Abstract
Background
The mechanical properties of fully crystallized lithium aluminosilicate ceramics may be influenced by intraoral temperature variations and postmilling surface treatment. The purpose of this study is to explore the interplay among glazing, thermocycling, and the mechanical characteristics (namely, fracture toughness and hardness) of fully crystallized lithium aluminosilicate ceramics.
Methods
Bending bars (n = 40) cut from LisiCAD blocks (GC, Japan) were randomly assigned to glazed or unglazed groups (n = 20) and subjected to the single edge v-notch beam method to create notches. A glazing firing cycle was applied to the glazed group, while the unglazed group was not subjected to glazing. Half of the specimens (n = 10) from both groups underwent thermocycling before fracture toughness testing. The fracture toughness (KIC) was evaluated at 23 ± 1 °C using a universal testing machine configured for three-point bending, and the crack length was measured via light microscopy. Seven specimens per group were selected for the hardness test. Hardness was assessed using a Vickers microhardness tester with a 1 kg load for 20 s, and each specimen underwent five indentations following ISO 14705:2016. The Shapiro–Wilk and Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests were used to evaluate the normality of the data and a two-way ANOVA was utilized for statistical analysis. The significance level was set at (α = 0.05).
Results
Regardless of the thermocycling conditions, the glazed specimens exhibited significantly greater fracture toughness than did their unglazed counterparts (P < 0.001). Thermocycling had no significant impact on the fracture toughness of either the glazed or unglazed specimens. Furthermore, statistical analysis revealed no significant effects on hardness with thermocycling in either group, and glazing alone did not substantially affect hardness.
Conclusions
The impact of glazing on the fracture toughness of LiSiCAD restorations is noteworthy, but it has no significant influence on their hardness. Furthermore, within the parameters of this study, thermocycling was found to exert negligible effects on both fracture toughness and hardness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Lithium disilicate (Li2Si2O5), a versatile glass-ceramic material, has gained immense popularity in restorative dentistry and prosthodontics due to its exceptional esthetic properties, biocompatibility, and strength. Its unique combination of translucency and mechanical robustness makes it an ideal choice for fabricating dental restorations such as inlays, crowns, veneers, and short span anterior bridges. Critical to the clinical success of these restorations are their mechanical properties, which play pivotal roles in ensuring durability and longevity [1].
In recent years, researchers and dental practitioners have focused on understanding the mechanical properties of lithium disilicate, particularly in the context of glazed and unglazed surfaces [2,3,4,5,6]. The mechanical properties, specifically fracture toughness and hardness, are vital factors that influence the longevity and clinical success of dental restorations [7]. Fracture toughness, a measure of a material’s resistance to crack propagation, is a key determinant of the material’s ability to withstand occlusal forces and resist chipping or cracking during mastication [8]. Hardness, on the other hand, reflects a material’s resistance to indentation or scratching, which can impact both aesthetics and durability [8].
Studies have shown that the application of glaze to the surface of dental ceramics can alter their mechanical properties, potentially enhancing or decreasing their fracture resistance and hardness [6, 9,10,11]. Glazing is a common step in the fabrication of dental ceramic restorations and is aimed at improving aesthetic properties and surface smoothness [12]. However, the effect of glazing on the mechanical behavior of lithium disilicate remains a topic of ongoing research and debate [6, 13]. Moreover, other factors, such as thermocycling, which simulates the cyclic temperature changes experienced in the oral environment, can induce thermal stresses that potentially compromise the mechanical performance of ceramics [9].
Recently, novel precrystallized lithium alumino disilicate blocks designed for computer-aided milling (CAM) have been introduced to the dental market. A significant advantage associated with these blocks is the elimination of the crystallization firing process, which results in cost and time savings. Additionally, these blocks have been promoted to be time-efficient due to their ability to yield restorations that can be polished chairside after milling, obviating the need for subsequent glazing to achieve a glossy surface [6]. However, comprehensive evaluation of the mechanical and surface characteristics of these materials is needed. Therefore, this laboratory study aimed to investigate the relationships between glazing and thermocycling and between glazing and the mechanical properties of new fully crystallized lithium aluminosilicate ceramics, with a specific focus on fracture toughness and hardness. The null hypothesis is that neither fracture toughness nor hardness will be affected by glazing or thermocycling.
Materials and methods
The materials used in the study are presented in Table 1.
