Abstract
Background
Accumulating evidence suggest that compromised CYP2D6 enzyme activity caused by gene mutation could contribute to primaquine failure for the radical cure of vivax malaria. The current study aims to preliminarily reveal the association between the recurrence of vivax malaria in Yunnan Province and CYP2D6 gene mutation by analysing polymorphisms in the entire coding region of human CYP2D6 gene.
Methods
Blood samples were collected from patients with vivax malaria, who received "chloroquine and 8-day course of primaquine therapy" in Yunnan Province. The suspected relapsed cases were determined by epidemiological approaches and gene sequence alignment. PCR was conducted to amplify the CYP2D6 gene in the human genome, and the amplified products were then sequenced to compare with the non-mutation “reference” sequence, so as to ensure correct sequencing results and to determine 9 exon regions. Subsequently, the DNA sequences of 9 exons were spliced into the coding DNA sequence (CDS), which, by default, is known as maternal CDS. The paternal CDS was obtained by adjusting the bases according to the sequencing peaks. The mutation loci, haplotypes (star alleles), genotypes and odds ratios (OR) of all the CDSs were analysed.
Results
Of the119 maternal CDS chains in total with 1491 bp in length, 12 mutation sites in the 238 maternal and paternal CDS chains were detected. The c.408G > C mutation was most frequently detected in both suspected relapsed group (SR) and non-relapsed group (NR), reaching 85.2% (75/88) and 76.0% (114/150), respectively. The c.886C > T mutation was most closely related to the recurrence of vivax malaria (OR = 2.167, 95% CI 1.104–4.252, P < 0.05). Among the 23 haplotypes (Hap_1 ~ Hap_23), Hap_3 was non-mutant, and the sequence structure of Hap_9 was the most complicated one. Five star alleles, including *1, *2, *4, *10 and *39, were confirmed by comparison, and CYP2D6*10 allele accounted for the largest percentage (45.4%, 108/238). The frequency of CYP2D6*2 allele in the SR group was significantly higher than that in the NR group (Χ2 = 16.177, P < 0.05). Of the defined 24 genotypes, 8 genotypes, including *4/*4, *4/*o, *2/*39, *39/*m, *39/*x, *1/*r, *1/*n, and *v/*10, were detected only in the SR group.
Conclusion
Mutation of CYP2D6*10 allele accounts for the highest proportion of vivax malaria cases in Yunnan Province. The mutations of c. 886C > T and CYP2D6*2 allele, which correspond to impaired PQ metabolizer phenotype, are most closely related to the relapse of vivax malaria. In addition, the genotype *4/*4 with null CYP2D6 enzyme function was only detected in the SR group. These results reveal the risk of defected CYP2D6 enzyme activity that diminishes the therapeutic effect of primaquine on vivax malaria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In recent years, the global malaria epidemic has gradually scaled down, yet the death tolls remain high and the number of malaria cases in certain areas has increased [1]. Meanwhile, multiple technological restrains, including the difficulty to identify low-density Plasmodium infection [2], the expansion of drug resistant Plasmodium [3, 4], and the lack of new drugs in the anti-malarial pipeline [5], pose daunting challenges to the elimination of malaria. Although the local cases of malaria have not been reported since 2016 [6], China still needs to cope with a large number of imported malaria cases, especially from Africa and Southeast Asian countries [7]. From 2011 to 2018, 50.7% of the imported malaria cases in Yunnan Province were caused by Plasmodium vivax [8]. Therefore, the elimination of malaria calls for the strict enforcement to block the transmission of P. vivax.
Tafenoquine and primaquine are recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the treatment of relapsed malaria owing to its efficiency of eradicating the hypnozoites of P. vivax via 5-hydroxy-primaquine (5-hydroxy-primaquine) formed by the enzyme CYP2D6 (Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily D, polypeptide 6) in human liver cells [9,10,11,12]. CYP2D6, also known as debrisoquine4-hydroxylase, is an isozyme in the Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) super family and an important phase I drug-metabolizing enzyme. Owing to its low capacity and high affinity, CYP2D6 is involved in the metabolism of ~ 30% of commonly used drugs, including primaquine although it only accounts for 4% of the total P450 enzyme protein in the liver [12]. Studies have found that the heterogeneity of CYP2D6 activity is predominantly governed by its genetic variation [13], and that decreased CYP2D6 isoenzyme activity caused by genetic polymorphisms would obstruct the generation of 5-hydroxy-primaquine, making large doses or repeated use of primaquine necessary to compensate for the declined efficacy of primaquine. Meanwhile, primaquine can cause life threatening haemolysis in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, subsequently inflicting low efficacy in anti-relapse and acute hemolysis [9, 14, 15]. Therefore, the risk of G6PD deficiency should be identified prior to receiving anti-relapse treatment of vivax malaria, and that the genotype and enzyme activity of CYP2D6 should be tested as well [14, 16, 17].
