Abstract
Background
Urogenital dysfunction is recognized as a serious complication affecting patient quality of life after rectal cancer surgery to treat rectal cancer; however, the studies focus on the urogenital function after robot-assisted rectal cancer surgery compared to laparoscopic surgery are limited.
Methods
Male patients undergoing robotic total mesorectal excision (R-TME) or laparoscopic total mesorectal excision (L-TME) were prospectively enrolled. The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and the five-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) scale were used to compare the urogenital function of the two groups preoperatively and 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively.
Results
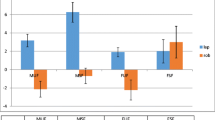
Eighty-nine patients who planned to undergo R-TME and L-TME were prospectively enrolled; 77 patients of these patients (86.5%) completed all questionnaires at all time points and were thus included in the final analysis. Of the included patients, 38 underwent R-TME and 39 underwent L-TME. There was no significant difference in age, BMI, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, tumor location, neoadjuvant therapy, operation method, postoperative pathological results and adjuvant therapy between the two groups. Preoperative urogenital function was similar in both groups; however, the IPSS was significantly lower in R-TME patients than that in T-TME patients at 6 months and 12 months [(7.82 ± 2.25 vs. 9.95 ± 3.01, P = 0.006; 7.62 ± 2.5 vs. 9.12 ± 2.64, P = 0.012)]. IIEF-5 scores decreased 3 months after R-TME and L-TME surgery (14.87 ± 3.27 vs. 13.92 ± 3.62, p = 0.231) and then gradually increased; at 12 months, IIEF-5 scores were comparable to those at baseline in both groups. IIEF-5 scores were higher in R-TME patients than those in L-TME patients at 6 months (18.55 ± 3.45 vs. 16.75 ± 3.26, P = 0.021), but there was no significant difference between the two groups at 12 months (21.22 ± 3.06 vs. 19.95 ± 3.03, P = 0.071).
Conclusions
The robotic approach for TME was associated with more rapid restoration of male urogenital function than the laparoscopic approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Rectal cancer is one of the most common malignant cancers worldwide, and its incidence is increasing in young people [1, 2]. Surgery is the main treatment for rectal cancer [3]. Total mesorectal excision (TME), proposed by Heald in 1982, greatly improved the survival rate and reduced recurrence in rectal cancer patients; however, after TME surgery, patients still exhibited higher urogenital dysfunction, which seriously affects the postoperative quality of life of patients [4, 5]. Therefore, Japanese researchers proposed TME with pelvic autonomic nerve preservation (PANP), which can preserve urogenital function to the maximum extent [6, 7].
At present, laparoscopy is widely used in the surgical treatment of rectal cancer, and its safety and oncologic outcomes are acknowledged [8, 9]. Laparoscopic rectal cancer surgery can reduce intraoperative blood loss, relieve postoperative pain and accelerate recovery from postoperative pain [10]; however, urogenital dysfunction after laparoscopic TME with PANP still persisted [11, 12].
In recent years, robotic surgery has gained greater popularity worldwide. This technique has several advantages over laparoscopic surgery, including an immersive three-dimensional view of the surgical field, better surgical dexterity, and a stable camera platform. Such innovative technology can alleviate some of the maneuverability and visibility challenges that surgeons encounter in narrow pelvic cavities [13]. Patients who undergo robotic surgery have better short-term outcomes and similar long-term outcomes to those who underwent laparoscopic surgery [13,14,15]; however, the studies focus on the urogenital function after robot-assisted rectal cancer surgery compared to laparoscopic surgery are limited [16,17,18].
Therefore, in this study, we evaluated urogenital function at several time points in male patients who underwent robotic-assisted or laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer to determine which surgery had better urogenital function outcomes.
