Abstract
Background
Deletions of 17p13 recurrently occur in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) but their prognostic role seems to be uncertain.
Methods
To determine prevalence, relationship with tumor phenotype, and patient prognosis, a tissue microarray containing samples from 1809 RCCs was evaluated using dual labeling fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with 17p13 and chromosome 17 centromere probes.
Results
A 17p13 deletion was found in 72 of 1429 interpretable tumors. The frequency of 17p13 deletions varied greatly between RCC subtypes and was highest in chromophobe RCC (24/72; 33.3%). 17p13 deletions were also found in 35 (3.7%) of 946 clear cell RCC, 9 (4.3%) of 208 papillary RCC, 1 of 121 oncocytomas (0.8%), as well as in several rare cases of comprising 1 of 7 Xp11.2 translocation cancers, 1 of 3 collecting duct carcinomas, and 1 of 20 not otherwise specified (NOS) carcinomas. In clear cell carcinomas, 17p13 deletions revealed a strong and consistent association with higher Fuhrman, ISUP, and Thoenes grade (p < 0.0001 each), and linked to advanced tumor stage (p = 0.0168), large tumor diameter (p = 0.0004), distant metastases (p = 0.0077), cancer-specific survival (p = 0.0391), and recurrence-free survival (p = 0.0072). In multivariate analysis, 17p13 deletions showed in clear cell RCC a dependent prognostic role for established clinical-pathological parameters.
Conclusion
17p13 deletions have a dual role in RCC. They are associated with disease progression in clear cell RCC and possibly other subtypes and they are linked to the development of chromophobe RCC—a subtype with a particularly favorable prognosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the 9th most common tumor worldwide [1]. Its incidence is rising and is highest in countries with high socio-economic status [2]. The reasons behind the growing incidence, especially in developing countries, are a persistently increasing impact of risk factors like smoking, obesity, hypertension, and increasing patient age, but also a more frequent use of common medical imaging types like ultrasound, computer-tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging [3] which lead to an earlier diagnosis. The latter is a likely reason for a reduction of mortality in many countries over the past decade [2].
Localized RCC treatment is generally achieved through radical or partial nephrectomy. Even in metastatic disease, a surgical approach plays a major role if metastases are resectable. Renal cell carcinomas are often resistant to radiation and to most chemotherapies [4]. However, several new drugs such as sunitinib or immune-checkpoint inhibitors have recently yielded better results [5, 6]. Currently, it is thus being evaluated in clinical trials, whether an adjuvant application of these new drugs can improve the prognosis of patients at high risk for disease recurrence or progression after nephrectomy (Keynote-564, iMmotion010, Checkmate-914). Sunitinib was approved by the FDA for this purpose in November 2017. If adjuvant treatment becomes a standard of care, risk stratification will become more important than ever before, to find out which patient is at risk and might benefit from adjuvant therapies. The increasing knowledge about the cell biology of RCC might eventually lead to the identification of molecular tumor features that might help to improve risk stratification.
Chromosomal deletions are often found in many cancers including kidney cancer [7]. In many tumor types, chromosomal deletions were found to be highly prognostic [8,9,10,11,12]. Deletion analysis appears to be particularly well suited for clinical applications and as they are easily detectable by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) resulting in a reproducible yes/no answer (deletion present or not present). The short arm of chromosome 17 (17p) has also been described to be recurrently deleted in kidney cancers, mainly in the chromophobe subtype [13,14,15,16]. The prognostic role of 17p13 deletions in RCC is currently unknown, however.
To learn more about the diagnostic and prognostic role of 17p13 deletions in RCC, we thus evaluated more than 1800 kidney tumors—many of which with attached follow-up data—in a tissue microarray (TMA) format by FISH.
