Abstract
Background
Breastfeeding is widely recognized for its potential to reduce childhood obesity. However, research investigating these benefits in children breastfed for a short duration (up to 6 months) remains limited despite this being a common practice globally.
Methods
This study focused on a population breastfed for 6 months or less to determine the potential benefits of short-term breastfeeding for preventing childhood obesity. Data were collected from five survey cycles of an US-based population study (the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES)), spanning 2009–2020. A sample of 3,211 children aged 2–6 years was selected, including 1,373 never breastfed and 1,838 ever breastfed. Logistic regression analysis examined the direct association between short-term breastfeeding and childhood obesity. Subsequent subgroup analyses were conducted. Additionally, stratified logistic regression explored the relationship between childhood obesity and the introduction of other early nutrition in both ever-breastfed and never-breastfed children.
Results
Overall, breastfeeding for 6 months or less did not directly prevent childhood obesity. However, among participants with older mothers (aged 35 or above), short-term breastfeeding was associated with a lower risk of childhood obesity compared to never being breastfed (OR 0.31, 95% CI: 0.17, 0.59). Similarly, children aged 3–4 years who were breastfed for > 3 ~ 6 months exhibited a lower obesity risk (OR 0.56, 95% CI: 0.35, 0.89). In ever-breastfed children, delayed infant formula introduction was linked to a lower risk of obesity (P-trend < 0.05: introduction at age ≤ 1 vs. >1 ~ 3 vs. >3 months). Conversely, for non-breastfed children, introducing milk (other than breast milk or formula) later (≥ 12 versus < 12 months) and introducing alternatives to whole cow’s milk were associated with lower obesity risks (OR 0.54, 95% CI: 0.37, 0.78; OR 0.21, 95% CI: 0.08, 0.60, respectively). Notably, these trends were not observed in ever-breastfed children.
Conclusions
Short-term breastfeeding may offer some benefits in preventing childhood obesity for specific populations. Additionally, it could potentially mitigate risks associated with the introduction of formula and cow’s milk at inappropriate times.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Childhood obesity poses a significant public health challenge worldwide. Its prevalence can reach as high as 18.4% in certain countries. Furthermore, childhood obesity often persists into adulthood and is widely recognized as a risk factor for cardiometabolic problems such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes [1]. Therefore, preventing childhood obesity is critical for promoting lifelong health. Early-life nutrition, particularly breastfeeding, has emerged as a key factor in childhood obesity prevention. Numerous studies consistently report a modest association between breastfeeding and a reduced risk of obesity later in childhood and adulthood [2,3,4]. Cross-national analyses further suggest that countries with higher rates and longer durations of breastfeeding tend to have lower obesity prevalence [5, 6]. The importance of breastfeeding in early childhood is further emphasized by the World Health Organization (WHO) Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity [7].
While recent research [8,9,10,11,12,13] underscores the positive influence of breastfeeding on childhood obesity, prior studies have primarily focused on breastfeeding durations exceeding six months, sometimes even exceeding a year. Additionally, past research often emphasized exclusive breastfeeding for at least six months. However, it is well-documented that over 30% of mothers discontinue breastfeeding within the first six months due to various factors [8, 10, 14,15,16,17]. Therefore, further investigation into the effects of breastfeeding for durations of six months or less on childhood obesity is warranted.
This study aimed to examine the association between breastfeeding duration of up to six months and childhood obesity in the United States. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) was utilized to assess the potential benefits of short-term breastfeeding for reducing childhood obesity. The findings of this study will contribute to the existing body of evidence regarding the importance of breastfeeding, even for durations of six months or less.
Methods
Study design and population
This study utilized data from the NHANES, an ongoing program established in the early 1960s to assess the health and nutritional status of the U.S. population. NHANES employs a unique, nationally representative sampling design, ensuring its findings are generalizable to the entire country. The program consists of sequential cross-sectional surveys, and publicly available data include demographics, dietary habits, physical examinations, laboratory results, and health-related questionnaires. More details about the NHANES survey design can be found at the official website [18]. Data from five NHANES survey cycles spanning 2009–2020 (pre-pandemic) were included (2009–2010, 2011–2012, 2013–2014, 2015–2016, and 2017-March 2020). The target population for this study comprised children aged 2 to less than 7 years. This age range was chosen due to the low prevalence of breastfeeding beyond age 2 and the lack of data on breastfeeding practices in children aged 7 or older. Since the questionnaires did not permit precise differentiation between breastfeeding durations of less than 6 months and exactly 6 months, the final sample included children who breastfed for no more than 6 months. A total of 3,211 participants were included, representing an estimated national sample size of 10,056,207 children across the combined survey cycles (Fig. 1).
