. One of the explanations for spermatogenesis-specific palindrome-mediated genomic instability is that during spermatogenesis a significant number of DNA replications take place. This would be a pre-meiosis hypothesis [2],[29]. Indeed, PATRR17 located within an intron of the NF1 gene contributes to some germ-line gross chromosomal rearrangements such as deletions and translocations resulting in neurofibromatosis type 1 [30]. The breakpoint features of these rearrangements are distinct from PATRR-mediated translocations [31],[32].
An alternative hypothesis is a post-meiosis hypothesis, which is based on replication-independent cruciform structure formation at the PATRRs by free negative supercoiling induced by extensive histone removal during late spermatogenesis. Symmetrical deletions on both the proximal and distal arms might imply that the deletions do not occur after DNA breakage at the central region of the PATRR followed by dissociation of the proximal and distal arms. Perhaps they occur after the central breakage with the PATRR maintaining its secondary structure, upon annealing of the proximal and distal arms. The symmetrical deletions are reflected in the identical nature of the der(8) and the der(22) sequences, which must be generated as independent events based on a classical DSB repair model for translocation formation [18]. The identical sequence of the der(8) and the der(22) might imply that rejoining occurs between the PATRRs while still keeping their secondary structure. Finally, the partner chromosome of a PATRR-mediated translocation is always another PATRR [2]. Thus, the hairpin-hairpin model proposed by Inagaki et al. might represent a plausible model for PATRR-mediated translocations in humans [33].
Conclusions
In our current study, comparison of der(8) to der(22) sequences shows identical breakpoint junctions between them, which likely represent products of two independent events on the basis of a classical model. Our data suggest the hypothesis that interactions between the two PATRRs prior to the translocation event might trigger illegitimate recombination resulting in the recurrent palindrome-mediated translocation.
Methods
Human samples
In this study, we used genomic DNA samples from cases 12 (CH00-180) and 13 (CH07-194) from the previous study [1]. In addition, we identified two new families of Japanese origin with the t(8;22)(q24;q11) translocation (Figure 5). One family (family 1) was identified through a female proband (FHU13-031) with typical features of the supernumerary der(22)t(8;22) syndrome characterized by clinodactyly, mild dysmorphia with preauricular pit, and intellectual disability. Her normal healthy mother was a balanced t(8;22) translocation carrier (FHU13-033). The other family (family 2) was identified by a female proband who was a balanced t(8;22) translocation carrier (FHU13-027) revealed by screening based upon intellectual disability and mild dysmorphia. The normal healthy mother also carried the same translocation. After informed consent was obtained, peripheral blood samples were obtained. This study was approved by the Ethical Review Board for Human Genome Studies at Fujita Health University (Accession number 145, approved on 16 April 2013).
Next generation sequencing
Genomic DNA was purified by QuickGene-610 L (Fuji Film). PATRR8 was amplified with primers flanking PATRR. PATRR8-512 F (5'-GATTACATATGGCATCTGGTAGGCTG-3') was used as the forward primer and PATRR8 + 227R (5'-GTGCCAAAATGTCAAGTCATCTGTG-3') was used as the reverse primer. PCR was performed with the KAPA Extra (KAPA Biosystems). The PCR products were separated by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and the genotypes for size polymorphism were determined.
To obtain the entire PATRR8 sequence, we used five t(8;22) balanced translocation carriers, who carry only one copy of the intact PATRR8. In addition, we selected 19 normal healthy donors who were heterozygous for size polymorphisms of PATRR8. The PCR products were separated by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and each PCR product derived from a different allele was purified separately.
For next generation sequencing, tagmentation were performed using a Nextera XT DNA sample prep kit (Illumina) according to the manufacturer's specifications. The libraries were amplified using the KAPA Library Amplification Kit (KAPA Biosystems) with the Nextera Index Kit to add indices and common adapters for subsequent cluster generation and sequencing. Prior to cluster generation, normalized libraries were further quantified by Qubit (Invitrogen Q32866) using the Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Invitrogen Q32851) and the 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies) using the High Sensitivity DNA Kit (Agilent Technologies, 5067–4626). PhiX control was added to the reaction to increase sequence diversity. Finally, the prepared library was loaded on an Illumina MiSeq clamshell style cartridge for paired end sequencing (Illumina). The data were analyzed using CLC Genomics Workbench. After trimming, reads were assembled as de novo assemblies or they were mapped to putative references prepared from junction fragments derived from t(8:22) translocation carriers to produce consensus sequences. Identity was calculated by Emboss Needle software, while ∆G was calculated by mfold.
