Abstract
Background
Postoperative delirium (POD), an acute and variable disturbance in cognitive function, is an intricate and elusive phenomenon that occurs after cardiac surgery. Despite progress in surgical techniques and perioperative management, POD remains a formidable challenge, imposing a significant burden on patients, caregivers, and healthcare systems.
Methods
This prospective observational study involved 307 patients who underwent cardiac surgery. Data on the occurrence of delirium, clinical parameters, and postoperative characteristics were collected. A multivariate analysis was performed to assess the relationship between POH and POD.
Results
Sixty-one patients (21%) developed delirium, with an average onset of approximately 5 days postoperatively and a duration of approximately 6 days. On multivariate analysis, POH was significantly associated with POD, and the adjusted odds ratios indicated that patients with POH were more likely to develop delirium (OR, 5.61; p = 0.006). Advanced age (OR, 1.11; p = 0.002), emergency surgery (OR, 8.31; p = 0.001), and on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting were identified as risk factors of POD. Patients who developed delirium were typically older, more likely to be male, and had higher morbidity rates than those who did not.
Conclusion
POH is significantly associated with delirium in critically ill patients after cardiac surgery. Surgical complexity and advanced age contribute to the risk of developing POD and poor postoperative outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The postoperative phase is a critical period that can immensely harm patients. Postoperative delirium (POD) is associated with cognitive impairment and other sequelae [1]. POD is a common complication of cardiac surgery that can significantly compromise the quality of postoperative care [2]. The number of major cardiac surgeries among elderly patients has been increasing owing to a higher prevalence of comorbidities, more severe illnesses, and poorer clinical outcomes after cardiac surgery in this aging population. POD is more frequently observed in older patients [3, 4].
Additionally, the high incidence of complications during postoperative critical care not only involves significant financial costs but also reduces the patient’s quality of life after hospitalization [5]. POD represents an acute and fluctuating disturbance of attention with unclear pathophysiology, and currently, no definitive preventive or therapeutic measures are available [6, 7]. POD is a multifactorial condition influenced by factors such as age, preexisting cognitive impairment, and the stress of surgery and has been correlated to temperature management and blood pressure fluctuations [8].
POD is a strong predictor of postoperative cognitive decline development and typically occurs within the first 3 postoperative days, whereas POCD occurs at the end of the first week. POD more significantly affects consciousness and potentially have prolonged impacts on patient health and the healthcare system [9]. Postoperative hypotension (POH) can arise due to various factors such as intraoperative hypotension, blood loss during surgery, changes in fluid balance, race, myocardial infarction, history of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or statins [10]. An increased blood pressure fluctuations could predict POD [11, 12]. Major adverse events are associated with POH [13]. Perioperative management of blood pressure influences short- and long-term POD during cardiac and noncardiac surgeries [14]. A mean arterial pressure of < 55 mmHg for a prolonged period is correlated with greater odds of POD [15].
The current study aimed to test the hypothesis that POH contributes to the incidence of delirium in patients undergoing postcardiac surgery.
Materials and methods
Patient enrollment
This prospective observational study was approved by Nanjing Medical University First Affiliated Hospital on June 9. 2021 (No:2021-SR-242) and conducted at a single center between September 2021 and April 2022. Informed consent was obtained from each participant before surgery. This study was a part of a previous study that determined the incidence of POD. Chinese-speaking adult patients ≤ 65 years old undergoing cardiac surgery were included. Individuals who did not provide informed consent, died before delirium onset, had intraoperative hypotension, or had a history of cognitive impairment were excluded.
The collected data included the occurrence of delirium, clinical parameters (vital signs and mean arterial pressure [MAP]) at the onset of delirium, treatment strategies, and postoperative characteristics. Notably, 34 patients who underwent off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) patients were included in this study. These patients were excluded from a previously published article that focused exclusively on cardiac surgery following the use of a cardiopulmonary bypass machine [16].
Delirium management
Delirium is a clinical disorder characterized by sudden onset and variable trajectory of changes in mental status, attention, and cognition. This condition is frequently identified in individuals admitted to healthcare facilities, especially those undergoing cardiac surgery, and is associated with diverse predisposing and precipitating factors.