Assessment of obesity and breastfeeding duration
Childhood obesity and normal weight (control group) were determined using age- and sex-specific body mass index (BMI) percentiles as established by the 2000 CDC growth charts [19]. Details regarding the specific BMI percentiles used for classification can be found at the official website [20]. Information on breastfeeding duration was collected from child proxies via interviews or questionnaires, specifically using the question item “Age stopped breastfeeding (days)”. This data was then categorized into two groups: never breastfed and ever breastfed for up to six months. The ever-breastfed group was further subdivided into those breastfed for three months or less (≤ 3 months) and those breastfed for more than three months but no more than six months (> 3 ~ 6 months).
Covariates
This study incorporated covariates that prior research has identified as potential confounders influencing the association between breastfeeding and childhood obesity [3, 8, 14, 16, 21,22,23]. Covariates were included if missing data was less than or equal to 20%. These covariates included child’s gender, age at screening (categorical), race/ethnicity, family income-to-poverty ratio (used to estimate socioeconomic status; categorized as < 1.85, 1.85 ~ 3.5, or > 3.5) [24], mother’s smoking status during pregnancy (ever/never), maternal age at child’s birth (< 20, 20 ~ 34, ≥ 35 years), and birth weight (< 2.5 kg, 2.5 ~ < 4 kg, ≥ 4 kg). While the gender of the household reference person (male/female) was hypothesized to potentially modify the breastfeeding-obesity association, this information was missing in the 2017-March 2020 pre-pandemic cycle, resulting in significant data loss across the pooled data. Therefore, this variable was only considered in a single subgroup analysis with a detailed explanation provided.
To investigate the influence of infant formula and milk (other than breast milk or formula) introduction on childhood obesity, this analysis incorporated three additional covariates regarding early nutrition. The first covariate, categorized as ≤ 1 month, > 1 ~ 3 months, and > 3 months, captured the age at which the formula was first introduced (formula-introducing age). The second covariate, categorized as < 12 months and ≥ 12 months, examined the age of the first milk introduction (milk-introducing age). Finally, the third covariate, categorized as whole cow milk, reduced cow milk, and other milk (e.g., soy milk), investigated the type of milk first introduced (milk-introducing type).
It is important to acknowledge that the NHANES data used in this study may have limitations regarding the assessment of breastfeeding practices. Since 2009, the NHANES survey instruments have de-emphasized the concept of exclusive breastfeeding. Additionally, while the questionnaires collect information on the age of the first introduction of other foods alongside breastfeeding duration data, they lack details on the specific proportions of different food components consumed during mixed feeding periods. Therefore, due to these limitations, our study methodology and conclusions do not incorporate terms such as “exclusive breastfeeding” or “mixed feeding”. While some information bias may be unavoidable, we have strived to provide the most accurate interpretation of the available data.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using STATA software (version 16; StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX, USA). All analyses accounted for the complex, multistage sampling design of the NHANES data and incorporated sample weights to ensure generalizability. Missing data for covariates were addressed using multiple imputations with five imputations and a chained equation approach. Weighted descriptive statistics were calculated and stratified by somatotype (body type) for breastfeeding and all covariates. Subsequently, univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed, followed by subgroup analyses, to examine the associations between short-term breastfeeding and childhood obesity. To further explore the potential benefits of short-term breastfeeding, a stratified logistic regression analysis was conducted, examining the associations between childhood obesity and the introduction of other early nutrition in both ever-breastfed and never-breastfed children. Odds ratios (OR) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) were used to estimate the strength and precision of these associations. Statistical significance was set at a two-tailed P < 0.05.
Results
Breastfeeding duration among the total population
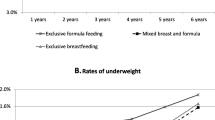
Analyses of the 4,842 children with available breastfeeding data revealed a trend towards lower breastfeeding prevalence among children ever diagnosed with obesity. Within the entire sample, 23.89% of children had never been breastfed. Furthermore, a substantial proportion (37.39%) of children discontinued breastfeeding within the first 6 months, and a significant percentage (23.52%) stopped breastfeeding even within the first 3 months (Fig. 2).
