Abstract
Background
Limb malformations are rare disorders with high genetic heterogeneity. Although multiple genes/loci have been identified in limb malformations, underlying genetic factors still remain to be determined in most patients.
Methods
This study consisted of 51 Japanese families with split-hand/foot malformation (SHFM), SHFM with long bone deficiency (SHFLD) usually affecting the tibia, or Gollop-Wolfgang complex (GWC) characterized by SHFM and femoral bifurcation. Genetic studies included genomewide array comparative genomic hybridization and exome sequencing, together with standard molecular analyses.
Results
We identified duplications/triplications of a 210,050 bp segment containing BHLHA9 in 29 SHFM patients, 11 SHFLD patients, two GWC patients, and 22 clinically normal relatives from 27 of the 51 families examined, as well as in 2 of 1,000 Japanese controls. Families with SHFLD- and/or GWC-positive patients were more frequent in triplications than in duplications. The fusion point was identical in all the duplications/triplications and was associated with a 4 bp microhomology. There was no sequence homology around the two breakpoints, whereas rearrangement-associated motifs were abundant around one breakpoint. The rs3951819-D17S1174 haplotype patterns were variable on the duplicated/triplicated segments. No discernible genetic alteration specific to patients was detected within or around BHLHA9, in the known causative SHFM genes, or in the exome.
Conclusions
These results indicate that BHLHA9 overdosage constitutes the most frequent susceptibility factor, with a dosage effect, for a range of limb malformations at least in Japan. Notably, this is the first study revealing the underlying genetic factor for the development of GWC, and demonstrating the presence of triplications involving BHLHA9. It is inferred that a Japanese founder duplication was generated through a replication-based mechanism and underwent subsequent triplication and haplotype modification through recombination-based mechanisms, and that the duplications/triplications with various haplotypes were widely spread in Japan primarily via clinically normal carriers and identified via manifesting patients. Furthermore, genotype-phenotype analyses of patients reported in this study and the previous studies imply that clinical variability is ascribed to multiple factors including the size of duplications/triplications as a critical factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Split-hand/foot malformation (SHFM), also known as ectrodactyly, is a rare limb malformation involving the central rays of the autopod [1],[2]. It presents with median clefts of the hands and feet, aplasia/hypoplasia of the phalanges, metacarpals, and metatarsals, and syndactyly. SHFM results from failure to maintain the central portion of the apical ectodermal ridge (AER) in the developing autopod [1],[2]. SHFM is divided into two forms: a non-syndromic form with limb-confined manifestations and a syndromic form with extra-limb manifestations [2]. Furthermore, non-syndromic SHFM can occur as an isolated abnormality confined to digits (hereafter, SHFM refers to this type) or in association with other limb abnormalities as observed in SHFM with long bone deficiency (SHFLD) usually affecting the tibia and in Gollop-Wolfgang complex (GWC) characterized by femoral bifurcation [1],[2]. Both syndromic and non-syndromic forms are associated with wide expressivity and penetrance even among members of a single family and among limbs of a single patient [2].
SHFM and SHFLD are genetically heterogeneous conditions reviewed in ref. [2]. To date, SHFM has been identified in patients with heterozygous deletions or translocations involving the DLX5-DLX6 locus at 7q21.2-21.3 (SHFM1) [3] (DLX5 mutations have been detected recently), heterozygous duplications at 10q24 (SHFM3), heterozygous mutations of TP63 at 3q27 (SHFM4), heterozygous deletions affecting HOXD cluster at 2q31 (SHFM5), and biallelic mutations of WNT10B at 12q31 (SHFM6); in addition, SHFM2 has been assigned to Xq26 by linkage analyses in a large Pakistani kindred [2]. Similarly, a genomewide linkage analysis in a large consanguineous family has identified two SHFLD susceptibility loci, one at 1q42.2-q43 (SHFLD1) and the other at 6q14.1 (SHFLD2); furthermore, after assignment of another SHFLD locus to 17p13.1-13.3 [4], duplications at 17p13.3 (SHFLD3) have been found in patients with SHFLD reviewed in ref. [2]. However, the GWC locus (loci) remains unknown at present.
The duplications at 17p13.3 identified to date are highly variable in size, and harbor BHLHA9 as the sole gene within the smallest region of overlap [5]-[9]. Bhlha9/bhlha9 is expressed in the limb bud mesenchyme underlying the AER in mouse and zebrafish embryos, and bhlha9 knockdown has resulted in shortening of the pectoral fins in zebrafish [6]. Furthermore, BHLHA9-containing duplications have been identified not only in patients with SHFLD but also in those with SHFM and clinically normal family members [4]-[10]. These findings argue for a critical role of BHLHA9 duplication in the development of SHFM and SHFLD, with variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance.
In this study, we report on BHLHA9-containing duplications/triplications with an identical fusion point and various haplotype patterns that were associated with a range of limb malformations including GWC, and discuss on characteristic clinical findings, genomic basis of Japanese founder copy number gains, and underlying factors for phenotypic variability.
Materials and methods
Patients/subjects
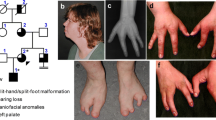
We studied 68 patients with SHFM (n = 55), SHFLD (n = 11), or GWC (n = 2), as well as 60 clinically normal relatives, from 51 Japanese families; the pedigrees of 27 of the 51 families and representative clinical findings are shown in Figure 1. All the probands 1-51 had a normal karyotype. Southern blot analysis for SHFM3 locus had been performed in 28 probands with SHFM, indicating 10q24 duplications in two of them [11]. Clinical features including photographs and roentgenograms of a proband with GWC and his brother with SHFLD (family 23 in Figure 1A) were as described previously [12]. The residencies of families 1-51 were widely distributed throughout Japan.
