Abstract
Background
SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (STIL) is associated with the progression of several tumors; however, the biological role of STIL in osteosarcoma remains poorly understood.
Methods
In this study, the clinical significance of STIL in osteosarcoma was analyzed by gene chip data recorded in public databases. STIL expression was silenced in osteosarcoma cell lines to observe the effects on proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and migration. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the osteosarcoma chip were analyzed using The Limma package, and STIL co-expressed genes were obtained via the Pearson correlation coefficient. The potential molecular mechanism of STIL in osteosarcoma was further explored by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways.
Results
Osteosarcoma was associated with higher STIL expression compared to the control samples, and the standardized mean difference (SMD) was 1.52. STIL also had a good ability to distinguish osteosarcoma from non-osteosarcoma samples [area under the curve (AUC) = 0.96]. After silencing STIL, osteosarcoma cell proliferation decreased, apoptosis increased, and the migratory and invasion ability decreased. A total of 294 STIL differentially co-expressed genes were screened, and a bioinformatics analysis found that differentially co-expressed genes were primarily enriched in the cell signaling pathways. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network indicated that the hub differentially co-expressed genes of STIL were CDK1, CCNB2, CDC20, CCNA2, BUB1, and AURKB.
Conclusions
STIL is associated with osteosarcoma proliferation and invasion, and may be promote the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating the expression of CDK1, CCNB2, CDC20, CCNA2, BUB1 and AURKB.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Among children and adolescents, osteosarcoma represents one of the most common type of malignant bone tumor, with an incidence of approximately 3 in 1 million people each year [1]. Osteosarcoma originates from the mesenchymal tissue, which is mainly located in the metaphysis of the long bones and is the most common around the knee joint [2]. Since osteosarcoma has the characteristics of rapid cell proliferation, strong invasive ability, and early metastasis [3, 4], the patient 5-year survival rate with non-metastatic and metastatic osteosarcoma is still only 60 % and 30 %, respectively [5,6,7], despite advances in treatment techniques (e.g., surgery and chemotherapy). Therefore, there is an urgent need to gain in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms that result in the development of osteosarcoma and identify novel molecular therapeutic targets.
STIL is an important factor in cellular mitosis and centriole replication. In the cell cycle, STIL expression increases gradually during the early stages, peak in the middle stage, and rapidly decreases in the later stage [8]. Throughout this process, STIL interacts with a variety of proteins to ensure mitotic stability [9,10,11]. Thus, changes in STIL expression are associated with chromosome instability and even cancer. Some studies have demonstrated that STIL is overexpressed in a variety of cancers. Erez et al. reported that the high STIL expression in lung cancer tissue is both a marker of cell proliferation, as well as a marker of the metastatic potential of lung cancer [12]. Moreover, the study by Ouyang et al. found that high STIL expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma may down-regulate the expression of ITGA2, Smad2, and JAK1, as well as promote the proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells [13]. Despite these findings, the clinical significance and biological function of STIL in osteosarcoma remains unknown. Of particular interest is whether STIL is also highly expressed in osteosarcoma, and whether it promotes the progression of osteosarcoma as observed in other cancers. Therefore, this study sought to elucidate the biological function of STIL in osteosarcoma and the underlying molecular mechanism.
In this study, we first analyzed the clinical characteristics of STIL in osteosarcoma by integrating the gene chip data in public databases. Second, the biological functions of STIL in osteosarcoma were investigated using proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion experiments. Finally, we obtained the differentially co-expressed genes related to STIL, and the potential molecular mechanism was analyzed using bioinformatics methods. The flow chart of this study is shown in Fig. 1.
Materials and methods
Source of public databases
The gene microarray data were acquired from the ArrayExpress and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases, respectively. The following keywords were used to search the databases: “osteosarcoma” OR “osteosarcomas” AND “Homo sapiens”. The inclusion criteria of the data were as follows: (1) the experimental group and control group consisted of the osteosarcoma group and non-osteosarcoma group; (2) the patient did not receive radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or additional adjuvant therapy prior to the patient’s tissue was extracted; and (3) the number of samples in the control group and experimental group is ≥ 3. In addition, GSE21257 contains clinical data that can be used to analyze the clinical significance of STIL in osteosarcoma.
