Abstract
Background
Compared with corn, wheat contains higher crude protein, amino acids concentration. However, wheat contains a mass of anti-nutritional factors, resulting in increased of the digesta viscosity and impaired the intestinal function in ruminant.
Objective
This study aimed to investigate the effects of substitution of different amounts of wheat for corn on hepatic metabolism in the Tibetan lamb.
Methods
Ninety Tibetan lambs (Body weight = 12.37 ± 0.92 kg) were randomly assigned to three groups: 0% wheat diet (Control), 10% wheat diet (Low group), and 15% wheat diet (High group). The feeding trial lasted for 130 d, including a 10 d adaption period. Hepatic gene expression profiling was performed via RNA sequencing after the conclusion of the feeding trials.
Results
Results showed that greater level of glutathione peroxidase levels in L group compared with those of the C and H groups (P < 0.05). The immune indexes, including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), immunoglobulin A (IgA), and IgM were also elevated in L group compared with the other groups (P < 0.05). Compared with H group, the hepatocytes were arranged radially, and hepatic plates anastomosed with each other to form a labyrinth-like structure in L group. Transcriptomic analysis showed 872 differentially expressed genes (DEG) between H and L group, of which 755 were down-regulated and 117 were up-regulated. Through Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis, 32 pathways were significantly enriched (Q-value < 0.05), such as the cAMP signaling pathway, Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, leukocyte transendothelial migration, platelet activation and adipocytokine signaling pathway. Additionally, the expression of comment DEGs were verified via quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction.
Conclusion
In summary, our findings suggest that wheat can be supplemented up to 10% in Tibetan sheep, contributing to improve the hepatic oxidative stress, immune response and lipid metabolism through regulating the expression of related genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries) is one of the original breeds in China, mainly distributed across Qinghai, Tibet, Gansu and Sichuan provinces, where they inhabit regions with an altitude of over 3000 m. Notably, this species demonstrates remarkable adaptation to the harsh environmental conditions prevalent in these areas, which include extreme cold, low oxygen and strong ultraviolet radiation [1]. Consequently, Tibetan sheep provide a wide variety of resources including meat, milk, fuel, and pelage for the indigenous herdsmen [2].
As the most intricate metabolic organ in mammals, the liver contributes to numerous vital functions, such as digestion, absorption and excretion, material and energy metabolism, immune responses, and detoxification [3]. The liver contributes significantly to gluconeogenesis and the regulation of blood glucose levels [4]. Furthermore, liver sinusoidal cells are responsible for removing harmful metabolites and exogenous microorganisms, thereby maintaining immune balance [5]. Therefore, the nutrient metabolism of the liver is crucial to the growth and development of livestock.
As the breeding industry has rapidly evolved, a significant challenge has emerged: the scarcity of corn resources, now a critical issue in animal husbandry. In the year 2022, there was a notable 7.0% rise in the average price of corn. In contrast, wheat’s average price saw a decrease of 3.76%. This disparity led to a major shift in China, where the breeding industry turned to wheat, using nearly 45 million tons—a staggering 95.7% increase from previous years. Meanwhile, in Europe, wheat has long been the go-to energy feed for animal husbandry, further cementing its status as the preferred alternative to corn.
In comparison to maize, wheat contains approximately 5% more crude protein and is second only to that of maize in terms of its effective energy content. This makes it a promising alternative to maize feed [6]. While both wheat and maize have significant starch content, the rumen only digests around 60% of maize starch, compared to over 90% of wheat starch [7]. Previous research has shown that increasing the dietary wheat ratio in livestock did not result in significant differences in growth performance and apparent nutrient digestibility [8]. However, it is important to note that wheat contains a high concentration of anti-nutritional factors, especially araboxylan. These factors increase the digesta viscosity in the gut, potentially impairing ruminant intestinal function [9]. Therefore, identifying an appropriate wheat replacement ratio is crucial for optimal livestock development and growth.
