Abstract
In recent years, 5-methylcytosine (m5C) RNA modification has emerged as a key player in regulating RNA metabolism and function through coding as well as non-coding RNAs. Accumulating evidence has shown that m5C modulates the stability, translation, transcription, nuclear export, and cleavage of RNAs to mediate cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, stress responses, and other biological functions. In humans, m5C RNA modification is catalyzed by the NOL1/NOP2/sun (NSUN) family and DNA methyltransferase 2 (DNMT2). These RNA modifiers regulate the expression of multiple oncogenes such as fizzy-related-1, forkhead box protein C2, Grb associated-binding protein 2, and TEA domain transcription factor 1, facilitating the pathogenesis and progression of cancers. Furthermore, the aberrant expression of methyltransferases have been identified in various cancers and used to predict the prognosis of patients. In this review, we present a comprehensive overview of m5C RNA methyltransferases. We specifically highlight the potential mechanism of action of m5C in cancer. Finally, we discuss the prospect of m5C-relative studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Post-transcriptional modifications have become an important field of research with more than 170 RNA modifications being identified [1]. These modifications can significantly affect the biogenesis and function of coding and non-coding RNAs to mediate metabolism and play a regulatory role in the occurrence and progression of diseases. 5-methylcytosine is observed in a wide range of RNAs; it is the most abundant in tRNA and rRNA but has also been identified in mRNA and other noncoding RNAs [2]. According to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis, the methylation level of m5C is estimated to be 0.02–0.09% [3]. Currently, m5C detection methods are divided into three groups based on their principles: (1) immunoprecipitation-based sequencing, (2) chemical-dependent sequencing, and (3) third-generation sequencing based on electronic current signals (extensively reviewed in [4]). Although numerous studies are being conducted on m5C modification, its molecular mechanism and role in the pathophysiology of an organism is largely unknown.
Similar to m6A methylation, the enzymes regulating m5C levels of RNAs can be functionally categorized as “writers,” “erasers,” and “readers”. Methyltransferases, or writers, can install m5C on RNA. NSUN1-7 and DNMT2 have been well documented as m5C writers. Erasers or m5C demethylases, such as alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase ABH1 (ALKBH 1) and ten-eleven translation family proteins (TET), are known to remove m5C modifications from RNAs. The former can oxidize m5C of tRNA into 5-formylcytosince (f5C) in the mitochondria [5, 6], while the latter can oxidize m5C of mRNA into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hm5C) [7, 8]. Binding proteins that recognize m5C in RNAs are called readers. Known readers include RNA and export factor-binding protein 2 (ALYREF) [9] and Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) [10], where the protein Lin-28 homologous B (LIN28B) is also reported to possess the characteristics of a reader [11].
At present, writers of m5C have been studied exhaustively thereby giving a better functional clarity in different processes. This review focuses on the effects of m5C methyltransferases in molecular and cellular functions and their potential roles in cancer.
Main body
RNA Methyltransferases mediating m5C
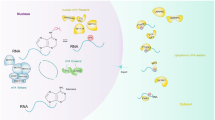
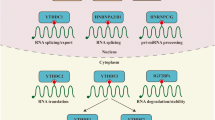
m5C methylation of human RNA is mainly catalyzed by the NOL1/NOP2/sun family and DNMT2, important for RNA stability and functionality. Methyltransferases transfer the methyl groups to cytosine through S-adenosylmethionine as a methyl donor to form m5C. Different cellular compartments possess the resident enzymes that bring about the modification. In the nucleus, m5C of mRNA, tRNA, 28S rRNA, and non-coding RNAs is mainly methylated by NSUN2, NSUN5, NSUN6, NSUN7, and NOP2. In the mitochondria, NSUN2 and NSUN3 methylate tRNA, and NSUN4 methylates 12S rRNA that promotes mitochondrial ribosome assembly (Table 1 and Fig. 1). The molecular mechanisms of m5C RNA methyltransferases and their biological functions are detailed below.
NOP2
NOP2 (Nucleolar protein 2, also termed NSUN1) methylates human 28S rRNA cytosine at position 4447 (C4447) [12]. It is necessary for the development of mammalian embryos by regulating nucleolar maturation at the preimplantation stage leading to blastocyst formation, and in ribosome biogenesis. Notably, rRNA processing requires the presence rather than the m5C modification activity of NOP2 [13, 14]. In addition, NOP2 promotes cell proliferation during nerve tissue regeneration [15]. In human tumor cells, NOP2 is shown to combine with the telomerase RNA component (TERC) via its rRNA methyltransferase domain, thereby activating and regulating cyclin D1 gene transcription, which maintains cell proliferation [16]. In HIV-1 virus, NOP2 binding to TAR RNA at the 5'-long terminal repeat (LTR) leads to addition of m5C, thereby inhibiting viral transcription and promoting its latency by competing with the TAT protein [17].
NOP2 is upregulated by microRNA PVT1 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) proliferation and prostate cancer metastasis [18, 19]. It also presents aberrant expression in several cancers, such as renal clear cell carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, colorectal cancer, and low-grade glioma, providing risk signatures associated with m5C methylation that can aid in the determination of patient prognosis [20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
NSUN2
NSUN2, predominantly located in the nucleus, is a direct target of c-MYC, which recruits nucleolar and spindle-associated protein (NuSAP) to stabilize the mitotic spindle in fast-dividing cells and adds m5C to mRNA and several noncoding RNAs [27, 28].
In mRNAs, m5C sites are distributed throughout the genome and are most frequently located in C-G rich regions. These sites are enriched in untranslated regions (UTRs) of mRNA, especially in the vicinity of the binding region of the Argonaute protein within the 3' UTRs [9, 29, 30]. The distribution of m5C sites in translation sequence (CDS) has not yet been determined. According to Tao Huang et al. [29], m5C sites had the lowest density in CDS; this view was not supported by Xin Yang et al. [9], who indicated that m5C sites were also abundant in regions immediately downstream of translation initiation sites. NSUN2-dependent m5C sites tend to be located at the 5' end of a stem-loop structure with a 3' G-rich triplet (3' CNGGG) motif as the specific structure and a sequence preference for NSUN2. This specific motif has been observed in multiple human and mouse tissues, demonstrating that NSUN2 is a major mRNA methyltransferase. Notably, another specific motif 3' CTCCA, which has also been detected in multiple tissues, has been identified as a specific sequence of NSUN6, another m5C methyltransferase of mRNA [29]. m5C modulates mRNA export through specific recognition of the mRNA export adaptor ALYREF [9] and regulates mRNA stability and translation. NSUN2 methylates interleukin-17A (IL-17A) mRNA to mediate the hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy)-induced upregulation of IL-17A expression and promotes its translation in T lymphocytes. [31] NSUN2 upregulates the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) by adding m5C to ICAM-1 mRNA, which affects vascular inflammation and allograft arteriosclerosis [32]. Moreover, NSUN2-mediated mRNA modification regulates the translation of various mRNAs such as SHC, cyclin-dependent kinase 1(CDK1), p21, and p27, to promote or delay cellular senescence [33,34,35,36]. Interestingly, m5C and m6A modifications of p21 mRNA facilitate each other and together they affect protein expression [35]. It has also been reported that NSUN2 introduces m6A in the 3' UTR of p16 mRNA to stabilize its structure and promote its expression under oxidative stress [37]. These findings indicate a novel methylation modification pattern via interaction with various RNA methyltransferases. Furthermore, NSUN2 appears to act as a double-edged sword in the regulation of mRNA stabilization. In bladder cancer, the cytoplasmic protein YBX1 recognizes the NSUN2-dependent m5C site located on the 3'UTR of heparin-binding growth factor (HDGF) mRNA and recruits ELAV-like RNA-binding protein 1 (ELAV1) to improve its stability. This specific recognition is attributed to the cold shock domain (CSD) of YBX1 [10]. LIN28B also has a similar structure [38] and stabilizes growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2) mRNA in an NSUN2-dependent manner in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), thus indicating that it is a potential m5C reader [11]. Additionally, in gastric cancer (GC), NSUN2 modifies the 3'UTR of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (CDKN1C, p57Kip2) mRNA to repress its stability, decreasing the half-life of p57Kip2 mRNA [39].
