Abstract
Background
Proctor and colleagues’ 2011 paper proposed a taxonomy of eight implementation outcomes and challenged the field to address a research agenda focused on conceptualization, measurement, and theory building. Ten years later, this paper maps the field’s progress in implementation outcomes research. This scoping review describes how each implementation outcome has been studied, research designs and methods used, and the contexts and settings represented in the current literature. We also describe the role of implementation outcomes in relation to implementation strategies and other outcomes.
Methods
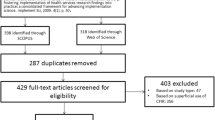
Arksey and O’Malley’s framework for conducting scoping reviews guided our methods. Using forward citation tracing, we identified all literature citing the 2011 paper. We conducted our search in the Web of Science (WOS) database and added citation alerts sent to the first author from the publisher for a 6-month period coinciding with the WOS citation search. This produced 1346 titles and abstracts. Initial abstract screening yielded 480 manuscripts, and full-text review yielded 400 manuscripts that met inclusion criteria (empirical assessment of at least one implementation outcome).
Results
Slightly more than half (52.1%) of included manuscripts examined acceptability. Fidelity (39.3%), feasibility (38.6%), adoption (26.5%), and appropriateness (21.8%) were also commonly examined. Penetration (16.0%), sustainability (15.8%), and cost (7.8%) were less frequently examined. Thirty-two manuscripts examined implementation outcomes not included in the original taxonomy. Most studies took place in healthcare (45.8%) or behavioral health (22.5%) organizations. Two-thirds used observational designs. We found little evidence of progress in testing the relationships between implementation strategies and implementation outcomes, leaving us ill-prepared to know how to achieve implementation success. Moreover, few studies tested the impact of implementation outcomes on other important outcome types, such as service systems and improved individual or population health.
Conclusions
Our review presents a comprehensive snapshot of the research questions being addressed by existing implementation outcomes literature and reveals the need for rigorous, analytic research and tests of strategies for attaining implementation outcomes in the next 10 years of outcomes research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Implementation outcomes reflect the progress towards success of efforts to implement evidence-based innovations. More specifically, they help disentangle the complex process of implementation so we can identify and target intermediate outcomes that may influence an intervention’s success in context. Robust conceptualization and rigorous measurement of these outcomes are essential for precision in implementation research, including understanding and testing the effectiveness of implementation strategies and explaining their mechanisms of action.
A 2011 paper by Proctor and colleagues advanced the concept of implementation outcomes, identified their critical role in implementation evaluation, and distinguished them from other traditionally measured outcomes (service system and clinical outcomes) [1]. The authors proposed a heuristic taxonomy of implementation outcomes and challenged the field to address a two-pronged research agenda: advance conceptualization and measurement and build theory including the identification and testing of change mechanisms. Ten years since the taxonomy’s publication, this paper maps the field’s progress in response to the originally proposed research agenda.
Conceptualization of implementation outcomes in the 2011 paper
Proctor and colleagues identified eight implementation outcomes [1] acceptability is defined as stakeholders’ perceptions that an implementation target is agreeable, palatable, or satisfactory. Adoption (also called uptake) is the intent, initial decision, or action to employ an implementation target. Appropriateness is the perceived fit, relevance, or compatibility of an implementation target for a given context or its perceived fit for a problem. Feasibility is the extent to which an implementation target can be successfully used or deployed within a given setting. Fidelity is the degree to which an intervention was implemented as prescribed or intended. Implementation cost is the financial impact of an implementation effort and must become bearable for implementation to proceed. Penetration—the integration or saturation of an intervention within a service setting and its subsystem—is calculated as a ratio of those to whom the intervention is delivered divided by the number of eligible or potential recipients. Sustainability is the extent to which an implementation target is maintained or institutionalized within a service setting. The 2011 paper encouraged further scholarship of this initial conceptualization, both in terms of the number of outcomes and in further refinements to their operationalization [1]. Cautioning that the original taxonomy included “only the more obvious”, that paper projected that new concepts would emerge as newly defined implementation outcomes [1].
Impact of the 2011 implementation outcomes paper
The 2011 paper spurred several critical developments in implementation science. Research funding announcements began to note the taxonomy’s importance for study conceptualization and design, including the U.S. National Institute of Health’s PAR 22–105 for Dissemination and Implementation Science in Health which identified these implementation outcomes as important for inclusion in investigator-initiated research applications [2]. Eighteen institutes and centers signed onto this crosscutting PAR.
The Implementation Outcomes Framework joined the ever-growing list of implementation research frameworks [3, 4], with unique contributions. First, the taxonomy signaled to researchers, policymakers, practitioners, and system leaders that implementation science has distinctive, legitimate outcomes warranting study alongside the outcomes traditionally prioritized in intervention trials. Second, the taxonomy provided direction for treating implementation outcomes as key targets of change, spurring the testing of implementation strategies designed to improve this new outcomes category. Third, the taxonomy raised widespread awareness around the lack of tools, instruments, and designs (e.g., hybrids II and III [5, 6]) that support the measurement of implementation outcomes either as standalone research aims or in conjunction with other outcomes and/or variables capturing contextual determinants.
The 2011 call for advances in the conceptualization and measurement
The first prong of the 2011 research agenda [1] called for advancing the conceptualization and measurement of implementation outcomes through consistent terminology, a call recently echoed by Murrell et al. [7]. The 2011 paper challenged researchers to report the referent for all implementation outcomes and to specify measurement levels and methods [5]. Subsequently, many scholars have helped refine implementation outcome conceptualization.