However, little attention has been paid to the effect of dietary wheat on liver of ruminant. In light of the above considerations, the objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of varying wheat proportions in the diet, on hepatic oxidative damage, immune response, and lipid metabolism in the Tibetan sheep by RNA-Seq sequencing technology.
Materials and methods
Ethical statement
All animal procedures for experiments were approved by the Committee of Experimental Animal care and handling techniques were approved (QUA-2020–0710) by the Qinghai University of Animal Care Committee. Moreover, all applicable rules and regulation of the organization and government were followed regarding the ethical use of experimental animals.
Animal diet and sample collection
A total of 90 healthy male Tibetan lambs with similar body weight (12.37 ± 0.92 kg) and physiological state were selected. According to dietary treatments, the lambs were randomly divided into three treatment groups, including a control group (100% corn), 10% wheat group (10% substitution for corn), 15% wheat group (15% substitution for corn), and 100% wheat group (100% substitution for corn) on a DM basis. This feeding trial was conducted at a commercial sheep farm in Gonghe County, Qinghai Province, China (Coordinate 100o75’N, 35o57’E, altitude at 3,370 m). All three diets contained approximately 30% forage and 70% concentrate (Table 1) and included 1:1 ratios of silage grass and oat hay. Daily nutrient requirements were met for all lambs (NRC, 2007) [10]. Fresh drinking water and feed were provided ad libitum. The adaptation period for the diet changes lasted 10 d, and the study continued for 120 d. At the end of the experiment, nine sheep, with three replicates each, were randomly selected and rendered unconscious with a stunning machine before being bled to death by neck bleeding (Stun machine model: AOSH 2000, AOSH Automation Technology Company, Wuxi, China). After slaughter, liver samples were taken and placed immediately into liquid nitrogen for RNA extraction, while the remaining tissue samples were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for tissue sectioning.
Chemical analysis
The dry matter (DM) content was determined by drying the feeds at 105 °C in a forced-air oven for 4 h. The CP (ID number 968.06), ether extract (EE) (ID number 920.39), and ash (ID number 942.05) contents in diet were measured as proposed by the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (1990). Neutral detergent fiber (NDF) was analyzed as proposed by Licitra et al. (1996) [11]. Acid detergent fiber (ADF) was determined using the methods described by Van Soest et al. (1991) [12].
Antioxidant and immune response index assays
Superoxide dismutase (SOD), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and malondialdehyde (MDA) values of hepatic oxidative stress parameters in sheep were analyzed by using Elisa Kit. IL-1β, TNF-α, immunoglobulin A (IgA), IgG, and IgM values of hepatic immune indices were also analyzed by using Elisa Kit. All ELISA kits used in this study were procured from Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China).
Histological analysis of the liver
Tissues were fixed, paraffin-embedded, and sectioned (5 μm) with a rotary microtome, as per the protocol outlined by Prophet et al. (Prophet et al., 1992). Hematoxylin and eosin were used to stain the tissue sections. The stained slides were evaluated using a DP2-BSW digital microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at 40 × magnification. Cross-sectional areas of the liver were determined using Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software (Media Cybernetics Inc., Bethesda, MD, USA).
RNA-Seq analysis
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and was quantified by the 260/280 nm absorbance ratio using a NanoDrop ND2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The integrity of RNA and the library was examined using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The final cDNA libraries were constructed using Illumina NovaseqTM 6000 following the vendor’s recommended protocol. The raw reads with low-quality reads, adaptors, and highly unknown base N content were trimmed using SOAPnuke, a filtering software developed by BGI. Then, clean reads were aligned to the sheep reference genome of Ovis aries (Oar_Version 3.1) using HISAT2 (Version 2.1.0).
DESeq2 package in R were used to normalize read counts and detect differentially expressed genes (DEGs) at a False Discovery Rate (FDR) threshold of 0.05. Genes with |log2Fold Change|> 0.5 and Q-values < 0.05 were recognized as DEGs.
The Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways were performed using the phyper package in R (Version 3.6.2). After FDR correction, a Q-value < 0.05 was used as a threshold. All analyses with a Q-value < 0.05 were considered significantly enriched. The gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed by GSEA software (Version 4.1.0) on three sets of genes (IL-6-JAK-STAT3-PATHWAY, REACTIVE-OXYGEN-SOECIES-PATHWAY, FATTY-ACID-METABOLISH) screened from the GSEA database. Additionally, the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was created by Cytoscape software (Version 3.8.0).
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
Nine DEGs were randomly selected for qRT-PCR to verify the accuracy of the transcriptome sequencing data. The mRNA expression of the DEGs was normalized to the expression of the housekeeping gene glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in the different samples. The primers used for this study were designed using an online primer design tool and the sequences are presented in Table 2. Relative expression of genes was calculated by the 2−ΔΔCt method.
Correlation analysis
Correlation network analysis was performed using the OmicStudio tools. The data for correlation analysis were derived from ELISA and fluorescence quantitative measurement results.
Results
Antioxidant and immune response index assays
As shown in Table 3, the indicators of glutathione peroxidase in L group demonstrated a statistically significant increase compared to the C and H groups (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the indicators of interleukin-1β, immunoglobulin (Ig)A, and IgM in L group were significantly elevated compared with the levels in the other two groups (P < 0.05).
Histological analysis of the liver
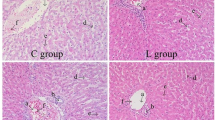
As illustrated in Fig. 1, the hepatocytes in the L group displayed a radial arrangement, forming hepatic plates that were centered around the central vein. Additionally, these plates anastomosed with each other, forming a lost-like structure. On the other hand, in the H group, hepatic lobules were indistinguishable from the surrounding liver tissue, and the hepatic plates were separated from each other, resulting in a loosely distributed arrangement of hepatocytes.
Characterization of RNA-Seq data
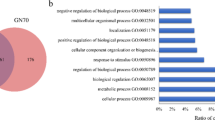
Mapping of the reads obtained from sequencing against the Ovis reference genome resulted in between 40 and 51 million reads per sample, with an average of 43 million reads. Quality control measures were applied to ensure that the Q30 (%) score was ˃98% for each sample, while the GC content (%) was > 45%. The mapping rate for reads were ˃90%, with an average of 92.36%. The nonsplice reads were > 37.57%, and the percentage of multi-mapped reads was 60% (average = 59.83%). Additionally, a total of 12160 genes were obtained based on the similarity > 97%. Of those, 492 genes were unique to the C group, 973 genes were unique to the L group, 338 genes were unique to the H group (Fig. 2A). Based on Binary-Jaccard algorithm, the first two axes of the PCA1 explained 97.26% and 1.34% of the variation and the two principal components covered 98.60% of the variation (Fig. 2B).
DEGs identification and KEGG pathways analyses
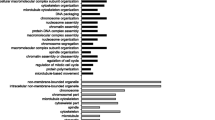
A total of 1346 DEGs were identified according to the Q values (< 0.05). Specifically, in C vs. L, 37 genes were upregulated and 81 genes were downregulated (Fig. 3A). In C vs. H, 134 genes were upregulated (Fig. 3B). In L vs. H, 117 genes were upregulated and 755 genes were downregulated (Fig. 3C). KEGG pathway analysis revealed that the common DEGs were enriched in 196 pathways and significantly enriched in 32 pathways. A number of significantly enriched pathways, including cAMP signaling pathway, Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, leukocyte transendothelial migration, platelet activation and adipocytokine signaling pathway were related to immune response and lipid metabolism (P < 0.05).
Volcano plot displaying DEGs between the C and L groups (A), between the C and H groups (B), and between the L and H groups (C). Sig-Up: Significantly upregulated genes. FC-Up-Only: Only FC values differ to upregulate genes. pval-Only: Only P-value difference genes. NoDiff: no significantly different genes. FC-Down-Only: Only FC values differ in down-regulated genes. Sig-Down: Significantly downregulated genes
GSEA and PPI network analyses
Three background gene sets, including IL-6-JAK-STAT3-PATHWAY, REACTIVE-OXYGEN-SOECIES-PATHWAY and FATTY-ACID-METABOLISH, were selected and analyzed (Fig. 4). The results revealed that the L group exhibited positive enrichment in all three gene sets when compared with the C group, while the H group exhibited negative enrichment in the gene sets.