Proportion of children breastfed by age and weight status. a With increasing age (months), a lower proportion of children with obesity were ever breastfed compared to children with normal weight. b A significant percentage of participants were never breastfed or breastfed for no more than 6 months (≤ 3 months and > 3 ~ 6 months). Children who were underweight (BMI < 5th percentile according to the 2000 CDC growth charts [19]) or overweight (BMI 85th to < 95th percentiles) were not shown in the figure, since the present study focused only on obesity (BMI ≥ 95th percentile), compared with normal weight (BMI 5th to < 85th percentiles)
Characteristics of children in the final sample
The final analysis included 3,211 participants, representing a weighted national sample of 10,056,207 children aged 2–6 years across the United States. Significant differences (P < 0.05) in somatotype (body type) distribution were observed across participants with varying characteristics, including age, race/ethnicity, household socioeconomic status (measured by family income-to-poverty ratio), and birth weight. However, no significant differences (P > 0.05) were found between the obesity and normal weight groups for breastfeeding status, gender, gender of household reference person, mother’s smoking history during pregnancy, or maternal age at birth (Table 1).
Associations between breastfeeding and childhood obesity in the final population and sub-populations
Following data preparation, the initial analysis examined the direct association between short-term breastfeeding (≤ 6 months) and childhood obesity. However, no significant effect of breastfeeding experience on childhood obesity was detected, either in the unadjusted model or in the multivariable model adjusted for potential confounding variables, including gender, age, race/ethnicity, family income-to-poverty ratio, mother’s smoking history during pregnancy, maternal age at birth, and birth weight (Table 2).
Subgroup analyses using multivariate regressions were conducted to further investigate the potential protective effect of short-term breastfeeding against childhood obesity. These analyses revealed that short-term breastfeeding was associated with a lower risk of childhood obesity in children born to mothers aged 35 years or older at delivery (compared to never being breastfed). Specifically, the OR for childhood obesity was 0.44 (95% CI: 0.22, 0.91) for breastfeeding duration ≤ 3 months and 0.15 (95% CI: 0.07, 0.33) for breastfeeding durations > 3 ~ 6 months (P-trend < 0.001). Additionally, in the subgroup with a female household reference person, breastfeeding was associated with a protective effect against childhood obesity. Children breastfed for more than 3 months (compared to never being breastfed) had an OR of 0.61 (95% CI: 0.40, 0.94) for childhood obesity (P-trend < 0.05) (Table 3).
Analyses revealed an interaction between breastfeeding duration and age in their associations with childhood obesity (Figure S1). While the overall incidence of obesity increased with age across the entire population (regardless of breastfeeding duration), this trend differed significantly between subgroups defined by breastfeeding duration (less than or exceeding 6 months). In this respect, children who breastfed for longer durations exhibited a slower rise in childhood obesity risk with increasing age. To further investigate this interaction, age was incorporated as a stratification variable in the final analysis, focusing on the subpopulation with breastfeeding durations of no more than 6 months. As shown in Table 4, children aged 3–4 years who had ever breastfed for > 3 ~ 6 months (compared to those never breastfed) demonstrated a protective effect against childhood obesity (OR 0.56, 95% CI: 0.35, 0.89, P-trend < 0.05).
Breastfed experience on the associations between childhood obesity and the introduction of other early nutrition including formula and milk
Formula and milk (other than breast milk or formula, e.g., cow’s milk) are commonly introduced as substitutes or complements to breastmilk during early childhood. These early nutrition sources can play a significant role in children’s growth and development. In this study, breastfeeding experience (ever vs. never breastfed) was used as a stratification variable to examine the association between childhood obesity and the timing of formula and milk introduction. The analysis of formula introduction age excluded the never-breastfed group, as these children typically received formula from birth. Within the ever-breastfed group, later introduction of formula (i.e., at an older age) was associated with a lower risk of childhood obesity. Specifically, compared to children introduced to the formula at ≤ 1 month of age, those introduced at > 3 months had an OR of 0.64 (95% CI: 0.45, 0.91) for obesity, with a statistically significant trend (P-trend < 0.05) observed in the adjusted model.