NSUN2 also modifies multiple cytoplasmic tRNAs with m5C, mediating cleavage and modulating stability to participate in the cell stress response. Exposure to oxidative stress effectively inhibits NSUN2, causing a decline in methylation at specific tRNA sites thereby resulting in increased angiogenin-mediated endonucleolytic cleavage of tRNA and accumulation of 5' tRNA-derived small RNA fragments (5' tRFs). The accumulation of 5' tRFs reduces the rate of protein translation and activates the stress pathway, leading to a decrease in cell size and increased apoptosis in the cortex, hippocampus, and striatal neurons in response to external stress stimuli [40, 41]. Modification of tRNA by NSUN2 also affects its translation efficiency. Knockout of NSUN2 in mouse neurons results in glycine-specific translation deficiency [42, 43]. In addition, NSUN2 methylates mitochondrial tRNA, however, inactivation of NSUN2 had no profound effect on the stability of mitochondrial tRNA and oxidative phosphorylation in differentiated cells [44].
It also methylates various ncRNAs to regulate their function. NSUN2 mediated methylation of miRNA-125b inhibits its processing and function in gene silencing [45, 46]. Notably, NSUN2 methylates miRNA-125b in an m6A manner rather than m5C. Vault RNA m5C modification by NSUN2 determines its processing to svRNA, which participates in the regulation of epidermal differentiation [47, 48], while its processing to lncRNA promotes tumorigenesis and aggression in several cancers [49, 50].
Owing to the extensive list of targets, NSUN2 plays a significant role in several processes including modulating cell functions in proliferation [34], stress response and metabolism [40, 41], migration and differentiation [51], and senescence processes [33,34,35,36]. It is associated with many diseases such as autism spectrum disorder [52], depression [42], Dubowitz syndrome [53, 54], intellectual disability [55,56,57], and is differentially expressed in a variety of cancers [20, 22, 58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68]. In recent years, several studies have explored its molecular mechanisms, constructed prognostic models, and attempted to find new targets for cancer treatment [11, 39, 46, 49, 50, 69,70,71,72,73,74]. Currently, studies regarding the regulation of NSUN2 in terms of biological function and cancer mechanism focus on its modification of mRNA. However, the pathway underlying the modifications of ncRNA induced by NSUN2 to interact with mRNA and proteins needs to be further investigated and explored. Moreover, although not yet discussed, the mechanism by which tRNA cleavage affects cellular stress responses may have significant potential for furthering the understanding of cancer.
NSUN3
In the mitochondria, NSUN3 mediates mt-tRNAMet methylation of cytosine at position 34 (C34) into m5C34 which is further oxidized by ALKBH1/ABH1 into f5C34 [75, 76]. f5C34 enables mt-tRNAMet to recognize AUA and AUG codons encoding methionine [6]. NSUN3 knockout and mutant cells show decreased mitochondrial protein synthesis and reduced oxygen consumption, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction [6]. A biallelic missense mutation in NSUN3 led to early onset mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and seizures [77]. Mutations in the NSUN3 gene may cause damage to the nervous system. Trixl et al. demonstrated the effect of inactivation of NSUN3 on the self-renewal and differentiation potential of mouse embryonic stem cells [78].
NSUN3 has been reported to be upregulated in several cancers, [20, 24, 79] and is associated with immune cell infiltration [79]. Its overexpression may play a regulatory role in sensitizing the cells against the chemotherapy drugs, thereby affecting patient prognosis [80, 81].
NSUN4
NSUN4 is a bifunctional protein playing a role in methylation of 12S rRNA at cytosine 911 (m5C911) [82,83,84,85], and interacting with MTERF4 to promote monomer assembly [82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91]. Though the mechanism is still unclear, m5C911 may cooperate with nearby m4C909 and other rRNA modifications to stabilize 12S rRNA folding, thereby facilitating mt-ribosome assembly [85].
NSUN4 expression affects embryonic development and mitochondrial protein synthesis. Germline knockout of the NSUN4 gene in mouse is embryonically lethal, and the conditional knockout in the heart is shown to interrupt mitochondrial protein translation, leading to impaired respiratory complex formation [92].
NSUN4 is aberrantly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and clear cell renal cell carcinoma and may be utilized to predict prognosis [20, 23, 79, 93].
NSUN5
NSUN5 introduces m5C at C3782 in the human 28S ribosomal RNA. Mammalian NSUN5 deficiency alters the ribosome affecting total protein synthesis impinging on cell size and proliferation [94]. This can be attributed to the maintenance of the tertiary rRNA-tRNA-mRNA complex due to m5C3782 [95].
NSUN5 also affects the development and function of the nervous system. Its deletion is associated with Williams–Beuren syndrome (WBS) [96,97,98]. The expression of NSUN5 is critical for cerebral cortex development. It controls the migration of neocortical neurons by regulating the radial glial scaffold of retinal ganglion cells [98]. NSUN5 deficiency disturbs the laminar organization of neocortical neurons and the development of pyramidal cells. This causes reduced proliferation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells and hypomyelination leading to agenesis of the corpus callosum (CC) and dysfunction of the NMDA receptor (NMDAr) in hippocampal pyramidal cells [96, 97]. Moreover, in the cardiovascular system, NSUN5-mediated m5C modification is essential for maintaining the expression of Tpm1, which is an essential gene for normal cardiac outflow tract (OFT) morphogenesis, suggesting the involvement of NSUN5 in the tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) [99].
NSUN5 is significantly upregulated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) [100] and acts as a promoter of colorectal cancer (CRC) by triggering cell cycle arrest.[101]. Its epigenetic inactivation is observed in gliomas and exhibits tumor-suppressive characteristics [95].
NSUN6
NSUN6 has a strong substrate specificity for mRNA, mainly targeting the 3' UTR at the consensus sequence motif CTCCA located in the loops of hairpin structures to install m5C modifications, rather than the 3' CNGGG motif targeted by NSUN2 [29, 102]. The NSUN6-targeted CTCCA motif marks the translational termination. The methylated hairpin structure at 3'UTR is likely responsible for translational termination, but there is no evidence to confirm this view [103]. In human HEK and H9 cell lines, NSUN6 primarily targets mRNAs encoding RNA- and protein-binding proteins. NSUN6-mediated m5C modification enhances mRNA abundance and translation efficiency. [102]. It also methylates cytosine 72 (C72) at the 3′-end receptor stems of tRNACys and tRNAThr. Target recognition depends on the presence of a 3′-CCA tail [104].
In tumors derived from tissues with high NSUN6 expression, NSUN6 mRNA levels are downregulated. In contrast, when tumors were derived from NSUN6 low-expressing tissues, there was no difference in RNA levels [102]. NSUN6 has also been shown to inactivate macrophage stimulating 1 (MST1) and activate yes-associated protein (YAP) target genes in breast cancer through m5C modification, thereby triggering osteoclast differentiation and bone metastasis [105]. As these are m5C methyltransferases of mRNA, correlations between NSUN2 and NSUN6 have been analyzed using bioinformatics, which have shown them to be positively correlated, uncorrelated and negatively correlated in renal cancer [23], triple-negative breast cancer [59], and cutaneous melanoma [24], respectively. However, all studies conducted to date have failed to provide direct evidence to support the correlation between the two enzymes. Furthermore, no reader has been detected to recognize NSUN6-dependent m5C sites on mRNA, which hinders further understanding of the regulatory role of NSUN6 in cell metabolism and cancer progression.
NSUN7
The interaction between NSUN7 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α) promotes transcription of fasting related genes. Meanwhile, NSUN7 enhances the stability of eRNAs through m5C modification and may be involved in the regulation of cell metabolism [106].
