Abstract
Background
In study TMC647055HPC2001, a 3-direct-acting-antiviral (DAA) regimen combining NS3/4A protease inhibitor simeprevir (SMV), non-nucleoside NS5B inhibitor TMC647055/ritonavir (RTV) and NS5A inhibitor JNJ-56914845 resulted in high sustained virologic response 12 weeks after actual end of treatment (SVR12) in chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1-infected patients. SVR12 rates were generally lower in the 2-DAA regimen SMV + TMC647055/RTV with or without ribavirin. The objective of this study was to identify and characterise pre-existing and emerging resistance-associated variants (RAVs) in patients enrolled in study TMC647055HPC2001.
Methods
HCV population sequencing analyses were performed on baseline isolates from all patients (n = 90) and post-baseline isolates from patients with virologic failure (n = 22). In addition, deep sequencing and phenotypic analyses were performed on selected baseline and post-baseline isolates.
Results
The majority of patients with virologic failure had emerging RAVs to all study drugs at the time of failure: in all 22 patients SMV RAVs emerged at NS3 positions 80, 155, 156 and/or 168, consistent with the known SMV resistance profile. Emerging TMC647055 RAVs at NS5B position 495 were detected in the majority of patients (16/22), and all 5 patients who failed the 3-DAA regimen had emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs at NS5A positions 30 and/or 31. While at the end of study emerging SMV and TMC647055 RAVs were no longer observed by population sequencing in 40% (8/20) and 62.5% (10/16) of patients with follow-up data available, respectively, emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs were still detected in all (5/5) patients.
Conclusions
Virologic failure in the 2- and 3-DAA combinations was, in the majority of patients, associated with the emergence of RAVs to all study drugs. While emerging SMV and TMC647055 RAVs became undetectable during follow-up, JNJ-56914845 RAVs in NS5A were still observed at end of study.
Trial registration number
NCT01724086 (date of registration: September 26, 2012)
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a leading cause of chronic liver disease with an estimated 130–150 million people infected worldwide [1]. Since the approval in 2011 of the first direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), current therapy includes well-tolerated interferon (IFN)-free DAA combination regimens with high efficacy rates [2, 3]. For some regimens, the addition of ribavirin is indicated in certain patient populations to increase efficacy rates [4].
In the Phase 2a study TMC647055HPC2001 (NCT01724086), a 12-week 3-DAA regimen of simeprevir (SMV), TMC647055/ritonavir (RTV) and JNJ-56914845 resulted in high sustained virologic response 12 weeks after actual end of treatment (SVR12; 93% for HCV genotype [GT]1a- and 100% for GT1b-infected patients in the JNJ-56914845 60 mg group) while SVR12 rates were lower in the 12-week 2-DAA regimens of SMV and TMC647055/RTV with or without ribavirin (RBV) (SVR12 33 − 86% depending on HCV geno/subtype, presence of RBV and TMC647055 dose) [5].
SMV is a once-daily (QD), oral HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor, approved with pegylated IFN (pegIFN)/RBV for the treatment of HCV GT1 and GT4 infection in the United States (US) and European Union (EU), and in IFN-free combination with sofosbuvir for GT1 infection in the US and GT1 and GT4 infection in the EU. The majority of HCV GT1-infected patients who failed SMV/pegIFN/RBV treatment in a Phase 2b/3 clinical trial had emerging mutations at NS3 positions 80, 122, 155 and/or 168, conferring high-level resistance to SMV in vitro [6]. Similar SMV high-level resistance mutations were observed in GT4-infected patients who failed SMV/pegIFN/RBV treatment and in GT1-infected patients with virologic failure upon 12 or 24 weeks’ SMV/sofosbuvir treatment [7,8,9,10]. At the end of study, these mutations could no longer be detected in half of the patients.