The findings regarding the timing and type of milk introduction differed by breastfeeding status. Among children who were never breastfed, the later introduction of milk (≥ 12 months old) was associated with a lower risk of childhood obesity compared to earlier introduction (< 12 months old) (OR 0.54, 95% CI: 0.37, 0.78). However, this association was not statistically significant (confidence interval crossed 1.0) among children with any breastfeeding experience. A similar pattern emerged for the type of milk first introduced. In the never-breastfed group, children who received milk other than whole or reduced-fat milk (e.g., soy milk) as their first milk had a lower risk of obesity compared to those initially fed whole milk (OR 0.21, 95% CI: 0.08, 0.60). Importantly, this association was not observed among children with any history of breastfeeding (Table 5).
Stratified analyses were also conducted within the subgroup of children who were breastfed for no more than 3 months to examine the associations between age and type of first milk introduction with childhood obesity. Similar to the overall analysis of ever-breastfed children, these analyses revealed no significant associations between the timing or type of milk introduction and childhood obesity risk within this subgroup (Table S1).
Discussion
This study investigated the potential protective effects of short-term breastfeeding (lasting no more than 6 months) against childhood obesity. Our analyses revealed that, within the overall population in the present study, short-term breastfeeding did not demonstrate a significant direct association with a reduced risk of childhood obesity. However, the study identified that short-term breastfeeding exhibited some protective benefits in specific subpopulations, particularly among children born to mothers 35 years or older at the time of delivery. Furthermore, the study revealed that short-term breastfeeding experience interacted with the timing of formula and milk introduction, potentially modifying the associations between these early nutrition practices and childhood obesity risk.
Breastfeeding is recognized as one of the most effective strategies for ensuring child survival and overall health. It has been hypothesized to protect against childhood obesity through several potential mechanisms. Firstly, breastfeeding may promote the development of a healthy gut microbiota profile, which has been linked to a lower risk of obesity [25]. Secondly, it is highly conceivable that breastfeeding may mitigate the genetic influence on obesity development, potentially through DNA methylation mechanisms [11, 26]. Thirdly, breastfeeding is often associated with the adoption of healthier dietary patterns in children, which plays a crucial role in obesity prevention [27, 28]. While some previous epidemiological studies conducted in the past few decades raised concerns that observed associations between breastfeeding and reduced obesity risk might be due to residual confounding factors rather than a direct causal effect [23, 29], a growing body of recent research reaffirms the potential benefits of breastfeeding against obesity. A recent meta-analysis of 159 studies concluded that breastfeeding indeed reduces the odds of childhood obesity and that this effect is unlikely to be attributable to publication bias or residual confounding [9].
Previous studies investigating the protective effects of breastfeeding against childhood obesity often relied on comparisons between individuals with no breastfeeding experience or minimal breastfeeding duration (less than 6 months) and those breastfed for longer periods (e.g., exceeding 6 or even 12 months). Several studies suggest that certain benefits may only become evident when exclusive breastfeeding is sustained for more than 6 months [2, 8,9,10, 30,31,32]. However, despite WHO recommendations for exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months followed by continued breastfeeding for at least the first 2 years of life [33], this study using NHANES data found a substantial proportion (37.39%) of children discontinued breastfeeding within the first 6 months. This early termination rate aligns with findings from prior research [8, 10, 15,16,17]. Furthermore, an even higher proportion of participants in our study did not achieve exclusive breastfeeding for more than 6 months. In this context, the analyses of both the childhood obesity distribution and adjusted regression models did not detect a direct protective effect of breastfeeding against childhood obesity for these children.
