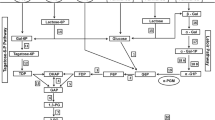
Abstract
Background
Efficient upgrading of inferior agro-industrial resources and production of bio-based chemicals through a simple and environmentally friendly biotechnological approach is interesting Lactobionic acid is a versatile aldonic acid obtained from the oxidation of lactose. Several microorganisms have been used to produce lactobionic acid from lactose and whey. However, the lactobionic acid production titer and productivity should be further improved to compete with other methods.
Results
In this study, a new strain, Pseudomonas fragi NL20W, was screened as an outstanding biocatalyst for efficient utilization of waste whey to produce lactobionic acid. After systematic optimization of biocatalytic reactions, the lactobionic acid productivity from lactose increased from 3.01 g/L/h to 6.38 g/L/h in the flask. In batch fermentation using a 3 L bioreactor, the lactobionic acid productivity from whey powder containing 300 g/L lactose reached 3.09 g/L/h with the yield of 100%. Based on whole genome sequencing, a novel glucose dehydrogenase (GDH1) was determined as a lactose-oxidizing enzyme. Heterologous expression the enzyme GDH1 into P. putida KT2440 increased the lactobionic acid yield by 486.1%.
Conclusion
This study made significant progress both in improving lactobionic acid titer and productivity, and the lactobionic acid productivity from waste whey is superior to the ever reports. This study also revealed a new kind of aldose-oxidizing enzyme for lactose oxidation using P. fragi NL20W for the first time, which laid the foundation for further enhance lactobionic acid production by metabolic engineering.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Lactobionic acid (4-O-β-galactopyranosyl-D-gluconic acid) is a versatile aldonic acid obtained from the oxidation of lactose, with a plethora of applications in the food, tissue engineering, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries, due to its excellent properties, like nontoxic, antioxidant, biocompatible, biodegradable, metal-chelating, and moisturizing properties [1,2,3]. Lactobionic acid is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a food additive, such as an acidulant with a sweet taste, a functional beverage additive and a meat water retention agents [4, 5]. Some studies suggested that the annual intake of lactobionic acid be 760 mg because it occurred in beverages and foods [6]. Commercially available lactobionic acid is primarily manufactured via chemical synthesis. This process is energy-intensive, with toxic, high-cost metals as catalysts, and generates undesirable by-products inevitably [7]. In contrast, biological synthesis has advantage of high selectivity, mild reaction, and non-toxicity, which is a more ideal alternative method. In recent years, production of lactobionic acid using biotechnological routes has been the focus of researchers, who produce lactobionic acid through enzymatic catalysis and microbial bioconversion [8,9,10]. For the enzymatic process, glucose/fructose dehydrogenase [11], cellobiose dehydrogenase [10], and carbohydrate oxidase [12] had been reported. However, the enzymes are complex to prepare, unstable in industrial environments, and require cofactors to be activated [12]. Compared with enzymes as biocatalysts, microbial cells are more desirable because of its easy preparation, cost-effectiveness, and strong robustness [1].
Many bacteria and fungi show the ability to oxidize lactose into lactobionic acid. Microorganisms belonging to the genera of Pseudomonas [4], Burkholderia [13, 14], Acetobacter [8] and Zymomonas [15] have been used for lactobionic acid production. In most cases, the cell bioconversion had lower productivity than the enzymatic catalysis method. Among these bacteria, P. taetrolens showed the highest production level (titer of 200 g/L and productivity of 7.41 g/L/h from lactose) [16, 17]. However, to compete with other methods, the lactobionic acid production titer and productivity should be further improved.
An important feature in the production of bio-based chemicals is the utilization of cheap feedstocks as raw materials in bioprocesses. Therefore, during the last few years, there have been several reports to obtain lactobionic acid through the biotechnological pathway with whey as low-cost feedstock [18,19,20]. In addition to a cheap resource, whey is also a potential pollutant generated in the dairy industry. It is difficult to be disposed of because of its high biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand and high annual production. The European Union is the world's largest producer of whey powder, with an annual production of about 1.9 million tons, but only a small portion of whey is processed into powder due to its low commercial value [21]. Apart from water, the main content in whey is lactose (up to 70% by dry weight), which can serve as an ideal substrate to produce lactobionic acid and thus upgrading this inferior raw substrate.
