Abstract
Background
Emergence of chloroquine resistant Plasmodium vivax is a serious obstacle towards malaria control in India. This study elucidates the temporal pattern of antifolate [sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine (SP)] resistance in P. vivax infection by means of genetic polymorphisms, especially analysing the single nucleotide polymorphisms of dihydrofolate reductase (pvdhfr) and dihydropteroate synthase (pvdhps) gene among the field isolates of urban Kolkata Municipal Corporation and rural Purulia region of West Bengal, India.
Methods
Blood samples were collected from 99 microscopically diagnosed P. vivax patients (52 from Kolkata Municipal Corporation and 47 from Purulia). Parasitic DNA was extracted followed by polymerase chain reaction and sequencing of different codons of pvdhfr gene (15, 33, 50, 57, 58, 61, 64, 117, and 173 codons) and pvdhps gene (373, 380, 382, 383, 384, 512, 553, 585, and 601 codons) were performed to identify the mutations.
Results
Prevalence of double mutant dhfr A15P33N50F57 R 58 T61V64 N 117 I173 allele (53.85 %) was observed in Kolkata Municipal Corporation (KMC) whereas in Purulia, wild dhfr A15P33N50F57S58T61V64S117I173 allele was predominated (48.94 %). In pvdhps gene a significant number of isolates (17.31 %) in KMC contained the double mutant S373E380S382 G 383 P384K512 G 553 V585M601 allele. pvdhfr and pvdhps combination haplotype revealed the emergence of quadruple (13.46 %) and quintuple (3.84 %) mutant allele in KMC, which might result in poor clinical response against antifolate drugs.
Conclusion
The study reveals that P. vivax parasites in rural Purulia may still be susceptible to SP but additional caution should be taken for treatment of vivax malaria in KMC to limit the blooming of quadruple and quintuple mutant allele in the remainder of the West Bengal, India.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Malaria has been the major public health problem for the past few decades in West Bengal, Eastern India where both Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax are equally prevalent. In 2013, 0.88 million people were affected by malaria, and of them 0.46 million patients were P. falciparum positive and 0.42 million patients were affected by P. vivax infection [1]. Although P. falciparum is the most deadly infection resulting in malignant malaria globally, P. vivax is the most widespread species in Southeast Asia, including India, causing severity and morbidity [2–5]. In 2009, artesunate plus sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine (SP) combination was recommended as the first-line drug against uncomplicated falciparum malaria, while chloroquine along with primaquine remains the first-line drug against vivax malaria in India [6]. The persistence of vast numbers of mixed P. falciparum and P. vivax infection in India is one of the major disease burdens as it is not easily discriminated by microscopy or rapid diagnostic test kits (RDTs). Consequently a large proportion of P. vivax parasites are often involuntarily exposed to SP drug pressure, resulting in the evolution of SP-resistant P. vivax parasites [7]. The target of pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine are respectively dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) and dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS), two major proteins of the folate biosynthesis pathway of parasites [8, 9]. Polymorphisms surrounded by the genes that encode these active enzymes are the major factor in SP resistance. In the case of P. falciparum infection, SP resistance has been predominantly observed with the polymorphism of dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) and dihydropteroate synthase (dhps) genes, throughout the globe [8–13]. Similarly, polymorphisms in pvdhfr and pvdhps genes are proven to be linked with antifolate resistance in P. vivax infection. Polymorphism in pvdhfr S58R and S117N are highly associated with pyrimethamine resistance; additional mutation in P33L, N50I, F57L, T61M, V64L, and I173L codons increases the degree of resistance, i.e., very high IC50 values for pyrimethamine [14–17]. Different field studies suggest that polymorphism at A383G and A553G of pvdhps gene are solely responsible for sulfadoxine resistance while additional mutations at S373T, E380K, S382A, P384L, K512E, V585G, and M601I codons confer higher levels of resistance [18, 19]. Predominance of pvdhfr codon S58R and S117N polymorphisms and pvdhps codon A383G mutation in clinical isolates was reported in studies, mainly from central, western, northern and south eastern regions of India [7, 20, 21], before the introduction of a new national drug policy. Very few studies are initiated in this part of eastern India although West Bengal is a malaria-endemic zone [7]. In 2010, 1.6 million confirmed malaria cases were reported in India; 134,795 patients were from West Bengal [1, 22].