While the present study did not observe a significant direct association between short-term breastfeeding (less than 6 months) and a reduced risk of childhood obesity in the overall population, it is important to consider the limitations of this categorical analysis approach. Several studies suggest a dose-dependent protective effect of breastfeeding duration, with some benefits potentially arising even from limited breastfeeding periods. For example, Li et al. [3] reported a decreasing trend in childhood obesity prevalence across groups transitioning from exclusive formula feeding to mixed feeding and then to exclusive breastfeeding, regardless of the specific proportion of breast milk in mixed feeding. This suggests a possible continuous, dose-dependent effect of breastfeeding on obesity risk. Similarly, Qiao et al. [2] employed a dose-response meta-analysis model and found that each additional month of breastfeeding was associated with an average 4% reduction in childhood obesity risk. While our subgroup analysis of the short-term breastfeeding group did not confirm a statistically significant effect using a categorical approach, these findings suggest that the potential benefit of short-term breastfeeding might be present but statistically masked or difficult to detect in our study. This possibility is further supported by the observation that the later introduction of the formula was associated with a lower risk of childhood obesity within the ever-breastfed subgroup, since later formula introduction suggests longer exclusive breastfeeding duration during early infancy. After all, breast milk and formula are the primary sources of nutrition in early life [34]. Our study also hints at potential effect modification by maternal age and household reference person gender. Furthermore, the observed trends in obesity incidence across age groups suggest that breastfeeding may be associated with a delayed onset of childhood obesity. Specifically, short-term breastfeeding duration was significantly associated with a lower obesity incidence in the 3-4-year-old age group, which aligns with findings from previous research [3]. These observations warrant further investigation using more comprehensive analytic approaches to explore potential dose-dependent effect and modification effects of short-term breastfeeding on childhood obesity risk.
The introduction of cow’s milk (regular milk) before 1 year of age is generally discouraged by some scientific society (e.g., American Academy of Pediatrics) due to its improper nutrient composition for infancy growth [35]. Soczynska et al. [36] reported no significant association between the timing of cow’s milk introduction and adiposity in children aged 3–5 years, which aligns with the preliminary findings of this study. However, our further analyses were conducted within subgroups defined by breastfeeding status (ever vs. never breastfed) among participants who had ever breastfed for ≤ 6 months. Interestingly, the earlier introduction of milk was associated with an adverse effect on children who were never breastfed, as evidenced by an increased risk of childhood obesity. This effect was not observed among children with any history of breastfeeding. These findings suggest that even a short duration of breastfeeding experience (≤ 6 months) may potentially mitigate the negative consequences of early milk introduction on childhood obesity risk. One possible explanation for this interaction is that the early introduction of cow’s milk might indeed promote a tendency towards childhood obesity. However, the experience of being breastfed, even for a short period, could potentially counteract this negative influence through various mechanisms, as discussed previously. These mechanisms may involve modifications to the gut microbiota profile, epigenetic regulation of gene expression, and the development of healthier eating behaviors. This study underscores the potential protective role of breastfeeding, even for relatively short durations, in the context of early milk introduction and its potential impact on childhood obesity risk.
This study offers several strengths and advantages. To our knowledge, it provides hitherto undocumented evidence of the potential benefits of short-term breastfeeding (lasting no more than 6 months) in protecting against childhood obesity within specific population subgroup. The findings provide valuable insights into the feeding patterns of children who breastfeed for ≤ 6 months. Additionally, the study leverages data from the NHANES, which offers a nationally representative sample, thus enhancing the generalizability of the results to the broader population. However, it is important to acknowledge certain limitations inherent to the study design. Firstly, the cross-sectional nature of NHANES data restricts our ability to establish a causal relationship between short-term breastfeeding (≤ 6 months) and a reduced risk of childhood obesity. Secondly, while the analyses adjusted for potential confounding variables, the possibility of residual confounding cannot be entirely eliminated. For example, factors such as maternal body mass index and gestational age at birth, which might influence childhood obesity risk, were not available in the dataset and could introduce unaccounted-for confounding effects. Lastly, the study is susceptible to recall bias, as data on early childhood nutrition were collected through questionnaires that rely on participants’ memory of events, potentially years in the past. To address these limitations and provide more robust evidence, future research efforts could benefit from large, prospective studies employing a longitudinal design. This approach would enable the collection of data over time and the establishment of stronger causal inferences.
Conclusions
This study investigated the potential protective effects of short-term breastfeeding (lasting no more than 6 months) against childhood obesity. Our analyses revealed that, within the overall population, there was no evidence of an association between short-term breastfeeding and a reduced risk of childhood obesity. However, the study also identified that short-term breastfeeding may offer some protective benefits in specific subpopulations, such as children born to mothers 35 years or older at the time of delivery. Additionally, the study suggests that short-term breastfeeding experience may interact with the timing of formula and cow’s milk introduction, potentially mitigating the negative consequences of early introduction on childhood obesity risk.
Data availability
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is available in the NHANES at https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm.