Cell culture
Human osteosarcoma cells, U-2 OS, MG-63, and Saos2, as well as human osteoblast hFOB1.19 cells were obtained from the Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). Human osteosarcoma HOS cells were acquired from the Cell Bank of Wuhan University (Wuhan, China). MG-63 cells were cultured in Minimum Essential Medium (MEM, Gibco, USA), U-2 OS in McCoy’s 5A medium (Boster, Wuhan, China). Saos2 and HOS cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Gibco, USA) containing 1 % penicillin and streptomycin (Gibco, USA), 10 % fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, USA) at 37℃. in a 5 % CO2 humidified incubator HFOB1.19 cells were maintained in MEM containing 10 % FBS, 1 % penicillin/streptomycin, and 0.3 mg/mL G418 (Gibco, USA) at 33.5 °C.
Cell transfection
To down-regulate the expression of STIL in the two osteosarcoma cell lines (U-2 OS and HOS) exhibiting the highest STIL expression, three siRNA (A: GCAGGATGGTACCTTTCCA; B: CGAAGAGTATCCTATAAGA; C: GGAATACCAAATCAGTTAA) were synthesized from Guangzhou RiboBio Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). According to the manual, Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent and Opti-MEM serum-lowering medium (Gibco, USA) was used to transfect the osteosarcoma cells.
Quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
According to the manufacturer’s instructions, TRIzol (TAKARA, Japan) reagent was used to extract the total RNA. cDNA was synthesized using PrimeScript RT Master Mix (TAKARA, Japan). The cDNA combined with Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Thermo Fisher, USA) were used for real-time PCR. The housekeeper gene, GAPDH, was used as a control. After normalizing GAPDH expression, the normal level of STIL expression in five cell lines was expressed as the relative expression and calculated in accordance with the 2-ΔΔCt method. The primer sequences in this study were as follows: GAPDH: 5′-TGACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG-3′ (F) and 5-AGGCAGGGATGATGTTCTGGAGAG-3′ (R). The following primers were used for STIL: 5′-CCCAACGCCAACTGGAGATTT-3′ (F) and 5-AGTCGGATGGTCTTCTCAGTC-3′ (R). Each experiment was repeated three times.
Western blot (WB) analysis
The cell lysates were prepared using RIPA cleavage buffer and phenylmethanesulfonylfluoride fluoride (Beyotime Biotechnology, China), to extract the proteins from the cells after full cleavage. The protein was fractionated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, electroblotted on 0.45 μm polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore, USA), blocked with 5 % skimmed milk powder at 37 °C for 1 h, washed three times with 1 × PBS-T (1000 mL 1×PBS + 0.5 mL Tween-20), and incubated with the primary antibody (diluted 1:1000) overnight at 4 °C. After three washes, a secondary antibody (diluted 1:10,000) was added to the membrane and incubated for 2 h, and the membrane was washed five times. Finally, an ECL kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, China) was used for detection. Anti-STIL and anti-GAPDH antibodies were purchased from Proteintech. A goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) -HRP secondary antibody was purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch. Each experiment was repeated three times.
Proliferation assay
A Cell Counting Assay Kit-8 (CCK-8, Dojindo Laboratories, Japan) was used to analyze the transfected U-2 OS and HOS cells. Each type of cell was transferred into 96-well plates at 5000 cells/well, and CCK8 was added to each well of the plate and incubated for 24 h, 48 h, or 72 h, respectively. The optical density was measured using an enzyme labeling instrument at a wavelength of 450 nm. Each experiment was repeated three times.
Cell apoptosis assay
Apoptotic cells were stained using a commercial FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I (Becton, Dickinson and Company, USA). The collected cells were washed with PBS, and resuspended in 100 μl Binding Buffer. The control group was resuspended in 400 μl Binding Buffer. Of the solution, 100 μl was mixed with 5 μl FITC-Annexin V and 5 μl PI, incubated for 15 min in the dark at 25 °C, and detected with a flow cytometer (Becton, Dickinson and Company, USA). Each experiment was repeated three times.
Transwell migration and invasion assays
The invasion and migratory ability of the cells was evaluated using the Transwell method. To determine the migratory ability, the transfected osteosarcoma cells were suspended in serum-free medium (cell density: 2 × 105/mL) and added to a Transwell chamber (8.0 μm; Becton, Dickinson and Company, USA). Next, 500 μl of complete medium was added to the lower chamber, and the plate was incubated for 48 h, fixed in paraformaldehyde, and washed with a crystal violet staining solution at room temperature for 20 min. The unbound crystal violet was washed away and the number of cells that had migrated were counted. The invasion ability involved the Transwell chamber to be covered with Matrigel (Becton, Dickinson and Company, USA) followed by steps similar to that used to assess the cell migration ability. Each experiment was repeated three times.