In such settings, molecular markers involved in SP resistance in P. vivax infection need to be evaluated after 5 years of a new national drug policy, help to understand the current scenario of antifolate resistance in P. vivax, as both Plasmodium spp. are predominate in this part of India, resulting in a rapid admixture of parasite population with selection pressure of drug. Prevalence of double or triple pfdhfr (AI 51 CN 108 I or AI 51 R 59 N 108 I) and triple or quadruple pfdhps (A 436 G 437 E 540 AA or A 436 G 437 E 540 AT 613 ) mutation was observed in early 2012 and 2013, in the same study sites of West Bengal, India, which surpassed the antifolate resistant (both in vitro and in vivo) P. falciparum disease burden in West Bengal, India. This alarming sign for malaria control might be due to population migration and probable admixture of different ethnic groups [10–12].
The present investigation aimed to assess polymorphisms of pvdhfr and pvdhps genes to identify the temporal pattern of antifolate resistance among field isolates of urban Kolkata Municipal Corporation (KMC) and rural Purulia. This study might also identify combinations of different mutations that may lead to different qualitative and quantitative multidrug-resistant phenotypes. This knowledge of haplotype variance of candidate gene is of importance for the adoption of future chemotherapy to surmount drug-resistant malaria.
Methods
Chemical and reagents
Phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol, chloroform: isoamyl alcohols, agarose, p-amino benzoic acid-free RPMI 1640 were purchased from Himedia, India. Tris–Hcl, Tris buffer, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4), dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (K2HPO4), ethylene diamine tetra acetate (EDTA), sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), sodium acetate, ammonium acetate, ethanol, boric acid, glacial acetic acid were procured from Merck Ltd, SRL Pvt, Ltd, Mumbai, India. Proteinases K, RNase A, ethidium bromide were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co, USA. Chloroquine tablets were procured from Resochin: Bayer. Oligonucleotide primers were purchased from New England Biolabs, USA. PCR grade nucleotide mixture, MgCl2, dNTPs and Taq DNA polymerase were purchased from Roche, USA. lambda exonuclease was purchased from Gibco-BRL Life Technologies, France. pLDH kit was purchased from Diatek, Kolkata, India. All other chemicals were purchased from Merck Ltd, Mumbai and were of the highest grade available.
Study area
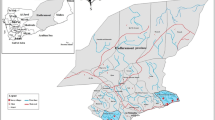
This study was conducted from December 2013 to November 2014 in KMC and Purulia, two malaria-endemic regions of West Bengal, India (Fig. 1). Kolkata is the main commercial and financial hub of east and northeast India, mainly comprised of service industries, business community members, industrial and manufacturing members of a high socio-economic status, whereas Purulia is a hilltop, rural, forest area, where the majority of the population are farmers and labourers with low socio-economic status. In 2010, KMC contributed the highest malaria incidences (96,693) as well as the highest slide-positive rate (SPR) (27.21 %), the majority (82,467) being P. vivax infection [1, 22]. The highest number of mixed P. falciparum + P. vivax co-infection (543) was reported from KMC region, whereas in Purulia, another malaria-endemic region, P. falciparum was prevalent (70.13 % of 4526 malaria-positive cases, 3174 cases of P. falciparum infection), with no P falciparum + P. vivax co-infection [22]. Details of epidemiological information on the study sites are reported elsewhere [22].
Selection of subjects
The criteria for selection to conduct the experiments included history of fever during previous 24 h; mono-infection with P. vivax based on microscopic examination of Giemsa-stained thin and thick blood smears; an RDT based on detection of Plasmodium-specific lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) (OptiMAL-DT) having parasite density of 1000–200,000 asexual parasites/µl blood; and no recent history of self-medication with anti-malarial drugs. 18S rRNA gene, pvcsp gene was amplified by nested PCR to identify P. vivax infection and rule out other mixed species infection [23, 24]. Patients with signs and symptoms of severe, complicated malaria, pregnant and lactating women, infants (under 2 years old), and those with haematocrit <20 %, were excluded [25]. Informed consent was taken from all the patients and consent of a guardian was taken for children. Experimental design and protocol of this study was duly approved by the Vidyasagar University ethical committee.
Sampling design
The sample size for the experiment was determined as described by Pal and colleagues [26], and by the standard formula (n = z2pq d−2). The minimum estimated sample size for each year was 31 [(1.962 × 0.00720 × 0.9928)/0.032)]. The calculation was based on the incidence of annual parasitological index (API) of malaria in India. In 2013 API was recorded as 0.72 by the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) [1]. The desired precision (d) was 3, where, API value was serve as p, q = p − 1 and z = 1.96. A total of 52 patients from KMC and 47 patients from Purulia (age ranging from 3 to 76 years) were included in this study. Plasmodium vivax-positive patients received standard 10 mg/kg chloroquine (CQ) on days 1 and 2, 5 mg/kg CQ on day 3, and 0.25 mg/kg primaquine daily for 14 days (primaquine is contra-indicated in G6PD-deficient patients) under the supervision of Prof Amiya Kumar Hati (ex-Director School of Tropical Medicine, Kolkata) and his team, as recommended by NVBDCP [6].