In this study, we aimed to isolate a microorganism to convert lactose into lactobionic acid with high catalytic performance. Various strategies were applied to improve the productivity of lactobionic acid biosynthesis at high substrate concentrations from cheese whey. We also sequenced the entire genome of the isolated strain (Pseudomonas fragi NL20W), and based on these informations, a novel pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase (PQQ-GDH) was determined as lactose-oxidizing enzyme. These findings expand the current understanding of P. fragi NL20W and GDH for aldonic acids biosynthesis and prove the potential industrial applicability of them for lactobionic acid production on a large-scale.
Results and discussion
Investigating the catalytic performance of P. fragi NL20W
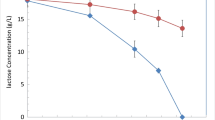
In order to test the ability of P. fragi NL20W to oxidize lactose, reactions were performed using resting cells of P. fragi NL20W with different cell concentration (OD600nm 5 and 20, 1.63*1010 CFU corresponding to OD600nm 1). As shown in Fig. 1, regardless of the cell dosage, all lactose was oxidized into lactobionic acid as the sole product (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). The catalytic rate at OD600nm 20 was significantly higher than that at OD600nm 5, which consumed all lactose in 24 h and 60 h, respectively.
In previous studies, Mao et al. found that P. fragi TCCC11892 had the ability to oxidize lactose into lactobionic acid when investigating the ability of four species of Pseudomonas to produce aldonic acids [22]. Beyond that, no P. fragi strain was reported as lactobionic acid producer. However, no further study of P. fragi TCCC11892 on lactobionic acid production was followed. This research on P. fragi NL20W is the first detailed investigation on lactobionic acid production by P. fragi species.
Effect of carbon source on the catalytic performance of P. fragi NL20W
Although LB medium is rich in carbon and nitrogen resource, which make the strain grow well, we tried to replace it with a cheap medium due to its high price. In a co-fermentation system, Alonso et al. combined cheese whey and glucose or glycerol as co-substrates to investigate their effects on lactobionic acid production patterns [23]. In this study, glucose or glycerol was used as a carbon source supplemented with a trace of yeast extract and mineral salts to determine which medium enabled the highest catalytic activity. P. fragi NL20W could grow fast in both glucose and glycerol media, comparable to that in LB medium, but the catalytic performances of cells collected from different media were obviously different. The oxidation rate of cells grown in glycerol medium was significantly faster than that in glucose medium, and even faster than that in LB medium unexpectedly, regardless of using resting cells or growing cells as biocatalysts (Fig. 2). For resting cells, the yield of lactobionic acid obtained from glycerol-cultured cells reached 87.98% at 48 h, which was 11.52% higher than that produced by glucose-cultured cells. For growing cells, the yields of lactobionic acid were 99.75%, 89.51% and 78.43% by glycerol-cultured, LB-cultured, and glucose-cultured cells at 48 h, with lactobionic acid productivity of 0.95 g/L/h, 0.92 g/L/h, and 0.77 g/L/h, respectively. The consumption rate of lactose was faster than that in the resting cells catalytic system. Overall, the results for cell growth and lactobionic acid production indicated that glycerol was a better carbon source, which was used in the following experiments.
Effect of carbon source on lactobionic acid production. Reaction conditions: A, resting cells harvested from different media, 50 g/L lactose, cell densities of 5 at OD600nm, 7.3 g/L CaCO3, 30 °C, pH 7.0, 200 rpm; B, growing cells in different media, initial inoculation of 0.2 at OD600nm, other conditions same as A
Production of lactobionic acid from lactose by resting cell in the flask
The biocatalytic conditions including pH, temperature, and metal ions were commonly surveyed to determine their effects on lactobionic acid production [4, 20, 24, 25]. In order to further increase the lactobionic acid productivity of P. fragi NL20W, these parameters were studied in detail. When the temperature was raised from 25 °C to 35 °C, there were no obvious differences in lactobionic acid yield and productivity. However, when the temperature was further increased to 40 °C, lactose oxidation occurred only in the initial 12 h, with final lactobionic acid yield of 29.62%. The concentration of lactose remained constant after 12 h, which indicated high temperature inhibiting the oxidative activity of P. fragi NL20W toward lactose (Fig. 3A, B). With the increase of pH from 6.0–7.5, the lactose oxidation ability of P. fragi NL20W substantially decreased. In the first 12 h, pH had little effect on the catalytic performance of P. fragi NL20W. In contrast, from 12 to 36 h, it could be obviously found that the catalytic efficiency was much higher under pH 6.0 (Fig. 3C, D). At pH 6.0, lactose was almost exhausted after 36 h, with lactobionic acid productivity of 1.20 g/L/h, which suggested the lactose oxidative activity of P. fragi NL20W favored slightly acidic conditions.