CYP2D6 enzyme activity is measured mainly through phenotypic observation and genotypic analysis. Compared with phenotypic characterization, genotypic prediction manifests the advantages of greater stability, more convenience and being less affected by environmental or physiological factors [18,19,20]. CYP2D6 enzyme activity can be detected from the blood sample of the patients; genotypic sequencing is currently the common technical method to determine the allelic form of CYP2D6 gene [21,22,23,24,25] by identifying the locus status of the CYP2D6 gene [13] or allelic combinations [26, 27], thereby predicting the activity level of CYP2D6. However, as the number of alleles of CYP2D6 gene continues to increase, efforts should be made to improve the precision and inclusiveness of genotyping results [28]. The better understanding of the genetic polymorphism of CYP2D6, which metabolizes about 25% of all medications in the human liver, can not only help deal with individual adverse event and but also enable the more precise DNA genotyping-based prediction.
Primaquine is commonly used in the malaria endemic areas of Yunnan Province, yet the systematic survey on the genetic polymorphisms of CYP2D6 has been not conducted. In this study, Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) was conducted to investigate the polymorphisms of CYP2D6 gene in the vivax malaria cases, thereby revealing the association between human CYP2D6 gene polymorphisms and the relapsed cases of vivax malaria.
Methods
Study subjects and sampling
A total of 120 subjects living in Yunnan province, China (97°31′ E to 106°11′ E; 21°8′ N to 29°15′ N) were enrolled in the study. The subjects were diagnosed of mono-infection of P. vivax by both microscopy examination and Plasmodium 18S rRNA gene detection (PCR) in Yunnan Province Malaria Diagnosis Referent Laboratory (YPMDRL) (Additional file 1). All the patients received oral chloroquine therapy (1550 mg in total) within 3 days, followed by the subsequent 8-day course of primaquine therapy (22.5 mg/day).
The subjects diagnosed from 2014 to 2018 were subdivided into suspected relapse of vivax malaria (SR group) and non-relapse of vivax malaria (NR group). The inclusion criteria of the SR group are: (1) the patients were re-diagnosed as P. vivax infection within the interval of 28–180 days after the initial diagnosis; (2) epidemiological investigation confirmed that the patients were not re-exposed to malaria endemic areas between the two malaria episodes; and (3) the comparative sequencing of CSP (Circumsporozoite Surface Protein) and MSP-1 (Merozoite Surface Protein 1) of P. vivax with those of the previously infected strains found 100% similarity and 0 variable sites.
A simple random sampling method was conducted to selected 75 NR cases from the 143 patients confirmed in 2018. The subjects in the NR group had no history of relapsed vivax malaria after 1 year of follow-up. The source of vivax malaria infection was determined through epidemiological investigations. The subjects had no travelling history to malaria endemic areas within 30 days before the onset of malaria were regarded as local cases, otherwise they were regarded as imported cases. The study was approved by Yunnan Institute of Parasitic Diseases and Ethical Committee document No. 201904 (January 25, 2019). Genotyping was performed by using the stored blood samples obtained from the suspected patients who experienced fever and chills. Informed consent was obtained from all the patients. The blood samples of the subjects were provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Yunnan Province, according to the described protocol [29]. Dried blood spots (DBS) sampling was conducted by collected 0.6 ml of venous blood, which was stored in a dried tube at − 80 ℃ before the extraction of DNA.
Extraction of genomic DNA
Three dried blood spots (diameter = 5 mm) were made, and genomic DNA was extracted according to the manufacturer’s instructions of the QIAgen Mini Kit (Germany, QIAamp Company's DNA Mini Kit), according to the manufacture’s instruction. The extracted DNA was stored at − 20 ℃.