Separation of red blood cells
Two ml of venous blood was collected from each of patient in a vacutainer (BD Falcon) coated with an anticoagulant (EDTA). Red blood cells (RBCs) were separated using Histopaque 1077 density gradient followed by centrifugation at 1450 rpm for 45 min at 4 °C. An aliquot of approximately 1 ml of RBC pellet was obtained. Finally, erythrocytes were washed three times in folate and p-amino benzoic acid-free RPMI 1640 medium and stored at −20 °C for further analysis [27].
Parasite DNA isolation
Parasite DNA was extracted from 1 ml (approximately) of infected RBC using the phenol–chloroform extraction method as described elsewhere [27]. After air drying, the extracted parasite DNA was re-suspended in TE buffer (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.4) and stored at −20 °C until further use. Isolated DNA was quantified by 1.2 % agarose gel electrophoresis. The purity of the parasite DNA was checked spectrophotometrically by calculating the A260/A280 ratio where A280 values determine protein impurities.
Primer designing and PCR amplification of pvdhfr and pvdhps genes
Point mutations in different variants of pvdhfr and pvdhps genes were investigated in all P. vivax isolates by nested PCR reactions, followed by sequencing analysis. Primers were designed on the basis of complete P. vivax strain sequence (accession number X98123 for pfdhfr and AY186730 for pvdhps) available in the GenBank. Approximately 200 ng of genomic parasite DNA, 10 pmol of primers, 1X reaction buffer (10 mM Tris, 50 mM KCl, pH 8.4), 2.7 mM MgCl2, 150 μM dNTPs, and 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase were used to prepare 25 μl reaction mixture (master mix). PCR cycle conditions were varied in different genes. Detailed primer sequence and cycle conditions are shown in Table 1. In nest-I reaction, pvdhfr gene was amplified by A1F and A1R primer pair whereas 2A F and 2A R primer was used to amplify the pvdhps gene. The amplicon produced by NEST I reaction was used as the template DNA in NEST II reaction. All PCR amplifications contained a positive control (genomic DNA from quality control 3D7 strain) and a negative control (no target DNA).
DNA sequencing of pvdhfr and pvdhps genes
After adequate PCR amplification of different amplicon, sequencing reactions were carried out in 3730xl genetic analyzer (Applied Biosystems) ≥2× coverage using an ABI Prism Big Dye Terminator cycle sequencing ready reaction kit. In the sequencing PCR reaction the final master mix volume was 20 µl, consisting of 1 µl of Terminator ready reaction mix (TRR), 3.2 pmol of gene-specific primer, and 0.5× sequencing buffer [28]. Sequencing experiments were carried out at the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur (IIT, Kharagpur), and Sci Genome Company (Kochin). Electrophoregrams were visualized and analysed with CEQ 2000 genetic analysis system software (Beckman Coulter), and the sequencing traits were translated in the translation tool, available online at the Expert Protein Analysis System proteomic server [28]. Translated sequences were aligned online by the multiple sequence alignment tool ClustalW2 [28] and compared with the wild-type allele sequences (GenBank accession numbers, X98123 for pvdhfr, AY186730 for pvdhps). Polymorphisms of these two genes were confirmed by reading both the forward and reverse strands.
Statistical analysis
The data were expressed as median ± SD values and % (percentage) variation; 95 % confidence intervals were calculated using Clopper-Pearson exact method. Graphical presentation of dhfr and dhps gene was carried out in Statistical Package, Origin 6.1.
Results
Polymorphism of pvdhfr gene
Monoclonal P. vivax infection was confirmed after allelic family-specific nested-PCR. A total of 99 P. vivax-positive patients confirmed by microscopy and PCR were recruited into the study population. The entire DHFR domain of pvdhfr gene was successfully sequenced in all 99 clinical P. vivax isolates. Predominance of wild type dhfr allele (n = 23, 48.94 %) was observed in Purulia whereas only 19 (36.54 %) isolates contained wild dhfr allele in KMC. Among these isolates, mutations were absent in codons 15, 33, 50, 61, 64, and 173. The frequency of non-synonymous polymorphism at S58R and S117N was higher among the isolates. In KMC 63.46 % of isolates presented mutant S58R codon, followed by mutant S117N codon (57.69 %) and F57L codon (3.84 %). Like KMC, polymorphism at codon S58R (42.55 %) was most prevalent in Purulia, followed by S117N polymorphism (36.17 %) (Fig. 2). Beside these known non-synonymous polymorphisms, three synonymous mutations at G38G {GGT → GGG; in five isolates (7.69 %)}, Y69Y {TAT → TAC; in three isolates (5.77 %)} and V134 V {GTC → GTT, in one isolate (1.92 %)} codon were identified in KMC. On the contrary in Purulia, a single synonymous mutation at E119E codon {GAG → GAA, in three isolates (6.38 %)} was observed.
