Abstract
Background
Rectal douching (RD) is widely practiced by men who have sex with men (MSM), and is associated with increased risk of HIV infection. However, the mechanism of how RD increases the risk of HIV infection is not well understood, and there is limited data on RD behavior in MSM practicing anal sex in China. We examine the purpose of RD, its timing in relation to anal sex, the types of RD products used, and risky sexual behaviors among MSM reporting anal sex.
Methods
Between August 2017 and December 2018, a cross-sectional study was conducted among adult MSM in Shenyang, China. Data were collected on demographics, sexual behaviors, and RD for the most recent sexual intercourse by means of interviewer-administered face-to-face questionnaires. Blood samples were collected to test for antibodies to HIV and syphilis. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to assess the risk factors associated with HIV infection.
Results
A total of 515 eligible MSM participated in this survey (median age: 31 years). During the most recent anal intercourse, 28.3% (146/515) had condomless receptive anal intercourse (CRAI), 21.4% (110/515) practiced serosorting, and more than half (61.6%, 317/515) reported RD before or after anal sex. Of those practicing RD, 96.8% (307/317) conducted RD before sex, while 62.5% (198/317) conducted RD after sex. The douching devices used were primarily shower hoses (85.3%, 262/307), and relatively few MSM used commercial RD products (8.1%, 25/307) before sex. The prevalence of HIV-1 and syphilis was 11.7% and 13.2%, respectively. HIV infection was positively associated with RD, practicing RD before sex, the interaction between RD and CRAI using a shower hose for RD and other risk factors, practicing RD after sex, CRAI, using nitrite inhalants, main sexual role with males as bottom and syphilis infection.
Conclusions
RD is popular among Chinese MSM. Improper noncommercial RD tools use (such as shower hose), the interaction effect between RD and CRAI associated with HIV infection. Public health workers and the MSM community should publicize scientific knowledge and prevention approaches relating to RD and HIV transmission to MSM. We recommend that further studies should be conducted to understand the detailed mechanism between RD and increased HIV prevalence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
HIV/AIDS is a serious global health concern, with 38.0 million people estimated to be living with HIV in 2019 around the world [1]. By the end of 2018, China had around 1.25 million people living with HIV [2]. The risk of getting HIV is 26 times higher among MSM compared to other populations. The proportion of newly diagnosed HIV infections contracted through male same-sex intercourse rapidly increased from 2.5% in 2006 to 25.5% in 2017 in China [3]. Moreover, China has an estimated MSM population of 18 million, with the average prevalence of HIV 4.9% [4, 5]. HIV is still a fatal disease, and HIV can cause lung cancer and other deadly tumors, reduce the life expectancy of infected MSM [4, 6,7,8]. Meanwhile, contracting syphilis increases HIV infections for MSM. A study conducted from 2000 to 2013 in 27 high-income countries found the syphilis infection rate among MSM grew from 26.8 to 55.0% [9]. The syphilis infection rate among MSM in China was estimated to be 11.8% in 2013, based on a study in 61 Chinese cities [5].
The World Health Organization (WHO) has proposed treatment as prevention (TasP), post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and behavior intervention strategies, etc. to control the HIV epidemic. However, the HIV epidemic among MSM populations in most countries around the world has not been effectively controlled [10]. Understanding the sexual behaviors and preferences of this key population group is essential for developing effective prevention strategies [11]. In recent years, the rectal douching (RD) behavior of MSM has received widespread attention. RD involves injecting various kinds of liquid into the rectum using tools to facilitate defecation and cleansing of the rectum. This behavior is common among MSM globally, both before and after anal sex. In the previous studies, around 66 and 63% of MSM in the USA and Kenya, respectively, were found to have conducted RD. [12, 13] The percentages of MSM employing RD hover around 53.4–54.0% in the UK, Brazil, and France [11, 14, 15]. In Peru, the Netherlands, and China (Beijing City), the prevalence of RD among MSM is 18.2–27.0%, 13.6–46.0, and 59.0%, respectively. Around a quarter of MSM in the USA did not know how to douche the rectum correctly [16], and more than 94% of MSM in Brazil had not received any professional instruction [14]. These reports indicate that RD is a widespread practice among the key populations vulnerable to HIV infection. If ignored, this behavior may result in increased transmission of HIV.