PCR amplification of CYP2D6 gene fragment
The primers of CYP2D6 for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification were designed by using GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/), reference sequence (ID: NC_000022.11) was used as template, following the reaction condition in previous studies [23, 30]. The primers for first-round nested PCR covering the coding region of CYP2D6 gene exons1–4 were: 5′-CCAGTGACAGATAAGGGTGC-3′ and 5′-GACGTGGATAGGAGGTAC AGAG-3′; the primers for second-round nested PCR were: 5′-GGTGACTTCTCCGACCAG G-3′ and 5′-TTCCCAAACCCATCTATGC-3′. The final amplification region was 42,131,088–42,128,678, and the expected fragment length of the product was 2411 bp. The primers that cover exons 5–9 of CYP2D6 gene were: 5′-GCCGACTGAGCCCTGGGA GGTAGGTA-3′ and 5′-GCTGGGGCCTGAGACTT-3. The amplification area was 42,126,035–42,128,422, and the amplification products had an expected fragment length of 2388 bp. For all the PCR reaction systems, we used 2.6 μl DNA template, 14.0 μl 2 × Taq PCR hybrid system (QIAGEN, Germany), 0.7 μl upstream primer (20umol/L), 0.7 μl downstream primers (20umol/L). The total volume was adjusted to 25.0 μl with ddH2O. PCR reaction conditions were clarified as follows: 92 to 94 °C for 2–5 min; 92 to 94 °C for 10–30 s, 50 to 56 °C for 15–30 s, 68 to 72 °C for 2 to 3 min, 35 cycles; 68 to 72 °C for 7 min. The triplicated parallel repetition was adopted for each PCR reaction. The amplified products were observed using 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. The positive amplification products were sent to Shanghai Meiji Biomedical Technology Co, Ltd. for sequencing by using the Sanger method. Only the sequences that showed identical results in at least two tests were used for subsequent analysis.
CYP2D6 gene mutations analysis
The sequencing reads were aligned by using DNAStar and BioEdit software packages. The obtained DNA sequences were assessed by using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST, http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) on the NCBI platform. The sequences having a homology of 100% and query cover of above 99% with the non-mutated “reference” sequence (ID: NC_000022.11) were considered as the human CYP2D6 gene sequence.
The sequence was further compared with the non-mutation reference sequence to identify 9 exon regions, the transcriptional starting point and the end point of CYP2D6 gene. The DNA sequences of the 9 exon regions were spliced into the maternal CDS (coding DNA sequence) of CYP2D6 gene in the order from exon 1 to exon 9. The paternal CDS was obtained by replacing the undisplayed diploid bases on the maternal CDS chain [31, 32], and the diploid bases were determined by searching the sequencing peaks (Additional file 2). This approach makes up for the shortcoming that the sequencer can only read one base signal for each site, whereas misses the other hybrid base. MEGA v5.04 software was used to analyse the missense mutations and synonymous mutation sites of maternal and paternal CDS, and the ID number of the defined mutation site was queried in Genbank. DnaSP 6.11.01 software was used to identify the haplotype of the CDS, to calculate the nucleic acid diversity index (π), expected heterozygosity (He) and other parameters [33].
The haplotype (allelic form) of CDSs was determined according to the criteria of Human Cytochrome P450 Allele Nomenclature Committee (NM_000106.6) [34] and previous study [35], and were termed to the level of sub-alleles (such as *10.001 and *39.001). The sub-alleles were then merged. Those haplotypes unmatched with known CYP2D6 alleles were grouped into the “other” category. The genotype of each sample was a diploid composed of the maternal CDS and parental CDS (such as *10/*39 and *1/*10). SPSS software (version 21.0; IBN; Chicago; IL) was used to conduct chi-square test on the frequency of genotypes and mutation loci co-existed in the SR cases and NR cases. The odds ratio (OR) of genotypes and mutation loci with statistical significance were calculated by comparing to the relapse rate of P. vivax. The significance level was set as P < 0.05; OR < 1 indicates that the haplotype is a protective factor, while OR < 1 indicates a risk factor.
Results
Demographics and clinical characteristics of the subjects and PCR amplification of human CYP2D6 gene
A total of 45 SR vivax malaria cases were confirmed by epidemiological investigation and gene sequence alignment (Additional file 3), including 43 cases with one suspected relapsed event, 1 case with two suspected relapsed events and 1 case with three suspected relapsed events. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the subjects are listed in Table 1. The male–female ratio was 3:1. Most of the patients presented only one suspected relapsed episode (95.6%).
Exons 1–4 and 5–9 of CYP2D6 gene in the blood samples collected from 45 SR patients and 75 NR patients were amplified by conducting PCR. The amplified product revealed a clear band at > 2000 bp, and therefore can be considered as the target band (Additional file 4). The CYP2D6 gene fragments of 75 NR patients and 44 SR patients were successfully amplified, expect for the PCR product of CYP2D6 gene was not effectively amplified for 1 SR patient.