Mutation assessment of pvdhps gene
Different variant of pvdhps gene flanking was successfully amplified and sequenced in all 52 patients from KMC and 47 patients from Purulia. Three different non-synonymous and two synonymous mutations were found in the study site. Non-synonymous mutation at codon A383G was most prevalent (61.54 %) in KMC, followed by A553G mutation (17.30 %). pfdhps A383G polymorphism was far lower in Purulia. Only 21.27 % of isolates presented the mutant A383G allele followed by A553G mutant allele (12.77 %). Another non- synonymous mutation at P384L codon (6.38 %) was observed in Purulia (Fig. 2). No mutation was observed at codons S373T, E380K, S382A, K512E, V585G, and M601I. Beside these non-synonymous polymorphisms, two synonymous mutations were identified at R487R codon {CGC → CGG; in two isolates (3.85 %)}, and L600L {CTA → CTG; in three isolates (6.38 %)} codon in KMC. No synonymous mutation was identified in Purulia.
Regional distribution of pvdhfr and pvdhps haplotype
Four different pvdhfr haplotypes were identified in KMC as well as in Purulia. In KMC, double mutant dhfr A15P33N50F57 R 58 T61V64 N 117 I173 allele (53.85 %) was frequently found after wild type A15P33N50F57S58T61V64S117I173 haplotype (36.54 %). In Purulia, wild type A15P33N50F57S58T61V64S117I173 allele was commonly (48.94 %) observed pvdhfr haplotype, followed by double mutant A15P33N50F57 R 58 T61V64 N 117 I17 allele (27.66 %). In KMC only 5.77 % of isolates represented pvdhfr single mutant A15P33N50F57 R 58 T61V64 S117I173 allele whereas 14.89 % isolates in Purulia contained this single mutant allele. Interestingly, 8.51 % of isolates presented the single mutant S117 N codon, i.e., A15P33N50F57S58T61V64 N 117 I173 allele in Purulia. In Purulia, 23.40 % of isolates contained single pvdhfr mutation which was far higher than KMC (Table 3). In KMC, triple mutant A15P33N50 L 57 R 58 T61V64 N 117 I173 allele was found in 3.84 % of isolates. No isolate was found to contain quadruple or quintuple pvdhfr mutations (Fig. 3).
In the case of pvdhps gene, three different haplotypes (wild type, 383G, 383G + 553G) were identified in KMC and four different haplotypes (wild type, 383G, 553G, 384L) in Purulia. Single mutant pvdhps S373E380S382 G 383 P384K512A553V585M601 haplotype (44.23 %) was most predominant haplotype in KMC, followed by wild type pvdhps S373E380S382A383P384K512A553V585M601 allele (38.46 %). To the contrary, in Purulia, wild type pvdhps S373E380S382A383P384K512A553V585M601 allele (59.57 %) was highly prevalent pvdhps haplotype after single mutant pvdhps S373E380S382 G 383 P384K512A553V585M601 allele (21.27 %). Interestingly, 17.31 % of isolates in KMC had represented the double mutant S373E380S382 G 383 P384K512 G 553 V585M601 allele but it was absent in isolates collected from Purulia (Fig. 3; Table 3).
Variation and distribution of different tandem repeat
Two different tandem repeat variants were found, depending on deletion/insertion of six amino acids (GDNTSG) at pvdhfr gene. The type 2 tandem repeat of pvdhfr gene was the most common repeat polymorph observed in KMC (80.77 %) as well as in Purulia (100 %). Monomorphic tandem repeat variant was observed in Purulia, whereas polymorphic tandem repeats were found in isolates of KMC.
In pvdhps gene, three different tandem repeats variants were identified on the basis of deletion/insertion of seven amino acid repeat (GEAKLTN). Type B tandem repeat of pvdhps gene was prevalent in the study site in KMC (89.36 %) as well as in Purulia (63.47 %). Two tandem repeats were identified in isolates from KMC and three in Purulia. Distribution of tandem repeat variants in the study sites are presented in Table 2.
