Abstract
Background
Interleukin (IL)-23 is one of the newly identified inflammatory cytokines, and inflammation is also known to be related to the development of gastric cancer (GC). The role of IL-23 in gastric cancer, however, is largely unknown. In the present study, we investigated the expression and possible role of IL-23A in human GC.
Methods
The expression of IL-23A and IL-17A in human GC tissues was determined by immunohistochemistry, and the relationship between IL-23A expression and clinical characteristics of GC was investigated. The serum concentration of IL-23A and IL-17A was also tested by ELISA. The source and role of IL-23A in GC were studied in vitro by Flowcytometry, MTS (Owen’s reagent) assay and Western blot.
Results
IL-23A, IL-23 receptor (IL-23R) and IL-17A were all overexpressed in human GC tissues, and the level of IL-23A was well correlated with IL-17A in GC tissues as well as in patient’s serum. Macrophages and GC cells were the main source of IL-23A secretion upon stimulation of H. pylori lysate. Furthermore, we found that IL-23A promoted proliferation of GC cell lines via IL-17A/IL-17 receptor antagonist (IL-17RA) /nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling.
Conclusions
The high expression of IL-23A is associated with GC. IL-23A can promoted GC cells growth by inducing the secretion of IL-17A in tumor microenvironment. Our results suggest that the serum concentration of IL-23A is a good biomarker of poor clinical prognosis in GC patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
IL-23A is a subunit of the heterodimeric cytokine, IL-23 by pairing with the other subunit, p40 (IL-12). It is known that IL-23A is expressed and secreted by macrophages and dendritic cells. IL-23 can activate signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4) through IL-23R distributed on the membrane of several types of immune cells, including T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes and dendritic cells. And IL-23 participates immune responses in identifying foreign substances and defending the body against infection and disease [1],[2].
IL-23A is involved in the inflammatory response through promoting matrix metalloprotease 9, increasing angiogenesis and reducing CD8+ T cells infiltration [3],[4]. By working together with IL-6 and transforming growth factor-β1, IL-23 can promote the differentiation of CD4+ naive T cells to Th17 cells, which is one of the well accepted T helper cell subsets [5]-[7]. Th17 cells secrete proinflammatory cytokine IL-17A that can induce Th17 response by stimulating the production of other proinflammatory molecules such as IL-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and chemokines, resulting in inflammation. It has been reported that IL-17 was closely associated with GC [8],[9]. A genome-wide association study has revealed that −197G > A polymorphism at position −197 in the IL-17 promoter region significantly increased GC risk in the general population [10],[11], while increased expression of IL-17 was found in patients with GC. IL-17 is also involved in the progression of GC by promoting angiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment [12]. Moreover, persistent inflammation induced in part by IL-17 may contribute to gastric mucosal pathology, thereby increase the risk of GC [9],[11],[13].
Compared to that of IL-17A, the studies concerning the role of IL-23A in human GC are largely lacking. In the present study, we investigated the expression of IL-23A in GC, and its clinical significance and possible mechanism were involved.
Results
IL-23A, IL-23R and IL-17A are excessive in human GC
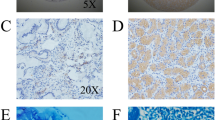
To investigate the expression of IL-23A and the related molecules in human GC, 141 paraffin-embedded tissues were studied for the expression and distribution of IL-23A, IL-23R and IL-17A using immunohistochemistry. First, we observed that IL-23A, IL-23R and IL-17A were all significantly overexpressed in human GC compared to normal controls. Although it was undetectable in the normal gastric glands and slightly positive in infiltrating inflammatory cells, IL-23A was detected at a high level in infiltrating inflammatory cells and cancer cells in cancer tissues (Figure 1A). IL-23R was exclusively expressed in infiltrating inflammatory cells in both cancer and normal tissues, but the expression level and ratio were much higher in cancer tissues (Figure 1B). IL-17A was located mainly in the infiltrated inflammatory cells in GC (Figure 1C). We next investigated the relationship between expression of IL-23A and different clinical characteristics, and found that the level of IL-23A was associated with H. pylori infection and tumor burden (Table 1).