PPI network interaction analysis was conducted for further evaluation of the differential gene relationships and identification of the hub genes. The results, as illustrated in Fig. 5, revealed that the top 10 hub genes were interleukin 1 beta (IL-1B), protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type A (PTPRA), transcription factor AP-1-like (C-JUN), tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein eta (YWHAH), phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 5 (PIK3R5), ATP synthase 5a1 (ATP5A1), mitochondrial Fo complex subunit C3 (ATP5G3), 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase (HMGCS), mitochondrial Fo complex subunit C3 (ATP5G3), and ornithine decarboxylase 1 (ODC1).
Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network. Red represents the FATTY-ACID-METABOLISM gene set, blue represents the REACTIVE-OXYGEN-SPECIES-pathway gene set, and purple represents the IL6-JAK-STAT3-SIGNALING gene set. The network diagram’s circle size indicates the number of nodes that are linked, and the greater the circle's diameter, the more nodes that are connected
Correlation of phenotypic data with sequencing data and verification of qRT-PCR
Nine functional DEGs, including succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit C (SDHC), NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase core subunit S1 (NDUFS1), malate dehydrogenase 2 (MDH2), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), acyl-CoA dehydrogenase long chain (ACADL), hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 4 (HSD17B4) and 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase (HIBCH), were selected for qRT-PCR verification of the RNA-Seq data. The results revealed consistent correlations between the RNA-Seq results and the mRNA levels measured by qRT-PCR (Fig. 6).
In addition, the association between antioxidant and immune response index data, and the level of gene expression identified through sequencing was also investigated. The results of this analysis revealed that MDA, GSH-Px, T-AOC, SOD, IL-1, TNF, IgG, IgM, and IgA were substantially connected with the stability and sequencing data as well as with the accuracy of the number of sequencing data (Fig. 7).
Correlation Network of antioxidant correlation (A) and immunity correlation (B). The number of nodes connected to the gene increases with increasing purple color, whereas nodes decrease with increasing green color. abs-rho: demonstrates the degree of association. The silver dotted line denotes a negative connection, whereas the solid gold line denotes a positive correlation
Discussion
The liver is an important organ and has very pivotal physiological functions, such as nutrient metabolism, detoxification and absorption [13]. However, excessive intake of nutrients or dietary components led to damage to the liver. It was found that a high-fat diet resulted in severe steatosis, swelling of hepatocytes, and a significant increase in apoptosis in rats [14]. Similarly, high starch in diet caused leds to disruption of hepatic glycogen metabolism and liver fibrosis via mediating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [15]. Additionally, high rumen degradable starch diet significantly reduced rumen pH and acetate-to-propionate ratio in dairy goats, and increased free lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in rumen fluid and plasma and induced inflammatory response in liver [16]. Our results showed that the histoarchitecture of hepatic cells depicted greater cell damage when fed 15% dietary wheat. One possible explanation is that, high inclusion of wheat in diet resulted in increases of LPS concentration in digestive tract [17], which translocated into the liver and induced hepatic damage.
Redox homoeostasis plays an important role in maintaining normal physiological functions in mammals. Oxidative stress results from an unbalance of oxidoreduction [18]. In the present study, no significant difference of MDA, SOD and T-AOC were observed in liver among those treatments, while GSHPx concentration was significantly higher in sheep fed 10% wheat diets compared with the control sheep. It was generally supposed that higher activity of GSHPx enhanced the free-radical scavenging capacity [19]. On the other hand, the immune system is closely involved in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. Among the five Igs, IgA was involved in antisepsis, sterilization, and antivirus [20]. IgM is the first indicator of the immune response, contributing to bacterial lysis and hemolysis [21]. The remarkable affects in IgM and IgA were observed when fed 10% wheat diets in the current study. This suggests that 10% wheat supplementation in the diet tended to increase oxidation resistance and immunity in liver, thereby promoting health status for Tibetan sheep.