Clinical summary. A. Pedigrees of 27 Japanese families with duplications (families 1-22) and triplications (families 23-27) of a ~200 kb region involving BHLHA9. The duplications/triplications are associated with GWC, SHFLD, SHFM, or normal phenotype (carriers). N.E.: Not examined molecularly. B. Representative clinical findings. Each patient is indicated by a family-generation-individual style and corresponds to the patient/subject shown in Figure 1A and Additional file 5. The top panel: GWC with right bifid femur; the second panel: SHFLD with bilateral tibial deficiencies, the third panel: SHFM with polydactyly; and the bottom panel: SHFM.
Ethical approval and samples
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board Committees of Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, RIKEN, and National Center for Child Health and Development, and was performed using peripheral leukocyte samples after obtaining written informed consent for the molecular analysis and the publication of genetic and clinical data after removing information for personal identification (e.g., name, birthday, and facial photograph) from the adult subjects (³ 20 years) or from the parents of the child subjects (below 20 years). Furthermore, informed assent was also obtained from child subjects between 6-20 years.
Samples and primers
The primers utilized in this study are summarized in Additional file 1.
Molecular studies
Sanger sequencing, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), microsatellite genotyping, Southern blotting, and bisulfite sequencing-based methylation analysis were performed by the standard methods, as reported previously [13]. Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) analysis was carried out by the SYBR Green methods on StepOnePlus system, using RNaseP as an internal control (Life Technologies). Genomewide oligonucleotide-based array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) was performed with a catalog human array (4 × 180 K format, ID G4449A) according to the manufacturer's instructions (Agilent Technologies), and obtained copy number variants/polymorphisms were screened with Agilent Genomic Workbench software using the Database of Genomic Variants (http://dgv.tcag.ca/dgv/app/home). Sequencing of a long region encompassing BHLHA9 was performed with the Nextera XT kit on MiSeq (Illumina), using SAMtools v0.1.17 software (http://samtools.sourceforge.net/). Exome sequencing was performed as described previously [14].
Assessment of genomic environments around the fusion points
Repeat elements around the fusion point were searched for using Repeatmasker (http://www.repeatmasker.org). Rearrangement-inducing DNA features were investigated for 300 bp regions at both the proximal and the distal sides of each breakpoint, using GEECEE (http://emboss.bioinformatics.nl/cgi-bin/emboss/geecee) for calculation of the average GC content, PALINDROME (http://mobyle.pasteur.fr/cgi-bin/portal.py#forms::palindrome) and Non-B DB (http://nonb.abcc.ncifcrf.gov) for the examination of the palindromes and non-B (non-canonical) structures, and Fuzznuc (http://emboss.bioinformatics.nl/cgi-bin/emboss/fuzznuc) for the assessment of rearrangement-associated sequence motifs and tri/tetranucleotides [15]-[20]. For controls, we examined 48 regions of 600 bp long selected at an interval of 1.5 Mb from the entire chromosome 17.
Statistical analysis
The statistical significance of the frequency was analyzed by the two-sided Fisher's exact probability test.
Results
Sequence analysis of the known causative/candidate genes
We performed direct sequencing for the previously known causative genes (DLX5, TP63, and WNT10B) reviewed in ref. [2] in the probands 1-51. Although no pathologic mutation was identified in DLX5 and TP63, the previously reported homozygous missense mutation of WNT10B (c.944C > T, p.R332W) [21] was detected in the proband 48 with SHFM who was born to healthy consanguineous parents heterozygous for this mutation. In addition, while no variation was detected in DLX5 and WNT10B, rs34201045 (4 bp insertion polymorphism) in TP63[21] was detected with an allele frequency of 61%.
We also examined BHLHA9, because gain-of-function mutations of BHLHA9 as well as BHLHA9-harboring duplications may lead to limb malformations. No sequence variation was identified in the 51 probands.
Array CGH analysis
Array CGH analysis was performed for the probands 1-51, showing increased copy numbers at 17p13.3 encompassing BHLHA9 (SHFLD3) in the probands 1-27 from families 1-27 (Figure 1A). Furthermore, heterozygous duplications at 10q24 (SHFM3) were detected in the probands 49-51, i.e., a hitherto unreported patient with paternally inherited SHFM (his father also had the duplication) and the two patients who had been indicated to have the duplications by Southern blot analysis [11]. No copy number alteration was observed at other SHFM/SHFLD loci in the probands 1-27 and 49-51. In the remaining probands 28-48, there was no copy number variation that was not registered in the Database of Genomic Variants.
Identical fusion points in BHLHA9-containing duplications/triplications
The array CGH indicated that the increased copy number regions at 17p13.3 were quite similar in the physical size in the probands 1-27 and present in three copies in the probands 1-22 and in four copies in the probands 23-27 (Figure 2A). Thus, FISH analysis was performed using 8,259 bp PCR products amplified from this region, showing two signals with a different intensity that was more obvious in the probands 23-27 (Figure 2A).