Acquisition of STIL differentially co‐expressed genes in osteosarcoma
The DEGs in each gene chip was calculated using the Limma software package, with LogFC ≥ 1 and p < 0.05 as the standards. Genes that appeared in at least two studies were selected as DEGs. In addition, the correlation between STIL and other genes in each gene chip was assessed. STIL co-expressed genes were selected using the Pearson’s correlation coefficient r ≥ 0.5 and p < 0.05 as the screening criteria, as well as genes that appeared in at least two studies. The genes obtained from the intersection of DEGs and co-expressed genes were considered to be STIL differentially co-expressed genes in osteosarcoma.
Enrichment analysis of STIL differentially co‐expressed genes and PPI analysis
The network tool, David (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/), was used to perform an enrichment analysis of the GO and KEGG pathways for the obtained differentially co-expressed genes. In addition, the differentially co-expressed genes were used to construct a PPI network through the STRING (https://string-db.org/) database, and Cytoscape 3.8.0 was used to visualize the PPI network with a score of 0.9 or higher.
Statistical analysis
SPSS23.0 statistical software was used to perform an independent sample t-test, and the results were displayed as the mean ± standard deviation. SMD and summarized receiver operating characteristic (SROC) were calculated using STIL expression by STATA15.0. The Q test of the χ2 test and I2 were used to detect heterogeneity. When p > 0.05 and I2 < 50 %, there was considered to be no heterogeneity, and the use of a fixed effects model was employed. Alternatively, a continuous variable meta-analysis was performed in conjunction with a random effects model. The overall results were subjected to a sensitivity analysis to determine the effects of each gene chip. Publication bias was evaluated using Begg’s and Egger’s tests. In addition, the Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis, and the difference in the survival rate was calculated with a log-rank test. Statistical significance was considered at p < 0.05.
Results
STIL expression in osteosarcoma
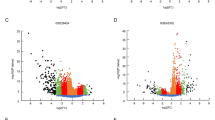
Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, we screened 13 osteosarcoma chips (Table 1). The STIL expression data were extracted from the 13 gene chips. As shown in Fig. 2, STIL was highly expressed in osteosarcoma tissues compared to normal tissues in the E-MEXP-3628, GSE14359, GSE126209, GSE33383, GSE36001, GSE39262, GSE42352, and GSE68591 chips. No highlighted difference was found between osteosarcoma tissues and normal tissues in the GSE11414, GSE12865, GSE87624, GSE99671, and GSE19276 chips.
STIL scatter plot based on osteosarcoma chips in the GEO and ArrayExpress databases. a E-MEXP-3628, b GSE11414, c GSE12865, d GSE14359, e GSE126209, f GSE33383, g GSE36001, h GSE39262, i GSE42352, j GSE68591, k GSE87625, l GSE99671, and m GSE19276. STIL, SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus. GEO Gene Expression Omnibus
In addition, in the meta-analysis of 13 chips, p < 0.05, and an I2 value of 66.9 % were considered to be heterogeneous. Therefore, the random effects model was used to conduct a variable continuous meta-analysis. STIL expression in 376 osteosarcoma samples was higher than that in 92 normal samples, and the total SMD integrated by the random effects model was 1.52 (95 % confidence interval [CI] 0.98–2.05) (Fig. 3a). The sensitivity analysis suggested that the exclusion of any chip data had little effect on the total effect (Fig. 3b). The results of the Begg’s test showed that p = 0.180 had no publication bias, while the Egger’s test showed an absence of publication bias (Fig. 3c).
The clinical diagnostic ability of STIL
To explore the diagnostic ability of STIL for osteosarcoma, we used the SROC curve and related analysis. The results of the SROC curve showed that the AUC was 0.96 (95 % CI 0.94–0.98), and STIL can distinguish osteosarcoma from non-osteosarcoma (Fig. 4a). The combined sensitivity and specificity were 0.89 (95 % CI 0.75–0.95) and 0.98 (95 % CI 0.68–1.00), respectively (Fig. 4b). The combined positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio were 37.44 (95 % CI 2.22–630.61) and 0.11 (95 % CI 0.05–0.26) (Fig. 4c). The diagnostic score and diagnostic odds ratio were 5.79 (95 % CI 3.18–8.39) and 325.99 (95 % CI 24.14–4401.95), respectively (Fig. 4d). The above results indicate that STIL has good clinical diagnostic ability.
