Abstract
Background
With concerns about depletion of fossil fuel and environmental pollution, synthesis of biofuels such as isobutanol from low-cost substrate by microbial cell factories has attracted more and more attention. As one of the most promising carbon sources instead of food resources, acetate can be utilized by versatile microbes and converted into numerous valuable chemicals.
Results
An isobutanol synthetic pathway using acetate as sole carbon source was constructed in E. coli. Pyruvate was designed to be generated via acetyl-CoA by pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase YdbK or anaplerotic pathway. Overexpression of transhydrogenase and NAD kinase increased the isobutanol titer of recombinant E. coli from 121.21 mg/L to 131.5 mg/L under batch cultivation. Further optimization of acetate supplement concentration achieved 157.05 mg/L isobutanol accumulation in WY002, representing the highest isobutanol titer by using acetate as sole carbon source.
Conclusions
The utilization of acetate as carbon source for microbial production of valuable chemicals such as isobutanol could reduce the consumption of food-based substrates and save production cost. Engineering strategies applied in this study will provide a useful reference for microbial production of pyruvate derived chemical compounds from acetate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In the area of microbial production of valuable compounds, selection of abundant and low-cost carbon sources is essential for products application and promotion [1]. Acetate, the second simplest carboxylic acid, is present in larger amounts in nature [2]. In general, acetate is a common by-product in microbial metabolism of sugars. In addition, acetate can be generated in anaerobic microbial fermentation of waste organic materials, such as lignocellulose depolymerization [3] and waste water treatment [4]. With properties of abundance, low price ($340 per metric ton) and easy utilization by versatile microbes, acetate become a feasible carbon source for microbial fermentation [5]. In fact, microbial production of value-added products from pure acetate or acetate-containing biorefinery stream has attract more and more attention over the past decade [6,7,8].
Many microorganisms can utilize acetate as alternative carbon source for cell growth, such as Escherichia coli [9], Cryptococcus curvatus [10], Clostridium sp. [11], and so on. Due to convenient genetic engineering tools and fast growth in cheap media, E. coli is a widely used host microorganisms in microbial fermentation industry [12]. In E. coli, acetate can be transformed into acetyl-CoA by AMP-forming acetyl CoA synthetase (Acs) or phosphotransacetylase/acetate kinase (Pta-AckA) pathways. The acetyl-CoA was then entered into the TCA cycle and glyoxylate cycle to supply energy and precursors for cell growth [13]. However, because of its toxicity and poor transformation efficiency compared with other carbon source, acetate is usually not a preferred carbon source. As a result, only a few products have been successfully synthesized in E. coli by using acetate as main carbon source, such as PHA [14, 15], ethanol [16], succinate [5, 17], fatty acid [18], itaconic acid [19], mevalonate [20], sweet protein [21], and glycolate [22].
Isobutanol (2-methyl-1-propanol) is a four-carbon alcohol which is a promising biofuel than ethanol due to its low hygroscopicity and vapor pressure, compatibility with existing engines, and high-energy capacity [23]. Therefore, isobutanol is considered as one of potential alternatives for traditional gasoline. In addition, isobutanol can also be served as a precursor for the production of a variety of polymers, paints, plastics and synthetic rubber [24]. In 2008, Atsumi et al. firstly reported isobutanol production in E. coli by employing native branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis pathway [25]. Subsequently, numerous recombinant E. coli with high yields and titers of isobutanol were obtained [26,27,28]. Apart from glucose, cellobiose [29], cellobionic acid [30] and sucrose [31] were also employed as substrate for synthesizing isobutanol in E. coli.
In this study, isobutanol production in E. coli with acetate as sole carbon source was investigated. Pyruvate was designed to be generated from acetate via acetyl-CoA by pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase YdbK or anaplerotic pathway. Overexpression of transhydrogenase and NAD kinase as well as optimization of acetate supplement concentration further increased the isobutanol titer of recombinant E. coli WY002 to 157.05 mg/L, representing the highest isobutanol titer by using acetate as sole carbon source.
