Abstract
In chronic myeloid leukemia, the identification of individual BCR-ABL1 fusions is required for the development of personalized medicine approach for minimal residual disease monitoring at the DNA level. Next generation sequencing (NGS) of amplicons larger than 1000 bp simplified and accelerated a process of characterization of patient-specific BCR-ABL1 genomic fusions. NGS of large regions upstream and downstream the individual breakpoints in BCR and ABL1 genes, respectively, also provided information about the sequence variants such are single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
BCR-ABL1 transcript level monitoring is a crucial part of therapy response evaluation in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Molecular response (MR) in CML is expressed in terms of log reduction in BCR-ABL1 transcript levels from a standardized baseline on an international scale [1]. An increasing number of chronic phase CML patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) achieve sustained deep MR, which has led to the initialization of TKI discontinuation studies [2,3]. Although existing results showing that permanent TKI discontinuation is feasible in a proportion of patients, more than half experience molecular relapse. More sensitive MRD detection might allow to more accurately stratifying patients according to the depth of response, hence to the greater or smaller likelihood of relapse after discontinuation. It was recently shown that MRD could be detected at DNA level despite patients were in stable MR with undetectable BCR-ABL1 transcripts [4,5]. It is supposed that quantification of BCR-ABL1 gene would be useful for MRD monitoring in patients with therapy cessation.
At the genomic level the BCR-ABL1 fusion is unique to each CML patient, since breakpoints are scattered within intron 13 (718 bp) or 14 (2128 bp) of BCR and within intron 1 of ABL1 (140 Kbp). The exact genomic sequence of the BCR-ABL1 fusion must therefore be characterized to design a personalized real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. The sensitivity of personalized real-time PCR assay quantifying clone-specific fusions was reported to be down to less than 10−5 (depending on the amount of DNA entering the reaction) when nested PCR was used [6,7]. As amplification of large regions (˃1 Kbp) is needed, the characterization of BCR-ABL1 genomic fusions using conventional sequencing has been a challenging task [8-10]. With the aim to characterize patient-specific BCR-ABL1 fusions, we set up a strategy based on the generation of large amplicons by multiplex Long-Range PCR (mLR-PCR) and on subsequent ultra-wide sequencing using NGS technology. NGS provided sequences of large regions upstream and downstream the BCR-ABL1 fusions, allowing us to assess the frequency of annotated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which could be associated with the fusion gene formation.
Findings
Next generation sequencing of large amplicons carrying BCR-ABL1 fusions
The patient cohort consisted of 24 males and 22 females with CML. Two BCR-ABL1 positive cell lines K562 and JURL-MK were included as controls of BCR-ABL1 fusion identification. Twelve healthy individuals were used as controls for SNP detection in the BCR region from exon 13 to exon 15.
DNA was isolated from total leukocytes of peripheral blood at the time of diagnosis ensuring high amount of BCR-ABL1 DNA present in the sample. Two-round mLR-PCR was performed with HiFi Accuprime Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen) enabling amplification of large regions. The amplification strategy is presented in Figure 1. In the first round PCR with one primer in BCR exon 13 and 10 primers in ABL1 intron 1 [9], the long PCR products of 29 patients were obtained. In the second round PCR with one primer in BCR exon 13 and 20 primers in ABL1 intron 1 [10-12] products were obtained in the remaining cases. Median length of long PCR products was 5 Kbp (range 1-12 Kbp). Subsequently, rapid library was prepared for 454 NGS technology according to the manufacturer’s instructions and was run on a GS Junior instrument (Roche Diagnostics). NextGene software (Softgenetics) and reference sequences NG_009244.1 (BCR) and NG_012034.1 (ABL1) were used for sequence analysis.
Schematic localization of primers. Forward primers hybridizing in exon 13 of the BCR gene are symbolized by arrows pointing to the right and reverse primers spanning the intron 1 of gene ABL1 are symbolized by arrows pointing to the left. Colors of arrows for each gene illustrate two-rounds of multiplex LR-PCR. LR-PCR products were obtained in 25/48 cases from the first round PCR using 1 forward primer (red color) localized in BCR exon 13 and 10 reverse primers (red color) spanning the whole ABL1 intron 1 [9]. LR-PCR products were obtained in the remaining 23/48 cases from the second round PCR with 1 forward primer (blue color) hybridizing to sequence of BCR exon 13 and 20 reverse primers (blue colors) hybridizing to ABL1 intron 1 [7,10].
Patient-specific BCR-ABL1 fusion characterization
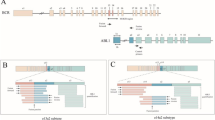
Breakpoints in BCR were located in intron 13 in 8/46 patients, carrying the e13a2 mRNA fusion, and in intron 14 in 38/46 patients and in both cell lines, carrying the e14a2 mRNA fusion (Figure 2A). All ABL1 breakpoints were spread within intron 1 (Figure 2A), which is in accordance with a previous study [7]. Sequences of characterized breakpoints are provided in the NCBI Nucleotide database (Accession numbers – KR091980-KR092025).