Identification and characterization of the duplications/triplications involving BHLHA9 at chromosome 17p13.3. A. Array CGH and FISH analyses in proband 1 and proband 23 with GWC. In array CGH analysis, the black and the red dots denote the normal and the increased copy numbers, respectively. Since the log2 signal ratios for a ~200 kb region encompassing BHLHA9 are around +0.5 in the proband 1 and around +1.0 in the proband 23, this indicates the presence of three and four copies of this region in the two probands, respectively. In FISH analysis, two red signals with an apparently different density are detected by the 8,289 bp PCR probe (the stronger signals are indicated with asterisks). The green signals derive from an internal control probe (CEP17). The arrows on the genes show transcriptional directions. Rs3951819 (A/G) resides within BHLHA9. B. Determination of the fusion point. The fusion has occurred between intron 1 of ABR and intron 1 of YWHAE, and is associated with a 4 bp (GACA) microhomology. P1-P4 show the position of primers. C. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis. The upper part denotes the fusion point. P5 & P6 show the position of primers. The lower part shows the copy number of the fusion point in patients/subjects with duplications/triplications (indicated by a family-generation-individual style corresponding to that in Figure 1 and Additional file 5). Subject-1 and subject-2 denote the two control subjects with the duplication, and control-1 and control-2 represent normal subjects without the duplication/triplication. D. The rs3951819 (A/G SNP)-D17S1174 (CA repeat number) haplotype patterns in family 24. Assuming no recombination between rs3951819 and D17S1174, the haplotype patterns of the family members are determined as shown here. The haplotype patterns of the remaining families have been interpreted similarly.
We next determined the fusion points of the duplications/triplications (Figure 2B). PCR products of 2,195 bp long were obtained with P1/P2 primers in the probands 1-27, and the fusion point was determined by direct sequencing for 418 bp PCR products obtained with P3/P4 primers. The fusion point was identical in all the probands 1-27; it resided on intron 1 of ABR and intron 1 of YWHAE, and was associated with a 4 bp microhomology.
Then, we performed qPCR analysis for a 214 bp region harboring the fusion point, using P5/P6 primers (Figure 2C and Additional file 2). The fusion point was present in a single copy in the probands 1-22 and in two copies in the probands 23-27. The results showed that the identical genomic segment harboring BHLHA9 was tandemly duplicated in the probands 1-22 and triplicated in the probands 23-27. According to GRCh37/hg19 (http://genome.ucsc.edu/), the genomic segment was 210,050 bp long.
We also performed array CGH and qPCR for the fusion point in 15 patients other than the probands and 47 clinically normal relatives from the 27 families (Figures 1 and 2C). The duplications/triplications were identified in all the 15 patients. Thus, in a total of 42 patients, duplications/triplications were found in 29 SHFM patients, 11 SHFLD patients, and two GWC patients. Furthermore, the duplications/triplications were also present in 22 of the 47 clinically normal relatives. In particular, they were invariably identified in either of the clinically normal parents when both of them were examined; they were also present in other clinically normal relatives in families 7, 12, 24, and 25.
Since the above data indicated the presence of duplications/triplications in clinically normal subjects, we performed qPCR for the fusion point in 1,000 Japanese controls. The fusion point was detected in a single copy in two subjects (Subjects 1 and 2 in Figure 2C). We also performed array CGH in 200 of the 1,000 controls including the two subjects, confirming the duplications in the two subjects and lack of other copy number variations, including deletions involving BHLHA9, which were not registered in the Database of Genomic Variants in the 200 control subjects. The frequency of duplications/triplications was significantly higher in the probands than in the control subjects (27/51 vs. 2/1,000, P = 3.5 × 10-37).
Various haplotype patterns on the duplicated/triplicated segments
We carried out genotyping for rs3951819 (A/G SNP on BHLHA9) and D17S1174 (CA repeat microsatellite locus) on the genomic segment subjected to duplications/triplications (Figure 2A), and determined rs3951819-D17S1174 haplotype patterns. Representative results are shown in Figure 2D, and all the data are available on request. Various haplotype patterns were identified on the single, the duplicated, and the triplicated segments, and the [A-14] haplotype was most prevalent on the duplicated/triplicated segments (Table 1). While the distribution of CA repeat lengths on the single segments was discontinuous, similar discontinuous distribution was also observed in the Japanese general population (see Additional file 3).
Genomic environments around the breakpoints
The breakpoint on YWHAE intron 1 resided on a simple Alu repeat sequence, and that on ABR intron 1 was present on a non-repetitive sequence. There was no low copy repeat around the breakpoints. Comparison of the frequencies of known rearrangement-inducing DNA features between 600 bp sequences around the breakpoints and those of 48 regions selected at an interval of 1.5 Mb from chromosome 17 revealed that palindromes, several types of non-B DNA structures, and a rearrangement-associated sequence motif were abundant around the breakpoint on YWHAE intron 1 (see Additional file 4).
Clinical findings of families 1-27
Clinical assessment revealed several notable findings. First, duplications/triplications were associated with SHFM, SHFLD, GWC, or normal phenotype, with inter- and intra-familial clinical variability (Figure 1A). Second, in the 42 patients, split hand (SH) was more prevalent than split foot (SF) (41/42 vs. 17/42, P = 6.2 × 10-9), and long bone defect (LBD) was confined to lower extremities (0/42 vs. 13/42, P = 4.1 × 10-5) (Table 2 and Additional file 5). Third, there was no significant sex difference in the ratio between patients with limb malformations and patients/carriers with duplications/triplications (26/38 in males vs. 16/26 in females, P = 0.60) (Table 2 and Additional file 5). Fourth, the ratio of LBD positive families was significantly higher in triplications than in duplications (4/5 vs. 16/22, P = 0.047) (Figure 1A and Table 2). Fifth, while the duplications/triplications were transmitted from patients to patients, from carriers to patients, and from a carrier to a carrier (from I-1 to II-2 in family 12), transmission from a patient to a carrier was not identified (Figure 1A); it should be pointed out, however, that molecular analysis in a clinically normal child born to an affected parent was possible only in a single adult subject (II-1 in family 27), and that molecular analysis in clinically normal children <20 years old was possible only in two subjects (II-2 in family 12 and II-1 in family 15). Lastly, limb malformation was inherited in an apparently autosomal dominant manner (from patients to patients), or took place as an apparently de novo event or as an apparently autosomal recessive trait (from clinically normal parents to a single or two affected children) (Figure 1A).
