Abstract
Shared decision-making (SDM) is a process in which the doctor provides clear and complete medical information to patients about their treatment, and patients provide information on his/her preferences. Patients and clinicians bring different, but equally important, knowledge to the decision-making process. Through the adoption of SDM, it should be possible to overcome the barriers that hinder the acceptance of long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) by patients, and often also by psychiatrists. The present paper is a critical appraisal of recent literature on the impact of SDM in improving adherence to pharmacological treatments and in implementing the use of LAIs in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. SDM is recognized as a promising strategy to improve collaboration between clinicians and patients in achieving recovery. When considering drug treatments, clinicians must evaluate the patient’s preferences, expectations and concerns towards the development of a personalized treatment strategy. Moreover, an active involvement in the decision process could reduce the patient’s perception of being coerced into the use of LAIs. Involving patients in the choice of therapy is not sufficient to increase pharmacological adherence if, at the same time, there is no constant work of comparison and communication with the reference psychiatric team. SDM can be particularly effective for LAI prescription, since patient can have prejudices and unjustified fears related to the LAI formulation, which the doctor must resolve.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Background
In accordance with its most common acceptation, clinical decision-making has been traditionally practiced as a one-way evidence-based process on behalf of the clinicians alone: a “contextual, continuous, and evolving process where data are gathered, interpreted, and evaluated by the clinician in order to select an evidence-based choice of action” [1]. In recent years, the process has been gradually remodeled to become a more patient-inclusive approach letting the voice of those directly affected by the decisions to be heard [2]. In such spirit, the clinician empowers the patient to take part on his/her own treatment strategy by providing the patient clear and exhaustive medical information, while listening to the patient’s preferences and priorities and facilitating the patient’s evaluations towards a balanced reasoned decision. It is a negotiation between the clinician and patient taking place for achieving a shared decision [3].
In the general medical setting, the type of decision-making is influenced by the balance achieved in the clinician–patients relationship and positions itself along a continuum, ranging from the paternalistic (clinician-led or passive style), through shared decision-making (SDM), up to the patient-led active style (also known as informed style) [4]. The unfolding and outcomes of such process depend on the variables informing the process related to: (a) the patients, and their personal attitudes/preferences, cognitive symptoms, levels of self-stigma; (b) the healthcare professionals, in terms of years of professional experience and professional role [5]; (c) contextual and unspecific factors, such as communication skills (verbal and non-verbal behaviors), setting, therapeutic alliance, and others [1, 6].
With specific reference to the SDM style, studies have demonstrated that it has a positive impact on the patient’s levels of satisfaction and adherence to treatments, as well as on his/her quality of life and empowerment [7]. This has been especially highlighted in the case of patients with severe mental disorders who report a greater desire of being involved in clinical decision-making and a need to have a say in the process of care, as compared to individuals receiving assistance for other medical conditions [8,9,10,11]. Patients and clinicians bring different—but equally important—knowledge and expertise to the decision process, which need to be integrated [12]. When patients are involved in choices about their own health and care, they ponder options carefully and are most likely to appreciate the value of proposed treatment, to agree to treatment with a favorable attitude. In fact, shared process has proven to increase adherence to the prescribed treatment and improve long-term outcomes. Furthermore, this has also translated in more efficient allocation of healthcare resources [13,14,15].