Moreover, NSUN7 mutation can lead to impaired sperm quality and infertility [107, 108]. This may be caused by the transversion mutation of exon7, thereby affecting protein structure and ligand-binding site [109]. However, this mutation is not associated with asthenospermia in Han Chinese men [110]. In addition, NSUN7 is also correlated with mental disorders [111] and is used in the prognosis of patients with Ewing sarcoma, low-grade glioma, and prostate cancer [112,113,114].
DNMT2
Compared with other DNA methyltransferases, such as DNMT1, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b, DNMT2 exclusively consists of the C-terminal catalytic domain but lacks the N-terminal regulatory domain. [115] DNMT2 (also termed TRDMT1) does not possess DNA catalytic activity but introduces m5C38 into tRNAAsp (GUC) [116].
The m5C modification mediated by DNMT2 improves tRNA stability, where tRNAAsp is protected from ribonuclease cleavage during the heat shock response in Drosophila and is protected from fragmentation in mice [43, 117]. Moreover, DNMT2 influences the expression and precision of protein synthesis via m5C. DNMT2-mediated tRNAAsp m5C38 regulates the translation of proteins containing poly-Asp sequences. Mouse aspartyl-tRNA synthetase shows a four-to-five-fold preference for C38 methylated tRNAAsp [118]. DNMT2 also ensures precise peptide synthesis through the discrimination of near-cognate codons and is necessary for cell differentiation and protein synthesis [119]. It also participates in the regulation of mRNA methylation and affects the migration and invasion of HEK293 cells [120].
DNMT2 plays a regulatory role in the cellular stress response. Under stress conditions, DNMT2 localizes to cytoplasmic stress granules and RNA-processing bodies [121, 122]. DNMT2 silencing results in enhanced oxidative stress, genomic instability, permanent inhibition of cell proliferation, diminished telomere length and telomerase activity, global RNA hypermethylation, and upregulation of multiple miRNAs related to proliferation and tumor suppression [123, 124].
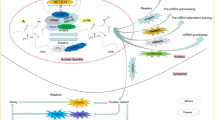
Potential roles of m5C RNA methyltransferases in cancer
m5C methyltransferases, especially NSUN2, regulates substrate levels by catalyzing m5C modification of target RNA to mediate the crosslinking of a series of oncogenic or antitumor factors, thus affecting tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Here, we elaborate on the aberrant expression and corresponding mechanism of m5C methyltransferase in cancer (Table 2 and Fig. 2).
Hepatocellular carcinoma
In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the mutation frequency of m5C regulatory genes is high, and the dysregulation of m5C related genes is associated with higher stages of HCC [93]. In HCC cells, lncRNA-PVT1 combines with NOP2 to upregulate its expression via stability enhancement. The hPVT1/NOP2/cell cycle pathway promotes carcinogenesis, cell proliferation, and stem cell-like properties. Targeting this pathway may have therapeutic potential in HCC [125].
The transcript level of NSUN2 is upregulated in HCC cells, which promotes proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis, and inhibits apoptosis of HCC cells [49, 58]. NSUN2 increases the stability of fizzy-related-1 (FZR1) mRNA thereby modulating FZR1 expression, leading to enhanced growth of HCC cells and tumors [58]. FZR1 is a coactivator of the anaphase-promoting complex or cyclosome [126]. As an E3 ubiquitin ligase, FZR1 regulates mitosis and the G1 phase of the cell cycle [127]. Recently, FZR1 has been found to play a regulatory role in colorectal cancer [126], breast cancer [128], B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia [129], and multiple myeloma [130]. NSUN2 silencing inhibits FZR1, inducing cell cycle arrest and increased apoptosis in HCC cells. Notably, NSUN2-KO cells inhibit the expression of FZR1 in gastric cancer cells, which is consistent with HCC [39]. However, the role of NSUN2-FZR1 in migration and invasion in HCC is not clear [58]. Moreover, NSUN2 introduced m5C986 at the H19 lncRNA to enhance its stability. NSUN2 deficiency significantly reduces the half-life of H19 RNA [49]. m5C modification of H19 RNA enhances its specific binding to the tumor protein G3BP1, which binds to MYC mRNA and promotes its decay [131]. In contrast, m5C-modified H19 RNA may compete with MYC mRNA to bind to G3BP1, leading to MYC accumulation and promoting the development of HCC cells. High levels of H19 expression and m5C-modification are related to poor differentiation in HCC [49].
In addition, NSUN4 and m5C reader ALYREF are upregulated in HCC and are associated with poor prognosis [93].
Gastrointestinal cancer
Bioinformatics analysis showed that the expression of all regulators of m5C, except NSUN6, was significantly upregulated from pathological stages I to IV in gastrointestinal (GI) cancer and, except NSUN7, was associated with shorter overall survival (OS). m5C regulators have the greatest impact on ErbB and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, and BSK3B is an important potential target of the m5C regulators [61].
Among GI tumors, NSUN2 has the highest mutation rate [61]. In gastric cancer (GC) cells, a small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)-2/3 interacts with the NSUN2 protein to promote its stability and mediate its import into the nucleus. NSUN2 promotes tumor progression through both m5C-dependent and -independent pathways [60]. NSUN2 is recruited by the lncRNA forkhead box protein C2 (FOXC2)-AS1 to modify FOXC2 mRNA in an m5C-dependent manner. The m5C reader YBX1 combines with methylated FOXC2 mRNA to enhance its stability, thereby facilitating the proliferation, migration, and invasion of GC cells [60]. FOXC2 is an oncogene, overexpressed in multiple cancers promoting cell proliferation and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [132,133,134,135,136]. Moreover, NSUN2 destabilizes the p57Kip2 transcript by introducing m5C modifications in the 3-UTR of p57Kip2 mRNA, thereby repressing its expression and promoting the proliferation of GC cells [39]. p57kip2 is a CDK inhibitor of the CIP/Kip family that participates in several biological processes [137, 138]. It functions as an antitumor factor in gastric cancer and is down-regulated in multiple cancers [139,140,141]. In addition, in NSUN2-KO GC cells, PIK3R1 and PCYT1A mRNAs were downregulated, with diminished m5C peaks. Bioinformatics analysis of the TCGA data set showed that high expression of phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 1 (PIK3R1) and phosphate cytidylyltransferase 1A (PCYT1A) was associated with a poor prognosis of GC [60].
In addition, DNMT2 is significantly overexpressed in adult gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) compared to adjacent non-tumor tissues [142].
Colorectal cancer
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs produced by back-splicing [143]. Circ NSUN2, NSUN2, and NSUN5 are upregulated in CRC and promote its progression. Overexpression of circNSUN2 promotes the metastasis, migration, and proliferation of CRC cells and inhibits tumor cell apoptosis. Mediated by YTH domain-containing 1 (YTHDC1) in an m6A-dependent manner, circNSUN2 is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where high levels of circNSUN2 enhance the stability of high-mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) mRNA by forming a circNSUN2/ insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2)/HMGA2 RNA–protein ternary complex, resulting in liver metastasis (LM) of CRC [73]. Moreover, as a miRNA sponge, circNSUN2 targets miR‑181a‑5p and downregulates its expression. The oncogene Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 (ROCK2) is downregulated by miR‑181a‑5p. The repression of the negative regulation of miR‑181a‑5p on ROCK2 mediated by circNSUN2 promotes the proliferation and migration of CRC cells and inhibits their apoptosis [70]. In addition, circNSUN2 targets miR-296-5p and is downregulated by alopperine (ALO), which upregulates the abnormally low expression of miR-296-5p in CRC. miR-296-5p binds to STAT3 and inhibits its expression, thus inhibiting the proliferation and promoting apoptosis of CRC cells. CircNSUN2 silencing inhibits CRC cell proliferation, which can be neutralized by a miR296-5p inhibitor. ALO regulates the circNSUN2/miR-296-5p/STAT3 pathway to prevent colorectal cancer [144].
In colorectal cancer specimens, NSUN2 is activated by protein activated receptor 2 (PAR2) and methylated pre-mir-125b in an m6A-dependent manner to interfere with its processing, thereby reducing the level of miR-125b. Grb associated-binding protein 2 (Gab2) mediates cell migration, which is repressed by miR-125b. The suppression of miR-125b enhances Gab2 expression, thereby promoting cell migration [46].
