Abstract
Background
Recent studies have reported improved diastolic function in patients administered sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i). We aimed to investigate the effect of dapagliflozin on left ventricular (LV) diastolic function in a diabetic animal model and to determine the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying its function.
Methods
A total of 30 male New Zealand white rabbits were randomized into control, diabetes, or diabetes+dapagliflozin groups (n = 10/per each group). Diabetes was induced by intravenous alloxan. Cardiac function was evaluated using echocardiography. Myocardial samples were obtained for histologic and molecular evaluation. For cellular evaluation, fibrosis-induced cardiomyoblast (H9C2) cells were obtained, and transfection was performed for mechanism analysis (serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) signaling analysis).
Results
The diabetes+dapagliflozin group showed attenuation of diastolic dysfunction compared with the diabetes group. Dapagliflozin inhibited myocardial fibrosis via inhibition of SGK1 and epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) protein, which was observed both in myocardial tissue and H9C2 cells. In addition, dapagliflozin showed an anti-inflammatory effect and ameliorated mitochondrial disruption. Inhibition of SGK1 expression by siRNA decreased and ENaC and Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1) expression was confirmed as significantly reduced as siSGK1 in the diabetes+dapagliflozin group.
Conclusions
Dapagliflozin attenuated left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis via regulation of SGK1 signaling. Dapagliflozin also reduced macrophages and inflammatory proteins and ameliorated mitochondrial disruption.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Sodium-glucose transporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) reduce blood glucose by inhibiting glucose reabsorption in the proximal tubule and are approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM).
Recent large clinical trials reported a cardiovascular benefit of SGLT2is in type 2 DM patients [1,2,3,4]. A meta-analysis of SGLT2is in cardiovascular outcome trials showed that SGLT2is reduced the risk of heart failure (HF) hospitalization by 31%, which was consistent in patients with or without a history of HF [5]. The pathophysiological mechanism of the beneficial effect of SGLT2i is likely to be independent of glucose-lowering. Both DAPA-HF (The Study to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Incidence of Worsening Heart Failure or Cardiovascular Death in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure) and the EMPEROPR Reduced trial (The Empagliflozin Outcome Trial in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction) showed significantly reduced HF hospitalization or death rates in patients with HF, regardless of the absence of diabetes [6, 7]. In addition, emerging evidence of the cardioprotective effect of SGTL2i in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy suggests a potential role of SGTL2i in the cardio-oncology field [8, 9]. Meanwhile, the mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular benefits of SGTL2i remain elusive.
Progression of diastolic dysfunction is a risk factor for HF [10]. Diastolic dysfunction predicts mortality in HF, irrespective of left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction [11, 12]. LV diastolic dysfunction results from increased myocardial stiffness and interstitial myocardial fibrosis [13]. Previous studies suggest SGLT2is may inhibit cardiac fibrosis and ameliorate diastolic dysfunction [14, 15]. However, the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms remain to be elucidated [16, 17].
In this study, we aimed to investigate the cellular and molecular mechanisms underpinning the effect of dapagliflozin (a widely-used SGLT2i) on cardiac fibrosis and diastolic function.
Methods
Experimental animal model
The study protocol was approved by the local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Yonsei University Health System (YUHS-IACUC: 2016-0157) and complies with the ARRIVE reporting guidelines. Healthy New Zealand white rabbits were purchased from Dooyeol Biotech (Dooyeol Biotech, Seoul, Korea) and were maintained under the same standard laboratory conditions, housed at room temperature with a 12-h light cycle with free access to diet and water in each cage. All animals were submitted to daily health status monitoring including weight, food intake, and general activity. All protocols followed the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals (National Research Council, USA). The main outcome variable was diastolic dysfunction assessed by echocardiography. Based on a previous study [18], a case number estimation had yielded a group size of n = 10 (8 animals + 2 reserve animals). A total of 30 male rabbits (3.0–3.5 kg, 22–24 weeks) were randomly allocated to three groups: control (n = 10), diabetes (n = 10), and diabetes + dapa (dapagliflozin, 1 mg/kg/day/P.O. for 8 weeks) (n = 10). Diabetic condition was induced by intravenous injection of Alloxan monohydrate (ALX, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) at a dose of 150 mg/kg. Rabbits exhibiting a fasting blood glucose level above 200 mg/dl were diagnosed as diabetic. All rabbits were fed for a 1% cholesterol diet (Dooyeol Biotech) for 6 weeks and a normal diet for 2 weeks thereafter. After follow-up, echocardiography was performed in the prone position after anesthesia with an intramuscular injection of an appropriate mixture of Zoletil and Rompun. After echocardiography, the animals were euthanized to minimize the discomfort experienced by animals. The experimental protocol is shown in Additional file 1: Fig. S3 in detail.