PCR amplification of the junction fragments
To amplify an ~850 bp product containing the der(8) breakpoint junction fragment and to amplify the ~650 bp product containing the der(22) breakpoint junction fragment, a two-step PCR system was used [17]. The der(8) products were amplified with PATRR8-512 F and PATRR22 + 178R (5'-CATGATTCTGGATAACTTCCAAA-3') or JF22 (5'-CCTCCAACGGATCCATACT-3') primers, while the der(22) products were amplified with PATRR8 + 227R and PATRR22-394 F (5'-TCAGTTTATTCCCAAACTCCCAAAT-3') or JF22 primers. PCRs were performed using LA Taq DNA Polymerase (Takara) and the PCR conditions were as follows: 94°C for 2 min, followed by 35 cycles of 98°C for 30 s, 60°C for 5 min. The resulting PCR products were checked on 2% agarose gels, subjected to ExoSAP-IT digestion (Affymetrix), and then sequenced bidirectionally by capillary electrophoresis (ABI3730 Genetic Analyzer, Applied Biosytems). Sequences were analyzed with Clustalw2, which was used to align the resulting sequences.
Authors' contributions
DM - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work, and drafted the manuscript. TKA - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work, and drafted the manuscript. HI - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. TKO - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. KW - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. YK - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. SS - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. MTI - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. NM - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. KI - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. YF - Participated in the design of the study, carried out the molecular biology work. BSE - Coordinated and conceived the study, being involved in the critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. HK - Coordinated and conceived the study, participated in the design of the study, drafted the manuscript, being involved in the critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional file
References
Sheridan MB, Kato T, Haldeman-Englert C, Jalali GR, Milunsky JM, Zou Y, Klaes R, Gimelli G, Gimelli S, Gemmill RM, Drabkin HA, Hacker AM, Brown J, Tomkins D, Shaikh TH, Kurahashi H, Zackai EH, Emanuel BS: A palindrome-mediated recurrent translocation with 3:1 meiotic nondisjunction: the t(8;22)(q24.13;q11.21). Am J Hum Genet 2010, 87: 209–218. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.07.002
Kurahashi H, Inagaki H, Ohye T, Kogo H, Tsutsumi M, Kato T, Tong M, Emanuel BS: The constitutional t(11;22): implications for a novel mechanism responsible for gross chromosomal rearrangements. Clin Genet 2010, 78: 299–309. 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2010.01445.x
Carter MT, St Pierre SA, Zackai EH, Emanuel BS, Boycott KM: Phenotypic delineation of Emanuel syndrome (supernumerary derivative 22 syndrome): clinical features of 63 individuals. Am J Med Genet A 2009, 149: 1712–1721. 10.1002/ajmg.a.32957
Liehr T, Cirkovic S, Lalic T, Guc-Scekic M, de Almeida C, Weimer J, Iourov I, Melaragno MI, Guilherme RS, Stefanou EG, Aktas D, Kreskowski K, Klein E, Ziegler M, Kosyakova N, Volleth M, Hamid AB: Complex small supernumerary marker chromosomes - an update. Mol Cytogenet 2013, 6: 46. 10.1186/1755-8166-6-46
Kurahashi H, Shaikh TH, Hu P, Roe BA, Emanuel BS, Budarf ML: Regions of genomic instability on 22q11 and 11q23 as the etiology for the recurrent constitutional t(11;22). Hum Mol Genet 2000, 9: 1665–1670. 10.1093/hmg/9.11.1665
Edelmann L, Spiteri E, Koren K, Pulijaal V, Bialer MG, Shanske A, Goldberg R, Morrow BE: AT-rich palindromes mediate the constitutional t(11;22) translocation. Am J Hum Genet 2001, 68: 1–13. 10.1086/316952
Tapia-Pàez I, Kost-Alimova M, Hu P, Roe BA, Blennow E, Fedorova L, Imreh S, Dumanski JP: The position of t(11;22)(q23;q11) constitutional translocation breakpoint is conserved among its carriers. Hum Genet 2001, 109: 167–177. 10.1007/s004390100560
Kurahashi H, Emanuel BS: Long AT-rich palindromes and the constitutional t(11;22) breakpoint. Hum Mol Genet 2001, 10: 2605–2617. 10.1093/hmg/10.23.2605
Kurahashi H, Inagaki H, Hosoba E, Kato T, Ohye T, Kogo H, Emanuel BS: Molecular cloning of a translocation breakpoint hotspot in 22q11. Genome Res 2007, 17: 461–469. 10.1101/gr.5769507
Bzymek M, Lovett ST: Evidence for two mechanisms of palindrome-stimulated deletion in Escherichia coli: single-strand annealing and replication slipped mispairing. Genetics 2001, 158: 527–540.