Despite the reported association between RD and increased HIV infection, RD’s mechanism contributes to HIV infection remains unclear [17]. RD timing and the types of RD tools used are two factors that may affect the HIV infection risk of MSM employing this practice. Percentages of MSM using RD is most frequently practiced before anal sex 87–97%, with only 13–48% conducting RD post-anal intercourse [18]. Considering this disparity between pre- and post-sex RD practice, it is essential to distinguish between the timings of RD in order to evaluate their impact on HIV infection. The main solutions used for RD are tap water and homemade solutions (e.g., water and soap) [14, 19]. For the difference in fluid osmotic pressure inside and outside the rectal epithelial cells, the latter are in a fully filled state following RD, and the risk of rupturing them is increased during anal sex. Water-based enema solutions are typically hypotonic and exert a lower osmotic pressure compared to the contents of the colon. As a result, excess water may be absorbed by epithelial cells, leading to water toxicity and cell lysis [20]. Currently, it is still unknown whether the timing of RD correlates with the rates of HIV infection among MSM. Also, RD is a complex behavior that may involve various douching tools, including a shower hose, a plastic pump, and plastic bottles [14], which can be either commercial products or noncommercial/homemade products (also called inappropriate douching tools) [19]. Even RD and other risky sexual behavior such as CARI has a positive relationship with the HIV infection [17, 21]. Whether these factors can interact with each other is still not clear while knowing this is vital for designing corresponding interventions for MSM. Until now, only scant attention has been paid to the association between the use of different kinds of douching tools and HIV infection, and there is a general lack of data on RD in China.
We, therefore, conducted a cross-sectional study to investigate the relationship between RD and risk behavior with HIV infection and examine whether there exists an interaction effect between RD and risk behavior on HIV infection among MSM. So we could promote better, safer-sex education and design useful HIV prevention guidelines in the MSM community.
Methods
Study design, duration and population
Between September 2017 and December 2018, we conducted a descriptive cross-sectional study. MSM respondents were deemed eligible to participate in the study if they were: (i) over 18 years old, (ii) MSM who reported having had anal or oral sex within the previous 6 months, (iii) MSM who agreed to be tested for HIV and disclose information about their most recent experience of sexual intercourse, and (iv) were willing and able to sign a written informed consent document. Subjects who had previously tested HIV-positive were excluded from the study.
Study setting
This study was completed in Shenyang, a politico-economic-cultural center in northeastern China and the provincial capital of Liaoning Province. Shenyang’s gross domestic product (GDP) ranked 34th of the 100 largest cities in China in 2018. Shenyang has a population of over 8.1 million, with an estimated 140,000 MSM [22]. 225 VCT clinics provide free HIV testing for MSM, FSWs, and other high-risk groups. Two HIV/AIDS designated hospitals to provide HARRT treatment for over 19,000 HIV infected people, and our VCT clinic is an outpatient department from one of the HIV/AIDS designated hospitals. The predominant HIV transmission route of annual newly reported HIV/AIDS cases in Shenyang was via the male-to-male sexual route, which accounted for 80.3% (712/887) cases in 2017. The reported HIV incidence was 6.9 (95% confidence interval (CI): 4.9–9.3)/100 person-years among MSM in Shenyang in 2013 [23, 24].