In this study, we employed the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM-ICU) to assess delirium following surgery. Doctors and intensive care unit (ICU) nurses closely evaluated patients throughout the day to ensure the diagnosis of delirium. The hospital implemented a standardized protocol for managing delirium, which involved the initiation of postoperative sedation through the administration of propofol for the first 5 days, which was subsequently replaced by midazolam. The management of individuals with delirium included the use of benzodiazepines to treat anxiety, haloperidol for hallucination management, and clonidine to manage agitation.
Hypotension evaluation
POH is characterized by an abnormal decrease in blood pressure or systemic arterial pressure after surgery. In the ICU, the assessment and recording of blood pressure follows a systematic protocol, which includes continuous monitoring through either a blood pressure cuff or an arterial catheter for any exposure diagnosed by the hospital staff. Beyond numerical blood pressure values, the evaluation considered clinical indicators such as hypotension symptoms, heart rate alterations, and other relevant physiological parameters. Blood pressure readings were aligned with the onset of delirium to ensure synchronized evaluation. The MAP was calculated using the following formula:
Hypotension was defined as MAP < 65 mmHg), which was used for any exposure [17, 18].
Surgery and anesthesia
The study included various cardiac surgeries, including coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), valve replacements, and combined procedures. Notably, 34 patients underwent off-pump CABG, a significant subgroup for analysis.
For surgeries requiring CPB, management focused on maintaining optimal perfusion and minimizing inflammatory responses. Standard protocols included temperature control, appropriate anticoagulation, and close monitoring of vital signs to ensure adequate organ perfusion throughout the procedure.
As for off-pump CABG procedures, the strategy was to maintain cardiac stability without using CPB. Stabilizing devices and careful handling of the heart were used to maintain blood flow while placing grafts. Hemodynamic stability was closely monitored to prevent significant blood pressure fluctuations.
The anesthesia protocol was standardized for all cardiac surgeries. Induction typically involved propofol, followed by maintenance with volatile anesthetics such as sevoflurane or isoflurane. Fentanyl was used for pain management, and muscle relaxants ensured optimal surgical conditions.
Statistical analysis
SPSS software (version 26.0; IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for data management and statistical analysis. We also examined the association between POH and POD. The bivariate analysis involved two-sample t-tests for continuous variables and two-sample proportion tests for group comparisons.
Multivariate analysis was performed to assess the significance of differences observed at the descriptive and univariate levels for all variables, with p-values less than 0.2 and indicated by the odds ratio with 95% confidence interval: sex, age, Hb level, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral vascular disease, cerebral artery disease, smoking, urgent surgeries, emergent surgeries, elective surgeries, on-pump, hypertension, hypotension, hospital stay, morbidity, home discharge, and transfer to other clinics for rehabilitation and treatment.
Results
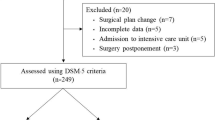
This study included 307 patients in total. Of them, 16 patients who experienced intraoperative hypotension or blood pressure fluctuations were excluded from the analysis (Fig. 1). The analysis focused on the remaining 291 participants.
Baseline patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The patients who developed POD were notably older and more likely to be male. Oxygen saturation (SO2) was 100% in the entire group, except for one case in the delirium group, a 64-year-old female with SO2 of 98%. A statistically significant difference in comorbidities and the type and urgency of surgery was noted between groups. Specifically, a significantly higher percentage of patients who developed delirium underwent emergency surgery and on-pump CABG than those who did not. Delirium and hypotension were evaluated at 8-h intervals throughout the day.
Delirium-related data and postoperative outcomes
Table 2 summarizes the postoperative outcomes and characteristics associated with delirium. Among all patients, 21% (n = 61) experienced delirium, with an average onset occurring 4.93 ± 3.40 days after surgery with a duration of 5.94 ± 1.87 days. Morbidities, including cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction, and low cardiac output syndrome, were significantly higher in patients who developed delirium than in those who did not (p < 0.001).