Patients and methods
Participants
This was a single-center, prospective, cohort study from the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University in Jiangxi, China. Male patients with rectal cancer, tumors located within 12 cm of the anal verge, age ≤ 60 years, and normal urogenital function before surgery and who underwent robotic or laparoscopic surgery were included. The exclusion criteria included emergency operations, patients with distant metastases, a history of previous pelvic organ operations, or conversion to laparotomy, and patients that refused to join the study. The choice of surgical approach (robotic or laparoscopic) was determined in accordance with the wishes of the patient. The study received ethical approval from the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, and all patients provided informed consent for participation in the study.
Surgical procedures
All operations were performed by one surgeon. All patients enrolled in the study underwent TME with PANP utilizing a medial-to-lateral approach. Lymph node dissection was performed to the root of the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA). High or low ligation was performed according to the length of the colon and rectum. All rectal cancer resections adhered to the principles of TME. For PANP, the superior hypogastric plexus (SHP) was preserved at the root of the IMA. The hypogastric plexus (HP) and pelvic splanchnic nerves (PSN) were preserved when dissecting the mesorectum posteriorly, the inferior hypogastric plexus (IHP), PSN and the neurovascular bundle (NVB) of its branches were preserved when dissecting the mesorectum laterally and anteriorly respectively. Linear stapler devices were used to transect the rectum 1–2 cm below the tumor. The specimen was extracted through a 4- to 5-cm mini-laparotomy in the lower abdomen with a wound protector. The bowel was anastomosed using a circular stapler. Ileostomy was conducted according to the risk factors for anastomotic leakage and reversed at 3 months after surgery. Abdominoperineal resection was performed if the distal resection margin of 1–2 cm cannot be confirmed with negative in low anterior resection.
Assessment of urogenital function
The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) [19] was used to assess urinary function. The IPSS includes seven items, each of which is assigned a score from 1 to 5 (for a maximum score of 35): emptying, frequency, intermittency, urgency, weak stream, hesitancy, nocturia, Higher scores indicate more severe urinary dysfunction.
The five-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) scale [20] was used to assess male erectile function. It consists of five questions: confidence in erectile function, success rate of insertion after erection, maintaining an erection, success rate of sexual intercourse and satisfaction after sexual intercourse. Each item is assigned a score from 0 to 5 points, with a total score of 25 points; higher scores indicate better sexual function.
Both questionnaires were administered preoperatively and 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 24.0. Categorical variables were compared with Chi-square tests; continuous variables were compared with Student’s t tests or Mann–Whitney U tests. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
From June 2018 to July 2020, 89 patients who were going to undergo R-TME or L-TME at the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University were prospectively enrolled in this study. Seventy-seven patients (86.5%) who completed all the questionnaires at all time points were included in the final analysis: 38 underwent surgery with a robotic approach and 39 underwent laparoscopy. The two groups did not significantly differ in age, body mass index (BMI), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, tumor location, neoadjuvant therapy, operation method, postoperative pathological results and adjuvant therapy (Table 1).
Urinary function
The preoperative total IPSS was similar in both groups, but the IPSS was significantly lower in the robotic group than in the laparoscopic group at 6 months and 12 months [(7.82 ± 2.25 vs. 9.95 ± 3.01, P = 0.006; 7.62 ± 2.5 vs. 9.12 ± 2.64, P = 0.012)], (Table 2; Fig. 1).
Sexual function
The baseline IIEF-5 scores of the two groups were similar. IIEF-5 scores decreased 3 months after surgery and then gradually increased; by 12 months, scores were comparable to those at baseline scores in both groups. However, IIEF-5 scores were higher in the robotic group than in the laparoscopic group at 6 months (18.55 ± 3.45 vs. 16.75 ± 3.26, P = 0.021), but there was no significant difference between the two groups at 12 months (21.22 ± 3.06 vs. 19.95 ± 3.03, P = 0.071), (Table 3; Fig. 2).
Discussion
Given the continuous advances in early diagnosis, surgical techniques chemo-radiotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy, the survival of patients with rectal cancer has greatly improved; however, urogenital dysfunction resulting from rectal cancer surgery is a major problem affecting their quality of life [5]. PANP provides a theoretical basis for improving postoperative urogenital dysfunction. In this study, we found that using the robotic approach was associated with more rapid restoration of male urogenital function than the laparoscopic approach.