TMC647055 is an oral non-nucleoside inhibitor (NNI) binding at the thumb-1 NNI-1 site of the HCV NS5B polymerase [11]. The antiviral activity of TMC647055 in HCV GT1-infected patients is dose-dependent, with a median maximum decrease from baseline in HCV RNA of 2.4 log10 IU/mL and 3.4 log10 IU/mL at 1000 mg twice daily (BID) for 5 days in GT1a- (n = 3) and GT1b-infected (n = 3) patients, respectively [12]. Emerging TMC647055 resistance-associated variants (RAVs) at NS5B position 495 were observed in two GT1b-infected patients. Combination of TMC647055 (1000 mg BID) with SMV (150 mg QD) for 10 days in GT1-infected patients (seven GT1a and one GT1b) led to potent antiviral activity with a 4.64 log10 IU/mL median decrease in HCV RNA from baseline at day 11 with no viral breakthrough observed [13]. RTV was used as a pharmacokinetic enhancer to counteract cytochrome P450 3A4 induction by TMC647055, therefore boosting circulating plasma concentrations of TMC647055 and SMV when given in combination in study TMC647055HPC2001.
JNJ-56914845 (previously GSK2336805) is an oral inhibitor of HCV replication targeting the NS5A replication complex [14]. Single-dose administration of JNJ-56914845 to HCV GT1-infected patients (15 GT1a; two GT1b) resulted in rapid reductions in HCV RNA, with a mean decrease in HCV RNA from baseline within the first 24 hours of 2.18 log10 IU/mL for 30 mg (one GT1a) and 2.84 log10 IU/mL for 60 mg (four GT1a; one GT1b) [15]. Emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs were detected in 13/23 patients at NS5A positions 28, 30, 31, 32 and/or 93.
The objective of this study was to identify and characterise pre-existing and emerging RAVs in patients enrolled in study TMC647055HPC2001.
Methods
Study design
The TMC647055HPC2001 study design is shown in Fig. 1 [5].
TMC647055HPC2001 study design. aRibavirin given BID at doses of 1000–1200 mg. bPanel 4 Arm 1 included 1 GT1c- and 1 GT1l-infected patient, based on NS5B-based geno/subtyping. Follow-up therapy with pegIFN + RBV was based on on-treatment response and was initiated only if: week 4 HCV RNA ≥25 IU/mL (Panels 1–3: 36 weeks of follow-up therapy); week 4 HCV RNA <25 IU/mL detectable or HCV RNA confirmed detectable between week 4 and week 11 (Panels 1–2: 12 weeks of follow-up therapy). BID: twice daily; GT: genotype; pegIFN: pegylated interferon; QD: once daily; RBV: ribavirin; RTV: ritonavir; SMV: simeprevir; SVR12: sustained virologic response 12 weeks after actual end of treatment
HCV geno/subtype determination
HCV geno/subtypes were determined at screening by the VERSANT® HCV Genotype 2.0 (LiPA v2.0) or, if failed, by the Trugene HCV Genotyping assay (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, IL, USA). HCV geno/subtypes were determined pretreatment by sequencing an NS5B 329-bp region followed by basic local alignment search tool analysis. The results of the NS5B-based assay or, if missing, from the LiPA v2.0 or Trugene assay were used for virology analyses.
HCV NS3/4A, NS5B and NS5A sequence analysis
The NS3/4A region or the NS3 protease, NS5B and NS5A gene were sequenced using population sequencing in baseline samples from all patients and post-baseline samples from patients with virologic failure [16] (see Additional file 1). In addition, Illumina deep sequencing was performed for a selection of samples (from Panels 1–2 and Panel 4), as described earlier [17]. Deep sequencing analysis was performed using a detection threshold of 1%. Sequencing resulted in an average coverage of 19,572 reads (range 7,177–36,508) per amino acid position in NS3 (amino acid position 1–181), of 20,594 reads (range 463–78,381) per amino acid position in NS5B, and of 23,045 reads (range 2,563–78,342) per amino acid position in NS5A. Baseline polymorphisms were defined as amino acid changes from the H77 (GenBank accession number AF009606) or the HCV Con1 (GenBank accession number AJ238799) reference sequences for HCV GT1a and GT1b, respectively. Emerging mutations were defined as amino acid changes from patient-specific baseline sequences based on population sequencing. RAVs were defined as amino acid substitutions with a fold change (FC) in 50% effective concentration (EC50) >2.0 for the respective drug, when tested as a site-directed mutant (SDM) in a transient replicon assay.