Abbreviations
- 95%CI:
-
Confidence intervals
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- HRP gender:
-
Gender of household reference person
- NHANES:
-
The project of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Smith JD, Fu E, Kobayashi MA. Prevention and management of childhood obesity and its psychological and health comorbidities. Annu Rev Clin Psycho. 2020;16:351–78. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-100219-060201.
Qiao J, Dai L, Zhang Q, Ouyang Y. A meta-analysis of the association between breastfeeding and early childhood obesity. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020;53:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2020.04.024.
Li W, Yuan J, Wang L, Qiao Y, Liu E, Wang S, et al. The association between breastfeeding and childhood obesity/underweight: a population-based birth cohort study with repeated measured data. Int Breastfeed J. 2022;17:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-022-00522-4.
Patro-Gołąb B, Zalewski BM, Kołodziej M, Kouwenhoven S, Poston L, Godfrey KM, et al. Nutritional interventions or exposures in infants and children aged up to 3 years and their effects on subsequent risk of overweight, obesity and body fat: a systematic review of systematic reviews. Obes Rev. 2016;17(12):1245–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12476.
Rito AI, Buoncristiano M, Spinelli A, Salanave B, Kunešová M, Hejgaard T, et al. Association between characteristics at birth, breastfeeding and obesity in 22 countries: the WHO European childhood obesity Surveillance Initiative - COSI 2015/2017. Obes Facts. 2019;12(2):226–43. https://doi.org/10.1159/000500425.
Wickramasinghe K, Chatterjee S, Williams J, Weber MW, Rito AI, Rippin H, et al. Childhood overweight and obesity abatement policies in Europe. Obes Rev. 2021;22(Suppl 6):e13300. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13300.
World Health Organization. Report of the commission on ending childhood obesity. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241510066. Accessed 20 July 2023.
Hildebrand JS, Ferguson PL, Sciscione AC, Grobman WA, Newman RB, Tita AT, et al. Breastfeeding associations with childhood obesity and body composition: findings from a racially diverse maternal-child cohort. Child Obes. 2022;18(3):178–87. https://doi.org/10.1089/chi.2021.0138.
Horta BL, Rollins N, Dias MS, Garcez V, Pérez Escamilla R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of breastfeeding and later overweight or obesity expands on previous study for World Health Organization. Acta Paediatr. 2023;112(1):34–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.16460.
Houle B, Rochat TJ, Newell M, Stein A, Bland RM, Breastfeeding. HIV exposure, childhood obesity, and prehypertension: a South African cohort study. PLoS Med. 2019;16(8):e1002889.
Briollais L, Rustand D, Allard C, et al. DNA methylation mediates the association between breastfeeding and early-life growth trajectories. Clin Epigenetics. 2021;13(1):231. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002889.
Blair A, MacGregor E, Lee N. Childhood obesity and breastfeeding rates in pennsylvania counties-spatial analysis of the lactation support landscape. Front Public Health. 2020;8:123. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00123.
Pena-Leon V, Folgueira C, Barja-Fernández S, Pérez-Lois R, Da Silva Lima N, Martin M, et al. Prolonged breastfeeding protects from obesity by hypothalamic action of hepatic FGF21. Nat Metab. 2022;4(7):901–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-022-00602-z.
Ma J, Qiao Y, Zhao P, Li W, Katzmarzyk PT, Chaput JP, et al. Breastfeeding and childhood obesity: a 12-country study. Matern Child Nutr. 2020;16(3):e12984. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12984.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.). Breastfeeding Report Card. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/data/reportcard.htm. Accessed 22 July 2023.
Dang J, Chen T, Ma N, Liu Y, Zhong P, Shi D, et al. Associations between breastfeeding duration and obesity phenotypes and the offsetting effect of a healthy lifestyle. Nutrients. 2022;14(10):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14101999.
Tomori C. Overcoming barriers to breastfeeding. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;83:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2022.01.010.
NHANES - National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Homepage. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm. Accessed 14 Feb 2023.
Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer-Strawn LM, Flegal KM, Mei Z, et al. CDC Growth Charts for the United States: methods and development. Vital Health Stat 11. 2000;2002(246):1–190.
NHANES 2013–2014. Body Measures Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/BMX_H.htm. Accessed 16 Feb 2023.
Lackey KA, Fehrenkamp BD, Pace RM, Williams JE, Meehan CL, McGuire MA, et al. Breastfeeding beyond 12 months: is there evidence for health impacts? Annu Rev Nutr. 2021;41:283–308. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-043020-011242.