Sample size
The determination of sample size for the fracture toughness test adhered to ISO 23,146 guidelines [14], specifying a minimum of 5 specimens and recommending a sample size of 7 specimens. In the present study, 10 specimens were used per group. In terms of the hardness test, we opted for a sample size of 7 specimens per group, aligning with the mean sample size in previous literature [15,16,17].
Fracture toughness test
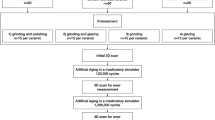
Forty bending bars 16 mm in length, 4 mm in thickness, and 3 mm in width were cut from LisiCAD blocks (GC Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) using a low-speed precision micromotor (NSK Ultimate XL-K, Kanuma Tochigi, Japan) and polished using 1500, 2500, and 4000-grit silicon carbide papers (Metaserv 250 Grinder Polisher; Buehler) at 350 rpm under running water. The bars’ dimensions were checked using a digital micrometer (Absolute Digimatic, Mitutoyo Corp., Japan). Afterwards, the bars were randomly assorted into two groups: glazed and unglazed groups. The bars in the glazed group were coated with a layer of GC Initial IQ Lustre Pastes (GC Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and subjected to a glazing firing cycle in a dental ceramic furnace (Programat P300 Oven, Ivoclar Vivadent) according to the manufacturer’s parameters (Table 2). The specimens in the unglazed group were left without glazing. The single edge v-notch beam method (SEVNB) was used to create a notch in each test specimen according to ISO 23,146 [14]. The specimens were securely held in metal holders, with the 3 mm wide surface facing upward. A diamond disc with a 0.6 mm thickness and a slow-speed handpiece mounted on a positioning device was employed to cut a sharp notch at the center of each beam. A pilot non-tested sample was first notched and examined under scanning electron microscope (JSM 6610 LV, Jeol Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) to confirm the notch quality and depth (Fig. 1). The notches of test specimens were examined using stereomicroscope (EMZ-5; Meiji Techno CO., Saitama, Japan) and had a typical depth ranging between 0.8 and 1.2 mm. A razor blade coated with diamond paste was inserted at the bottom of the notch to initiate a small fracture, which could penetrate to a depth of 0.1 to 0.2 mm. Subsequently, the beams were removed and cleaned for 10 min in an ultrasonic bath filled with distilled water. Crack length measurements were conducted using stereomicroscope (EMZ-5; Meiji Techno CO., Saitama, Japan) at a magnification of X50.
Half of the glazed and unglazed specimens were selected for the initial fracture toughness measurements. The remaining specimens were subjected to a thermocycling process (THE-1100, SD Mechatronik, Feldkirchen-Westerham, Germany) for 30,000 cycles (5 °C to 55 °C; 30-second dwell time in each bath with a transfer time of 10 s) in distilled water before testing [18].
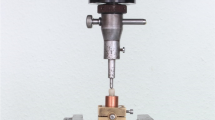
Fracture toughness (KIC) was evaluated at 23 ± 1 °C using a universal testing machine (INSTRON 5965, Norwood, MA, USA) with a 5 kN load cell. The machine was configured for three-point bending, with a 12 mm span, and the loads were recorded at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min until fracture occurred. The notch in the specimen was positioned perpendicular to the load plunger at the center of the span (Fig. 2). A central load was applied to the beam specimen until it reached its fracture point. All the experimental groups were tested on the same day and under identical ambient conditions to minimize measurement bias.
The fracture toughness (KIC) in MPa.m1/2 was calculated using Eq. (1), which involves the maximum load (P) capable of causing a fracture.
where P is the maximum fracture load in Newtons (N), L is the span length (mm), B is the specimen width (mm), and W is the specimen height (mm). The calibration function for the given geometry, Y, was calculated using Eq. (2).
where a represents the notch depth.
Hardness test
The hardness was assessed following ISO 14705:2016 [19]. Seven specimens from each group were subjected to a 1 kg load applied for 20 s at room temperature using a Vickers microhardness tester (FM-700, Future Tech, Kawasaki, Japan). Each specimen was subjected to five indentations, and the Vickers hardness was automatically calculated according to the following formula:
where F is the intender load in newtons and d is the mean of the two diagonal lengths in millimeters. The average of the five readings was then calculated and assigned as the final hardness value. The final value was subsequently calculated in GPa to facilitate comparison with previous results in the literature.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis for this study was conducted using SPSS software (version 27, Chicago, IL, USA). To ensure the normality of the data, the Shapiro–Wilk and Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests were employed. A two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test was utilized to investigate the effects of two factors, “Glazing” and “Thermocycling”, and their interaction on the fracture toughness and hardness of the material. The significance level was set at (α = 0.05).
