Abstract
Background
Family doctors, serving as gatekeepers, are the core of primary health care to meet basic health needs, provide accessible care, and improve attainable health. The study objective was to evaluate the impact of the family doctor system on health service utilization among patients with hypertension and diabetes in China.
Methods
Difference-in-Differences (DID) models are constructed to estimate the net effect of the family doctor system, based on the official health management records and medical insurance claim data of patients with hypertension and diabetes in an eastern city of China.
Results
The family doctor system significantly increases follow-up visits (hypertension patients coef. = 0.13, diabetes patients coef. = 0.08, both p < 0.001) and outpatient visits (hypertension patients coef. = 0.08, diabetes patients coef. = 0.05, both p < 0.001) among the contracted compared to the non-contracted. The proportion of outpatient visits in community health centers among the contracted significantly rose (hypertension patients coef. = 0.02, diabetes patients coef. = 0.04, both p < 0.001) due to significantly more outpatient visits in community health centers and fewer in secondary and tertiary hospitals. It also significantly mitigates the increase in inpatient admissions among hypertension patients but not among diabetes patients.
Conclusions
The examined family doctor system strengthens primary care, both by increasing follow-up visits and outpatient visits and promoting a rationalized structure of outpatient utilization in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Primary health care (PHC) addresses meeting the basic health needs of individuals throughout their lives by providing people-centered care in the community, to guarantee the right to the most accessible health care, the utmost equity, and the highest level of attainable health [1]. As the core of primary care, gatekeepers, globally known as family physicians (FP), or general practitioners (GP), and in China family doctors (FD), provide standardized services including preventive and basic medical services to advocate a healthy lifestyle, manage common diseases, and treat patients in primary care setting [2,3,4].
The effectiveness of gatekeepers on health service utilization has been proven that having gatekeepers promotes more preventive and outpatient service utilization, and decreases unnecessary emergency visits or avoidable inpatient utilization [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. In the United States, the pilot practices found that GP collaborative practice in 27 sites has statistically significantly higher rates of diabetes care, breast cancer screening, and ambulatory primary care visits; lower rates of all-cause hospitalization, emergency department visits, and ambulatory visits to specialists [5]. In Australia, GP care utilization is associated with reduced risk for any emergency department presentations [7]; and using GP services lowers the rate of potentially preventable hospitalizations in people with diabetes [6]. In Portuguese, a study shows that having an assigned GP increases the appropriate use of emergency departments by 1% [8]. In Hungary, GPs motivate participation in cervical cancer screening by 27% of women who initially refused [9]. In Iran, the GP program reduces the number of not only hospitalizations but also specialist visits [10]. In China, Family Physician Integrated Care Program in Taiwan indicates that it might reduce hospital admissions in the long term [11] and a survey of 3148 residents in Hongkong demonstrates people with regular GPs are 2.3% less likely to use emergency services than people without FDs [12].
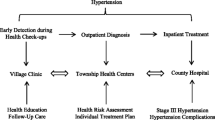
China has been striving to establish referral systems since major healthcare reform nationwide in 2009, and family doctors serve as gatekeepers to strengthen primary care [13]. Several pilot programs of family doctor system reform were launched in multiple regions, and in 2016, seven departments, led by the State Council’s Medical Reform Office and the National Health Commission, officially launched family doctor system reform nationwide, which provided explicit guidelines on contracted services, content, fees, incentive mechanisms, performance assessment, and technical support [14]. Residents are encouraged to voluntarily contract with family doctors and then contracted residents would be provided with family doctor contract services [15]. The main objectives of the family doctor system were as follows: (1) to expand the family doctor services by enhancing service capacity, improving the quality of basic public health and health management services, ensuring rational drug use, and providing home-based services. (2) to cover patients with chronic diseases as well as vulnerable populations (the elderly, the pregnant, the children, and the disabled), and to provide accessible health management in primary care, delay disease progression, and prevent unnecessary hospitalization for chronic disease patients. (3) to establish a well-functioning referral system with more health service utilization in community health centers rather than in secondary and tertiary hospitals. In 2018, the coverage rate among the key population reached over 71.3% [16], which initially forms the function of gatekeeping in several pilot cities [17].