Expression and distribution of IL-23A, IL-23R and IL-17A in human GC and normal gastric tissue. (A) Expression and distribution of IL-23A was analyzed by immunohistochemistry in both human GC and normal gastric tissue. Average integrated optical density was obtained by analyzing five fields of view for each slide evaluated by Image-Pro Plus version 5.0. (B) Expression, distribution and average integrated optical density of IL-23R. (C) Expression, distribution and average integrated optical density of IL-17A. **P < 0.01.
IL-23A is correlated with IL-17A secretion in human GC
Recent studies have shown that secretion of IL-23A was one of the main factors in normal Th17 cell differentiation. We questioned whether IL-23A was also associated with Th17 cell in GC. Indeed, elevated IL-23A expression coincided with increased expression of IL-17A (Figure 2A). To explore the further relationship between them, we quantitated the expression of both cytokines within IHC staining of GC patients and revealed that IL-23A expression was significantly correlated with IL-17A expression through a linear correlation test (r2 = 0.7148, P < 0.001) (Figure 2B).
Serum IL-23A concentration is an indicator of poor prognosis in GC patients
Both IL-23A and IL-17A may be secreted into the blood, therefore, we hypothesized that the level of IL-23A and IL-17A in the serum of GC patients or healthy controls may be determined by ELISA as biomarkers. We first detected the level of both cytokines as 213 ± 75 pg/ml for IL-23A and 286 ± 101 pg/ml for IL-17A in 50 healthy individuals (Figure 3A and B). The serum level of both cytokines were increased significantly in GC patients as 517 ± 247 pg/ml for IL-23A and 422 ± 284 pg/ml for IL-17A (Figure 3A and B). And the linear correlation of serum concentration between IL-23A and IL-17A was also seen in GC patients (r2 = 0.5841, P < 0.001) (Figure 3C). The threshold of healthy controls was obtained according to the 95% confidence interval (CI), which was 285 pg/ml for IL-23A. According to the threshold, the GC patients were divided into IL-23A high and IL-23A low subsets. To compare their clinical prognosis between the two subsets of GC patients, serum IL-23A expression was examined using the Kaplan–Meier method. We found that IL-23A level (>285 pg/ml) was significantly associated with shorter overall survival (OS) [P = 0.027, hazard ratio (HR) 2.246, 95% CI: 1.212–4.160] (Figure 3D).
Serum IL-23A concentration as an indicator of poor prognosis in GC patients. (A) Serum concentration of IL-23A in GC patients and healthy controls. (B) Serum concentration of IL-17A in GC patients and healthy controls. (C) The correlation between IL-23A and IL-17A in serum of GC patients was accessed by linear correlation test. (D) The Kaplan–Meier curves for OS of GC patients with different expression of IL-23A.
IL-23A can be secreted by macrophages and GC cells
Immunohistochemical staining showed that IL-23A was abundantly expressed in multiple cell types, including T cells, macrophages and GC cells (Figure 1A). To examine the exact origin of IL-23A, we accessed IL-23A expression in an vitro stimulation system using H. pylori lysate as the cytokine-inducing agent, which based on a previous observation that H. pylori was a robust inducer for the secretion of IL-23A. In T cells, IL-23A secretion was increased slightly upon stimulation with H. pylori lysate (Figure 4A). In macrophages, the number of IL-23A-positive cells increased from 1.15 ± 0.18% to 13.21 ± 6.21% (Figure 4B). While in GC cell lines, IL-23A-positive SGC-7901 cells increased from 2.64 ± 1.12% to 13.11 ± 3.12%, and IL-23A positive MKN45 cells increased from 1.16 ± 0.46% to 17.55 ± 5.42% (Figure 4C). Overall, macrophages and GC cells showed H. pylori lysate-induced stimulation of IL-23A secretion (Figure 4D).