The ability of STIL to differentiate between osteosarcoma tissue and normal tissue. a SROC curve of STIL and b combined sensitivity and specificity of STIL. c The combined positive and negative likelihood ratio of STIL. d The combined diagnostic score and diagnostic odds ratio of STIL. SROC summarized receiver operating characteristic
Effect of STIL on osteosarcoma cell proliferation and apoptosis
To study the expression of STIL in osteosarcoma cells, we detected the level of STIL mRNA by qRT-PCR. Of the osteoblast cell lines and four osteosarcoma cell lines, it was found that the up-regulation of STIL mRNA was the most significant in the U-2 OS and HOS cell lines (Fig. 5a). In addition, to study the effect of STIL on osteosarcoma cells, we inhibited STIL expression in the two cell lines with the highest expression levels (U-2 OS and HOS). The WB results showed that the knockdown effect at the siRNA-2 site was the most significant (Fig. 5b). A CCK8 assay was used to observe the effect of STIL on osteosarcoma cell proliferation, and the results revealed that a knockdown of STIL could significantly inhibit the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells (Fig. 5c). In addition, the apoptosis experiments revealed that compared with the control group, there was an increase in the level of apoptotic osteosarcoma cells after knocking down STIL, which was statistically significant in U-2 OS cells, but not in HOS cells (Fig. 5d). These results indicate that silencing STIL inhibits proliferation and increases apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells.
Effect of silencing STIL on the proliferation and apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. a qRT-PCR detection of STIL expression in osteoblast and osteosarcoma cell lines. b WB detects the silencing efficiency of STIL. c CCK8 analysis showing that silencing STIL inhibited the proliferation of U-2 OS and HOS cell lines. d Apoptosis tests showed that silencing STIL promoted the apoptosis of the U-2 OS cell line. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. hFOB1.19 or si-NC
Effect of STIL on osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion
Next, we conducted a Transwell assay to study the effect of STIL on the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. The Transwell assay results revealed that osteosarcoma cell migration was significantly inhibited after STIL was silenced (Fig. 6a). In addition, the invasive ability was tested and there was a significantly weakened invasive ability of STIL compared to that of the control group after STIL was silenced in the two cell lines (Fig. 6b). These results indicate that silencing STIL inhibits the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells.
The effect of silencing STIL on the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. a Transwell migration experiment showing that silencing STIL inhibits the migratory ability of osteosarcoma cell lines. b Transwell invasion experiment demonstrating the ability of silencing STIL to inhibit the invasion of osteosarcoma cell lines. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01
Expression and clinical characteristics of STIL
To study the prognostic value of STIL in osteosarcoma, the data of 53 osteosarcoma cases were extracted from the GSE21257 tissue microarray and their clinical features were analyzed (Table 2). A significant difference was observed in the level of STIL expression between the group aged < 16 years old and that aged ≥ 16 years old (p < 0.010). A significant difference was also observed between the metastasis and non-metastasis groups (p < 0.007), whereas there was no statistical significance based on gender. At the same time, the survival analysis in Fig. 7a shows that the prognosis of high STIL expression was lower than that of low STIL expression, and the 5-year survival rates were 0.44 and 0.727, respectively (p < 0.05). The above results indicate that STIL may have prognostic value.
GO and KEGG analysis of STIL differentially co‐expressed genes
A total of 2425 DEGs and 1663 STIL co-expressed genes were screened from the public database, and there were 294 differentially co-expressed genes identified in the overlapping regions (Fig. 7b). The GO enrichment analysis of STIL differentially co-expressed genes (Fig. 8a–c) revealed that the biological process (BP) was primarily enriched in the areas of cellular and mitotic nuclear division, as well as sister chromatid cohesion. The nucleoplasm, kinetochore, and spindle exhibited the primary enrichment of cellular component (CC). Protein binding, ATP binding, and single-stranded DNA-dependent ATPase activity were mainly enriched in molecular function (MF). The KEGG analysis indicated that the primary enrichment of the STIL differentially co-expressed genes was in the areas of cell cycle, mismatch repair, and oocyte meiosis (Fig. 8d). Tables 3 and 4 list the top 10 most significant pathways in the GO and KEGG analyses.
GO and KEGG analysis of 294 STIL differentially co-expressed genes. a Bubble chart of the first 10 Biological processes. b Bubble chart of the first 10 cellular components. c Bubble chart of the first 10 molecular functions. d The first 10 KEGG pathways. GO Gene Ontology, KEGG Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
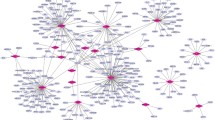
PPI network analysis
To identify the differentially co-expressed genes closely related to STIL, the STIL differentially co-expressed genes were analyzed by PPI network. The first six genes (CDK1, CCNB2, CDC20, CCNA2, BUB1, and AURKB) were selected as hub differentially co-expressed genes by degree analysis in Cytoscape (Fig. 9). Therefore, these six hub differentially co-expressed genes were considered to be the key genes that interact with STIL.