Locus polymorphisms of CDS and its association with relapsed cases of vivax malaria
A total of 119 maternal CDS of CYP2D6 gene (Genbank accession number: MT339075-MT339193) were obtained. Base substitutions at 12 loci, including c.31 and c.100, on the 238 maternal and paternal CDS, were determined (Table 2). The proportions of third-base and first-base substitution in the triplet codon were 41.7% (5/12), and the proportion of second-base substitution was 16.6% (2/12). 7 missense mutation loci and 5 synonymous mutation loci were determined. 91.7% (11/12) of the mutation sites were found in the sequences of SR group, while 66.7% (8/12) of the mutation sites were determined in the sequences of NS group (Table 2).
The comparative results of 12 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between the two groups were listed in Table 2. In the SR group, the frequency of mutation allele was the highest at c.1457 G > C (85.2%, 75/88), and c. 408 G > C (85.2%,75/88). In the NR group, the highest frequency of mutation was at c. 408 G > C (76.0%, 114/150), followed by c. 1457 G > C (72.0%, 108/150). Eight mutation loci found both in SR group and NR group were selected to analyse the association between loci mutation and vivax malaria relapse. Correlation analysis showed that the ratio of c.886C > T site mutation to the occurrence of vivax malaria recurrence was 2.167 (95% CI 1.104–4.252), and that statistically significance was determined (P˂ 0.05). Such result suggests that c.886 mutation increases the risk of recurrence of vivax malaria, which is 2.167 times higher than that of other SNPs (Table 2).
Haplotype diversity
A total of 23 haplotypes (Hap_1 ~ Hap_23) were identified amongst the 238 CDSs of CYP2D6 gene. Of them, 9 haplotypes were only observed in the sequences of SR group (π = 0.0015, He = 0.821), while 6 haplotypes were only found in the NR group (π = 0.0014 and He = 0.760). 8 haplotypes, including Hap_2, Hap_3, Hap_4, Hap_5, Hap_6, Hap_7, Hap_13 and Hap_14, were found in both SR and NR group. The compositions of every haplotype were shown in Fig. 1. Hap_3 did not contain mutation loci, and the rest haplotypes contained different mutation loci.
Haplotype structure of CYP2D6 gene. 9 exons are indicated by numbered boxes with DNA polymorphisms indicated on top. Predicted amino acid changes are indicated below; no change is synonymous mutation. Hap: Haplotypes; *m-*x: They could not meet the allele inclusion criteria provided by the Allele Nomenclature Committee
Alleles/genotypes and their association with vivax malaria relapse
Among the 23 haplotypes, 11 sub-alleles (such as *1.001, *1.011, *2.001 and *2.004) that could be accurately termed belonged to 5 star (*) alleles, including *1, *2, *4, *10 and *39. Moreover, 12 sub-alleles (*m-*x) had no referencing information. The most common alleles included *10 (45.4%, 108/238), *1 (19.7%, 47/238) and *39 (11.8%, 28/238) (Table 3). In addition, *10 alleles accounted for the highest proportion in both SR group and NR group, reaching the frequencies of 38.6% (34/88) and 49.3% (74/150), respectively, yet the difference did not reach statistically significant level (x2 = 2.560, P > 0.05). The frequency of alleles *1 in the NR group (x2 = 6.193, P < 0.05), and the frequency of alleles *2 in SR group was significantly higher (x2 = 16.177, P < 0.05).
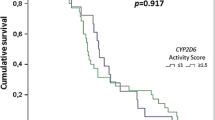
The current study defined 32 sub-allelic genotypes, which can be classified into 24 star alleles genotypes (Additional file 5). Among them, the frequency of *10/*10 was the highest in both SR group and NR group, reaching 24.2% (12/44) and 32.0% (24/75), respectively (Additional file 5). In addition, 8 sub-allelic genotypes, including *4/*4, *4/*o, *2/*39, *39/*m, *39/*x, *1/*r, *1/*n, *v/*10, were only detected in SR group. We conducted correlational analysis on the 9 genotypes distributed in both two groups (including *1/*1, *2/*2, *1/*2, *1/*10, *10/*10, *10/ *39, *39/*39, *10/*s and *39/*s), and revealed that the odd ratios of all genotypes were not statistically significant (P > 0.05) (Table 3). This result suggested that the different CYP2D6 genotypes in this study did not affect the recurrence of vivax malaria.
