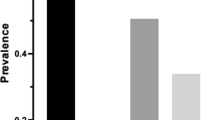Abstract
Background
There is a lack of awareness regarding temporomandibular disorder (TMD) and its association with psychological and sociodemographic factors in the Turkish population. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between signs/symptoms of anxiety-depression, sociodemographic factors, parafunctional habits, bruxism, and the presence and severity of the symptoms of TMD in Turkish adults.
Methods
The participants completed an online questionnaire consisting of sociodemographic questions, the Fonseca Anamnestic Index, and the Patient Health Questionnaire-4.
Results
The mean age of the 2580 participants was 35.29 ± 12.70 years, and 63.3% were women. The frequency of the participants who showed symptoms of TMD was 69.8%. The severity of TMD symptoms was significantly greater in participants who had signs/symptoms of anxiety and depression (p < 0.05). Sociodemographic and psychological data showed an association between the presence and severity of the symptoms of TMD and sex (OR 1.52, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.26–1.85), parafunctional habits (OR 2.64, 95% CI 2.36–2.99), bruxism (OR 3.14, 95% CI 1.78–4.90), signs/symptoms of anxiety (OR 2.30, 95% CI 1.76–3.00), and signs/symptoms of depression (OR 1.90, 95% CI 1.48–2.42).
Conclusions
The results of the present study suggest that females and those who report bruxism, parafunctional habits, and signs/symptoms of anxiety-depression are more likely to show symptoms of TMD with different severity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Temporomandibular disorder (TMD) encompasses a group of disorders affecting the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), chewing muscles, and surrounding structures [1]. The clinical manifestations of TMD, including pain, limitations in the ability to open the mouth, deviation/deflection in the path of opening, and joint sounds, can impact the quality of life negatively [2,3,4]. A recent meta-analysis reported the prevalence of TMD to be approximately 31% for adults [5]. The peak occurrence of TMD is seen between ages 20 and 50 years, and it predominantly affects females [2, 6].
The etiology of TMD is complex and not fully understood. Genetic, hormonal factors, stress sensitivity, and sex are reported among the factors in the multifactorial etiology [6, 7]. With the increasing recognition of the biopsychosocial model of illness, which considers the etiology of TMD within a multifactorial framework, several studies have investigated the psychosocial aspects of TMD [3, 6, 7]. The reported data indicate that psychological factors, such as depression and anxiety, play an important role in the onset, perpetuation, and prognosis of TMD [8,9,10,11]. Depression and anxiety are considered to trigger the occurrence of TMD by increasing bruxism, parafunctional habits, initiating muscular hyperactivity and joint inflammation, and changing the pain threshold by affecting the transmission of nociceptive impulses and releasing neurotransmitters [12, 13].
In addition, the symptoms of TMD, including pain, can be the cause of psychological disorders [3]. To determine the presence and severity of the symptoms of TMD, the Fonseca Anamnestic Index (FAI) is considered a reliable tool for screening in population studies [14, 15]. The FAI provides useful data in epidemiologic studies by enabling low-cost data collection that is not influenced by the researcher; it can also help to identify TMD symptoms that people are not aware of and prevent further deterioration [16]. For psychological assessment, the Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4) instrument, which is an ultra-short subscale of the Diagnostic Criteria for TMD (DC/TMD) Axis II, is recommended as an initial screening tool for signs/symptoms of depression and anxiety [17, 18].
There is a lack of data regarding TMD and its association with psychological and sociodemographic factors in the Turkish population. Therefore, this cross-sectional study aimed to explore the presence and severity of symptoms of TMD and its association with psychological (signs/symptoms of depression and anxiety) and sociodemographic factors, parafunctional habits, and bruxism in the Turkish adult population and to create awareness of TMD and its psychosocial aspects.