Phenotypic characterisation using a transient replicon assay
SDMs were engineered in a GT1a or GT1b replicon. For the chimeric replicon assay, sequences of the NS3 protease domain (aa7-192), NS5B polymerase (full length) or NS5A (full length) from patient isolates were introduced in a GT1b replicon backbone generating chimeric replicons [18,19,20,21]. The NS5A chimeric replicon assay was performed at Monogram Bioscience Inc., LabCorp, San Francisco, CA, USA. Antiviral activity of the inhibitors against the NS3 protease and NS5B chimeric replicons was assessed in a transient replicon assay using luciferase read-out, as described earlier [22]. EC50 values were determined and compared with the EC50 of a reference GT1b wild-type replicon to calculate the FC in EC50 values.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board or Independent Ethics Committee at each participating centre, and met the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice guidelines. All patients provided written, informed consent.
Results
Baseline polymorphisms
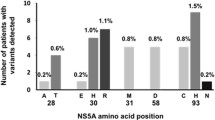
At baseline, SMV RAVs were observed in 6/89 GT1-infected patients (6.7%) with NS3 sequencing data available. These included Q80K (in 5/89 GT1 [5.6%]; 4/44 GT1a [9.1%]; 1/44 GT1b [2.3%]) and Q80R (in 1/89 GT1 [1.1%]) (Fig. 2). Two out of the four GT1a-infected patients with baseline Q80K were treated with the 2-DAA regimen in Panel 1 and did not achieve SVR. The two other GT1a-infected patients with baseline Q80K received the 3-DAA regimen in Panel 4; one patient achieved SVR while the other experienced viral relapse. The GT1b-infected patient with Q80R at baseline had detectable HCV RNA at the end of treatment and did not achieve SVR. TMC647055 RAVs were not observed at baseline. In Panel 4, JNJ-56914845 RAVs were detected in 2/42 (4.8%) GT1-infected patients with NS5A sequencing data available; L31M and Y93C (in combination with M28V), respectively (both in 1/27 GT1a [3.7%]). Both patients with baseline JNJ-56914845 RAVs achieved SVR.
Prevalence of NS3 (a), NS5B (b) and NS5A (c) baseline polymorphisms in study TMC647055HPC2001. aFC in EC50 values compared with GT1b wild-type replicon assessed as SDM in a transient replicon assay. bSDM in GT1b replicon backbone. cSDM in GT1a replicon backbone. dSDM data for single Y93C. Baseline NS3 sequencing data were not available for 1 patient (HCV GT1l-infected patient); baseline NS5B and NS5A sequencing data were not available for 2 of the evaluable patients (HCV GT1l-infected patient and HCV GT1c-infected patient). EC50: 50% effective concentration; FC: fold change; GT: genotype; NAP: not applicable; ND: not determined; SDM: site-directed mutant; SMV: simeprevir
In the phenotypic analysis of a subset of baseline isolates (Fig. 3), low-level resistance to SMV was observed for four GT1a isolates with SMV RAV Q80K (median FC in EC50 = 8.5; range 5.6–11). All baseline isolates remained fully susceptible to TMC647055 (FC in EC50 ≤ 2.0). One GT1a baseline isolate with NS5A RAV L31M displayed a 150-fold reduction in susceptibility to JNJ-56914845. For the baseline isolate with NS5A Y93C (+M28V), which was present as mixture with wild-type, the FC in EC50 was ≤2.0.