NSUN5 is upregulated in CRC tissues and cells. NSUN5-KO mice showed a significant reduction in cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest. GSEA suggested that NSUN5 may promote the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells through the Rb-CDK signal transduction pathway [101].
Glioma
In low-grade gliomas, several m5C regulators of DNA and RNA are upregulated, including NSUN3, TET2, DNMT2, ALYREF, DNMT3b, DNMT1, NOP2, and NSUN2. Furthermore, multiple m5C regulators were correlated with OS. NSUN4, NSUN7, DNMT1, DNMT3b, DNMT3a, NOP2, and NSUN5 were negatively correlated with OS, whereas NSUN6 was positively correlated with OS. Based on this, a prognostic model consisting of NSUN7, DNMT1, NSUN4, and NSUN6 was constructed [22].
In the human glioma cell line U87, NSUN2 mediates tumor cell migration by regulating the autotaxin (ATX)- lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) axis. NSUN2 methylates ATX mRNA 3’-UTR at cytosine 2756, thereby enhancing ATX mRNA translation. ATX-LPA pathway mediates the migration of cancer cells. Moreover, ALYREF interacts with methylated ATX mRNA to promote its export from the nucleus to cytoplasm. NSUN2-KO inhibits the migration of U87 cells, which can be recovered by the addition of LPA [72].
In the in vivo glioma models, NSUN5 showed hypermethylation of the CpG island promoter, leading to a reduction in transcripts and epigenetic silencing. NSUN5 silencing induced the deletion of 28S rRNA methylation at position C3782. The unmethylated state leads to the overall depletion of protein synthesis while activating the specific mRNA translation program under stress conditions, which results in the upregulation of NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) protein. NQO1 overexpression confers sensitivity to drugs that target NQO1. Therefore, NSUN5 epigenetic silencing is a protective factor in gliomas and is correlated with a better prognosis [95].
Breast cancer
In breast cancer cells and tissues, NSUN2 DNA hypomethylation leads to overexpression of NSUN2 mRNA and protein. Upregulation of NSUN2 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells, whereas NSUN2-KO inhibits these processes [67]. In triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), NSUN2 expression is upregulated thereby acting as a tumor-promoting factor, whereas NSUN6 is downregulated as a tumor suppressor. NSUN2 and NSUN6 affect tumorigenicity and the tumor immune microenvironment (TIM) of breast cancer [59]. Furthermore, the upregulation of NSUN2 and NOP2 mRNA was significantly associated with shorter disease-free survival in breast cancer patients [62].
Conversely, Li Chunlai et al. showed that NSUN6 promotes bone metastasis in breast cancer. HER3 is phosphorylated by tyrosine kinase (RTK)-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1). NSUN6 is recruited by p-HER3 to methylate MST1, thus affecting the kinase activity of MST1 and activating YAP. The activation and accumulation of YAP in the nucleus stimulates the expression of target genes that correlate with tumor cell proliferation and bone metastasis [105].
Urinary tumor
In urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (UCB), NSUN2 and m5C reader YBX1 are upregulated, which are positively correlated with T and N stages, the tumor grades of UCBs and poor disease-free survival of UCB patients. As described previously, NSUN2 introduces m5C into the 3'UTR of HDGF mRNA. YBX1 further recruits ELAV1 to stabilize m5C-modified mRNA to modulate the expression of HDGF. Invasion and metastatic abilities were significantly diminished in NSUN2- and YBX1-KO T24 cells [10]. As an oncogene in multiple cancers, HDGF has been shown to promote aggression and invasion [145,146,147].
In prostate cancer, the expression of NOP2 is elevated, which promotes metastasis and invasion through the EMT pathway [18]. NOP2 is the target gene of miR-PVT1 and miR-542-3p and is indirectly regulated by the lncRNA LINC00963 [18, 19]. Moreover, the level of DNMT2 is higher in tumor cells than in non-tumor epithelium, and in lymph node metastatic foci than in primary cancer. The expression of DNMT2 also increases in patients receiving androgen ablation therapy [148].
In clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), the mRNA levels of NOP2 and NSUN4 are higher in tumor tissues than in normal tissues, whereas the mRNA levels of NSUN6 and m5C eraser TET2 are lower. The four m5C regulators constitute a risk signature for determining prognosis of patients [23]. High NOP2 expression in ccRCC was associated with poor OS [21]. Another study showed upregulation of NSUN5, ALYREF, DNMT3b, DNMT3A, NSUN2, NOP2, and DNMT1, and downregulation of NSUN3, NSUN4, NSUN7, and TET2 in ccRCC. The study proposed a risk signature consisting of seven m5C regulators: NOP2, NSUN2, NSUN3, NSUN4, NSUN5, TET2, and DNMT3b [20].
Other cancers
In gallbladder carcinoma (GBC), the expression of NSUN2 is elevated in both cells and tissues. NSUN2 silencing inhibits the proliferation and tumorigenesis of GBC cells, whereas its overexpression promotes their growth. RPL6 modulates the translation of NSUN2 mRNA to exert carcinogenic effects. In RPL6 silenced cells, the level of NSUN2 protein was reduced, resulting in NSUN2 mRNA accumulation [149].
In lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), NSUN3 and NSUN4 are upregulated and associated with poor prognosis. These are utilized to construct a prognostic risk signature. Furthermore, NSUN3 and NSUN4 are correlated with the infiltration of six major immune cells [79]. In lung adenocarcinoma, in vitro experiments indicated that cells with high expression of NOP2 or heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) are more likely to be poorly differentiated [26]. Interestingly, loss of the region containing NSUN3 is common in non-smokers with lung adenocarcinoma at a frequency of 15% [150].
In cutaneous melanoma (CM), DNMT2, NSUN3, NSUN6, YBX1, and NOP2 are differentially expressed and used to calculate risk scores in patients. In particular, the upregulation of NOP2 and the downregulation of NSUN6 are closely associated with the progression of melanoma [24].
In esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), NSUN2 is overexpressed and plays an oncogenic role [11, 50]. NSUN2 is known to be positively regulated by E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) and induces m5C modification in the 3'UTR of growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2) mRNA. The Lin-28 homologous B (LIN28B) recognizes the modification to enhance GRB2 stability, through which elevated GRB2 activates PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK signaling [11]. Another study showed that NSUN2 methylated a novel lncRNA named NSUN2 methylated lncRNA (NMR). NMR promotes the metastasis and invasion of ESCC and enhances their resistance to cisplatin, possibly because m5C modified NMR inhibits the methylation of potential mRNAs [50].
In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), the expression of NSUN2 is significantly upregulated, which correlates with shorter OS as well as the expression of cell cycle checkpoint-related genes [66]. NSUN2 may be regulated by Klotho (KL) where its low expression is positively correlated with the higher expression of KL and KL DNA hypomethylation [65]. Moreover, NSUN2 expression was negatively correlated with T-cell activation score. Higher mortality was observed in patients with low NSUN2 expression and high T cell activation scores [63].
In hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HPSCC), mRNA and protein levels of NSUN2 are upregulated. NSUN2 modified 3'UTR of TEA domain transcription factor 1 (TEAD1) mRNA with m5C which promotes the expression of TEAD1, thereby enhancing the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells [71]. TEAD1 coordinates and integrates multiple signaling pathways. Its downregulation affects the expression of various oncogenes that modulate the progression, metastasis, and resistance of tumor cells to chemotherapy [151,152,153].