These latter aspects related to adherence are especially relevant in the setting of schizophrenia and psychotic disorders, where adherence to pharmacological treatments is frequently far from optimal and represents the main cause of relapse [16,17,18] and hospitalizations [19, 20]. The advent of new long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) had appeared to overcome the issue of poor adherence [21,22,23,24], but did not solve the widespread lack of adherence, as these drugs still remain largely underutilized. Currently, a number of studies have proven the effectiveness, safety and tolerability of LAIs [25], yet recommendations on their use in the clinical routine care differ from one guideline to another, and their current use is still limited despite their proved efficacy on long-term patient management [26]. In some cases, the use of LAIs is recommended only for patients with frequent relapses and/or poor adherence [27] and for those preferring LAIs over oral therapy [28]. The Canadian Schizophrenia Guidelines suggest that early use of LAIs in the management of schizophrenia should be advocated, without limiting its use to those patients for whom non-adherence is a concern [26]. Moreover, only the French Association for Biological Psychiatry and Neuropsychopharmacology expert consensus guidelines propose LAIs to patients upon their first episode of psychosis and only after an adequate patient-informed consensus [29]. In the United States only 15–28% of patients with schizophrenia receive a LAI [30, 31]. In Europe only 40% of clinicians would use LAIs for treating first-episode psychosis [32], while a large portion of them tend to use LAIs only in the case of patients with long-term disease and poor compliance [33, 34]. Finally, the routine use of LAIs is delayed by other issues such as the patients’ attitude towards the drug (the fear of needles or of side-effects), the perception that LAIs are imposed on them in a punitive and coercive manner, or as result of a previous negative experience with LAIs, or in consideration of the negative perception of LAIs by their family members. Resolving such resistances hence could lead to more patients benefitting from LAIs.
In such scenario, SDM is certainly an interesting approach to achieve greater knowledge of LAIs and acceptance on behalf of patients and families [35, 36]. Although SDM has been repeatedly advocated as the preferred style in routine clinical practice, its dissemination in ordinary settings is not satisfying. According to the CEDAR multicenter study, SDM is adopted only when patients present a good level of personal and social functioning and when professionals have a long-term experience in working in the mental health field [5]. It is thus necessary to develop strategies for improving the adoption of SDM in clinical routine care.
The present clinical review aims to provide an update on the available interventions for improving SDM in routine care and to discuss the positive role of SDM style in improving adherence to pharmacological treatments and in the definition of a personalized treatment plan for patients with schizophrenia, particularly in switching pharmacological regimen from oral to LAI formulations.
Methods
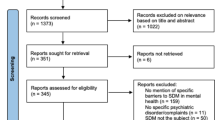
The present review was based on search of key words “shared decision making”, “intervention”, “schizophrenia”, “psychosis”, “schizophrenia spectrum disorder” matched with “adherence”, “intervention”, “training”, “long-acting injectable antipsychotic”, “LAI” in the main databases MEDLINE, ISI Web of Knowledge—Web of Science Index, Cochrane Reviews Library and PsychoINFO. The search considered recent papers published between 2009 and 2019, as publications from previous years had already been covered by Duncan et al. [37]. The search was limited to papers in English and published in peer-reviewed journals. The references’ lists of all included papers have been carefully searched in order to identify further papers relevant for the review. In case of discrepancies between the two evaluators in the study selection, these were solved through discussion with a senior expert researcher. Finally, recent international guidelines on the management of patients with schizophrenia were searched as well. Randomized-controlled trials, quasi-experimental studies, and pilot studies were included in the review in order to provide an updated overview on the topic, as extensive as possible. The selection process of the articles included is illustrated in Fig. 1.
Results
The main features of the included studies [35, 38,39,40,41,42,43,44] are summarized in Table 1.
Ishii et al. [42] developed a training program tailored to patients with schizophrenia during their stay in an acute psychiatric ward. The intervention consists in evaluating the patients’ attitudes on the treatments received, sharing this information with the other clinicians and then identifying a shared plan. Patients in the SDM group reported a higher level of satisfaction towards treatments compared to the usual care group, while no differences were found in attitude toward medication, treatment continuation and the levels of global functioning.
Finnerty et al. [44] proposed interventions based on the use of smartphone applications or “apps”, implemented the MyCHOIS-CommonGround, a decision-making Web-based tool. The “My Collaborative Health Outcomes Information System” (MyCHOIS) is part of a Web-based platform for supporting shared decision-making and quality improvement, developed by the New York State Office of Mental Health. Within the MyCHOIS system, CommonGround application engages patients to complete a CommonGround SDM report prior to the appointments with their doctors. The report evaluates the patient’s perspective on symptoms, functioning, treatment progress and concerns. During the medical examination, patient and clinician review together the report and work towards developing a shared decision. The Web-based tool has been proven to be effective in increasing the level of engagement with the mental health services and in improving adherence to the prescribed treatments.