In vitro activity of SMV (a), TMC647055 (b) and JNJ-56914845 (c) against chimeric replicons containing the NS3 protease, NS5B polymerase or NS5A sequences, respectively, from isolates obtained at baseline, time of failure (TOF) and end of study (EOS) or follow-up week 12 (FU W12). Patients with RAVs, as detected by population sequencing in the corresponding plasma samples, are indicated with filled circles; patients without RAVs are indicated with open circles; for three samples at TOF, indicated with an asterisk, the SMV EC50 was above the highest test concentration with a censored FC in EC50 (i.e. >2200); the two isolates with SMV or TMC647055 RAVs detected in the plasma samples at TOF and wild-type sensitivity to SMV and TMC647055, respectively, did not contain these RAVs in the respective sequences included in the chimeric replicons. EC50: 50% effective concentration; EOS: end of study, corresponding to the sample from the last available time point in the study; FC: fold change; FU W12: follow-up week 12, corresponding to the sample obtained at 12 weeks after end of treatment; NAP: not applicable; RAV: resistance-associated variant; SMV: simeprevir; TOF: time of failure, corresponding to the sample obtained at TOF
Emergence of RAVs
Emergence of RAVs was investigated using population sequencing in the 22 patients with virologic failure (viral breakthrough, detectable HCV RNA at end of treatment [without viral breakthrough] or viral relapse [before or after follow-up week 12]) (Table 1).
In 14/17 patients (82.4%) with virologic failure in the 2-DAA regimen, emerging RAVs to both SMV and TMC647055 were detected at time of failure. SMV RAVs at NS3 positions 80, 155, 156 and/or 168 were observed in all 17 patients. The majority (9/10) of GT1b-infected patients had an emerging mutation at NS3 position 168, while either an emerging R155K (alone or in combination with a Q80R) (in 4/7) or an emerging mutation at NS3 position 168 (in 3/7) was observed in the GT1a-infected patients. Emerging TMC647055 RAVs at NS5B position 495 were detected in 14/17 patients, and included mainly P495L (in 11/14).
In all five patients with virologic failure in the 3-DAA regimen (all GT1a), emerging RAVs to both SMV and JNJ-56914845 were observed at time of failure. SMV RAVs emerged at NS3 positions 80 or 155; emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs were detected at NS5A positions 30 and/or 31 (Q30E [n = 2], Q30R [n = 1], L31M [n = 1] and Q30H + L31M [n = 1]). Emerging TMC647055 RAVs were observed in 2/5 patients, and involved P495L in both.
Illumina deep sequencing data were available for a subset of time of failure isolates (Table 1). In the three patients in Panel 4 without emerging TMC647055 RAVs at time of failure based on population sequencing, no RAVs could be detected by deep sequencing. Additional RAVs at a read frequency ≤25% were detected by deep sequencing in three patients with RAVs detected by population sequencing (patients 8, 18, 20). Deep sequencing identified additional emerging RAVs at a read frequency >25% in two patients at time of failure (patients 1, 2). RAVs emerging at time of failure were not detected at baseline by deep sequencing in the set of samples analysed.
For all three inhibitors, a reduction in in vitro activity was observed against time of failure isolates that contained SMV, TMC647055 or JNJ-56914845 RAVs (Fig. 3). Isolates collected at time of failure, with no TMC647055 RAVs detected, remained fully susceptible to TMC647055 (FC in EC50 ≤ 2.0).