Validation of hub differentially co‐expressed genes based on 13 gene chips
Using the 13 gene chips, we found that six hub differentially co-expressed genes (CDK1, CCNB2, CDC20, CCNA2, BUB1, and AURKB) were highly expressed in osteosarcoma (Fig. 10). In addition, according to the SROS curve results, these genes also exhibit the ability to distinguish osteosarcoma from non-osteosarcoma samples (Fig. 11).
Discussion
In this study, 13 gene chips were collected and it was found that STIL expression was significantly increased in osteosarcoma. Highly expressed STIL was associated with the ability to distinguish osteosarcoma from non-osteosarcoma samples, and the patients with high STIL expression are associated with a poor prognosis. Additionally, the in vitro experiments revealed that the silencing of STIL could significantly block proliferation, induce apoptosis, and reduce migration and invasion in osteosarcoma cells. Previous research has identified a wide range of molecular markers that can be used for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases [14,15,16]. Moreover, several molecular markers for osteosarcoma have also been discovered, including MYC, Cyclin E1, and MiR-455-3p, which are all considered to be promising therapeutic targets [17,18,19]. In this study, STIL was found to play a role of a proto-oncogene in osteosarcoma and was significantly involved in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma. Compared with previous studies, our findings provide new insight into molecular markers and therapeutic targets for osteosarcoma.
STIL was first isolated from T cell chromosomes from T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia [20]. Early studies that commonly used mice and zebrafish as animal models found that a deletion of the STIL locus was embryonically lethal [21,22,23]. Moreover, STIL mutations in humans can lead to primary hereditary microcephaly and even cancer [24,25,26]. This is the first study to report the overexpression of STIL in osteosarcoma, and demonstrate that silencing STIL inhibits cell proliferation, promotes cell apoptosis, and suppresses invasion and migration capabilities. Kasai et al. found that STIL was able to regulate the Hh signaling pathway through interacting with Sufu and Gli1 to affect cell proliferation [11]. Wu et al. found STIL to be highly expressed in prostate cancer and could regulate the growth of prostate cancer cells through the MAPK/ERK, PI3K/Akt, and AMPK signaling pathways [27]. Furthermore, Rabinowicz et al. reported that the targeted inhibition of highly expressed STIL could significantly improve the efficacy of DNA-damaging drugs for the treatment of ovarian cancer, and suggested that STIL might be a novel therapeutic target [28]. In recent studies, Wang et al. attenuated the IGF-1/PI3K/AKT pathway by knocking out STIL in gastric cancer, which inhibited cellular proliferation and reduced clone formation ability [29]. These results are consistent with our results and provide evidence for the role of STIL as a proto-oncogene.
To further clarify the potential molecular mechanism of STIL in osteosarcoma, we performed a GO and KEGG enrichment analysis on the STIL differentially co-expressed genes, and they were found to be significantly enriched in the cell cycle pathway. The PPI network results also showed that STIL and the hub co-expressed genes were proteins involved in the cell cycle. The above results indicate that STIL and the differentially co-expressed genes may affect the mitosis and cell proliferation of osteosarcoma cells through cell cycle signaling pathways. The cell cycle is known to have an important function in cellular growth and proliferation. Prior studies have reported that miR-671-5p and miR-299-5p target cell cycle regulation and mediate osteosarcoma proliferation [30, 31]. Zhang et al. found that Ludartin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at the G2/M checkpoint through the elevated expression of p21WAF1 in osteosarcoma cells [32]. Cell cycle pathways have also been established to play an important role in other tumors [33,34,35]. As an important factor in the process of mitosis, STIL may participate in the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating the cell cycle.