For example, Lyon and Bruns [70] distinguished two types of implementation outcomes. They proposed that acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility comprise perceptual implementation outcomes, while adoption, fidelity, and reach/penetration are behavioral implementation outcomes. An updated Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) distinguished between anticipated (forward-looking) and actual (backward-looking) implementation outcomes [8]. An Implementation Science editorial indicated that observable implementation outcomes such as adoption, fidelity, penetration, and sustainability are of most interest to the journal [9].
Significant measurement advances also occurred in response to the 2011 research agenda. The Grid-Enabled Measures Project [10] and The Society for Implementation Research Collaborative (SIRC) Instrument Review Project [11] are organized around the Proctor 2011 taxonomy. Weiner and colleagues’ study of the psychometric properties for measures of three key implementation outcomes [12]. Moullin and colleagues further refined pragmatic measurement via the PRESS measure for provider-rated sustainment in inner contexts [13], while the NoMAD instrument, based on normalization process theory, may also enhance implementation outcomes’ measurement [14]. We now have systematic reviews of implementation outcomes [15] and their measurement properties in behavioral health [16], public policy [17], stroke care [7], and physical healthcare [18]. Given these advancements in measurement tools, the field needs to examine commensurate progress toward their conceptual precision and linguistic harmony.
The 2011 call for theory building
Improved conceptualization and measurement positions researchers to move from asking descriptive questions about implementation outcomes to causal mechanistic ones [9], which is essential for building testable theory that describes, explains, and predicts how and why the implementation process worked (or not). Accordingly, the second prong of the 2011 research agenda called for theory-building research focused on employing implementation outcomes as key constructs in efforts to model successful implementation [1]. Researchers were challenged to explore the salience of implementation outcomes to different stakeholders and to investigate the importance of various implementation outcomes by phase in the implementation process—both of which can help researchers detect modifiable indicators of successful implementation [1].
Proctor and colleagues also called for research that tests and models various roles that implementation outcomes can play and research that illuminates how different implementation outcomes are associated with one another [1]. Their paper called for researchers to test several types of hypotheses related to how implementation outcomes are associated with each other, how the attainment of implementation outcomes influences service system and clinical outcomes, and how the effectiveness of implementation strategies affects implementation outcome attainment [20]. This call for hypothesis testing in implementation outcomes research has been echoed by a number of recent papers [21,22,23,24]. Current literature also reflects an increasing number of studies testing the effectiveness of implementation strategies and the mechanisms that explain how these strategies may influence implementation outcomes [25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. A 2021 scoping review paper [7] of adult stroke rehabilitation research using the Proctor 2011 framework revealed that adoption was the most frequently measured implementation outcome. No studies examined implementation cost, and fewer than half found that implementation strategies were effective in attaining implementation outcomes [7].
The 2011 paper also noted that measuring and empirically testing implementation outcomes can help specify the mechanisms and causal relationships within implementation processes and advance an evidence base around successful implementation. Since then, the field has responded. Recent publications raise awareness of mechanisms and advance their conceptualization in the context of implementation research. Emerging topics include prospectively building mechanism-focused hypotheses into research designs, developing approaches for identifying and prioritizing mechanisms, and advancing mechanisms measurement [19, 27]. Overall, the field still lacks conclusive evidence about interrelationships, particularly causal relationships, among implementation outcomes, strategies, subsequent outcomes, and their contextual and strategy determinants.
Study purpose
This review was designed to examine advances in (1) conceptualization of implementation outcomes (including the outcomes that have received empirical attention, the contexts for their study, and methods employed) and (2) theory building around implementation outcomes (interrelationships among implementation outcomes and their relationship to implementation strategies). We synthesize progress against the challenges posted in the 2011 paper and propose directions for the next 10 years of implementation outcomes research.
Methods
The first five steps of Arksey and O’Malley’s methodological framework for conducting scoping reviews guided our approach [32]. We also replicated the iterative and reflexive approach modeled by Marchand et al. [33] and Kim et al. [34] during each step of our scoping review process. Our published review protocol describes methods [35]. Here, we summarize and review key steps and note refinements to the protocol.
Stage 1: Defining the research questions
This review addressed three questions about advances in implementation outcomes conceptualization and measurement:
-
1.
To what extent has each of the eight implementation outcomes been examined empirically in the literature? What other implementation outcomes did these studies identify?
-
2.
What research designs and methods have been used to study each outcome?
-
3.
In what contexts have implementation outcomes been studied? What service settings, populations, health conditions, and innovation types are represented?
To understand advances in theory-building around implementation outcomes, we addressed two additional questions:
-
4.
Which implementation outcomes have been studied as dependent variables in tests of implementation strategy effectiveness?
-
5.
What interrelationships between implementation outcomes have been studied empirically? This includes relationships among implementation outcomes and other outcome types, specifically service, and clinical outcomes.
Stage 2: Identifying relevant literature
Using forward citation tracking, we identified all literature that cited the 2011 paper and was published between October 2010 (date of online publication) and October 30, 2020. We conducted our search in the WOS database in July 2020. To account for any delays in archiving more recent publications in WOS, we also located articles using citation alerts sent to the first author from the publisher for a 6-month period coinciding with the end of the WOS citation search (February to July 2020). In May 2023, we used the same forward citation tracking procedures in WOS to confirm all articles that cited the 2011 paper and were published through October 2020 because of archiving lags and to collect a full 10 years of implementation outcomes papers. Citations were managed in Mendeley and then exported to Covidence.
Stage 3: Article selection
As reported in our protocol paper [35], we screened articles and included them if they (a) reported results of an empirical study, (b) were published in a peer-reviewed journal, and (c) were designed to assess at least one of the identified implementation outcomes or their synonyms as specified in the original implementation outcome taxonomy.