Discussion
Located on chromosome 22q13.1, CYP2D6 gene (4383 bp in length) consists of 8–9 exons and 7–8 introns. Its CDS is 1338–1491 bp in length and encodes 446–497 amino acids. The heterogeneity of CYP2D6 monooxygenase activity varies from complete dysfunction to ultra-rapid enzyme metabolism, depending on the various genotypes of CYP2D6 [14]. Among the 150 identified alleles, multiple mutations such as CYP2D6*3, CYP2D6*4, CYP2D6*5 and CYP2D6*6 are considered to represent null CYP2D6 enzyme activity [30, 32, 33, 36].
The current study is the first one that attempts to analyse CYP2D6 polymorphisms in the entire coding region sequence in the blood specimen of relapsed vivax malaria patients in Yunnan. The current study reveals the association between CYP2D6 polymorphisms and thwarted CYP2D6 enzyme activity, which is accountable to the failed treatment of using primaquine. This study found that mutation at c. 886 locus of CYP2D6 gene elevated the risk of vivax malaria relapse risk by 2.167-fold (P < 0.05). In the findings of Wang et al. [37] and Gaedigk et al. [38], it is concluded that the relapse of vivax malaria may be relate to c.886. locus mutation of CYP2D6 gene in Yunnan Province.
Among the 23 alleles defined by the 23 haplotypes in all the CDSs, CYP2D6*10 accounts for the highest proportion, reaching as high as 45.4% (108/238). Consistently, previous studies found the highest frequency of CYP2D6*10 alleles mutation in the Chinese Han population and in Asian subjects [31, 39,40,41]. Although the frequency of CYP2D6*10 alleles did not show statistical significant difference between the SR group and the SR group, CYP2D6*10 mutation was considered to indicate decreased enzyme activity [24, 34]. This notion suggested that the wide distribution of CYP2D6 gene*10 alleles in the population of Yunnan should not be disregarded, as it will amplify the accumulated risk of reduced therapeutic efficacy of primaquine in eliminating P. vivax hypnozoites in Yunnan Province.
The current study found that CYP2D*2 allele was more frequently determined in the relapsed patients. This result was not in agreement with that of Brasil et al. [30], which reported that the frequency of CYP2D*2 mutation was significantly higher in the non-relapsed patients. Such inconsistent results might be attributed to the different subjects enrolled in the two studies. Specifically, the subjects included in this study were vivax malaria patients who live in the malaria endemic areas in Yunnan Province, hence the long-term malaria epidemic environment could positively screen the human defective genes [42,43,44].
In this study, all the alleles were identified based on the mutations in the exon regions of CYP2D6, which is different from allelic recognition that covers intron mutations [32, 45]. Therefore, the homogeneity of CYP2D6*2 allele in the two studies could not be ruled out. Although CYP2D6*2 allele is generally considered to be an allelic type of CYP2D6 normal enzyme activity, multiple mutation that contains c. 886 locus could result in lowered activity of CYP2D6 enzyme [38, 42]. At present, the complicated multi-directional change of CYP2D6 enzyme activity caused by *2 allelic mutation is yet to be validated [35, 37, 38, 45].
Eight mutant allelic types were found only in the SR group, yet the association between these different CYP2D6 genotypes and the relapse of vivax malaria could not be established. Given that the *10/*10 genotype still accounted for the largest proportion (30.3%) in the overall study cohort and the no-function *4/*4 genotype was found in the SR group [39], the risk of declined therapeutic efficacy of primaquine caused by defective CYP2D6 enzyme activity in malaria endemic areas should not be ignored. In addition, effort should be made to validate whether the one case of amplification failure case in this study was caused by full gene deletion (*5/*5) or other factors.
The limitations of the current study should be noted. Firstly, the sample size of suspected recurrence of vivax malaria is not large enough, and the alleles (*4, *m-*x,) of CYP2D6 genes with low frequency of distribution might not be quantitatively analyzed (Additional file 5). Secondly, while the re-infection with P. vivax was ruled out from the SR group, the influences of primaquine doses and primaquine resistance were not evaluated. Finally, polymorphisms in the entire coding region of CYP2D6 gene were investigated yetthe possible mutation in intron region and the copy number of CYP2D6 gene, which has been considered to disturb the activity of CYP2D6 enzyme, were not analysed. Thusly, the activity of CYP2D6 cannot be indirectly predicted based on the results of CYP2D6 genotyping in the present study. In view of such shortcoming, the sampling size should be expanded to conduct molecular epidemiological investigations on CYP2D6 genotype.
Currently, the number of CYP2D6 gene CDS has increased to 320, and consistent results pertaining to the loci mutation and allelic type were found. Moreover, multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) and other advanced methods will be applied to optimize the accurate identification of human CYP2D6 genotypes, so as to swiftly predict CYP2D6 enzyme activity of individual subjects. These findings will contribute to the efficacy of primaquine in the treatment of vivax malaria in Yunnan province.
