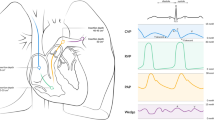
Abstract
Background
Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) induces ventilation-perfusion mismatch and hypoxia and increases pulmonary pressure and right ventricular (RV) afterload, entailing potentially fatal RV failure within a short timeframe. Cardiopulmonary factors may respond differently to increased clot burden. We aimed to elucidate immediate cardiopulmonary responses during successive PE episodes in a porcine model.
Methods
This was a randomized, controlled, blinded study of repeated measurements. Twelve pigs were randomly assigned to receive sham procedures or consecutive PEs every 15 min until doubling of mean pulmonary pressure. Cardiopulmonary assessments were conducted at 1, 2, 5, and 13 min after each PE using pressure-volume loops, invasive pressures, and arterial and mixed venous blood gas analyses. ANOVA and mixed-model statistical analyses were applied.
Results
Pulmonary pressures increased after the initial PE administration (p < 0.0001), with a higher pulmonary pressure change compared to pressure change observed after the following PEs. Conversely, RV arterial elastance and pulmonary vascular resistance was not increased after the first PE, but after three PEs an increase was observed (p = 0.0103 and p = 0.0015, respectively). RV dilatation occurred following initial PEs, while RV ejection fraction declined after the third PE (p = 0.004). RV coupling exhibited a decreasing trend from the first PE (p = 0.095), despite increased mechanical work (p = 0.003). Ventilatory variables displayed more incremental changes with successive PEs.
Conclusion
In an experimental model of consecutive PE, RV afterload elevation and dysfunction manifested after the third PE, in contrast to pulmonary pressure that increased after the first PE. Ventilatory variables exhibited a more direct association with clot burden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Acute pulmonary emboli (PE) induce a ventilation-perfusion mismatch through combined mechanical vascular obstruction and pulmonary vasoconstriction. This combination augments right ventricular (RV) afterload [1, 2] leading to RV dilatation and progressive RV failure in severe cases [1, 3]. Acute PE is a cardiac emergency where death can ensue within hours due to RV failure [4]. Diagnosis of PE is challenged by the urgency of the disease, the unspecific symptoms and the fact that patients may have been severely affected initially but have clinically improved by the time they seek medical advice. This change in symptoms and severity argues that acute PE is a dynamic condition that warrants evaluation of hemodynamics and RV function.
Despite the acute nature of PE, most assessments of RV function in clinical studies are delayed several hours [5, 6] or even days after symptom onset [7, 8]. Even in highly controlled pre-clinical setups, initial hemodynamic evaluations of PE are often performed 30 min or later after the event [9,10,11], leaving the physiological responses occurring immediately following acute PE largely unexplored. Given the rapid onset of fatal outcomes within minutes to hours and the complexities of conducting diagnostic procedures in critically ill patients, understanding the immediate cardiopulmonary responses may aid physicians diagnosing and treating patients with acute PE.
Previously, we have developed a porcine model simulating acute central PE [12, 13], allowing early and consecutive measurements with high temporal resolution. The objective of our present exploratory study is to describe the cardiopulmonary responses occurring within minutes after consecutive acute PE events. We hypothesized that successive PE episodes induced stepwise circulatory and ventilatory deteriorations.
Methods
Design
We conducted a randomized, controlled, blinded experimental study of repeated measurements. Baseline assessment was performed after stabilizing the animals. Subsequently, animals were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive pulmonary emboli (n = 6) or sham procedures (n = 6). In the PE group, consecutive emboli (up to six emboli) were administered every 15 min until the mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) had doubled from baseline or reached a minimum mPAP > 34 mmHg 15 min following the last PE. Cardiopulmonary responses were assessed at 1, 2, 5, and 13 min after each PE episode. Load-independent biventricular pressure-volume (PV) data were recorded solely at the 5-minute timepoint. Sham animals underwent six consecutive sham-embolisations with an equivalent volume of saline, followed by evaluations. See Fig. 1.
Inclusion criteria involved a baseline mPAP < 25 and post-instrumentation sinus rhythm. Exclusion criteria comprised infection, significant hemorrhage (> 1 L) during instrumentation, or the inability to complete the protocol.