A few studies in China focused on the impact of family doctors on health service utilization but the net effect was unclear [18,19,20,21]. After controlling factors such as age, occupation, income level, and medical insurance type, contracted Chinese residents are proven to utilize more primary medical consultations, as well as chronic disease follow-up services, rehabilitation, and nursing services [19]. A similar result is concluded from research that contracted patients with chronic diseases have higher utilization rates of chronic disease follow-up services than non-contracted patients [18]. Besides that, surveys conducted in Shanghai [20, 22], Hangzhou [23], and Shenzhen [21] found more contracted residents first go to and contact community health centers than non-contracted residents. A higher proportion (51.9%) in the first-visit to primary care was presented among the contracted residents [24]. However, these studies were based on cross-sectional data with a relatively small sample size, and mainly on self-reported services utilization. The net effect of the family doctor system on health service utilization cannot be conducted and more solid data are required. There is also a lack of research to shed light on the change in health service utilization among different institutions, to reflect the role of FD in re-allocating resources and optimizing the referral system.
To evaluate the impact of the family doctor system on health service utilization among patients with hypertension and diabetes, this study presents the change in follow-up service utilization, outpatient service utilization, and inpatient service utilization. The hypotheses of this study were:
-
1.
The family doctor system would promote the follow-up service and the outpatient service utilization as a result reduce or mitigate the increase in the inpatient service utilization among patients with hypertension and diabetes.
-
2.
The family doctor system would increase the health service utilization in community health centers and decrease it in secondary and tertiary hospitals among patients with hypertension and diabetes.
Methods
Aim and setting
This study aims to evaluate the impact of the family doctor system on health service utilization among patients with hypertension and diabetes in China.
An eastern city in China was selected as the sample city, since it was one of the earliest pilot cities and implemented the family doctor system on January 1st, 2015. In this city, the coverage of social insurance was 98% in 2015, which was slightly higher than the 95% coverage of social insurance nationwide. According to the family doctor system, the insured residents could voluntarily contract with a family doctor, who cooperates with nurses, and public health practitioners as a team. For the contracted, the uniform service contents of the family doctor system included four aspects: (1) improving the accessibility of timely counseling services in community health centers (2) offering high-quality diagnosis and treatment services, and a green channel for accurate referral services (3) providing integrated healthcare and home-based services (4) implementing health management for chronic patients through regular follow-ups. For the non-contracted, services were provided in a traditional way, where they did not have a designated family doctor during visits and received less comprehensive services such as fewer follow-ups for chronic diseases, home care, and rehabilitation. As a result, the non-contracted may directly seek care at secondary or tertiary healthcare institutions, leading to poor continuity of health services and chronic disease management.
Regarding the family doctor system in this city as an intervention, we chose the years 2014 and 2017 as the pre-treatment period and post-treatment period, considering the effect of this reform. The national family doctor system was designed and formulated based on the practices and experiences of our pilot city, which are fundamentally consistent. Also, we focus on the chronic disease patients who are diagnosed with diabetes and hypertension in our study, because they are the key population of registration in the pilot city and also the mainland China.
Data sources
We extracted individual-level data in 2014 and 2017 from two databases and then linked the data by pseudonymous patients’ identification. To be specific, the official health management records were provided by the Community Chronic Disease Management System of the city’s Health Information Center, including patients’ individual information such as demographic information and chronic disease follow-up records. Medical insurance claim data during the study period were extracted from the municipal Medical Insurance Bureau, providing information about outpatient and inpatient service utilization, and the level of medical institutions.
This study restricted the research sample according to the following criteria (Fig. 1):
-
1.
Insurers of social medical insurance before January 1, 2014.
-
2.
Participants diagnosed with diabetes and hypertension who registered in community health centers before January 1, 2014.
-
3.
Patients without missing follow-up records in both years.
Measures
We examined six outcome variables in three sets as follows. (1) We examined the outcome of follow-up service utilization by the average number of annual follow-up visits per capita. The follow-up visits include outpatient visits, phone calls, text messages, and home visits. (2) We examined the four measures of outpatient service utilization: annual outpatient visits per capita, annual outpatient visits in community health centers per capita, annual outpatient visits in secondary and tertiary hospitals per capita, and the proportion of outpatient visits in community health centers. We included the total number of outpatient visits and outpatient visits in different institutions respectively. (3) We examined the outcome of inpatient service utilization, as indicated by annual inpatient admissions per capita.
The key independent variables were two dummy variables “groupi”, “timet”, and their interaction term “groupi*timet”. The dummy variable “groupi” was created, which equals “1” for the treatment group of contracted patients, who contracted with FDs in 2015 and remained so from then; and “0” for the control group of non-contracted patients, who never contracted with FDs from 2015 to 2017. The other dummy variable “timet” was conducted to capture the tendency of change within the group. It equals “0” when the year is 2014 and “1” when the year is 2017.