Materials and methods
Study participants
This cross-sectional study was approved by the Ordu University Clinical Research Ethics Committee (No. 2021/99), and informed consent was obtained from all participants. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations of the Declaration of Helsinki. Individuals aged over 18 years who lived in provinces/districts in Turkey, had access to social media, had mastered the language in which the survey was written, and who agreed to participate in the study were included in the study. Individuals aged under 18 years and those who did not agree to participate were excluded. The sample size was calculated as 1326 by accepting the total Turkish population as 60,737,564, the prevalence as 50%, the confidence interval as 99%, and the pattern effect as 2. Accordingly, 1459 individuals were planned to be included in the sample, considering the 10% non-response margin. Individuals were reached through a questionnaire prepared via Google Forms (Google LLC, Mountain View, California, USA) using a snowball non-probability sampling method between April and June 2021. A survey was considered the most appropriate way to reach the target population, considering the COVID-19 pandemic.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire consists of three parts: the first part focused on sociodemographic characteristics including age, sex, employment, monthly income, education level, bruxism, and parafunctional habits (pulling/keeping chin forward; squeezing mobile phone between ear and shoulder; biting tongue, cheek, or lip; talking a lot during the day; chewing gum; biting a foreign object; nail biting), the second part focused on the presence and severity of symptoms of TMD using the FAI, and the third part focused on the presence of signs/symptoms of depression/anxiety using the PHQ-4. Self-reported bruxism and parafunctional habits were answered as yes or no.
Fonseca Anamnestic Index (FAI)
The FAI evaluates the presence or absence of symptoms caused by TMDs and their severity. The Turkish adaptation and reliability study of the scale, which was conducted in 2020, consists of 10 questions, to which the possible answers are “yes” (10 points), “sometimes” (5 points), or “no” (0 points). The total score is interpreted as follows: 0–15 points = no TMD, 20–40 points = mild TMD, 45–65 points = moderate TMD, and 70–100 points = severe TMD [19]. The questions are shown in Table 1.
Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4)
The PHQ-4 was used to evaluate participants’ depression and anxiety [18]. The scale, which has been adapted into Turkish, consists of four questions: two questions assess anxiety (Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by feeling nervous, anxious or on edge?, Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by not being able to stop or control worrying?), and two questions assess depression (Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by little interest or pleasure in doing things?, Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by feeling down, depressed, or hopeless?) [20]. The PHQ-4 is a questionnaire answered on a 4-point Likert-type scale; (0) ‘not at all,’ (1) ‘several days,’ (2) ‘more than half the days,’ (3) ‘nearly every day.’ The total scores are interpreted as follows: 0–2 points = no distress, 3–5 points = mild distress, 6–8 points = moderate distress, and 9–12 points = severe distress. On each subscale, a score of 3 points or higher is considered positive for the purposes of screening for signs/symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Data collection
Questionnaires were delivered to seven geographic regions of Turkey via e-mail and social media platforms (WhatsApp, Twitter, and Facebook).
A pilot study was conducted by administering the questionnaire to 20 individuals who were not included in the study. The pilot study was performed on a small sample from every educational level because the target population was the general population from every degree of education. It was aimed to determine the parts or medical terms that reduce the intelligibility of the questionnaire except the parts comprising the FAI and PHQ4. After that, the parts that were determined to reduce the intelligibility of the questionnaire were revised.
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using version 25.0 of the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). Descriptive statistics are given as numbers and percentages for categorical variables and mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables. Chi-square analysis was used to evaluate the relationship between the categorical variables and TMD. Multivariate regression analysis was used for advanced analysis by modeling the variables that were found to be significant. A P value < 0.05 was considered significant with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results
Study participants
Two thousand five hundred eighty individuals who completed the questionnaire were included in the study. The mean age of the participants was 35.29 ± 12.70 years, and 63.3% of the participants were women. Of the participants, 84% were university graduates, 53.3% were married, 55% were employed, and 24% were students. The monthly income of 35% of the participants was 3000 Turkish liras or less. The sociodemographic characteristics of the participants with and without TMD are shown in Table 2.
Bruxism
A total of 36% of the participants reported bruxism. Nearly half (46.8%) of the participants who reported symptoms of TMD, also reported bruxism; 10.9% of the participants who did not report symptoms related to TMD reported bruxism (Fig. 1).
Parafunctional habits
The parafunctional habit frequencies of the participants are shown in Fig. 1; 56% of the participants stated they had at least one parafunctional habit as follows: 6.5% (n = 167) of the participants indicated that they habitually pulled/kept their chins forward; 14.2% (n = 366) of the participants reported that they habitually squeezed their mobile phone between their ears and shoulders; 25% (n = 646) indicated that they bit their tongue, cheek, or lip; 36% (n = 928) reported grinding their teeth while sleeping or awake; 18.4% (n = 474) reported talking a lot during the day; 8.8% (n = 167) reported chewing gum; 5% (n = 128) reported biting foreign objects; 12.3% (n = 317) reported biting their nails.