Results and discussion
Construction of an isobutanol biosynthetic pathway from acetate in E. coli
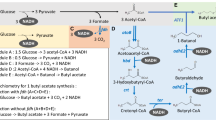
In previous studies, an effective isobutanol biosynthetic pathway had been created by combining branched-chain amino acids synthetic pathway from glucose and Ehrlich pathway with 2-keto-isovalerate serving as a precursor [25]. The alaS gene encoding acetolactate synthase from Bacillus subtilis was responsible for converting pyruvate to acetolactate. And then, 2,3-dihydroxy-isovalerate and 2-ketoisovalerate were generated in sequence by two E. coli endogenous genes ilvC and ilvD, encoding keto-acid reductoisomerase and dihydroxy-acid dehydratase respectively. Finally, isobutanol was generated from 2-ketoisovalerate by using two Lactococcus lactis enzymes, kivd encoding 2-keto acid decarboxylase and adhA encoding alcohol dehydrogenase. To facilitate the construction process, these five genes were overexpressed and distributed into plasmids pCL1920 and pTrc99a respectively. As AlsS is vital for the redirection of pyruvate into the isobutanol pathway, it was overexpressed in both plasmids. In addition, acs encoding the acetyl-CoA synthetase was also overexpressed in pCL1920 to improve the acetate assimilation. Thus, an entire pathway from acetate to isobutanol was constructed (Fig. 1).
In E. coli, ydbK encoding a putative pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase which can catalyze a reversible reaction between acetyl-CoA and pyruvate. Accordingly, we deduced acetate can be directly transformed into pyruvate via acetyl-CoA in wild E. coli. In other hand, the native pyruvate fermentation pathways, including pyruvate formate-lyase, pyruvate oxidase, aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase, and lactate dehydrogenase, which compete for pyruvate with isobutanol synthetic pathway were inactivated in turn in BW25113 to generate BWΔPPAL. Then, pCL1920-1 and pTrc99a-1 was co-transformed into BWΔPPAL to generate recombinant strain NH000. Unfortunately, no isobutanol accumulation was detected for NH000, and even no pyruvate was found in NH000 (data not shown). In previous report, isobutanol production could increase by up to 75% from acetate when pyruvate was added compared with the control [32]. Deficiency of intracellular pyruvate may result in no isobutanol synthesis of NH000. In addition, no lactate, formate and ethanol were detected in NH000 (data not shown), demonstrating the effective of blocking byproduct generation pathway.
Isobutanol synthesis from acetate by overexpression of ydbK or anaplerotic pathway genes
To improve the pyruvate generation from acetate, the ydbK gene was inserted into plasmid pTrc99a-1 to generate pTrc99a-2 and co-transformed with pCL1920-1 into BWΔPPAL to generate NH001. As shown in Fig. 2a, recombinant strain NH001 showed a lag phase of 18 h. And then, the OD600 of NH001 began to increase quickly and reach a maximum OD600 4.005 at 30 h. Acetate was completely consumed after 36 h batch fermentation. In addition, isobutanol accumulation was extremely low before 12 h and could reach a maximum isobutanol titer of 111.08 mg/L at 30 h. This phenomenon further suggested low intracellular expression level of ydbK and lack of pyruvate may result in no isobutanol accumulation in NH000. When the residual acetate was below 2 mM, isobutanol production of NH001 began to decrease. To our knowledge, this is the first report related to YdbK utilization in microbial production of chemicals from acetate.
Afterwards, we carefully analyzed the pyruvate metabolism and found pyruvate could also be generated from acetyl-CoA via two anaplerotic pathways in E. coli (Fig. 1). One is originated from decarboxylation of oxaloacetate by pckA encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. And then, phosphoenolpyruvate generated from oxaloacetate can convert into pyruvate through glycolytic pathway. The other pathway is responsible by NADP+-dependent malate dehydrogenase MaeB, which can transform malate into pyruvate [33]. It was reported these gluconeogenic pathways are highly activated when E. coli is grown with acetate, indicating that pyruvate could be supplemented by these two pathways [34]. Thus, pckA and maeB were inserted into pTrc99a-1 and then co-transformed with pCL1920-1 into BWΔPPAL to generate WY001. In batch cultivation, WY001 exhibited a maximum OD600 of 3.69, and the acetate assimilation curve between NH001 and WY001 were similar (Fig. 2b). In addition, isobutanol was increased quickly from 12 h and 121.21 mg/L of isobutanol could be obtained from 100 mM acetate sodium. As MaeB generate one NADPH by converting malate into pyruvate, overexpression of maeB was found be able to supply NADPH as well as pyruvate [35]. In addition, overexpression of pckA could increase intracellular level of phosphoenolpyruvate, a direct precursor of pyruvate. Accordingly, co-expression maeB and pckA exhibited positive effect on isobutanol production.