Persistence of emerging RAVs
In 8/20 patients (40%) with emerging SMV RAVs at time of failure and follow-up NS3 sequencing data available, these SMV RAVs were no longer observed by population sequencing at end of study (Table 1). The median time between time of failure and end of study NS3 sequence was 20.6 weeks (range: 4.7–34.1 weeks) and 25.5 weeks (range: 4.1–28.1 weeks), respectively, for the eight patients without and 12 patients with emerging SMV RAVs detected at end of study. Ten out of 16 patients (62.5%) with emerging TMC647055 RAVs at time of failure and follow-up NS5B sequencing data available had lost these mutations at end of study, as assessed by population sequencing. The median time between time of failure and end of study NS5B sequence was 25.8 weeks (range: 20.1–28.4 weeks) and 23.9 weeks (range: 4.1–34.1 weeks), respectively, for the 10 patients without and the six patients with emerging TMC647055 RAVs detected at end of study. For all five patients with emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs at time of failure, these RAVs were still observed at end of study, with a median time between time of failure and end of study NS5A sequence of 20.1 weeks (range: 0–26.6 weeks). In the majority of patients with emerging RAVs no longer observed at end of study by population sequencing, these were also not detected by deep sequencing. In four patients (patients 2, 4, 18, 21), emerging TMC647055 or SMV RAVs were still detected by deep sequencing (read frequency <25%), while no longer present based on population sequencing.
In vitro susceptibility to the respective drugs was reduced when SMV, TMC647055 or JNJ-56914845 RAVs were still observed by population sequencing at end of study or follow-up week 12 (in case end of study isolate was not tested) (Fig. 3). When these RAVs were no longer detected by population sequencing, including in two patients (patients 2 and 4) with TMC647055 RAVs still detected by deep sequencing (read frequency <25%), wild-type sensitivity to the respective drugs was found.
Discussion
In this study, pre-existing RAVs were identified at low frequency. Baseline SMV RAVs were observed in 6.7% of patients with NS3 sequencing data available, and included Q80K in 5.6% of GT1-infected patients and in 9.1% of GT1a-infected patients. In the SMV/pegIFN/RBV Phase 2b/3 studies, the baseline prevalence of Q80K was higher (13.6% in GT1-infected patients; 29.5% in GT1a-infected patients), which can be explained by the fact that the global Phase 2b/3 studies included North America, a region with a high GT1a prevalence and a high Q80K prevalence within GT1a, while study TMC647055HPC2001 was performed in Europe [6]. In the SMV/pegIFN/RBV Phase 2b/3 studies, SVR rates were substantially reduced in GT1a-infected patients with baseline Q80K compared to those without this polymorphism [23,24,25]. The two GT1a-infected patients with baseline Q80K in the 2-DAA regimen did not achieve SVR; however, virologic failure rates were generally high (6/10) in Panel 1. In the 3-DAA regimen, one of the two GT1a-infected patients with baseline Q80K achieved SVR. Baseline JNJ-56914845 RAVs were present in 4.8% (2/42) of patients with NS5A sequencing data available; both patients achieved SVR. However, the low number of patients with baseline RAVs did not allow conclusions to be drawn on the impact of the presence of baseline RAVs on treatment outcome.
In the majority of patients with virologic failure, emerging RAVs to all study drugs were observed at time of failure. Similar findings of emerging resistance to multiple classes of DAAs have been described in patients with virologic failure in other 12-week combination regimens of DAAs with similar mechanisms of action i.e. an NS3/4A protease inhibitor, paritaprevir/ritonavir, combined with an NNI, dasabuvir, with or without an NS5A inhibitor, ombitasvir [26, 27]. All patients had SMV RAVs at time of failure, detected at NS3 positions 80, 155, 156 and/or 168, consistent with the previously characterised SMV resistance profile [6, 7, 9, 10, 28]. Emerging TMC647055 RAVs were found at time of failure in the majority of patients (in 14/17 and 2/5 patients with virologic failure in the 2- and 3-DAA regimens, respectively). These were observed at NS5B position 495 only, similar to the findings from in vitro TMC647055 selection experiments [11] and from the Phase 1b study that evaluated TMC647055 in monotherapy and in combination with SMV [12, 13]. There was no difference found in emerging RAVs between a low dose of TMC647055/RTV (450 mg QD; Panels 1–2) and a high dose (600 mg QD; Panel 3) or between HCV geno/subtypes. All five 3-DAA failure patients had emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs at NS5A positions 30 and/or 31. RAVs at these positions were also identified in JNJ-56914845 in vitro selection experiments and in the Phase 1 monotherapy study [14, 15]. The RAVs observed at time of failure were associated with a >100-fold reduction in JNJ-56914845 in vitro activity [14]. No in vitro JNJ-56914845 susceptibility data were available for Q30E; however, from data available from other NS5A inhibitors, it can be expected that this mutation also confers resistance to JNJ-56914845 [29]. Illumina deep sequencing, performed for a subset of time of failure isolates, confirmed the absence of TMC647055 RAVs in patients without these RAVs detected by population sequencing. For the selected set of samples, none of the RAVs emerging at time of failure were found to be already present at baseline by using deep sequencing.