Stage 4: Data charting
Data were charted using a customized Google Form, depicted in Table 1 of the study protocol paper [35]. Since protocol publication, we added two variables: health condition, which was defined as the primary health, disease, or problem targeted by the intervention or prevention effort, and funding source variable, defined as the first listed funder of the study.
Stage 5: Collating, summarizing, and reporting the results
We calculated and report frequencies, averages, and trends over time to identify the extent to which implementation outcomes are studied empirically in the 400 included manuscripts. To identify progress in research on implementation outcomes, we examined the role of implementation outcomes in analyses—as correlates of contextual factors and other implementation outcomes, and as dependent variables in relation to implementation outcomes.
Results
Our identification process generated 1346 abstracts for screening, which yielded 479 manuscripts for full-text review. After a full-text review, we excluded 79 manuscripts. A total of 400 manuscripts met the inclusion criteria (Fig. 1). Among the manuscripts qualifying for a full-text review, 82% were published in or after 2017 (Fig. 2). A wide range of funders supported implementation outcomes research globally and domestically. The National Institutes of Health (NIH)—especially the National Institute for Mental Health (NIMH)—was the most frequent funding source (24.5%). We found little evidence of foundation, state, or the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) funding (Table 1).
Question 1: To what extent has each of the eight implementation outcomes been examined empirically in the literature? What additional implementation outcomes were identified?
More than half (52%) of the included manuscripts examined acceptability, followed by fidelity (38.8%), feasibility (36.9%), adoption (24.0%), and appropriateness (20.1%). Penetration (15.4%), sustainability (15.1%), and cost (7.5%) were examined less frequently (Table 2). Most manuscripts indicated the stage or phase of implementation investigated, which we coded using the EPIS framework (exploration, adoption/preparation, implementation, sustainment). Focus on implementation outcomes varied by stage or phase, bearing out projections in the 2011 paper. In studies conducted during the exploration phase, appropriateness, feasibility, acceptability, and adoption were most frequently examined. Adoption, cost, and feasibility were addressed most frequently in studies conducted during the preparation phase. As hypothesized in 2011, sustainability was the outcome examined most during sustainment phase studies.
Eight percent (n = 32) of manuscripts identified implementation outcomes that were not in the original taxonomy. Our coding’s free text entry captured 24 unique alternative implementation outcome constructs, including evidence of delivery (e.g., use, provision, or receipt of an intervention; n = 4), usefulness (e.g., usability, utility; n = 14), clients’ responsiveness/engagement (n = 4), features of the intervention (e.g., adaptability, effectiveness; n = 7); clinician features (e.g., efficacy, competence; n = 8), level of implementation (n = 1), scale up (n = 1), and timely initiation (n = 1). Some of these terms (e.g., provider skill) may reflect determinants of implementation. Others—notably usefulness, usability, and utility—were identified in the 2011 paper as “other terms in the literature.”
Question 2: What research designs and methods have been used to study each outcome?
As Table 3 shows, most analyses of implementation outcomes were descriptive, with two-thirds employing on observational designs (n = 266). Experimental (n = 86, 21.5%) and quasi-experimental studies (n = 27; 6.8%) were less common; these studies accounted for about 30% of manuscripts every year, and this proportion did not fluctuate greatly over time (Fig. 2). Acceptability, adoption, and fidelity were most likely to be studied through experimental designs. Appropriateness was most likely to be studied qualitatively. Quantitative methods were used primarily for assessing adoption, cost, fidelity, and penetration. Less than a third of manuscripts presented mixed or multiple methods.
Question 3: In what contexts have implementation outcomes been studied? What service settings, populations, health conditions, and innovation types are represented in the studies?
To describe the context in which implementation outcomes have been studied, we captured study settings and populations, the innovations (implementation objects [36]) studied, and the health conditions addressed by the study (Table 4). Most manuscripts were situated in healthcare (n = 183, 45.8%) or behavioral health (n = 90, 22.5%) organizations—both inpatient and outpatient, with an additional 50 manuscripts (12.5%) set in schools. Studies predominantly addressed mental health (n = 129, 32.3%) or medical (n = 103, 25.8%) concerns. Manuscripts varied in their focus on the age group, with some including more than one age group. Nearly two-thirds of studies addressed adults and over 40% included children. The most common implementation object studied was a single evidence-based practice (n = 161, 40.3%). Implementation outcomes were studied in relation to screening and technological innovations in fewer than 22% of the manuscripts.
Question 4: Which outcomes have been studied as dependent variables in tests of implementation strategy effectiveness—a theory-building question?
Despite being conceptualized as outcomes (because of exposure to different conditions and strategies), implementation outcomes were treated as dependent variables in only one-quarter (n = 97) of included manuscripts. Only 56 (14.0%) manuscripts examined implementation outcomes in relation to implementation strategies. Fidelity was most frequently studied as an outcome of implementation strategies (7.0%) (Fig. 3). Although over half of the manuscripts examined acceptability, only 5.0% assessed its role as an outcome of implementation strategies. Similarly, few manuscripts presented tests of implementation strategies for their ability to attain fidelity, feasibility, appropriateness, or address cost barriers. Most manuscripts examining implementation strategies presented experimental (n = 24) or quasi-experimental (n = 22) designs (Fig. 4).
Question 5: What interrelationships between implementation outcomes have been studied empirically? This theory-building question includes relationships among implementation outcomes and other outcome types, specifically service and clinical outcomes
Finally, we examined the role of each implementation outcome in the analysis (Tables 5 and 6). Fifteen percent of included manuscripts examined relationships between implementation outcomes and other outcomes. Only 5.0% (n = 21) tested relationships among different implementation outcomes. As Tables 5 and 6 show, the cost was not examined in relation to other implementation outcomes. Sustainability was examined most often, particularly in relation to fidelity (n = 3), penetration (n = 3), and adoption (n = 2).