Sample size and sampling procedure/technique
The MSM respondents were recruited via a mixed-method, including outreach recruitment by community volunteers in places such as bars, parks, and baths, peer referrals, and recruitment on gay websites and gay chat rooms. This study was conducted at the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University. The questionnaire was administered by professionally trained staff in one-to-one, face-to-face interviews. After obtaining written informed consent from each research participant, we collected their sociodemographic information, sexual behaviors, and RD behaviors from the questionnaire developed for this study (see Additional file 1 for the questionnaire). The sociodemographic information included age, place of residence, educational level, highest educational degree obtained, marital status, and ethnicity. Sexual behaviors included the main channel for finding sexual partners, sexual roles, and usage of condoms and nitrite inhalants during their most recent sexual intercourse. For RD behaviors in the most recent experience of anal intercourse, we asked MSM participants if they had cleansed their rectum before and/or after RAI, the type of liquid used for douching, the type of douching product, the reasons for RD, and their serosorting behavior, defined as the practice of agreeing to have unprotected anal intercourse only with partners of the same HIV status, which is becoming increasingly popular among MSM in general [7]. All MSM who participated in this study received a HIV consultation before and after HIV testing, as well as condoms, lubricant, and educational materials on HIV.
The required sample size was calculated using an estimation formula based on the difference between two sample rates for the cross-sectional survey study [25]. The significance level was 0.05, and power was 0.8. To compare the difference of HIV prevalence between the RD and non-RD group, the sample size calculated referred to a published study in which HIV prevalence was 4.3%(11/258) in the non-RD group and 14.9%(47/315) in RD group [11]. After calculations, each group should have a minimum sample of 121 participants. We utilized PASS (Power Analysis & Sample Size) software version 15 to calculate the sample size.
Laboratory tests
Following completion of the questionnaire, 10 ml of venous blood was collected from each research participant for HIV-1 antibody screening, HIV-1 Pooled-RT-PCR, Western blot (WB), and Treponema pallidum (TP) testing.
HIV antibodies were screened using Biomérieux’s Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV 1/2) antibody diagnostic kit (ELISA method). Secondary screening was performed using Abbott Laboratories’ Human Immunodeficiency Virus Antibody Rapid Detection Kit (colloidal gold method). Once HIV-positive status was confirmed by the screening, the HIV confirmation test was performed using Gene Lab’s serum HIV Western blot (WB) method. Antibody-negative specimens were tested with the 24 mini-pool nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Blood samples giving a positive ELISA result but a negative or indeterminate WB result were tested with NAAT individually without mixing, using COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITORTM Test, v1.5 diagnostic kit (Roche, 21,118,390,123), according to the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 Test method [26].
For the detection of plasma TP, a rapid serotonin ring card test (RPR) was used for screening (Shanghai Kehua Bio-Engineering Co., Ltd.), and those who tested positive were further confirmed with Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TPPA) (Fuji Corporation, Japan). Those who were screened and confirmed as positive were deemed to be TP-positive.
Data analysis
Questionnaire and laboratory test results were recorded by two research assistants twice using EpiData 3.02 software until the data from both questionnaires were fully consistent. Descriptive statistical analysis was performed using mean ± standard deviation or the median and interquartile range (IQR) as a measure of statistical dispersion. Categorical variables were described using percentages of its frequency. Chi-square tests were used to compare differences in the categorical variables (e.g., marital status, education, and information related to the most recent anal sex). We used the median and interquartile range to describe the central tendency and dispersion of age, respectively.
Factors associated with HIV infection were analyzed using logistic regression models. We controlled for confounders in the multivariable logistic models and added one independent variable to the model each time. In the multivariable model, we controlled for age, education, and household registration. Independent variables with p < 0.2 in the univariate logistic model were entered into the multivariable model separately. We chose p < 0.2 as the cut-off point to include more RD-related behaviors that might be associated with HIV infection. The interaction between RD and CRAI was evaluated by the above multivariable logistic regression models. The inspection level α was set at 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 17.0 statistical software (IBM).
Results
Characteristics of the study participants
In this study, 95.4% (515/540) of the MSM approached were eligible to participate in the cross-sectional study. The main reasons for exclusion were: (i) being underage (3.7%, 20/540) and (ii) 0.9% (5/540) refusing to participate in the research (Fig. 1). The median age among the research participants was 31 (IQR 25–37) years. If the time frame was the most recent anal sex, 28.3% (146/515) had CRAI, and 28.9% (149/515) consumed nitrite inhalants. Other demographic and sexual behaviors characteristics are given in Table 1.