Results
Fracture toughness
The fracture toughness results met the criteria for a normal distribution, ensuring the validity of subsequent statistical tests. Irrespective of the thermocycling conditions, the glazed specimens exhibited notably greater fracture toughness than did their unglazed counterparts (P < 0.001). The interaction between thermocycling and glazing did not show significance (p = 0.385). Furthermore, the fracture toughness was not significantly influenced by thermocycling in either the glazed (p = 0.125) or unglazed (p = 0.740) groups. (Fig. 3).
Hardness
The hardness data showed a normal distribution. In the context of thermocycling, our statistical analysis revealed no statistically significant effects on hardness in either the glazed or unglazed groups. Additionally, the application of glazing itself had no substantial impact on hardness, regardless of thermocycling (Fig. 3). Similar to fracture toughness results, the interaction between thermocycling and glazing did not show significance (p = 0.651).
Discussion
This study investigated the impact of glazing and thermocycling on the mechanical behavior of a new fully crystallized lithium disilicate CAD/CAM block (LisiCAD; GC) regarding fracture toughness and hardness. The null hypothesis was accepted in the context of the hardness results. Nevertheless, concerning the fracture toughness results, the null hypothesis was partially supported, as it was found that glazing indeed led to a statistically significant increase in fracture toughness.
The computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technique employs diamond burs for precise carving of the designed restoration from premanufactured ceramic blocks. This precision machining procedure is documented to engender mechanical residual stresses as well as significant surface and subsurface defects within the ultimate ceramic restoration, subsequently compromising its mechanical strength [20, 21]. For example, Curran et al. observed a 40–60% reduction in the strength of densely crystallized lithium disilicate following grinding [22]. Consequently, hard machining should be avoided due to its detrimental impact on both the material strength and the longevity of grinding burs.
The LiSiCAD blocks, which were originally developed as fully crystallized lithium disilicate blocks for subtractive milling, are interesting materials. The manufacturer suggests that glazing is not mandatory, and that adequate strength can be achieved through polishing alone, potentially offering time and cost savings to clinicians. However, extant research has emphasized the potential impact of glazing on enhancing the fracture resistance of lithium disilicate restorations [4, 9], and glazing may also influence material hardness.
The fracture toughness of ceramic restorations is important because of its ability to predict the resistance of materials to crack propagation during the masticatory process. The single edge V-Notch beam (SEVNB) method employed for fracture toughness assessment in this investigation has been widely applied in previous research [23,24,25].
In the present study, glazing substantially augmented the fracture toughness of fully crystallized lithium disilicate specimens, a phenomenon consistent across both thermocycled and nonthermocycled specimens. Notably, the literature predominantly addresses the impact of glazing on flexural strength, with a conspicuous absence of studies focusing on the influence of glazing on fracture toughness. Consequently, the comparison of our findings with those of previous research was rendered unfeasible.
Lisi blocks primarily consist of SiO2 and Li2O, alongside additional oxides like Al2O3, K2O, and CeO2. These additives primarily serve to enhance resistance to solubility and reduce melting temperatures [26]. The process of machining induces numerous surface cracks and defects [21]. Glazing ceramic restorations involves a procedure where a low viscosity glaze is fired onto the restoration surface to seal pores and create a glossy finish [9]. Furthermore, subjecting the ceramic to elevated temperatures after milling is believed to be advantageous, as glass ceramics have been noted to exhibit a phenomenon known as “self-crack-healing”. This phenomenon involves the flow of SiO2 at high temperatures to fill the cracks [27].
The impact of glazing on flexural strength has been investigated in prior literature and found to be controversial [2, 9, 28]. Aurelio et al. reported that a prolonged glaze firing process enhances the biaxial flexural strength of hard-machined lithium disilicate ceramics [28]. This finding supports the hypothesis that the glazing process initiates the development of a superficial vitreous layer that permeates submicroscopic surface defects, facilitating defect healing and enhancing the structural integrity of the restoration [9]. Moreover, subjecting the material to elevated firing temperatures can alter the microstructure [29]. Conversely, in a study by Fraga et al., glaze firing was reported to reduce ceramic strength. These authors attributed this to the ability of glaze firing to potentially alter the ceramic microstructure through the formation of amorphous material [10]. Moreover, in a recent study that investigated the fracture resistance of polished and glazed LisiCAD crowns, no significant difference was observed [6].