As shown in Table 7, only 23 manuscripts (5.8%) examined implementation outcomes in relation to service outcomes. Among implementation outcomes, feasibility (n = 9) was most often correlated with service outcomes. Effectiveness (n = 15) was the service outcome most frequently tested in relation to implementation outcomes. No studies of implementation outcomes in our sample addressed service outcomes of safety or equity. We also coded whether each manuscript examined implementation outcomes in relation to clinical outcomes, although given the wide heterogeneity in clinical outcomes of interest and in the absence of a corresponding taxonomy, we did not categorize specific clinical outcomes in this review. Only 22 studies (5.5%) examined implementation outcomes in relation to clinical outcomes. Fidelity was the implementation outcome most examined relative to clinical outcomes (10.2% of the manuscripts).
Discussion
One decade later, this scoping review assessed the field’s response to the 2011 paper’s research agenda calling for advances in conceptualization, measurement, and theory-building around implementation outcomes. Our results show a proliferation of literature on implementation outcomes. However, empirical investigations accounted for less than one-third of manuscripts citing the 2011 paper. While descriptive work can enrich our conceptual understanding of implementation outcomes, more work remains to advance a theory that explains the attainment and effects of implementation outcomes.
How has research on implementation outcomes advanced over the past 10 years?
Implementation outcomes research is supported by a range of funding sources and is conducted in many settings and disciplines. Most included studies were conducted in health and behavioral health organizations. Similar research is needed in less frequently studied settings where health and other social care interventions are delivered (e.g., schools, social service organizations, and home-based services) [37,38,39,40,41,42] to diverse communities and consumers with a range of intersecting needs. The context for implementation, often varying by setting, has been shown to affect certain implementation outcomes [43]. Building knowledge in varying settings can help advance conceptualization and theory building around implementation outcomes like penetration (or reach), propel incorporation of equity in the study of implementation outcomes, and provide unique opportunities to further articulate the relationships between implementation outcomes and other service outcomes, particularly equity.
Most included studies examined the implementation of a single evidence-based intervention or implementation object, failing to capture the reality of organizations and systems that typically work to introduce, implement and sustain the simultaneous delivery of multiple interventions. Studying the implementation of multiple interventions carries logistic, resource, and design challenges but can make scientific leaps, particularly regarding external validity. Future research should examine how service system directors weigh acceptability, feasibility, and cost while selecting interventions and strategies and how they juggle simultaneous implementation efforts, stagger their timing, and sustain them in dynamic and unpredictable environments.
Our results reflected considerable variation in the degree to which different implementation outcomes have been studied, with a heavy emphasis on acceptability, echoing other recent reports. In a systematic review of quantitative measures assessing health policy implementation determinants and outcomes, Allen and colleagues found that acceptability, feasibility, appropriateness, and compliance were most frequently measured [17]. Moreover, Mettert and colleagues reported that acceptability had the greatest number of measurement options [15]. Other implementation outcomes like cost, penetration, and sustainability (the observable implementation outcomes prioritized by Implementation Science [9]) were measured less frequently in our review sample.
This suggests that, currently, implementation outcomes research reveals more about which interventions and strategies people like (important for refining interventions, improving patient-centeredness, and supporting initial uptake), but less about the degree to which interventions reach and benefit communities. Insufficient attention to outcomes like penetration and cost (those highly prioritized in real-world decision making) limits our field’s ability to take evidence-based practices to scale for public health impact. Building strong evidence about these more observable implementation outcomes is critical for supporting policymakers and program leaders as they make decisions about strategic priorities and resource allocation to deploy, scale, and sustain interventions that will reach an adequate number of consumers equitably.
Our review explored the field’s progress toward conceptual and linguistic harmony and the promise of uncovering new implementation outcomes. Some manuscripts cited the 2011 paper but employed alternative concepts and terminology for implementation outcomes despite their close alignment with the 2011 taxonomy. For example, terms such as “evidence of delivery,” “use,” “provision,” or “receipt of services” could be more precisely operationalized by adoption or penetration. Similarly, outcomes such as “client response,” “participant responsiveness,” and “engagement” align closely with the term acceptability. Where authors discover granular distinctions between more commonly used terms, a rationale for proposing new terms is welcome and necessary. Nonetheless, we reiterate the importance of common implementation outcome terminology, where possible, so that the field can continue to build and harmonize knowledge across studies. Moreover, some of the alternative terms may be more accurately labeled as determinants of implementation outcomes rather than new outcomes (e.g., client and provider factors).
The results of our review also identified emerging implementation outcomes that are distinct from those proposed in the 2011 taxonomy. For example, there has been widespread attention to scale-up [44,45,46,47,48,49]. Although the 2011 paper conceptualized actual or perceived utility as a synonym for feasibility and usefulness as a synonym for appropriateness, the number of studies using this term as a distinct outcome suggests that perceived usefulness, usability, and utility may be conceptually distinct from constructs in the 2011 outcome taxonomy. The expansion of implementation outcomes taxonomy was encouraged by Proctor et al. in the 2011 manuscript. For such outcomes, we encourage the provision of common use and operational definitions, psychometric research to refine measurement, and clear reporting and justification for how these are conceptually distinct from the original taxonomy.
Reflecting the phased nature of implementation, Proctor et al. 2011 proposed that some implementation outcomes might be most salient—and thus likely to be measured—at different times [1]. Although all outcomes were likely to be studied during active implementation phases, outcomes like appropriateness, feasibility, acceptability, and adoption were especially common in studies conducted during the early phases of exploration and preparation. Outcomes like cost, fidelity, penetration, and sustainability were more common during later implementation and sustainment phases. This may reflect the importance of different implementation outcomes for decision making over time and at certain points in the implementation lifecycle. However, we found little evidence of testing hypotheses about the optimal order of attaining specific implementation outcomes. We hope this can be improved as methods such as causal pathway diagrams, causal loop diagrams, and directed acyclic graphs gain traction in mechanistic implementation research [19, 30, 50,51,52,53].