Rectal douching characteristics of the study participants
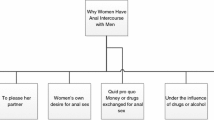
Among all of the research participants, 61.6% (317/515) reported douching their rectum at some time during their most recent anal intercourse, with 59.6% (307/515) conducting RD before sex and 38.4% (198/515) conducting RD after sex. Douching devices used before anal intercourse include a shower hose (85.3%, 262), commercial RD products (8.1%, 25), a bulb syringe (2.9%, 9), a syringe (1.6%, 5), a basin and water bottle (1.3%, 4), as well as other items (0.7%, 2). The types of douching liquids used (before/after RD, n = 317) included tap water (98.1%, 311), mixed solutions of water and soap (1.6%, 5), and commercial douching liquids (0.6%, 2). Almost all (97.4%, 299) of those who conducted RD reported doing so before anal sex for hygienic reasons, 23.1% (71) for feeling greater pleasure during sex, and 6.8% (21) for satisfying their sexual partner. The primary reason for RD post-anal intercourse was similar: 95.5% (189) did so in personal hygiene. Others douched their rectum after sex because their sexual partners did not use a condom during sex (14.1%, 28), and they felt that RD would prevent HIV infection (4.0%, 8).
Compared with RD non-users, RD users had: a higher level of education, were more likely to have had CRAI, were more likely to use nitrite inhalants, and were more likely to be living with HIV. Differences in the sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics among MSM who reported RD and those who did not are listed in Table 1.
RD and other factors associated with HIV infection
Of the 515 MSM recruited, 60 men (11.7%) (95% CI: 9.0–14.7) tested HIV-1-positive and 68 men (13.2%) (95% CI: 10.4–16.4) tested syphilis-positive. None were detected HIV-1 screening negative but pooled NAAT positive. Univariate and multivariable logistic regressions were utilized to assess the factors associated with HIV infection (Table 2). The univariate logistic regression results indicated that HIV infection was statistically associated with RD during the most recent anal intercourse, RD before and after anal intercourse, playing the receptive sexual role (bottom), having condomless sex when playing the receptive role CRAI, being infected by syphilis, the interaction between RD and CRAI, and using nitrite inhalants before sex.
According to Table 2, in multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that variables that were statistically associated with HIV infection in the most recent anal intercourse included: RD (adjusted odds ratio (AOR), 2.8; 95% CI, 1.4–5.4), practicing RD before sex (AOR, 2.2; 95% CI, 1.2–4.2), the interaction between RD and CRAI (AOR = 3.5; 95% CI, 2.0–6.2), using a shower hose for RD (AOR, 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0–11.3) and other risk factors, practicing RD after sex, CRAI, using nitrite inhalants before anal sex in the most recent anal sex main sexual role with males as bottom and syphilis infection (Fig. 2).
AORs and 95% CI between high-risk behavior and HIV infection among MSM participants
HIV infection-related factors were analyzed using multivariable logistic regression model analysis. Multivariable logistic Model controlled for fixed covariates (age, education, and household registration). Abbreviations RD, rectal douching; CRAI, condomless receptive anal intercourse; CIAI, condomless insertive anal intercourse.
Discussion
This cross-sectional study of 515 MSM in Shenyang, China, reports the proportion of and reasons for practicing RD among MSM in China. It investigated the impacts of RD products, douching liquid types, and the timing of RD on HIV infection. We found that using a shower hose (inappropriate douching tools) to assist RD was positively associated with the odds of HIV-1 infection among MSM. Meanwhile, we found the interaction between RD and CRAI was associated with HIV infection. This finding contributes to our understanding of RD behavior and the risks of HIV infection among MSM. It also helps to clarify the possible reasons for the high HIV disease burden of MSM in China, and our study provides first-hand evidence to include in future publicity materials and educational activities about the risks associated with RD and HIV infection among MSM.