Another factor that could affect the strength of glazed ceramics is the mismatch in coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) between the glaze and ceramic substrate [30]. Any fired ceramic object experiences expansion as it is heated and contraction as it is cooled. The ideal glaze should have a slightly lower expansion than the body to put it under some compression. Glazes that have a higher expansion than the body by implication also contract more on cooling. This puts the glaze under tension and will likely form a network of cracks to relieve the stress [30, 31]. The CTE of liSi block is 10.3 × 10− 6 K− 1, while the CTE of the glaze is unknow but the manufacturer claims that it is suitable for ceramics with a CTE range of 6.9 to 13.3.
Thermocycling is commonly used in literature for aging dental restorative materials [32, 33]. There is no agreement among researchers about the number of thermal cycles, however it is suggested that 10,000 cycles approximately correspond to one year of clinical function [33]. In the present study, 30,000 cycle were employed to simulate three years. Thermocycling was performed to simulate the rigorous conditions encountered within the oral environment. Temperature fluctuations occurring in the oral cavity have been reported to negatively impact the strength of dental restorations and accelerate crack development [32]. Silicate glasses are subjected to stress corrosion in the presence of water due to the capacity of water vapor in the surrounding environment to break strained Si-O bonds through chemical reactions [34].
No notable impact of thermocycling on either fracture toughness or material hardness was discerned in the present study. The concentrated crystalline content found within glass ceramics enhances their hardness and elastic modulus values, rendering them more resistant to the deteriorating effect of thermal changes compared to hybrid materials, such as resin nanoceramics and polymer infiltrated ceramic networks [32].
Measuring the surface hardness holds substantial significance in examining the intraoral performance of restorative materials. This reflects a material’s ability to resist permanent indentation or penetration [35]. The elevated hardness levels observed in dental porcelains and ceramics are undesirable, as they have been correlated with excessive wear in antagonist teeth [35]. In the present study, the glazing process had no discernible impact on the material’s hardness. In the current literature, the exact relationship between glazing/firing and material hardness has not been fully elucidated. Our research findings suggest that the stability of surface hardness is likely attributed to an equilibrium state between the beneficial influence of the glaze layer in ameliorating surface defects arising from machining [9] and the well-documented adverse impact of elevated temperatures on the mechanical properties of lithium disilicate-based ceramics as a result of microstructural alteration [10, 13, 36]. This assumption should be further investigated in future studies.
The results of our KIC and hardness measurements are consistent with the established ranges reported in the scientific literature for silica-based ceramic materials [8, 15, 35]. Specifically, the mean KIC values for LisiCAD were 2.82 ± 0.14 MPa.m1/2 for unglazed specimens and 3.13 ± 0.18 MPa.m1/2 for glazed specimens. Similarly, the mean hardness values were 6.70 ± 0.30 GPa for the unglazed specimens and 6.43 ± 0.36 GPa for the glazed specimens.
In a comparative investigation, Elsaka and Elnaghy [24] reported KIC values of 2.31 ± 0.17 MPa.m1/2 for Vita Suprinity and 2.01 ± 0.13 MPa.m1/2 for EmaxCAD. Additionally, they reported Vickers hardness values of 6.53 ± 0.46 GPa for Vita Suprinity and 5.45 ± 0.28 GPa for EmaxCAD. Notably, LiSiCAD is distinguished by a higher Al2O3 content relative to EmaxCAD [37, 38], which contributes to increased mechanical strength and reduced chemical solubility in glass ceramics [39]. Furthermore, previous research has demonstrated that even minor additions of Al2O3 to pure lithium disilicate result in enhanced densification and improved mechanical strength [40].
Due to the complex nature of clinical situations, the findings of the current in-vitro investigation necessitate careful consideration when applied to predict clinical consequences. Although thermocycling served as a method of simulating artificial aging to forecast the long-term deterioration of glass ceramics, it is noteworthy that other influential factors such as mechanical and chemical stimuli were not explored, thus representing a limitation in this study. Future investigations incorporating various aging protocols are essential to validate the findings of the present study.
Conclusion
These findings collectively suggest that while glazing has a pronounced effect on fracture toughness, it does not significantly influence the hardness of the specimens. Moreover, the data imply that thermocycling, under the conditions of this study, does not exert a substantial influence on either fracture toughness or hardness, offering valuable insights for further research and practical applications in material science.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- KIC:
-
Fracture toughness
- CAM:
-
Computer aided milling
- CAD/CAM:
-
Computer-aided design/ Computer-aided manufacturing
- SEM:
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy
References
Zarone F, Ferrari M, Mangano FG, Leone R, Sorrentino R. Digitally Oriented Materials: Focus on Lithium Disilicate Ceramics. Int J Dent 2016, 2016:9840594.