Animals and Ethics
This is a sub-analysis of a previously published study [12] involving Danish female slaughter pigs weighing 60 ± 2 kg. The Danish Animal Research Inspectorate approved the study (no.: 2016-15-0201-00840), ensuring compliance with Danish legislation, the ARRIVE guidelines, and the 3R framework [14]. We ensured humane endpoints, as sufficient levels of anesthesia were checked regularly throughout protocol, and the animals were post-protocol euthanized with a lethal dose of pentobarbital while in deep anesthesia.
Animal Preparation
We previously detailed the model, preparation, instrumentation, and surveillance [12]. Notably, animals were anesthetized with use of propofol (2.5 mg/kg/h, Propolipid, Fresnius Kabi, Germany) and fentanyl (6.25 mg/kg/h, Hameln Pharma, Germany). They were mechanically ventilated (Datex-Ohmeda S/5 Avance, GE Healthcare, USA) with an adjusted O2 inspiratory fraction to achieve arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) between 17 and 21 kPa. Respiratory frequency targeted an end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) of 5.0-5.5 kPa.
Invasive accesses and measurements
As described previously, a 26 F sheath (Dry-Seal, Gore Medical, USA) was fluoroscopically placed via the right external jugular vein for embolus administration and right heart catheterization [12]. Additionally, an IVC balloon (PTS-X, Metec, Denmark) was inserted through the femoral vein. PV catheters were advanced through the left jugular vein and carotid artery into the right and left ventricle, respectively [15].
To maintain normal physiology, we utilized a closed-chest approach. Details of the instrumentation have been previously described [12, 15]. A Swan-Ganz catheter (7.5 F, CCOmbo, Edwards Lifescience, USA) was positioned in the pulmonary trunk to measure mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP). A 7 F sheath was placed in the left femoral artery for mean arterial pressure (MAP) measurements. Pulmonary and systemic vascular resistances (PVR and SVR, respectively) were calculated. Admittance-based PV catheters (emka Technologies, Paris, France, and ADV500, Transonic Scisense, London, Canada) facilitated bi-ventricular PV measurements. Data were recorded in LabChart through PowerLab 8/35 (ADInstruments, Oxford, UK). Most PV data were captured during continuous ventilation as an average over three respiratory cycles. Load-independent measurements occurred during transient apnea during IVC occlusion. PV data analysis was performed with the observer blinded to its source.
Embolus formation
The model has been validated and described elsewhere [12, 13]. Each of six plastic tubes were filled with 30 mL of the animals’ blood forming cylindric clots mimicking thrombus from a deep leg vein. The clots were later introduced en bloc through the 26 F sheath, embedded in saline, to induce central PE [13].
Blood gases
Simultaneous arterial and mixed venous blood samples were drawn for analysis of partial pressures of O2 and CO2 (PaO2, PaCO2, PvO2, and PvCO2, respectively, using ABL90 Flex Plus, Radiometer Medical, Denmark). Physiological dead space was computed following Bohr’s principle, and pulmonary shunt fraction was calculated [16].
Statistics
Sample size calculations were previously described [12]. The Shapiro-Wilks test and QQ-plots were used to assess normality. Normally distributed data are presented as mean ± SD, otherwise as median [interquartile range]. Two-way ANOVA or mixed-effect analysis assessed overall differences between randomization groups. To control for power in multiple comparisons, hierarchical testing was applied from the last time point backward. Paired t-tests (non-parametric when necessary) evaluated differences in 1-minute measurements immediately preceding any PE induction. We used linear least-squares regression analysis without weighting or interaction to correlate the number of PE (clot mass) or sham inductions to cardiopulmonary variables, each forced through the baseline mean value. The slope of the regression line was compared to a hypothetical value of 0, i.e. no change in the given variable by the number of PE/sham inductions. GraphPad Prism 8.3.0 (GraphPad Software, LCC, CA) was used for statistical analyses, with a p-value < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
Results
Twelve out of thirteen animals were included in the study. One was excluded due to equipment failure. Baseline cardiopulmonary variables were similar among the included animals (12).