Other control variables were considered to obtain more robust results. Firstly, unequal health service utilization exists by demographic characteristics [25,26,27]. To address this issue, age, gender, and insurance type were included. Two main medical insurance in China were the Urban-Rural Resident Basic Medical Insurance (URRBMI), and the Urban Employee Basic Medical Insurance (UEBMI) with further classification of UEBMI for employees and UEBMI for retirees [28]. Besides that, health status and severity of the disease were also controlled, such as comorbidity of diabetes and hypertension, body mass index (BMI), disease duration (in years), as well as respectively average scores of systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and fasting blood glucose (FBG). The average scores of SBP, DBP, and FBG were calculated by the proportion of normal results to total tests annually and the higher scores the better disease controlled. These are detailed in Table 1.
Statistical analysis
A descriptive analysis was conducted and the demographic characteristics at baseline are reported. The t-test was used to compare the difference between contracted and non-contracted patients, with the threshold of statistical significance at P < 0.05 (two-tailed).
We assumed that determinants of outcomes remained stable within the same city in two groups over time. Differences-in-differences (DID) approach is adopted to measure the net effect of the family doctor system among patients with hypertension and diabetes using the following model:
Considering that healthcare service utilization follows a positively skewed distribution with a right tail, and the values are discrete and non-negative, we used generalized linear models (GLM) with the Poisson distribution and a log link function to regress Eq. (1) respectively for the hypertension models and the diabetes models. The dummy variable “groupi” and “timet” indicated groups and time periods. For six outcomes (Yi), the average treatment effect (ATT) is estimated by comparing the change within the treatment group with the change within the control group during the study period. The parameter of interest is the coefficient of the interaction term β3, which would capture the different changes in Yit among patients in two groups if the family doctor system had an impact. Xij consists of the control variables as mentioned, and εit is the error term [29,30,31].
As for propensity score matching (PSM), the study included age, gender, comorbidities, insurance type, BMI for all patients, hypertension duration, SBP, and DBP additionally for hypertensive patients, and FBS additionally for diabetes patients as matching variables at the baseline in 2014. Propensity score matching was attempted using 1:1 nearest neighbor matching, 1:3 nearest neighbor matching, kernel matching, and radius matching. It was found that 1:1 nearest neighbor matching yielded the best results but only 31.63% of hypertension patients and 26.46% of diabetes patients were matched. Therefore, the propensity score matching DID (PSM-DID) analysis with 1:1 nearest neighbor matching was chosen for robustness analysis rather than the main analysis.
Results
Baseline characteristics
154,755 patients were finally included as the research sample, consisting of 123,607 patients with hypertension and 31,148 patients with diabetes. 130,697 patients contracted with family doctors and 24,058 were non-contracted. As seen in Table 1, contracted patients were older than non-contracted patients, who were more likely to be female and enrolled in the Urban-Rural Resident Basic Medical Insurance. The contracted had higher odds of comorbidity of hypertension and diabetes and tended to be overweight (BMI≥25). For the contracted hypertension patients, the course of hypertension was shorter than the non-contracted with an average of 10.39 years. The average scores and absolute value of SBP and DBP implied that at least 93% of hypertension patients controlled their blood pressure and there was a small but significant difference. As for the diabetes patients, the average score and value of FBG also demonstrated the contracted patients were in worse health status than the non-contracted.
Difference-in-differences regression
The study presented the annual follow-up visits, outpatient visits (both in community health centers and in secondary and tertiary hospitals), and inpatient admissions, as well as the proportion of outpatient visits in community health centers for the contracted and non-contracted groups in 2014 and 2017, as shown in Table 2. We compared different outcome variables between and within groups and all the differences were significant (p < 0.001), and a similar pattern of health service utilization among hypertension and diabetes patients was observed.
Compared with the non-contracted patients, the contracted significantly utilized more follow-up services and outpatient services both in 2014 and 2017, with a higher proportion of outpatient visits to community health centers, and the difference between groups became greater in 2017. Fewer outpatient visits in secondary and tertiary hospitals and inpatient admissions remained among the contracted from 2014 to 2017.