In Germany, Hamann et al. [38] tested the efficacy of a new shared decision making intervention developed for patients with psychotic disorders. The experimental intervention is tailored for mental health care staff and patients, with the aim of improving communication skills and patient empowerment. The SDM training yielded higher participation preferences and increased patients’ desire to have more responsibility in treatment decisions, which continued at 6-month follow-up.
Another randomized-controlled study carried out in Germany [43] included a SDM-training program for staff members focused on motivational and behavioral aspects. At the end of the study, only short-term differences were found between patients allocated to the experimental group. In 2017, Ramon et al. tested the efficacy of a training program tailored to patients, psychiatrists and care-coordinators [41]. The main training goal was to improve SDM style by using role-play techniques, web-site materials and group discussion. The training program which was dedicated to both service users and practitioners, confirmed the usefulness of SDM on psychiatric medication. In 2015, a group of Korean researchers evaluated the levels of patients’ self-esteem, problem-solving strategies and quality-of-life following a structured SDM training program (eight-session group program for inpatients), which in fact resulted in improvement [39]. In United Kingdom, McCabe et al. [40] developed the TEMPO manualized intervention, addressed to mental health professionals’ and aiming to increase their understanding of patients with psychotic experiences, improve their communication skills while empowering the patient and promoting SDM. Psychiatrists receiving the intervention reported to have a more satisfying therapeutic relationship with their patients.
In US, Kane et al. promoted the PRELAPSE study, which is a randomized-controlled trial including first episode and first-phase patients with schizophrenia allocated to receiving either LAI or treatment as usual [35]. In the study, clinicians attended a training course on the importance of using LAI medication, the role of shared decision-making and on communication strategies for improving patient adherence to pharmacological treatment. At the end of the preliminary recruitment phase [35], authors found that 91% of patients included would have accepted LAIs in the early stage of disease, if this therapeutic choice had been proposed in a supportive way.
Discussion
In recent years, much effort has been dedicated to find ways of making SDM more effective. The main differences among these experiences are related to the target group (either patients, clinicians, or both), the type of decision-supporting tool (face-to-face or technologically based engagement), and the duration of the follow-up period.
Regarding the target groups, all experimental interventions specifically addressed to patients [38, 39, 44, 45] resulted in a more active behavior during psychiatric consultations within the hospitalization period. However, no clear effects have been found in terms of adherence rate to pharmacological treatments, evidencing the need for adding decision-support tools and stronger communication skills by mental health professionals in order to achieve this objective.
Interestingly, projects specifically addressed to mental health professionals have shown promising results in improving the quality of therapeutic alliance and patient acceptance of pharmacological treatments. In the case of the TEMPO training [40], long-term effectiveness of the intervention was associated with the inclusion of a dedicated session (4-step approach) on SDM in patients with psychosis aimed at changing the patient decision-making style. In the PRELAPSE trial, good short-term results had been achieved by including communication skills training with emphasis on the role of SDM in routine clinical care. Efficacy of the shared approach was also confirmed by the only experience of SDM training course developed for both patients and psychiatrists and care-coordinators by Ramon et al. [41].
Albeit encouraging, however, none of the approaches above could provide key data regarding the stability and the maintenance of the positive effects over time, due to their short-term follow-up. Another issue is the feasibility of these interventions in the clinical routine care, their cost-effectiveness and their usefulness in managing crisis situations.
As regards the web-based tools, engagement through the MyCHOIS–CommonGround website was associated with a higher level of ongoing engagement in out-patient mental health service compared to that of the control group, although no significant differences were found in the adherence rate with antipsychotic medication. Another noticeable advantage was the cost-effectiveness of the intervention which makes it particularly suitable for attaining long-term outcomes in patients with severe mental disorders [46,48,48,49,50]. More recently, the ongoing “Momentum trial” in Denmark [51] is evaluating the effectiveness of a smartphone application in the outcome of treatment consultations, by engaging people with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders and encouraging patient activation and SDM.