Effects of temperature (A, B) and pH (C, D) on lactobionic acid production. Reaction conditions: A, 50 g/L lactose, cell densities of 5 at OD600nm, 7.3 g/L CaCO3, temperature in the range of 25 °C–40 °C, pH 7.0, 200 rpm; B, same as A; C, 50 g/L lactose, cell densities of 5 at OD600nm, 7.3 g/L CaCO3, 30 °C, pH in the range of 6.0–7.5, 200 rpm; D, same as A
Figure 4A showed the effect of metal ions on lactobionic acid production. It was found that all examined metal ions, including Ca2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, and Cu2+ had positive effects on lactose oxidation. Among them, Mg2+ played the most significant role, with lactobionic acid yield increased by 85% at 12 h compared to the control. Although other metal ions could also promote the production of lactobionic acid, but their effects were not as positive as Mg2+. Next, the optimal concentration of Mg2+ ranging from 0.1 mM to 2.0 mM was further investigated. When the concentration of Mg2+ varied from 0.1 mM to 0.5 mM, the yields of lactobionic acid at 36 h increased from 87.93% to 93.54%, but the yields did not further increase at higher Mg2+ concentration (Fig. 4B). Finally, the catalytic performance of P. fragi NL20W before and after optimization was evaluated and compared under high lactose concentration. As shown in Fig. 5, lactose was basically converted until 84 h before optimization, while 250 g/L lactose could be completely converted at 40 h and 300 g/L lactose at 84 h after optimization. The productivities were increased from 3.01 g/L/h to 6.38 g/L/h at 250 g/L, and 3.56 g/L/h to 6.25 g/L/h at 300 g/L, indicating the effectiveness of the combined optimal reaction conditions.
Production of lactobionic acid from whey powder by growing cell in the bioreactor
To further investigate the performance of P. fragi NL20W and elevate the cost effectiveness, batch cultivation experiments were carried out in a 3 L bioreactor with whey powder as substrate under controlled conditions. Glycerol was still adopted as carbon source to facilitate cell growth and lactose conversion. Two different strategies were undertaken to evaluate the effect of whey powder adding time on lactobionic acid production. When whey powder was added simultaneously with cell inoculation, a total of 200 g/L lactose could be completely converted in 87 h with an average productivity of 1.62 g/L/h (Additional file 1: Fig. S2). Due to the turbidity of the whey components, the optical density of the strain could not be accurately measured. However, the unspecified components in whey or other harmful effects including high osmolality might influence the cell growth of P. fragi NL20W, and render the reaction rate sluggish. Therefore, we also determined the lactobionic acid production profiles when whey powder was added at the middle and late logarithmic phase. In any case, the productivities of lactobionic acid could be enhanced to a large extent. In the case that the whey powder containing 200 g/L lactose was added at 8 h (late logarithmic phase), and the yield of lactobionic acid reached 100% at 78 h with average productivity of 3.01 g/L/h (Fig. 6A), which was 85.80% higher than that of adding whey powder at 0 h. We also tried to increase the lactose concentration in whey to 300 g/L. In this case, the whey powder was added at 6 h (middle logarithmic phase), and all lactose could be quickly converted into lactobionic acid in 102 h with a yield of 100% and average productivity of 3.09 g/L/h (Fig. 6B). Although the lactobionic acid productivities using whey powder as substrate were lower than that using pure lactose, the results in this study outperformed the best reports with P. taetrolens as biocatalyst (Table 1). Compared with previous studies, this study made significant progress both in improving lactobionic acid titer and productivity. These results also demonstrated the new isolated P. fragi NL20W strain had great application potential in the valorization of waste cheese whey to lactobionic acid.