Attempts to identify a possible modifier(s)
The variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance in families 1-27 suggest the presence of a possible modifier(s) for the development of limb malformations. Thus, we performed further molecular studies in patients/subjects in whom DNA samples were still available, and compared the molecular data between patients with SHFM and those with SHFLD for the assessment of variable expressivity and between SHFM, SHFLD, or total patients and carriers for the evaluation of incomplete penetrance.
We first examined the possibility that the modifier(s) resides within or around BHLHA9 (see Additional file 6). There was no BHLHA9 mutation in all the 21 examined probands with SHFM, SHFLD, or GWC, as described in the section of "Sequence analysis of the known causative/candidate genes". The rs3951819 A/G SNP pattern on the duplicated/triplicated segments was apparently identical between patients and carriers (e.g. Figure 2D), and the frequency of A/G allele on the normal chromosome 17 was similar between SHFM and SHFLD patients and between SHFM, SHFLD, or total patients and carriers (see Additional file 7). The results of other known SNPs on BHLHA9 (rs185242872, rs18936498, and rs140504068) were not informative, because of absence or extreme rarity of minor alleles. Furthermore, in SHFM families 7, 12, and 18, sequencing of a 7,406 bp region encompassing BHLHA9 and Southern blot analysis using five probes and MfeI-, SspI-, and SacI-digested genomic DNA revealed no variation specific to the patients, and methylation analysis for a CpG rich region at the upstream of BHLHA9 delineated massive hypomethylation in all the patients/carriers examined.
Next, we examined the possibility that a variant(s) of known causative genes constitutes the modifier(s). Since rs34201045 in TP63 was identified in the mutation analysis, we compared rs34201045 genotyping data between the 27 probands and the 15 carriers. The allele and genotype frequencies were similar between SHFM and SHFLD patients and between SHFM, SHFLD, or total patients and carriers (see Additional file 8).
We finally performed exome sequencing in SHFM families 13 and 17-19. However, there was no variation specific to the patients. In addition, re-examination of the genomewide array CGH data showed no discernible copy number variation specific to the patients.
Discussion
BHLHA9 overdosage and clinical characteristics
We identified duplications/triplications of a ~ 200 kb genomic segment involving BHLHA9 at 17p13.3 in 27 of 51 families with SHFM, SHFLD, or GWC. To our knowledge, this is the first study revealing the underlying genetic factor for the development of GWC, and demonstrating the presence of triplications involving BHLHA9 that were suggested but not confirmed in the previous studies [5],[9]. Furthermore, this study indicates that BHLHA9-containing duplications/triplications are the most frequent underlying factor for the development of limb malformations at least in Japan. Notably, SHFLD and GWC with LBD were significantly more frequent in patients with triplications than in those with duplications, and the duplications/triplications were identified in clinically normal familial members and in the general population. These findings imply that increased BHLHA9 copy number constitutes a strong susceptibility, rather than a causative, factor with a dosage effect for the development of a range of limb malformations. Since Bhlha9 is expressed in the developing ectoderm adjacent to the AER rather than the AER itself in mouse embryos [6], BHLHA9 appears to play a critical role in the limb development by interacting with the AER. While the duplications/triplications identified in this study included TUSC5 and generated an ABR-YWHAE chimeric gene (Figure 2C), TUSC5 duplication and the chimeric gene formation are not common findings in the previously reported patients with duplications at 17p13.3 and SHFM and/or SHFLD [5]-[9]. In addition, none of Tusc5, Abr, and Ywhae is specifically expressed in the developing mouse limb buds [22] (A Transcriptome Atlas Database for Mouse Embryo of Eurexpress Project, http://www.eurexpress.org/ee/project/).
Several clinical findings are noteworthy in patients/subjects with duplications/triplications. First, SH was more frequent than SF in this study as well as in the previous studies, and LBD was confined to lower extremities in this study and was more frequent in lower extremities than in upper extremities in the previous studies (Table 2) [4]-[10]. This implies that BHLHA9 overdosage exerts differential effects on the different parts of limbs. Second, while limb malformations were similarly identified between males and females in this study, they were more frequently observed in males than in females in the previous studies (Table 2) [4]-[10]. In this regard, it has been reported that testosterone influences the digital growth pattern as indicated by the lower second to fourth digit length ratio in males than in females [23]-[25], and that Caucasian males have higher serum testosterone values and lower second to fourth digit length ratios than Oriental males [26],[27]. Such testosterone effects on the digital growth pattern with ethnic difference may explain why male dominant manifestation was observed in the previous studies primarily from Caucasian countries and was not found in this study. Lastly, LBD was more prevalent in patients with triplications than in those with duplications. This suggests that LBD primarily occurs when the effects of BHLHA9 overdosage are considerably elevated.