While emerging SMV and TMC647055 RAVs became undetectable by population sequencing at end of study in 40% (8/20) and 62.5% (10/16) of patients, respectively, emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs were still observed at the end of study in all five 3-DAA failure patients. These observations confirm earlier findings of disappearance of emerging SMV RAVs in half of the patients at end of study in SMV/pegIFN/RBV studies [6] (as assessed by population sequencing), as well as the long-term persistence of emerging NS5A RAVs that has been demonstrated in patients who failed ledipasvir-containing regimens [30].
In the majority of patients in whom emerging RAVs in the NS3 and NS5B regions were no longer observed at end of study by population sequencing, these were also no longer detected by the more sensitive Illumina deep sequencing technology, in line with findings from previous studies [31, 32].
Phenotypic analysis showed a reduction in sensitivity to the study drugs when RAVs were detected by population sequencing. Consistency between the detection of SMV RAVs in clinical isolates and their in vitro susceptibility to SMV was also demonstrated in a recent study investigating clinical isolates of HCV GT1-infected patients enrolled in SMV Phase 1–3 clinical studies [20].
Conclusions
Virologic failure in study TMC647055HPC2001 was associated with the emergence of RAVs to all study drugs in the majority of patients. Treatment-emergent SMV and TMC647055 RAVs became undetectable over time in many of the patients after treatment was stopped, while emerging JNJ-56914845 RAVs could still be detected at end of study in the five 3-DAA failure patients.
Abbreviations
- BID:
-
Twice daily
- DAA:
-
Direct-acting antiviral
- EC50 :
-
50% effective concentration
- EU:
-
European Union
- FC:
-
Fold change
- GT:
-
Genotype
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- NAP:
-
Not applicable
- ND:
-
Not determined
- NNI:
-
Non-nucleoside inhibitor
- pegIFN:
-
Pegylated interferon
- QD:
-
Once daily
- RAV:
-
Resistance-associated variant
- RBV:
-
Ribavirin
- RTV:
-
Ritonavir
- SDM:
-
Site-directed mutant
- SMV:
-
Simeprevir
- SVR12:
-
Sustained virologic response 12 weeks after actual end of treatment
- US:
-
United States
References
World Health Organization. WHO Fact Sheet 164 - Hepatitis C 2012. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en/. Accessed 23 Nov 2016.
Lam BP, Jeffers T, Younoszai Z, Fazel Y, Younossi ZM. The changing landscape of hepatitis C virus therapy: focus on interferon-free treatment. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2015;8:298–312.
Pawlotsky JM, Feld JJ, Zeuzem S, Hoofnagle JH. From non-A, non-B hepatitis to hepatitis C virus cure. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S87–99.
Hezode C, Bronowicki JP. Ideal oral combinations to eradicate HCV: The role of ribavirin. J Hepatol. 2016;64:215–25.
Bourgeois S, Van Vlierberghe H, Moreno C, Orlent H, Nevens F, Arasteh K, et al. Efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of simeprevir and TMC647055/ritonavir with or without ribavirin and JNJ-56914845 in HCV genotype 1 infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017;17:26.
Lenz O, Verbinnen T, Fevery B, Tambuyzer L, Vijgen L, Peeters M, et al. Virology analyses of HCV isolates from genotype 1-infected patients treated with simeprevir plus peginterferon/ribavirin in Phase IIb/III studies. J Hepatol. 2015;62:1008–14.