Materials and methods
Patients
The kidney tumor TMA utilized in this study included samples collected from 1809 patients who underwent surgery at the Institute of Pathology of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Germany, between 1994 and 2016. All tumors have been histologically reviewed by two pathologists expertized in genitourinary pathology (FB, CF) at the Institute of Pathology (UKE) following WHO 2016 classification [17]. The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading has been applied to each tumor. The TMA consists of four blocks, including one that was built earlier [18]. The TMA construction has been previously described [19]. Supplementary Table 1 summarizes the clinical and pathological parameters of the evaluated cancers. In this report, the mean follow-up period was 48 months. Local laws (HmbKHG, §12,1) and the local ethics committee (Ethics Commission Hamburg, WF-049/09) approved the use of archived diagnostic left-over tissues for the analysis of TMA construction for research purposes as well as the analysis of patient data. All work has been carried out in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
The general FISH protocol was carried out as described before [20]. The probe set included a spectrum-green labeled 17p13 (targeting the TP53 gene locus) probe (BACs RP11-89D11, RP11-404G1; Source Bioscience, Nottingham, UK), and a commercial spectrum-orange-labeled centromere 17 reference probe (#06J36-017; Abbott, Chicago, USA).In our evaluation, we excluded tissue spots (tumor or normal cells) without green 17q13 signals or any normal cells as an internal control for successful FISH probe hybridization. For each tissue spot, the predominant FISH signal numbers were recorded. Lack of green signal in ≥ 60% of tumor nuclei indicated homozygous 17q13 deletion, whereas a reduced number of 17p13 probe signals compared to the centromeric 17 probe in ≥ 60% of tumor nuclei indicated heterozygous 17q13 deletion. Thresholds were selected on the basis of the previous study on PTEN deletion results obtained by FISH and single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in a cohort of prostate cancers [21].
Statistics
The software JMP 12 (SAS Institute Inc., NC, USA) was used for statistical calculations. Contingency tables and the Chi-square test were used to study associations between 17p13 deletions and tumor phenotype. Survival curves were generated using the Kaplan-Meier method and significant survival differences between groups were estimated using the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was carried out to verify the differences in data for significant associations between pT, ISUP grade, and 17p13 deletions.
Results
Technical issues
In total, 1429 out of 1809 (79%) tissue spots provided comprehensive data. Reasons for non-informative cases (380 spots; 21%) included insufficient hybridization with absence of clear 17p13 and/or centromere 17 signals, missing tissue spots, or unclear presence of a cancer tissue on the TMA spot.
17p13 deletion in renal cell cancer
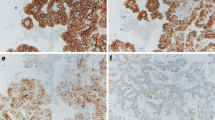
Representative images of cancers with and without 17p13 deletion are shown in Fig. 1. A total of 72 out of 1429 analyzable tumor samples (5%) featured 17p13 deletions. The frequency of 17p13 deletions was markedly higher in chromophobe carcinomas (24/72, 33.3%) as compared to clear cell RCC (35/946, 3.7%) and papillary RCC (9/208, 4.3%). 17p13 deletion was present in only one oncocytoma (1/121, 0.8%) and was not seen in 24 clear cell tubulo-papillary RCCs (Table 1). 17p13 deletion was also found in rare subtypes such as in collecting duct carcinomas (1/3, 33%), Xp11.2 translocation RCC (1/7, 14%), and in not otherwise specified tumors (1/20, 5%) (Table 1). In clear cell RCC, 17p13 deletions were strongly linked to ISUP, Fuhrman, and Thoenes grade (p < 0.0001 each); pT stage (p = 0.0168); and presence of distant metastases (M stage, p = 0.0077; Table 2). Clear cell RCC with 17p13 deletions were significantly larger than those without deletions (p = 0.0004, Table 3). In papillary and chromophobe RCC, 17p13 deletions were unrelated to tumor phenotype (data not shown) and tumor diameter (Table 3).
Associations with patient survival
In the present study, follow-up data for 789 clear cell and 177 papillary cancers were accessible. Figure 2a, b shows associations between ISUP grade and tumor stage with the survival data for our clear cell cancers. These findings demonstrate the validity of our follow-up data. 17p13 deletions were significantly associated with progression-free survival in the joint analysis of all tumors (p = 0.0411). Also, in the largest subgroup of clear cell cancers, 17p13 deletions were significantly associated with shortened cancer-specific (p = 0.0391) and recurrence-free (p = 0.0072) survival. 17p13 deletions were unrelated to patient prognosis in papillary cancers, probably due to the small minority of cases with 17p13 deletion. All data are shown in Fig. 3. Follow-up data were insufficient (only 73 patients with follow-up information) to analyze the prognostic role of 17p13 deletions in chromophobe carcinomas. In a multivariate analysis including pT, pN, M status, and ISUP grade, 17p13 deletions did not show an independent prognostic significance for all endpoints (supplement table 2).
Discussion
The results of this study identify a dual role of 17p13 deletions in RCC. These deletions are involved in the progression of clear cell and possibly other RCCs. They are also relevant for the development of chromophobe RCC, a less aggressive kidney cancer subtype.