RV afterload
Consecutive PE increased mPAP (ANOVA p < 0.0001, Fig. 2A), particularly pronounced after the first PE (PE1 9.9 ± 5.5 vs. PE2 3.9 ± 1.5 mmHg, p = 0.025). Pulmonary vascular resistance and pulmonary arterial elastance (Ea) increased progressively (ANOVA p = 0.0015 and p = 0.0103, respectively) but from a later time point after the third PE (Fig. 2B-C). The PVR/SVR ratio increased notably after the first PE (ANOVA p = 0.0005, Fig. 2D).
Measures of right ventricular afterload
Responses to consecutive, acute pulmonary emboli on mean pulmonary arterial pressure (A), arterial elastance (B), pulmonary vascular resistance alone (C) and indexed to systemic vascular resistance (D). Please note the different responses to increased clot burden
RV function
RV end-systolic pressure (ESP) was increased, particularly after the first PE (ANOVA p < 0.0001, Fig. 3A). RV end-systolic volume (ESV) and RV end-diastolic volume (EDV) increased, but not consistently (Fig. 3B). RV stroke volume (SV) initially increased followed by declining RV output, although the overall ANOVA was not statistically significant (p = 0.109). RV ejection fraction (EF) decreased (p = 0.004, Fig. 3D) despite increased RV mechanical work (p = 0.003). End-systolic elastance (Ees) remained unchanged (p = 0.56), and the Ees/Ea ratio decrease was non-significant (p = 0.095, Fig. 3C). Acute changes in RV diastolic function were minimal (p = 0.723 for RV end-diastolic elastance, p = 0.0246 for RV dP/dtmin).
Clot burden correlation
In PE animals, all variables correlated with clot mass, particularly pulmonary pressure, PVR, and RV end-systolic pressure (Table 1). No correlations were observed in the sham group.
Pulmonary function
Consecutive PEs led to a stepwise increase in PaCO2 (Fig. 4A) and similar PaO2 decrease (Fig. 4B), while pulmonary shunt and physiological dead space increased consistently from baseline (Fig. 4C).
Clot mass correlated to ventilatory function in PE animals, with some correlations observed in sham animals, albeit with different correlation coefficients (p < 0.0001 for all). See Table 1.
Ventilatory and pressure-volume loop responses to consecutive acute pulmonary embolism
Consecutive, acute pulmonary embolism caused changes in arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide PaCO2, A) and oxygen (PaO2, B) as well as physiological dead space (C), all in stepwise manners. (D) shows representative pressure-volume loops from the right ventricle (RV) from baseline (BL) and after consecutive pulmonary embolism (PE). Note how both volume (dilatation) and pressure (afterload) increases with repeated PE. Furthermore, the shape of the loop changes with an increasingly evident end-systolic notch on the loop representing increased afterload and early wave reflection. At baseline and last loop (PE6), the arterial elastance (Ea) lines are drawn with the increased slope representing increased afterload
Systemic circulation
Consecutive PE induced increases in heart rate (HR) and central venous pressure (CVP) compared to baseline (Supplementary Fig. 1A-B). Systolic blood pressure transiently dropped with each PE, but not statistically significantly (Supplementary Fig. 1C). Cardiac output (CO) showed compensatory increases initially, followed by a decrease (not statistically different in overall ANOVA analysis, Supplementary Fig. 1D).
Left ventricle
LV PV data were similar between sham and PE animals at baseline. Inductions of PE caused a tendency to underfilled LV with reduced LV pressures and volumes, most evident for LV end-diastolic volume and LV stroke work (Supplementary Fig. 2), but this was not statistically different (data not shown).
Discussion
In this study we evaluated immediate and early cardiopulmonary responses to successive PEs revealing time-dependent variable cardiopulmonary responses. We showed that pulmonary arterial (PA) pressure increased as an early response compared to RV afterload and function, which were affected at a later point.
Our observations of RV dilatation, afterload increase and increased pressure from successive PE episodes are all evident in representative RV pressure-volume loops (Fig. 4D).
RV afterload and pulmonary vasculature
We confirmed an increase in mPAP from acute PE [9,10,11, 13]. However, our observations underscored acute PE being a highly dynamic condition as the largest mPAP increase was induced by the very first PE with smaller and stepwise increments in mPAP by the following PEs. Of particular interest, the PA pressure almost normalized within 15 min (i.e. before the second PE, see Fig. 2A). This may explain the clinical experience of patients reporting severe symptoms from the index event while being only slightly affected at the time of hospital admission. Other animal models have similarly shown excessive but transient mPAP increases with a following stabilization period [17, 18]. The prominent PA pressure response seen with the first of a series of consecutive emboli could possibly be related to an initial strong vasoconstrictor response that are weaker for the following emboli. However, we know that there is a substantial contribution of pulmonary vasoconstriction in acute PE that persists for hours, as we have previously shown prominent effects of pulmonary vasodilatory agents in this model [19, 20].