Identification of enzyme involved in lactose oxidation
After demonstrating that P. fragi NL20W was a good biocatalyst for conversion of lactose and cheese whey to lactobionic acid, we expected to better understand the enzyme involved in this oxidation reaction. Presently, many kinds of lactose-oxidizing enzymes had been identified from both fungal and bacteria. For bacteria, such lactose-oxidizing enzymes included PQQ-dependent glucose dehydrogenase [26], glucose-fructose oxidoreductase [29], and malate:quinone oxidoreductase [28]. In this research, based on genome annotation and sequence alignment, six candidate enzymes of P. fragi NL20W were selected, including four PQQ-dependent glucose dehydrogenases and two malate:quinone oxidoreductases (Additional file 1: Table S1). Their functions in lactose oxidation were assessed through heterologous overexpression in P. putida KT2440, which innately had poor ability to convert lactose into lactobionic acid.
The four GDH genes and two MQO genes were cloned into the expression vector pBBR1MCS2, resulting in 6 different plasmids, which were individually transformed into P. putida KT2440 to examine their roles in the synthesis of lactobionic acid. As shown in Fig. 7A, although wild-type P. putida KT2440 could convert lactose into lactobionic acid to some extent, the conversion rate was rather low, with yields of 13.57% and 26.69% after 12 h and 24 h, respectively. By contrast, the derivative strain overexpressing GDH1 showed significantly increased yields, at 79.54% and 100% after 12 h and 24 h, respectively. The lactobionic acid yield increased by 486.1%. These results were almost as good as those obtained by P. fragi NL20W. However, the other 5 candidate genes gave detrimental effects on lactose conversion, presumably due to the additional burden caused by exogenous plasmids. Furthermore, we performed homologous expression of GDH1 gene in P. fragi NL20W, and the lactobionic acid yields of 12 h slightly increased from 89.07% to 93.54% (Fig. 7B). As wild-type P. fragi NL20W was outstanding enough, further strengthen of lactobionic acid production might require more than just enzyme overexpression. Other strategies should also be considered, such as balanced coexpression of GDH and cofactor PQQ, sufficient oxygen supply, etc. Anyway, the GDH1 from P. fragi NL20W was identified as a novel lactose-oxidizing enzyme of P. fragi.
We performed amino acid sequence analysis of GDH1 from P. fragi NL20W, which was predicted to be a membrane-bound PQQ glucose dehydrogenase (http://harrier.nagahama-i-bio.ac.jp/sosui/sosui_submit.html). Glucose dehydrogenases harboring PQQ are widely distributed in Pseudomonas sp., which participate in glucose metabolism to oxidize glucose into gluconic acid. Among them, the PQQ-dependent glucose dehydrogenase from P. putida KT2440 is the most scientifically and industrially attractive [30]. Although it exhibits high catalytic efficiency upon glucose, its narrow substrate specificity limits the application in lactose oxidation. In addition to this, the PQQ-dependent glucose dehydrogenase from P. taetrolens had been reported to convert lactose into lactobionic acid [17]. In terms of substrate specificity, the GDH from P. taetrolens varied significantly with that of our research. For example, the GDH from P. taetrolens had no activity towards arabinose [17], but the GDH from P. fragi NL20W did (data not shown), which also indicated the GDH in this study is a new kind of aldose-oxidizing enzyme.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a new strain identified as P. fragi with high lactobionic acid production ability was isolated and its potential in the upgrading of cheese whey was fully exploited. An efficient approach was developed for improving lactobionic acid titer and yield even the substrate up to 300 g/L. In addition, scale-up synthesis was realized in the bioreactor, which laid the foundation for large-scale industrial production processes. It is of interest to uncover a novel membrane-bound GDH (GDH1) playing a pivotal role in lactose oxidation. Further study on the substrate spectrums of P. fragi NL20W and GDH1 might reveal their advantages in the production of other aldonic acids.