More theory-building work and more experimental studies are needed
Our results suggested limited progress toward theory development. Few manuscripts focused on explaining, testing, or modeling the processes that reveal how implementation outcomes can change, be intervened upon, or affect other outcomes. Few studies treated implementation outcomes as dependent variables in studies that investigate associations or causal relationships between determinants and implementation outcomes. We also found few studies testing the relationships between implementation strategies and implementation outcomes—a key part of the 2011 proposed agenda. This gap is concerning given the purpose of implementation science, that is, to advance strategies for integrating innovations into everyday practice. Our results suggested that implementation scholars are still in the early stages of building evidence for the causal effects of implementation determinants and strategies and still do not know how to achieve implementation outcomes. We hope that can be ameliorated with a continued increase in study designs that include prospective theorizing about what mechanisms explain strategy effectiveness and precise measurement of these mechanisms in relation to specific implementation outcome attainment [19, 27, 54].
Although some have questioned testing implementation outcomes as dependent variables [55], rigorous trials of implementation strategies are important for learning how to achieve acceptability, feasibility, adoption, and sustainment. For example, random assignment of train-the-trainer or coaching to clinics can inform the most effective approach to provider adoption. Debate also surrounds the question of whether or not implementation outcomes are ever sufficient as “endpoint”-dependent variables and whether they should always be tested in relation to more distal service systems and clinical outcomes (as discussed below). While we argue for more research testing the intermediate role of implementation outcomes, testing their role as endpoint-dependent variables seems warranted as we continue to advance knowledge about how to most effectively attain them, and which implementation strategies to prioritize and invest in to do so.
Though correlational studies serve the function of suggesting variables for further testing to reveal building blocks for theory, scientific leaps require a shift from the descriptive work that, as evidenced by our findings, dominates the field. Though observational research is important for laying a foundation, particularly as implementation research moves into newer fields and settings (e.g., large-scale policy implementation), theoretical advances are necessary to understand how contextual factors such as organizational leadership [24] and implementation strategies affect outcome attainment. More work is needed to specify and test mechanistic pathways and empirical hypotheses about drivers, moderators, and mediators of implementation outcomes in a replicable way so that it is clear what knowledge is generalizable across settings versus what needs to be learned and assessed locally. Furthermore, finer-grained identification of the measurable proximal outcomes that precede implementation outcome attainment can help us better understand how exactly a strategy works to improve the implementation outcome(s) it is targeted to change (and thus what is core vs. adaptable about the strategy itself), as well as more clearly isolate what factors are not addressed by the strategy and thus need additional attention in order to achieve the desired implementation outcome(s). Notably, the frequency with which mixed methods were employed in our sample suggested the availability of rich data to pursue the theoretical advances we encourage here.
Studies in our reviews rarely addressed relationships among implementation outcomes. Given our finding that various implementation outcomes might be more salient at different phases, studies should examine the optimal temporal ordering of their pursuit. For instance, clinician perceptions about the acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility of an intervention might predict adoption [56]. Longitudinal studies that measure and test relationships among multiple implementation outcomes before, during, and after implementation can generate new insights about phasing implementation efforts and the potential additive and interactive effects of thoughtful sequencing.
Few studies tested hypothesized impacts of implementation outcomes on other important outcome types, such as service system changes and improved individual or population health, thereby limiting theory building and testing the impact of implementation outcomes. This finding echoes recent reflections on the promises and pitfalls of implementation science [54] and suggests that our field has yet to empirically demonstrate the value of implementation science for improving health and healthcare quality.
Such inquiry is critical in work to reduce health disparities [40, 57,58,59,60,61]. Equity is a key service system outcome [1, 62]. Delivering interventions that are unacceptable to clients will surely block equitable care. Data on acceptability and feasibility can be used to adapt interventions and the associated implementation processes to build local capacity. Using implementation outcomes, equity in service delivery may be modeled and tested as follows:
Similarly, penetration and sustainment of evidence-based care to the entirety of a system’s service recipients or a community’s under-resourced populations can serve as measurable indicators of equitable access and reach [63, 64], consistent with calls to prioritize structural racism in contextual analyses [65]. We hypothesize the following:
[63,64,65]. Future studies that investigate relationships among different outcome types are necessary for achieving the system and population health impact that motivates the field of implementation science and are essential for demonstrating tangible impact and the value of investing in implementation work.
Strengths and limitations of our review
Our paper complies with recommendations that review articles in implementation science be rigorous, comprehensive of the questions being asked, and provide accurate attributions [66]. Given our review’s aims, we included only articles that cited the 2011 Proctor et. al implementation outcomes paper. Thus, our results likely underestimated advances in the field from studies anchored in alternative theories and taxonomies (e.g., those anchored by the RE-AIM framework), particularly those in adjacent disciplines or that focus on alternative implementation outcomes. Our rigorous calibration process to ensure reliability in the screening and data charting phases, and the iterative adaptation of our data charting procedures contributed to the strength of our review. For example, when coding revealed the need for new variables, we re-reviewed all articles. The reviewed articles presented many coding challenges, particularly around the precision of reporting, which could have introduced errors during the data charting. See Lengnick-Hall et al. [67] for detail on the coding challenges we encountered, along with recommendations to improve reporting.