Association between psychological factors and TMD
Of the participants, 69.8% reported symptoms of TMD as follows: 43.6% reported symptoms of mild TMD, 19.5% reported symptoms of moderate TMD, and 6.7% reported symptoms of severe TMD. According to the PHQ-4 scores, 75.6% of the participants had signs/symptoms of distress (anxiety/depression), including 41.9% with mild distress, 19.1% with moderate distress, and 14.6% with severe distress. According to the PHQ-4 scores, 32.7% of the participants showed signs/symptoms of anxiety, and 39.9% showed signs/symptoms of depression. Figure 2 shows the distribution of the frequency of anxiety and depression among the participants according to the presence and severity of symptoms of TMD. The presence of mild, moderate, and severe TMD symptoms was significantly higher in those with signs/symptoms of anxiety than in those without anxiety (p < 0.05). A similar trend was observed for signs/symptoms of depression (p < 0.05). The results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses for TMD are shown in Table 3. The frequency of TMD symptoms was associated with sex, age, marital status, professional status, monthly income, bruxism, parafunctional habits, anxiety, and depression (p < 0.05). When multivariate analyses were performed on these variables, female sex, bruxism, parafunctional habits, and the presence of signs/symptoms of depression and anxiety were found to increase the risk for TMD symptoms.
The risk of showing symptoms of TMD for females was 1.52 (95% CI 1.26–1.85) fold greater than for males. The risk of symptoms of TMD for the participants who reported parafunctional habits was 2.64 (95% CI 2.36–2.99) fold greater than for those who did not report parafunctional habits. The risk of symptoms of TMD for the participants who reported bruxism was 3.14 (95% CI 1.78–4.90) fold greater than for those who did not report bruxism. The risk of symptoms of TMD increased 2.30 fold (95% CI 1.76–3.00) in the presence of signs/symptoms of anxiety and 1.90 (95% CI 1.48–2.42) fold in the presence of signs/symptoms of depression (Table 3).
Discussion
This cross-sectional study explored the presence and severity of symptoms of TMD and the association between TMD and psychological (signs/symptoms of anxiety-depression) and sociodemographic factors, parafunctional habits, and bruxism in the Turkish adult population. The results showed that 70% of the participants had mild-to-severe TMD, and females and those who reported bruxism, parafunctional habits, or signs/symptoms of anxiety-depression were more likely to develop TMD. The prevalence of symptoms of TMD in this study was significantly higher than indicated by the results of studies of different populations [21,22,23,24] and by the results of a previous study of the Turkish population [25]. This difference may originate from the differences in the samples, the methodology, and the evaluation methods used in the studies. However, this result may also be explained by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has had a negative impact on people’s mental health [26, 27].
Psychological factors and TMD
The role of psychological factors in TMD has not been entirely elucidated. Several studies have demonstrated an association between psychological factors and TMD, with higher depression/anxiety levels found in patients with TMD [3, 8, 13, 28]. On the other hand, other studies have failed to find any such association [29, 30]. In this study, a significant association was found between the presence and severity of symptoms of TMD and signs/symptoms of depression/anxiety. The prevalence of the signs/symptoms of depression and anxiety among the participants who had TMD symptoms in different severity were 47% and 40%, respectively. This result is similar to previous studies that reported the prevalence of depression in patients with TMD as 21–60% [31] and the prevalence of anxiety as 12–75% [3, 17, 32]. In addition, the comorbidity of anxiety and depression was reported to increase the prevalence and severity of TMD compared with the presence of either anxiety or depression alone [17, 33]. The results of the present study confirmed this finding.
In the current study, signs/symptoms of anxiety and depression were found to be associated with the presence and severity of symptoms of TMD, with a higher risk of 2.30 and 1.90 fold, respectively. This result is in line with the findings of previous studies with different designs that investigated the association of depression and anxiety with TMD [8, 9, 11, 13, 34]. Although further longitudinal research is needed to determine the causal relationship between physiological factors and TMD, evidence from previous studies and the present study reinforces the importance of understanding psychological factors in the management of patients with TMD.