From 2014 to 2017, for contracted patients, there was a tendency that follow-up visits, outpatient visits, and outpatient visits in community health centers and its proportion, and inpatient admissions steadily increased while outpatient visits in secondary and tertiary hospitals decreased. The contracted group exhibited a greater increase in outpatient visits in community health centers compared to the overall increase in outpatient visits. During the same period, a slight but significant increase in outpatient visits, outpatient visits in community health centers, and its proportion were observed among non-contracted hypertension and diabetes patients, while follow-up visits and outpatient visits in secondary and tertiary hospitals among them declined. Furthermore, the non-contracted group experienced an increase in inpatient admissions from 2014 to 2017, and the magnitude of this increase was greater than that observed in the contracted group.
We identified a statistically significant impact of the family doctor system on health service utilization in patients with both diseases with the main DID results shown in Table 2. After controlling other factors, the family doctor system increased the follow-up service and outpatient service utilization. The results of DID models indicate that the contracted patients increased the number of annual follow-up visits (hypertension patients coef. = 0.13, diabetes patients coef. = 0.08, both p < 0.001), and outpatient visits (hypertension patients coef. = 0.08, diabetes patients coef. = 0.05, both p < 0.001).
In addition, the structure of outpatient service utilization has changed. More contracted patients went to community health centers for outpatient visits (hypertension patients coef. = 0.09, diabetes patients coef. = 0.07, both p < 0.001). The proportion of outpatient visits in community health centers among hypertension and diabetes patients also significantly rose (hypertension patients coef. = 0.02, diabetes patients coef. = 0.04, both p < 0.001). At the same time, outpatient visits in secondary and tertiary hospitals decreased with a greater magnitude in both disease groups (hypertension patients coef. = -0.14, diabetes patients coef. = -0.13, both p < 0.001).
As for inpatient admissions, the family doctor system may have a lower increase in annual inpatient admissions for contracted patients, but the results are mixed. The results of DID models demonstrate that among hypertensive patients, the family doctor system had a lower increase in annual inpatient admissions of contracted patients compared to non-contracted patients (coef. = -0.02, p = 0.042). Among diabetes patients, the contracted patients also had less annual inpatient admissions compared to non-contracted patients, but the lower increase is not statistically significant (coef. = -0.09, p = 0.124).
Robustness analysis
PSM-DID was conducted as the robustness test due to a large number of unmatched samples. After comparing the matching results of four different methods by the reduced bias and t-test of each variable before and after matching, 1:1 nearest matching with logit regression was selected as the best method and the k-density plots before and after matching are shown in Fig. 2. After 1:1 nearest matching, a total of 47,336 patients (39,094 hypertension patients and 8242 diabetes patients) were propensity score matched and two groups were balanced (Table 1).
The description of outcome variables for the matched contracted and non-contracted groups in 2014 and 2017 and the full results of PSM-DID are presented in Table 3. Consistent with the main analysis results, the differences observed in the comparison of outcome variables between and within the matched groups remained statistically significant (p < 0.001). The magnitude of differences between and within groups was similar to that observed in the main analysis. The PSM-DID results showed slightly small estimates for some outcome measures (follow-up visits among hypertension and diabetes patients, and the proportion of outpatient visits in community health centers among diabetes patients). However, all the estimates for the outcome measures were still significant, so the main DID results withstood the robustness test.
Discussion
Main findings
The study adds to the evidence of the impact of FD on health service utilization, which reveals that the family doctor system increases follow-up visits among contracted patients as well as outpatient visits, while it mitigates the increase in inpatient admissions. It also increases the health service utilization in community health centers and decreases it in secondary and tertiary hospitals among patients with hypertension and diabetes, implying a better structure of outpatient utilization. This paper not only extends previous study findings on the impact of the family doctor system but also enriches practical evidence for developing countries with similar contexts.
The results show that the family doctor system increased the follow-up service and outpatient service utilization and mitigated the increase in inpatient admissions, suggesting that contracted patients may shift their utilization from the inpatient care to the outpatient setting. Consistent with other studies, our study found that the family doctor system increases follow-up visits and outpatient visits among contracted patients. Compared to residents without FDs, contracted residents are proven to utilize more follow-up services, ambulatory primary care visits, and less hospitalization in developed countries [5, 6, 9,10,11, 18, 19]. Though surveys found the first-visit to primary care might increase [20,21,22,23,24], we made a marginal contribution by using the indicator, the proportion of outpatient visits in community health centers, and directly revealing that the family doctor system changes the structure of outpatient care by attracting patients with hypertension and diabetes to community health centers and decreasing the health service utilization in secondary and tertiary hospitals. At the same time, the results revealed an increase in outpatient visits, exceeding the reduction in hospital admissions. This may indicate that in developing countries like China, after systematic optimization of service content within the family doctor system, the accessibility of healthcare services for patients has improved. This has led to the release of unmet medical needs, resulting in an increase in the utilization of related services in the short term [2, 32].