Overexpression of transhydrogenase and NAD kinase further increased isobutanol titer of E. coli
Although NADH-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase, such as AdhA from L. lactis, was recruited to reduce NADPH dependence in this study, one NADPH molecular is still required for one molecular isobutanol production. In wild E. coli, there are three pathways including pentose phosphate pathway, tricarboxylic acid cycle and membrane-bound transhydrogenase PntAB are responsible for generation of NADPH [33]. Among them, PntAB is a membrane-bound proton translocating pyridine nucleotide transhydrogenase which transfers a hydride from NADH to NADP+ with the concurrent production of NADPH and NAD+ [36, 37]. It was reported about 35–45% of NADPH applied in intracellular biosynthesis was supplied via PntAB [37]. Accordingly, improving the expression level of pntAB may be benefit for isobutanol production in E. coli, which has been proved in a previous report [38]. In addition, yfjB encoding NAD kinase in E. coli, can catalyze phosphorylation of NAD+ to NADP+ [39]. In previous report, it was found overexpression of pntAB and yfjB showed over 20% improvement in isobutanol titer for recombinant E. coli [28].
In this study, pntAB and yfjB were inserted into pCL1920-1 and then co-transformed with pTrc99a-3 into BWΔPPAL to generate WY002, and batch fermentation was performed for this strain. As shown in Fig. 2c, WY002 exhibited similar growth curve with WY001, indicating nearly no further metabolic burden occurred for overexpression of yfjB and pntAB compared with WY001. In addition, 131.5 mg/L isobutanol was detected at 30 h which was 8.49% higher than that of WY001. Song et al. also constructed a recombinant E. coli HM501::MAP for the production of isobutanol with acetate as carbon source. However, they found NADPH pool were not limiting factors for isobutanol production in E. coli when acetate was utilized [32]. Two reasons may be responsible for this discrepancy. Firstly, the engineering genes of HM501::MAP and WY002 in this work was quite different. In HM501::MAP, fdh from C. boidinii and pntAB from E. coli were employed for regeneration of NADPH, while pntAB and yfjB was overexpressed in WY002. Secondly, 5 mM of formate was supplemented into the medium when HM501::MAP was cultivated, while no further carbon source apart from acetate was used for WY002.
Considering no huge gap was exhibited for the isobutanol titers between NH001 and WY001, pntAB and yfjB were also over expressed in NH001 to generate NH002. And then batch fermentation were also performed for NH002. To our surprise, NH002 exhibited worse growth than NH001 indicated by the maximum OD600 of 1.635 at 36 h (Fig. 2d). In addition, only a 6 h rapid growth period was showed for NH002. The acetate assimilation rate was also obviously slower than NH001, WY001 and WY002. Especially, NH002 only produced 51.22 mg/L isobutanol at 30 h, representing only 42.25% of that of NH001. After 18 h, increase of isobutanol titer become very slow. These results indicated introduction of pntAB and yfjB into NH001 seriously affect its normal growth and isobutanol production, while overexpression of these two genes is advantage for WY001.