Combination mutation of pvdhfr and pvdhps gene and emergence of quadruple and quintuple mutant allele
A total of ten different pvdhfr–pvdhps two-locus haplotype combinations were identified among the total 99 isolates (Fig. 3). Seven different pvdhfr–pvdhps haplotype combinations (G1, G2, G3, G5, G6, G7, G10) were found in KMC and eight different haplotype combinations (G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, G6, G8, G9) were observed in Purulia (Table 3). Eleven isolates (21.15 %) in KMC and 17 isolates (36.17 %) in Purulia respectively presented the wild type two-locus genotypes, i.e., G1 genotype. A large number of isolates (28.84 % of isolates in KMC and 14.89 % of isolates in Purulia) had represented the double mutant pvdhfr and single mutant pvdhps (G6) allele. Haplotype data revealed that pvdhfr–pvdhps combination mutation begun to increase in number in KMC compared to Purulia. Some 13.46 % of isolates in KMC contained double mutation in both pvdhfr and pvdhps (G7) gene (quadruple mutation in two-locus combinations) but this haplotype was not observed in Purulia. Interestingly, in KMC, a very low proportion of quintuple mutation in two-locus combination (G10 genotype, triple mutation in dhfr gene and double mutation in dhps gene) was observed in 3.84 % (n = 2) of isolates but this haplotype was absent in isolates of Purulia (Table 3).
Discussion
Genetic diversity in Plasmodium is well known in India as both P. falciparum and P. vivax are prevalent in the same ecological niche. As P. falciparum and P. vivax parasites co-exist in this region and both have the same drug target against antifolate drug [7–11], the risk of resistance development is high. Polymorphisms in different variants of pvdhfr and pvdhps genes were known to be associated with antifolate resistance [8, 9]. However, mathematical modelling, in vitro experiments, and transcriptomic studies all suggest that reduced susceptibility to SP is solely related to pvdhfr and pvdhps [8, 13, 15, 19]. Therefore, genotyping of these candidate gene markers of P. vivax may elucidate trends of SP resistance in India.
The predominance of pvdhfr double mutant 58R + 117N (53.84 % in KMC and 27.65 % in Purulia) polymorphism was observed followed by single mutant S58R and S117N mutation. Non-synonymous 57L mutation was detected in combination with 58R + 117N in low frequency (3.85 %). These findings were similar to those reported from different parts of India [7, 20], Pakistan [29, 30], Afghanistan [31], China [32], Nepal [33], Thailand [18, 34, 35], and Indonesia [36]. In the study did not identify any polymorphism at codons A15, P33L, N50I, T61M, V64L, and I173L of pvdhfr gene, as previously reported from different parts of India [20, 22, 37]. It was postulated that pvdhfr S117N mutation might occur first, followed by the S58R mutation. Polymorphisms at codons F57L and T61M might take place independently with an increase in drug pressure [14]. The triple (L57R58N117) and quadruple (L57R58M61N117) pvdhfr polymorphism possessed progressive tolerance in P. vivax to SP, thus these genotypes were associated with high risk of therapeutic SP failure [35]. Unlike previous reports in India [20, 21], no quadruple mutation was observed in study site, although only two isolates (3.85 %) in KMC had represented the triple mutant allele, which was previously not observed in KMC [7].
Different studies from various geographical locations imply that polymorphism of dhfr gene was associated with tandem repeat polymorphism. In the study, it was observed that predominance of double dhfr mutation was associated with type-2 tandem repeat variant, which strongly supported the previous report in India [21]. On the contrary, previous reports from different geographical regions suggested that type-1 tandem repeat variant was highly associated with triple or quadruple mutant dhfr alleles [17, 21]. Similarly, not a single type-1 tandem repeat was identified in Purulia where no triple or quadruple mutations were observed, although a single exception to this was previously observed in Myanmar [38]. In the case of dhps gene, type B tandem repeat was prevalent in KMC as well as in Purulia, which was previously reported in different parts of India and Pakistan [29, 39]. Previous genome-wide analysis suggested that the type B tandem repeat was generally associated with wild type pvdhps gene, as happened in the study site, whereas the existence of double mutant pvdhps (383G + 553G) haplotype was generally associated with type A tandem repeat [29, 39]. Thus, the tandem repeat could be used as a molecular marker to predict the risk mutant genotypes that confer higher level resistance.
Polymorphism in dhps gene was higher in KMC than in Purulia isolates but there were some similarities in both places. In the case of pvdhps gene, polymorphisms were mainly observed at codons A383G and A553G. Unlike a previous report from KMC [7], double dhps mutation at 383G + 553G was predominantly observed in KMC. Absence of double dhps mutation (A383G + A553G) in Purulia indicated about there was less drug pressure of SP, in contrast to KMC. Predominance of double dhps 383G + 553G mutations were previously observed in isolates from Asaam, Nadiad and Tamil Nadu [20, 21]. It now proved that polymorphism at A383G and A553G were solely responsible for sulfadoxine resistance in vitro as well as in vivo as they possessed the sulfadoxine binding site in dhps gene, additional mutations at E380 K, S382A, P384L, K512E, V585G, and M601I codons confer higher levels of sulfadoxine resistance [18, 19].