We observed that PVR and PA elastance did not immediately surge despite early increases in mPAP. Initial compensatory mechanisms like CO elevation or recruitment of non-embolized lung regions might underlie this delay, which is supported by the observation of an immediate increase in PVR/SVR ratio where CO is omitted from the equation.
The correlation between clot burden and pulmonary pressure as seen in this experimental study has also been observed in clinical studies [21,22,23]. Unfortunately, clot burden scores are poor predictors of clinical outcomes [24, 25], whereas pulmonary trunk dilatation, as a marker of increased pulmonary pressure, has been associated with adverse outcome in acute PE [26, 27].
Right ventricular function
RV adaptation to increased afterload involves complex changes including dilatation and increased contractility (Anrep effect). We observed RV dilatation comparable to other animal models of acute PE [11, 28]. The dilatation manifested early and plateaued at higher clot burdens, possibly due to pericardial constraints in our closed-chest approach. Secondly, we noticed a decrease in RV coupling (Ees/Ea) from the first PE which diverged from previous studies showing stepwise increases in RV Ea initially followed by decreased contractility and RV uncoupling at higher clot burdens [9, 11]. Differences in PE models and evaluation methods may explain this discrepancy.
RV dysfunction with reduced EF became apparent only when compensatory mechanisms were exhausted, aligning with increased Ea and PVR. Our observation of preserved CO combined with reduced RV EF confirms previous findings [17]. Compromised RV function but maintain systemic circulation mimics the intermediate-risk group according to ESC risk stratification [1].
In a clinical comparison, studies exhibit inconsistent associations between clot burden and RV dysfunction [29,30,31]. Clot burden association may be most pronounced in previously healthy individuals (comparable to our animals) where the compensatory mechanisms are larger [23, 32].
Ventilatory function
Our observations align with some previous studies demonstrating stepwise changes in pulmonary variables during successive PEs [11, 16], emphasizing clot burden’s direct relationship with ventilation-perfusion mismatch. Our finding of hypercapnia is likely due to the animals being anesthetized and ventilated with a fixed respiratory frequency opposite to awake PE patients with tachypnea and hypocapnia [33].
Limitations
Despite the strengths of our animal model mirroring human physiology [34], caution is warranted in translating our findings to clinical settings. Though patients may also experience successive PEs, it will occur less strictly and predictable than in our study design. The add-on cardiopulmonary responses from one PE to the next may therefore differ, also due to potential comorbidity of real-world patients. Secondly, while our model of PE relies on autologous blood, we acknowledge that our thrombi are quite fresh and uniform compared to a more heterogeneous picture in clinical settings. Thirdly, mechanical ventilation with a fixed respiratory rate affects the blood gasses.
Conclusion
In an experimental model of consecutive PE, we showed an immediate and pronounced increase in PA pressure in response to the first PE, whereas consistent increase in RV afterload and onset of RV dysfunction ensued later after the third PE. Ventilatory variables were more directly associated with clot burden. The results emphasize the importance of hemodynamic evaluation in acute PE regardless of clot burden as well as the dynamics of acute PE where immediate cardiopulmonary changes may occur.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- 3R:
-
refine replace reduce
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ARRIVE:
-
Animal ResearchReporting of In Vivo Experiments
- CO:
-
cardiac output
- CVP:
-
central venous pressure
- Ea:
-
arterial elastance
- EDV:
-
end-diastolic volume
- EF:
-
ejection fraction
- Ees:
-
end-systolic elastance
- ESP:
-
end-systolic pressure
- ESV:
-
end-systolic volume
- EtCO< Subscript>2</Subscript>:
-
end-tidal carbon dioxide
- HR:
-
heart rate
- IVC:
-
inferior vena cava
- mPAP:
-
mean pulmonary arterial pressure
- PA:
-
pulmonary arterial
- PaCO< Subscript>2</Subscript>:
-
partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide
- PaO< Subscript>2</Subscript>:
-
partial pressure of arterial oxygen
- PE:
-
pulmonary embolism
- PV:
-
pressure-volume
- PvCO< Subscript>2</Subscript>:
-
partial pressure of venous carbon dioxide
- PvO< Subscript>2</Subscript>:
-
partial pressure of venous oxygen
- PVR:
-
pulmonary vascular resistance
- RV:
-
right ventricle/ventricular
- SV:
-
stroke volume
- SVR:
-
systemic vascular resistance
References
Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C, Bueno H, Geersing GJ, Harjola VP, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J. 2020;41:543–603.