Under the family doctor system reform, the substitution effect between outpatient and inpatient care may exist [33,34,35]. A possible explanation is that chronic disease management services, such as regular examinations, follow-up services, and health education or counseling, prevent or delay further progress and diminish avoidable inpatient admissions. For example, controlling blood glucose can prevent renal failure in diabetic patients, thus avoiding the utilization of inpatient services due to renal failure [33]. From the societal perspective, the family doctor system may be beneficial to harnessing health expenditure growth and promoting population health.
Among patients with hypertension and diabetes, in our study, the family doctor system promotes the utilization of follow-up services and outpatient services but mitigates the increase in inpatient services. On the one hand, this result is consistent with former results from developed countries which verified more outpatient service utilization [5, 6, 10, 11]. On the other hand, unlike previous studies, our research findings do not support the hypothesis that the family doctor system reduces hospital service utilization [5]. We only observed that in the period of 2014–2017, while both the signed and non-signed groups experienced an increase in hospitalization rates, the family doctor system helped mitigate the growth rate of hospitalizations within the signed group. This may be attributed to the following reasons: Firstly, with the progress of universal health coverage in China, residents’ healthcare demands have been released and met, leading to an overall increase in various types of services including inpatient care. Secondly, the content of China’s family doctor system primarily focuses on strengthening chronic disease management and providing organized and continuous services, with implementation effects mainly concentrated on increasing follow-up and outpatient visits and optimizing the structure of outpatient care. Lastly, as the family doctor system has only recently been implemented in China, its impact on hospital service utilization requires more time, as the effect transmission exhibits a certain lag.
The family doctor system promotes a better structure of outpatient utilization among different institutions. Corresponding to our hypothesis, DID results show that after controlling other factors, compared with non-contracted patients, FD increases the health service utilization in community health centers, but decreases it in secondary and tertiary hospitals among contracted patients with hypertension and diabetes. In other words, FD effectively guides the reasonable diversion of patients to different medical institutions and attracts more patients to community health service centers. In China, the national policy requires “Patients firstly utilize primary care to distinguish patients with urgent or chronic diseases for referrals; establishing a two-way referral system linking the primary health centers with secondary or tertiary hospitals”, and family doctors and their services are identified as the cornerstone of primary health care and the entry point to the referral systems [17, 36]. At this stage, we proved that the family doctor system partly realizes the policy goal of referral systems and strengthens the function of community health centers by attracting more outpatient visits from secondary and tertiary hospitals [18,19,20]. However, we did not observe the change in emergency visits due to data limitations, while other studies found fewer emergency services were utilized among people with FDs than people without FDs [5, 7, 8, 12].
Under the backdrop of the family doctor system reform, the chronic disease management implemented in China has been shifting its focus from treatment to prevention and management. In China, before the implementation of the family doctor system, traditional management of chronic diseases was primarily carried out by secondary and tertiary hospitals, neglecting the role of community health centers in follow-up and daily management, which was characterized by fragmentation, lack of systematicity, and disorderliness. The family doctor system introduced a contract-based model for managing chronic diseases, which emphasized the role of community health centers and multidisciplinary team collaboration, to provide comprehensive services such as health assessments, regular follow-ups, health education, and medication management. As a result, by emphasizing prevention, early intervention, and continuous services, the family doctor system would facilitate rational management of chronic diseases, promote the development of primary care, and elevate patients’ health.
Strengths and weaknesses of the study
This study fills the gap in China to quantitively evaluate the effect of the family doctor system for adequate observation time and adds to the evidence of the impact of FD on health service utilization with real-world data and appropriate methods. The study uses panel data to compare changes among contracted and non-contracted patients with hypertension and diabetes in health service utilization before and after the implementation of the family doctor system in real-world settings. The study combined two objective records with detailed information into the big sample size of 154,755 patients and then conducted the DID models and PSM method to rigorously evaluate this intervention with great validity.