Optimization of acetate concentration in the batch fermentation
In a previous study, we found acetate is toxic to E. coli and inhibit its normal growth when the concentration of acetate exceeding 200 mM [17]. Considering different genes was engineered for WY002 compared with previous strains, the effect of acetate concentration on isobutanol production for WY002 was then explored. Four gradients of acetate, 50, 100, 150 and 200 mM were employed to perform batch cultivation of WY002. As shown in Fig. 3, Fig. S1 and Fig. S2, 150 and 200 mM of acetate interfered the growth seriously, indicated by the maximum OD600 of 0.83 and 0.38 respectively. As a result, the isobutanol production of WY002 was also very low for these two conditions. Although the final maximum OD600 were almost similar when 50 mM or 100 mM acetate was used for WY002, the growth curve were quite different (Fig. S1). When 50 mM acetate was used, WY002 could enter into logarithmic phase quickly and achieve the maximum OD600 of 3.774 at 24 h. In contrast, the OD600 of WY002 was only 1.01 at 24 and 42 h batch cultivation was needed to reach the maximum OD600 of 4.055. Consistent with growth curve, the maximum isobutanol production titer 157.05 mg/L of WY002 was also quickly achieved only for 18 h when 50 mM acetate was used as carbon source. To our knowledge, this was the highest isobutanol titer when acetate was selected as sole carbon source. Song et al. also constructed a recombinant E. coli to achieve isobutanol production from acetate, but the final strain HM501::MAP could only synthesize about 125 mg/L isobutanol after 120 h cultivation [32]. In addition, three compatible plasmids were employed to overexpress key genes which brought a heavy metabolic burden for host strain. Compared with HM501::MAP, WY002 engineered in this study could achieve 25.6% higher isobutanol production after only 18 h batch fermentation. Moreover, we also explored the effect of YdbK overexpression on isobutanol production in E. coli for the first time, which was not investigated by the report of Song et al. [32].
As 50 mM acetate exhibited higher isobutanol titer than that of 100 mM for WY002, NH001, WY001 and NH002 were also performed batch fermentation with 50 mM acetate as sole carbon source. As shown in Fig. S3, NH001, WY001 and NH002 showed a relatively quick growth when 50 mM acetate was employed and only 18–24 h was needed to achieve the maximum OD600. However, the maximum OD600 values of NH001, WY001 and NH002 were not obviously increased using 50 mM acetate. In addition, the isobutanol production titers of NH001, WY001 and NH002 were increased by 3.8%, 5.8% and 7.8% respectively when 50 mM acetate was used compared with these of the same strains using 100 mM acetate (Fig. S4). These results suggested 50 mM acetate could accelerate strain growth and slightly improve isobutanol production for NH001, WY001 and NH002 in batch fermentation.
Conclusions
In this study, isobutanol production in E. coli with acetate as sole carbon source was investigated. Pyruvate could be generated from acetate via acetyl-CoA by pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase YdbK or anaplerotic pathways. To our knowledge, this is the first report about utilization of YdbK for isobutanol production. In addition, overexpression of transhydrogenase and NAD kinase coordinating with optimized acetate concentration further increased the isobutanol titer of WY002 to 157.05 mg/L, representing the highest isobutanol titer using acetate as sole carbon source.
However, compared with other carbon sources, such as glucose and glycerol, isobutanol titer from acetate as sole carbon source in E. coli is still slow and far from industrial production. Accordingly, further strain engineering should be carried out. For example, increasing the acetate tolerance will be benefit for strain biomass accumulation. As exhibited in this work, the maximum OD600 of recombinant strain were all below 4.5. Different strategies such as laboratory metabolic evolution [40], engineering of cobalamin-independent methionine synthase [41], rewiring global regulator cAMP receptor protein [42] and engineered global regulator H-NS [43] can be investigated to increase acetate tolerance in E. coli. In other hand, increasing the tolerance of isobutanol may also be advantageous for isobutanol production in E. coli. In a previous report, isobutanol-tolerant E. coli mutant obtained by evolution were capable of growth at 20 g/L isobutanol in glucose containing media [44]. Moreover, further improving the pyruvate transformation efficiency from acetate is crucial for isobutanol production. Regardless of YdbK or anaplerotic pathways, intracellular pyruvate titer may be not enough for strain growth and isobutanol production. As a result, exploration novel and effective pyruvate generation pathways from acetate as few enzymic reaction steps as possible is vital.