Genomic basis of the Japanese founder copy number gains
The duplications/triplications were associated with the same fusion point and variable haplotype patterns. Since there was no sequence homology or low-copy repeats around the breakpoints, it is unlikely that such duplications/triplications were recurrently produced in different individuals by non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) [17],[20]. Instead, it is assumed that a Japanese founder duplication took place in a single ancestor, and was spread with subsequent triplication and modification of the haplotype patterns.
The most likely genomic basis of the Japanese duplications/triplications is illustrated in Additional file 9. Notably, a 4 bp (GACA) microhomology was identified at the duplication fusion point (Figure 2B). A microhomology refers to two to five nucleotides common to the sequences of the two breakpoints, and is found as an overlapping sequence at the join point [16],[19],[20]. This suggests that the Japanese founder duplication was generated by replication-based mechanisms such as fork stalling and template switching (FoSTeS) and microhomology-mediated break-induced replication (MMBIR), because the presence of such a microhomology is characteristic of FoSTeS/MMBIR [17]-[20]. Indeed, such a simple tandem duplication with a microhomology can be produced by one time FoSTeS/MMBIR [17]-[20], although it could also be generated by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) [17]. Since the [A-14] haplotype was most prevalent on the duplicated/triplicated segments, it is inferred that a genomic rearrangement occurred in an ancestor with the [A-14] haplotype, yielding the founder duplication with the [A-14] + [A-14] haplotype. Furthermore, the presence of multiple stimulants for genomic rearrangements around the breakpoint on YWHAE intron 1 would have facilitated the generation of the founder duplication. In particular, non-B structures are known to stimulate the occurrence of both replication-based FoSTeS/MMBIR and double-strand breaks and resultant NHEJ [17],[28],[29], although the relative importance of each non-B DNA structure is largely unknown.
Subsequent triplication and haplotype modification can develop from the Japanese founder duplication through unequal interchromatid and interchromosomal recombinations [17],[20]. Indeed, a tandem triplication with the [A-14] + [A-14] + [A-14] haplotype can be generated by unequal exchange between sister chromatids with the [A-14] + [A-14] haplotype, and various haplotype patterns are yielded by unequal interchromosomal exchanges involving the duplicated or triplicated segments. Furthermore, the haplotype variation would be facilitated by unequal exchanges between sister chromatids harboring duplications/triplications with various haplotype patterns and by the further unequal interchromosomal exchanges.
Underlying factors for the phenotypic variability
The duplications/triplications were accompanied by limb malformations with variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance. Although this may suggest the presence of a possible modifier(s) for the development of limb malformations, such a modifier(s) was not detected. In particular, while patient-to-carrier transmission of duplications/triplications was not identified in this study, even patient-to-carrier-to-patient transmission has been reported in three pedigrees [5],[6],[10]. Such transmission pattern with incomplete penetrance characterized by skipping of a generation is apparently inexplicable by assuming a modifier(s) interacting with BHLHA9 or independent of BHLHA9 on the duplication/triplication positive chromosome 17, on the normal chromosome 17, or on other chromosomes (Figure 3, Models A, B, and C, see also the legends in Figure 3).
Models for a modifier(s) and effects of the duplication size. In models A-C, the yellow bars show chromosome 17, and the light green bars indicate other chromosomes. The two red dots represent the duplication at 17p13.3, and the blue dots indicate a putative modifier(s). Black painted diamonds represent limb malformation positive patients, dot-associated and gray painted diamonds indicate clinically normal carriers with the duplications and the modifier(s) respectively, and white painted diamonds denote clinically normal subjects without both the duplications and the modifier(s). A. This model assumes that co-existence of the duplication and a cis-acting modifier(s) causes limb malformation. If co-existence of the duplication and the cis-acting modifier(s) is associated with incomplete penetrance, this can explain all the transmission patterns observed to date, including the patient-to-carrier transmission and the presence of ≥ 2 affected children. B. This model postulates that the presence of a cis-acting modifier(s) on the normal chromosome 17 leads to limb malformation by enhancing the expression of the single BHLHA9, together with duplicated BHLHA9 on the homologous chromosome. C. This model postulates that co-existence of the duplication at 17p13.3 and a modifier(s) on other chromosome causes limb malformation. In models D-E, the red bars represent BHLHA9, the blue circles indicate a physiological cis-regulatory element for BHLHA9, and the green circles indicate a non-physiological modifier(s) for BHLHA9. D. The physiological cis-regulatory element may be duplicated or non-duplicated, depending on its position relative to the size of the duplications. BHLHA9 expression can be higher in small duplications than large duplications. E. The non-physiological modifier(s) can be transferred to various positions of the duplication positive chromosome 17, depending on the recombination places (see Model A). BHLHA9 expression can be higher in small duplications than large duplications irrespective of the position of the modifier(s).
In this regard, it is noteworthy that the development of limb malformations is obviously dependent on the size of genomic segment subjected to copy number gains. Actually, limb malformation has occurred in only one of 21 large duplications encompassing BHLHA9 (average 1.55 Mb, mean 1.12 Mb) and in 29 of 80 small duplications encompassing BHLHA9 (average 244 kb, mean 263 kb) (P = 5.9 × 10-3) [8]. Consistent with this, the patients with large and small duplications were ascertained primarily due to developmental retardation and limb malformation, respectively [8]. It is likely that a physiological cis-regulatory element for BHLHA9 (e.g., an enhancer) can frequently but not invariably work on both of the duplicated BHLHA9 when the duplication size is small but is usually incapable of working on duplicated BHLHA9 when the duplication size is large, probably because of the difference in the chromatin structure (see Model D in Figure 3). Similar findings have also been reported in other genes. For example, small (~150 kb) and relatively small (600-800 kb) duplications involving a putative testis-specific enhancer(s) for SOX9 have caused 46,XX testicular and ovotesticular disorders of sex development respectively, whereas large duplications (~2 Mb) involving the enhancer(s) have permitted normal ovarian development in 46,XX individuals [30].