IL-23A is secreted by macrophages and GC cells. (A) The expression of IL-23A and cell surface marker CD3 were detected by Flowcytometry in T cells with different treatment. (B) The expression of IL-23A and cell surface marker CD14 were detected by Flowcytometry in macrophages with different treatment. (C) The expression of IL-23A was detected by FCS in SGC-7901 and MKN45 cells treated with H. pylori lysate. (D) The ratio of IL-23A positive cells in T cells, macrophages and GC cell lines.
IL-23A promotes survival of GC cells through IL-17A/IL-17RA/nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling
To investigate the effect of IL-23A on tumor growth, a co-culture assay in vitro was utilized. First, we found that IL-23A had no significant effect on cell proliferation when the GC lines SGC-7901 and MKN45 were treated with human recombinant IL-23A directly. We next found that there was no significant effect on tumor cell SGC-7901 or MKN45 growth co-cultured with naive T lymphocytes in the presence of IL-23A. However, the significant cell-growth-promoting effect was seen when either macrophages or H. pylori lysate was added to the co-culture system. When both macrophages and H. pylori were added, the effect was synergistic (Figure 5A and B).
IL-23A promotes survival of GC cell lines through IL-17A/IL-17RA/NF-κB signaling. (A) The cell viability of SGC-7901 with the treatment was examined. (B) The cell viability of MKN45 with the treatment was examined. (C) The concentration of IL-17A in the cell culture medium of SGC-7901 and MKN45 were determined by ELISA. **P < 0.01. (D) The expression of IL-17RA and IL-23R in both MKN45 and SGC-7901. (E) The expression of p-IkBa, IkBa and CyclinD1 in both MKN45 and SGC-7901.
We investigated the possible mechanism underpinning the association between IL-17A and IL-23A. Concentration of IL-17A in the culture medium was determined, and there was no significant difference when GC cells were treated with IL-23A alone or IL-23A plus T lymphocytes. However, the secretion of IL-17A increased when either H. pylori lysate or macrophages was added (Figure 5C). Activation of NF-κB signaling was also examined, and the expression of both IL-17RA and IL-23R was detected in both SGC-7901 and MKN45 cells, relatively strong expression of IL-17RA and almost no expression of IL-23R were identified (Figure 5D). Phosphorylated IκBα and cyclinD1, the products of NF-κB signaling, were both increased in SGC-7901 and MKN45 cells along with increased presence of IL-17A (Figure 5E). IL-23A was secreted from both macrophages and GC cells and promoted cancer proliferation through IL-17A/IL-17RA/NF-κB signaling.
Discussion
GC is the fourth most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Among several histological types, intestinal-type GC is commonly associated with H.Pylori infection, and its course is characterized by acute gastritis, chronic gastritis, gastric atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, and finally, formation of GC [10].
The exact causes of GC are unknown, but a number of factors can increase the risk of the disease, including sex, race, genetics, geography, blood type, advanced age, family history, and H.pylori infection of the stomach. H. pylori infects the lining of the stomach and causes chronic inflammation and ulcers. The detailed molecular pathways responsible for the stimulation of H. pylori are still not completely known [14]-[16].
Several studies have reported an immune effector molecules of H. pylori, such as CagA. CagA promoted expression of the proinflammatory chemokines IL-8, CXC-chemokine ligand 2 (also known as macrophage inflammatory protein) and the antimicrobial peptide human β-defensin-2 through activation of NF-κB signaling [17]. Other studies have revealed that CagA translocated into epithelial cells by inducing high levels of IL-8 infected by certain H. pylori strains, accompanied by induction of an inflammatory response [16],[18],[19]. Ras-dependent kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1 and ERK2, are also activated by CagA-triggered tyrosine phosphorylation, leading to activation of the transcription factors NF-κB, activator protein-1, and ultimately, IL-8 production by host cells [9].