Materials and methods
Isolation and genome sequencing of P. fragi NL20W
P. fragi NL20W was isolated from soil samples obtained from Purple Mountain (Nanjing, China). Based on the analysis of 16S ribosomal RNA and phylogenetic tree (Additional file 1: Fig. S3), strain NL20W was identified as P. fragi. Whole-genome sequencing of P. fragi NL20W was also performed and submitted to GenBank under accession No. CP064354.1.
Microorganism, medium, and growth condition
P. fragi, P. putida and Escherichia coli strains (Additional file 1: Table S2) were grown and proliferated in Luria–Bertani (LB) broth at 30 °C and 37 °C, respectively, with 200 rpm shaking for 12 h. If required, 50 µg mL−1 kanamycin was added to the medium to avoid loss of the plasmid. All used solid media contained 15 g L−1 agar.
To replace LB medium with a cheap medium, glucose mineral medium and glycerol mineral medium were used. The medium consisted of 5.0 g/L glucose or glycerol, 5.0 g/L yeast extract, 3.4 g/L Na2HPO4, 1.5 g/L KH2PO4, 0.25 g/L NaCl, 0.5 g/L NH4Cl, 0.52 g/L MgSO4, and 2.5 mL/L A9 solution, with pH 7.0. A9 solution was composed of the following: H3BO3 300 mg/L, ZnCl2 50 mg/L, MnCl2·4H2O 30 mg/L, CoCl2 200 mg/L, CuCl2·2H2O 10 mg/L, NiCl2·6H2O, 20 mg/L, and Na2MoO4·2H2O 30 mg/L.
Lactobionic acid production by resting cells in the flask
To examine the effect of carbon resource on lactose catalytic performance of P. fragi NL20W, overnight culture in LB medium was spun by centrifugation (12000 g, 25 °C, 5 min), and transferred to fresh LB medium, glucose mineral medium and glycerol mineral medium, respectively, with a starting OD600nm of 0.2. After incubating at 30 °C and 200 rpm for 12 h, cells were harvested by centrifugation (8000 g for 10 min) and washed with 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) three times. Biotransformation experiments were conducted in 250 mL flasks containing 10 mL of resting cells with optical density of 5 at OD600nm, 50 g/L lactose, and 7.3 g/L CaCO3 in 200 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C and 200 rpm.
To investigate the effect of temperature on lactobionic acid production, biotransformation experiments were carried out at 25 °C, 30 °C, 35 °C, and 40 °C, respectively, while other reaction conditions remained the same. To investigate the effect of pH on lactobionic acid production, biotransformation experiments were carried out at pH 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, and 7.5, respectively, while other reaction conditions remained the same. Effect of metal ions, including Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+, and Cu2+, on lactobionic acid production was tested at the final concentrations of 1 mM, and the effect of Mg2+ concentration was evaluated from 0.1 mM to 2.0 mM. Other reaction conditions remained the same.
Lactobionic acid production by growing cells in the flask
Overnight culture in LB medium was spun by centrifugation (12000 g, 25 °C, 5 min), and transferred to fresh LB medium, glucose mineral medium and glycerol mineral medium, respectively, with a starting OD600nm of 0.2. All media also contained 50 g/L lactose and 7.3 g/L CaCO3. Cell growth and lactose bioconversion were accomplished 30 °C and 200 rpm.
Fermenter condition
Batch fermentation was carried out in a 3 L bioreactor (BXBio, Shanghai, China) at a working volume of 1 L. P. fragi NL20W was pre-cultured in glycerol mineral medium, spun by centrifugation and transferred to fresh glycerol mineral medium with a starting OD600nm of 1. Whey powder was directly added to the medium, making lactose with final concentration of 200 g/L or 300 g/L. Bioreactor experiments were conducted with an agitation rate of 350 rpm, and an aeration rate of 1.0 vvm. Excessive foam formation was prevented by the addition of a drop of defoamer. During lactobionic acid production, pH was maintained at 6.0 via automatic addition of 25% NaOH.