In pancreatic cancer (PC), the level of NSUN6 decreased significantly. Overexpression of NSUN6 inhibits the proliferation of PC cells and enhances CDK10 levels, suggesting that NSUN6 may regulate the growth of PC tumors by modulating CDK10. High expression of NSUN6 can predict lower risk and better prognosis in patients with PC [154].
m5C RNA methyltransferases in cancer therapy
Although no specific inhibitor of m5C RNA methyltransferase has been developed thus far, several chemicals can interact with these methyltransferases to inhibit cancer progression. It has been reported that azacytidine can inhibit the methylation of C38 of tRNAAsp, catalyzed by DNMT2, to reduce the metabolic activity of cancer cells [155]. In breast cancer cells, the phytochemicals sulforaphane (SFN), ursolic acid (UA), and betulinic acid (BA) can reduce the expression of NOP2 and inhibit cell proliferation, possibly contributing to reduced translation efficiency caused by interference of ribosome formation [156].
m5C RNA methyltransferase also regulates drug resistance in cancer cells. In leukemia, RNA m5C enzymes regulate sensitivity and resistance to 5-Azacytidine (5-AZA). In 5-AZA-sensitive leukemia cells (ASLCs), NSUN3 and DNMT2 interact directly with hnRNP, which is involved in the formation of a 5-AZA-sensitive chromatin structure which forms a complex essential for the integrity of these proteins. In 5-AZA-resistant leukemia cells (ARLC), the interaction of NOP2, BRD4, and RNA pol-II is associated with the formation of an active chromatin structure with resistance to 5-AZA but is highly sensitive to the inhibition of BRD4 and NOP2 [81]. Moreover, NSUN2 and methyltransferase 1 (METTL1), another tRNA methyltransferase, enhance the cancer cell resistance to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) by stabilizing tRNA and preventing RTD through methylation [157]. Notably, NSUN2 phosphorylation by Aurora-B led to its reduced enzymatic activity [158]. In glioblastoma, NSUN2 is a target gene of nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1), and its high expression is associated with resistance to temozolomide (TMZ) therapy [64]. In melanoma, the increased expression of NSUN5 is used to predict the sensitivity of melanoma cells to the pyrazopyrimidine derivative c-Src inhibitor 10a [159].
DNMT2 also modulates the adverse effects on cancer cells associated with chemotherapy-induced senescence [160].
Conclusion
In this review, we have summarized the molecular mechanisms and biological implications of m5C RNA methyltransferases and discussed their potential roles in cancer. m5C RNA methyltransferases are modifiers which introduce m5C into a variety of RNAs. In mRNAs, m5C modifications can modulate stability and mediate nuclear export and translation, while in ncRNAs, m5C modifications affects their stability, processing, cleavage, transcription, and translation. The downstream effects of these molecular functions/processes further mediate the regulation of various cellular functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence, stress response, and inflammation. Interestingly, m5C RNA methyltransferase is also involved in the catalysis of m6A, which has a combinatorial effect with m5C. In conclusion, m5C methyltransferase is being recognized as a significant factor in post-transcriptional regulation because emergent studies on its regulatory mechanism, prognostic function, and target therapy are emphasizing its potential and feasibility for clinical application.
Although the functions of m5C RNA methyltransferase in cancer have become the focus of many studies in recent years, our knowledge is still far from complete. At present, no studies have discussed the interaction network between m5C methyltransferases, which may cause the regulatory mechanisms of key pathways in cancer to be neglected. Moreover, the specific function of some m5C sites, such as the methylation of tRNA by NSUN2 and NSUN6 and the methylation of 28S rRNA by NOP2, has not been determined. Notably, most current studies focus on mRNA, but the modification of rRNA by NSUN5 and the modification of lncRNA and miRNA by NSUN2 suggest the potential of m5C modification of non-coding RNA for cancer development. Furthermore, for RNA methyltransferases with multiple substrates, it is difficult to confirm which RNA modification causes phenotypic changes through single gene silencing experiments. More precise experimental designs are required to clarify their functions. In addition, the reader and eraser for m5C modifications should closely examined. Compared with the understanding of m6A modification, the current knowledge on m5C-related regulators is lacking, because it is hard to describe their biological processes and functions comprehensively. In mRNAs, m5C levels are lower (0.02–0.09%) [3] than m6A levels (0.4–0.7%) [161, 162], which entails the development of a more sensitive and reliable detection method for m5C. At present, none of the specific m5C RNA methyltransferase inhibitors have been developed as antitumor drugs.
Though studies of m5C RNA methyltransferases are helpful in revealing the mechanisms and roles of RNA methylation, a deep understanding of the pathogenesis and development of cancer becomes essential for efficient evaluation and treatment of patients. Based on the detailed review, we expect that upcoming studies on m5C RNA methyl transferases would address the following four aspects: (a) detecting the aberrant expression of m5C methyltransferases in cancers and constructing risk scores to assess patient survival; (b) exploring the targets of m5C RNA methyltransferases and constructing a regulatory crosslink model consisting of the associated molecular pathways; (c) developing targeted therapies related to m5C to provide new potential options for cancer treatment; and (d) developing high-precision and universal m5C detection sequencing techniques suitable for mRNAs.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- m5C:
-
5-Methylcytosine
- NSUN:
-
NOL1/NOP2/sun
- DNMT2:
-
DNA methyltransferase 2
- ALKBH:
-
1Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase ABH1
- TET:
-
Ten-eleven translator family proteins
- ALYREF:
-
RNA and export factor-binding protein 2
- f5C:
-
5-Formylcytosince
- hm5C:
-
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine
- YBX1:
-
Y-box-binding protein 1
- LIN28B:
-
Lin-28 homologous B
- SAM:
-
S-adenosylmethionine
- TERC:
-
Telomerase RNA component
- LTR:
-
Long terminal repeat
- NuSAP:
-
Nucleolar and spindle-associated protein
- IL-17A:
-
Interleukin-17A
- HHcy:
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
- CDK1:
-
Cyclin dependent kinase 1
- UTR:
-
Untranslated regions
- 5' tRFs:
-
5' TRNA-derived small RNA fragments
- WBS:
-
Williams-Beuren syndrome
- CC:
-
Corpus callosum
- NMDAr:
-
NMDA receptor
- OPCs:
-
Oligodendrocyte precursor cells
- OFT:
-
Outflow tract
- TOF:
-
Tetralogy of Fallot
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- MST1:
-
Macrophage stimulating 1
- YAP:
-
Yes-associated protein
- PGC-1α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- FZR1:
-
Fizzy-related-1
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- SUMO:
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier
- FOXC2:
-
Forkhead box protein C2
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- CDKN1C, p57Kip2 :
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C
- PIK3R1:
-
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 1
- PCYT1A:
-
Phosphate cytidylyltransferase 1A
- GIST:
-
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- circRNAs:
-
Circular RNAs
- YTHDC1:
-
YTH domain containing 1
- HMGA2:
-
High mobility group AT-hook 2
- IGF2BP2:
-
Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2
- LM:
-
Liver metastasis
- ROCK2:
-
Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2
- ALO:
-
Aloperine
- PAR2:
-
Protein activated receptor 2
- Gab2:
-
Grb associated-binding protein 2
- ATX:
-
Autotaxin
- LPA:
-
Lysophosphatidic acid
- NQO1:
-
NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- TIM:
-
Tumor immune microenvironment
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- ROR1:
-
RTK-like orphan receptor1
- UCB:
-
Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder
- HDGF:
-
Heparin binding growth factor
- ELAV1:
-
ELAV like RNA binding protein 1
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- GBC:
-
Gallbladder carcinoma
- LUSC:
-
Lung squamous cell carcinoma
- hnRNP:
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein
- CM:
-
Cutaneous melanoma
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- E2F1:
-
E2F Transcription Factor 1
- GRB2:
-
Growth factor receptor-bound protein2
- CSD:
-
Cold shock domain
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- KL:
-
Klotho
- HPSCC:
-
Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- TEAD1:
-
TEA Domain Transcription Factor 1
- PC:
-
Pancreatic cancer
- SFN:
-
Sulforaphane
- UA:
-
Ursolic acid
- BA:
-
Betulinic acid
- 5-AZA:
-
5-Azacitidine
- ASLC:
-
AZA-sensitive leukemia cells
- ARLC:
-
5-AZA-resistant leukemia cells
- METTL1:
-
Methyltransferase 1
- NRF1:
-
Nuclear respiratory factor 1
References
Boccaletto P, et al. MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D303-d307.