Lyhne MD, Kline JA, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Andersen A. Pulmonary vasodilation in acute pulmonary embolism – a systematic review. Pulm Circ. 2020;10:1–16.
Konstam MA, Kiernan MS, Bernstein D, Bozkurt B, Jacob M, Kapur NK, et al. Evaluation and management of right-sided heart failure: a Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e578–622.
Bĕlohlávek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A. Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2013;18:129–38.
Kooter AJ, Ijzerman RG, Kamp O, Boonstra AB, Smulders YM. No effect of epoprostenol on right ventricular diameter in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pulm Med. 2010;10:18.
Hariharan P, Dudzinski DM, Okechukwu I, Takayesu JK, Chang Y, Kabrhel C. Association between Electrocardiographic Findings, Right Heart strain, and short-term adverse clinical events in patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Clin Cardiol. 2015;38:236–42.
Meyer G, Vicaut E, Danays T, Agnelli G, Becattini C, Beyer-Westendorf J, et al. Fibrinolysis for patients with Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism. New Engl J Med. 2014;370:1402–11.
Hofmann E, Limacher A, Méan M, Kucher N, Righini M, Frauchiger B, et al. Echocardiography does not predict mortality in hemodynamically stable elderly patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res. 2016;145:67–71.
Ghuysen A, Lambermont B, Kolh P, Tchana-Sato V, Magis D, Gerard P et al. Alteration of right ventricular-pulmonary vascular coupling in a porcine model of progressive pressure overloading. Shock. 2008;29:197–204.
Roehl AB, Steendijk P, Baumert JH, Schnoor J, Rossaint R, Hein M. Comparison of 3 methods to induce acute pulmonary hypertension in pigs. Comp Med. 2009;59:280–6.
Kerbaul F, Gariboldi V, Giorgi R, Mekkaoui C, Guieu R, Fesler P, et al. Effects of levosimendan on acute pulmonary embolism-induced right ventricular failure. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1948–54.
Lyhne MD, Schultz JG, Kramer A, Mortensen CS, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Andersen A. Right ventricular adaptation in the critical phase after acute intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2021;10:243–9.
Schultz J, Andersen A, Gade IL, Ringgaard S, Kjaergaard B, Nielsen-Kudsk JE. A porcine in-vivo model of acute pulmonary embolism. Pulm Circ. 2018;8:204589321773821.
Sert NPdu, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A, Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: updated guidelines for reporting animal research. J Physiol. 2020;598:3793–801.
Lyhne MD, Schultz JG, Dragsbaek SJ, Hansen JV, Mortensen CS, Kramer A, et al. Closed chest biventricular pressure-volume Loop recordings with Admittance Catheters in a Porcine Model. J Vis Exp. 2021;18:e62661.
Zwissler B, Welte M, Habler O, Kleen M, Messmer K. Effects of inhaled prostacyclin as compared with inhaled nitric oxide in a canine model of pulmonary microembolism and oleic acid edema. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1995;9:634–40.
Meinel FG, Nance JW, Schoepf UJ, Hoffmann VS, Thierfelder KM, Costello P et al. Predictive value of computed tomography in Acute Pulmonary Embolism: systematic review and Meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2015;128:747– 59.e2.
Vedovati MC, Germini F, Agnelli G, Becattini C. Prognostic role of embolic burden assessed at computed tomography angiography in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:2092–102.
Kramer A, Mortensen CS, Schultz JG, Lyhne MD, Andersen A, Nielsen-Kudsk JE. Inhaled nitric oxide has pulmonary vasodilator efficacy both in the immediate and prolonged phase of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2021;10:265–72.