Plasmid and strain constructions
To express GDH1 (QPC34881.1), GDH2 (QPC33644.1), GDH3 (QPC33554.1), GDH4 (QPC37981.1), MQO1 (QPC37714.1), and MQO2 (QPC35030.1) encoding genes from P. fragi NL20W, pBBR1MCS2 was used as the expression vector. Oligonucleotide primers used were listed in Table S3. pBBR1MCS-GDH1, pBBR1MCS-GDH2, pBBR1MCS-GDH3, pBBR1MCS-GDH4, pBBR1MCS-MQO1, and pBBR1MCS-MQO2 were constructed by replacing the lacZα fragment of pBBR1MCS2 with GDH and MQO genes, respectively, using the pEASY®-Basic Seamless Cloning and Assembly Kit (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China). The resultant plasmids were individually transformed into P. fragi NL20W and P. putida KT2440 via electroporation at 2400 V, 200 Ω, and 25 μF.
Analytical methods
Bacterial growth was measured using a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 600 nm (OD600nm). Lactobionic acid and lactose contents of culture samples were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (Agilent 1100 series, USA) equipped with a Coregel ION 300 column (Concise Separations, USA) and a refractive index detector (Shimadzu, Japan). The column was eluted with 0.5 mM H2SO4 at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min with the column temperature set at 75 °C.
The lactobionic acid yield was calculated as follows:
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article.
Abbreviations
- GDH:
-
Glucose dehydrogenase
- PQQ:
-
Pyrroloquinoline quinone
- LB:
-
Luria–bertani
- OD:
-
Optical density
References
Alonso S, Rendueles M, Díaz M. Bio-production of lactobionic acid: current status, applications and future prospects. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31:1275–91.
Sarenkova I, Ciprovica I. The current status and future perspectives of lactobionic acid production: a review. Res Rural Dev. 2018;1:233–9.
Cardoso T, Marques C, Dagostin JLA, Masson ML. Lactobionic acid as a potential food ingredient: recent studies and applications. J Food Sci. 2019;84:1672–81.
Alonso S, Rendueles M, Díaz M. Efficient lactobionic acid production from whey by Pseudomonas taetrolens under pH-shift conditions. Biores Technol. 2011;102:9730–6.
Gutiérrez LF, Hamoudi S, Belkacemi K. Lactobionic acid: a high value-added lactose derivative for food and pharmaceutical applications. Int Dairy J. 2012;26:103–11.
Kiryu T, Kiso T, Nakano H, Ooe K, Kimura T, Murakami H. Involvement of Acetobacter orientalis in the production of lactobionic acid in caucasian yogurt (“caspian sea yogurt”) in Japan. J Dairy Sci. 2009;92:25–34.
Pleissner D, Dietz D, van Duuren JBJH, Wittmann C, Yang X, Lin CSK, et al. Biotechnological production of organic acids from renewable resources. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2019;166:373–410.
Kiryu T, Yamauchi K, Masuyama A, Ooe K, Kimura T, Kiso T, et al. Optimization of lactobionic acid production by Acetobacter orientalis isolated from caucasian fermented milk, “caspian sea yogurt.” Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76:361–3.
Goderska K, Szwengiel A, Czarnecki Z. The utilization of Pseudomonas taetrolens to produce lactobionic acid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014;173:2189–97.
Yang J, Xu P, Long L, Ding S. Production of lactobionic acid using an immobilized cellobiose dehydrogenase/laccase system on magnetic chitosan spheres. Process Biochem. 2021;100:1–9.
Borges da Silva EA, Pedruzzi I, Rodrigues AE. Simulated moving bed technology to improve the yield of the biotechnological production of lactobionic acid and sorbitol. Adsorption. 2011;17:145–58.
Nordkvist M, Nielsen PM, Villadsen J. Oxidation of lactose to lactobionic acid by a microdochium nivale carbohydrate oxidase: Kinetics and operational stability. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1996;189:503–5.
Murakami H, Seko A, Azumi M, Kiso T, Kiryu T, Kitahata S, et al. Microbial conversion of lactose to lactobionic acid by resting cells of Burkholderia cepacia No 24. J Appl Glycosci. 2006;53:7–11.
Murakami H, Seko A, Azumi M, Ueshima N, Yoshizumi H, Nakano H, et al. Fermentative production of lactobionic acid by Burkholderia cepacia. J Appl Glycosci. 2003;50:117–20.
Malvessi E, Carra S, Pasquali FC, Kern DB, Da Silveira MM, Ayub MAZ. Production of organic acids by periplasmic enzymes present in free and immobilized cells of Zymomonas mobilis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;40:1–10.