Recent studies have attempted to identify the genes associated with liver and understand the underlying mechanisms of ovine liver metabolism function. By combining the RNA-seq results of Hu sheep and Tibetan sheep, Li et al. (2022) identified 1179 DEGs in liver, including 25 fat-metabolism-related genes [22]. Peng, et al. (2022) found that 2188 DEGs were markedly up or downregulated between muscle and liver. There were 950,160 upregulated and 100,771 downregulated genes in the liver and muscle, respectively [23]. In the current study, 1346 genes were found to be differentially expressed in the subcutaneous fat of sheep fed different levels of wheat diets of Tibetan sheep.
Nine of these DEGs, including SDHC, NDUFS1, MDH2, CXCL10, TNF, TYK2, ACADL, HSD17B4 and HIBCH were identified as candidate genes that might be involved in regulating hepatic oxidative stress, and immune response. For the oxidative stress, SDHC mutation was significantly increased oxidative stress, resulting in cellular apoptosis and tumorigenesis [24]. NDUFS1 regulated the oxidative stress by altering the mitochondrial reactive oxygen species formation [25]. SIRT3 knockdown changed the acetylation status of NDUFS1, which induced altered mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, and eventually defects in the cellular insulin signaling pathway [26]. MDH2 produced oxaloacetate was a metabolic switch rewiring the fuelling of respiratory chain and tri-carboxylic acid cycle [27]. For the immune response, miR-15a expression facilitates proinflammatory cytokines production and contributes to immune response at least in part via regulating CXCL10 expression [28]. TNF was an important pro-inflammatory cytokine in the innate immune systems, which was primarily produced by macrophages in response to microbial exposures including lipopolysaccharide [29]. TYK2 belonged to the JAK family and acts as an intermediary between cytokine receptors and STAT transcription factors, which involving in immune and inflammatory signaling [30]. As a key enzyme that regulates β-oxidation of long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs, ACADL prevented immune evasion by targeting Hippo/YAP signaling [31]. Currently, our analysis revealed consistent correlations between the RNA-Seq results and the mRNA levels measured by qRT-PCR. We speculated that 10% dietary wheat significantly decreases the hepatic oxidative stress and immune response of Tibetan sheep by modulating the expression of related functional genes.
Conclusions
The present study was designed to investigate the impact of three levels of wheat substitution for corn on hepatic metabolism. The results showed that as the amount of wheat included in the diet increased, there were irregular changes in the arrangement of hepatocytes, with the 10% wheat-added group having more tightly-packed hepatocytes. Furthermore, significant upregulation of genes related to oxidative stress, immune response, and fatty acid metabolism was observed in the 10% wheat-supplemented group. These results provide significant insight into the effects of various wheat supplementation levels on hepatic metabolism in Tibetan lamb.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: NCBI SRA (accession: SAMN35795877) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/).
References
Gui LS, Raza SHA, Allam F, Zhou L, Hou SZ, Khan I, Kakar IU, Abd El-Aziz AH, Jia JL, Sun YG, Wang ZY. Altered milk yield and rumen microbial abundance in response to concentrate supplementation during the cold season in Tibetan sheep. Electron J Biotechn. 2021;53:80–6.
Li H, Yu QL, Li TT, Shao LY, Su M, Zhou HK, Qu JP. Rumen microbiome and metabolome of Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries) reflect animal age and nutritional requirement. Front Vet Sci. 2020;7:609.
Gao C, Peng JJ. All routes lead to Rome:multifaceted origin of hepatocytes during liver regeneration. Cell Regen. 2021;10:2.
Han HD, Zhang TY, Jin ZC, Guo HL, Wei X, Liu YZ, Chen Q, He J. Blood glucose concentration and risk of liver cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Oncotarget. 2022;8:50164–73.
Casey LM, Hughes KR, Saunders MN, Miller SD, Pearson RM, Shea LD. Mechanistic contributions of Kupffer cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in nanoparticle-induced antigen-specific immune tolerance. Biomaterials. 2022;238:121457.