Blood chemistry
Glucose and cholesterol levels were measured in blood samples at baseline, diabetes modeling, and follow-up after 8 weeks using a Blood Glucose Monitoring System (Osang healthcare, Anyang, Korea) and DRI-CHEM 4000i (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan). Blood samples were drawn from the ear veins of the rabbits after they had been fasted overnight.
Conventional echocardiography
All images were obtained using a commercial ultrasound machine (Vivid 7 Dimension; GE Vingmed Ultrasound AS, Horten, Norway) with an S10 probe (2.5 megahertz). Images were acquired from apical three-chamber, four-chamber, and two-chamber views; and short-axis views of the mitral valves, papillary muscles, and apex [19].
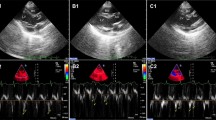
The left atrial end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), left atrial end-systolic diameter (LVESD), septal, LV posterior wall thicknesses, and left atrial diameter (LAD) were measured from standard planes. The LV ejection fraction (EF) was calculated using the Teicholz formula [19]. Pulsed Doppler echocardiography of the transmitral flow was performed. The sample volume was positioned at the level of the mitral tips in the apical four-chamber view. From the transmitral recording, the peak early (E) and late diastolic filling velocities were obtained. An apical four-chamber view was also used to obtain Doppler tissue imaging of the mitral annulus. Sample volumes were placed on the septal and lateral sides of the mitral annulus. Values for systolic (S′), early (e′), and late (a′) diastolic annular velocities were obtained. Echocardiography and analysis were performed in blind conditions.
Ultrastructure analysis using transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
The samples were cut into 1 mm squares and immediately placed in primary TEM fixation. After pretreatment, specimens were embedded with a Poly/Bed 812 kit (Polysciences, Warrington, USA) and then placed in resin and polymerized in an electron microscope oven (TD-700, DOSAKA, Kyoto, Japan) at 65 °C for 12 h. Ultrathin sections (80 nm) were placed on copper grids and double stained with 3% uranyl acetate and 3% lead citrate for 30 min and 7 min, respectively. The stained sections were then imaged using a transmission electron microscope (JEM-1011, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a Mega-View III CCD camera (Soft imaging system, Münster, Germany).
Quantification of interstitial fibrosis and immunostaining
Heart tissue was fixed in 10% normal buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4μm thickness, cut on a microtome RM2235 (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany), then deparaffinized through the dewatering process. Masson’s Trichrome and Sirius Red were used to stain for collagens. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) were used to evaluate fibrosis, macrophage, or inflammation expression. Tissue sections were immunostained at 4°C overnight with antibody. IHC was used to detect α-SMA (Abcam, Cambridge, UK, ab-7817), Fibronectin (Abcam, ab-6328), TGF-β1 (Abbkine, Wuhan, China, ABP52598), 3-nitrotyrosine (Abcam, ab-61392), Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) (LifeSpan Biosciences, Seattle, USA, LS-C122375), RAM11 (DAKO, CA, USA, M0633), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (Abcam, ab6671), NHE1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, CA, USA, sc-136239), SGLT1 (Millipore, Overijse, Belgium, 07-1417), SGLT2 (Abcam, ab85626), Fis1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, CA, USA, sc-376447), and Mfn1/Mitofusin1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, CA, USA, sc-166644). The primary antibody was detected using a peroxidase-based kit (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) and visualized using DAB substrate with enhancer (DAKO). The sections were subsequently counterstained with hematoxylin (DAKO). The IHC staining was performed as previously described [20]. Digital images of the heart tissue were scanned using a SCN 400 scanner (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany), and histomorphometry was performed using LAS 4.2 software (Leica). Ten random images from 10 heart tissues per group were analyzed in a blinded procedure.