Age, tumor location, use of preoperative radiotherapy, the operation method and the stoma can affect postoperative urogenital function [5, 21,22,23]. Havenga K reported that [24] more than 86% of patients under 60 years of age were sexually active, while only 60% of patients over 60 years of age were sexually active; thus, in this study, we only included patients who were sexually active one month before surgery and were younger than 60 years old. Preoperative pelvic radiotherapy can cause inflammatory pelvic reactions, leading to injury of the pelvic nerve and fibrosis of the genitals. Tumor location determines the type of operation. The lower the dissecting level of the TME is, the greater the probability of damaging the pelvic plexus and NVB. Abdominoperineal excision and stoma have multiple physiological and psychological effects on patients, leading to postoperative urogenital dysfunction. In our study, patients who underwent neoadjuvant therapy, tumor location, type of operation, and the stoma were no significant difference between the two groups. Therefore, we further evaluated the influence of the robot and laparoscopic operation platforms on postoperative urogenital function.
Our results showed that male urinary function decreased at 3 months in the two groups and then gradually improved. Urinary function recovered to baseline scores after 6 months in the robotic group, while in the laparoscopic group, urinary function still had not recovered after 12 months. This finding was similar to the studies of Kim et al. [17, 25], robotic surgery can provide more rapid recovery of urinary function. However, Park and ROLARR [26, 27] found that robotic surgery and laparoscopic surgery had similar effects on postoperative urinary function. When TME is performed in rectal cancer surgery, nerve damage usually occurs during ligation of the IMA, and during posterior, lateral and anterior rectal dissection [28]. Intraoperative traction, the heat of the platform and postoperative inflammation can cause temporary nerve damage, which can be compensated for and recovers more quickly; in contrast, intraoperative electrocoagulation and ligation lead to permanent nerve damage. The enlarged visual field, dexterity of surgical instruments and use of electric scissors in robotic surgery can not only accurately perform TME but also prevent permanent nerve injury caused by unclear or blind separation.
In this study, IIEF-5 scores decreased 3 months after surgery and then gradually increased; at 12 months, scores were comparable to those at baseline in both groups. However, IIEF-5 scores were higher in the robotic group than in the laparoscopic group at 6 months, which was in line with previous studies [17, 25, 27, 29]. Erectile function is restored to preoperative levels more quickly after robotic surgery. Erectile function is mainly dependent on the pudendal nerve, pelvic plexus and the NVB of its branches; it is easy to damage the pelvic plexus and NVB during laparoscopic surgery due to insufficient or excessive traction and difficulty in identifying the nerve and the operation plane in the narrow pelvis. The enlarged three-dimensional view provided by the robot can clearly identify the Denonvilliers’ fascia during anterior rectal dissections, and its unique operating platform can maintain stable tension when performing lateral and posterior rectal dissection, which effectively protects the pelvic plexus and NVB at 2 o’clock and 10 o’clock in the plane of the seminal vesicle.
Our study also had some limitations. First, this study was not a randomized controlled trial; thus, the validity of our data may be weaker. Second, the evaluation indices of genitourinary function in this study were subjective and easily affected by psychological factors, making it difficult to distinguish whether symptoms were caused by psychological factors or physiological factors. Third, due to ethical and cultural factors, the sample size of this study was small and did not evaluate female genitourinary function.
Conclusions
Our study found that the robotic approach for TME was associated with a more rapid restoration of male urogenital function compared to that of the laparoscopic approach. Multicenter randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm the advantages of robotic surgery for rectal cancer.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors, but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of ethics committee First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University.