Considering high yields, high productivities are usually hard to achieve in cell-based systems due to the need to maintain life processes, a cell-free system containing enzymes in a bioreactor with continuous product removal is an alternative method for biofuel production. By using this technology, isobutanol from glucose at a maximum productivity of 4 g/L/h and a titer of 275 g/L with 95% yield could be achieved, which far exceed these parameters obtained by isobutanol producing strains [45]. However, NADPH, NADP, ATP and purified enzymes need to be added in the in-vitro production system, which will add the overall cost of isobutanol production. In comparison, direct fermentation of isobutanol from simple substrates by microbial cells may be a better choice for isobutanol production at present stage due to low cost, tolerance to complex environments and easy manipulation process.
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains
All strains, plasmids and oligonucleotides used in this study were listed in Table 1 and Table S1 respectively. E. coli BW25113 was employed for the construction of isobutanol producing strain. E. coli DH5α was selected as a base strain for the construction of recombinant plasmids.
Plasmids construction
The genes of ilvC and ilvD, encoding ketol-acid reductoisomerase and dihydroxy-acid dehydratase respectively, was fused together by overlap extension PCR. Firstly, the genome DNA of BW25113 and primers ilvC-QF/ilvC-QR were employed to obtain ilvC fragment. In the meantime, primers PCL-ilvD-NF and IlvD-ilvC-NR were used to obtain ilvD fragment. And then, ilvC and ilvD with homologous sequences were fused by two-step overlap extension PCR. Step 1: GoldenStar T6 DNA polymerase mix (TSINGKE Biological Technology) 45 µL, ilvC fragment 0.5 µL and ilvC fragment 0.5 µL. Cycling parameters: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, subsequent cycle steps containing 94 °C 30 s, annealing at 56 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 3.5 min, 10 cycles total, final extension at 72 °C for 10 min, and hold at 4 °C. Step 2: adding 2 µL of PCL-ilvD-NF and 2 µL of ilvC-QR into the tube. Cycling parameters: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, subsequent cycle steps containing 94 °C 30 s, annealing at 56 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 3.5 min, 25 cycles total, extension at 72 °C for 10 min, hold at 4 °C. All reactions were run with heated lid. The resulting 3.5 kb PCR product was analyzed electrophoresis in 0.8% agarose and performed DNA sequencing at TSINGKE Biological Technology. And then, acs gene encoding acetyl-CoA synthetase were fused with ilvD-ilvC fragment by overlap extension PCR. Primers Ilvc-acs-NF/Acs-PCL-NR were applied to amplify acs gene fragment containing homologous sequences with ilvC. Then, ilvD-ilvC-acs fragment with homologous sequences was assembled into pCL1920 by ClonExpress MultiS One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme). Finally, alaS encoding acetolactate synthase from B. subtilis were directly synthesized by TSINGKE Biological Technology and ligated into the SalI and BamHI sites of pCL1920-ilvD-ilvC-acs. The resulting plasmid was named pCL1920-1.
Similarly, alaS encoding acetolactate synthase from B. subtilis, kivd encoding 2-keto acid decarboxylase from L. lactis and adhA encoding alcohol dehydrogenase from L. lactis was amplified and fused to an entire DNA fragment by overlap extension PCR. And then, adhA-kivD-alsS fragment was assembled with linear pTrc99a digested by SmaI site, resulting recombinant plasmid pTrc99a-1.
Next, ydbK encoding pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase was amplified by primers ydbk-zu-F/ydbk-zu-R and assembled with linear pTrc99a-1 digested by SmaI to generate pTrc99a-2. In the meantime, pck and maeB encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and malate dehydrogenase from E. coli respectively were firstly fused together, and then assembled with linear pTrc99a-1 digested by SmaI. As a result, recombinant pTrc99a-3 was generated.
Then, pCL1920-1 was linear by PCR, using PCR-120-4-QF/PCR-120-4-QR as primers. And then, pntA, pntB, and yfjB encoding H+-translocating NAD(P) transhydrogenase subunit alpha, H+-translocating NAD(P) transhydrogenase subunit beta, and NAD kinase from E. coli respectively were fused by overlap extension PCR and assembled with linear pCL1920-1 to generate pCL1920-2. The organization of plasmids pTrc99a-1, pTrc99a-2, pTrc99a-3, pCL1920-1 and pCL1920-2 were shown in Fig. 4. The ribosome binding site RBSB0034 (AAAGAGGAGAAA) derived from Community RBS Collection (http://parts.igem.org/Ribosome_Binding_Sites/Prokaryotic/Constitutive/Community_Collection) was applied for genes overexpressed in plasmids.