When juxtaposed with Proctor et al.’s 2011 recommendations and a recent paper on recommendations for reporting implementation outcomes [67], our data provide a basis for projecting priorities for a “next stage agenda” on implementation outcomes 2022–2023. Summarized in Table 8, work must further harmonize implementation outcome terminology. Beyond observational measurement of implementation outcomes, studies should specify their role in analyses, test how to achieve them, and demonstrate their impact on clinical, system, and public health improvements. Especially pressing is understanding how implementation outcomes—particularly acceptability, feasibility, and sustainability—can advance equitable health service delivery. Testing hypothesized sequencing, impact, and efficiency of attaining implementation outcomes via strategies is essential to understanding and accelerating implementation processes [68, 69].
Conclusion
This review illustrated growth in implementation outcomes research, but with empirical evaluation reflecting a small subset of publications (30%). Over the past 10 years, manuscripts described implementation outcomes across many settings, emphasizing perceived outcomes like acceptability, feasibility, and appropriateness. We continue to lack robust evidence about strategies that help attain outcomes. Advancing the field demands that the next 10 years further both aims of the 2022 research agenda focusing on building strong theory, more objective measurement, and evidence about how to achieve implementation outcomes. Moreover, we must empirically demonstrate that successful implementation matters for the improvement of clinical service systems and public health outcomes.
Availability of data and materials
Data are available upon reasonable request directed to the corresponding author.
Change history
08 September 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-023-01294-z
25 October 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-023-01313-z
References
Proctor E, Silmere H, Raghavan R, Hovmand P, Aarons G, Bunger A, et al. Outcomes for implementation research: conceptual distinctions, measurement challenges, and research agenda. Adm Policy Ment Health and Ment Health Serv Res. 2011;38:65–76.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. PAR-19–274.
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4.1(2009):1–15.
Aarons GA, Hurlburt M, Horwitz SM. Advancing a conceptual model of evidence-based practice implementation in public service sectors. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2011;38(2011):4–23.
Curran GM, Bauer M, Mittman B, Pyne JM, Stetler C. Effectiveness-implementation hybrid designs. Med Care. 2012;50.3(2011):217.
Curran GM, Landes SJ, McBain SA, Pyne JM, Smith JD, Fernandez ME, et al. Reflections on 10 years of effectiveness-implementation hybrid studies. Front Health Serv. 2022;2:125.
Murrell JE, Pisegna JL, Juckett LA. Implementation strategies and outcomes for occupational therapy in adult stroke rehabilitation: a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2021;16:105.
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Opra Widerquist MA, Lowery J. Conceptualizing outcomes for use with the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR): the CFIR Outcomes Addendum. Implement Sci. 2022;17:7.
Wensing M, Sales A, Wilson P, Armstrong R, Kislov R, Rankin NM, et al. Implementation Science and Implementation Science Communications: a refreshed description of the journals’ scope and expectations. Implement Sci. 2021;16:103.
Moser RP, Hesse BW, Shaikh AR, Courtney P, Morgan G, Augustson E, et al. Grid-enabled measures. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40:S134–43.
Society for Implementation Research Collaboration. The SIRC Instrument Review Project (IRP) [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 12]. https://societyforimplementationresearchcollaboration.org/sirc-instrument-project/.
Weiner BJ, Lewis CC, Stanick C, Powell BJ, Dorsey CN, Clary AS, et al. Psychometric assessment of three newly developed implementation outcome measures. Implement Sci. 2017;12:108.
Moullin JC, Sklar M, Ehrhart MG, Green A, Aarons GA. Provider REport of Sustainment Scale (PRESS): development and validation of a brief measure of inner context sustainment. Implement Sci. 2021;16.1L:1–10.
Finch TL, Girling M, May CR, Mair FS, Murray E, Treweek S, et al. Improving the normalization of complex interventions: part 2 - validation of the NoMAD instrument for assessing implementation work based on normalization process theory (NPT). BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18:135.
Mettert K, Lewis C, Dorsey C, Halko H, Weiner B. Measuring implementation outcomes: an updated systematic review of measures’ psychometric properties. Implement Res Pract. 2020;1:263348952093664.
Lewis CC, Fischer S, Weiner BJ, Stanick C, Kim M, Martinez RG. Outcomes for implementation science: an enhanced systematic review of instruments using evidence-based rating criteria. Implement Sci. 2015;10:155.
Allen P, Pilar M, Walsh-Bailey C, Hooley C, Mazzucca S, Lewis CC, et al. Quantitative measures of health policy implementation determinants and outcomes: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2020;15.1:1–17.
Khadjesari Z, Boufkhed S, Vitoratou S, Schatte L, Ziemann A, Daskalopoulou C, et al. Implementation outcome instruments for use in physical healthcare settings: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2020;15:66.
Lewis CC, Klasnja P, Powell BJ, Lyon AR, Tuzzio L, Jones S, et al. From classification to causality: advancing understanding of mechanisms of change in implementation science. Front Public Health. 2018;6:136.
Proctor EK, Powell BJ, Baumann AA, Hamilton AM, Santens RL. Writing implementation research grant proposals: ten key ingredients. Implement Sci. 2012;7.1:1–13.
Presseau J, McCleary N, Lorencatto F, Patey AM, Grimshaw JM, Francis JJ. Action, actor, context, target, time (AACTT): a framework for specifying behaviour. Implement Sci. 2019;14:102.
Rudd BN, Davis M, Beidas RS. Integrating implementation science in clinical research to maximize public health impact: a call for the reporting and alignment of implementation strategy use with implementation outcomes in clinical research. Implement Sci. 2020;15.1:1–11.
Nilsen P, Bernhardsson S. Context matters in implementation science: a scoping review of determinant frameworks that describe contextual determinants for implementation outcomes. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19:189.
Meza RD, Triplett NS, Woodard GS, Martin P, Khairuzzaman AN, Jamora G, et al. The relationship between first-level leadership and inner-context and implementation outcomes in behavioral health: a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2021;16:69.