Thus, a plausible explanation may be that a range of limb malformations emerge when the effects of BHLHA9 overdosage exceed the threshold for the development of SHFM, SHFLD, or GWC, depending on the conditions of other genetic and environmental factors including the size of duplications/triplications as an important but not definitive factor. One may argue that this notion is inconsistent with the apparent anticipation phenomenon that is suggested by the rare patient-to-carrier transmission and the frequent carrier-to-patient transmission of the duplications/triplications, because no specific factor(s) exaggerating the development of limb malformations is postulated in the next generation. However, the skewed transmission pattern would primarily be ascribed to ascertainment bias rather than anticipation [31]. Indeed, while clinically normal parents of disease positive children would frequently be examined for the underlying genetic factor(s) of the children, clinically normal children born to disease positive parents would not usually be studied for such factor(s), as exemplified in this study. Similarly, the frequent patient-to-patient transmission of the duplications/triplications would also be ascribed to ascertainment bias, because molecular studies would preferentially be performed in such families. Nevertheless, the apparently autosomal dominant inheritance pattern of limb malformations in several families may still suggest the relevance of a non-physiological cis-acting modifier(s) (see Models A and E in Figure 3). It is possible that such a modifier(s), once transferred onto the duplication/triplication positive chromosome 17, is usually co-transmitted with the duplications/triplications, leading to a specific condition in which the effects of BHLHA9 overdosage frequently but not invariably exceed the threshold for the development of limb malformations in offsprings with the duplications/triplications.
Remarks
Several matters should be pointed out in the present study. First, in contrast to diverse duplication sizes in non-Japanese populations [5]-[9], the size of the genomic segment subjected to duplications/triplications was identical in this study. Since families 1-27 were derived from various places of Japan, there is no selection bias in terms of a geographic distribution. Rather, since the small duplications/triplications identified in this study were not associated with developmental retardation, it is likely that they spread throughout Japan primarily via carriers with normal fitness and were found via patients with limb malformations. Obviously, this notion does not exclude the possible presence of other types of duplications/triplications at 17p13.3 in Japan. Second, except for the duplications/triplications at 17p13.3, we could reveal a homozygous WNT10B mutation (SHFM6) only in a single SHFM family and chromosome 10q24 duplications (SHFM3) only in three SHFM families. Thus, underlying factors are still unknown in the remaining 20 families, although tiny deletions and/or duplications affecting the known SHFM loci might have been overlooked because of the low resolution of the array. In addition, although all the probands had a normal karyotype, there might be cryptic translocations and/or inversions involving the known SHFM loci. Third, no deletion of BHLHA9 was identified in the 51 probands and in the 200 control subjects. This argues against the relevance of BHLHA9 haploinsufficiency to limb malformations, and coincides with the Japanese founder duplication being produced by a replication-mediated mechanism rather than an interchromatid/interchromosomal (but not an intrachromatid) NAHR that can lead to both deletions and duplications as a mirror image [17]. Furthermore, it remains to be determined (i) whether gain-of-function mutations (and possibly loss-of-function mutations as well) of BHLHA9 are identified in patients with limb malformations, (ii) whether duplications/triplications involving BHLHA9 underlie limb malformations other than SHFM, SHFLD, and GWC, and (iii) whether BHLHA9-containing duplications/triplications are also the most frequent underlying factors for limb malformations in non-Japanese populations.
Conclusions
The results imply that (i) duplications/triplications involving BHLHA9 at chromosome 17p13.3 constitute a strong susceptibility factor for the development of a range of limb malformations including SHFM, SHFLD, and GWC; (ii) the Japanese founder duplication was generated by a replication-based mechanism and spread with subsequent triplication and haplotype modification through recombination-based mechanisms; and (iii) clinical variability appears to be due to multiple factors including the size of duplications/triplications. Thus, the present study provides useful information on the development of limb malformations.
Additional files
Abbreviations
- AER:
-
Apical ectodermal ridge
- CEP17:
-
Centromere of chromosome 17
- CGH:
-
Comparative genomic hybridization
- Dup:
-
Duplication
- FoSTeS:
-
Fork stalling and template switching
- GWC:
-
Gollop-Wolfgang complex
- L:
-
Lower
- LBD:
-
Long bone defect
- MMBIR:
-
Microhomology-mediated break-induced replication
- NAHR:
-
Non-allelic homologous recombination
- N.E.:
-
Not examined
- NHEJ:
-
Non-homologous end-joining
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- SF:
-
Split foo17)t
- SH:
-
Split hand
- SHFLD:
-
SHFM with long bone deficiency
- SHFM:
-
Split-hand/foot malformation
- Trip:
-
Triplication
- U:
-
Upper
References
Duijf PH, van Bokhoven H, Brunner HG: Pathogenesis of split-hand/split-foot malformation. Hum Mol Genet. 2003, 12: R51-60. 10.1093/hmg/ddg090.
Gurrieri F, Everman DB: Clinical, genetic, and molecular aspects of split-hand/foot malformation: an update. Am J Med Genet A. 2013, 161A: 2860-2672. 10.1002/ajmg.a.36239.