Age/sex and TMD
The relationship between TMD and age/sex is well-established in the literature. Several studies have found that young females reported TMD symptoms more frequently than others. In a cross-sectional study conducted on the Brazilian population, the majority of individuals with TMD were found to be female (66%) and young adults (85%) [23]. In another study on Canadian subjects, females and those in younger age groups were more likely to report one or more TMD symptoms [24]. In a study on the Finnish population, female sex was found to be significantly associated with the occurrence of nearly all the signs of TMD [22]. However, in another cross-sectional study on the Turkish population, age-related differences in TMD symptoms were not observed, and sex differences were observed only for the symptom of pain [25]. Similarly, in their study on the Hong Kong Chinese population, Pow et al. [35] found no difference in TMD symptoms between the sexes. However, in our study, young individuals (80%) and females (67%) constituted the majority of the individuals with had symptoms of TMD. In a meta-analysis, Bueno et al. [36] reported an increase of 2.2-fold in the risk of TMD in females compared with males. Resende et al. [3] found a 3.5-fold higher OR for the incidence of TMDs in females compared with males. In a cross-sectional study, Goncalves et al. [4] observed that the risk of females reporting at least one and up to three or more TMD symptoms was 1.31–2.49 fold higher, respectively, than for males. The risk of having symptoms of TMD was found 1.52 fold higher in females than in males in this study. In the literature, the predominance of TMD in females has been attributed to genetic, hormonal, psychosocial, and cultural factors, as well as differences in pain perception/thresholds and treatment-seeking behaviors between the two genders; these factors are also likely at play in the present study [1, 12, 36]. Regarding the effect of age, in the current study, the significant effect found with the univariate analysis was not observed in the multivariate analysis. This finding may indicate that when factors such as depression, anxiety, and sex associated with TMD are controlled, the risk associated with young age disappears.
Parafunctional habits, bruxism and TMD
In the present study, parafunctional habits and bruxism were found in nearly 62% and 47% of the individuals who reported mild-to-severe symptoms of TMD. Parafunctional habits and bruxism were found to increase the risk of present symptoms of TMD by 2.64 and 3.14 fold, similar to the results of previous studies [37,38,39]. This increased risk is possibly associated with greater and more severe signs/symptoms of anxiety and depression in individuals who present with symptoms of TMD, which may trigger parafunctional activities and bruxism. Similarly, Kmeid et al. [21] suggested that the presence and severity of TMD were associated with greater distress, bruxism, and the number of hours spent on the phone per day in the Lebanese population.
Strengths and limitations
The strength of this study is that it evaluated factors that might be associated with TMD by controlling for these factors through a regression model. Thus, the authors provide reliable results by eliminating the effects of confounding factors. The findings of the study should be interpreted with caution because of certain limitations. First, the study was conducted during the most intense period of the COVID-19 pandemic. For this reason, online data collection was used instead of a face-to-face method. Thus, a selection bias is probable because the sample is not representative of the entire population; the online data collection method may have limited the participation of certain disadvantaged groups, such as those without internet access and those with low socioeconomic status. Second, the study data are cross-sectional; in the future, longitudinal study designs are needed to confirm the causal relationship between the study variables and TMD. Third, because we aimed to perform a general screening on the adult population, individuals with a recent trauma to the face, underlying motor, autoimmune, and neurologic conditions that could influence the occurrence of the symptoms of TMD and thereby the results of the study were not excluded. Although the PHQ-4 used in this study is a reliable screening tool for depression and anxiety symptoms/signs, its reliability as a diagnostic tool is limited. Finally, information bias might be present because the assessment is based on information provided by the participants.
Conclusion
This study considers self-reported TMD symptoms and psychological symptoms as roughly screened, no diagnoses of either TMD, bruxism, anxiety, or depression were made. Despite its limitations, this study showed an association between symptoms of TMD and sex, bruxism, parafunctional habits, signs/symptoms of anxiety, and depression. The results showed that females and those who report bruxism, parafunctional habits, and signs/symptoms of anxiety-depression were more likely to develop TMD symptoms. This result supports the biopsychosocial model and reinforces the need for a multidimensional evaluation of TMD and a multidisciplinary approach in the management of patients with TMD, as well as the need to increase awareness of the role of psychosocial factors in TMD. Also, further clinical studies are needed to determine the real physiological mechanism that links stress, anxiety-depression, TMD, and bruxism more clearly.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kim YK, Kim SG, Im JH, Yun PY. Clinical survey of the patients with temporomandibular joint disorders, using Research Diagnostic Criteria (Axis II) for TMD: preliminary study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40:366–72.