Abbreviations
- TME:
-
Total mesorectal excision
- PANP:
-
Pelvic autonomic nerve preservation
- SHP:
-
Superior hypogastric plexus
- IMA:
-
Inferior mesenteric artery
- HP:
-
Hypogastric plexus
- PSN:
-
Pelvic splanchnic nerves
- NVB:
-
Neurovascular bundle
- IPSS:
-
International Prostate Symptom Score
- IIEF:
-
International Index of Erectile Function
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- ASA:
-
American Society of Anesthesiologists
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30.
Tawadros PS, Paquette IM, Hanly AM, Mellgren AF, Rothenberger DA, Madoff RD. Adenocarcinoma of the rectum in patients under age 40 is increasing: impact of signet-ring cell histology. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015;58:474–8.
You YN, Hardiman KM, Bafford A, Poylin V, Francone TD, Davis K, Paquette IM, Steele SR, Feingold DL. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Rectal Cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 2020;63:1191–222.
Heald RJ, Ryall RD. Recurrence and survival after total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Lancet. 1986;1:1479–82.
Hendren SK, O’Connor BI, Liu M, Asano T, Cohen Z, Swallow CJ, Macrae HM, Gryfe R, McLeod RS. Prevalence of male and female sexual dysfunction is high following surgery for rectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2005;242:212–23.
Maas CP, Moriya Y, Steup WH, Kiebert GM, Kranenbarg WM, van de Velde CJ. Radical and nerve-preserving surgery for rectal cancer in The Netherlands: a prospective study on morbidity and functional outcome. Br J Surg. 1998;85:92–7.
Moriya Y, Sugihara K, Akasu T, Fujita S. Nerve-sparing surgery with lateral node dissection for advanced lower rectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31a:1229–32.
Jeong SY, Park JW, Nam BH, Kim S, Kang SB, Lim SB, Choi HS, Kim DW, Chang HJ, Kim DY, Jung KH, Kim TY, Kang GH, Chie EK, Kim SY, Sohn DK, Kim DH, Kim JS, Lee HS, Kim JH, Oh JH. Open versus laparoscopic surgery for mid-rectal or low-rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (COREAN trial): survival outcomes of an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:767–74.
Park JW, Kang SB, Hao J, Lim SB, Choi HS, Kim DW, Chang HJ, Kim DY, Jung KH, Kim TY, Kang GH, Chie EK, Kim SY, Sohn DK, Kim JS, Lee HS, Kim JH, Jeong SY, Oh JH. Open versus laparoscopic surgery for mid or low rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (COREAN trial): 10-year follow-up of an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:569–77.
van der Pas MH, Haglind E, Cuesta MA, Furst A, Lacy AM, Hop WC, Bonjer HJ, Group COcLoORIS. Laparoscopic versus open surgery for rectal cancer (COLOR II): short-term outcomes of a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:210–8.
Andersson J, Abis G, Gellerstedt M, Angenete E, Angerås U, Cuesta MA, Jess P, Rosenberg J, Bonjer HJ, Haglind E. Patient-reported genitourinary dysfunction after laparoscopic and open rectal cancer surgery in a randomized trial (COLOR II). Br J Surg. 2014;101:1272–9.
Jayne DG, Brown JM, Thorpe H, Walker J, Quirke P, Guillou PJ. Bladder and sexual function following resection for rectal cancer in a randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic versus open technique. Br J Surg. 2005;92:1124–32.
Crippa J, Grass F, Dozois EJ, Mathis KL, Merchea A, Colibaseanu DT, Kelley SR, Larson DW. Robotic surgery for rectal cancer provides advantageous outcomes over laparoscopic approach: results from a large retrospective cohort. Ann Surg. 2020.
Park SY, Lee SM, Park JS, Kim HJ, Choi GS. Robot surgery shows similar long-term oncologic outcomes as laparoscopic surgery for mid/lower rectal cancer but is beneficial to ypT3/4 after preoperative chemoradiation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2021;64:812–21.
Crippa J, Grass F, Achilli P, Mathis KL, Kelley SR, Merchea A, Colibaseanu DT, Larson DW. Risk factors for conversion in laparoscopic and robotic rectal cancer surgery. Br J Surg. 2020;107:560–6.