IF staining of the heart tissue to detect serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) (ABCAM, ab43606) and epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) (Biorbyt, Cambridge, UK, orb100662) was performed following a published protocol [21]. The sections were washed for 10 min in 1% PBS and then incubated with FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies) for 1 h in the dark at room temperature. The sections were washed in PBS for 10 min, mounted with Fluoroshield containing DAPI (ImmunoBioscience, Mukilteo, WA, USA), and stored in the dark at 4°C. Confocal microscopy was performed with an LSM 700 system (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
Cell culture and transfection
Cells of the rat cardiomyoblast cell line H9C2 were cultured in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (both from Biowest, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% non-essential amino acids, 1% 2-mercaptoethanol, and 10% penicillin (all from Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Cells were maintained at 37°C in humidified air with 5% carbon dioxide. Before treatment, the cells were washed twice with pH 7.4 phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, Gibco). The cells were incubated in 500 μM palmitate (diluted in 5% bovine serum albumin [BSA]) with or without 35mM high glucose (HG) for 24 h and then treated with 0.4 μM dapagliflozin with 10 μg/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24 h (all from Sigma-Aldrich).
siRNA targeting rat siSGK1 (5′- AGGAGAACAUCGAGCACAATT -3′) and siControl (5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′) were synthesized (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea). H9C2 cells were then transfected with the siRNAs using LipofectamineTM RNAiMAX (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to a previously described method [22].
Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR and real-time PCR
The heart tissues and H9C2 cells of total RNA were isolated using a published procedure [23]. cDNA was synthesized using Quantitect Reverse Transcription Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany), then the cDNA was amplified using AccuPower PCR Premix (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea) and the SYBR Green kit of the 2X Fast Q-PCR Master Mix (SMOBIO, Hsinchu City, Taiwan). Relative mRNA levels were determined by comparison with GAPDH or β-actin. The rabbit and H9C2 primers used for the target genes are shown in Additional file 1: Table S1 and S2.
Western blot analysis
The heart tissues and H9C2 cells were lysed with RIPA buffer (Biosesang, Seongnam, Korea) containing Complete Mini and EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). The protein samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and then electrotransferred to an Immuno-Blot PVDF membrane (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk (Noble Bio, Hwaseong, Korea) in 10% TBS-T for 1 h at room temperature. Membranes were incubated with primary antibodies against Fibronectin (Abcam, ab-6328), TGF-β1 (Abbkine, Wuhan, China, ABP52598), SGK1 (Abcam, ab43606), ENaC Gamma (Biorbyt, Cambridge, UK, orb100662), NHE1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, CA, USA, sc-136239), TNF-α (Abcam, ab6671), IL-6 (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies), NF-kB (p65, Enzo life sciences, Farmingdale, NY, USA), and pNF-kB (p65, Santa Cruz Biotechnologies) at 4°C overnight and washed with TBS-T. They were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h room temperature and then subjected to ECL (GE Healthcare, Chicago, USA) detection. GAPDH was detected on the same membrane to serve as a loading control. Densitometry analysis was performed using Image J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS v26 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and dots graphs were created using the GraphPad Prism 8.4 (GraphPad Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). When our data follow normal distribution, parametric tests otherwise nonparametric methods are used to compare the groups. P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Metabolic parameters of animal models at baseline and 8 weeks follow-up
Baseline characteristics were comparable among the three groups; however, the fasting blood glucose level was significantly higher in the diabetes groups compared with the control group (P < 0.001, Table 1). At 8 weeks follow-up, body weights did not differ among the three groups, but total cholesterol, triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein, and fasting blood glucose were significantly higher in the diabetes group compared to those in the control and diabetes+dapa groups (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, Table 1).
Attenuation of LV diastolic dysfunction in diabetes+dapa group
Baseline echocardiographic parameters were similar among the three groups. Table 2 shows comparisons of echocardiographic parameters at 8 weeks follow-up among the three groups. In the diabetes+dapa group, septal e′ and lateral e′ velocities were significantly higher than that of the diabetes group (P < 0.05). The E/septal e′ ratio was significantly lower in the diabetes+dapa group compared with that in the diabetes groups (P < 0.05).
Dapagliflozin attenuates myocardial fibrosis
A qualitative assessment by Masson’s trichrome stain revealed prominent fibrosis in the myocardium of the diabetes group (Fig. 1A). Sirius red staining revealed that the Diabetes group exhibited significantly increased myocardial fibrosis compared with the control and diabetes+dapa groups (P < 0.001, Fig. 1A, B), reflecting increased collagen deposition. Extracellular remodeling was assessed by immunostaining for α-SMA, fibronectin, and TGF-β1 protein levels (Fig. 1C–E). The diabetes+dapa group showed significantly decreased fibronectin and TGF-β1 compared with the diabetes group (P < 0.01, P < 0.001). Dapagliflozin significantly reduced expression of fibronectin and TGF-b1 based on RT-PCR and Western blot findings (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, Fig. 1I, J). This finding provides visual evidence that dapagliflozin can influence the extracellular remodeling of rabbit myocardium.