Manfredini D, Guarda-Nardini L, Winocur E, Piccotti F, Ahlberg J, Lobbezoo F. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: a systematic review of axis I epidemiologicfindings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112:453–62.
Resende C, Rocha L, Paiva RP, et al. Relationship between anxiety, quality of life, and sociodemographic characteristics and temporomandibular disorder. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2020;129:125–32.
Goncalves DA, Dal Fabbro AL, Campos JA, Bigal ME, Speciali JG. Symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in the population: an epidemiological study. J Orofac Pain. 2010;24:270–8.
Valesan LF, Da-Cas CD, Reus JC, et al. Prevalence of temporomandibular joint disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25:441–53.
Huhtela OS, Napankangas R, Suominen AL, Karppinen J, Kunttu K, Sipila K. Association of psychological distress and widespread pain with symptoms of temporomandibular disorders and self-reported bruxism in students. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2021;7:1154–66.
Suvinen TI, Reade PC, Kemppainen P, Kononen M, Dworkin SF. Review of aetiological concepts of temporomandibular pain disorders: Towards a biopsychosocial model for integration of physical disorder factors with psychological and psychosocial illness impact factors. Eur J Pain. 2005;9:613–33.
Fillingim RB, Ohrbach R, Greenspan JD, et al. Psychological factors associated with development of TMD: the OPPERA prospective cohort study. J Pain. 2013;14:75–90.
Slade GD, Diatchenko L, Bhalang K, et al. Influence of psychological factors on risk of temporomandibular disorders. J Dent Res. 2007;86:1120–5.
Giannakopoulos NN, Keller L, Rammelsberg P, Kronmuller KT, Schmitter M. Anxiety and depression in patients with chronic temporomandibular pain and in controls. J Dent. 2010;38:369–76.
Liao CH, Chang CS, Chang SN, et al. The risk of temporomandibular disorder in patients with depression: a population-based cohort study. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2011;39:525–31.
Gameiro GH, da Silva Andrade A, Nouer DF, Ferraz de Arruda Veiga MC. How may stressful experiences contribute to the development of temporomandibular disorders? Clin Oral Investig. 2006;10:261–268.
Kindler S, Samietz S, Houshmand M, et al. Depressive and anxiety symptoms as risk factors for temporomandibular joint pain: a prospective cohort study in the general population. J Pain. 2012;13:1188–97.
Pastore GP, Goulart DR, Pastore PR, Prati AJ, de Moraes M. Comparison of instruments used to select and classify patients with temporomandibular disorder. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2018;31:16–22.
Stasiak G, Maracci LM, de Oliveira Chami V, et al. TMD diagnosis: Sensitivity and specificity of the Fonseca Anamnestic Index. Cranio. 2020;66:1–5.
Topuz MF, Oghan F, Ceyhan A, et al. Assessment of the severity of temporomandibular disorders in females: validity and reliability of the Fonseca anamnestic index. Cranio. 2020;66:1–4.
ChuinsiriN, Jitprasertwong P. Prevalence of self-reported pain-related temporomandibular disorders and association with psychological distress in a dental clinic setting. J Int Med Res. 2020;48:300060520951744.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, Lowe B. An ultra-brief screening scale for anxiety and depression: the PHQ-4. Psychosomatics. 2009;50:613–21.
Kaynak BA, Tas S, Salkin Y. The accuracy and reliability of the Turkish version of the Fonseca anamnestic index in temporomandibular disorders. Cranio. 2020;66:1–6.
Demirci İ, Ekşi H. Don't bother your pretty little head otherwise you can’t enjoy life. In: ERPA international congresses on education, 28 June–1 July 2018, Istanbul/Turkey.
Kmeid E, Nacouzi M, Hallit S, Rohayem Z. Prevalence of temporomandibular joint disorder in the Lebanese population, and its association with depression, anxiety, and stress. Head Face Med. 2020;16:19.
Qvintus V, Sipila K, Le Bell Y, Suominen AL. Prevalence of clinical signs and pain symptoms of temporomandibular disorders and associated factors in adult Finns. Acta Odontol Scand. 2020;78:515–21.