Lawitz E, Sulkowski MS, Ghalib R, Rodriguez-Torres M, Younossi ZM, Corregidor A, et al. Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir, with or without ribavirin, to treat chronic infection with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 in non-responders to pegylated interferon and ribavirin and treatment-naive patients: the COSMOS randomised study. Lancet. 2014;384:1756–65.
Moreno C, Hezode C, Marcellin P, Bourgeois S, Francque S, Samuel D, et al. Efficacy and safety of simeprevir with PegIFN/ribavirin in naive or experienced patients infected with chronic HCV genotype 4. J Hepatol. 2015;62:1047–55.
Lawitz E, Matusow G, DeJesus E, Yoshida EM, Felizarta F, Ghalib R, et al. Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and cirrhosis: a phase 3 study (OPTIMIST-2). Hepatology. 2016;64:360–9.
Kwo P, Gitlin N, Nahass R, Bernstein B, Rojter S, Schiff E, et al. Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir (12 and 8 weeks) in HCV genotype 1-infected patients without cirrhosis: OPTIMIST-1, a phase 3, randomized study. Hepatology. 2016;64:370–80.
Devogelaere B, Berke JM, Vijgen L, Dehertogh P, Fransen E, Cleiren E, et al. TMC647055, a potent nonnucleoside hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor with cross-genotypic coverage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56:4676–84.
Leempoels J, Reesink H, Bourgeois S, Vijgen L, Rouan MC, Vandebosch A, et al. Human safety, pharmacokinetics and antiviral activity of TMC647055, a novel HCV non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitor. 2011. http://www.natap.org/2011/AASLD/AASLD_04.htm. Accessed 23 Nov 2016.
Bourgeois S, Reesink HW, Leempoels J, Vijgen L, Rouan MC, Marien K, et al. Combination therapy of TMC647055 with simeprevir (TMC435) in chronic hepatitis C patients [abstract]. J Hepatol. 2013;58:S483.
Walker J, Crosby R, Wang A, Woldu E, Vamathevan J, Voitenleitner C, et al. Preclinical characterization of GSK2336805, a novel inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication that selects for resistance in NS5A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:38–47.
Wilfret DA, Walker J, Adkison KK, Jones LA, Lou Y, Gan J, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral activity of GSK2336805, an inhibitor of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A, in healthy subjects and subjects chronically infected with HCV genotype 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:5037–44.
Koletzki D, Pattery T, Fevery B, Vanhooren L, Stuyver LJ. Amplification and sequencing of the hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease and the NS5B polymerase regions for genotypic resistance detection of clinical isolates of subtypes 1a and 1b. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1030:137–49.
Thys K, Verhasselt P, Reumers J, Verbist BM, Maes B, Aerssens J. Performance assessment of the Illumina massively parallel sequencing platform for deep sequencing analysis of viral minority variants. J Virol Methods. 2015;221:29–38.
Nyanguile O, Devogelaere B, Vijgen L, Van den Broeck W, Pauwels F, Cummings MD, et al. 1a/1b subtype profiling of nonnucleoside polymerase inhibitors of hepatitis C virus. J Virol. 2010;84:2923–34.
Vijgen L, Verbeeck J, van Kerckhove B, Berke JM, Koletzki D, Fanning G, et al. A cellular replicon-based phenotyping assay to determine susceptibility of hepatitis C virus clinical isolates to NS3/4A protease inhibitors. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1030:105–17.
Verbinnen T, Fevery B, Vijgen L, Jacobs T, De Meyer S, Lenz O. In vitro activity of simeprevir against hepatitis C virus genotype-1 clinical isolates and its correlation with NS3 sequence and site-directed mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:7548–57.
Huang W, Newton A, Cook J, Toma J, Frantzell A, Choe S, et al. Development of recombinant replicon report assays for characterization of HCV NS5A and NS3/4A protease inhibitors. Antiviral Ther. 2011;16(Suppl. 1):A29.