SDM is recognized as a promising strategy for enhancing collaboration between clinicians and patients, given the complementary knowledge and expertise of both parties [52]. Patient recovery can be fostered by adopting a SDM style, enhancing empowerment and self-efficacy of patients [52,53,54,55]. In turn, SDM has shown its usefulness in improving treatment adherence [27]. Konrad et al. [56] found that during clinical encounters, the most frequent decisions taken by clinicians were related to medications and to the severity of symptoms, while patients were rarely involved in the medication choice or given a choice at all.
It is clear that in many cases patients being prescribed antipsychotics would need to understand the advantages and long-term positive impacts on their functional outcome, especially in the case of LAIs where this should be discussed as early as possible [26]. Many mental health care professionals consider the matter of medication to be too sensitive to be discussed with the patient and approached by SDM, too time-consuming for them and somewhat discouraging for the patient (in terms of adverse effects).
From the patients’ viewpoint, patients admit preferring a more directive/paternalistic practitioner style during crisis, but they report also to feel pressured or being persuaded or coerced into accepting pharmacological treatments like LAIs if they fail to take their oral prescribed medication. Clinical decision-making should change on the basis of contextual variables and the style should be tailored to fit patients’ needs and preferences, according to the stage of the illness [2].
However, the adoption of SDM appears useful in the long-term treatment of patients with schizophrenia where medication non-adherence plays an important role in relapse rates, poor outcome, and high costs [36]. As suggested by NICE guidelines, clinicians should negotiate with patients and their carers as early as possible on how information will be shared [27]. NICE guidelines emphasize the need to check how information is shared regularly, especially when communication difficulties are likely to occur. These aspects need to be fostered in order to improve adherence to both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments proposed. In particular, when considering pharmacological treatments, it is essential to evaluate the patient’s preferences, expectations and worries about the treatment in order to develop a personalized treatment strategy [57]. The adoption and the implementation of SDM for psychiatric medication management in the clinical routine care represents a big challenge for both mental health professionals as well as for users and carers.
Suggestions for clinical practice
In recent years, considerable resources have been invested to make the SDM a routine way of working: computerized programs, role-play techniques, training groups for mental health staff [58]. The main target of these interventions are patients with schizophrenia and psychotic disorders.
SDM can be promoted in several ways: either by having the patient complete questionnaires during hospitalization to express their opinion regarding the satisfaction with the treatment received or through online platforms in which patients can express their treatment preferences, even before seeing their doctor—in a positive perspective of an active involvement of patients in the treatment of their mental illness.
The introduction of specific smartphone apps has led to the dissemination of a SDM protocol, but it must be considered that the use of apps requires specific skills. Therefore, it is likely that only patients with high level of personal functioning and less severe symptomatology can use these support tools, gaining a positive reinforcement [59, 60].
Based on the results of the eight studies included in this literature review, interventions focused on enhancement of the adoption in SDM in the clinical routine care seem promising, although these results are preliminary and only the short-term efficacy of these approaches has been confirmed. The interventions proposed appear feasible and well-accepted by both patients and clinicians, confirming the findings from the ROAMER study which showed that all stakeholders of mental health want to be actively involved in the planning and management of care [61, 62]. Before developing SDM interventions aiming to improve the acceptance rate of LAIs in patients with schizophrenia, further longitudinal methodologically rigorous studies are needed.
However, as pointed out by Das et al. [63], patients’ and clinicians’ attitudes towards LAIs are a critical element in their underutilization in the clinical practice. Psychiatrists generally believe that patients are less willing to accept LAIs, than oral treatments and they avoid proposing it [64]. In fact, in the study by Kane et al. [35], when clinicians are adequately informed on how to appropriately manage it, the patients’ acceptance rate increases. In a qualitative study with young patients with psychosis, Das et al. [63] found that patients prefer LAIs, since they do not have to remember to take pills every day.