Liu XB, Herbert SJ, Jin JA, Zhang QY, Wang GH. Responses of photosynthetic rates and yield/quality of main crops to irrigation and manure application in the black soil area of Northeast China. Plant Soil. 2004;261:55–60.
Simko M, Ceresnakova Z, Biro D, Juracek M, Galik B, Strakova E, France J, Alzahal O, McBride B. Influence of wheat and maize starch on fermentation in the rumen, duodenal nutrient flow and nutrient digestibility. Acta Vet Brno. 2010;79:533–41.
Han TH, Hong JS, Fang LH, Do SH, Kim BO, Kim YY. Effects of wheat supplementation levels on growth performance, blood profiles, nutrient digestibility, and pork quality in growing-finishing pigs. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2017;30:1150–9.
Li F, Yang XJ, Cao YC, Li SX, Yao JH, Li ZJ, Sun FF. Effects of dietary effective fiber to rumen degradable starch ratios on the risk of sub-acute ruminal acidosis and rumen content fatty acids composition in dairy goat. Anim Feed Sci Tech. 2014;189:54–62.
NRC. Nutrient requirements of small ruminants. Sheep, goats, cervids, and new world camelids. Washington, DC: Natl Acad Press. 2007
Licitra G, Hernandez TM, VanSoest PJ. Standardization of procedures for nitrogen fractionation of ruminant feeds. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 1996;57:347–58.
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci. 1991;74:3583–97.
Hoekstra LT, de Graaf W, Nibourg GAA, Heger M, Bennink RJ, Stieger B, van Gulik TM. Physiological and biochemical basis of clinical liver function tests. Ann Surg. 2013;257:27–36.
Bedê TP, Jesuz VA, Souza VR, Elias MB, Oliveira FL, Dias JF, Teodoro AJ, Azeredo VB. Effects of grape juice, red wine and resveratrol on liver parameters of rat submitted high-fat diet. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias. 2020;92:e20191230.
Zhong L, Liu HL, Zhang HQ, Zhang WD, Li MH, Huang Y, Yao JY, Huang XL, Geng Y, Chen DF, Ouyang P, Yang SY, Luo W, Yin LZ. High starch in diet leads to disruption of hepatic glycogen metabolism and liver fibrosis in largemouth bass (micropterus salmoides), which is mediated by the pi3k/akt signaling pathway. Front Physiol. 2022;13:880513.
Zheng LX, Shen J, Han XY, Jin CJ, Chen XD, Yao JH. High rumen degradable starch diet induced blood bile acids profile changes and hepatic inflammatory response in dairy goats. Anim Nutr. 2023;14:121–9.
Shen J, Han XY, Zheng LX, Liu SM, Jin CJ, Liu T, Cao YC, Lei XJ, Yao JH. High rumen-degradable starch diet promotes hepatic lipolysis and disrupts enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in dairy goats. J Nutr. 2020;150:2755–63.
Shao HH, Tu YY, Wang YJ, Jiang CM, Ma L, Hu ZH, Wang JF, Zeng B, He B. Oxidative stress response of aspergillus oryzae induced by hydrogen peroxide and menadione sodium bisulfite. Microorganisms. 2019;7:225.
Cui JJ, Yuan JF, Zhang ZQ. Anti-oxidation activity of the crude polysaccharides isolated from Polygonum Cillinerve (Nakai) Ohwi in immunosuppressed mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;132:512–7.
Bhaskara V, Leal MT, Seigner J, Friedrich T, Kreidl E, Gadermaier E, Tesarz M, Rogalli A, Stangl L, Wallwitz J, Hammel K, Rothbauer M, Moll H, Ertl P, Hahn R, Himmler G, Bauer A, Casanova E. Efficient production of recombinant secretory IgA against Clostridium difficile toxins in CHO-K1 cells. J Biotechnol. 2021;331:1–13.