Alao AR, Stoll R, Song XF, Abbott JR, Zhang Y, Abduo J, Yin L. Fracture, roughness and phase transformation in CAD/CAM milling and subsequent surface treatments of lithium metasilicate/disilicate glass-ceramics. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;74:251–60.
Albakry M, Guazzato M, Swain MV. Effect of sandblasting, grinding, polishing and glazing on the flexural strength of two pressable all-ceramic dental materials. J Dent. 2004;32(2):91–9.
Aurelio IL, Fraga S, Dorneles LS, Bottino MA, May LG. Extended glaze firing improves flexural strength of a glass ceramic. Dent Mater. 2015;31(12):e316–324.
Celik G, Uludag B, Usumez A, Sahin V, Ozturk O, Goktug G. The effect of repeated firings on the color of an all-ceramic system with two different veneering porcelain shades. J Prosthet Dent. 2008;99(3):203–8.
Fouda AM, Stawarczyk B, Ozcan M, Singer L, Bourauel C. Impact of glazing on wear, fracture load, and optical properties of a new fully crystallized lithium disilicate ceramic material. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;146:106102.
Albakry M. Insightful understanding of the role of the Mechanical properties in defining the reliability of All-Ceramic Dental restorations: a review. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol. 2021;12(04):57–78.
Albakry M, Guazzato M, Swain MV. Fracture toughness and hardness evaluation of three pressable all-ceramic dental materials. J Dent. 2003;31(3):181–8.
Vasiliu RD, Porojan SD, Birdeanu MI, Porojan L. Effect of Thermocycling, Surface treatments and microstructure on the Optical properties and Roughness of CAD-CAM and Heat-pressed Glass ceramics. Mater (Basel) 2020, 13(2).
Fraga S, Valandro LF, Bottino MA, May LG. Hard machining, glaze firing and hydrofluoric acid etching: do these procedures affect the flexural strength of a leucite glass-ceramic? Dent Mater. 2015;31(7):e131–140.
Longhini D, Rocha CO, Medeiros IS, Fonseca RG, Adabo GL. Effect of glaze cooling rate on Mechanical properties of Conventional and pressed porcelain on Zirconia. Braz Dent J. 2016;27(5):524–31.
Kurt M, Bankoglu Gungor M, Karakoca Nemli S, Turhan Bal B. Effects of glazing methods on the optical and surface properties of silicate ceramics. J Prosthodont Res. 2020;64(2):202–9.
Miranda JS, Barcellos ASP, Campos TMB, Cesar PF, Amaral M, Kimpara ET. Effect of repeated firings and staining on the mechanical behavior and composition of lithium disilicate. Dent Mater. 2020;36(5):e149–57.
ISO23146: Test methods for determining the fracture toughness of monolithic ceramics using V-notch bend specimens (SEVNB method). European Committee for Standardization (CEN). 2016, Brussels:1–26.
Alencar-Silva FJ, Barreto JO, Negreiros WA, Silva PGB, Pinto-Fiamengui LMS, Regis RR. Effect of beverage solutions and toothbrushing on the surface roughness, microhardness, and color stainability of a vitreous CAD-CAM lithium disilicate ceramic. J Prosthet Dent. 2019;121(4):711. e711-711 e716.
Cruz MEM, Simoes R, Martins SB, Trindade FZ, Dovigo LN, Fonseca RG. Influence of simulated gastric juice on surface characteristics of CAD-CAM monolithic materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2020;123(3):483–90.
Kukiattrakoon B, Hengtrakool C, Kedjarune-Leggat U. Chemical durability and microhardness of dental ceramics immersed in acidic agents. Acta Odontol Scand. 2010;68(1):1–10.
Hampe R, Theelke B, Lumkemann N, Eichberger M, Stawarczyk B. Fracture toughness analysis of ceramic and Resin Composite CAD/CAM Material. Oper Dent. 2019;44(4):E190–201.
ISO14705:2016. Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Test Method for Hardness of Monolithic Ceramics at Room Temperature. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland 2016.
Denry I. How and when does fabrication damage adversely affect the clinical performance of ceramic restorations? Dent Mater. 2013;29(1):85–96.
Rice RW. Monolithic and composite ceramic machining flaw-microstructure-strength effects: model evaluation. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2002;22(9–10):1411–24.