Other factors hampering the underutilization of LAIs in clinical routine care include the overestimation of patient’s adherence; the time-consuming process of using SDM style for proposing the LAIs treatment; the heterogeneity of international guidelines and the prejudice that therapeutic relationship would be weakened by the adoption of LAIs, particularly in the early stages of the disease [65].
Therefore, international and national scientific associations should clearly state the potential beneficial role of using LAIs in the early stage of the disorder, supporting the use of LAIs and SDM style in proposing the switch from oral to LAI formulation to patients with schizophrenia.
It is essential that psychiatrists introduce the use of SDM into their clinical practice, not limiting themselves to accepting the patient’s preferences, but providing clear and comprehensive information [66]. The SDM seems to be particularly effective in the case of LAIs prescription, since patient have prejudices and fears related to the formulation, which the doctor must contrast [35]. At the same time, the active involvement of the patient in the discussion on the type of formulation to be adopted can be useful to reduce the perceived coercion reported by patients in receiving pharmacological treatments. The current and future increasing availability of LAIs will enrich the choice for the clinicians who intend to use a long-acting formulation [67]. Some effective strategies to actively involve patients in the discussion about the type of LAI include to discuss his/her fear about the injection procedure, discussing previous negative personal experiences with LAI medications, describe the positive effects of such formulation, evaluate the level of patient’s motivation towards the pharmacological treatment. Possible recommendations for best clinical practice and on how to propose to start a treatment with LAIs are summarized in Table 2.
Involving patients in the choice of therapy is not sufficient to increase pharmacological adherence if, at the same time, there is no constant work of comparison and communication with the reference psychiatric team. Therefore, in our opinion, resources should be allocated for health personnel dedicated training and to support patients, for example with ad hoc courses (e.g., TEMPO training). The results will then be monitored over time in order to evaluate the impact of these interventions on the recovery rates in patients with schizophrenia.
References
Tiffen J, Corbridge S, Slimmer L. Enhancing clinical decision making: development of a contiguous definition and conceptual framework. J Prof Nurs. 2014;30(5):399–405.
Coulter A. Shared decision making: everyone wants it, so why isn’t it happening? World Psychiatry. 2017;16(2):117–8.
Fukui S, Salyers MP, Matthias MS, et al. Predictors of shared decision making and level of agreement between consumers and providers in psychiatric care. Community Ment Health J. 2014;50(4):375–82.
Slade M. Implementing shared decision making in routine mental health care. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(2):146–53.
Luciano M, Sampogna G, Del Vecchio V, Loos S, Slade M, Clarke E, Nagy M, Kovacs A, Munk-Jørgensen P, Krogsgaard Bording M, Kawohl W, Rössler W, Puschner B, Fiorillo A, CEDAR Study Group. When does shared decision making is adopted in psychiatric clinical practice? Results from a European multicentric study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-019-01031-y.
Wampold E. How important are the common factors in psychotherapy? An update. World Psychiatry. 2015;14:270–7.
Matthias MS, Salyers MP, Rollins AL, Frankel RM. Decision making in recovery-oriented mental health care. Psychiatr Rehabil. 2012;35:305–14.
Bär Deucher A, Hengartner MP, Kawohl W, Konrad J, Puschner B, Clarke E, Slade M, Del Vecchio V, Sampogna G, Égerházi A, Süveges Á, Krogsgaard Bording M, Munk-Jørgensen P, Rössler W, CEDAR study group. Participation in medical decision-making across Europe: an international longitudinal multicenter study. Eur Psychiatry. 2016;35:39–46.
Loos S, Arnold K, Slade M, Jordan H, Del Vecchio V, Sampogna G, Süveges Á, Nagy M, Krogsgaard Bording M, Østermark Sørensen H, Rössler W, Kawohl W, Puschner B, CEDAR study group. Courses of helping alliance in the treatment of people with severe mental illness in Europe: a latent class analytic approach. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2015;50:363–70.
O’Sullivan M-J, Rae S. Shared decision-making in psychiatric medicines management. Mental Health Practice. 2014;17:16–22.
Zimmerman M, Morgan TA, Stanton K. The severity of psychiatric disorders. World Psychiatry. 2018;17(3):258–75.