The mechanism linked Hp infection and Th17 response was not fully revealed. Some of the cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-21 were reported to be associated. Lee et al. revealed that persistent Hp infection can induce Hp-specific Th17 cells, rather than other immune cells that have also been described to secrete IL-17A. Moreover, IL-1β was also persistently elevated, and neutralization of IL-1β reduced the Hp-specific IL-17A response, suggesting a functional association between IL-1β and the persistent Th17 response [20]. Other group also revealed that IL-21 regulates Th1 and Th17 effector responses during chronic H. pylori infection in a STAT1- and STAT3-dependent manner, therefore playing a major role controlling H. pylori infection and gastritis [21].
We reported that IL-23A was secreted from GC cells and macrophages. We found that serum level of IL-23A was an indicator of poor prognosis in GC patients, and its expression was related to tumor volume and H.pylori infection. Our results also indicated that IL-23A had no direct effect on the proliferation of cancer cells. However, it did affect the tumor microenvironment by increasing secretion of IL-17A, which is a hallmark cytokine of Th17 cells. In conclusion, we found that IL-23A could be a potential index and target for diagnosis and treatment of GC.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study showed that the high expression of IL-23A is associated with GC. IL-23A may induce the secretion of IL-17A activate IL-17A/IL-17RA/NF-κB signaling in tumor microenvironment. Serum IL-23A concentration is an indicator of poor prognosis in GC patients and IL-23A will be a potential index and target for diagnosis and treatment of GC.
Materials and methods
Patients
The present study included 141 patients with GC who underwent surgery from 2008 to 2013 at the Kunshan People’s Hospital, Kunshan, Jiangsu and Kunshan Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine. Documented informed consent for gene expression analyses of all tissues was obtained from all patients prior to surgery. This study was approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Kunshan People’s Hospital. Histological subtype according to Lauren’s classification [22] was determined after a review of tumor sections by two pathologists. Follow-up data were available from all GC patients, who were assessed at 3, 6,12 months and then every 6 months for 5 years or until death.
Immunohistochemistry
All tissues were removed and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight at 4°C, then processed and sectioned at 5 μm thickness. Sectioned slides were stained by immunohistochemistry for IL-23A, IL-23R and IL-17A (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), followed by incubation with secondary antibody at 37°C for 30 min and reaction with DAB reagent for 5–10 min. The slides were mounted with neutral gum for microscopic examination. Cells with brown intracellular granules (cytoplasm or nucleus) were considered to be positively stained.
ELISA
Concentration of IL-23A and IL-17A in serum of GC patients and healthy candidates were measured using commercially available sandwich ELISA kits (eBioscience).
Stimulation of IL-23A in vitro
T cells and macrophage was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells by using isolation kit to T cells and monocyte respectively (Miltenyi Biotec). T cells and macrophages plus GC cell lines (MKN45 and SGC-7901 were purchased from ATCC) were maintained in vitro and stimulated by Helicobacter pylori lysate (NCTC 11637, CagA + and VacA+) and analyzed by intracellular cytokine staining. For intracellular cytokine staining, T cells were stimulated at 37°C for 5 hours with a Leukocyte Activation Cocktail (BD Pharmingen). Furthermore, T cells, macrophages and GC cell lines were stained with surface markers, fixed, and permeabilized with IntraPre Reagent (Beckman Coulter), and finally stained with intracellular markers. Data were acquired on FACSVantage SE and analyzed with CellQuest software. Fluorochrome-conjugated mAbs against IL-23A were purchased from BD Pharmingen (Cat. 562468).
Flowcytometry
For intracellular cytokine staining, cells were stimulated at 37°C for 5 hours with a Leukocyte Activation Cocktail (BD Pharmingen). Cells were then stained with surface markers, fixed, and permeabilized with IntraPre Reagent (Beckman Coulter), and finally stained with intracellular markers. Data were acquired on FACSVantage SE and analyzed with CellQuest software. Fluorochrome-conjugated monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against IL-23A, CD3 served as marker for T cells and CD14 serve as markers for monocyte and macrophage were purchased from BD Pharmingen.