In case of combination mutation of pvdhfr and pvdhps gene, it was clearly observed that the proportion of triple mutation (R58N117–G383), quadruple mutation (R58N117–G383G553), and quintuple mutation (L57R58N117–G383G553) were higher in KMC than Purulia. The probability for these major variations might be embedded in the basis of geographical variations of parasite infection. It was reported that P. falciparum + P. vivax mixed infection was highest in KMC whereas not a single case of P. falciparum + P. vivax mixed infection was observed in Purulia [22]. Thus, the parasite from KMC might possess higher SP partial pressure than those isolates from Purulia. Secondly, KMC was the gateway to Southeast Asia in India and the mixed population was very high in that part of India, which might produce westward movement of CQ and SP-resistant parasites from Greater Mekong Sub-region to Africa through India [40, 41].
In India, SP was never prescribed against P. vivax [7]; the emergence of point mutations in pvdhfr and pvdhps genes was quite unexpected. Exposure of P. vivax to SP might arise due to several reasons: first, P. falciparum and P. vivax mixed infections were very common here; artesunate plus SP was generally recommended in those patients and thus, P. vivax parasites may be directly exposed to SP drug pressure. In the study site, the proportion of P. falciparum isolates with increased pfdhfr and pfdhps polymorphisms has been identified over the past decade [10–12]. The increase in the number of P. falciparum + P. vivax co-infection might exert some selection pressure of SP over the P. vivax population; secondly, there could be a situation where a clinician recommended an anti-malarial drug depending upon the clinical grounds but with a lack of immediate diagnosis, as well as erroneous diagnosis of the parasite species; thirdly, presumptive treatment of malaria without proper diagnosis and use of SP combination by private practitioners could not be ruled out [21, 34]. Emergence and subsequent spread of multidrug-resistant parasites is a problem for malaria control and elimination programme. It is essential to identify and assess drug resistance markers in a regular, synchronous manner to recognize drug-resistant areas on the basis of candidate gene polymorphism analysis, which ultimately helps to manage suitable anti-malarial drug policy.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that P. vivax parasites in rural Purulia may still be susceptible to SP, but additional caution should be taken for treatment of vivax malaria in KMC to limit blooming of quadruple and quintuple mutant allele in the remainder of West Bengal, India. Synchronized research, surveillance and containment strategies are essential to optimize the current use of anti-malarial drugs to limit resistance and to understand the proper genetic lineage of resistant parasites.
Abbreviations
- API:
-
annual parasite index
- CQ:
-
chloroquine
- DHFR:
-
dihydrofolate reductase
- DHPS:
-
dihydropteroate synthase
- DNA:
-
deoxyribonucleic acid
- dNTPs:
-
deoxynucleotides
- DNase:
-
deoxyribonuclase
- EDTA:
-
ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid
- IC:
-
inhibitory concentration
- KCl:
-
potassium chloride
- KMC:
-
Kolkata Municipal Corporation
- mg:
-
milligram
- MgCl2 :
-
Magnesium Chloride
- ml:
-
millilitre
- mM:
-
millimolar
- NVBDCP:
-
National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme
- ng:
-
nanogram
- OD:
-
optical density
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- Pf:
-
Plasmodium falciparum
- Pv:
-
Plasmodium vivax
- RBC:
-
red blood cells
- RDT:
-
rapid diagnostic test
- rpm:
-
rounds per minute
- RPMI 1640:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium 1640
- SEM:
-
standard error of mean
- SNPs:
-
single nuclear polymorphisms
- SP:
-
sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine
- TBE:
-
tris-borate EDTA
- TE:
-
tris-EDTA
- TRR:
-
terminator ready reaction
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- μg:
-
microgram
- μl:
-
microliter
- μM:
-
micromolar
References
Annual epidemiological report of malaria, NVBDCP_2014-2015. http://www.nvbdcp.gov.in/Doc/Annual-report-NVBDCP-2014-15.pdf.
Kochar DK, Das A, Kochar SK, Saxena V, Sirohi P, Garg S, et al. Severe Plasmodium vivax malaria: a report on serial cases from Bikaner in northwestern India. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;80:194–8.
Kochar DK, Saxena V, Singh N, Kochar SK, Kumar SV, Das A. Plasmodium vivax malaria. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:132–4.
Genton B, D’Acremont V, Rare L, Baea K, Reeder JC, Alpers MP, et al. Plasmodium vivax and mixed infections are associated with severe malaria in children: a prospective cohort study from Papua New Guinea. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e127.