Puras D, Gooding P. Mental health and human rights in the 21st century. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(1):42–3.
Foot C, Gilburt H, Dunn P. People in control of their own health and care: the state of involvement. London: King’s Fund; 2014.
Kilbourne AM, Beck K, Spaeth-Rublee B, Ramanuj P, O’Brien RW, Tomoyasu N, Pincus HA. Measuring and improving the quality of mental health care: a global perspective. World Psychiatry. 2018;17(1):30–8.
Priebe S, Miglietta E. Assessment and determinants of patient satisfaction with mental health care. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(1):30–1.
Correll CU, Rubio JM, Kane JM. What is the risk-benefit ratio of long-term antipsychotic treatment in people with schizophrenia? World Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):149–60.
Emsley R. Antipsychotic maintenance treatment in schizophrenia and the importance of preventing relapse. World Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):168–9.
Howes OH, Kaar SJ. Antipsychotic drugs: challenges and future directions. World Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):170–1.
Lysaker PH, Pattison ML, Leonhardt BL, Phelps S, Vohs JL. Insight in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: relationship with behavior, mood and perceived quality of life, underlying causes and emerging treatments. World Psychiatry. 2018;17(1):12–23.
Stevens GL, Dawson G, Zummo J. Clinical benefits and impact of early use of long-acting injectable antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2016;10(5):365–77.
Fava M. The promise and challenges of drug repurposing in psychiatry. World Psychiatry. 2018;17(1):28–9.
Fleischhacker WW. The long-term treatment of schizophrenia with antipsychotics: a perennial debate. World Psychiatry. 2018;17:169–70.
Pompili M, Giordano G, Luciano M, Lamis DA, Del Vecchio V, Serafini G, Sampogna G, Erbuto D, Falkai P, Fiorillo A. Unmet needs in schizophrenia. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(8):870–84.
Samalin L, Garnier M, Auclair C, Llorca PM. Clinical decision-making in the treatment of schizophrenia: focus on long-acting injectable antipsychotics. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(11):1935.
Correll CU, Citrome L, Haddad PM, Lauriello J, Olfson M, Calloway SM, Kane JM. The use of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in schizophrenia: evaluating the evidence. J Clin Psychiatry. 2016;77(suppl 3):1–24.
Remington G, Addington D, Honer W, Ismail Z, Raedler T, Teehan M. Guidelines for the pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia in adults. Can J Psychiatry. 2017;62(9):604–16.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: treatment and management. London: NICE; 2014.
Lehman AF, Lieberman JA, Dixon LB, et al. Sterring committee on practice guidelines. Practice guidelines for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia, second edition. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(2 Suppl):1–56.
Samalin L, Abbar M, Courtet P, Guillaume S, Lancrenon S, Llorca PM. French society for biological psychiatry and neuropsychopharmacology task force: formal consensus for the prescription of depot antipsychotics. Encephale. 2013;39(Suppl 4):189–203.
Isohanni M, Miettunen J, Jääskeläinen E, Moilanen J, Hulkko A, Huhtaniska S. Under-utilized opportunities to optimize medication management in long-term treatment of schizophrenia. World Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):172–3.
Offord S, Wong B, Mirski D, Baker RA, Lin J. Healthcare resource usage of schizophrenia patients initiating long-acting injectable antipsychotics vs oral. J Med Econ. 2013;16(2):231–9.
Geerts P, Martinez G, Schreiner A. Attitudes towards the administration of long-acting antipsychotics: a survey of physicians and nurses. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:58.
Potkin S, Bera R, Zubek D, Lau G. Patient and prescriber perspectives on long-acting injectable (LAI) antipsychotics and analysis of in-office discussion regarding LAI treatment for schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:261.
Sajatovic M, Ross R, Legacy SN, Correll CU, Kane JM, Di Biasi F, Fitzgerald F, Byerly M. Identifying patients and clinical scenarios for use of long-acting injectable antipsychotics-expert consensus survey part 1. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018;14:1463–74.