Some limitations should be mentioned. Firstly, according to the comparison of the characteristics between contracted and non-contracted patients at baseline, there is a propensity whether a patient chooses to register with family doctors. Patients with hypertension and diabetes, who are female, elderly, with higher BMI and commodity of hypertension and diabetes, and enrolled in URRBMI intended to register with FD. It is consistent with previous Chinese research [37,38,39]. A possible reason is that the older the patients are, the worse their health condition, and the greater their motivation exists, and the more likely they register [32]. Our following study will also pay attention to the long-term impact of this selective behavior on health outcomes and disparity as a consensus mentioned in a local study [40]. Secondly, we cannot obtain more detailed data on emergency department utilization, medication usage, specific outpatient departments visited, diagnostic and treatment processes, and inpatient treatment, so we were unable to provide a comprehensive analysis of the overall impact of the family doctor system on healthcare utilization. The study can only draw conclusions regarding the optimization of outpatient utilization patterns but cannot infer policy implications regarding resource reallocation and the optimization of the referral system. Thirdly, due to a lack of relevant data, other variables that could reflect the severity of diseases among patients with hypertension and diabetes, were not collected. The severity of diseases was not included in the analysis and matching algorithms, and there may be other unobserved variables that could influence the outcome variables of this study. However, during the matching process, we included comorbidity as an indicator, primarily to capture the coexistence of diabetes and hypertension, attempting to partially reflect the complexity and severity of patients’ conditions. Nevertheless, it would be more accurate if we could conclude more related diseases such as heart disease, stroke, etc. Lastly, due to unavailable data in any other pre-treatment period earlier than 2014 as the baseline, the preliminary analysis cannot be conducted. To solve these two issues, the PSM method was conducted to balance the two groups as well as possible, which also showed robust results [41]. We will track the dynamic change of the family doctor system and evaluate its impact on health services in future studies.
Implications for policy and practice
Three significant implications are instructive internationally as China and several developing countries consider strengthening gatekeepers in primary care reform. Firstly, drawing upon the experiences from pilot cities and the positive impact of the family doctor system, it is recommended to tailor and improve local regulations based on specific circumstances and implement the family doctor system nationwide. Secondly, considering the insufficient signing rate and selective signing, there is still much room for enhancing publicity across multiple channels so residents can improve awareness of the importance and necessity of contracting with family doctors [4, 42, 43]. Lastly, the key to enhancing the effectiveness of the family doctor system primarily lies in focusing on services related to standard, personalized chronic disease management. For the younger and healthier residents, providing health education, counseling, and individualized services is necessary to attract them to register with FDs [42]. For other higher-demand groups besides chronic disease patients, such as the poor and the disabled, identifying these populations and fully understanding their requirements are important to promote universal coverage and reduce health disparity [44, 45].
Conclusions
In conclusion, this paper constructed Difference-in-Differences models based on the official health management records and medical insurance claim data of the patients with hypertension and diabetes to evaluate the family doctor system on health service utilization. The family doctor system increases follow-up visits and outpatient visits, and mitigates the increase inpatient admissions, and it also promotes a better structure of outpatient utilization with more outpatient visits in community health centers and fewer in secondary and tertiary hospitals. The examined family doctor system strengthens primary care, both by increasing follow-up visits and outpatient visits and promoting a rationalized structure of outpatient utilization in China.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the H city’s Health Information Center and the municipal Medical Insurance Bureau but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available.
Abbreviations
- PHC:
-
Primary Health Care
- FP:
-
Family Physicians
- GP:
-
General Practitioner
- FD:
-
Family Doctors
- DID:
-
Differences-In-Differences
- PSM:
-
Propensity Score Matching
References
World Health Organization. Primary health care.|.*2020*2020.; 2020.
Yip WN, Fu HQ, Chen AT, Zhai TM, Jian WY, Xu RM, Pan J, Hu M, Zhou ZL, Chen QL et al. 10 years of health-care reform in China: progress and gaps in Universal Health Coverage. LANCET 2019, 394(10204):1192–1204.
World Health Organization. Operational Framework for Primary Health Care.|.*2020*2020.; 2020.
Yuan SS, Wang F, Li X, Jia M, Tian MM. Facilitators and barriers to implement the family doctor contracting services in China: findings from a qualitative study. BMJ OPEN 2019, 9(10).
Friedberg MW, Rosenthal MB, Werner RM, Volpp KG, Schneider EC. Effects of a Medical Home and Shared Savings Intervention on Quality and Utilization of Carevol 175, pg 1362, (2015). JAMA INTERN MED 2015, 175(8):1426.
Ha NT, Harris M, Preen D, Robinson S, Moorin R. Identifying patterns of general practitioner service utilisation and their relationship with potentially preventable hospitalisations in people with diabetes: the utility of a cluster analysis approach. DIABETES RES CLIN PR. 2018;138:201–10.