Tjitra E, Anstey NM, Sugiarto P, Warikar N, Kenangalem E, Karyana M, et al. Multidrug-resistant Plasmodium vivax associated with severe and fatal malaria: a prospective study in Papua, Indonesia. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e128.
Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of malaria in India, 2009. Government of India. http://www.nvbdcp.gov.in/Doc/Guidelines_for_Diagnosis_Treatment.pdf.
Ganguly S, Saha P, Chatterjee M, Maji AK. Prevalence of polymorphisms in antifolate drug resistance molecular marker genes pvdhfr and pvdhps in clinical isolates of Plasmodium vivax from Kolkata, India. Antimicrob Agent Chemother. 2014;58:196–200.
Foote SJ, Cowman AF. The mode of action and the mechanism of resistance to antimalarial drugs. Acta Trop. 1994;56:157–71.
Triglia T, Menting JG, Wilson C, et al. Mutations in dihydropteroate synthase are responsible for sulfone and sulfonamide resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:13944–9.
Das S, Chakraborty SP, Tripathy S, Hati AK, Roy S. The novel quadruple mutations in dihydropteroate synthase genes of Plasmodium falciparum in West Bengal, India. Trop Med Int Health. 2012;17:1329–34.
Das S, Chakraborty SP, Hati AK, Roy S. Malaria treatment fails with novel mutation in Plasmodium falciparum di-hydrofolate reductase (pfdhfr) gene in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;41:447–51.
Das S, Chakraborty SP, Tripathy S, Hati AK, Roy S. Association between prevalence of pyrimethamine resistance and double mutation in pfdhfr gene in West Bengal, India. Asian Pac J Trop Dis. 2012;2:31–5.
Peterson DS, Walliker D, Wellems TE. Evidence that a point mutation in dihydrofolate reductase–thymidylate synthase confers resistance to pyrimethamine in falciparum malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;85:9114–8.
Brega S, de Monbrison F, Severini C, Udomsangpetch R, Sutanto I, Ruckert P, et al. Real-time PCR for dihydrofolate reductase gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Plasmodium vivax isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:2581–7.
De Pecoulas PE, Tahar R, Ouatas T, Mazabraud A, Basco LK. Sequence variations in the Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase thymidylate synthase gene and their relationship with pyrimethamine resistance. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998;92:265–73.
Hastings MD, Porter KM, Maguire JD, Susanti I, Kania W, Bangs MJ, et al. Dihydrofolate reductase mutations in Plasmodium vivax from Indonesia and therapeutic response to sulfadoxine plus pyrimethamine. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:744–50.
Imwong M, Pukrittayakamee S, Renia L, Letourneur F, Charlieu JP, Leartsakulpanich U, et al. Novel point mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase gene of Plasmodium vivax: evidence for sequential selection by drug pressure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:1514–21.
Imwong M, Pukrittayakamee S, Cheng Q, Moore C, Looareesuwan S, Snounou G, et al. Limited polymorphism in the dihydropteroate synthetase gene (dhps) of Plasmodium vivax isolates from Thailand. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:4393–5.
Triglia T, Wang P, Sims PF, Hyde JE, Cowman AF. Allelic exchange at the endogenous genomic locus in Plasmodium falciparum proves the role of dihydropteroate synthase in sulfadoxine-resistant malaria. EMBO J. 1998;17:3807–15.
Prajapati SK, Joshi H, Dev V, Dua VK. Molecular epidemiology of Plasmodium vivax anti-folate resistance in India. Malar J. 2011;10:102.
Alam MT, Dev V, Bora H, Kumar A, Bharti PK, Singh N, et al. Similar trends of pyrimethamine resistance-associated mutations in Plasmodium vivax and P. falciparum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:857–63.
Annual district wise epidemiological report of malaria of West Bengal; 2010. http://www.wbhealth.gov.in/Health_Stat/2010_2011/8/VIII.1.3.pdf.
Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Zhu XP, Jarra W, Pinheiro L, et al. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993;61:315–20.
Johnston SP, Pieniazek NJ, Xayavong MV, Slemenda SB, Wilkins PP, et al. PCR as a confirmatory technique for laboratory diagnosis of malaria. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:1087–9.
WHO. Assessment and monitoring of antimalarial drug efficacy for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003. http://www.cdc.gov/malaria/resources/pdf/drug_resistance/who2003_monitoring.pdf.
Pal A, De S, Sengupta P, Maity P, Dhara PC. Relationship of body compositional and nutritional parameters with blood pressure in adults. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2013;27:489–500.
Das S, Chakraborty SP, Hati AK, Roy S. Association between prevalence of chloroquine resistance and unusual mutation in pfmdr-1 and pfcrt genes in India. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;2012(88):828–34.