Progiante PS, Pattussi MP, Lawrence HP, Goya S, Grossi PK, Grossi ML. Prevalence of temporomandibular disorders in an adult Brazilian community population using the research diagnostic criteria (Axes I and II) for temporomandibular disorders (The Maringa Study). Int J Prosthodont. 2015;28:600–9.
Locker D, Slade G. Prevalence of symptoms associated with temporomandibular disorders in a Canadian population. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1988;16:310–3.
Nekora-Azak A, Evlioglu G, Ordulu M, Issever H. Prevalence of symptoms associated with temporomandibular disorders in a Turkish population. J Oral Rehabil. 2006;33:81–4.
Gas S, EksiOzsoy H, Cesur Aydin K. The association between sleep quality, depression, anxiety and stress levels, and temporomandibular joint disorders among Turkish dental students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Cranio. 2021;66:1–6.
Korukcu O, Ozkaya M, Faruk Boran O, Boran M. The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on community mental health: a psychometric and prevalence study in Turkey. Health Soc Care Community. 2021;29:204-e213.
Simoen L, Van den Berghe L, Jacquet W, Marks L. Depression and anxiety levels in patients with temporomandibular disorders: comparison with the general population. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24:3939–45.
Delgado-Delgado R, Iriarte-Alvarez N, Valera-Calero JA, Centenera-Centenera MB, Garnacho-Garnacho VE, Gallego-Sendarrubias GM. Association between temporomandibular disorders with clinical and sociodemographic features: an observational study. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75:13961.
FernandesAzevedo AB, Camara-Souza MB, Dantas IS, de Resende C, Barbosa GAS. Relationship between anxiety and temporomandibular disorders in dental students. Cranio. 2018;66:36.
De La Torre CG, Camara-Souza MB, Munoz Lora VRM, et al. Prevalence of psychosocial impairment in temporomandibular disorder patients: a systematic review. J Oral Rehabil. 2018;45:881–9.
Lei J, Liu MQ, Yap AU, Fu KY. Sleep disturbance and psychologic distress: prevalence and risk indicators for temporomandibular disorders in a Chinese population. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2015;29:24–30.
Reiter S, Emodi-Perlman A, Goldsmith C, Friedman-Rubin P, Winocur E. Comorbidity between depression and anxiety in patients with temporomandibular disorders according to the research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2015;29:135–43.
Boscato N, Almeida RC, Koller CD, Presta AA, Goettems ML. Influence of anxiety on temporomandibular disorders-an epidemiological survey with elders and adults in Southern Brazil. J Oral Rehabil. 2013;40:643–9.
Pow EH, Leung KC, McMillan AS. Prevalence of symptoms associated with temporomandibular disorders in Hong Kong Chinese. J Orofac Pain. 2001;15:228–34.
Bueno CH, Pereira DD, Pattussi MP, Grossi PK, Grossi ML. Gender differences in temporomandibular disorders in adult populational studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Rehabil. 2018;45:720–9.
Miyake R, Ohkubo R, Takehara J, Morita M. Oral parafunctions and association with symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in Japanese university students. J Oral Rehabil. 2004;31:518–23.
Huang GJ, LeResche L, Critchlow CW, Martin MD, Drangsholt MT. Risk factors for diagnostic subgroups of painful temporomandibular disorder (TMD). J Dent Res. 2002;81:284–8.
Johansson A, Unell L, Carlsson GE, Soderfeldt B, Halling A. Gender difference in symptoms related to temporomandibular disorders in a population of 50-year-old subjects. J Orofac Pain. 2003;17:29–35.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MMO: Reviewed the literature, developed the concept and design of the study, involved in data collection and drafting the manuscript, and revised the manuscript DT: Reviewed the literature, developed the concept and design of the study, involved in data analysis/interpretation and drafting the manuscript. CVA: involved in concept/design, data collection, involved in data analysis/interpretation, and drafting. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This cross-sectional study was approved by the Ordu University Clinical Research Ethics Committee (No. 2021/99), and informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Omezli, M.M., Torul, D. & Varer Akpinar, C. Temporomandibular disorder severity and its association with psychosocial and sociodemographic factors in Turkish adults. BMC Oral Health 23, 34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-023-02737-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-023-02737-1