Conclusions
This pilot study reveals the polymorphisms of CYP2D6 gene coding region and its association with the recurrence of vivax malaria in the population of Yunnan Province, suggesting that the radical cure of vivax malaria by using primaquine could be hampered due to the impaired CYP2D6 enzyme activity in the population of Yunnan Province. The study revealed that (1) CYP2D6*10 allele accounts for the highest proportion in the vivax malaria cases of Yunnan Province; (2) mutation at c. 886 locus is most closely related to the relapse of vivax malaria and CYP2D6*2 allele containing this mutation locus was significantly higher in SR; and (3) The *4/*4 genotype that indicates null CYP2D6 enzyme function (poor metabolizers) was only found in the SR cases.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- CYP2D6:
-
Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily D, polypeptide 6
- G6PD:
-
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
- CDS:
-
Coding DNA sequence
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- YPMDRL:
-
Yunnan Province Malaria Diagnosis Referent Laboratory
- CDC:
-
Center for Disease Control
- DBS:
-
Dried blood spots
- NR:
-
Non-relapsed cases of vivax malaria
- SR:
-
Suspected relapsed cases of vivax malaria
- csp :
-
circumsporozoite surface protein
- msp-1 :
-
merozoite surface protein 1
- Hap:
-
Haplotype
- π:
-
Diversity index
- He:
-
Expected heterozygosity
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- MPLA:
-
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
References
Newby G, Bennett A, Larson E, Cotter C, Shretta R, Phillips AA, et al. The path to eradication: a progress report on the malaria-eliminating countries. Lancet. 2016;387:1775–84.
Recker M, Bull PC. Recent advances in the molecular epidemiology of clinical malaria. F1000Res. 2018;7:1159.
Thuy-Nhien N, Tuyen NK, Tong NT, Vy NT, Thanh NV, Van HT, et al. K13 Propeller mutations in Plasmodium falciparum populations in regions of malaria endemicity in Vietnam from 2009 to 2016. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:e01578-e1616.
Dong Y, Wang J, Sun A, Deng Y, Chen M, Xu Y, et al. Genetic association between the Pfk13 gene mutation and artemisinin resistance phenotype in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Yunnan Province, China. Malar J. 2018;17:478.
WHO Malaria Policy Advisory Committee and Secretarial. Malaria Policy Advisory Committee to the WHO: conclusions and recommendations of September 2012 meeting. Malar J. 2012;11:424.
Feng J, Zhang L, Huang F, Yin ZH, Tu H, Xia ZG, et al. Ready for malaria elimination: zero indigenous case reported in the People’s Republic of China. Malar J. 2018;17:315.
Feng J, Xiao H, Zhang L, Yan H, Feng X, Fang W, et al. The Plasmodium vivax in China: decreased in local cases but increased imported cases from Southeast Asia and Africa. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8847.
Chen TM, Zhang SS, Feng J, Xia ZG, Luo CH, Zeng XC, et al. Mobile population dynamics and malaria vulnerability: a modelling study in the China-Myanmar border region of Yunnan Province, China. Infect Dis Poverty. 2018;7:36.
Bennett JW, Pybus BS, Yadava A, Tosh D, Sousa JC, McCarthy WF, et al. Primaquine failure and cytochrome P-450 2D6 in Plasmodium vivax malaria. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1381–2.
Marcsisin SR, Reichard G, Pybus BS. Primaquine pharmacology in the context ofCYP2D6 pharmacogenomics: current state of the art. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;161:1–10.
Vale N, Moreira R, Gomes P. Primaquine revisited six decades after its discovery. Eur J Med Chem. 2009;44:937–53.
Pybus BS, Sousa JC, Jin X, Ferguson JA, Christian RE, Barnhart R, et al. CYP450 phenotyping and accurate mass identification of metabolites of the 8-aminoquinoline, anti-malarial drug primaquine. Malar J. 2012;11:259.
Twist GP, Gaedigk A, Miller NA, Farrow EG, Willig LK, Dinwiddie DL, et al. Constellation: a tool for rapid, automated phenotype assignment of a highly polymorphic pharmacogene, CYP2D6, from whole-genome sequences. NPJ Genome Med. 2016;1:15007.
Baird JK, Battle KE, Howes RE. Primaquine ineligibility in anti-relapse therapy of Plasmodium vivax malaria: the problem of G6PD deficiency and cytochrome P-450 2D6 polymorphisms. Malar J. 2018;17:42.