Lango Allen H, Caswell R, Xie W, Xu X, Wragg C, Turnpenny PD, Turner CL, Weedon MN, Ellard S: Next generation sequencing of chromosomal rearrangements in patients with split-hand/split-foot malformation provides evidence for DYNC1/1 exonic enhancers of DLX5/6 expression in humans. J Med Genet. 2014, 51: 264-267. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-102142.
Lezirovitz K, Maestrelli SR, Cotrim NH, Otto PA, Pearson PL, Mingroni-Netto RC: A novel locus for split-hand/foot malformation associated with tibial hemimelia (SHFLD syndrome) maps to chromosome region 17p13.1-17p13.3. Hum Genet. 2008, 123: 625-631. 10.1007/s00439-008-0515-7.
Armour CM, Bulman DE, Jarinova O, Rogers RC, Clarkson KB, DuPont BR, Dwivedi A, Bartel FO, McDonell L, Schwartz CE, Boycott KM, Everman DB, Graham GE: 17p13.3 microduplications are associated with split-hand/foot malformation and long-bone deficiency (SHFLD). Eur J Hum Genet. 2011, 19: 1144-1151. 10.1038/ejhg.2011.97.
Klopocki E, Lohan S, Doelken SC, Stricker S, Ockeloen CW, Soares Thiele de Aguiar R, Lezirovitz K, Mingroni Netto RC, Jamsheer A, Shah H, Kurth I, Habenicht R, Warman M, Devriendt K, Kordass U, Hempel M, Rajab A, M Kitie O, Naveed M, Radhakrishna U, Antonarakis SE, Horn D, Mundlos S: Duplications of BHLHA9 are associated with ectrodactyly and tibia hemimelia inherited in non-Mendelian fashion. J Med Genet. 2012, 49: 119-125. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100409.
Petit F, Andrieux J, Demeer B, Collet LM, Copin H, Boudry-Labis E, Escande F, Manouvrier-Hanu S, Mathieu-Dramard M: Split-hand/foot malformation with long-bone deficiency and BHLHA9 duplication: two cases and expansion of the phenotype to radial agenesis. Eur J Med Genet. 2013, 56: 88-92. 10.1016/j.ejmg.2012.11.002.
Curry CJ, Rosenfeld JA, Grant E, Gripp KW, Anderson C, Aylsworth AS, Saad TB, Chizhikov VV, Dybose G, Fagerberg C, Falco M, Fels C, Fichera M, Graakjaer J, Greco D, Hair J, Hopkins E, Huggins M, Ladda R, Li C, Moeschler J, Nowaczyk MJ, Ozmore JR, Reitano S, Romano C, Roos L, Schnur RE, Sell S, Suwannarat P, Svaneby D, et al: The duplication 17p13.3 phenotype: analysis of 21 families delineates developmental, behavioral and brain abnormalities, and rare variant phenotypes. Am J Med Genet A. 2013, 161A: 1833-1852. 10.1002/ajmg.a.35996.
Luk HM, Wong VC, Lo IF, Chan KY, Lau ET, Kan AS, Tang MH, Tang WF, She WM, Chu YW, Sin WK, Chung BH: A prenatal case of split-hand malformation associated with 17p13.3 triplication - a dilemma in genetic counseling. Eur J Med Genet. 2014, 57: 81-84. 10.1016/j.ejmg.2013.12.005.
Petit F, Jourdain AS, Andrieux J, Baujat G, Baumann C, Beneteau C, David A, Faivre L, Gaillard D, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Jouk PS, Le Caignec C, Loget P, Pasquier L, Porchet N, Holder-Espinasse M, Manouvrier-Hanu S, Escande F: Split hand/foot malformation with long-bone deficiency and BHLHA9 duplication: report of 13 new families. Clin Genet. 2014, 85: 464-469. 10.1111/cge.12219.
Kano H, Kurosawa K, Horii E, Ikegawa S, Yoshikawa H, Kurahashi H, Toda T: Genomic rearrangement at 10q24 in non-syndromic split-hand/split-foot malformation. Hum Genet. 2005, 118: 477-483. 10.1007/s00439-005-0074-0.
Matsuyama J, Mabuchi A, Zhang J, Iida A, Ikeda T, Kimizuka M, Ikegawa S: A pair of sibs with tibial hemimelia born to phenotypically normal parents. J Hum Genet. 2003, 48: 173-176. 10.1007/s10038-003-0003-9.
Kagami M, Sekita Y, Nishimura G, Irie M, Kato F, Okada M, Yamamori S, Kishimoto H, Nakayama M, Tanaka Y, Matsuoka K, Takahashi T, Noguchi M, Tanaka Y, Masumoto K, Utsunomiya T, Kouzan H, Komatsu Y, Ohashi H, Kurosawa K, Kosaki K, Ferguson-Smith AC, Ishino F, Ogata T: Deletions and epimutations affecting the human 14q32.2 imprinted region in individuals with paternal and maternal upd(14)-like phenotypes. Nat Genet. 2008, 40: 237-242. 10.1038/ng.2007.56.
Iida A, Okamoto N, Miyake N, Nishimura G, Minami S, Sugimoto T, Nakashima M, Tsurusaki Y, Saitsu H, Shiina M, Ogata K, Watanabe S, Ohashi H, Matsumoto N, Ikegawa S: Exome sequencing identifies a novel INPPL1 mutation in opsismodysplasia. J Hum Genet. 2013, 58: 391-394. 10.1038/jhg.2013.25.