This study found that the proportion of RD among MSM in Shenyang, a city with a lower level of GDP than other cities in China, was over 60%, similar to the percentage reported for Beijing (59.3%) [27]. These figures suggest that RD might be a common practice among MSM in urban China whatever their economic level. The prevalence of RD behavior among MSM in China is close to that of the USA (66%), Kenya (63%) [12, 13], the UK, Brazil, and France (53.4–54.3%) [11, 14, 15], but higher than that in Peru (18.2–27.0%) [28, 29] and the Netherlands (13.6–46%) [30, 31]. Despite this high prevalence among MSM worldwide, scientific data for and knowledge of RD in the Chinese MSM population is still insufficient. Around a quarter of MSM in the USA did not know how to douche the rectum correctly [16], and more than 94% of MSM in Brazil had not received any professional instruction [14]. Currently, there is no authoritative information on RD for MSM in China. The disparity between the prevalence of RD and the lack of instruction about it highlights the importance of delivering accurate and relevant information about RD to the MSM population via social media.
This study found that RD is positively correlated with the odds of HIV infection (AOR = 2.8) in MSM participants, consistent with previous findings from the USA and Europe and a recent meta-analysis [16, 17, 21, 31, 32]. We found inappropriate tools used for rectal douching is associated with higher HIV infection risk in MSM participants, compared with the commercial equipment. The most common inappropriate tool used for RD in MSM participants was shower hose. We also found that the use of a shower hose associated with increased odds of HIV infection. Shower hoses are not expressly designed for RD as they have irregular edges. The process of using a shower hose to complete RD may cause damage to the perianal skin, and hence increase the risk of HIV infection. More than 85% of MSM participants used the shower hose to flush their anus in this survey, which is significantly higher than in foreign MSM populations. According to our study results, health workers and MSM community based organizations (CBOs) should widely publicize the potential for this type of RD to increase HIV infection in the MSM community. Besides, this study found that most MSM conducted pre-anal intercourse RD using tap water. Due to the difference in fluid osmotic pressure inside and outside the rectal epithelial cells, the latter are in a fully filled state following RD, and the risk of rupturing them is increased during anal sex. Water-based enema solutions are typically hypotonic and exert a lower osmotic pressure compared to the contents of the colon. As a result, excess water may be absorbed by epithelial cells, leading to water toxicity and cell lysis [20]. So enemas consisting of saline solution are recommended for MSM who practice RD frequently. For the benefit of MSM who engage in RD, it is recommended that they receive proper educational materials on how to select the most appropriate douching products and liquids so as to reduce the risk of HIV and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) resulting from rectal mucosal injuries.
This study found that, compared to MSM who do not perform RD, MSM who do use RD engaged in a greater proportion of bottom and versatile roles during anal sex.. The bottom and versatile sexual roles has different risk of HIV infection compared with the top role [33], hence controlling the sexual role may help well explain the association between RD and HIV infection. The results of our analysis have given us more reliable evidence of the association between RD behavior and HIV infection in the MSM population.
Understanding the reasons why MSM practice RD is important for promoting HIV-related education and conducting further studies. Over 95% of MSM participants did so because they wanted to remain clean and hygienic before and/or after anal intercourse and increase pleasure during sex. A proportion (14.6%) were under the misconception that RD could wash semen away from the rectum and prevent HIV infection and STIs. This suggests that MSM participants were very concerned about their health and preventing HIV infection and other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Given the positive correlation between RD behavior and a willingness to use rectal microbicides among Peruvian MSM [29], our study findings indicate that Chinese MSM are likely to be good candidates to be recruited to use rectal microbicide enemas for HIV prevention.
This study also found that factors contributing to HIV-1 infection include: (i) condomless anal intercourse; (ii) using nitrite inhalants before anal intercourse; and (iii) not serosorting in the most recent anal intercourse and main sexual role with males as bottom. These findings are consistent with those of international peer reports [17, 34]. It is worth noting that previously there was a lack of evidence to support the implementation of serosorting behavior to prevent HIV infection in MSM in China, although the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC) had issued related serosorting guidelines for MSM in 2016. Hence, in China, pertinent interventions, such as promoting serosorting among MSM who practice RD and partner notification promotion, are urgently needed. The results of this study will help China and other countries in a similar situation to promote serosorting measures among MSM to reduce HIV infection.