Oh YR, Jang YA, Hong SH, Han JJ, Eom GT. Efficient production of lactobionic acid using genetically engineered Pseudomonas taetrolens as a whole-cell biocatalyst. Enzyme Micro Technol. 2020;141:109668.
Oh YR, Jang YA, Lee SS, Kim JH, Hong SH, Han JJ, et al. Enhancement of lactobionic acid productivity by homologous expression of quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase in Pseudomonas taetrolens. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68:12336–44.
Alonso S, Rendueles M, Díaz M. Feeding strategies for enhanced lactobionic acid production from whey by Pseudomonas taetrolens. Biores Technol. 2013;134:134–42.
Alonso S, Rendueles M, Díaz M. Microbial production of specialty organic acids from renewable and waste materials. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2015;35:497–513.
Alonso S, Rendueles M, Díaz M. Tunable decoupled overproduction of lactobionic acid in Pseudomonas taetrolens through temperature-control strategies. Process Biochem. 2017;58:9–16.
Rocha JM, Guerra A. On the valorization of lactose and its derivatives from cheese whey as a dairy industry by-product: an overview. Eur Food Res Technol. 2020;246:2161–74.
Mao S, Liu Y, Hou Y, Ma X, Yang J, Han H, et al. Efficient production of sugar-derived aldonic acids by Pseudomonas fragi TCCC11892. RSC Adv. 2018;8:39897–901.
Alonso S, Rendueles M, Díaz M. Simultaneous production of lactobionic and gluconic acid in cheese whey/glucose co-fermentation by Pseudomonas taetrolens. Biores Technol. 2015;196:314–23.
Alonso S, Rendueles M, Díaz M. Selection method of pH conditions to establish Pseudomonas taetrolens physiological states and lactobionic acid production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97:3843–54.
Wang DM, Sun L, Sun WJ, Cui FJ, Gong JS, Zhang XM, et al. Purification, characterization and gene identification of a membrane-bound glucose dehydrogenase from 2-keto-D-gluconic acid industrial producing strain Pseudomonas plecoglossicida JUIM01. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118:534–41.
Kiryu T, Kiso T, Koma D, Tanaka S, Murakami H. Identifying membrane-bound quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase from acetic acid bacteria that produce lactobionic and cellobionic acids. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2019;83:1171–9.
Miyamoto Y, Ooi T. Kinoshita S. Production of lactobionic acid from whey by Pseudomonas sp. LS13–1. Biotechnol Lett. 2000;22:427–30.
Oh YR, Jang YA, Hong SH, Eom GT. Purification and characterization of a malate:quinone oxidoreductase from Pseudomonas taetrolens capable of producing valuable lactobionic acid. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68:13770–8.
Satory M, Fürlinger M, Haltrich D, Kulbe KD, Pittner F, Nidetzky B. Continuous enzymatic production of lactobionic acid using glucose-fructose oxidoreductase in an ultrafiltration membrane reactor. Biotech Lett. 1997;19:1205–8.
An R, Moe LA. Regulation of pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase activity in the model rhizosphere-dwelling bacterium Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016;82:4955–64.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22078163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW and PL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing—original draft. ZZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing—review & editing. JO: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1. A
Chromatogram of commercial lactose. B Chromatogram of commercial lactobionic acid. C Chromatogram of lactose and lactobionic acid in the sample. Figure S2 Lactobionic acid production from whey powder in 3 L bioreactor. Reaction conditions: whey powder containing 200 g/L lactose added at the beginning, initial inoculation of 1 at OD600nm, 30 °C. Figure S3. Phylogenetic tree derived from 16S rDNA sequence of different strains based on the Neighbor-Joining method. Bootstrap values are given on each branch. Strain NL20W clearly clusters with other strains in the so-called P. fragi lineage. Table S1 BLAST results of GDHs and MQOs from P. fragi NL20W with reported lactose-oxidizing enzymes. Table S2 Strains and plasmids used in this study. Table S3 Oligonucleotide primers used in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Liu, P., Zheng, Z. et al. Valorization of cheese whey to lactobionic acid by a novel strain Pseudomonas fragi and identification of enzyme involved in lactose oxidation. Microb Cell Fact 21, 184 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01907-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01907-0