Reduction of fibrosis by dapagliflozin and morphologic changes by histological analysis. A Myocardial tissue was stained with Masson’s trichrome. B Collagen fiber deposition of the plaques is represented using Sirius Red staining. Sirius Red percentage for myocardial tissue in each group. C–F The plaques were shown using immunohistochemistry staining of α-SMA, Fibronectin, TGF-β1, and 3-nitrotyrosine. G, H The expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 and direct effects of dapagliflozin on immunohistochemistry analysis in myocardial tissue. Scale bar = 200μm. I RT-PCR analyses of indicated genes in myocardial tissue. J Western blot analyses of indicated genes in myocardial tissue (n = 4 per group). K Real-time PCR expressions of SGLT1 and SGLT2 in myocardial tissue. Values are means ± SEM (n = 10 per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to control group, †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001 compared to diabetes group
To further investigate the mechanism of dapagliflozin in the attenuation of cardiac fibrosis and extracellular remodeling, we compared the expression of myocardial SGK1 protein and its downstream proteins, ENaC and NHE1.
Myocardial SGK1 and ENaC proteins were significantly decreased in the diabetes+dapa group compared with the diabetes group, and comparable to the control group, when assessed by immunofluorescence techniques (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, Fig. 2A, B). Similarly, NHE1 was significantly decreased in the Diabetes+Dapa group compared with the Diabetes group (P < 0.01, Fig. 2C). The RT-PCR showed a significant reduction in SGK1, ENaC, and NHE1 levels in the diabetes + dapa group compared to that in the diabetes group (P < 0.01, P < 0.05, Fig. 2D) and similarly tend to decreased expression level in Western blot (Fig. 2E).
Dapagliflozin inhibits the expression of profibrotic proteins SGK1 and ENaC assessed by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. A Comparison of SGK1 (green) expression in myocardial tissue. B Comparison of ENaC (green) expression in myocardial tissue. Relative area measurements were determined using a Zeiss LSM 700. Scale bar = 50μm. n = 3 each slide of 3 sections. C The direct effects of dapagliflozin on immunohistochemistry analysis of NHE1 in myocardial tissue (n = 10 per group). Scale bar = 200μm. D RT-PCR analyses of indicated genes in myocardial tissue (n = 10 per group). E Western blot analyses of indicated genes in myocardial tissue (n = 4 per group). Values are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to control group, †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 compared to diabetes group
To confirm the effect of dapagliflozin at the cellular level, hyperglycemic fibrosis was induced in cardiomyoblast H9C2 cells using RT-PCR and Western blot (Fig. 3A, B). Fibronection and TGF-β1 mRNA and protein levels were significantly lower in the H9C2 cells in the high glucose group treated with dapagliflozin than in those in the high glucose group without dapagliflozin treatment (P < 0.001, P < 0.01). SGK1, ENaC, and NHE1 mRNA and protein levels were significantly lower in the dapagliflozin-treated group compared with those in the high glucose group (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05).
The anti-fibrotic effect of dapagliflozin in H9C2. A RT-PCR expression of Fibronectin, TGF-β1, SGK1, ENaC, and NHE1. B Western blot expression of Fibronectin, TGF-β1, SGK1, ENaC, and NHE1. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to Control, †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 compared to DMSO, §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01, §§§p < 0.001 compared to HG
To test whether SGK1 was directly inhibited by dapagliflozin, we assessed SGK1 expression in dapagliflozin-treated H9C2 cells. SGK1 siRNA (20 nM) effectively suppressed the transcriptional and translational level of SGK1 (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, Fig. 4A, B). Dapagliflozin suppressed the SGK1 level and subsequently suppressed ENaC and NHE1, similar to SGK1 downregulated cells (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, Fig 4C, D).