MTS assay
Cultured cells were plated at a density of 6 × 103 cells/well in a 96-well plate and maintained with DMEM plus 10% fetal calf serum (Invitrogen). Cell viability was evaluated by MTS assay. CellTiter 96Aqueous One Solution Reagent (Promega) was added to each well according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and the plates were returned to the incubator. After 4 hours, cell viability was determined by measuring the absorbance at 490 nm using a computer controlled plate-reader.
Western blot
Proteins were extracted from cells and quantitated using a protein assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). Protein samples (30 μg) were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Immunoblot was carried out using antibodies against p-IκBα, IκBα, CyclinD1 and IL-17RA (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). The results were visualized using a chemiluminescent detection system (Pierce ECL substrate western blot detection system; Thermo Scientific) and exposed to autoradiography film (Kodak XAR film).
Statistical analysis
The results are expressed as mean ± SD of at least triplicate experiments. Comparisons between two groups were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test. The comparison of IL-23A expression between various clinical characteristics was analyzed using the χ2 test. Correlation analysis between expression of IL-23A and IL-17A in GC tissues was performed using Spearman non-parametric relation analysis. Survival curves were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier product-limit method, and significant differences between the survival curves were determined using the log-rank test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Abbreviations
- IL-23:
-
Interleukin-23
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- IL-23R:
-
IL-23 receptor
- IL-17RA:
-
IL-17 receptor subunit A
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- STAT4:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4
- NK:
-
Natural killer
References
Cordoba-Rodriguez R, Frucht DM: IL-23 and IL-27: new members of the growing family of IL-12-related cytokines with important implications for therapeutics. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2003, 3: 715-723. 10.1517/14712598.3.5.715.
Vaknin-Dembinsky A, Balashov K, Weiner HL: IL-23 is increased in dendritic cells in multiple sclerosis and down-regulation of IL-23 by antisense oligos increases dendritic cell IL-10 production. J Immunol. 2006, 176: 7768-7774. 10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7768.
Burton MJ, Ramadhani A, Weiss HA, Hu V, Massae P, Burr SE, Shangali W, Holland MJ, Mabey DC, Bailey RL: Active trachoma is associated with increased conjunctival expression of IL17A and profibrotic cytokines. Infect Immun. 2011, 79: 4977-4983. 10.1128/IAI.05718-11.
Langowski JL, Zhang X, Wu L, Mattson JD, Chen T, Smith K, Basham B, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Oft M: IL-23 promotes tumour incidence and growth. Nature. 2006, 442: 461-465. 10.1038/nature04808.
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H: The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2006, 116: 1218-1222. 10.1172/JCI28508.
Thakker P, Leach MW, Kuang W, Benoit SE, Leonard JP, Marusic S: IL-23 is critical in the induction but not in the effector phase of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2007, 178: 2589-2598. 10.4049/jimmunol.178.4.2589.
Ahern PP, Izcue A, Maloy KJ, Powrie F: The interleukin-23 axis in intestinal inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2008, 226: 147-159. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00705.x.
Li Q, Chen J, Liu Y, Zhao X, Tan B, Ai J, Zhang Z, Song J, Shan B: Prevalence of Th17 and Treg cells in gastric cancer patients and its correlation with clinical parameters. Oncol Rep. 2013, 30: 1215-1222.
Zhou Y, Toh ML, Zrioual S, Miossec P: IL-17A versus IL-17 F induced intracellular signal transduction pathways and modulation by IL-17RA and IL-17RC RNA interference in AGS gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Cytokine. 2007, 38: 157-164. 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.06.002.
Amedei A, Munari F, Bella CD, Niccolai E, Benagiano M, Bencini L, Cianchi F, Farsi M, Emmi G, Zanotti G, de Bernard M, Kundu M, D'Elios MM: Helicobacter pylori secreted peptidyl prolyl cis, trans-isomerase drives Th17 inflammation in gastric adenocarcinoma. Intern Emerg Med. 2014, 9: 303-309. 10.1007/s11739-012-0867-9.