In the PPI network, we selected six genes (CDK1, CCNB2, CDC20, CCNA2, BUB1, and AURKB) as the core STIL differentially co-expressed genes in osteosarcoma. CDK1 is a gene related to the cell cycle, and its abnormal expression leads to the development of tumors [36]. In the study conducted by Huang et al., microRNA-199a-3p, as a tumor suppressor gene was found to exhibit low expression in osteosarcoma and may interact with highly expressed CDK1 in the development of osteosarcoma [37]. CCNA2 and CCNB2 are members of cyclin family, which are critical for both cellular proliferation and apoptosis. Shekhar et al. found that CCNA2 is the common target of miR-449a and miR-424 in osteosarcoma, which inhibits tumor progression by inhibiting CCNA2 expression [38]. In another study, silencing CDC6 reduced CCNA2 expression and suppressed osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion [39]. CDC20 is a gene that regulates the cell cycle, and is reported to be involved in osteosarcoma development by analyzing the gene chip data [40]. Moreover, apcin blocks osteosarcoma cell growth and invasion by reducing the level of CDC20 expression, indicating that CDC20 may represent a potential therapeutic target [41, 42]. In a recent study, CDC20 was found to exhibit high levels of expression in osteosarcoma cisplatin-resistant cell lines, which enhanced the sensitivity of drug-resistant cell lines to cisplatin by knocking out CDC20 [43]. Moreover, studies using bioinformatics analyses have found that RFC4 may interact with BUB1, which may function to promote osteosarcoma occurrence and development of [44]. AURKB is a serine/threonine kinase that has been proposed to stimulate the invasion and proliferation of osteosarcoma through PTK2/PI3K/AKt/NF-κB signaling pathway and VCP [45, 46]. Thus, AURKB inhibitors may also provide a new option for the treatment of osteosarcoma [47]. In our study, we found that these six genes are highly expressed in osteosarcoma. Therefore, these findings suggest that STIL may play a role in osteosarcoma progression through regulation of expression of these identified genes.
Our study is associated with certain limitations: (1) there is a large heterogeneity in our analysis (67 %). Although we attempted to identify the source of heterogeneity through a sensitivity analysis, the results showed that no particular research to be the source of the heterogeneity; and (2) although we have demonstrated that STIL functions as a proto-oncogene in osteosarcoma, its potential molecular mechanism requires further verification both in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusions
In general, we confirmed that STIL plays a role as a proto-oncogene, is highly expressed in osteosarcoma, and is involved in osteosarcoma proliferation and invasion. Moreover, the bioinformatics analysis showed that STIL may participate in the biological function of osteosarcoma by regulating CDK1, CCNB2, CDC20, CCNA2, BUB1, and AURKB. These findings provide a new perspective for the use of STIL as a potential biomarker and molecular therapeutic target for osteosarcoma.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- STIL:
-
SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- SMD:
-
Standardized mean difference
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- PPI:
-
Protein-protein interaction
- GEO:
-
Gene expression omnibus
- MEM:
-
Minimum essential medium
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
- WB:
-
Western blot
- CCK-8:
-
Cell Counting Assay Kit-8
- SROC:
-
Summarized receiver operating characteristic
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- BP:
-
Biological process
- CC:
-
Cellular component
- MF:
-
Molecular function
References
Picci P. Osteosarcoma (osteogenic sarcoma). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-2-6.
Bielack S, Carrle D, Casali PG. Osteosarcoma: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(Suppl):137–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp154.
Moore DD, Luu HH. Osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 2014;162:65–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07323-1_4.
Czarnecka AM, Synoradzki K, Firlej W, Bartnik E, Sobczuk P, Fiedorowicz M, Grieb P, Rutkowski P. Molecular biology of osteosarcoma. Cancers. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082130.
Chen Y, Cao J, Zhang N, Yang B, He Q, Shao X, Ying M. Advances in differentiation therapy for osteosarcoma. Drug Discov Today. 2020;25(3):497–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2019.08.010.
Picci P, Mercuri M, Ferrari S, Alberghini M, Briccoli A, Ferrari C, Pignotti E, Bacci G. Survival in high-grade osteosarcoma: improvement over 21 years at a single institution. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21(6):1366–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp502.
Kager L, Zoubek A, Pötschger U, Kastner U, Flege S, Kempf-Bielack B, Branscheid D, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Winkelmann W, et al. Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: presentation and outcome of patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(10):2011–8. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2003.08.132.
Izraeli S, Colaizzo-Anas T, Bertness VL, Mani K, Aplan PD, Kirsch IR. Expression of the SIL gene is correlated with growth induction and cellular proliferation. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8(11):1171–9.
Zitouni S, Francia ME, Leal F, Montenegro Gouveia S, Nabais C, Duarte P, Gilberto S, Brito D, Moyer T, Kandels-Lewis S, et al. CDK1 prevents unscheduled PLK4-STIL complex assembly in centriole biogenesis. Curr Biol. 2016;26(9):1127–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.03.055.
Arquint C, Nigg EA. STIL microcephaly mutations interfere with APC/C-mediated degradation and cause centriole amplification. Curr Biol. 2014;24(4):351–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.12.016.