Kane JM, Schooler NR, Marcy P, Achtyes ED, Correl CU, Robinson DG. Patients with early-phase schizophrenia will accept treatment with sustained-release medication (long-acting injectable antipsychotics): results from the recruitment phase of the PRELAPSE trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2019;80:3.
Sendt KV, Tracy DK, Bhattacharyya S. A systematic review of factors influencing adherence to antipsychotic medication in schizophrenia-spectrum disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2015;225(1–2):14–30.
Duncan E, Best C, Hagen S. Shared decision making interventions for people with mental health conditions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Art. No. CD007297; 2010.
Hamann J, Mendel R, Meier A, Asani F, Pausch E, Leucht S, Kissling W. “How to speak to your psychiatrist”: shared decision-making training for in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatr Serv. 2011;62:1218–21.
An SY, Kim GH, Kim JY. Effectiveness of shared decision-making training program in people with schizophrenia in South Korea. Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2017;53(2):111–8.
McCabe R, John P, Dooley J, Healey P, Cushing A, Kingdon D, Bremner S, Priebe S. Training to enhance psychiatrist communication with patients with psychosis (TEMPO): cluster randomised controlled trial. Br J Psychiatry. 2016;209(6):517–24.
Ramon S, Morant N, Stead U, Perry B. Shared decision-making for psychiatric medication: a mixed-methods evaluation of a UK training programme for service users and clinicians. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2017;63(8):763–72.
Ishii M, Okumura Y, Sugiyama N, Hasegawa H, Noda T, Hirayasu Y, Ito H. Feasibility and efficacy of shared decision making for first-admission schizophrenia: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2017;17(1):52.
Hamann J, Parchmann A, Sassenberg N, Bronner K, Albus M, Richter A, Hoppstock S, Kissling W. Training patients with schizophrenia to share decisions with their psychiatrists: a randomized-controlled trial. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2017;52(2):175–82.
Finnerty MT, Layman DM, Chen Q, Leckman-Westin E, Bermeo N, Ng-Mak DS, Rajagopalan K, Hoagwood KE. Use of a web-based shared decision-making program: impact on ongoing treatment engagement and antipsychotic adherence. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(12):1215–21.
Ishii M, Okumura Y, Sugiyama N, Hasegawa H, Noda T, Hirayasu Y, Ito H. Efficacy of shared decision making on treatment satisfaction for patients with first-admission schizophrenia: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2014;14:111.
Andersson G, Titov N, Dear BF, Rozental A, Carlbring P. Internet-delivered psychological treatments: from innovation to implementation. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(1):20–8.
Firth J, Torous J, Stubbs B, Firth JA, Steiner GZ, Smith L, Alvarez-Jimenez M, Gleeson J, Vancampfort D, Armitage CJ, Sarris J. The “online brain”: how the Internet may be changing our cognition. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):119–29.
Linardon J, Cuijpers P, Carlbring P, Messer M, Fuller-Tyszkiewicz M. The efficacy of app-supported smartphone interventions for mental health problems: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(3):325–36.
Salyers MP, Fukui S, Bonfils KA, Firmin RL, Luther L, Goscha R, Rapp CA, Holter MC. Consumer outcomes after implementing common ground as an approach to shared decision making. Psychiatr Serv. 2017;68(3):299–302.
Torous J, Andersson G, Bertagnoli A, Christensen H, Cuijpers P, Firth J, Haim A, Hsin H, Hollis C, Lewis S, Mohr DC, Pratap A, Roux S, Sherrill J, Arean PA. Towards a consensus around standards for smartphone apps and digital mental health. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(1):97–8.
Vitger T, Austin SF, Petersen L, Tønder ES, Nordentoft M, Korsbek L. The Momentum trial: the efficacy of using a smartphone application to promote patient activation and support shared decision making in people with a diagnosis of schizophrenia in outpatient treatment settings: a randomized controlled single-blind trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2019;19(1):185.
Morant N, Kaminskiy E, Ramon S. Shared decision making for psychiatric medication management: beyond the micro-social. Health Expect. 2016;19(5):1002–11.