Nelwan EJ, Ekawati LL, Tjahjono B, Setiabudy R, Sutanto I, Chand K, et al. Randomized trial of primaquine hypnozoitocidal efficacy when administered with artemisinin-combined blood schizontocides for radical cure of Plasmodium vivax in Indonesia. BMC Med. 2015;13:294.
Sutanto I, Tjahjono B, Basri H, Taylor WR, Putri FA, Meilia RA, et al. Randomized, open-label trial of primaquine against vivax malaria relapse in Indonesia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:1128–35.
Baird JK, Louisa M, Noviyanti R, Ekawati L, Elyazar I, Subekti D, et al. Association of impaired Cytochrome P450 2D6 activity genotype and phenotype with therapeutic efficacy of primaquine treatment for latentPlasmodium vivax malaria. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1:e181449.
McElroy S, Sachse C, Brockmoller J, Richmond J, Lira M, Friedman D, et al. CYP2D6 genotyping as an alternative to phenotyping for determination of metabolic status in a clinical trial setting. AAPS PharmSci. 2000;2:E33.
Gaedigk A, Bradford LD, Marcucci KA, Leeder JS. Unique CYP2D6 activity distribution and genotype-phenotype discordance in black Americans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002;72:76–89.
Lindpaintner K. Pharmacogenetics and the future of medical practice. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;54:221–30.
Griese EU, Zanger UM, Brudermanns U, Gaedigk A, Mikus G, Morike K, et al. Assessment of the predictive power of genotypes for the in-vivo catalytic function of CYP2D6 in a German population. Pharmacogenetics. 1998;8:15–26.
De Gregori M, Allegri M, De Gregori S, Garbin G, Tinelli C, Regazzi M, et al. How and why to screen for CYP2D6 inter individual variability in patients under pharmacological treatments. Curr Drug Metab. 2010;11:276–82.
Sistonen J, Fuselli S, Levo A, Sajantila A. CYP2D6 genotyping by a multiplex primer extension reaction. Clin Chem. 2005;51:1291–5.
Zanger UM, Raimundo S, Eichelbaum M. Cytochrome P450 2D6: overview and update on pharmacology, genetics, biochemistry. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004;369:23–37.
Gaedigk A, Simon SD, Pearce RE, Bradford LD, Kennedy MJ, Leeder JS. The CYP2D6 activity score: translating genotype information into a qualitative measure of phenotype. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008;83:234–42.
Kamenski G, Ayazseven S, Berndt A, Fink W, Kamenski L, Zehetmayer S, et al. Clinical relevance of CYP2D6 polymorphisms in patients of an Austrian Medical Practice: a family practice-based observational study. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2020;7:63–73.
Gaedigk A, Sangkuhl K, Whirl-Carrillo M, Klein T, Leeder JS. Prediction of CYP2D6 phenotype from genotype across world populations [published correction appears in Genet Med. 2016;18:1167]. Genet Med. 2017;19:69–76.
Caudle KE, Sangkuhl K, Whirl-Carrillo M, Swen JJ, Haidar CE, Klein TE, et al. Standardizing CYP2D6 genotype to phenotype translation: consensus recommendations from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium and Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group. Clin Transl Sci. 2020;13:116–24.
Dong Y, Deng Y, Xu Y, Chen M, Wei C, Zhang C, et al. Analysis of initial laboratory diagnosis of malaria and its accuracy compared with re-testing from 2013 to 2018 in Yunnan Province, China. Malar J. 2020;19:409.
Brasil LW, Rodrigues-Soares F, Santoro AB, Almeida ACG, Kuhn A, Ramasawmy R, et al. CYP2D6 activity and the risk of recurrence of Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Brazilian Amazon: a prospective cohort study. Malar J. 2018;17:57.
Swadi AA, Mohammad BI, Hadi NR. Correlation of CYP2D6 allelic polymorphism to outcome of acute coronary syndrome in mid-Euphrates Iraqi patients on metoprolol therapy. Gene. 2019;703:112–9.
NM_000106.6 Database. https://www.pharmvar.org/gene/CYP2D6. Accessed 09 Nov 2020.
St Jean PL, Xue Z, Carter N, Koh GC, Duparc S, Taylor M, et al. Tafenoquine treatment of Plasmodium vivax malaria: suggestive evidence that CYP2D6 reduced metabolism is not associated with relapse in the Phase 2b DETECTIVE trial. Malar J. 2016;15:97.