Lobachev KS, Gordenin DA, Resnick MA: The Mre11 complex is required for repair of hairpin-capped double-strand breaks and prevention of chromosome rearrangements. Cell 2002, 108: 183–193. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00614-1
Cunningham LA, Coté AG, Cam-Ozdemir C, Lewis SM: Rapid, stabilizing palindrome rearrangements in somatic cells by the center-break mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23: 8740–8750. 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8740-8750.2003
Kurahashi H, Emanuel BS: Unexpectedly high rate of de novo constitutional t(11;22) translocations in sperm from normal males. Nat Genet 2001, 29: 139–140. 10.1038/ng1001-139
Kurahashi H, Inagaki H, Ohye T, Kogo H, Kato T, Emanuel BS: Palindrome-mediated chromosomal translocations in humans. DNA Repair (Amst) 2006, 5: 1136–1145. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.05.035
Kurahashi H, Inagaki H, Ohye T, Kogo H, Kato T, Emanuel BS: Chromosomal translocations mediated by palindromic DNA. Cell Cycle 2006, 5: 1297–1303. 10.4161/cc.5.12.2809
Gotter AL, Nimmakayalu MA, Jalali GR, Hacker AM, Vorstman J, Conforto Duffy D, Medne L, Emanuel BS: A palindrome-driven complex rearrangement of 22q11.2 and 8q24.1 elucidated using novel technologies. Genome Res 2007, 17: 470–481. 10.1101/gr.6130907
Inagaki H, Ohye T, Kogo H, Yamada K, Kowa H, Shaikh TH, Emanuel BS, Kurahashi H: Palindromic AT-rich repeat in the NF1 gene is hypervariable in humans and evolutionarily conserved in primates. Hum Mutat 2005, 26: 332–342. 10.1002/humu.20228
Richardson C, Jasin M: Frequent chromosomal translocations induced by DNA double-strand breaks. Nature 2000, 405: 697–700. 10.1038/35015097
Kato T, Franconi CP, Sheridan MB, Hacker AM, Inagakai H, Glover TW, Arlt MF, Drabkin HA, Gemmill RM, Kurahashi H, Emanuel BS: Analysis of the t(3;8) of hereditary renal cell carcinoma: a palindrome-mediated translocation. Cancer Genet 2014, 207: 133–140. 10.1016/j.cancergen.2014.03.004
Kato T, Inagaki H, Yamada K, Kogo H, Ohye T, Kowa H, Nagaoka K, Taniguchi M, Emanuel BS, Kurahashi H: Genetic variation affects de novo translocation frequency. Science 2006, 311: 971. 10.1126/science.1121452
Tong M, Kato T, Yamada K, Inagaki H, Kogo H, Ohye T, Tsutsumi M, Wang J, Emanuel BS, Kurahashi H: Polymorphisms of the 22q11.2 breakpoint region influence the frequency of de novo constitutional t(11;22)s in sperm. Hum Mol Genet 2010, 19: 2630–2637. 10.1093/hmg/ddq150
Kurahashi H, Shaikh TH, Zackai EH, Celle L, Driscoll DA, Budarf ML, Emanuel BS: Tightly clustered 11q23 and 22q11 breakpoints permit PCR-based detection of the recurrent constitutional t(11;22). Am J Hum Genet 2000, 67: 763–768. 10.1086/303054
Kato T, Inagaki H, Kogo H, Ohye T, Yamada K, Emanuel BS, Kurahashi H: Two different forms of palindrome resolution in the human genome: deletion or translocation. Hum Mol Genet 2008, 17: 1184–1191. 10.1093/hmg/ddn008
Kurahashi H, Inagaki H, Kato T, Hosoba E, Kogo H, Ohye T, Tsutsumi M, Bolor H, Tong M, Emanuel BS: Impaired DNA replication prompts deletions within palindromic sequences, but does not induce translocations in human cells. Hum Mol Genet 2009, 18: 3397–3406. 10.1093/hmg/ddp279