Cer RZ, Donohue DE, Mudunuri US, Temiz NA, Loss MA, Starner NJ, Halusa GN, Volfovsky N, Yi M, Luke BT, Bacolla A, Collins JR, Stephens RM: Non-B DB v2.0: a database of predicted non-B DNA-forming motifs and its associated tools. Nucl Acids Res. 2013, 41: D94-D100. 10.1093/nar/gks955.
Kornreich R, Bishop DF, Desnick RJ: α-Galactosidase A gene rearrangements causing Fabry disease: identification of short direct repeats at breakpoints in an Alu-rich gene. J Biol Chem. 1990, 265: 9319-9326.
Gu W, Zhang F, Lupski JR: (2008) Mechanisms for human genomic rearrangements. Pathogenetics. 2008, 1: 4-10.1186/1755-8417-1-4.
Vissers LE, Bhatt SS, Janssen IM, Xia Z, Lalani SR, Pfundt R, Derwinska K, de Vries BB, Gilissen C, Hoischen A, Nesteruk M, Wisniowiecka-Kowalnik B, Smyk M, Brunner HG, Cheung SW, van Kessel AG, Veltman JA, Stankiewicz P: Rare pathogenic microdeletions and tandem duplications are microhomology-mediated and stimulated by local genomic architecture. Hum Mol Genet. 2009, 18: 3579-3593. 10.1093/hmg/ddp306.
Hastings PJ, Ira G, Lupski JR: A microhomology-mediated break-induced replication model for the origin of human copy number variation. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5: e1000327-10.1371/journal.pgen.1000327.
Colnaghi R, Carpenter G, Volker M, O'Driscoll M: The consequences of structural genomic alterations in humans: genomic disorders, genomic instability and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011, 2011 (22): 875-885. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.010.
Ugur SA, Tolun A: Homozygous WNT10b mutation and complex inheritance in Split-Hand/Foot Malformation. Hum Mol Genet. 2008, 17: 2644-2653. 10.1093/hmg/ddn164.
Oort PJ, Warden CH, Baumann TK, Knotts TA, Adams SH: Characterization of Tusc5, an adipocyte gene co-expressed in peripheral neurons. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007, 276: 24-35. 10.1016/j.mce.2007.06.005.
Manning JT, Scutt D, Wilson J, Lewis-Jones DI: The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length: a predictor of sperm numbers and concentrations of testosterone, luteinizing hormone and oestrogen. Hum Reprod. 1998, 13: 3000-3004. 10.1093/humrep/13.11.3000.
Manning JT, Trivers RL, Singh D, Thornhill R: The mystery of female beauty. Nature. 1999, 399: 214-215. 10.1038/20341.
Williams TJ, Pepitone ME, Christensen SE, Cooke BM, Huberman AD, Breedlove NJ, Breedlove TJ, Jordan CL, Breedlove SM: Finger-length ratios and sexual orientation. Nature. 2000, 404: 455-456. 10.1038/35006555.
Heald AH, Ivison F, Anderson SG, Cruickshank K, Laing I, Gibson JM: Significant ethnic variation in total and free testosterone concentration. Clin Endocrinol. 2003, 58: 262-266. 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2003.01653.x.
Manning JT, Stewart A, Bundred PE, Trivers RL: Sex and ethnic differences in 2nd to 4th digit ratio of children. Early Hum Dev. 2004, 80: 161-168. 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2004.06.004.
Wang G, Vasquez KM: Non-B DNA structure-induced genetic instability. Mutat Res. 2006, 598: 103-119. 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.01.019.
Zhao J, Bacolla A, Wang G, Vasquez KM: Non-B DNA structure-induced genetic instability and evolution. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010, 67: 43-62. 10.1007/s00018-009-0131-2.
Benko S, Gordon CT, Mallet D, Sreenivasan R, Thauvin-Robinet C, Brendehaug A, Thomas S, Bruland O, David M, Nicolino M, Labalme A, Sanlaville D, Callier P, Malan V, Huet F, Molven A, Dijoud F, Munnich A, Faivre L, Amiel J, Harley V, Houge G, Morel Y, Lyonnet S: Disruption of a long distance regulatory region upstream of SOX9 in isolated disorders of sex development. J Med Genet. 2011, 48: 825-830. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100255.
Fraser FC: Trinucleotide repeats not the only cause of anticipation. Lancet. 1997, 350: 459-460. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)63077-2.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas [22132004-A01] from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, by Grant for Research on Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare [H24-048], and by Grants from National Center for Child Health and Development [23A-1, 24-7]. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors have nothing to declare.
Authors' contributions
Molecular analysis using human samples was performed by EN, HK, FK. RY, SN, SW, KY, TT, SS, MF, and TT, ST, and SY; clinical assessment and blood sampling by RK, HT, SM, TK, TH, MK, AS, KS, HO, NH, HN, EH, TN, HY, GN, and TO; design of this study and interpretations of the data by HA, SI, and TO; and paper writing by TO. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
13023_2014_125_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Additional file 3: Figure S2.: D17S1174 analysis in 200 Japanese control subjects, showing discontinuous distribution of the CA repeat numbers, as observed in the Japanese families with limb malformations. (PDF 12 KB)
13023_2014_125_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Additional file 4: Table S2.: In silico analysis for specific structures around the breakpoint-flanking regions and control regions. (PDF 66 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Nagata, E., Kano, H., Kato, F. et al. Japanese founder duplications/triplications involving BHLHA9 are associated with split-hand/foot malformation with or without long bone deficiency and Gollop-Wolfgang complex. Orphanet J Rare Dis 9, 125 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-014-0125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-014-0125-5