The fraction of 17p13-deleted clear cell RCCs was 5% in our FISH analysis. A lower percentage than in most earlier studies, which described 17p deletions in 7–11% by classical comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) [22, 23], 4–77% by loss of heterozygosity (LOH) analysis [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], 20% by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis [30, 41], 31–53% by single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array hybridization [42, 43], 12% by classical cytogenetics [44], and 18% using FISH [45]. Next-generation sequencing data available from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) [7] show 17p13 (TP53) deletions in 8% of 345 analyzed clear cell RCC. It appears obvious that these differences in the frequency of reported 17p deletions are at least partly connected to technical issues related to the different methods. LOH, CGH, RFNP, SNP, and NGS share the disadvantage that the analysis is performed on isolated DNA, which always bears the risk of DNA contamination from adjacent non-neoplastic cells such as stroma, immune cells, blood vessels, and so on. In addition, most studies used less sensitive methods than this study. FISH is considered the gold standard for detection of deletions. FISH allows a precise cell by cell assessment of the copy number of genomic regions of interest. FISH is independent of the presence and quantity of inflammatory or stroma cells. Some “false deletions” can be assumed in FISH analyses because some signals are always missing due to truncated cell nuclei that are incompletely represented on a tissue slide measuring only 3–4 μm in thickness. A rigorous cut-off of 60% of tumor cells having less 17p13 than centromere 17 signals was thus selected in this project to define 17p13-deleted tumors. This is based on the assumption that clinically relevant intratumoral heterogeneity will not occur in a TMA spot measuring 0.6 mm in diameter. In an earlier study, we had found a 100% concordance between FISH and array CGH data for identifying PTEN deletions using this definition for deletion [21].
17p13 deletions were clearly associated with an unfavorable tumor phenotype and poor prognosis in clear cell RCC. Given the striking association of 17p13 deletions with tumor grade and stage, it is possible that the rather low number of 17p13-deleted cases in our study is due to the consecutive nature of our cohort including a large number of pT1 tumors. Considering the low frequency of 17p13 deletions and the low number of papillary carcinomas in this study, it is not surprising that clear-cut associations between 17p13 deletions and unfavorable tumor features could not be found in this RCC subtype. The significant link between 17p13 deletions and progression-free survival would be consistent, however, with 17p13 deletions representing a universal feature of disease progression in RCCs derived from the proximal tubule. The tumor suppressor p53 residing on chromosome 17p13 is an apparent candidate target gene of 17p13 deletions. An altered p53 function occurs in less than 5% of clear cell and papillary RCCs [46]. Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) PanCancer database show concomitant p53 mutations only in 4 of 27 clear cell RCCs with 17p13 deletions [7]. It is possible, however, that a reduced p53 function in 17p13-deleted cells contributes to increased potential for further progression.
A large number of candidate prognostic markers have been suggested for kidney cancer in the past. These include deletions of chromosomal material such as losses of 1p, 3p, 8p, 9p, and 14q in clear cell cancers [47,48,49,50,51,52], 3p, and X-chromosome loss in papillary cancers [53, 54], and monosomies of chromosome 1, 2, 10, 13, 17, and 21 in chromophobe RCC [55]. However, none of these markers was so far strong enough to compete with classical histo-pathological prognostic parameters in multivariable analyses. As a consequence, no molecular marker has entered routine clinical diagnostic procedures so far. Nevertheless, these abovementioned findings suggest that genomic instability is typically related with adverse renal cell cancer phenotype. It is, therefore, well possible that combinations of multiple genomic deletions may better predict the clinical course than one of these deletions alone. This is supported by studies showing that combinations of multiple deletions such as 3p and 14q [47] or ploidy changes [56] are particularly strongly linked to poor prognosis. Future molecular prognostic test may, therefore, combine multiple genomic alterations. Although the 17p deletion did not show independent prognostic value in this study, it may be a valuable marker to be included in such potential future multiparametric tests, particularly for clear cell RCC.