Strengths of the study
This study demonstrates an association between RD products’ types and HIV infection among MSM, providing empirical evidence for informing future sexual health education efforts. Further, our study demonstrated that RD and CRAI interact with each other in promoting HIV infection, and MSM with both higher RD practice and CRAI behavior were more likely to have HIV infection. Previous studies have also found RD associated with CRAI [11, 13]. It is recommended that condom use promotion is the most critical behavioral interventions among MSM practice RD before or after sex.
Limitations of the study
In order to reduce the effects of recall bias, this study only collected information on RD behavior during the most recent sexual experience. It did not analyze the cumulative effect of RD frequency and timing on HIV infection. Additionally, sampling technique used in our study may affect the representativeness of the sample, MSM came to our VCT clinic might have higher health awareness and research participants from the sample pool all came from 1 of 225 VCT clinics in Shenyang, and thus were not representative of other areas in Shenyang and China. Third, the questionnaire has not been tested for reliability and validity before, so interpreting related study results should be cautious. Lastly, the cross-sectional study design used in this study cannot determine the cause-effect relationship between RD and the risk of HIV infection, for which further prospective cohort studies should be undertaken.
Conclusions
RD behavior is prevalent among MSM in Shenyang in northeastern China. Because RD, CRAI, the interaction effect of RD and CRAI, might increase the odds of HIV infection, it is suggested that relevant health information targeting MSM who have used shower hoses for RD before/after sex and who have CRAI should be promoted. This may help MSM to understand the association between RD and HIV infection to reduce the spread of HIV among the MSM population. Moreover, safer types of douching products and liquids should be formulated in order to contain a potential new channel of HIV dissemination.
Availability of data and materials
The data bank analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CAI:
-
Condomless anal intercourse
- CDC:
-
(China) Center for Disease Control and Prevention
- CIAI:
-
Condomless insertive anal intercourse
- CRAI:
-
Condomless receptive anal intercourse
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GDP:
-
Gross domestic product
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- IRB:
-
Institutional review board
- MSM:
-
Men who have sex with men
- NAAT:
-
Nucleic acid amplification testing
- RAI:
-
Receptive anal intercourse
- RD:
-
Rectal douching
- RPR:
-
Rapid serotonin ring card test
- TP:
-
Treponema pallidum
- TPPA:
-
Treponema pallidum particle agglutination
- WB:
-
Western blot
References
UNAIDS: UNAIDS DATA 2019. Available from:. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2019-UNAIDS-data_en.pdf 2019.
Lyu P, Chen FF. National HIV/AIDS epidemic estimation and interpretation in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2019;40(10):1191–6.
CDC NNC. Update on the AIDS/STD epidemic in China the third quarter of 2018. Chin J AIDS & STD. 2018;24(11):1075.
Shang H, Xu J, Han X, Spero Li J, Arledge KC, Zhang L. HIV prevention: bring safe sex to China. Nature. 2012;485(7400):576–7.
Wu Z, Xu J, Liu E, Mao Y, Xiao Y, Sun X, Liu Y, Jiang Y, McGoogan JM, Dou Z, et al. HIV and syphilis prevalence among men who have sex with men: a cross-sectional survey of 61 cities in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57(2):298–309.
Giacomet V, Trabattoni D, Zanchetta N, Biasin M, Gismondo M, Clerici M, Zuccotti G. No cure of HIV infection in a child despite early treatment and apparent viral clearance. Lancet. 2014;384(9950):1320.
Mayer KH, Bekker L-G, Stall R, Grulich AE, Colfax G, Lama JR. Comprehensive clinical care for men who have sex with men: an integrated approach. Lancet. 2012;380(9839):378–87.
Reddy KP, Kong CY, Hyle EP, Baggett TP, Huang M, Parker RA, Paltiel AD, Losina E, Weinstein MC, Freedberg KA, et al. Lung Cancer mortality associated with smoking and smoking cessation among people living with HIV in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(11):1613–21.