Indicators of postoperative delirium
The multivariate analysis of delirium indicators revealed several key associations (Fig. 2). Age was a significant factor, with each additional year increasing the odds of developing delirium by 11% (p = 0.002). Emergency surgery dramatically increased the risk of delirium, making patients more than eight times as likely to develop delirium (p = 0.001). Hypotension also significantly increased the odds, with patients more than five times more likely to develop delirium (p = 0.006). Additionally, high morbidity nearly tripled the risk (p = 0.026).
Forest plot showing the odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for various factors associated with postoperative delirium. Significant associations were found with age (OR 1.11, 95% CI 1.04-1.19, p = 0.002), morbidity (OR 2.84, 95% CI 1.13-7.1, p = 0.026), hypotension (OR 5.61, 95% CI 1.65-19.11, p = 0.006), and emergency surgery (OR 8.31, 95% CI 3.25-21.3, p = 0.001)
However, some of the factors were not significantly associated with delirium: hemoglobin levels, heart failure, cerebral artery disease, smoking, urgent surgery, and hypertension. These findings suggest that while factors such as age, emergency surgery, hypotension, and morbidity are critical in predicting delirium, other factors such as hemoglobin level, heart failure, and smoking do not have a significant impact.
Discussion
Research and clinical interest in POD, particularly in cardiac surgery patients, has increased tremendously. Delirium, a disabling condition, is likely to cause prolonged cognitive impairment. The postoperative phase is a critical period for patients during which complications such as POD can significantly affect recovery.
In the context of cardiac surgery, the prevalence of POD poses challenges to the quality of postoperative care, specifically in the aging population, in whom major cardiac surgeries are being increasingly performed. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between POH and delirium in patients who underwent cardiac surgery.
In the current adult patient study, an independent association was observed between POH and early-onset delirium, which aligns with our initial hypothesis and differs from the findings of previous studies. However, no correlation was observed, and no relationship between hypertension and POD [19]. Based on our findings, the adjusted models demonstrated a significant association between delirium and POH. The odds ratios exceeded 5 (p < 0.006), indicating that individuals who developed POH were highly prone to POD.
Similar to our previous and other published reports, we found that most patients with delirium were older adults [20,21,22].
The explanation lies in the physiological processes linked to aging, as advanced-age individuals tend to become frail [22]. Therefore, any disabling condition or comorbidity could affect the individual’s cognition and overall health. We also observed a higher prevalence of delirium in patients undergoing emergency surgery. This observation is supported by a previous report [23]. Our study found that delirium was associated with increased morbidity, consistent with findings from previous research [24]. In this investigation, we observed an increased occurrence of delirium in on-pump CABG and other non-coronary cardiac surgeries compared with off-pump CABG. This finding is consistent with that of a previous study, which independently linked the type of surgery operation to delirium [25].
Intraoperative hypotension or fluctuations in blood pressure independently pose a risk for the development of POH, POD, and various complications [26,27,28]. Individuals who experienced intraoperative hypotension were excluded from the study. The exclusion of patients with intraoperative hypotension aimed to ensure a focused investigation into the specific impact of hypotension on delirium in the ICU setting, thus contributing to the rigor of our study design. Contrary to earlier findings that indicated a correlation between extended operative time and increased risk of POD, our study did not find an association between the two [29].
Statistical differences between the groups regarding ICU stay duration and postoperative complications were noted. Importantly, these results align with those reported in a previous study [30].
Shirvani et al. reported that delirium occurring in the postoperative period after CABG is associated with electrolyte imbalances and metabolic disturbances. One potential rationale for this is that patients undergoing major cardiac surgery often experience blood loss and oxygen saturation fluctuations during the operation, which may account for the onset of hypotension during the postoperative period [31]. Maintaining a baseline regional cerebral oxygen saturation level > 50% is recommended to decrease the likelihood of POD development [32].