That 17p13 deletions were strongly linked to chromophobe tumor subtype in this study fits well with data from earlier studies. As seen for clear cell RCCs, other investigators had earlier described even higher frequencies of 17p13 deletions in chromophobe cancers than the 33% in our study. Speicher et al. found a chromosome 17 loss in 13/17 cases of chromophobe RCC using CGH [13]. Yusenko et al. found 17p13 deletions in 90% of 30 chromophobe RCC using SNP array analysis [15]. Nagy et al. described LOH in 90% of 21 chromophobe RCC by microsatellite allelotyping [16]. Brunelli et al. found 17p13 deletions in 9 of 11 chromophobe cancers by FISH [14]. The TCGA database identified 17p13 deletions in 75% of 65 analyzed chromophobe RCCs [7]. The clinical outcome of chromophobe RCC is generally better than seen in clear cell RCC. It is thus unlikely, that the particular role of 17p13 deletions in these tumors is related to the TP53 gene, inactivation of which is generally associated with aggressive cancer [46].
Increasing evidence suggests that the association of 17p13 deletions with chromophobe RCC subtype may be driven by the Folliculin (FLCN) gene on 17p11.2. FLCN interacts with TFE3 and the Wnt pathway and plays a critical role for the exit from human pluripotency [57]. FLCN germline mutations cause the Birt-Hogg-Dubé (BHD) syndrome characterized by benign hair follicle hamartomas, spontaneous pneumothorax, lung cysts, and an increased risk for renal carcinoma. Patients with BHD syndrome tend to develop RCC, which primarily are chromophobe RCC (34%) or renal hybrid oncocytic/chromophobe tumors (50%) with areas reminiscent of chromophobe RCC and oncocytoma [58]. According to the cBioPortal database [7], FLCN mutations were not found in 65 chromophobe carcinomas that had been sequenced in the TCGA project [7]. This suggests that the rare BHD syndrome is only linked to a small fraction of chromophobe RCCs. Based on all these data, it is tempting to speculate, that partial inactivation of FLCN in 17p13-deleted cells from the distal tubule favors the development of chromophobe cancers. It is of note that 17p13 deletions were exceptionally rare (0.8% deleted cancers) in oncocytomas. Oncocytomas, the benign counterpart of chromophobe carcinoma, share the origin from the distal tubule with chromophobe carcinoma but are very uncommon in BHD syndrome. Given the tight link of 17p13 deletion and chromophobe RCC, one might assume that an additional loss of 17p13 occurring in an oncocytoma could result in a progression to renal hybrid oncocytic/chromophobe tumors, the most common RCC in BHD syndrome.
Conclusion
In summary, our data provide evidence for a dual role of 17p13 deletions in RCC. In cells from the distal tubule, 17p13 deletions contribute to the development of chromophobe RCC. In clear cell and papillary RCC derived from the proximal tubule, they are linked to disease progression. Together with other molecular parameters, the assessment of 17p13 deletions may have clinical utility for prognosis assessment in clear cell RCC and perhaps also papillary RCC.
Availability of data and materials
Data will be made available upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- NOS:
-
Not otherwise specific
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
- UKE:
-
University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- ISUP:
-
International Society of Urological Pathology
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- CGH:
-
Comparative genomic hybridization
- LOH:
-
Loss of heterozygosity
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- BHD:
-
Birt-Hogg-Dubé
References
Jonasch E, Gao J, Rathmell WK. Renal cell carcinoma. BMJ. 2014;349:g4797.
Wong MCS, Goggins WB, Yip BHK, Fung FDH, Leung C, Fang Y, Wong SYS, Ng CF. Incidence and mortality of kidney cancer: temporal patterns and global trends in 39 countries. Sci Rep. 2017;7:15698.
Rossi SH, Klatte T, Usher-Smith J, Stewart GD. Epidemiology and screening for renal cancer. World J Urol. 2018;36:1341–53.
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bensalah K, Dabestani S, Fernandez-Pello S, Giles RH, Hofmann F, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2019 Update. Eur Urol. 2019(75):799–810.
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Aren Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK, Plimack ER, Barthelemy P, Porta C, George S, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1277–90.
Choueiri TK, Halabi S, Sanford BL, Hahn O, Michaelson MD, Walsh MK, Feldman DR, Olencki T, Picus J, Small EJ, et al. Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of poor or intermediate risk: the Alliance A031203 CABOSUN Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:591–7.
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:401–4.
Chen M, Yang Y, Liu Y, Chen C. The role of chromosome deletions in human cancers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1044:135–48.
Kluth M, Runte F, Barow P, Omari J, Abdelaziz ZM, Paustian L, Steurer S, Christina Tsourlakis M, Fisch M, Graefen M, et al. Concurrent deletion of 16q23 and PTEN is an independent prognostic feature in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2015;137:2354–63.