Dapagliflozin for suppression of fibrosis via SGK1, ENaC, and NHE1. A Representative RT-PCR bands of SGK1 in H9C2 transfected with SGK1 10-30 nM siRNA. B Representative Western blot bands of SGK1 in H9C2 transfected with SGK1 10-30 nM siRNA. Values are means ± SEM (n = 4). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the siCon group. C RT-PCR analyses of indicated genes in H9C2. D Western blot analyses of indicated genes in H9C2. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the siCon group, †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001 compared to palmitic acid + LPS siCon, ∥p < 0.05 compared to palmitic acid + LPS siSGK + dapa, §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01, §§§p < 0.001 compared to palmitic acid + LPS HG + siCon, ¶p < 0.05 compared to palmitic acid + LPS HG + siSGK + dapa
Dapagliflozin reduces inflammation and ameliorates mitochondrial disruption
To explore other possible mechanisms for the cardiovascular benefit of dapagliflozin, 3-nitrotyrosine (an oxidative stress marker) expression was compared between the three groups. 3-nitrotyrosine expression was significantly lower in the diabetes+dapa group than in the Diabetes group, and comparable to the control group (P < 0.05, Fig. 1F). In the expression of macrophage and inflammation protein markers, including RAM11, RAGE, and TNF-α, using immunohistochemistry analysis. RAM11, RAGE, and TNF-α expression were significantly lower in the Diabetes+Dapa group compared with the Diabetes group, and comparable to the Control group (Additional file 1: Fig. S1 A-C). Decreased expression of inflammatory markers, TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-kB, was observed in dapagliflozin-treated H9C2 cells compared with the high glucose group. (Additional file 1: Fig. S2 A-B).
To address possible mechanisms for decreased 3-nitrotyrosine expression in the diabetes+dapa group, mitochondria structures were analyzed. In the diabetes group, mitochondria showed a disrupted cristae structure with diminution of matrix electron density, loss and fusion of cristae, and mitochondrial fragmentation compared with the control group (Fig. 5A). In the diabetes+dapa group, the cristae structure in the mitochondria was preserved and a lesser degree of the diabetes-induced ultrastructural anomalies of the mitochondria was noted. Additionally, to further investigate the impact of dapagliflozin on mitochondrial dysfunction, we analyzed the expression levels of mitofission or mitofusion proteins, Fis1 and Mfn1. Levels of Fis-1 land Mfn-1 were significantly reduced in the Diabetes+Dapa group compared with the diabetes group (P < 0.05, Fig. 5B). RT-PCR and Western blot analysis also showed similar results (P < 0.05, Fig. 5C, D).
Protective effect of dapagliflozin for mitochondrial cristae in myocardial tissue. Comparison of mitochondrion changes. A Transmission electron microscopy images of myocardial tissue treated with dapagliflozin. Scale bar = 5μm, 2μm, and 500nm from low to high magnification. B Immunohistochemistry analysis of Fis-1 and Mfn-1 expression and quantification of myocardial tissue cross-sectional area. Scale bar = 200μm. C RT-PCR analyses of indicated genes in myocardial tissue. D Western blot analyses of indicated genes in myocardial tissue (n = 4 per group). Values are means ± SEM (n = 10 per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the Control group, †p < 0.05 compared to the diabetes group
In the expression levels of SGLT1 and SGLT2 in heart tissue, both SGLT1 and SGLT2 were significantly higher expressions in the diabetes group when compared to those in the control group (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, Fig. 1G–H and K).
Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrated attenuation of LV diastolic dysfunction using a diabetic rabbit model and evaluated the underlying mechanisms. Our results showed that dapagliflozin (1) attenuated myocardial fibrosis through SGK1/ENaC/NHE1 signaling and (2) reduced myocardial inflammation, and ameliorated mitochondrial disruption.
The most important finding of our study is that we identified the potential mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular benefit of dapagliflozin. In our study, dapagliflozin attenuated LV diastolic dysfunction in a diabetic rabbit model. This finding is consistent with previous clinical and animal studies, which reported improved diastolic function with SGLT2i [16, 17, 24, 25]. The dapagliflozin-treated group showed attenuation of myocardial fibrosis with reduction of SGK1/ENaC/NHE1 proteins in myocardial tissue and H2C2 cells. SGK1 is an emerging mediator of cardiac fibrosis, which activates the ENaC proteins responsible for promoting fibrosis and upregulating NHE1 activity, which are key factors in cardiac remodeling [18, 26]. A previous study using a murine model reported activation of SGK1-induced adverse ventricular remodeling, fibrosis, and increased size of cardiomyocytes, suggesting that SGK1 is a key mediator of cardiac remodeling [27,28,29].
In addition to inhibition of fibrosis, our results also demonstrate that dapagliflozin reduces inflammation and ameliorates mitochondrial disruption attenuation. This finding could contribute to the attenuation of LV diastolic dysfunction. Decreased mitochondrial function, increased reactive oxygen species production, and inflammation are hallmarks of a diabetic heart [30]. A previous report demonstrated that SGTL2i prevents mitochondrial dysfunction, reflected by reduced H2O2 release and increased ATP synthesis, which supports our finding on mitochondria structure [31].