Yang BH, Messom R. Association between potential primary care emergency service and general practitioner care utilisation inNew South Wales. EMERG MED AUSTRALAS. 2021;33(1):52–7.
Almeida A, Vales J. The impact of primary health care reform on hospital emergency department overcrowding: evidence from the Portuguese reform. INT J HEALTH PLAN M. 2020;35(1):368–77.
Gyulai A, Nagy A, Pataki V, Tonte D, Adany R, Voko Z. General practitioners can increase participation in cervical cancer screening - a model program in Hungary. BMC FAM PRACT 2018, 19.
Bayati M, Keshavarz K, Lotfi F, KebriaeeZadeh A, Barati O, Zareian S, Amiri A, Delavari S. Effect of two major health reforms on health care cost and utilization in Fars Province of Iran: family physician program and health transformation plan. BMC HEALTH SERV RES 2020, 20(1).
Huang PT, Kung PT, Kuo WY, Tsai WC. Impact of family physician integrated care program on decreasing utilization of emergency department visit and hospital admission: a population-based retrospective cohort study. BMC HEALTH SERV RES 2020, 20(1).
Fung C, Wong C, Fong D, Lee A, Lam C. Having a family doctor was associated with lower utilization of hospital-based health services. BMC HEALTH SERV RES 2015, 15.
The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Opinions on Deepening the Reform of the Medical and Health System.|.*2020*2020.; 2009.
National Medical Reform Office. Notice on Promoting Guidance for Family Doctor Contract Services.; 2016.
Shang XP, Huang YM, Li BE, Yang Q, Zhao YR, Wang W, Liu Y, Lin JF, Hu CG, Qiu YW. Residents’ Awareness of Family Doctor Contract Services, Status of Contract with a Family Doctor, and Contract Service Needs in Zhejiang Province, China: A Cross-Sectional Study. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH AND PUBLIC HEALTH 2019, 16(18).
Liang WWCWP. Development Report on Health Reform in China 2020. Beijing: Social Sciences Academic Press (China); 2020.
World Health Organization. Healthy China: Deepening Health Reform in China. Washington, DC: World Bank and World Health Organization; 2019.
Li M, Gao Y, Mao Q. Study on the Impact of Family Doctor Contracting Service on Health Service utilization of chronic patients. Health Econ Res. 2019;2(36):38–42.
Qiu B, Huang J, Liang H. A comparative study on the health services utilization and satisfaction of the family doctor service. Chin J Health Policy. 2016;1(9):31–6.
Wang Y, Wang J, Maitland E. Growing old before growing rich: inequality in health service utilization among the mid-aged and elderly in Gansu and Zhejiang Provinces, China. Bmc Health Serv Res. 2012;12(12):302–13.
Zheng QM, Shi L, Pang TT, Leung W. Utilization of community health care centers and family doctor contracts services among community residents: a community-based analysis in Shenzhen, China. BMC FAM PRACT 2021, 22(1).
Huang JL, Liu Y, Zhang T, Wang L, Liu SS, Liang H, Zhang YM, Chen G, Liu CJ. Can family doctor contracted services facilitate orderly visits in the referral system? A frontier policy study from Shanghai, China. INT J HEALTH PLAN M. 2022;37(1):403–16.
Yu Y, Ye AZ, Chen C, Dai WD, Liu X. The impact of family doctor system on patients’ utilisation of general practitioner in primary care facilities-Evidence from Hangzhou, China. INT J HEALTH PLAN M 2022.
Huang JL, Lu W, Wang L, Zhang T, Liu CJ, Liu SS, Liang H, Zhang YM, Guo DF. A preliminary effect analysis of family doctor and medical insurance payment coordination reform in Changning District of Shanghai, China. BMC FAM PRACT 2019, 20.
Wu R. The effects of Contract Service Status from General Practitioner on the Utilization of Health Services among Community residents in Pukou District, Nanjing City. Med Soc. 2019;2(32):9–15.
Klein J, von Dem Knesebeck O. Social disparities in outpatient and inpatient care. An overview of current findings in Germany. BUNDESGESUNDHEITSBLA. 2016;59(2):238–44.
Qian Y, Zhou Z, Yan J, Gao J, Wang Y, Yang X, Xu Y, Li Y. An economy-ralated equity analysis of health service utilization by women in economically underdeveloped regions of western China. INT J EQUITY HEALTH. 2017;16(1):186.