POH and POD are significant complications associated with surgical procedures, particularly in older adults. Several mechanisms link POH with POD. Cerebral hypoperfusion due to reduced blood pressure impairs brain oxygen and nutrient delivery and increases delirium risk, particularly in vulnerable populations [33]. Hypotension also triggers inflammatory responses, releasing cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α, contributing to delirium. Metabolic disturbances, such as hypoxia and acidosis, disrupt neuronal function, whereas sustained hypotension compromises the blood–brain barrier, allowing toxins to affect the brain. Additionally, hypotension alters the neurotransmitter balance, affects cognitive function, and leads to delirium [34, 35].
In our study, all patients underwent major cardiac surgeries under general anesthesia, and delirious patients were treated postoperatively using a standardized protocol for delirium. The use of dexmedetomidine has been identified as being linked to decreased occurrence of POD in the early days after the procedure [36].
Furthermore, our findings also indicate a substantial influence of delirium on postoperative outcomes. Individuals who experienced delirium during their hospital stay experienced more severe postoperative complications than those who did not, which is similar to that of previous studies [37].
Moreover, our study revealed that patients experiencing delirium were more likely to be transferred to other healthcare facilities for ongoing treatment, in contrast to patients without delirium.
Our study had some limitations. First, the timing, duration, and frequency of blood pressure measurement during the postoperative days were not reported in this investigation; however, they were reported for any exposure. Second, hypotension management was beyond the scope of this investigation. Third, the etiology of delirium in the late postoperative period may differ from that in the early postoperative period, and extending the measurements beyond ICU discharge is unlikely to alter our findings. Fourth, its single-center design might have limited the generalizability of our findings to healthcare settings with different protocols and patient demographics. Considering the sample size of 307 patients, excluding 16 participants may have affected the statistical power. A larger sample size would have enhanced the reliability and precision of this study. The variety of surgeries and the use of on-pump versus off-pump techniques.
Finally, our study reported a standardized delirium management protocol without specific anesthesia and medication administration details, introducing variability in treatment approaches that may influence the observed outcomes.
Conclusions
Our investigation substantiated the study hypothesis, revealing a robust association between POH and delirium in a single center. This report provides novel insights into POD among critically ill patients after cardiac surgery, as no prior study has explored this association in the absence of intraoperative blood pressure fluctuations.
Availability of data and materials
Data availability statement.
Data will be made available on request.
References
Migirov A, Chahar P, Maheshwari K. Postoperative delirium and neurocognitive disorders. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2021;27(6):686–93. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCC.0000000000000882.
Rhee J, Kuznetsov A, McKay T, Lyons M, Houstis N, Mekkonen J, et al. Serum Proteomics of Older Patients Undergoing Major Cardiac Surgery: Identification of Biomarkers Associated With Postoperative Delirium. Frontiers in aging neuroscience. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.699763.
Cohen CL, Atkins KJ, Evered LA, Silbert BS, Scott DA. Examining Subjective Psychological Experiences of Postoperative Delirium in Older Cardiac Surgery Patients. Anesth Analg. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000006226.
Li YW, Li HJ, Li HJ, Zhao BJ, Guo XY, Feng Y, et al. Delirium in Older Patients after Combined Epidural-General Anesthesia or General Anesthesia for Major Surgery: A Randomized Trial. Anesthesiology. 2021;135(2):218–32. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000003834.
Smischney, N. J., Shaw, A. D., Stapelfeldt, W. H., Boero, I. et al. Postoperative hypotension in patients discharged to the intensive care unit after non-cardiac surgery is associated with adverse clinical outcomes. Critical care (London, England).2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03412-5.
Maldonado J. R. Acute Brain Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management, and Sequelae of Delirium. Critical care clinics. 2017;33(3):461–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2017.03.013.
Aldecoa C, Bettelli G, Bilotta F, Sanders RD, Audisio R, Borozdina A, et al. European Society of Anaesthesiology evidence-based and consensus-based guideline on postoperative delirium. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0000000000000594.
Jin Z, Hu J, Ma D. Postoperative delirium: perioperative assessment, risk reduction, and management. Br J Anaesth. 2020;125(4):492–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2020.06.063.
Glumac, S., Kardum, G., & Karanovic, N. Postoperative Cognitive Decline After Cardiac Surgery: A Narrative Review of Current Knowledge in 2019. Medical science monitor: international medical journal of experimental and clinical research. 2019. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.914435.