The anti-inflammatory effect of SGLT2 inhibitors, including dapagliflozin, has been reported by reducing the expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α [3, 32,33,34]. In an angiotensin II stressed diabetic mouse model, dapagliflozin decreased intracellular calcium transients, thereby reducing production of reactive oxygen species and inflammation [35]. Similarly, a recent study reported attenuation of diastolic dysfunction in a diabetic model with nutraceuticals like quercetin and boswellic acid through NLRP3 inflammasome and cytokines, which showed a potential effect against cancer cell survival and chemoresistance [36].
The possible anti-inflammatory mechanism of dapagliflozin is activation of adenosine mono-phosphate kinase (AMPK) with downstream inhibition of the Na+ /H+ Exchanger-1 (NHE-1) for the attenuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation [37]. Furthermore, a recent study suggested that dapagliflozin may activate mTORC2, leading to the activation of Akt and FOXO3 [36] and depends on AMPK and mTOR activation. Similar to previous studies, our results showed an anti-inflammatory effect of dapagliflozin in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Inflammatory markers, RAM11, RAGE, and TNF-α were significantly reduced in the Diabetes+Dapa group compared to those in the Diabetes group (Additional file 1: Fig. S1-S2).
This study is meaningful in demonstrating the favorable effect of dapagliflozin and elucidates the mechanism underlying SGLT2 inhibition in diastolic heart failure using a diabetic rabbit model. Dapagliflozin is a known selective SGTL2 inhibitor, but also has a relatively weak inhibitory activity for SGLT1 [38, 39]. We tested the expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 by immunostaining rabbit myocardial tissue (Fig. 1G, H). In the Diabetes+Dapa group, expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 were significantly reduced compared with the diabetes group. This finding is consistent with the inhibitory mechanism of dapagliflozin in an in-vivo model.
There are several limitations to our study. First, our study lacks data on the effect of dapagliflozin on myocardial metabolism and mitochondrial function. Second, the present study did not include the long-term effect of dapagliflozin. Third, we assessed the effect of dapagliflozin on a diabetic model; whether dapagliflozin exerts a cardioprotective effect via the same mechanisms in a non-diabetic model needs to be explored. Despite these limitations, our study is valuable in demonstrating that dapagliflozin attenuates cardiac fibrosis via SGK1 signaling and ameliorates diastolic dysfunction in a diabetic rabbit model. Our results convey important therapeutic benefits beyond lowering blood glucose and simple intravascular volume loss by increasing the urinary excretion of glucose and sodium (Fig. 6).
Conclusion
In conclusion, dapagliflozin attenuated left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis via regulation of SGK1 signaling in a rabbit diabetic model. In addition, dapagliflozin reduced inflammation and ameliorated mitochondrial disruption in the myocardium. Our study may contribute to broadening the scopes of understanding the mechanism of cardiovascular benefit of SGLT2 inhibitor.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ALX:
-
Alloxan monohydrate
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- EF:
-
Ejection fraction
- ENaC:
-
Epithelial sodium channel
- HF:
-
Heart failure
- HG:
-
High glucose
- IF:
-
Immunofluorescence
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- LAD:
-
Left atrial diameter
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- LV:
-
Left ventricular
- LVEDD:
-
Left atrial end-diastolic diameter
- LVESD:
-
Left atrial end-systolic diameter
- NHE1:
-
Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1
- RAGE:
-
Receptor for advanced glycation end products
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- SGK1:
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1
- SGLT2i:
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Mahaffey KW, Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin for Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Events: Results From the CANVAS Program (Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study). Circulation. 2018;137(4):323–34.
Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):347–57.
Kim SR, Lee SG, Kim SH, Kim JH, Choi E, Cho W, et al. SGLT2 inhibition modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity via ketones and insulin in diabetes with cardiovascular disease. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):2127.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117–28.
Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Bonaca MP, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019;393(10166):31–9.
McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(21):1995–2008.
Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1413–24.
Quagliariello V, De Laurentiis M, Rea D, Barbieri A, Monti MG, Carbone A, et al. The SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin improves myocardial strain, reduces cardiac fibrosis and pro-inflammatory cytokines in non-diabetic mice treated with doxorubicin. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021;20(1):150.
Sabatino J, De Rosa S, Tammè L, Iaconetti C, Sorrentino S, Polimeni A, et al. Empagliflozin prevents doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19(1):66.
Kane GC, Karon BL, Mahoney DW, Redfield MM, Roger VL, Burnett JC Jr, et al. Progression of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and risk of heart failure. JAMA. 2011;306(8):856–63.