Lebok P, Roming M, Kluth M, Koop C, Ozden C, Taskin B, Hussein K, Lebeau A, Witzel I, Wolber L, et al. p16 overexpression and 9p21 deletion are linked to unfavorable tumor phenotype in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:81322–31.
Bohn BA, Mina S, Krohn A, Simon R, Kluth M, Harasimowicz S, Quaas A, Bockhorn M, Izbicki JR, Sauter G, et al. Altered PTEN function caused by deletion or gene disruption is associated with poor prognosis in rectal but not in colon cancer. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:1524–33.
Simon R, Richter J, Wagner U, Fijan A, Bruderer J, Schmid U, Ackermann D, Maurer R, Alund G, Knonagel H, et al. High-throughput tissue microarray analysis of 3p25 (RAF1) and 8p12 (FGFR1) copy number alterations in urinary bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4514–9.
Speicher MR, Schoell B, du Manoir S, Schrock E, Ried T, Cremer T, Storkel S, Kovacs A, Kovacs G. Specific loss of chromosomes 1, 2, 6, 10, 13, 17, and 21 in chromophobe renal cell carcinomas revealed by comparative genomic hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1994;145:356–64.
Brunelli M, Delahunt B, Gobbo S, Tardanico R, Eccher A, Bersani S, Cossu-Rocca P, Parolini C, Balzarini P, Menestrina F, et al. Diagnostic usefulness of fluorescent cytogenetics in differentiating chromophobe renal cell carcinoma from renal oncocytoma: a validation study combining metaphase and interphase analyses. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;133:116–26.
Yusenko MV, Kuiper RP, Boethe T, Ljungberg B, van Kessel AG, Kovacs G. High-resolution DNA copy number and gene expression analyses distinguish chromophobe renal cell carcinomas and renal oncocytomas. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:152.
Nagy A, Buzogany I, Kovacs G. Microsatellite allelotyping differentiates chromophobe renal cell carcinomas from renal oncocytomas and identifies new genetic changes. Histopathology. 2004;44:542–6.
Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM: The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol 2016, 70:93-105.
Eichelberg C, Minner S, Isbarn H, Burandt E, Terracciano L, Moch H, Kell A, Heuer R, Chun FK, Sauter G, et al. Prognostic value of alpha-methyl CoA racemase (AMACR) expression in renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol. 2013;31:847–53.
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med. 1998;4:844–7.
Kluth M, Amschler NN, Galal R, Moller-Koop C, Barrow P, Tsourlakis MC, Jacobsen F, Hinsch A, Wittmer C, Steurer S, et al. Deletion of 8p is an independent prognostic parameter in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:379–92.
Krohn A, Diedler T, Burkhardt L, Mayer PS, De Silva C, Meyer-Kornblum M, Kotschau D, Tennstedt P, Huang J, Gerhauser C, et al. Genomic deletion of PTEN is associated with tumor progression and early PSA recurrence in ERG fusion-positive and fusion-negative prostate cancer. The American journal of pathology. 2012;181:401–12.
Reutzel D, Mende M, Naumann S, Storkel S, Brenner W, Zabel B, Decker J. Genomic imbalances in 61 renal cancers from the proximal tubulus detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 2001;93:221–7.
Gronwald J, Baur AS, Holtgreve-Grez H, Jauch A, Mosimann F, Jichlinski P, Wauters JP, Cremer T, Guillou L. Chromosomal abnormalities in renal cell neoplasms associated with acquired renal cystic disease. A series studied by comparative genomic hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Pathol. 1999;187:308–12.
Contractor H, Zariwala M, Bugert P, Zeisler J, Kovacs G. Mutation of the p53 tumour suppressor gene occurs preferentially in the chromophobe type of renal cell tumour. J Pathol. 1997;181:136–9.
Kovacs A, Storkel S, Thoenes W, Kovacs G. Mitochondrial and chromosomal DNA alterations in human chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 1992;167:273–7.
Reiter RE, Anglard P, Liu S, Gnarra JR, Linehan WM. Chromosome 17p deletions and p53 mutations in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3092–7.
Bi M, Zhao S, Said JW, Merino MJ, Adeniran AJ, Xie Z, Nawaf CB, Choi J, Belldegrun AS, Pantuck AJ, et al. Genomic characterization of sarcomatoid transformation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:2170–5.