Deegan PE, Rapp C, Holter M, Riefer M. A program to support shared decision making in an outpatient psychiatric medication clinic. Psychiatric Serv. 2008;59:603–5.
Goodwin N, Dixon A, Poole T, Raleigh V, Gao H, Lyscom T. Improving the quality of care in general practice. Report of an independent inquiry commissioned by The King’s Fund; 2011.
Vita A, Barlati S. Recovery from schizophrenia: is it possible? Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2018;31(3):246–55.
Konrad J, Loos S, Neumann P, Zentner N, Mayer B, Slade M, Jordan H, De Rosa C, Del Vecchio V, Égerházi A, Nagy M, Bording MK, Sørensen HØ, Kawohl W, Rössler W, Puschner B. Content and implementation of clinical decisions in the routine care of people with severe mental illness. J Ment Health. 2015;24(1):15–9.
Achtyes E, Simmons A, Skabeev A, Levy N, Jiang Y, Marcy P, Weiden PJ. Patient preferences concerning the efficacy and side-effect profile of schizophrenia medications: a survey of patients living with schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18(1):292.
Alguera-Lara V, Dowsey MM, Ride J, Kinder S, Castle D. Shared decision making in mental health: the importance for current clinical practice. Aust Psychiatry. 2017;25(6):578–82.
Harvey PD, Strassnig MT. Cognition and disability in schizophrenia: cognition-related skills deficits and decision-making challenges add to morbidity. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):165–7.
Reichenberg A, Velthorst E, Davidson M. Cognitive impairment and psychosis in schizophrenia: independent or linked conditions? World Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):162–3.
Fiorillo A, Luciano M, Del Vecchio V, Sampogna G, Obradors-Tarragó C, Maj M, ROAMER Consortium. Priorities for mental health research in Europe: a survey among national stakeholders’ associations within the ROAMER project. World Psychiatry. 2013;12(2):165–70.
Wykes T, Haro JM, Belli SR, Obradors-Tarragó C, Arango C, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Bitter I, Brunn M, Chevreul K, Demotes-Mainard J, Elfeddali I, Evans-Lacko S, Fiorillo A, Forsman AK, Hazo JB, Kuepper R, Knappe S, Leboyer M, Lewis SW, Linszen D, Luciano M, Maj M, McDaid D, Miret M, Papp S, Park AL, Schumann G, Thornicroft G, van der Feltz-Cornelis C, van Os J, Wahlbeck K, Walker-Tilley T, Wittchen HU. ROAMER consortium: mental health research priorities for Europe. Lancet Psychiatry. 2015;2(11):1036–42.
Das AK, Malik A, Haddad PM. A qualitative study of the attitudes of early patients in an early intervention service towards antipsychotic long-acting injections. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2014;4(5):179–85.
Heres S, Reichhart T, Hamann J, Mendel R, Leucth S, Kissling W. Psychiatrists’ attitude antipsychotic depot treatment in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Eur Psychiatry. 2011;26:297–301.
Emsley R, Chiliza B, Asmal L, Mashile M, Fusar-Poli P. Long-acting injectable antipsychotics in early psychosis: a literature review. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2013;7:247–54.
Deegan PE, Deake RE. Shared decision making and medication management in the recovery process. Psychiatr Serv. 2006;57:1636–9.
Llorca PM, Abbar M, Courtet P, Guillame S, Lancrenon S, Samalin L. Guidelines for the use and management of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in seriuos mental illness. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:340.
Acknowledgements
Unconditional funding support for editorial assistance was provided by Lundbeck Italy and Otsuka Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AF, SF, AB, GC, GN, VS, FV, GM and AV conceive the original concept idea. GS and SB performed the literature search. AF, SB, GS and AV wrote the first draft of the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
None of the authors have any competing interests in the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorillo, A., Barlati, S., Bellomo, A. et al. The role of shared decision-making in improving adherence to pharmacological treatments in patients with schizophrenia: a clinical review. Ann Gen Psychiatry 19, 43 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-020-00293-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-020-00293-4