Das S, KarMahapatra S, Tripathy S, Chattopadhayaya S, Dash SK, Mandal D, et al. Double mutation in the pfmdr1 gene is associated with emergence of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Eastern India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:5909–15.
Raza A, Ghanchi NK, Khan MS, Beg MA. Prevalence of drug resistance associatedmutations in Plasmodium vivax against sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine in southern Pakistan. Malar J. 2013;12:261.
Zakeri S, Afsharpad M, Ghasemi F, Raeisi A, Kakar Q, Atta H, et al. Plasmodium vivax: prevalence of mutations associated with sulfadoxine pyrimethamine resistance in Plasmodium vivax clinical isolates from Pakistan. Exp Parasitol. 2011;127:167–72.
Zakeri S, Afsharpad M, Ghasemi F, Raeisi A, Safi N, Butt W, et al. Molecular surveillance of Plasmodium vivax dhfr and dhps mutations in isolates from Afghanistan. Malar J. 2010;9:75.
Lu F, Wang B, Cao J, Sattabongkot J, Zhou H, Zhu G, et al. Prevalence of drug resistance-associated gene mutations in Plasmodium vivax in Central China. Korean J Parasitol. 2012;50:379–84.
Ranjitkar S, Schousboe ML, Thomsen TT, Adhikari M, Kapel CM, Bygbjerg IC, et al. Prevalence of molecular markers of antimalarial drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum in two districts of Nepal. Malar J. 2011;10:75.
Rungsihirunrat K, Sibley CH, Mungthin M, Na-Bangchang K. Geographical distribution of amino acid mutations in Plasmodium vivax DHFR and DHPS from malaria endemic areas of Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;78:462–7.
Imwong M, Pukrittakayamee S, Looareesuwan S, Pasvol G, Poirriez J, White NJ, et al. Association of genetic mutations in Plasmodium vivax dhfr with resistance to sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine: geographical and clinical correlates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45:3122–7.
Hastings MD, Porter KM, Maguire JD, Susanti I, Kania W, Bangs MJ, et al. Dihydrofolate reductase mutations in Plasmodium vivax from Indonesia and therapeutic response to sulfadoxine plus pyrimethamine. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:744–50.
Ahmed A, Bararia D, Vinayak S, Yameen M, Biswas S, Dev V, et al. Plasmodium falciparum isolates in India exhibit a progressive increase in mutations associated with sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:879–89.
Na BK, Lee HW, Moon SU, In TS, Lin K, Maung M, et al. Genetic variations of the dihydrofolate reductase gene of Plasmodium vivax in Mandalay Division, Myanmar. Parasitol Res. 2005;96:321–5.
Garg S, Saxena V, Lumb V, Pakalapati D, Boopathi PA, Subudhi AK, et al. Novel mutations in the antifolate drug resistance marker genes among Plasmodium vivax isolates exhibiting severe manifestations. Exp Parasitol. 2012;132:410–6.
Wootton JC, Feng X, Ferdig M, et al. Genetic diversity and chloroquine selective sweeps in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 2002;418:320–3.
Roper C, Pearce R, Nair S, Sharp B, Nosten F, Anderson T. Intercontinental spread of pyrimethamine-resistant malaria. Science. 2004;305:1124.
Authors’ contributions
SR, AKH and SD conceptualized the study and designed the experiments; SD and AB isolated the parasite DNA and assessed the molecular characterization of different candidate gene; SD, AB and SR analysed the data and interpreted the results. AKH, SD and SR wrote the manuscript and AKH critically amended it. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors express gratefulness to Vidyasagar University, Midnapore for providing the facilities to execute these studies. We are very much thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India for fellowship to SD. We are thankful to Gautam Laboratories, Kolkata, India (NABL accredited laboratory, ISO 15,189:2007-M-0423) for collecting the blood samples. We are thankful to Purulia District Hospital for their help in completing the work.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All essential data are put in the manuscript which is all available. The informed consent and ethical approval guaranteed limited access to data. However, the detailed dataset is available on request to the corresponding author, SR, at roysomenath1954@yahoo.in.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Experimental design and protocol of this study was duly approved by the Vidyasagar University Human Ethical Committee. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants and consent of guardians was taken for children, with the help of standardized participant information form.
Funding
This work was not supported by any external funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Banik, A., Hati, A.K. et al. Low prevalence of dihydro folate reductase (dhfr) and dihydropteroate synthase (dhps) quadruple and quintuple mutant alleles associated with SP resistance in Plasmodium vivax isolates of West Bengal, India. Malar J 15, 395 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-016-1445-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-016-1445-9