A. Breakpoint traces in BCR intron 13 and intron 14 and in ABL1 intron 1. B. SNPs detected in individual BCR-ABL1 alleles upstream the BCR breakpoints. Dots show detected SNPs; colors of dots correspond to each patient in whom SNPs were detected; colors of BCR breakpoints indicate each patient in whom SNPs were detected; BCR breakpoints shown in black represent patients in whom SNPs were not detected; *novel SNPs (numbers indicate position in ref. seq. NG_009244.1) **minor allele in a homozygous form;  BCR region sequenced in all patients; SNPs whose rs code is in red font are localized within this region.
BCR region sequenced in all patients; SNPs whose rs code is in red font are localized within this region.  SNPs not detectable in patients because of their localization beyond the breakpoints. Twelve healthy donor samples (controls) were used as controls for SNP detection in the BCR region from exon 13 to exon 15.
SNPs not detectable in patients because of their localization beyond the breakpoints. Twelve healthy donor samples (controls) were used as controls for SNP detection in the BCR region from exon 13 to exon 15.
SNPs detection upstream and downstream from the BCR-ABL1 fusions
Downstream the individual breakpoints in ABL1, 56 annotated SNPs were detected in 15/46 patients (median 3 SNPs/patient, range 1–11). Only 10 of them recurred in two patients, whereas the remaining 46 were detected only once. This heterogeneity in SNP detection was caused by the extreme length of intron 1 (Figure 1, Figure 2A), where the breakpoints were spread, so that the individual ABL1 regions sequenced could not overlap.
Upstream the individual BCR breakpoints, 17 annotated SNPs and 3 novel variants were found altogether in 27/48 cases (56%) (Figure 2B). The dbSNP assigned accessions of newly detected variants (putative SNPs) are as follows:
-
NG_009244.1:g.114249A > G|rs527236141|ss1227131697;NG_009244.1:g.114278G > T|rs527236142|ss1227132188;NG_009244.1:g.115017 T > A|rs527236143|ss1227132282.
The 300 bp region downstream of primers hybridizing to BCR exon 13 was sequenced in all cases (Figure 2B). Four SNPs were identified within this region altogether in 9% of patients with e13a2 mRNA fusion and in 12% of patients with e14a2 mRNA. Other 16 SNPs were detected almost exclusively in patients with e14a2 mRNA fusion, which is in accordance with the fact, that the BCR region sequenced in these patients was larger than in the patients with e13a2 mRNA. The minor allele frequency among the BCR-ABL1 alleles analyzed corresponds to that found in the 1000 GenomePhase Population and in the cohort, although small, of healthy donors (Figure 2B).
Conclusion
Although increasing number of studies has been published in last few years [6-16], analysis of BCR-ABL1 at the DNA level has been limited and difficult so far. Our mLR-PCR-NGS approach streamlined the laboratory workflow for patient-specific BCR-ABL1 fusion characterization allowing personalizing real-time PCR assays for patients with MRD. The large collection of 46 BCR-ABL1 fusion sequences was obtained in the short time and is at disposal in the NCBI Nucleotide database. Moreover, the NGS enabled to detect SNPs upstream and downstream the patient-specific breakpoints of the BCR-ABL1 gene. NGS of this region in large series of patients has the potential to provide insights on the association between particular SNPs or haplotypes and CML. Although we describe the method on BCR-ABL1 in patients with CML, the strategy can be used in the same manner as a base for DNA-based MRD monitoring in BCR-ABL1 positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), where significant differences between MRD levels measured by BCR-ABL1 expression and Ig/TCR DNA-based approach were described [17]. Moreover identical approach can be used for breakpoints localization and sequence features calling in other large fusion genes associated with various cancers, e.g. TEL/ABL1 (atypical CML or ALL) [18], TEL/AML1 (acute lymphoid leukemia) [19], TMPRSS2/ERG (prostate cancer) [20] or EML4/ALK (non-small cell lung cancer) [21].
References
Cross NC, White HE, Müller MC, Saglio G, Hochhaus A. Standardized definitions of molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26:2172–5.
Falchi L, Kantarjian HM, Wang X, Verma D, Quintás-Cardama A, O'Brien S, et al. Significance of deeper molecular responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in early chronic phase treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am J Hematol. 2013;88:1024–9.
Hehlmann R, Müller MC, Lauseker M, Hanfstein B, Fabarius A, Schreiber A, et al. Deep molecular response is reached by the majority of patients treated with imatinib, predicts survival, and is achieved more quickly by optimized high-dose imatinib: results from the randomized CML-study IV. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:415–23.
Ross DM, Branford S, Seymour JF, Schwarer AP, Arthur C, Yeung DT, et al. Safety and efficacy of imatinib cessation for CML patients with stable undetectable minimal residual disease: results from the TWISTER study. Blood. 2013;122:515–22.
Rousselot P, Charbonnier A, Cony-Makhoul P, Agape P, Nicolini FE, Varet B, et al. Loss of major molecular response as a trigger for restarting tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia who have stopped imatinib after durable undetectable disease. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:424–30.