García-Vílchez R, Sevilla A, Blanco S. Post-transcriptional regulation by cytosine-5 methylation of RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019;1862(3):240–52.
Huber SM, et al. Formation and abundance of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in RNA. ChemBioChem. 2015;16(5):752–5.
Chen YS, et al. Dynamic transcriptomic m(5) C and its regulatory role in RNA processing. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021;12(4): e1639.
Haag S, et al. NSUN3 and ABH1 modify the wobble position of mt-tRNAMet to expand codon recognition in mitochondrial translation. Embo j. 2016;35(19):2104–19.
Nakano S, et al. NSUN3 methylase initiates 5-formylcytidine biogenesis in human mitochondrial tRNA(Met). Nat Chem Biol. 2016;12(7):546–51.
Shen Q, et al. Tet2 promotes pathogen infection-induced myelopoiesis through mRNA oxidation. Nature. 2018;554(7690):123–7.
Fu L, et al. Tet-mediated formation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in RNA. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136(33):11582–5.
Yang X, et al. 5-methylcytosine promotes mRNA export - NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as an m(5)C reader. Cell Res. 2017;27(5):606–25.
Chen X, et al. 5-methylcytosine promotes pathogenesis of bladder cancer through stabilizing mRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(8):978–90.
Su J, et al. NSUN2-mediated RNA 5-methylcytosine promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via LIN28B-dependent GRB2 mRNA stabilization. Oncogene. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01978-0.
Bourgeois G, et al. Eukaryotic rRNA modification by yeast 5-methylcytosine-methyltransferases and human proliferation-associated antigen p120. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7): e0133321.
Cui W, et al. Nop2 is required for mammalian preimplantation development. Mol Reprod Dev. 2016;83(2):124–31.
Wang H, et al. The nucleolar protein NOP2 is required for nucleolar maturation and ribosome biogenesis during preimplantation development in mammals. Faseb j. 2020;34(2):2715–29.
Kosi N, et al. Nop2 is expressed during proliferation of neural stem cells and in adult mouse and human brain. Brain Res. 2015;1597:65–76.
Hong J, Lee JH, Chung IK. Telomerase activates transcription of cyclin D1 gene through an interaction with NOL1. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(8):1566–79.
Kong W, et al. Nucleolar protein NOP2/NSUN1 suppresses HIV-1 transcription and promotes viral latency by competing with Tat for TAR binding and methylation. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16(3): e1008430.
Sun F, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00963 induces NOP2 expression by sponging tumor suppressor miR-542-3p to promote metastasis in prostate cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(12):11500–16.
Sun F, et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by increasing NOP2 expression via targeting tumor suppressor MicroRNAs. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:6755–65.
Wu J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of m(5)C RNA methylation regulator genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Genomics. 2021;2021:3803724.
Wang G, et al. Nucleolar protein NOP2 could serve as a potential prognostic predictor for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):4841–55.
Li X, Meng Y. Expression and prognostic characteristics of m(5) C regulators in low-grade glioma. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(3):1383–93.
Li H, et al. Prognostic value of an m(5)C RNA methylation regulator-related signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:6673–87.
Huang M, et al. m5C-related signatures for predicting prognosis in cutaneous melanoma with machine learning. J Oncol. 2021;2021:6173206.
Gong Y, et al. Age-associated proteomic signatures and potential clinically actionable targets of colorectal cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2021;20: 100115.
Sun L, et al. Large-scale transcriptome analysis identified RNA methylation regulators as novel prognostic signatures for lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(12):751.
Shinoda S, et al. Mammalian NSUN2 introduces 5-methylcytidines into mitochondrial tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(16):8734–45.
Hussain S, et al. The nucleolar RNA methyltransferase Misu (NSun2) is required for mitotic spindle stability. J Cell Biol. 2009;186(1):27–40.
Huang T, et al. Genome-wide identification of mRNA 5-methylcytosine in mammals. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019;26(5):380–8.
Squires JE, et al. Widespread occurrence of 5-methylcytosine in human coding and non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(11):5023–33.
Wang N, et al. Homocysteine upregulates interleukin-17A expression via NSun2-mediated RNA methylation in T lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;493(1):94–9.
Luo Y, et al. NSun2 deficiency protects endothelium from inflammation via mRNA methylation of ICAM-1. Circ Res. 2016;118(6):944–56.
Cai X, et al. RNA methyltransferase NSUN2 promotes stress-induced HUVEC senescence. Oncotarget. 2016;7(15):19099–110.
Xing J, et al. NSun2 promotes cell growth via elevating cyclin-dependent kinase 1 translation. Mol Cell Biol. 2015;35(23):4043–52.
Li Q, et al. NSUN2-mediated m5C methylation and METTL3/METTL14-mediated m6A methylation cooperatively enhance p21 translation. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(9):2587–98.
Tang H, et al. NSun2 delays replicative senescence by repressing p27 (KIP1) translation and elevating CDK1 translation. Aging (Albany NY). 2015;7(12):1143–58.
Zhang X, et al. The tRNA methyltransferase NSun2 stabilizes p16INK4 mRNA by methylating the 3’-untranslated region of p16. Nat Commun. 2012;3:712.
Budkina KS, et al. Cold shock domain proteins: structure and interaction with nucleic acids. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020;85(Suppl 1):S1-s19.
Mei L, et al. RNA methyltransferase NSUN2 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation by repressing p57(Kip2) by an m(5)C-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(4):270.
Blanco S, et al. Aberrant methylation of tRNAs links cellular stress to neuro-developmental disorders. Embo j. 2014;33(18):2020–39.
Gkatza NA, et al. Cytosine-5 RNA methylation links protein synthesis to cell metabolism. PLoS Biol. 2019;17(6): e3000297.
Blaze J, et al. Neuronal Nsun2 deficiency produces tRNA epitranscriptomic alterations and proteomic shifts impacting synaptic signaling and behavior. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4913.
Tuorto F, et al. RNA cytosine methylation by Dnmt2 and NSun2 promotes tRNA stability and protein synthesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19(9):900–5.
Van Haute L, et al. NSUN2 introduces 5-methylcytosines in mammalian mitochondrial tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(16):8720–33.
Yuan S, et al. Methylation by NSun2 represses the levels and function of microRNA 125b. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34(19):3630–41.
Yang L, et al. Proteinase-activated receptor 2 promotes cancer cell migration through RNA methylation-mediated repression of miR-125b. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(44):26627–37.
Hussain S, et al. NSun2-mediated cytosine-5 methylation of vault noncoding RNA determines its processing into regulatory small RNAs. Cell Rep. 2013;4(2):255–61.
Sajini AA, et al. Loss of 5-methylcytosine alters the biogenesis of vault-derived small RNAs to coordinate epidermal differentiation. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2550.
Sun Z, et al. Aberrant NSUN2-mediated m(5)C modification of H19 lncRNA is associated with poor differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2020;39(45):6906–19.
Li Y, et al. Novel long noncoding RNA NMR promotes tumor progression via NSUN2 and BPTF in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2018;430:57–66.
Flores JV, et al. Cytosine-5 RNA methylation regulates neural stem cell differentiation and motility. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;8(1):112–24.
Doan RN, et al. Recessive gene disruptions in autism spectrum disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51(7):1092–8.
Innes AM, McInnes BL, Dyment DA. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in Dubowitz syndrome: Implications for diagnosis, management and further research. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2018;178(4):387–97.
Martinez FJ, et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies a splicing mutation in NSUN2 as a cause of a Dubowitz-like syndrome. J Med Genet. 2012;49(6):380–5.
Kato K, et al. Expanding the phenotype of biallelic loss-of-function variants in the NSUN2 gene: Description of four individuals with juvenile cataract, chronic nephritis, or brain anomaly as novel complications. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185(1):282–5.
Sun S, et al. Further delineation of autosomal recessive intellectual disability syndrome caused by homozygous variant of the NSUN2 gene in a chinese pedigree. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020;8(12): e1518.