Read P, Fairley CK, Chow EP. Increasing trends of syphilis among men who have sex with men in high income countries. Sex Health. 2015;12(2):155–63.
Stannah J, Dale E, Elmes J, Staunton R, Beyrer C, Mitchell KM, Boily MC. HIV testing and engagement with the HIV treatment cascade among men who have sex with men in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Llancet HIV. 2019;6(11):e769–87.
Hambrick HR, Park SH, Goedel WC, Morganstein JG, Kreski NT, Mgbako O, Duncan DT. Rectal douching among men who have sex with men in Paris: implications for HIV/STI risk behaviors and rectal Microbicide development. AIDS Behav. 2018.
Hassan A, Blumenthal JS, Dube MP, Ellorin E, Corado K, Moore DJ, Morris SR. Effect of rectal douching/enema on rectal gonorrhoea and chlamydia among a cohort of men who have sex with men on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis. Sex Transm Infect. 2018.
Saleska JL, Turner AN, Syvertsen J, Nakhumwa J, Soo L, Ohaga S, Agot K. Correlates of rectal douching practices among men who have sex with men in Kenya. Sex Transm Dis. 2018.
Lamblet LCR, da Silva RJC. Prevalence and types of rectal douches used for anal intercourse among men who have sex with men in Brazil. BMJ Open. 2017;7(5):e011122.
Macdonald N, Sullivan AK, French P, White JA, Dean G, Smith A, Winter AJ, Alexander S, Ison C, Ward H. Risk factors for rectal lymphogranuloma venereum in gay men: results of a multicentre case-control study in the U.K. Sex Transm Infect. 2014;90(4):262–8.
Noor SW, Rosser BR. Enema use among men who have sex with men: a behavioral epidemiologic study with implications for HIV/STI prevention. Arch Sex Behav. 2014;43(4):755–69.
Li P, Yuan T, Fitzpatrick T, Smith K, Zhao J, Wu G, Ouyang L, Wang Y, Zhang K, Zhou Y, et al. Association between rectal douching and HIV and other sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex Transm Infect. 2019.
Carballo-Dieguez A, Lentz C, Giguere R, Fuchs EJ, Hendrix CW. Rectal douching associated with receptive anal intercourse: a literature review. AIDS Behav. 2018;22(4):1288–94.
Javanbakht M, Stahlman S, Pickett J, LeBlanc MA, Gorbach PM. Prevalence and types of rectal douches used for anal intercourse: results from an international survey. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:95.
Schmelzer M, Schiller LR, Meyer R, Rugari SM, Case P. Safety and effectiveness of large-volume enema solutions. Appl Nurs Res. 2004;17(4):265–74.
Carballo-Dieguez A, Bauermeister JA, Ventuneac A, Dolezal C, Balan I, Remien RH. The use of rectal douches among HIV-uninfected and infected men who have unprotected receptive anal intercourse: implications for rectal microbicides. AIDS Behav. 2008;12(6):860–6.
Xu JJ, Zhang M, Brown K, Reilly K, Wang H, Hu Q, Ding H, Chu Z, Bice T, Shang H. Syphilis and HIV seroconversion among a 12-month prospective cohort of men who have sex with men in Shenyang. China Sex Transm Dis. 2010;37(7):432–9.
Zhang W, Xu JJ, Zou H, Zhang J, Wang N, Shang H. HIV incidence and associated risk factors in men who have sex with men in mainland China: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex Health. 2016.
Z-x C, Xu J-j, Y-h Z, Zhang J, Hu Q-h, Yun K, Wang H-y, Jiang Y-J, Geng W-Q, Shang H. Poppers use and Sexual Partner Concurrency Increase the HIV Incidence of MSM: a 24-month Prospective Cohort Survey in Shenyang, China. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1).
Machin D, Campbell MJ, Tan SB, Tan SH. Sample sizes tables for clinical, laboratory and epidemiology studies, Fourth Edition. New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell; 2018. p. 43.