Williams NJ. Multilevel mechanisms of implementation strategies in mental health: integrating theory, research, and practice. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2016;43:783–98.
Waltz TJ, Powell BJ, Fernández ME, Abadie B, Damschroder LJ. Choosing implementation strategies to address contextual barriers: diversity in recommendations and future directions. Implement Sci. 2019;14:1–15.
Lewis CC, Boyd MR, Walsh-Bailey C, Lyon AR, Beidas R, Mittman B, et al. A systematic review of empirical studies examining mechanisms of implementation in health. Implement Sci. 2020;15:1–25.
Motamedi M, Lau AS, Lind T, Lui JH, Rodriguez A, Smith A, et al. What educational strategies and mechanisms facilitate EBP use? A mixed methods examination of therapist perceptions within a system-driven implementation of multiple EBPs. Implement Res Pract. 2021;2:263348952098290.
Lyon AR, Liu FF, Connors EH, King KM, Coifman JI, Cook H, et al. How low can you go? Examining the effects of brief online training and post-training consultation dose on implementation mechanisms and outcomes for measurement-based care. Implement Sci Commun. 2022;3:79.
Kilbourne AM, Geng E, Eshun-Wilson I, Sweeney S, Shelley D, Cohen DJ, et al. How does facilitation in healthcare work? Using mechanism mapping to illuminate the black box of a meta-implementation strategy. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4:53.
Springer MV, Sales AE, Islam N, McBride AC, Landis-Lewis Z, Tupper M, et al. A step toward understanding the mechanism of action of audit and feedback: a qualitative study of implementation strategies. Implement Sci. 2021;16:35.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology: Theory and Practice. 2005;8:19–32.
Marchand K, Beaumont S, Westfall J, MacDonald S, Harrison S, Marsh DC, et al. Patient-centered care for addiction treatment: a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2018:8–12.
Kim B, Weatherly C, Wolk CB, Proctor EK. Measurement of unnecessary psychiatric readmissions: a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2019;9: e030696.
Lengnick-Hall R, Proctor EK, Bunger AC, Gerke DR. Ten years of implementation outcome research: a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2021;11(6):e049339.
Wensing M, Sales A, Aarons GA, Xu D, Wilson P. Evidence for objects of implementation in healthcare: considerations for Implementation Science and Implementation Science Communications. Implement Sci. 2022;17:83.
Bunger AC, Lengnick-Hall R. implementation science and human service organizations research: opportunities and challenges for building on complementary strengths. Hum Serv Organ Manag Research. 2020:32–42.
Lyon AR, Cook CR, Locke J, Davis C, Powell BJ, Waltz TJ. Importance and feasibility of an adapted set of implementation strategies in schools. J Sch Psychol. 2019;76:66–77.
Juckett LA, Bunger AC, Jarrott SE, Dabelko-Schoeny HI, Krok-Schoen J, Poling RM, et al. Determinants of fall prevention guideline implementation in the home- and community-based service setting. Gerontologist. 2021;61:942–53.
Baumann AA, Cabassa LJ. Reframing implementation science to address inequities in healthcare delivery. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20:190.
Becan JE, Bartkowski JP, Knight DK, Wiley TRA, DiClemente R, Ducharme L, et al. A model for rigorously applying the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework in the design and measurement of a large scale collaborative multi-site study. Health Justice. 2018;6:9.
Zielinski MJ, Allison MK, Brinkley-Rubinstein L, Curran G, Zaller ND, Kirchner JAE. Making change happen in criminal justice settings: leveraging implementation science to improve mental health care. Health Justice. 2020;8:21.
Livet M, Blanchard C, Richard C. Readiness as a precursor of early implementation outcomes: an exploratory study in specialty clinics. Implement Sci Commun. 2022;3:94.
Goldberg E, Conte K, Loblay V, Groen S, Persson L, Innes-Hughes C, et al. Scale-up of prevention programmes: sustained state-wide use of programme delivery software is explained by normalised self-organised adoption and non-adoption. Implement Sci. 2022;17:5.
Mugwanya KK, Irungu E, Bukusi E, Mugo NR, Odoyo J, Wamoni E, et al. Scale up of PrEP integrated in public health HIV care clinics: a protocol for a stepped-wedge cluster-randomized rollout in Kenya. Implement Sci. 2018;13:118.
Sherr K, Ásbjörnsdóttir K, Crocker J, Coutinho J, de Fatima CM, Tavede E, et al. Scaling-up the Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach for prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in Mozambique (SAIA-SCALE): a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial. Implement Sci. 2019;14:41.
Nguyen MXB, Chu A v., Powell BJ, Tran H v., Nguyen LH, Dao ATM, et al. Comparing a standard and tailored approach to scaling up an evidence-based intervention for antiretroviral therapy for people who inject drugs in Vietnam: study protocol for a cluster randomized hybrid type III trial. Implementation Sci. 2020;15:64.
Ilott I, Gerrish K, Pownall S, Eltringham S, Booth A. Exploring scale-up, spread, and sustainability: an instrumental case study tracing an innovation to enhance dysphagia care. Implement Sci. 2013;8:128.
Williams CR, Bogdewic S, Owen MD, Srofenyoh EK, Ramaswamy R. A protocol for evaluating a multi-level implementation theory to scale-up obstetric triage in referral hospitals in Ghana. Implement Sci. 2020;15:31.
Vejnoska SF, Mettert K, Lewis CC. Mechanisms of implementation: an appraisal of causal pathways presented at the 5th biennial Society for Implementation Research Collaboration (SIRC) conference. Implement Res Pract. 2022;3:263348952210862.