Gene deletion
The four genes, pflB, poxB, adhE and ldhA in E. coli, which encoding pyruvate formate-lyase, pyruvate oxidase, aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase, and lactate dehydrogenase respectively were knocked out in BW25113 sequentially by one-step inactivation method [46]. The resulting strain was named as BWΔPPAL. Finally, NH001 was generated by co-transforming pTrc99a-2 and pCL1920-1 into BWΔPPAL, NH002 was generated by co-transforming pTrc99a-2 and pCL1920-2 into BWΔPPAL, WY001 was generated by co-transforming pTrc99a-3 and pCL1920-1 into BWΔPPAL, WY002 was generated by co-transforming pTrc99a-3 and pCL1920-2 into BWΔPPAL and NH000 was generated by co-transforming pTrc99a-1 and pCL1920-1 into BWΔPPAL.
Growth conditions
E. coli strains for cloning were cultivated in Luria-Bertani media (1% tryptone, 0.5% yeast extract and 1% NaCl) at 37 °C for 8–12 h. Different antibiotics were supplemented with appropriate concentrations, including ampicillin (100 mg/L), chloramphenicol (17 mg/L), kanamycin (25 mg/L), and spectinomycin (50 mg/L). For batch fermentation, a medium containing Na2HPO4 33.9 g/L, KH2PO4 15 g/L, NaCl 2.5 g/L, NH4Cl 5 g/L, MgSO4 1mM, CaCl2 0.1 mM, yeast extract 5 g/L was used, and sodium acetate was added with different concentration as indicated. 1 mL overnight cells were inoculated into 50 mL fermentation medium for batch fermentation, and strains were cultivated at 30 °C with 200 rpm shaking. Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added at a final concentration of 0.2 mM, when the OD600 of E. coli cells reached 0.4–0.6.
Analytical methods
High-performance liquid chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) equipped with a column of Aminex HPX-87 H ion exclusion particles (300 mm × 7.8 mm, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was used for determining sodium acetate concentration. The mobile phase was 5 mM sulfuric acid, with the flow rate of 0.6 mL/min and the column was maintained at 65 °C. Cell growth was monitored by OD600 using a UV5100H spectrophotometer (METASH, Shanghai China). The concentration of isobutanol was determined by gas chromatography (CROCKWAY, China) using an HP-FFAP column (25 m × 0.20 mm × 0.3 μm) (Agilent Technologies, USA) and a flame ionization detector (FID) described previously [32].
Data Availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study were included in this manuscript.
References
Choi JI, Sang YL. Process analysis and economic evaluation for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by fermentation. Bioproc Eng. 1997;17:335–42.
Hu P, Chakraborty S, Kumar A, Woolston B, Liu H, Emerson D, Stephanopoulos G. Integrated bioprocess for conversion of gaseous substrates to liquids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:3773–8.
Wu QL, Guo WQ, Zheng HS, Luo HC, Feng XC, Yin RL, Ren NQ. Enhancement of volatile fatty acid production by co-fermentation of food waste and excess sludge without pH control: the mechanism and microbial community analyses. Bioresour Technol. 2016;216:653–60.
Zhao Z, Li Y, Zhao Z, Yu Q, Zhang Y. Effects of dissimilatory iron reduction on acetate production from the anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge under alkaline conditions. Environ Res. 2020;182:109045.
Li Y, Huang B, Wu H, Li Z, Ye Q, Zhang YP. Production of succinate from acetate by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol. 2016;5:1299–307.
Kim Y, Lama, Agrawal D, Kumar V, Park S. Acetate as a potential feedstock for the production of value-added chemicals: metabolism and applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2021;49:107736.
Kutscha R, Pflügl S. Microbial upgrading of acetate into value-added products-examining microbial diversity, bioenergetic constraints and metabolic engineering approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:8777.