Azad MB, Vehling L, Chan D, Klopp A, Nickel NC, McGavock JM, et al. Infant feeding and weight gain: separating breast milk from breastfeeding and formula from food. Pediatrics. 2018;142(4):e20181092. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2018-1092.
Lefebvre CM, John RM. The effect of breastfeeding on childhood overweight and obesity: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract. 2014;26(7):386–401. https://doi.org/10.1002/2327-6924.12036.
National Center for Statistics (U.S.). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: Analytic Guidelines, 1999–2010. 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/analyticguidelines/99-10-analytic-guidelines.pdf. Accessed 21 March 2023.
Petraroli M, Castellone E, Patianna V, Esposito S. Gut microbiota and obesity in adults and children: the state of the art. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:657020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.657020.
Horta BL, Victora CG, França GVA, Hartwig FP, Ong KK, Rolfe EL, et al. Breastfeeding moderates FTO related adiposity: a birth cohort study with 30 years of follow-up. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2530. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20939-4.
Specht IO, Rohde JF, Olsen NJ, Heitmann BL. Duration of exclusive breastfeeding may be related to eating behaviour and dietary intake in obesity prone normal weight young children. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(7):e0200388. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200388.
Kim K, Shin M. Feeding characteristics in infancy affect fruit and vegetable consumption and dietary variety in early childhood. Nutr Res Pract. 2023;17(2):307–15. https://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2023.17.2.307.
Smithers LG, Kramer MS, Lynch JW. Effects of breastfeeding on obesity and intelligence: causal insights from different study designs. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(8):707–8. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.0175.
Liu F, Lv D, Wang L, Feng X, Zhang R, Liu W, et al. Breastfeeding and overweight/obesity among children and adolescents: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2022;22:347. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-022-03394-z.
Odusanya AO, Reid KS, Amutah-Onukagha N, Robinson K, Kalu OU, Lawrence WR, et al. Association between sociodemographic characteristics and age stopped breastfeeding on early childhood weight status. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2022;16(3):214–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2022.05.001.
Song Q, Yang Y, Liu X, Yang C, Huang X, Zhou H, et al. Breastfeeding practices and overweight/obesity among children under 5 years of age: a multistage random sampling survey in central and western China. Matern Child Health J. 2020;24(8):998–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-020-02945-z.
World Health Organization. Breastfeeding. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/breastfeeding#tab=tab_2. Accessed 7 August 2023.
Ibrahim C, Bookari K, Sacre Y, Hanna-Wakim L, Hoteit M. Breastfeeding practices, infant formula use, complementary feeding and childhood malnutrition: an updated overview of the eastern mediterranean landscape. Nutrients. 2022;14(19):4201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194201.
Bailey RL, Stang JS, Davis TA, Naimi TS, Schneeman BO, Dewey KG, et al. Dietary and complementary feeding practices of US infants, 6 to 12 months: a narrative review of the federal nutrition monitoring data. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2022;122(12):2337–e451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2021.10.017.
Soczynska I, Dai D, O’Connor DL, Birken CS, Maguire JL. TARGet kids! Collaboration. Age of cow milk introduction and growth among 3-5-year-old children. Public Health Nutr. 2021;24(16):5436–42. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980020001925.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the NHANES for providing data freely as well as the participants who kindly participated in this project. We would also like to thank Home for Researchers editorial team (www.home-for-researchers.com) for the language editing service.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No.2021YFC2700700), the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No.2022C03058), Medical and Health Technology Program of Zhejiang Province (WKJ-ZJ-2324) and 4 + X Clinical Research of Women’s Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine (ZDFY2022-4XB101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Menglin Zhou and Zhaoxia Liang conceived the study. Menglin Zhou, Luyao Hu, Fan Li, and Jie Wen analyzed the data. Danqing Chen supervised the study. All authors were involved in writing the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The NHANES study protocols were approved by the National Center for Health Statistics institutional review board, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants or legal proxies before any data collection. All data retrieval processes and analyses were conducted in accordance with the guidelines outlined on the NHANES website (https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it.The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Hu, L., Li, F. et al. Beneficial effects of short-term breastfeeding versus non-breastfeeding in early life against childhood obesity: findings from the US-based population study NHANES. Int Breastfeed J 19, 56 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-024-00659-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-024-00659-4