Lyhne MD, Hansen JV, Dragsbæk SJ, Mortensen CS, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Andersen A. Oxygen therapy lowers right ventricular afterload in experimental Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Crit Care Med. 2021;49:e891–901.
Kjaergaard J, Schaadt BK, Lund JO, Hassager C. Quantification of right ventricular function in acute pulmonary embolism: relation to extent of pulmonary perfusion defects. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2008;9:641–5.
Rodrigues AC, Guimaraes L, Guimaraes JF, Monaco C, Cordovil A, Lira E, et al. Relationship of clot burden and echocardiographic severity of right ventricular dysfunction after acute pulmonary embolism. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;31:509–15.
McIntyre KM, Sasahara AA. The hemodynamic response to pulmonary embolism in patients without prior cardiopulmonary disease. Am J Cardiol. 1971;28:288–94.
Lyhne MD, Schultz JG, MacMahon PJ, Haddad F, Kalra M, Tso DMK, et al. Septal bowing and pulmonary artery diameter on computed tomography pulmonary angiography are associated with short-term outcomes in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Emerg Radiol. 2019;26:623–30.
Bach AG, Nansalmaa B, Kranz J, Taute BM, Wienke A, Schramm D, et al. CT pulmonary angiography findings that predict 30-day mortality in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Eur J Radiol. 2015;84:332–7.
Townsley MI. Structure and composition of pulmonary arteries, capillaries and veins. Compr Physiol. 2013;2:675–709.
Feeley JW, Lee TD, Milnor WR. Active and passive components of pulmonary vascular response to vasoactive drugs in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1963;205:1193–9.
Ducas J, Girling L, Schick U, Prewitt RM. Pulmonary vascular effects of hydralazine in a canine preparation of pulmonary thromboembolism. Circulation. 1986;73:1050–7.
Furlan A, Aghayev A, Chang CCH, Patil A, Jeon KN, Park B et al. Short-term Mortality in Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Clot Burden and Signs of Right Heart Dysfunction at CT Pulmonary Angiography. Radiology. 2012.
Ceylan N, Tasbakan S, Bayraktaroglu S, Cok G, Simsek T, Duman S, et al. Predictors of clinical outcome in acute pulmonary embolism: correlation of CT pulmonary angiography with clinical, echocardiography and laboratory findings. Acad Radiol. 2011;18:47–53.
Bauer RW, Frellesen C, Renker M, Schell B, Lehnert T, Ackermann H et al. Dual energy CT pulmonary blood volume assessment in acute pulmonary embolism – correlation with D-dimer level, right heart strain and clinical outcome. Eur Radiol. 2011;21:1914–21.
McIntyre KM, Sasahara AA. Determinants of right ventricular function and Hemodynamics after Pulmonary Embolism. Chest. 1974;65:534–43.
Ozsu S, Abul Y, Yilmaz I, Ozsu A, Oztuna F, Bulbul Y, et al. Prognostic significance of PaO2/PaCO2 ratio in normotensive patients with pulmonary embolism. Clin Respir J. 2011;6:104–11.
Swindle MM, Makin A, Herron AJ, Clubb FJ, Frazier KS. Swine as models in Biomedical Research and Toxicology Testing. Vet Pathol. 2012;49:344–56.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
MDL was supported by a scholarship from Aarhus University. Running costs were covered by the Laerdal Foundation for Acute Medicine (no. 3374), Soester and Verner Lipperts Foundation, and Holger and Ruth Hesse’s Memorial Foundation (all granted for MDL). AA received funding from the Karen Elise Jensens Foundation. MDL and AA were funded by NIH (R01-grant no. 1R01HL168040-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MDL, JGS, AA, and JENK conceptualized the study. MDL, JSG, CM, and AK performed data acquisition. MDL performed analyses and drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to data interpretation, provided input to the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Danish Animal Research Inspectorate, Danish Ministry of Agriculture, approved the study (no.: 2016-15-0201-00840).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lyhne, M.D., Schultz, J.G., Mortensen, C.S. et al. Immediate cardiopulmonary responses to consecutive pulmonary embolism: a randomized, controlled, experimental study. BMC Pulm Med 24, 233 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-024-03006-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-024-03006-9