Fei P, Luo Y, Lai N, Wu H. Biosynthesis of (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid from syngas-derived acetate in engineered Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol. 2021;336:125323.
Chen GQ. A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio- and materials industry. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:2434–46.
Chi Z, Zheng Y, Ma J, Chen S. Oleaginous yeast Cryptococcus curvatus culture with dark fermentation hydrogen production effluent as feedstock for microbial lipid production. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2011;36:9542–50.
Canganella F, Kuk SU, Morgan H, Wiegel J. Clostridium thermobutyricum: growth studies and stimulation of butyrate formation by acetate supplementation. Microbiol Res. 2002;157:149–56.
Matsumoto T, Tanaka T, Kondo A. Engineering metabolic pathways in Escherichia coli for constructing a microbial chassis for biochemical production. Bioresour Technol. 2017;245:1362–8.
Bernal V, Castano-Cerezo S, Canovas M. Acetate metabolism regulation in Escherichia coli: carbon overflow, pathogenicity, and beyond. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:8985–9001.
Yang YH, Brigham CJ, Budde CF, Boccazzi P, Willis LB, Hassan MA, Yusof ZA, Rha C, Sinskey AJ. Optimization of growth media components for polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production from organic acids by Ralstonia eutropha. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;87:2037–45.
Chen J, Li W, Zhang ZZ, Tan TW, Li ZJ. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates using acetate as a main carbon source. Microb Cell Fact. 2018;17:102.
Lee HM, Jeon BY, Oh MK, Engineering B. Microbial production of ethanol from acetate by engineered Ralstonia eutropha. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2016;21:402–7.
Niu H, Li R, Wu J, Cai Z, Yang D, Gu P, Li Q. Production of succinate by recombinant Escherichia coli using acetate as the sole carbon source. 3 Biotech. 2018;8:421.
Xiao Y, Ruan Z, Liu Z, Wu SG, Varman AM, Liu Y, Tang Y. Engineering Escherichia coli to convert acetic acid to free fatty acids. Biochem Eng J. 2013;76:60–9.
Noh MH, Lim HG, Woo SH, Song J, Jung GY. Production of itaconic acid from acetate by engineering acid-tolerant Escherichia coli W. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018;115:729–38.
Xu X, Xie M, Zhao Q, Xian M, Liu H. Microbial production of mevalonate by recombinant Escherichia coli using acetic acid as a carbon source. Bioengineered. 2018;9:116–23.
Leone S, Sannino F, Tutino ML, Parrilli E, Picone D. Acetate: friend or foe? Efficient production of a sweet protein in Escherichia coli BL21 using acetate as a carbon source. Microb Cell Fact. 2015;14:106.
Li W, Chen J, Liu CX, Yuan QP, Li ZJ. Microbial production of glycolate from acetate by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol. 2019;291:41–5.
Tashiro Y, Rodriguez GM, Atsumi S. 2-Keto acids based biosynthesis pathways for renewable fuels and chemicals. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;42:361–73.
Deb SS, Reshamwala SMS, Lali AM. Activation of alternative metabolic pathways diverts carbon flux away from isobutanol formation in an engineered Escherichia coli strain. Biotechnol Lett. 2019;41:823–36.
Atsumi S, Hanai T, Liao JC. Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels. Nature. 2008;451:86–9.
Atsumi S, Wu TY, Eckl EM, Hawkins SD, Buelter T, Liao JC. Engineering the isobutanol biosynthetic pathway in Escherichia coli by comparison of three aldehyde reductase/alcohol dehydrogenase genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;85:651–7.
Liu Z, Liu P, Xiao D, Zhang X. Improving isobutanol production in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli by co-producing ethanol and modulation of pentose phosphate pathway. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;43:851–60.
Shi A, Zhu X, Lu J, Zhang X, Ma Y. Activating transhydrogenase and NAD kinase in combination for improving isobutanol production. Metab Eng. 2013;16:1–10.
Desai SH, Rabinovitch-Deere CA, Tashiro Y, Atsumi S. Isobutanol production from cellobiose in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98:3727–36.