Liu J, Wang Y, Min Q, Xiong EM, Heyman B, Wang JY. Regulation of humoral immune responses and B cell tolerance by the IgM Fc receptor (Fc mu R). Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1254:75–86.
Li TT, Jin ML, Fei XJ, Yuan ZH, Wang YQ, Quan K, Wang TP, Yang JX, He MC, Wei CH. Transcriptome comparison reveals the difference in liver fat metabolism between different sheep breeds. Animals. 2022;12:1650.
Peng HY, Hu MY, Liu ZX, Lai WN, Shi LL, Zhao ZL, Ma HH, Li YM, Yan SQ. Transcriptome analysis of the liver and muscle tissues of dorper and small-tailed Han sheep. Front Genet. 2022;13: 868717.
Ishii T, Yasuda K, Akatsuka A, Hino O, Hartman PS, Ishii N. A mutation in the SDHC gene of complex II increases oxidative stress, resulting in apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Can Res. 2005;65:203–9.
Wan SL, Maitiabula G, Wang P, Zhang YP, Gao XJ, Zhang L, Gao TT, Wang XY. Down regulation of NDUFS1 is involved in the progression of parenteral-nutrition-associated liver disease by increasing oxidative stress. J Nutr Biochem. 2023;112:109221.
Zhang Q, Ren J, Wang FF, Pan MM, Cui L, Li MQ, Qu F. Mitochondrial and glucose metabolic dysfunctions in granulosa cells induce impaired oocytes of polycystic ovary syndrome through Sirtuin 3. Free Radical Biol Med. 2022;187:1–16.
Molinié T, Cougouilles E, David C, Cahoreau E, Portais JC, Mourier A. MDH2 produced OAA is a metabolic switch rewiring the fuelling of respiratory chain and TCA cycle. BBA-Bioenergetics. 2022;1863:148532.
Liu XF, Wang RQ, Hu B, Luo MC, Zeng QM, Zhou H, Huang K, Dong XH, Luo YB, Luo ZH, Yang H. MiR-15a contributes abnormal immune response in myasthenia gravis by targeting CXCL10. Clin Immunol. 2016;164:106–13.
Lee HS, Park HW, Song WJ, Jeon EY, Bang B, Shim EJ, Moon HG, Kim YK, Kang HR, Min KU, Cho SH. TNF-α enhance Th2 and Th17 immune responses regulating by IL23 during sensitization in asthma model. Cytokine. 2016;79:23–30.
Karjalainen A, Shoebridge S, Krunic M, Simonovic N, Tebb G, Macho-Maschler S, Strobl B, Müller M. TYK2 in tumor immunosurveillance. Cancers. 2020;12:150.
Li L, Wang LL, Wang TL, Zheng FM. ACADL suppresses PD-L1 expression to prevent cancer immune evasion by targeting HIPPO/YAP signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. Med Oncol. 2023;40:118.
Acknowledgements
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R294), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
The current work was funded by Construction of Standardized Production System for Improving quality and efficiency of Tibetan sheep industry (2022-NK-169).
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R294), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Boyan Ma and Sayed Haidar Abbas Raza: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and; editing. Sameer D Pant, Zhanhong Gao, Fengshuo Zhang, Zhiyou Wang, Shengzhen Hou: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing—review and; editing. Mariam Abdulaziz Alkhateeb, Waleed Al Abdulmonem: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing—review and; editing. Yousef Mesfer Alharbi, Abdullah S.M. Aljohani: Formal analysis, Writing—review and; editing. Data curation, Formal analysis Linsheng Gui: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing—review and; editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal procedures for experiments were approved by the Committee of Experimental Animal care and handling techniques were approved (QUA-2020–0710) by the Qinghai University of Animal Care Committee. Moreover, all applicable rules and regulation of the organization and government were followed regarding the ethical use of experimental animal.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, B., Raza, S.H.A., Pant, S.D. et al. The impact of different levels of wheat diets on hepatic oxidative stress, immune response, and lipid metabolism in Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries). BMC Vet Res 20, 26 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-023-03874-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-023-03874-z