Aljaroudi W, Alraies MC, Halley C, Rodriguez L, Grimm RA, Thomas JD, et al. Impact of progression of diastolic dysfunction on mortality in patients with normal ejection fraction. Circulation. 2012;125(6):782–8.
Machino-Ohtsuka T, Seo Y, Ishizu T, Hamada-Harimura Y, Yamamoto M, Sato K, et al. Clinical utility of the 2016 ASE/EACVI recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function in the stratification of post-discharge prognosis in patients with acute heart failure. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;20(10):1129–37.
Borlaug BA, Paulus WJ. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Eur Heart J. 2011;32(6):670–9.
Kang S, Verma S, Hassanabad AF, Teng G, Belke DD, Dundas JA, et al. Direct Effects of Empagliflozin on Extracellular Matrix Remodelling in Human Cardiac Myofibroblasts: Novel Translational Clues to Explain EMPA-REG OUTCOME Results. Can J Cardiol. 2020;36(4):543–53.
Santos-Gallego CG, Requena-Ibanez JA, San Antonio R, Garcia-Ropero A, Ishikawa K, Watanabe S, et al. Empagliflozin Ameliorates Diastolic Dysfunction and Left Ventricular Fibrosis/Stiffness in Nondiabetic Heart Failure: A Multimodality Study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;14(2):393–407.
Matsutani D, Sakamoto M, Kayama Y, Takeda N, Horiuchi R, Utsunomiya K. Effect of canagliflozin on left ventricular diastolic function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):73.
Shim CY, Seo J, Cho I, Lee CJ, Cho IJ, Lhagvasuren P, et al. Randomized, Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The IDDIA Trial. Circulation. 2021;143(5):510–2.
Habibi J, Aroor AR, Sowers JR, Jia G, Hayden MR, Garro M, et al. Sodium glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibition with empagliflozin improves cardiac diastolic function in a female rodent model of diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017;16(1):9.
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28(1):1-39.e14.
Kim JS, Lee SG, Oh J, Park S, Park SI, Hong SY, Kim S, Lee SH, Ko YG, Choi D, et al. Development of Advanced Atherosclerotic Plaque by Injection of Inflammatory Proteins in a Rabbit Iliac Artery Model. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(5):1095-105.
Lee SG, Lee SJ, Thuy NVP, Kim JS, Lee JJ, Lee OH, Kim CK, Oh J, Park S, Lee OH, et al. Synergistic protective effects of a statin and an angiotensin receptor blocker for initiation and progression of atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 2019;14(5):e0215604.
Lee SG, Lee SJ, Lee JJ, Kim JS, Lee OH, Kim CK, Kim D, Lee YH, Oh J, Park S, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect for Atherosclerosis Progression by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitor in a Normoglycemic Rabbit Model. Korean Circ J. 2020;50(5):443-57.
Lee SG, Oh J, Bong SK, Kim JS, Park S, Kim S, Park S, Lee SH, Jang Y. Macrophage polarization and acceleration of atherosclerotic plaques in a swine model. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0193005.
Hammoudi N, Jeong D, Singh R, Farhat A, Komajda M, Mayoux E, et al. Empagliflozin Improves Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in a Genetic Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017;31(3):233–46.
Connelly KA, Zhang Y, Visram A, Advani A, Batchu SN, Desjardins JF, et al. Empagliflozin Improves Diastolic Function in a Nondiabetic Rodent Model of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2019;4(1):27–37.
Voelkl J, Pasham V, Ahmed MS, Walker B, Szteyn K, Kuhl D, et al. Sgk1-dependent stimulation of cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger Nhe1 by dexamethasone. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(1):25–38.
Das S, Aiba T, Rosenberg M, Hessler K, Xiao C, Quintero PA, Ottaviano FG, Knight AC, Graham EL, Boström P, et al. Pathological role of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in adverse ventricular remodeling. Circulation. 2012;126(18):2208-19.
Aoyama T, Matsui T, Novikov M, Park J, Hemmings B, Rosenzweig A. Serum and glucocorticoid-responsive kinase-1 regulates cardiomyocyte survival and hypertrophic response. Circulation. 2005;111(13):1652-9.
Lang F, Shumilina E. Regulation of ion channels by the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase SGK1. Faseb j. 2013;27(1):3-12.
Ritchie RH, Abel ED. Basic Mechanisms of Diabetic Heart Disease. Circ Res. 2020;126(11):1501-25.