Desai SH, Rabinovitch-Deere CA, Fan Z, Atsumi S. Isobutanol production from cellobionic acid in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact. 2015;14:52.
Felpeto-Santero C, Rojas A, Tortajada M, Galan B, Ramon D, Garcia JL. Engineering alternative isobutanol production platforms. AMB Express. 2015;5:119.
Song HS, Seo HM, Jeon JM, Moon YM, Hong JW, Hong YG, Bhatia SK, Ahn J, Lee H, Kim W, et al. Enhanced isobutanol production from acetate by combinatorial overexpression of acetyl-CoA synthetase and anaplerotic enzymes in engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018;115:1971–8.
Sauer U, Eikmanns BJ. The PEP-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node as the switch point for carbon flux distribution in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005;29(4):765–94.
Oh MK, Rohlin L, Kao KC, Liao JC. Global expression profiling of acetate-grown Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:13175–83.
Bologna FP, Andreo CS, Drincovich MF. Escherichia coli malic enzymes: two isoforms with substantial differences in kinetic properties, metabolic regulation, and structure. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:5937–46.
Clarke DM, Bragg PD. Cloning and expression of the transhydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985;162:367–73.
Sauer U, Canonaco F, Heri S, Perrenoud A, Fischer E. The soluble and membrane-bound transhydrogenases UdhA and PntAB have divergent functions in NADPH metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:6613–9.
Bastian S, Liu X, Meyerowitz JT, Snow CD, Chen MM, Arnold FH. Engineered ketol-acid reductoisomerase and alcohol dehydrogenase enable anaerobic 2-methylpropan-1-ol production at theoretical yield in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng. 2011;13:345–52.
Kawai S, Mori S, Mukai T, Hashimoto W, Murata K. Molecular characterization of Escherichia coli NAD kinase. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:4359–65.
Fernandez-Sandoval MT, Huerta-Beristain G, Trujillo-Martinez B, Bustos P, Gonzalez V, Bolivar F, Gosset G, Martinez A. Laboratory metabolic evolution improves acetate tolerance and growth on acetate of ethanologenic Escherichia coli under non-aerated conditions in glucose-mineral medium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;96:1291–300.
Mordukhova EA, Pan JG. Evolved cobalamin-independent methionine synthase (MetE) improves the acetate and thermal tolerance of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:7905–15.
Chong H, Yeow J, Wang I, Song H, Jiang R. Improving acetate tolerance of Escherichia coli by rewiring its global regulator cAMP receptor protein (CRP). PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e77422.
Gao X, Yang X, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen P, Lin Z. Engineered global regulator H-NS improves the acid tolerance of E. coli. Microb Cell Fact. 2018;17:118.
Minty JJ, Lesnefsky AA, Lin F, Chen Y, Zaroff TA, Veloso AB, Xie B, McConnell CA, Ward RJ, Schwartz DR, et al. Evolution combined with genomic study elucidates genetic bases of isobutanol tolerance in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact. 2011;10:18.
Sherkhanov S, Korman TP, Chan S, Faham S, Liu H, Sawaya MR, Hsu WT, Vikram E, Cheng T, Bowie JU. Isobutanol production freed from biological limits using synthetic biochemistry. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4292.
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:6640–5.
Kuhlman TE, Cox EC. Site-specific chromosomal integration of large synthetic constructs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e92.
Cherepanov PP, Wackernagel W. Gene disruption in Escherichia coli. TcR and KmR cassettes with the option of Flp-catalyzed excision of the antibiotic-resistance determinant. Gene. 1995;158:9–14.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32270093, 31600066, 32070111), Rizhao Science and Technology Innovation Project (2020CXZX1206), the Science and Technology Program of the University of Jinan (XKY2028), and the Higher Educational Science and Technology Program of Jinan City (2021GXRC088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG conceived the study, participated in its design, and drafted the manuscript; PG, SZ and HN constructed the plasmids and strains; CL, SJ, HZ and QL performed batch cultivation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, P., Zhao, S., Niu, H. et al. Synthesis of isobutanol using acetate as sole carbon source in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 22, 196 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-023-02197-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-023-02197-w