Lenz O, Verbinnen T, Lin T-I, Vijgen L, Cummings MD, Lindberg J, et al. In vitro resistance profile of the hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitor TMC435. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:1878–87.
Fried MW, Buti M, Dore GJ, Flisiak R, Ferenci P, Jacobson I, et al. Once-daily simeprevir (TMC435) with pegylated interferon and ribavirin in treatment-naîve genotype 1 hepatitis C: the randomized PILLAR study. Hepatology. 2013;58:1918–29.
Forns X, Lawitz E, Zeuzem S, Gane E, Bronowicki JP, Andreone P, et al. Simeprevir with peginterferon and ribavirin leads to high rates of SVR in patients with HCV genotype 1 who relapsed after previous therapy: a phase 3 trial. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1669–79.
Jacobson IM, Dore GJ, Foster GR, Fried MW, Radu M, Rafalskiy VV, et al. Simeprevir with pegylated interferon alfa 2a plus ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (QUEST-1): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;384:403–13.
Poordad F, Lawitz E, Kowdley KV, Cohen DE, Podsadecki T, Siggelkow S, et al. Exploratory study of oral combination antiviral therapy for hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:45–53.
Krishnan P, Tripathi R, Schnell G, Reisch T, Beyer J, Irvin M, et al. Resistance analysis of baseline and treatment-emergent variants in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 in the AVIATOR study with paritaprevir-ritonavir, ombitasvir, and dasabuvir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:5445–54.
Fevery B, Vijgen L, Van Eygen V, Jessner W, Corbett C, Schlag M, et al. Consistent simeprevir resistance profile in hepatitis C virus genotype 1-infected patients failing simeprevir interferon-free compared with interferon-containing regimens [abstract]. J Hepatol. 2016;64:S399.
Sarrazin C. The importance of resistance to direct antiviral drugs in HCV infection in clinical practice. J Hepatol. 2016;64:486–504.
Wyles D, Mangia A, Cheng W, Shafran A, Schwabe C, Ouyang W, et al. Long-term persistence of HCV NS5A variants after treatment with NS5A inhibitor ledipasvir. J Hepatol. 2015;62(Suppl. 2):S221.
Fevery B, Thys K, Van Eygen V, Verbinnen T, Van Rossem E, Buelens A, et al. Pre-existence and persistence of resistant minority hepatitis C virus variants in genotype 1-infected patients treated with simeprevir/peginterferon/ribavirin. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3:ofw052.
Dierynck I, Thys K, Ghys A, Sullivan JC, Kieffer TL, Aerssens J, et al. Deep-sequencing analysis of the gene encoding the hepatitis C virus nonstructural 3-4A protease confirms a low prevalence of telaprevir-resistant variants at baseline and the end of the REALIZE study. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:1871–80.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patients and investigators for their contributions to this study. Medical writing support was provided by Luc Geeraert of Bench-to-Pen and by Chrissie Kouremenou of Complete Medical Communications, and funded by Janssen. Additional statistical and programming support was provided by Hilde Wuyts, Moshine El Ghazi and Gert Van Beek.
Funding
The study was funded by Janssen. Janssen were responsible for the study design and the collection and interpretation of data. Medical writing support was funded by Janssen.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors’ contributions
LV, KT, AV, PVR, RV, and SDM were involved in the study concept and design, and the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of study data. They have also been involved in the critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
LV, KT, AV, PVR, and SDM are employees of Janssen and may own stock in Johnson & Johnson. RV was an employee of Janssen at the time this study took place.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board or Independent Ethics Committee at each participating centre, and met the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice guidelines. All patients provided written, informed consent.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Study design. HCV NS3/4A, NS5B and NS5A sequence analysis. (DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Vijgen, L., Thys, K., Vandebosch, A. et al. Virology analysis in HCV genotype 1-infected patients treated with the combination of simeprevir and TMC647055/ritonavir, with and without ribavirin, and JNJ-56914845. Virol J 14, 101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-017-0760-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-017-0760-2