Li C, Tang C, Wang H. Effects of health insurance integration on health care utilization and its equity among the mid-aged and elderly: evidence from China. INT J EQUITY HEALTH. 2019;18(1):166.
Rao M, Katyal A, Singh PV, Samarth A, Bergkvist S, Kancharla M, Wagstaff A, Netuveli G, Renton A. Changes in addressing inequalities in access to hospital care in Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra states of India: a difference-in-differences study using repeated cross-sectional surveys. BMJ OPEN 2014, 4(6).
Stokes J, Kristensen SR, Checkland K, Bower P. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary team case management: difference-in-differences analysis. BMJ OPEN 2016, 6(4).
Keeble E, Bardsley M, Durand MA, Hoomans T, Mays N. Area level impacts on emergency hospital admissions of the integrated care and support pioneer programme in England: difference-in-differences analysis. BMJ OPEN 2019, 9(8).
Yip W, Hsiao W. Harnessing the privatisation of China’s fragmented health-care delivery. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):805–18.
Elek P, Molnar T, Varadi B. The closer the better: does better access to outpatient care prevent hospitalization? EUR J HEALTH ECON. 2019;20(6):801–17.
Adhikari SR. An assessment of a substitute or complement for inpatient and outpatient care of visceral leishmaniasis in Nepal. J VECTOR DIS. 2012;49(4):242–8.
WICKIZER TM, WHEELER J, FELDSTEIN PJ. Have hospital inpatient cost containment programs contributed to the growth in outpatient expenditures - analysis of the substitution effect associated with hospital utilization review. MED CARE. 1991;29(5):442–51.
Yip W, Hsiao W, Meng QY, Chen W, Sun XM. Realignment of incentives for health-care providers in China. Lancet. 2010;375(9720):1120–30.
Huang Y, Feng L, Li Z. Studying on the Status of General practitioners’ services and its influencing factors sampled with Longhua District of Shenzhen. Chin Health Service Manage. 2018;2(31):49–51.
Liu Q, Zhong W, Wang Z. Demands for Family Physician Service among Community Elderly in Wuhan City and Influcing factors. 2018, 2(31):49–51.
Li Q, Huang W, Miao C. Study on urban residents’ willingness of family doctor contract and its influencing factors in Xuzhou. 2018, 3(21):262–6.
Huang J, Zhu Q, Guo J. Can Health Disparity be eliminated? The role of Family Doctor played in Shanghai, China. INT J ENV RES PUB HE 2020, 17(15).
Tang B, Wang Y, Gao Y, Wu S, Li H, Chen Y, Shi Y. The Effect of Boarding on the Mental Health of Primary School students in Western Rural China. INT J ENV RES PUB HE 2020, 17(21).
Mercer SW, Siu JY, Hillier SM, Lam CL, Lo YY, Lam TP, Griffiths SM. A qualitative study of the views of patients with long-term conditions on family doctors in Hong Kong. BMC FAM PRACT. 2010;11:46.
Fu P, Wang Y, Liu S, Li J, Gao Q, Zhou C, Meng Q, Sylvia S. Analysing the preferences for family doctor contract services in rural China: a study using a discrete choice experiment. BMC FAM PRACT. 2020;21(1):148.
World Health Organization. WHO global strategy on people-centred and integrated health services interim report. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Document Production Services; 2015.
Huang SS, Yin AT, Liu QQ, Sun XH. Can the implementation of family doctor contracted service enable the elderly to utilize primary health care services more equally? Empirical evidence from Shandong, China. BMC Prim CARE 2022, 23(1).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Qiuyue Zhu for her supporting work on data cleaning and analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China, 20ZDA072; the Shanghai Pujiang Program, 21PJC024; the Shanghai Philosophy and Social Science Research Program, 2020BGL003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LZ and WC conceived and designed the study. LZ and ZP analyzed the data. ZP wrote the manuscript. LZ and WC revised the manuscript. The first two authors LZ and PZ contributed equally to this paper and should be regarded as co-first authors. All authors read and approved this manuscript before submission to this journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Since the data we used came from anonymized and secondary databases, human participants were not directly involved in the study, and the informed consent was exempted. The Ethics Review Committee of the School of Public Health, Fudan University approved our study (IRB# 2016-03-19) and waived the requirement of informed consent. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations (declarations of helsinki).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Zhang, P. & Chen, W. Can family doctor system improve health service utilization for patients with hypertension and diabetes in China? A difference-in-differences study. BMC Health Serv Res 24, 454 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10903-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10903-6