Brauch H, Pomer S, Hieronymus T, Schadt T, Lohrke H, Komitowski D. Genetic alterations in sporadic renal-cell carcinoma: molecular analyses of tumor suppressor gene harboring chromosomal regions 3p, 5q, and 17p. World J Urol. 1994;12:162–8.
Kuczyk MA, Serth J, Bokemeyer C, Jonassen J, Arndt H, Paeslack U, Werner M, Tan HK, Jonas U. Detection of p53 gene alteration in renal-cell cancer by micropreparation techniques of tumor specimens. Int J Cancer. 1995;64:399–406.
Uchida T, Wada C, Shitara T, Egawa S, Mashimo S, Koshiba K. Infrequent involvement of p53 mutations and loss of heterozygosity of 17p in the tumorigenesis of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1993;150:1298–301.
Fogt F, Zhuang Z, Linehan WM, Merino MJ. Collecting duct carcinomas of the kidney: a comparative loss of heterozygosity study with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 1998;5:923–6.
Morita R, Ishikawa J, Tsutsumi M, Hikiji K, Tsukada Y, Kamidono S, Maeda S, Nakamura Y. Allelotype of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991;51:820–3.
Ogawa O, Habuchi T, Kakehi Y, Koshiba M, Sugiyama T, Yoshida O. Allelic losses at chromosome 17p in human renal cell carcinoma are inversely related to allelic losses at chromosome 3p. Cancer Res. 1992;52:1881–5.
Presti JC Jr, Rao PH, Chen Q, Reuter VE, Li FP, Fair WR, Jhanwar SC. Histopathological, cytogenetic, and molecular characterization of renal cortical tumors. Cancer Res. 1991;51:1544–52.
Presti JC Jr, Reuter VE, Cordon-Cardo C, Mazumdar M, Fair WR, Jhanwar SC. Allelic deletions in renal tumors: histopathological correlations. Cancer Res. 1993;53:5780–3.
Foster K, Crossey PA, Cairns P, Hetherington JW, Richards FM, Jones MH, Bentley E, Affara NA, Ferguson-Smith MA, Maher ER. Molecular genetic investigation of sporadic renal cell carcinoma: analysis of allele loss on chromosomes 3p, 5q, 11p, 17 and 22. Br J Cancer. 1994;69:230–4.
Hoglund M, Gisselsson D, Mandahl N, Johansson B, Mertens F, Mitelman F, Sall T. Multivariate analyses of genomic imbalances in solid tumors reveal distinct and converging pathways of karyotypic evolution. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001;31:156–71.
Chen M, Ye Y, Yang H, Tamboli P, Matin S, Tannir NM, Wood CG, Gu J, Wu X. Genome-wide profiling of chromosomal alterations in renal cell carcinoma using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:2342–8.
Sugimura J, Tamura G, Suzuki Y, Fujioka T. Allelic loss on chromosomes 3p, 5q and 17p in renal cell carcinomas. Pathol Int. 1997;47:79–83.
Thrash-Bingham CA, Greenberg RE, Howard S, Bruzel A, Bremer M, Goll A, Salazar H, Freed JJ, Tartof KD. Comprehensive allelotyping of human renal cell carcinomas using microsatellite DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:2854–8.
Morita R, Saito S, Ishikawa J, Ogawa O, Yoshida O, Yamakawa K, Nakamura Y. Common regions of deletion on chromosomes 5q, 6q, and 10q in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991;51:5817–20.
Malouf GG, Monzon FA, Couturier J, Molinie V, Escudier B, Camparo P, Su X, Yao H, Tamboli P, Lopez-Terrada D, et al. Genomic heterogeneity of translocation renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:4673–84.
Perrino CM, Hucthagowder V, Evenson M, Kulkarni S, Humphrey PA. Genetic alterations in renal cell carcinoma with rhabdoid differentiation. Hum Pathol. 2015;46:9–16.
Dijkhuizen T, Van den Berg E, Van den Berg A, Storkel S, De Jong B, Seitz G, Henn W. Chromosomal findings and p53-mutation analysis in chromophilic renal-cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1996;68:47–50.
Yoshioka K, Nakamura S. Chromosome 9 and 17 aberrations and p53 gene deletion detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization in renal-cell carcinoma. Mol Urol. 2001;5:11–7.
Li VD, Li KH, Li JT. TP53 mutations as potential prognostic markers for specific cancers: analysis of data from The Cancer Genome Atlas and the International Agency for Research on Cancer TP53 Database. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145:625–36.