Komara M, et al. A novel single-nucleotide deletion (c.1020delA) in NSUN2 causes intellectual disability in an emirati child. J Mol Neurosci. 2015;57(3):393–9.
Zhai CT, et al. RNA methyltransferase NSUN2 promotes growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating fizzy-related-1 in vitro and in vivo. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12430.
Huang Z, et al. Prognostic significance and tumor immune microenvironment heterogenicity of m5C RNA methylation regulators in triple-negative breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 657547.
Hu Y, et al. NSUN2 modified by SUMO-2/3 promotes gastric cancer progression and regulates mRNA m5C methylation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(9):842.
Xiang S, et al. m(5)C RNA methylation primarily affects the erbb and pi3k-akt signaling pathways in gastrointestinal cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7: 599340.
Manning M, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of RNA methyltransferases identifies FTSJ3 as a potential regulator of breast cancer progression. RNA Biol. 2020;17(4):474–86.
Lu L, et al. Transfer RNA methyltransferase gene NSUN2 mRNA expression modifies the effect of T cell activation score on patient survival in head and neck squamous carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2020;101: 104554.
Bhawe K, et al. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) transcriptional activity-driven gene signature association with severity of astrocytoma and poor prognosis of glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(9):3827–45.
Zhu Y, et al. DNA methylation-mediated Klotho silencing is an independent prognostic biomarker of head and neck squamous carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:1383–90.
Lu L, et al. High tRNA transferase NSUN2 gene expression is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous carcinoma. Cancer Invest. 2018;36(4):246–53.
Yi J, et al. Overexpression of NSUN2 by DNA hypomethylation is associated with metastatic progression in human breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(13):20751–65.
Yang JC, et al. Association of tRNA methyltransferase NSUN2/IGF-II molecular signature with ovarian cancer survival. Future Oncol. 2017;13(22):1981–90.
Yan J, et al. FOXC2-AS1 stabilizes FOXC2 mRNA via association with NSUN2 in gastric cancer cells. Hum Cell. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00583-3.
Chi J, et al. circNSUN2 promotes the malignant biological behavior of colorectal cancer cells via the miR-181a-5p/ROCK2 axis. Oncol Rep. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2021.8093.
Chen L, et al. RNA methyltransferase NSUN2 promotes hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and migration by enhancing TEAD1 expression in an m(5)C-dependent manner. Exp Cell Res. 2021;404(2): 112664.
Xu X, et al. NSun2 promotes cell migration through methylating autotaxin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(52):18134–47.
Chen RX, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4695.
Frye M, et al. Genomic gain of 5p15 leads to over-expression of Misu (NSUN2) in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2010;289(1):71–80.
Kawarada L, et al. ALKBH1 is an RNA dioxygenase responsible for cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNA modifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(12):7401–15.
Van Haute L, et al. Deficient methylation and formylation of mt-tRNA(Met) wobble cytosine in a patient carrying mutations in NSUN3. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12039.
Paramasivam A, et al. Novel biallelic NSUN3 variants cause early-onset mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and seizures. J Mol Neurosci. 2020;70(12):1962–5.
Trixl L, et al. RNA cytosine methyltransferase Nsun3 regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation by promoting mitochondrial activity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(8):1483–97.
Pan J, Huang Z, Xu Y. m5C RNA methylation regulators predict prognosis and regulate the immune microenvironment in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 657466.
Alshaker H, et al. Transcriptome-wide effects of sphingosine kinases knockdown in metastatic prostate and breast cancer cells: implications for therapeutic targeting. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:303.
Cheng JX, et al. RNA cytosine methylation and methyltransferases mediate chromatin organization and 5-azacytidine response and resistance in leukaemia. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1163.
Lenarčič T, et al. Stepwise maturation of the peptidyl transferase region of human mitoribosomes. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3671.
Cipullo M, et al. Human GTPBP5 is involved in the late stage of mitoribosome large subunit assembly. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(1):354–70.
Cheng J, Berninghausen O, Beckmann R. A distinct assembly pathway of the human 39S late pre-mitoribosome. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4544.
Metodiev MD, et al. NSUN4 is a dual function mitochondrial protein required for both methylation of 12S rRNA and coordination of mitoribosomal assembly. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(2): e1004110.
Hillen HS, et al. Structural basis of GTPase-mediated mitochondrial ribosome biogenesis and recycling. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3672.
Lavdovskaia E, et al. Dual function of GTPBP6 in biogenesis and recycling of human mitochondrial ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(22):12929–42.
Lavdovskaia E, et al. The human Obg protein GTPBP10 is involved in mitoribosomal biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(16):8471–82.
Ye X, et al. MTERF4 regulates the mitochondrial dysfunction induced by MPP(+) in SH-SY5Y cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(1):214–20.
Yakubovskaya E, et al. Structure of the essential MTERF4:NSUN4 protein complex reveals how an MTERF protein collaborates to facilitate rRNA modification. Structure. 2012;20(11):1940–7.
Cámara Y, et al. MTERF4 regulates translation by targeting the methyltransferase NSUN4 to the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome. Cell Metab. 2011;13(5):527–39.
Mulder H. Transcribing β-cell mitochondria in health and disease. Mol Metab. 2017;6(9):1040–51.
He Y, et al. Role of m(5)C-related regulatory genes in the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(3):912–22.
Heissenberger C, et al. Loss of the ribosomal RNA methyltransferase NSUN5 impairs global protein synthesis and normal growth. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(22):11807–25.
Janin M, et al. Epigenetic loss of RNA-methyltransferase NSUN5 in glioma targets ribosomes to drive a stress adaptive translational program. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138(6):1053–74.
Zhang T, et al. Cognitive deficits in mice lacking Nsun5, a cytosine-5 RNA methyltransferase, with impairment of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Glia. 2019;67(4):688–702.
Yuan Z, et al. Agenesis and hypomyelination of corpus callosum in mice lacking Nsun5, an RNA methyltransferase. Cells. 2019;8(6):552.
Chen P, et al. Expression of the RNA methyltransferase Nsun5 is essential for developing cerebral cortex. Mol Brain. 2019;12(1):74.
Wang Y, et al. Mutations in RNA methyltransferase gene NSUN5 confer high risk of outflow tract malformation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 623394.
Xue M, et al. Gene signatures of m5C regulators may predict prognoses of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(10):6841–52.
Jiang Z, et al. High expression of NSUN5 promotes cell proliferation via cell cycle regulation in colorectal cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(7):3858–70.
Selmi T, et al. Sequence- and structure-specific cytosine-5 mRNA methylation by NSUN6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(2):1006–22.
Hussain S. The emerging roles of cytosine-5 methylation in mRNAs. Trends Genet. 2021;37(6):498–500.
Haag S, et al. NSUN6 is a human RNA methyltransferase that catalyzes formation of m5C72 in specific tRNAs. RNA. 2015;21(9):1532–43.
Li C, et al. A ROR1-HER3-lncRNA signalling axis modulates the Hippo-YAP pathway to regulate bone metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(2):106–19.
Aguilo F, et al. Deposition of 5-methylcytosine on enhancer RNAs enables the coactivator function of PGC-1α. Cell Rep. 2016;14(3):479–92.
Harris T, et al. Sperm motility defects and infertility in male mice with a mutation in Nsun7, a member of the Sun domain-containing family of putative RNA methyltransferases. Biol Reprod. 2007;77(2):376–82.
Khosronezhad N, HosseinzadehColagar A, Mortazavi SM. The Nsun7 (A11337)-deletion mutation, causes reduction of its protein rate and associated with sperm motility defect in infertile men. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32(5):807–15.
Khosronezhad N, Colagar AH, Jorsarayi SG. T26248G-transversion mutation in exon7 of the putative methyltransferase Nsun7 gene causes a change in protein folding associated with reduced sperm motility in asthenospermic men. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2015;27(3):471–80.