Sheldrick RC, Breuer DJ, Hassan R, Chan K, Polk DE, Benneyan J. A system dynamics model of clinical decision thresholds for the detection of developmental-behavioral disorders. Implement Sci. 2016;11:156.
Sullivan JL, Yousefi-Nooraie R, D’Arcy D, Levine A, Zimmerman L, Shin MH, et al. Hospital In Home: Evaluating Need and Readiness for Implementation (HENRI) in the Department of Veterans Affairs: protocol for a mixed-methods evaluation and participatory implementation planning study. Implement Sci Commun. 2022;3:93.
Lee H, Hall A, Nathan N, Reilly KL, Seward K, Williams CM, et al. Mechanisms of implementing public health interventions: a pooled causal mediation analysis of randomised trials. Implement Sci. 2018;13:42.
Beidas RS, Dorsey S, Lewis CC, Lyon AR, Powell BJ, Purtle J, et al. Promises and pitfalls in implementation science from the perspective of US-based researchers: learning from a pre-mortem. Implement Sci. 2022;17:55.
Wolfenden L, Foy R, Presseau J, Grimshaw JM, Ivers NM, Powell BJ, et al. Designing and undertaking randomised implementation trials: guide for researchers. BMJ. 2021;m3721.
Coxe-Hyzak KA, Bunger AC, Bogner J, Davis AK, Corrigan JD. Implementing traumatic brain injury screening in behavioral healthcare: protocol for a prospective mixed methods study. Implement Sci Commun. 2022;3:17.
Woodward EN, Matthieu MM, Uchendu US, Rogal S, Kirchner JE. The health equity implementation framework: proposal and preliminary study of hepatitis C virus treatment. Implement Sci. 2019;14:26.
Kerkhoff AD, Farrand E, Marquez C, Cattamanchi A, Handley MA. Addressing health disparities through implementation science—a need to integrate an equity lens from the outset. Implement Sci. 2022;17:13.
Brownson RC, Kumanyika SK, Kreuter MW, Haire-Joshu D. Implementation science should give higher priority to health equity. Implement Sci. 2021;16:28.
Odeny B. Closing the health equity gap: a role for implementation science? PLoS Med. 2021;18: e1003762.
McNulty M, Smith JD, Villamar J, Burnett-Zeigler I, Vermeer W, Benbow N, et al. Implementation research methodologies for achieving scientific equity and health equity. Ethn Dis. 2019;29:83–92.
Proctor EK, Landsverk J, Aarons G, Chambers D, Glisson C, Mittman B. Implementation research in mental health services: an emerging science with conceptual, methodological, and training challenges. Adm Policy Ment Health and Ment Health Serv Res. 2009;36:24–34.
Shelton RC, Chambers DA, Glasgow RE. An extension of RE-AIM to enhance sustainability: addressing dynamic context and promoting health equity over time. Front Public Health. 2020;8:134.
Glasgow RE, Harden SM, Gaglio B, Rabin B, Smith ML, Porter GC, et al. RE-AIM planning and evaluation framework: adapting to new science and practice with a 20-year review. Front Public Health. 2019;7:64.
Shelton RC, Adsul P, Oh A, Moise N, Griffith DM. Application of an antiracism lens in the field of implementation science (IS): recommendations for reframing implementation research with a focus on justice and racial equity. Implement Res Pract. 2021;2:263348952110494.
Aarons GA. Reviews of attitude research in implementation science require comprehensiveness, accuracy, and specificity. Implement Sci. 2022;17:28.
Lengnick-Hall R, Gerke DR, Proctor EK, Bunger AC, Phillips RJ, Martin JK, et al. Six practical recommendations for improved implementation outcomes reporting. Implement Sci. 2022;17:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-021-01183-3.
Proctor E, Ramsey AT, Saldana L, Maddox TM, Chambers DA, Brownson RC. FAST: a framework to assess speed of translation of health innovations to practice and policy. Global Implementation Research and Applications. 2022;2:107–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43477-022-00045.
Quanbeck A, Hennessy RG, Park L. Applying concepts from “rapid” and “agile” implementation to advance implementation research. Implement Sci Commun. 2022;3:118.
Lyon AR, Bruns EJ. User-Centered Redesign of Evidence-Based Psychosocial Interventions to Enhance Implementation—Hospitable Soil or Better Seeds? JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(1):3–4. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3060.
Funding
Dr. Proctor is supported by NIH grants R25 MH0809, P50CA19006, and P50MH113660. Dr. Bunger receives support from the National Institute of Health (R34DA046913). Dr. Lengnick-Hall is funded by NIMH P50MH113662. Additionally, Drs. Lengnick-Hall and Bunger are alumni, and Dr. Proctor is the core faculty with the Implementation Research Institute (IRI), at the George Warren Brown School of Social Work, Washington University in St. Louis; through an award from the National Institute of Mental Health (R25 MH080916–08). The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EP: conceptualization; methodology; formal analysis; investigation; data curation; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing; and supervision. AB: methodology; formal analysis; investigation; data curation; writing—review and editing; and administration. RL-H: conceptualization; investigation; data curation; writing—original draft; and writing–review and editing. DRG: investigation; data curation writing—original draft; and writing–review and editing. RJP: investigation and data curation writing—review and editing. JKM: investigation, data curation, and writing—review and editing. JCS: investigation, data curation, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval and consent are not applicable for the current manuscript because we did not collect any human subject data.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: The incorrect citation and missing reference have been corrected.
The original version of this article was revised: There was a mislabeled figure in the section entitled 'Conceptualization of implementation outcomes in the 2011 paper'.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Proctor, E.K., Bunger, A.C., Lengnick-Hall, R. et al. Ten years of implementation outcomes research: a scoping review. Implementation Sci 18, 31 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-023-01286-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-023-01286-z