Croteau D, Luptak I, Chambers JM, Hobai I, Panagia M, Pimentel DR, Siwik DA, Qin F, Colucci WS. Effects of Sodium-Glucose Linked Transporter 2 Inhibition With Ertugliflozin on Mitochondrial Function, Energetics, and Metabolic Gene Expression in the Presence and Absence of Diabetes Mellitus in Mice. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(13):e019995.
Dekkers CCJ, Petrykiv S, Laverman GD, Cherney DZ, Gansevoort RT, Heerspink HJL. Effects of the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on glomerular and tubular injury markers. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(8):1988–93.
Yu YW, Que JQ, Liu S, Huang KY, Qian L, Weng YB, et al. Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitor of Dapagliflozin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Limiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Modulating Autophagy. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:768214.
Chen H, Tran D, Yang HC, Nylander S, Birnbaum Y, Ye Y. Dapagliflozin and Ticagrelor Have Additive Effects on the Attenuation of the Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and the Progression of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: an AMPK-mTOR Interplay. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2020;34(4):443–61.
Arow M, Waldman M, Yadin D, Nudelman V, Shainberg A, Abraham NG, Freimark D, Kornowski R, Aravot D, Hochhauser E, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor Dapagliflozin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19(1):7.
Quagliariello V, Armenia E, Aurilio C, Rosso F, Clemente O, de Sena G, Barbarisi M, Barbarisi A. New Treatment of Medullary and Papillary Human Thyroid Cancer: Biological Effects of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Loaded With Quercetin Alone or in Combination to an Inhibitor of Aurora Kinase. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(8):1784-95.
Ye Y, Jia X, Bajaj M, Birnbaum Y. Dapagliflozin Attenuates Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger-1 in Cardiofibroblasts via AMPK Activation. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018;32(6):553-8.
Abdul-Ghani MA, DeFronzo RA, Norton L. Novel hypothesis to explain why SGLT2 inhibitors inhibit only 30-50% of filtered glucose load in humans. Diabetes. 2013;62(10):3324-8.
Takebayashi K, Inukai T. Effect of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors With Low SGLT2/SGLT1 Selectivity on Circulating Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Clin Med Res. 2017;9(9):745-53.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank MID (Medical Illustration & Design) for providing excellent support with the medical illustrations.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2020M3A9I4038455 and 2021R1I1A1A01056048), Ministry of Science & ICT (2017M3A9E9073585), Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (No: HI20C1566) and the Cardiovascular Research Center (Seoul, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kim JS, Hong GR, Lee YH, Park SI, Jeon OH, and Choi DH designed the study. Lee SG performed the in vivo and in vitro experiments. Kim DR performed Echo enforcement and analysis. Lee YJ, Lee SJ, Lee OH, Kim CK, Oh JW, and Lee CJ performed animal experiments. Lee SG, Lee JJ, Lee HJ, and Moon RK analyzed the data. Lee SG and Kim DR drafted the manuscript. Kim JS and Hong GR reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental animal studies were approved by the local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Yonsei University Health System approved the study protocol (YUHS-IACUC: 2016-0157).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Anti-inflammatory effects of dapagliflozin on immunohistochemistry analysis. A-C The expression of RAM11, RAGE and TNF-α in the myocardium was detected by immunostaining. Values are means ± SEM (n = 10 per group). Scale bar = 200 μm. ***p < 0.001 compared to Control group, ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001 compared to Diabetes group. Figure S2. Dapagliflozin significantly decreased inflammation markers in H9C2. A RT-PCR expression of TNF-α and IL-6. Comparisons of relative mRNA expression, normalized to expression of β-actin. B Western blot expression of pNF-kB, NF-kB, TNF-α and IL-6. Representative data showing protein expression, normalized to expression of GAPDH. Values are means ± SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to Control, †p < 0.05 compared to DMSO, §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.01 compared to HG. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IL-6, interlukin-6; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α. Figure S3. Schematic design of the study protocol. Animals were randomized to Control, Diabetes, Diabetes+Dapa groups. Diabetic condition was induced for animals in Diabetes and Diabetes+Dapa groups. Dapagliflozin (1mg/kg/day) treated depending on their group assignment, for 8 weeks. After follow up echocardiography, animals were subsequently sacrificed and tissue samples were collected for assessment of histological and molecular remodeling. Table S1. List of rabbit primers. Table S2. List of H9C2 primers.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SG., Kim, D., Lee, JJ. et al. Dapagliflozin attenuates diabetes-induced diastolic dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis by regulating SGK1 signaling. BMC Med 20, 309 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-022-02485-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-022-02485-z