Rafiei A, Hosseini V, Janbabai G, Ghorbani A, Ajami A, Farzmandfar T, Azizi MD, Gilbreath JJ, Merrell DS: Polymorphism in the interleukin-17A promoter contributes to gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2013, 19: 5693-5699. 10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5693.
Iida T, Iwahashi M, Katsuda M, Ishida K, Nakamori M, Nakamura M, Naka T, Ojima T, Ueda K, Hayata K, Nakamura Y, Yamaue H: Tumor-infiltrating CD4+ Th17 cells produce IL-17 in tumor microenvironment and promote tumor progression in human gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011, 25: 1271-1277. 10.3892/or.2010.1118.
Shibata T, Tahara T, Hirata I, Arisawa T: Genetic polymorphism of interleukin-17A and -17 F genes in gastric carcinogenesis. Hum Immunol. 2009, 70: 547-551. 10.1016/j.humimm.2009.04.030.
Benberin V, Bektayeva R, Karabayeva R, Lebedev A, Akemeyeva K, Paloheimo L, Syrjanen K: Prevalence of H. pylori infection and atrophic gastritis among symptomatic and dyspeptic adults in Kazakhstan. A hospital-based screening study using a panel of serum biomarkers. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33: 4595-4602.
Carrasco G, Corvalan AH: Helicobacter pylori-Induced Chronic Gastritis and Assessing Risks for Gastric Cancer. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013, 2013: 393015-10.1155/2013/393015.
Qadri Q, Rasool R, Afroze D, Naqash S, Gulzar GM, Yousuf A, Siddiqi MA, Shah ZA: Study of TLR4 and IL-8 gene polymorphisms in H.pylori-induced inflammation in gastric cancer in an ethnic Kashmiri population. Immunol Invest. 2014, 43: 324-336. 10.3109/08820139.2013.854378.
Leung WK, Chan MC, To KF, Man EP, Ng EK, Chu ES, Lau JY, Lin SR, Sung JJ: H. pylori genotypes and cytokine gene polymorphisms influence the development of gastric intestinal metaplasia in a Chinese population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006, 101: 714-720. 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00560.x.
Sakitani K, Hirata Y, Hayakawa Y, Serizawa T, Nakata W, Takahashi R, Kinoshita H, Sakamoto K, Nakagawa H, Akanuma M, Yoshida H, Maeda S, Koike K: Role of interleukin-32 in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammation. Infect Immun. 2012, 80: 3795-3803. 10.1128/IAI.00637-12.
Sieveking D, Mitchell HM, Day AS: Gastric epithelial cell CXC chemokine secretion following Helicobacter pylori infection in vitro. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004, 19: 982-987. 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2004.03413.x.
Serelli-Lee V, Ling KL, Ho C, Yeong LH, Lim GK, Ho B, Wong SB: Persistent Helicobacter pylori specific Th17 responses in patients with past H. pylori infection are associated with elevated gastric mucosal IL-1beta. PLoS One. 2012, 7: e39199-10.1371/journal.pone.0039199.
Carbo A, Olivares-Villagomez D, Hontecillas R, Bassaganya-Riera J, Chaturvedi R, Piazuelo MB, Delgado A, Washington MK, Wilson KT, Algood HM: Systems modeling of the role of interleukin-21 in the maintenance of effector CD4+ T cell responses during chronic Helicobacter pylori infection. mBio. 2014, 5: e01243-01214-10.1128/mBio.01243-14.
Kim JP, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Yu HJ, Yang HK: Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors in 10 783 patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 1998, 1: 125-133. 10.1007/s101200050006.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Social Development Technology Projects of Kunshan City, China (KS1255).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
CL and WZ conceived and designed the experiments. CL, YZ, JZ, YZ, QW and Hp performed the experiments. CL and WZ performed statistical analysis of all data. CL wrote the paper. All authors are in agreement with the content of the manuscript and this submission. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zhang, Y., Zhan, J. et al. Interleukin-23A is associated with tumor growth in Helicobacter-pylori-related human gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int 14, 104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-014-0104-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-014-0104-x