Kasai K, Inaguma S, Yoneyama A, Yoshikawa K, Ikeda H. SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus derepresses GLI1 from the negative control of suppressor-of-fused in pancreatic cancer cell. Cancer Res. 2008;68(19):7723–9. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-07-6661.
Erez A, Perelman M, Hewitt SM, Cojacaru G, Goldberg I, Shahar I, Yaron P, Muler I, Campaner S, Amariglio N, et al. Sil overexpression in lung cancer characterizes tumors with increased mitotic activity. Oncogene. 2004;23(31):5371–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207685.
Ouyang Y, Jin YB, Chen XP, Zhang GY, Mao SL, Ling F, Luo W. STIL is upregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues and promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation, migration and invasion. Neoplasma. 2020;67(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2019_190306N192.
Abdelaal A, Attalla E, Elshemey W. Estimation of out-of-field dose variation using Markus ionization chamber detector. SciMed J. 2020;2:8–15. https://doi.org/10.28991/SciMedJ-2020-0201-2.
Amini Khorasgani M, Mohammady Nejad P, Moghani Bashi MM, Hedayati M. Evaluation of mir-377-3p expression in patients with multiple sclerosis. SciMed J. 2019;1(2):48–54. https://doi.org/10.28991/SciMedJ-2019-0102-2.
Nicoleau S, Wojciak-Stothard B. Beyond thrombosis: the role of platelets in pulmonary hypertension. SciMed J. 2020;2(4):243–71. https://doi.org/10.28991/SciMedJ-2020-0204-7.
Feng W, Dean DC, Hornicek FJ, Spentzos D, Hoffman RM, Shi H, Duan Z. Myc is a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020;12:1758835920922055. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835920922055.
Wei R, Thanindratarn P, Dean DC, Hornicek FJ, Guo W, Duan Z. Cyclin E1 is a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(9):1952–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.24659.
Yi X, Wang Y, Xu S. MiR-455-3p downregulation facilitates cell proliferation and invasion and predicts poor prognosis of osteosarcoma. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):454. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01967-1.
Aplan PD, Lombardi DP, Kirsch IR. Structural characterization of SIL, a gene frequently disrupted in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mole Cell Biol. 1991;11(11):5462–9. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.11.11.5462.
Fasching K, Panzer S, Haas OA, Marschalek R, Gadner H, Panzer-Grümayer ER. Presence of clone-specific antigen receptor gene rearrangements at birth indicates an in utero origin of diverse types of early childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2000;95(8):2722–4.
Pfaff KL, Straub CT, Chiang K, Bear DM, Zhou Y, Zon LI. The zebra fish cassiopeia mutant reveals that SIL is required for mitotic spindle organization. Mole Cell Biol. 2007;27(16):5887–97. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00175-07.
Jeevanandam J, Chan YSS, Danquah M. Zebrafish as a model organism to study nanomaterial toxicity. Emerg Sci J. 2019;3:195–208. https://doi.org/10.28991/esj-2019-01182.
Kaindl AM, Passemard S, Kumar P, Kraemer N, Issa L, Zwirner A, Gerard B, Verloes A, Mani S, Gressens P. Many roads lead to primary autosomal recessive microcephaly. Prog Neurobiol. 2010;90(3):363–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.11.002.
Arquint C, Nigg EA. The PLK4-STIL-SAS-6 module at the core of centriole duplication. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016;44(5):1253–63. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20160116.
Nigg EA. Centrosome aberrations: cause or consequence of cancer progression? Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(11):815–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc924.
Wu X, Xiao Y, Yan W, Ji Z, Zheng G. The human oncogene SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus (STIL) promotes tumor growth through MAPK/ERK, PI3K/Akt and AMPK pathways in prostate cancer. Gene. 2019;686:220–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.11.048.
Rabinowicz N, Mangala LS, Brown KR, Checa-Rodriguez C, Castiel A, Moskovich O, Zarfati G, Trakhtenbrot L, Levy-Barda A, Jiang D, et al. Targeting the centriolar replication factor STIL synergizes with DNA damaging agents for treatment of ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(16):27380–92. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16068.
Wang J, Zhang Y, Dou Z, Jiang H, Wang Y, Gao X, Xin X. Knockdown of STIL suppresses the progression of gastric cancer by down-regulating the IGF-1/PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(8):5566–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14440.
Xin C, Lu S, Li Y, Zhang Y, Tian J, Zhang S, Yang S, Gao T, Xu J. miR-671-5p inhibits tumor proliferation by blocking cell cycle in osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 2019;38(9):996–1004. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.4870.