Kroeger N, Klatte T, Chamie K, Rao PN, Birkhauser FD, Sonn GA, Riss J, Kabbinavar FF, Belldegrun AS, Pantuck AJ. Deletions of chromosomes 3p and 14q molecularly subclassify clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2013;119:1547–54.
Monzon FA, Alvarez K, Peterson L, Truong L, Amato RJ, Hernandez-McClain J, Tannir N, Parwani AV, Jonasch E. Chromosome 14q loss defines a molecular subtype of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma associated with poor prognosis. Mod Pathol. 2011;24:1470–9.
Eichenauer T, Bannenberg DC, Kluth M, Wittmer C, Buscheck F, Moller K, Dum D, Fraune C, Hube-Magg C, Moller-Koop C, et al. 8p deletions in renal cell carcinoma are associated with unfavorable tumor features and poor overall survival. Urol Oncol. 2020;38:43 e13–20.
Eichenauer T, Simmendinger L, Kluth M, Chirico V, Luebke AM, Hoflmayer D, Hinsch A, Jacobsen F, Hube-Magg C, Moller-Koop C, et al. Chromosomal deletion of 9p21 is linked to poor patient prognosis in papillary and clear cell kidney cancer. Urol Oncol. 2020;38(6):605.e1.
Lichner Z, Scorilas A, White NM, Girgis AH, Rotstein L, Wiegand KC, Latif A, Chow C, Huntsman D, Yousef GM. The chromatin remodeling gene ARID1A is a new prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 2013;182:1163–70.
de Oliveira D, Dall'Oglio MF, Reis ST, Zerati M, Souza IC, Leite KR, Srougi M. Chromosome 9p deletions are an independent predictor of tumor progression following nephrectomy in patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 2014;32:601–6.
Jiang F, Richter J, Schraml P, Bubendorf L, Gasser T, Sauter G, Mihatsch MJ, Moch H. Chromosomal imbalances in papillary renal cell carcinoma: genetic differences between histological subtypes. Am J Pathol. 1998;153:1467–73.
Klatte T, Rao PN, de Martino M, LaRochelle J, Shuch B, Zomorodian N, Said J, Kabbinavar FF, Belldegrun AS, Pantuck AJ. Cytogenetic profile predicts prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:746–53.
Yap NY, Rajandram R, Ng KL, Pailoor J, Fadzli A, Gobe GC. Genetic and chromosomal aberrations and their clinical significance in renal neoplasms. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:476508.
Buscheck F, Fraune C, Kluth M, Lennartz M, Simon R, Hube-Magg C, Morlock C, Barbieri S, Wahl C, Eichelberg C, et al. A non-diploid DNA status is linked to poor prognosis in renal cell cancer. World J Urol. 2020.
Mathieu J, Detraux D, Kuppers D, Wang Y, Cavanaugh C, Sidhu S, Levy S, Robitaille AM, Ferreccio A, Bottorff T, et al. Folliculin regulates mTORC1/2 and WNT pathways in early human pluripotency. Nat Commun. 2019;10:632.
Pavlovich CP, Walther MM, Eyler RA, Hewitt SM, Zbar B, Linehan WM, Merino MJ. Renal tumors in the Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:1542–52.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Inge Brandt, Sünje Seekamp, Melanie Witt, Maren Eisenberg, Sylvia Schnöger, and Sascha Eghteshadi for excellent technical assistance.
Funding
No funding was received
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TE, CF, RS, MK, SM, CB, TC, and CHM contributed to conception, design, data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing. NS, MK, FB, and EB to fish analysis. SW, RD, TE, MR, and SR to conception and design and collection of samples. DH, FJ, CG, CMK, and KK to collection and data analysis. MF, WW, GS, and TC to study supervision. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the ethics committee Ärztekammer Hamburg (WF-049/09). The work has been carried out in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. Informed consent: According to local laws (HmbKHG, §12,1), informed consent was not necessary.
Consent for publication
No individual person’s data have been used in this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Pathological and clinical data of the arrayed renal cell tumors.
Additional file 2: Table S2.
Multivariate analysis in clear cell renal cell cancers using the endpoints overall survival (OS), tumor specific survival (TSS) and progression-free survival (TFS).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Eichenauer, T., Shadanpour, N., Kluth, M. et al. Chromosome 17p13 deletion is associated with an aggressive tumor phenotype in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. World J Surg Onc 18, 128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-020-01902-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-020-01902-y