Gaedigk A, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Miller NA, Leeder JS, Whirl-Carrillo M, Klein TE, et al. The Pharmacogene Variation (PharmVar) Consortium: incorporation of the human Cytochrome P450 (CYP) allele nomenclature database. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018;103:399–401.
Hertz DL, Snavely AC, McLeod HL, Walko CM, Ibrahim JG, Anderson S, et al. In vivo assessment of the metabolic activity of CYP2D6 diplotypes and alleles. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;80:1122–30.
Silvino AC, Costa GL, Araujo FC, Ascher DB, Pires DE, Fontes CJ, et al. Variation in human cytochrome P-450 drug-metabolism genes: a gateway to the understanding of Plasmodium vivax relapses. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0160172.
Wang D, Poi MJ, Sun X, Gaedigk A, Leeder JS, Sadee W. Common CYP2D6 polymorphisms affecting alternative splicing and transcription: long-range haplotypes with two regulatory variants modulate CYP2D6 activity. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:268–78.
Gaedigk A, Dinh JC, Jeong H, Prasad B, Leeder JS. Ten years’ experience with the CYP2D6 activity score: a perspective on future investigations to improve clinical predictions for precision therapeutics. J Pers Med. 2018;8:15.
Dong AN, Ahemad N, Pan Y, Palanisamy UD, Yiap BC, Ong CE. Functional and structural characterisation of common cytochrome P450 2D6 allelic variants-roles of Pro34 and Thr107 in catalysis and inhibition. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019;392:1015–29.
Qian JC, Xu XM, Hu GX, Dai DP, Xu RA, Hu LM, et al. Genetic variations of human CYP2D6 in the Chinese Han population. Pharmacogenomics. 2013;14:1731–43.
Nguyen HH, Ma TTH, Vu NP, Bach QTN, Vu TH, Nguyen TD, et al. Single nucleotide and structural variants of CYP2D6 gene in Kinh Vietnamese population. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98:e15891.
Louicharoen C, Patin E, Paul R, Nuchprayoon I, Witoonpanich B, Peerapittayamongkol C, et al. Positively selected G6PD-Mahidol mutation reduces Plasmodium vivax density in Southeast Asians. Science. 2009;326:1546–9.
Guindo A, Fairhurst RM, Doumbo OK, Wellems TE, Diallo DA. X-linked G6PD deficiency protects hemizygous males but not heterozygous females against severe malaria. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e66.
Goo YK, Ji SY, Shin HI, Moon JH, Cho SH, Lee WJ, et al. First evaluation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in vivax malaria endemic regions in the Republic of Korea. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e97390.
Nofziger C, Turner AJ, Sangkuhl K, Whirl-Carrillo M, Agúndez JAG, Black JL, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP2D6. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020;107:154–70.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in states/cities and counties such as Dehong, Baoshan, Kunming, Pu’er, Lincang, Dali, Nujiang, Lijiang, Xishuangbanna, Yuxi, Chuxiong, Honghe, Zhaotong, Diqing, Qujing, and Whenshan.
Funding
This study was supported by National Science Foundation, China (Nos. 81660559, 81960579).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH wrote the manuscript, and was responsible for gene testing, design of study, and statistical analysis; YD coordinated the project, the study design, data analysis and revised the manuscript. SL participated in the study design; YL, YD, YX, MC, CZ performed the collection of blood samples and microscopy examination. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Yunnan Institute of Parasitic Diseases and Ethical Committee. Genetic testing were performed on stored blood samples obtained as part of the routine diagnostic work-up of patients with fever who were suspected to have malaria. Although there was no risk and the data processing after sample collection was done anonymously, informed consent was obtained. Database access will be restricted by password, and Yunnan Institute Parasitic Diseases will not allow retrieving and saving the personal identification information into the project database. It is committed not to provide information about the patient to any person unrelated to the study.
Consent for publication
All authors provided their consent for the publication of this report.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
The details of nested PCR testing for differentiating between various Plasmodium species.
Additional file 2.
Sequencing Peak Map of CYP2D6 Gene Polymorphic loci.
Additional file 3.
Epidemiological information and alignment results of the genes of suspected recurrent cases of vivax malaria.
Additional file 4.
Electrophoretic map of PCR products in the coding region of CYP2D6 gene.
Additional file 5.
Analysis the CYP2D6 genotypes in SR group and NR group.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Dong, Y., Xu, Y. et al. The association of CYP2D6 gene polymorphisms in the full-length coding region with higher recurrence rate of vivax malaria in Yunnan Province, China. Malar J 20, 160 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-021-03685-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-021-03685-3