Lee S, Conway AM, Nguyen Tranh N, Anand G, Leung TM, Fatakhova O, et al. Risk Factors for Postoperative Hypotension and Hypertension following Carotid Endarterectomy. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2020.05.057.
Hirsch J, DePalma G, Tsai TT, Sands LP, Leung JM. Impact of intraoperative hypotension and blood pressure fluctuations on early postoperative delirium after non-cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aeu458.
Ushio M, Egi M, Fujimoto D, Obata N, Mizobuchi S. Timing, Threshold, and Duration of Intraoperative Hypotension in Cardiac Surgery: Their Associations With Postoperative Delirium. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2022.06.013.
Khanna AK, Shaw AD, Stapelfeldt WH, Boero IJ, Chen Q, et al. Postoperative Hypotension and Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients Without Intraoperative Hypotension. After Noncardiac Surgery Anesthesia and analgesia. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000005374.
Lizano-Díez I, Poteet S, Burniol-Garcia A, Cerezales M. The burden of perioperative hypertension/hypotension: A systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(2):e0263737. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263737.
Wachtendorf LJ, Azimaraghi O, Santer P, Linhardt FC, Blank M, Suleiman A, et al. Association Between Intraoperative Arterial Hypotension and Postoperative Delirium After Noncardiac Surgery: A Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Anesth Analg. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000005739.
Othman SMA, Xu Q, Zhao K, Kafi L, Aziz MAA. Identification of early delirium and its outcomes after cardiopulmonary bypass among adult patients with cardiovascular disease: a prospective observational study. Indian journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-023-01613-5.
Wesselink EM, Kappen TH, Torn HM, Slooter AJC, van Klei WA. Intraoperative hypotension and the risk of postoperative adverse outcomes: a systematic review. Br J Anaesth. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2018.04.036.
Sun LY, Wijeysundera DN, Tait GA, Beattie WS. Association of intraoperative hypotension with acute kidney injury after elective noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology. 2015;123(3):515–23. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000000765.
Maheshwari K, Ahuja S, Khanna AK, Mao G, Perez-Protto S, Farag E, et al. Association Between Perioperative Hypotension and Delirium in Postoperative Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Anesth Analg. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000004517.
Austin CA, O’Gorman T, Stern E, Emmett D, Stürmer T, Carson S, et al. Association Between Postoperative Delirium and Long-term Cognitive Function After Major Nonemergent Surgery. JAMA Surg. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2018.5093.
Iamaroon, A., Wongviriyawong, T., Sura-Arunsumrit, P., Wiwatnodom, N., Rewuri, N., & Chaiwat, O. (2020). Incidence of and risk factors for postoperative delirium in older adult patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: a prospective study. BMC geriatrics. 2020;20(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-1449-8.
Clegg A, Young J, Iliffe S, Rikkert MO, Rockwood K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet (London, England). 2023;381(9868):752–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62167-9.
Hoogma DF, Venmans E, Al Tmimi L, Tournoy J, Verbrugghe P, Jacobs S, et al. Postoperative delirium and quality of life after transcatheter and surgical aortic valve replacement: A prospective observational study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2021.11.023.
Zhang M, Zhang X, Gao L, Yue J, Jiang X. Incidence, predictors and health outcomes of delirium in very old hospitalized patients: a prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):262. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-022-02932-9.
Gottesman RF, Grega MA, Bailey MM, Pham LD, Zeger SL, Baumgartner WA, et al. Delirium after coronary artery bypass graft surgery and late mortality. Ann Neurol. 2010;67(3):338–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21899.
Li N, Kong H, Li SL, Zhu SN, Zhang Z, Wang DX. Intraoperative hypotension is associated with increased postoperative complications in patients undergoing surgery for pheochromocytoma-paraganglioma: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020;20(1):147. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-020-01066-y.
Duan W, Zhou CM, Yang JJ, Zhang Y, Li ZP, Ma DQ, et al. A long duration of intraoperative hypotension is associated with postoperative delirium occurrence following thoracic and orthopedic surgery in elderly. J Clin Anesth. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2023.111125.