Voineagu I, Narayanan V, Lobachev KS, Mirkin SM: Replication stalling at unstable inverted repeats: interplay between DNA hairpins and fork stabilizing proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105: 9936–9941. 10.1073/pnas.0804510105
Hastings PJ, Lupski JR, Rosenberg SM, Ira G: Mechanisms of change in gene copy number. Nat Rev Genet 2009, 10: 551–564. 10.1038/nrg2593
Tanaka H, Bergstrom DA, Yao MC, Tapscott SJ: Widespread and nonrandom distribution of DNA palindromes in cancer cells provides a structural platform for subsequent gene amplification. Nat Genet 2005, 37: 320–327. 10.1038/ng1515
Ohye T, Inagaki H, Kogo H, Tsutsumi M, Kato T, Tong M, Macville MV, Medne L, Zackai EH, Emanuel BS, Kurahashi H: Paternal origin of the de novo constitutional t(11;22)(q23;q11). Eur J Hum Genet 2010, 18: 783–787. 10.1038/ejhg.2010.20
Thomas NS, Morris JK, Baptista J, Ng BL, Crolla JA, Jacobs PA: De novo apparently balanced translocations in man are predominantly paternal in origin and associated with a significant increase in paternal age. J Med Genet 2010, 47: 112–115. 10.1136/jmg.2009.069716
Hsiao MC, Piotrowski A, Alexander J, Callens T, Fu C, Mikhail FM, Claes KB, Messiaen L: Palindrome-mediated and replication-dependent pathogenic structural rearrangements within the NF1 Gene. Hum Mutat 2014, 35: 891–898. 10.1002/humu.22569
Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Häussler J, Krone W, Bode H, Jenne DE, Mehnert KU, Tümmers U, Assum G: The second case of a t(17;22) in a family with neurofibromatosis type 1: sequence analysis of the breakpoint regions. Hum Genet 1997, 99: 237–247. 10.1007/s004390050346
Kurahashi H, Shaikh T, Takata M, Toda T, Emanuel BS: The constitutional t(17;22): another translocation mediated by palindromic AT-rich repeats. Am J Hum Genet 2003, 72: 733–738. 10.1086/368062
Inagaki H, Ohye T, Kogo H, Tsutsumi M, Kato T, Tong M, Emanuel BS, Kurahashi H: Two sequential cleavage reactions on cruciform DNA structures cause palindrome-mediated chromosomal translocations. Nat Commun 2013, 4: 1592. 10.1038/ncomms2595
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Drs. Tamae Ohye and Makiko Tsutsumi for helpful discussions, Mrs. Narumi Kamiya for technical assistance. These studies were supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (H.K.), grants for Research on Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (H.K, Y.F.), grants CA39926 and funds from the Charles E.H. Upham chair in pediatrics (B.S.E.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
13039_2014_55_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1: Figure S1.: Complete sequence of the polymorphic PATRR8 with flanking regions. Large arrows indicate the proximal and distal PATRR arms. Direct repeats at the flanking regions proximal and distal to the PATRR8 are underlined (blue solid or dotted lines). The black lines indicate homology between the proximal and distal region to the PATRR8 deletion that appears in the human genome database. (PDF 160 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, D., Kato, T., Inagaki, H. et al. Breakpoint analysis of the recurrent constitutional t(8;22)(q24.13;q11.21) translocation. Mol Cytogenet 7, 55 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-014-0055-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-014-0055-x