Zhang CL, Li LB, She C, Xie Y, Ge DW, Dong QR. MiR-299-5p targets cell cycle to promote cell proliferation and progression of osteosarcoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(9):2606–13. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201805_14954.
Zhang SL, Li BL, Li W, Lu M, Ni LY, Ma HL, Meng QG. The effects of ludartin on cell proliferation, cell migration, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis are associated with upregulation of p21WAF1 in Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells in vitro. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:4926–33. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.909193.
Shen CQ, Yan TT, Liu W, Zhu XQ, Tian XL, Fu XL, Hua R, Zhang JF, Huo YM, Liu DJ, et al. High expression of FAM83B predicts poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and correlates with cell cycle and cell proliferation. J Cancer. 2017;8(16):3154–65. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.20086.
Li Y, Kong R, Chen H, Zhao Z, Li L, Li J, Hu J, Zhang G, Pan S, Wang Y, et al. Overexpression of KLF5 is associated with poor survival and G1/S progression in pancreatic cancer. Aging. 2019;11(14):5035–57. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102096.
Zhang L, Kang W, Lu X, Ma S, Dong L, Zou B. LncRNA CASC11 promoted gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro by regulating cell cycle pathway. Cell cycle. 2018;17(15):1886–900. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1502574.
Liu P, Kao TP, Huang H. CDK1 promotes cell proliferation and survival via phosphorylation and inhibition of FOXO1 transcription factor. Oncogene. 2008;27(34):4733–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.104.
Huang WT, Liu AG, Cai KT, He RQ, Li Z, Wei QJ, Chen MY, Huang JY, Yan WY, Zhou H, et al. Exploration and validation of downregulated microRNA-199a-3p, downstream messenger RNA targets and transcriptional regulation in osteosarcoma. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(12):7538–54.
Shekhar R, Priyanka P, Kumar P, Ghosh T, Khan MM, Nagarajan P, Saxena S. The microRNAs miR-449a and miR-424 suppress osteosarcoma by targeting cyclin A2 expression. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(12):4381–400. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.005778.
Jiang W, Yu Y, Liu J, Zhao Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Dang X. Downregulation of Cdc6 inhibits tumorigenesis of osteosarcoma in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;115:108949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108949.
Wu MS, Ma QY, Liu DD, Li XJ, Deng LJ, Li N, Shen J, Zhao Z, Chen JX. CDC20 and its downstream genes: potential prognosis factors of osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 2019;24(11):1479–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01500-3.
Gao Y, Zhang B, Wang Y, Shang G. Cdc20 inhibitor apcin inhibits the growth and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(2):841–8. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6467.
Shang G, Ma X, Lv G. Cell division cycle 20 promotes cell proliferation and invasion and inhibits apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2017.1387700.
Qiu E, Gao Y, Zhang B, Xia T, Zhang Z, Shang G. Upregulation of cell division cycle 20 in cisplatin resistance-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma cells. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(4):1309–18.
Peng C, Yang Q, Wei B, Yuan B, Liu Y, Li Y, Gu D, Yin G, Wang B, Xu D, et al. Investigation of crucial genes and microRNAs in conventional osteosarcoma using gene expression profiling analysis. Mole Med Rep. 2017;16(5):7617–24. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.75062017.7506.
He JY, Xi WH, Zhu LB, Long XH, Chen XY, Liu JM, Luo QF, Zhu XP, Liu ZL. Knockdown of aurora-B alters osteosarcoma cell malignant phenotype via decreasing phosphorylation of VCP and NF-κB signaling. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(5):3895–902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3032-4.
Zhu LB, Jiang J, Zhu XP, Wang TF, Chen XY, Luo QF, Shu Y, Liu ZL, Huang SH. Knockdown of aurora-B inhibits osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration via modulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(7):3984–91.
Zhao Z, Jin G, Yao K, Liu K, Liu F, Chen H, Wang K, Gorja DR, Reddy K, Bode AM, et al. Aurora B kinase as a novel molecular target for inhibition the growth of osteosarcoma. Mole Carcinog. 2019;58(6):1056–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22993.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant number 81760485].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HML designed and managed the entire study; JSF performed the Experiments; WSL, HPW and WH collected the data and performed data analysis; JSF and SY wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Sf., Wen, SL., Sun, Y. et al. The biological function and clinical significance of STIL in osteosarcoma. Cancer Cell Int 21, 218 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-01922-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-01922-y