Galata C, Vassilev G, Haas F, Kienle P, Büttner S, Reißfelder C, Hardt J. Clinical, oncological, and functional outcomes of Da Vinci (Xi)-assisted versus conventional laparoscopic resection for rectal cancer: a prospective, controlled cohort study of 51 consecutive cases. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019;34:1907–14.
Kim HJ, Choi GS, Park JS, Park SY, Yang CS, Lee HJ. The impact of robotic surgery on quality of life, urinary and sexual function following total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: a propensity score-matched analysis with laparoscopic surgery. Colorectal Dis. 2018;20:O103-o13.
Panteleimonitis S, Ahmed J, Ramachandra M, Farooq M, Harper M, Parvaiz A. Urogenital function in robotic vs laparoscopic rectal cancer surgery: a comparative study. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2017;32:241–8.
Barry MJ, Fowler FJ, Jr., O’Leary MP, Bruskewitz RC, Holtgrewe HL, Mebust WK, Cockett AT. The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol. 1992;148:1549–57; discussion 64.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology. 1997;49:822–30.
Svanström Röjvall A, Buchli C, Bottai M, Ahlberg M, Flöter-Rådestad A, Martling A, Segelman J. Effect of radiotherapy for rectal cancer on female sexual function: a prospective cohort study. Br J Surg. 2020;107:525–36.
Luca F, Valvo M, Ghezzi TL, Zuccaro M, Cenciarelli S, Trovato C, Sonzogni A, Biffi R. Impact of robotic surgery on sexual and urinary functions after fully robotic nerve-sparing total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2013;257:672–8.
Ledebo A, Bock D, Prytz M, Haglind E, Angenete E. Urogenital function 3 years after abdominoperineal excision for rectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2018;20:O123-o34.
Havenga K, DeRuiter MC, Enker WE, Welvaart K. Anatomical basis of autonomic nerve-preserving total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Br J Surg. 1996;83:384–8.
Kim JY, Kim NK, Lee KY, Hur H, Min BS, Kim JH. A comparative study of voiding and sexual function after total mesorectal excision with autonomic nerve preservation for rectal cancer: laparoscopic versus robotic surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:2485–93.
Jayne D, Pigazzi A, Marshall H, Croft J, Corrigan N, Copeland J, Quirke P, West N, Rautio T, Thomassen N, Tilney H, Gudgeon M, Bianchi PP, Edlin R, Hulme C, Brown J. Effect of robotic-assisted vs conventional laparoscopic surgery on risk of conversion to open laparotomy among patients undergoing resection for rectal cancer the rolarr randomized clinical trial. JAMA J Am Med Assoc. 2017;318:1569–80.
Park SY, Choi GS, Park JS, Kim HJ, Ryuk JP, Yun SH. Urinary and erectile function in men after total mesorectal excision by laparoscopic or robot-assisted methods for the treatment of rectal cancer: a case-matched comparison. World J Surg. 2014;38:1834–42.
Moszkowicz D, Alsaid B, Bessede T, Penna C, Nordlinger B, Benoît G, Peschaud F. Where does pelvic nerve injury occur during rectal surgery for cancer? Colorectal Dis. 2011;13:1326–34.
D’Annibale A, Pernazza G, Monsellato I, Pende V, Lucandri G, Mazzocchi P, Alfano G. Total mesorectal excision: a comparison of oncological and functional outcomes between robotic and laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:1887–95.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: TL, JS; Acquisition of data: BT, GG; Analysis and interpretation of data: BT, GG; Drafting of the manuscript: BT, SY, DL; Critical revision of the manuscript: QJ, XL, JA. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University and carried out in accordance with the principles of Helsinki Declaration. Informed consent was received from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, B., Gao, G., Ye, S. et al. Male urogenital function after robot-assisted and laparoscopic total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: a prospective cohort study. BMC Surg 22, 185 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-022-01592-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-022-01592-1