Putowski Z, Czok M, Krzych ŁJ. The impact of intraoperative blood pressure variability on the risk of postoperative adverse outcomes in non-cardiac surgery: a systematic review. J Anesth. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-022-03035-w.
Ravi, B., Pincus, D., Choi, S., Jenkinson, R., Wasserstein, D. N., & Redelmeier, D. A. Association of Duration of Surgery With Postoperative Delirium Among Patients Receiving Hip Fracture Repair. JAMA network open.2019. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.0111.
Zukowska A, Kaczmarczyk M, Listewnik M, Zukowski M. The Association of Infection with Delirium in the Post-Operative Period after Elective CABG Surgery. J Clin Med. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12144736.
Shirvani F, Sedighi M, Shahzamani M. Metabolic disturbance affects postoperative cognitive function in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2022;43(1):667–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05308-w.
Eertmans W, De Deyne C, Genbrugge C, Marcus B, Bouneb S, Beran M, et al. Association between postoperative delirium and postoperative cerebral oxygen desaturation in older patients after cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2020;124(2):146–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2019.09.042.
Feng X, Hu J, Hua F, Zhang J, Zhang L, Xu G. The correlation of intraoperative hypotension and postoperative cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020;20(1):193. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-020-01097-5.
Hirsch J, Vacas S, Terrando N, Yuan M, Sands LP, Kramer J, et al. Perioperative cerebrospinal fluid and plasma inflammatory markers after orthopedic surgery. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0681-9.
Saugel B, Sessler DI. Perioperative Blood Pressure Management. Anesthesiology. 2021;134(2):250–61. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000003610.
Shin HJ, Woo Nam S, Kim H, Yim S, Han SH, Hwang JW, Do SH, et al. Postoperative Delirium after Dexmedetomidine versus Propofol Sedation in Healthy Older Adults Undergoing Orthopedic Lower Limb Surgery with Spinal Anesthesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesthesiology. 2023;138(2):164–71. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000004438.
Yan E, Veitch M, Saripella A, Alhamdah Y, Butris N, Tang-Wai DF, et al. Association between postoperative delirium and adverse outcomes in older surgical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Anesth. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2023.111221.
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to everyone who contributed to and participated in the study, including all team members, teachers, staff, and patients.
Hunan and animal rights statement
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Human ethics and consent to participate declarations
Human Ethics and Consent to Participate declarations: not applicable.
Funding
This study received funding from the Priority Discipline Development Program of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (General Office, the People Government of Jiangsu Province under Grant Agreement No (2018) No.87).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
[Saleh Othman1 2, Mohammed Aziz1, Mohammed Al-Qudaimi, Chanyanud Sriwayyapram,Tecleab Okubai, Gamil Al-Muwaffaq, Gaber Al-Mushiki and Qin Xu]
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization: Saleh Othman, Mohammed Aziz and Tecleab Okubai; Methodology: Saleh Othman, Mohammed Al-Qudaimi and Chanyanud Sriwayyapram ; Data curation: Saleh Othman, Mohammed Aziz, Gaber Al-Mushiki and Gamil Al-Muwaffaq]; Formal analysis and investigation: Saleh Othman, Mohammed Al-Qudaimi, Gaber Al-Mushiki and Chanyanud Sriwayyapram; Writing—original draft preparation: Saleh Othman andTecleab Okubai; Writing—review and editing: [Saleh Othman, Prof. Qin Xu, Mohammed Aziz and Gamil Al-Muwaffaq ; Funding acquisition: [prof. Qin Xu; Resources: all authors; Supervision: Prof. Qin Xu. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to particpate
The study was approved by the Medical Institutional Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. Patients all signed the written informed consents before taking part into this study. The study project conforms to the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. No: (2021-SR-242).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Othman, S.M.A., Aziz, M.A.A., Al-Mushiki, G.M.A. et al. Association of postoperative delirium with hypotension in critically ill patients after cardiac surgery: a prospective observational study. J Cardiothorac Surg 19, 476 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-024-02958-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-024-02958-7