Bartley PA, Ross DM, Latham S, Martin-Harris MH, Budgen B, Wilczek V, et al. Sensitive detection and quantification of minimal residual disease in chronic myeloid leukaemia using nested quantitative PCR for BCR-ABL DNA. Int J Lab Hematol. 2010;32:e222–228.
Morley AA, Latham S, Brisco MJ, Sykes PJ, Sutton R, Hughes E, et al. Sensitive and specific measurement of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Mol Diagn. 2009;11:201–10.
Sobrinho-Simões M, Wilczek V, Score J, Cross NC, Apperley JF, Melo JV. In search of the original leukemic clone in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in complete molecular remission after stem cell transplantation or imatinib. Blood. 2010;116:1329–35.
Waller CF, Dennebaum G, Feldmann C, Lange W. Long-template DNA polymerase chain reaction for the detection of the bcr/abl translocation in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:4146–51.
Krumbholz M, Karl M, Tauer JT, Thiede C, Rascher W, Suttorp M, et al. Genomic BCR-ABL1 breakpoints in pediatric chronic myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012;51:1045–53.
Ross DM, Branford S, Seymour JF, Schwarer AP, Arthur C, Bartley PA, et al. Patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who maintain a complete molecular response after stopping imatinib treatment have evidence of persistent leukemia by DNA PCR. Leukemia. 2010;24:1719–24.
Score J, Calasanz MJ, Ottman O, Pane F, Yeh RF, Sobrinho-Simões MA, et al. Analysis of genomic breakpoints in p190 and p210 BCR-ABL indicate distinct mechanisms of formation. Leukemia. 2010;24:1742–50.
Burmeister T, Gröger D, Kühn A, Hoelzer D, Thiel E, Reinhardt R. Fine structure of translocation breakpoints within the major breakpoint region in BCR-ABL1-positive leukemias. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011;10:1131–7.
Mattarucchi E, Spinelli O, Rambaldi A, Pasquali F, Lo Curto F, Campiotti L, et al. Molecular monitoring of residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia by genomic DNA compared with conventional mRNA analysis. J Mol Diagn. 2009;11:482–7.
Karl M, Krumbholz M, Tauer JT, Jacobs U, Metzler M, Suttorp M. Identification of the genomic BCR-ABL1 fusion sequence from blood specimen stored on filter paper. Leuk Res. 2013;37:117–9.
Shibata Y, Malhotra A, Dutta A. Detection of DNA fusion junctions for BCR-ABL translocations by Anchored ChromPET. Genome Med. 2010; doi:10.1186/gm191.
Zaliova M, Fronkova E, Krejcikova K, Muzikova K, Mejstrikova E, Stary J, et al. Quantification of fusion transcript reveals a subgroup with distinct biological properties and predicts relapse in BCR/ABL-positive ALL: implications for residual disease monitoring. Leukemia. 2009;23:944–51.
Zuna J, Zaliova M, Muzikova K, Meyer C, Lizcova L, Zemanova Z, et al. Acute leukemias with ETV6/ABL1 (TEL/ABL) fusion: poor prognosis and prenatal origin. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010;49:873–84.
Zuna J, Hrusak O, Kalinova M, Muzikova K, Stary J, Trka J. TEL/AML1 positivity in childhood ALL: average or better prognosis? Czech Paediatric Haematology Working Group. Leukemia. 1999;13:22–4.
Wang J, Cai Y, Ren C, Ittmann M. Expression of variant TMPRSS2/ERG fusion messenger RNAs is associated with aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8347–51.
Choi YL, Takeuchi K, Soda M, Inamura K, Togashi Y, Hatano S, et al. Identification of novel isoforms of the EML4-ALK transforming gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:4971–6.
Acknowledgement
This work has been supported by the Internal Grant Agency of Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic grant number NT11555, the conceptual development of research organization (00023736) from Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic and ERDF OPPK CZ.2.16/3.1.00/28007. The authors thank also the Czech Leukemia Study Group for Life - CELL for support. LH was supported by GAUK 554214.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
KMP – Novartis and Bristol Myers-Squibb - research grant and honoraria; SS - Novartis, Bristol Myers-Squibb and Ariad – consultancy; HK - Novartis and Bristol Myers-Squibb - consultancy and honoraria.
Authors’ contributions
JL- has made substantial contributions to analysis and drafting the manuscript; LH- have made substantial contributions to analysis; AB and MJ- have contributed to NGS analysis; SS, JZ and HK - have been involved in drafting the manuscript end revising it critically for important intellectual content; KMP – evaluate and interpreted data, contributed to manuscript drafting, design and coordinate the work. All authors gave final approval for submission.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Linhartova, J., Hovorkova, L., Soverini, S. et al. Characterization of 46 patient-specific BCR-ABL1 fusions and detection of SNPs upstream and downstream the breakpoints in chronic myeloid leukemia using next generation sequencing. Mol Cancer 14, 89 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0363-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0363-8