Curran P, Cattani-Lorente M, Anselm Wiskott HW, Durual S, Scherrer SS. Grinding damage assessment for CAD-CAM restorative materials. Dent Mater. 2017;33(3):294–308.
Liu H, Zhao W, Ji Y, Cui JP, Chu YH, Rao PG. Determination of fracture toughness of zirconia ceramics with different yttria concentrations by SEVNB method. Ceram Int. 2017;43(13):10572–5.
Quinn JB, Sundar V, Lloyd IK. Influence of microstructure and chemistry on the fracture toughness of dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2003;19(7):603–11.
Domingues NB, Galvão BR, Ribeiro S, Almeida Junior AAd, Longhini D, Adabo GL. Comparison of the indentation strength and single-edge-v-notched beam methods for dental ceramic fracture toughness testing. Brazilian J Oral Sci. 2017;15(2):109.
Lubauer J, Belli R, Peterlik H, Hurle K, Lohbauer U. Grasping the Lithium hype: insights into modern dental Lithium Silicate glass-ceramics. Dent Mater. 2022;38(2):318–32.
Hammood I, Barber G, Wang B. A review of some of experimental and numerical studies of self-crack‐healing in ceramics. Int J Ceramic Eng Sci. 2020;2(6):274–91.
Aurelio IL, Prochnow C, Guilardi LF, Ramos GF, Bottino MA, May LG. The effect of extended glaze firing on the flexural fatigue strength of hard-machined ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2018;120(5):755–61.
Kamnoy M, Pengpat K, Intatha U, Eitssayeam S. Effects of heat treatment temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of lithium disilicate-based glass-ceramics. Ceram Int. 2018;44:S121–4.
Plešngerová B, Kovalcikova M. Influence of the thermal expansion mismatch between body and glaze on the crack density of glazed ceramics. Ceram Silik. 2003;47:100–7.
Kavanová M, Klouzková A, Klouzek J. Characterization of the Interaction between glazes and ceramic bodies. Ceram-Silikaty. 2017;61(3):267–75.
Kim SY, Bae HJ, Lee HH, Lee JH, Kim YJ, Choi YS, Lee JH, Shin SY. The effects of Thermocycling on the physical properties and biocompatibilities of various CAD/CAM restorative materials. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15(8).
Morresi AL, D’Amario M, Capogreco M, Gatto R, Marzo G, D’Arcangelo C, Monaco A. Thermal cycling for restorative materials: does a standardized protocol exist in laboratory testing? A literature review. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;29:295–308.
Krohn MH, Hellmann JR, Pantano CG, Lower NP, Brow RK. Effects of Tin on the Physical Properties and Crack Growth in Soda-Lime-Silica Float Glass. In: Fracture Mechanics of Ceramics: 2005// 2005; Boston, MA: Springer US; 2005: 135–148.
Elsaka SE, Elnaghy AM. Mechanical properties of zirconia reinforced lithium silicate glass-ceramic. Dent Mater. 2016;32(7):908–14.
Serrado de Pinho Barcellos A, Soares Miranda J, Amaral M, Araujo Alvarenga J, Nogueira L, Tomomitsu Kimpara E. Effect of staining on the mechanical, surface and biological properties of lithium disilicate. Saudi Dent J. 2022;34(2):136–41.
Fouda AM, Atta O, Kassem AS, Desoky M, Bourauel C. Wear behavior and abrasiveness of monolithic CAD/CAM ceramics after simulated mastication. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;26(11):6593–605.
Garoushi S, Sailynoja E, Vallittu PK, Lassila L. Fracture-Behavior of CAD/CAM ceramic crowns before and after cyclic fatigue aging. Int J Prosthodont. 2023;36(5):649.
El-Meliegy E. RvN: Glasses and Glass Ceramics for Medical Applications. New York: Springer; 2012.
Fernandes HR, Tulyaganov DU, Goel A, Ribeiro MJ, Pascual MJ, Ferreira JMF. Effect of Al2O3 and K2O content on structure, properties and devitrification of glasses in the Li2O–SiO2 system. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2010;30(10):2017–30.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Open access funding provided by DEAL agreement.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.F.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing of original draft; C.B.: resources, supervision, and extensive editing; A.S. and A.K.: visualization, interpretation of data. A.A.: methodology, formal analysis, validation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Fouda, A.M., Bourauel, C., Samran, A. et al. Effect of glazing and thermocycling on the fracture toughness and hardness of a New fully crystallized aluminosilicate CAD/CAM ceramic material. BMC Oral Health 24, 620 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-024-04398-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-024-04398-0