Ren HY, et al. Investigation of polymorphisms in exon7 of the NSUN7 gene among Chinese Han men with asthenospermia. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(3):9261–8.
Tang J, et al. A logical relationship for schizophrenia, bipolar, and major depressive disorder. Part 4: evidence from chromosome 4 high-density association screen. J Comp Neurol. 2019;527(2):392–405.
Xing Q, et al. A novel 13 RNA binding proteins (RBPs) signature could predict prostate cancer biochemical recurrence. Pathol Res Pract. 2021;225: 153587.
Chen Y, et al. Identification of an RNA-binding-protein-based prognostic model for ewing sarcoma. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(15):3736.
Sato K, Tahata K, Akimoto K. Five genes associated with survival in patients with lower-grade gliomas were identified by information-theoretical analysis. Anticancer Res. 2020;40(5):2777–85.
Lyko F. The DNA methyltransferase family: a versatile toolkit for epigenetic regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2018;19(2):81–92.
Goll MG, et al. Methylation of tRNAAsp by the DNA methyltransferase homolog Dnmt2. Science. 2006;311(5759):395–8.
Schaefer M, et al. RNA methylation by Dnmt2 protects transfer RNAs against stress-induced cleavage. Genes Dev. 2010;24(15):1590–5.
Shanmugam R, et al. Cytosine methylation of tRNA-Asp by DNMT2 has a role in translation of proteins containing poly-Asp sequences. Cell Discov. 2015;1:15010.
Tuorto F, et al. The tRNA methyltransferase Dnmt2 is required for accurate polypeptide synthesis during haematopoiesis. Embo j. 2015;34(18):2350–62.
Xue S, et al. Depletion of TRDMT1 affects 5-methylcytosine modification of mRNA and inhibits HEK293 cell proliferation and migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;520(1):60–6.
Dev RR, et al. Cytosine methylation by DNMT2 facilitates stability and survival of HIV-1 RNA in the host cell during infection. Biochem J. 2017;474(12):2009–26.
Thiagarajan D, Dev RR, Khosla S. The DNA methyltranferase Dnmt2 participates in RNA processing during cellular stress. Epigenetics. 2011;6(1):103–13.
Lewinska A, et al. Reduced levels of methyltransferase DNMT2 sensitize human fibroblasts to oxidative stress and DNA damage that is accompanied by changes in proliferation-related miRNA expression. Redox Biol. 2018;14:20–34.
Lewinska A, et al. Downregulation of methyltransferase Dnmt2 results in condition-dependent telomere shortening and senescence or apoptosis in mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(12):3714–26.
Wang F, et al. Oncofetal long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2. Hepatology. 2014;60(4):1278–90.
Zhang C, et al. PRL-3 promotes ubiquitination and degradation of AURKA and colorectal cancer progression via dephosphorylation of FZR1. Cancer Res. 2019;79(5):928–40.
Seah MK, et al. The APC activator fizzy-related-1 (FZR1) is needed for preimplantation mouse embryo development. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 24):6030–7.
Liu S, et al. FZR1 as a novel biomarker for breast cancer neoadjuvant chemotherapy prediction. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):804.
Ishizawa J, et al. FZR1 loss increases sensitivity to DNA damage and consequently promotes murine and human B-cell acute leukemia. Blood. 2017;129(14):1958–68.
Crawford LJ, et al. Identification of the APC/C co-factor FZR1 as a novel therapeutic target for multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(43):70481–93.
Tourrière H, et al. RasGAP-associated endoribonuclease G3Bp: selective RNA degradation and phosphorylation-dependent localization. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(22):7747–60.
Pham TND, et al. Protein kinase C α enhances migration of breast cancer cells through FOXC2-mediated repression of p120-catenin. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):832.
Zheng CH, et al. Expression of transcription factor FOXC2 in cervical cancer and effects of silencing on cervical cancer cell proliferation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(4):1589–95.
Ren YH, et al. De-SUMOylation of FOXC2 by SENP3 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2014;5(16):7093–104.
Hollier BG, et al. FOXC2 expression links epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73(6):1981–92.
Mortazavi F, et al. p120-catenin is transcriptionally downregulated by FOXC2 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8(5):762–74.
Zhang P, et al. Altered cell differentiation and proliferation in mice lacking p57KIP2 indicates a role in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Nature. 1997;387(6629):151–8.
Yan Y, et al. Ablation of the CDK inhibitor p57Kip2 results in increased apoptosis and delayed differentiation during mouse development. Genes Dev. 1997;11(8):973–83.
Qiu Z, et al. Downregulated CDKN1C/p57(kip2) drives tumorigenesis and associates with poor overall survival in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1):187–93.
Ru Y, et al. CyclinD1 and p57(kip2) as biomarkers in differentiation, metastasis and prognosis of gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(43):73860–70.
Zhang E, et al. Increased expression of long noncoding RNA TUG1 predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation by epigenetically silencing of p57. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(2): e2109.
He M, et al. Expression of DNMTs and MBD2 in GIST. Biomed Rep. 2013;1(2):223–7.
Kristensen LS, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(11):675–91.
Han W, et al. Aloperine inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by regulating the circNSUN2/miR-296-5p/STAT3 pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:857–70.
Chen SC, et al. Hepatoma-derived growth factor regulates breast cancer cell invasion by modulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Pathol. 2012;228(2):158–69.
Uyama H, et al. Hepatoma-derived growth factor is a novel prognostic factor for patients with pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(20 Pt 1):6043–8.
Ren H, et al. Expression of hepatoma-derived growth factor is a strong prognostic predictor for patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(16):3230–7.
Tzelepi V, et al. Epigenetics and prostate cancer: defining the timing of DNA methyltransferase deregulation during prostate cancer progression. Pathology. 2020;52(2):218–27.
Gao Y, et al. NOP2/Sun RNA methyltransferase 2 promotes tumor progression via its interacting partner RPL6 in gallbladder carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(11):3510–9.
Job B, et al. Genomic aberrations in lung adenocarcinoma in never smokers. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(12): e15145.
Huh HD, et al. Regulation of TEAD transcription factors in cancer biology. Cells. 2019;8(6):600.
Zanconato F, et al. Genome-wide association between YAP/TAZ/TEAD and AP-1 at enhancers drives oncogenic growth. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(9):1218–27.
Harvey KF, Zhang X, Thomas DM. The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(4):246–57.
Yang R, et al. The RNA methyltransferase NSUN6 suppresses pancreatic cancer development by regulating cell proliferation. EBioMedicine. 2021;63: 103195.
Schaefer M, et al. Azacytidine inhibits RNA methylation at DNMT2 target sites in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2009;69(20):8127–32.
Lewinska A, et al. Phytochemical-induced nucleolar stress results in the inhibition of breast cancer cell proliferation. Redox Biol. 2017;12:469–82.
Okamoto M, et al. tRNA modifying enzymes, NSUN2 and METTL1, determine sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in HeLa cells. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(9): e1004639.
Okamoto M, et al. Frequent increased gene copy number and high protein expression of tRNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase (NSUN2) in human cancers. DNA Cell Biol. 2012;31(5):660–71.
Kucukkaraduman B, et al. Predictive gene signature for pyrazolopyrimidine derivative c-Src inhibitor 10a sensitivity in melanoma cells. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11(5):928–32.
Bloniarz D, et al. The lack of functional DNMT2/TRDMT1 gene modulates cancer cell responses during drug-induced senescence. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(12):15833–74.
Liu J, et al. A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10(2):93–5.
Zheng G, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 2013;49(1):18–29.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This study was supported by the 345 Talent Project (Grant No. M0716), by the Joint plan of key research and development program of Liaoning Province (Grant No. 2020JH 2/10300137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CXN and LMY designed the study. LMY and TZJ reviewed the information. LMY wrote the manuscript. LL, ZYQ, ZJY and LZY critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed on the contents of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Tao, Z., Zhao, Y. et al. 5-methylcytosine RNA methyltransferases and their potential roles in cancer. J Transl Med 20, 214 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03427-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03427-2