Han X, Xu J, Chu Z, Dai D, Lu C, Wang X, Zhao L, Zhang C, Ji Y, Zhang H, et al. Screening acute HIV infections among Chinese men who have sex with men from voluntary counseling & testing centers. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28792.
Zhou ZH, Li SM, Liu YJ, Jiang SL, Zhang XX, Li QC, Li DL, Luo FJ, Ruan YH, Shao YM. Study on the relationship between behavioral factors, psychological status and HIV infection among men who have sex with men in Beijing. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2010;31(3):273–6.
Galea JT, Kinsler JJ, McLean S, Calvo G, Sanchez H, Leon SR, Brown B. Rectal douching prevalence and practices among Peruvian men who have sex with men and Transwomen: implications for rectal Microbicides. AIDS Behav. 2016;20(11):2555–64.
Kinsler JJ, Galea JT, Lama JR, Segura P, Peinado J, Casapia M, Ortiz A, Nadjat-Haiem C, Montano SM, Sanchez J. Rectal douching among Peruvian men who have sex with men, and acceptability of a douche-formulated rectal microbicide to prevent HIV infection. Sex Transm Infect. 2013;89(1):62.
Achterbergh R, van der Helm JJ, van den Boom W, Heijman T, Stolte IG, van Rooijen MS, de Vries H. Is rectal douching and sharing douching equipment associated with anorectal chlamydia and gonorrhoea? A cross-sectional study among men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Infect. 2017;93(6):431–7.
Heiligenberg M, Rijnders B, van der Loeff MF S, de Vries HJ, van der Meijden WI, Geerlings SE, Fennema HS, Prins M, Prins JM. High prevalence of sexually transmitted infections in HIV-infected men during routine outpatient visits in the Netherlands. Sex Transm Dis. 2012;39(1):8–15.
de Vries HJ, van der Bij AK, Fennema JS, Smit C, de Wolf F, Prins M, Coutinho RA, Morre SA. Lymphogranuloma venereum proctitis in men who have sex with men is associated with anal enema use and high-risk behavior. Sex Transm Dis. 2008;35(2):203–8.
Patel P, Borkowf CB, Brooks JT, Lasry A, Lansky A, Mermin J. Estimating per-act HIV transmission risk: a systematic review. AIDS. 2014;28(10):1509–19.
Grewal R, Allen VG, Gardner S, Moravan V, Tan DH, Raboud J, Bayoumi AM, Kaul R, Mazzulli T, McGee F, et al. Serosorting and recreational drug use are risk factors for diagnosis of genital infection with chlamydia and gonorrhoea among HIV-positive men who have sex with men: results from a clinical cohort in Ontario, Canada. Sex Transm Infect. 2017;93(1):71–5.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff at Shenyang Sunny Workgroup for the help with MSM participant enrollment. We also thank Jiaming Li, Erlei Peng, Xiang Mao, Bowen Zhang and Yong Kang for their efforts in the implementation of the project. Finally, we thank all who participated in the study.
Funding
This research was supported by the Mega-Projects National Science Research for 13th Five-Year Plan (2017ZX10201101–002-007) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81872674) and the National Science and Technology Major Project (2018ZX10101–001–001-003). The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZXC, HS, and JJX conceived and designed the experiments. ZXC, QHH, HYW, JZ, WQG, and YJJ carried out the study and experiments. ZXC, GQS, and WD analyzed and interpreted the results of study. ZXC, GQS, WD, and JJX, wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript. ZXC and GQS contributed equally to this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The relevant research plan and the procedure for obtaining informed consent were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the China Medical University ([2017]2015–140-4). All participants must complete written informed consent procedures to participate.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
The questionnaire contains sociodemographic information, sexual behaviors, and RD behaviors information.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, Z.X., Shen, G., Hu, Q. et al. The use of inappropriate anal douching tool associates with increased HIV infection among men who have sex with men: a cross-sectional study in Shenyang, China. BMC Public Health 21, 235 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10276-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10276-z