Abstract
Background
This study aimed to examine factors associated with postpartum depression (PPD) symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic among postpartum women in five countries, a subject that has not been investigated thus far.
Methods
A multi-country, cross-sectional, online survey was conducted with a convenience sample of 3,523 postpartum women in Brazil, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, and the United Kingdom, from July to November 2021. Sociodemographic and obstetric data, food insecurity, COVID-19 positive status, COVID-19 vaccination, infant feeding, breastfeeding belief score, and social support were investigated. PPD and social support were measured using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale and Maternal Social Support Scale, respectively. Descriptive statistics, chi-squared tests, and t-tests were used to identify associations with PPD symptoms. A binary logistic regression model was used to identify explanatory factors associated with PPD and adjusted odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
Results
Women in Taiwan (AOR = 0.5; 95%CI 0.34, 0.73) and Thailand (AOR = 0.68; 95%CI 0.46, 0.99) had a lower risk of PPD symptoms than those in Brazil. In addition, women with planned pregnancies had a lower risk of PPD (AOR = 0.74; 95%CI 0.60, 0.91). Younger women (AOR = 1.62; 95%CI 1.05, 2.51), health problems during pregnancy, delivery, or postpartum (AOR = 1.71; 95%CI 1.42, 2.06), and no change or worse food insecurity during COVID-19 (AOR = 1.66; 95%CI 1.21, 1.27 for no change and AOR = 1.68; 95%CI 1.27, 1.23, respectively) presented a higher likelihood of having PPD. Feeding babies with expressed human milk (AOR = 1.25; 95%CI 1.03, 1.50) and/or complementary food (AOR = 1.51; 95%CI 1.17, 1.94) were associated with PPD symptoms. Women who received low (AOR = 7.74; 95%CI 5.43, 11.03) or medium support (AOR = 3.25; 95%CI 2.71, 3.88) had higher likelihoods of PPD.
Conclusion
PPD symptoms during the pandemic were high in young women, particularly Brazilian women, with health problems in the puerperal pregnancy cycle who fed their babies expressed breast milk and/or complementary food. Low social support also impacted PPD symptoms. This study highlights the need for the professional screening for PPD and provision of virtual or personal support.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected mental health globally [1]. A survey conducted in the United Kingdom (UK) showed the effect of social isolation or social distancing on well-being. An increase in depression, anxiety, stress, and other negative feelings were identified, which may be related to individual, social, and population factors [2].
Specific populations, such as pregnant and breastfeeding women, have also been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. A study conducted in Ireland, Norway, Switzerland, the Netherlands, and the UK showed that the prevalence of major depression symptoms (Edinburgh Depression Scale ≥ 13) was 15% in pregnant women and 13% in breastfeeding women up to three months postpartum. In addition, the authors identified moderate and severe generalized anxiety symptoms in 11% and 10% of the patients, respectively [3].
PPD is the most common psychological condition following delivery [4]. It can start at any time after childbirth within the first year, and continue for many years [4, 5]. The global prevalence of PPD is 17.2% with South America being 21.7%, Northern Europe 13.8%, Eastern Asia 17.4%, Southern Asia 19.8%, and South-Eastern Asia 13.5% [6].
The prevalence of PPD is very high in some countries and might be due to cross-cultural variables, biological vulnerability factors, and different socio-economic environments, such as levels of social support and stress [7]. Nations with a higher prevalence of PPD have a higher rates of income inequality, higher maternal mortality, infant mortality, or women of childbearing age working 40 h or more/week [8]. High levels of depressive symptoms and anxiety in pregnant and breastfeeding women during the COVID-19 pandemic were found to be associated with chronic mental illness, chronic postpartum somatic illness, and unplanned pregnancy [3]. Low social support was also a predictor of PPD [9].
Women with PPD are less sensitive to their infants and more negative about their infant experience. They can also present with disturbances in early mother-infant interactions and are associated with poorer infant cognitive outcomes at 18 months [10]. It may also have a negative impact on breastfeeding initiation and duration [11, 12]. Women in conflict with partners are associated with a higher risk of PPD [13]. Early life abuse, adult abuse, maternal low education, low socioeconomic status at the time of pregnancy, and lack of social support have been consistently identified as risk factors for PPD in low- and middle-income countries [14]. However, there is a lack of research on the association between breastfeeding and PPD, and the association between COVID-19 related factors and PPD.
The lockdown periods and limited social contact and social support during the COVID-19 pandemic have been a major challenge for mothers, children, and families [15]. Investigating the factors causing PPD symptoms during the pandemic could help healthcare professionals and policymakers understand the situation and provide strategies to support postpartum women with PPD.
This study aimed to examine the factors associated with postpartum depression symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic among postpartum women in five countries.
Methods
Study design and Sites
Data from a multi-country, cross-sectional, online survey on postpartum women’s COVID-19-breastfeeding practices, including vaccination and postpartum depression, were collected in five countries: Brazil, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, and the UK. The analysis focused on postpartum depression and associated factors in postpartum women during the COVID-19 pandemic between July 2021 and November 2021.
Population and data collection
We considered postpartum women who were 18 to 49 years old (Taiwan: between 20 and 49 years old), literate in their country’s official language, and up to six months postpartum as criteria of inclusion. Women who did not live in one of the study countries during the survey period were excluded. To ensure participants were postpartum women, before filling in the questionnaire, they had to confirm: “I gave birth in the past 6 months” and “I understand that I must not take part if I do not meet the criteria for participation”.
A questionnaire in the local languages of participating countries (Portuguese, Korean, Chinese, Thai, and English) was used to collect information after being created in English, translated into the local language, and back-translated into English.
The Google Forms survey link was distributed via email posted on social media platforms (Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and WhatsApp) and sent by personal networks, health professional groups, and nonprofit organizations.
Data collection proceeded after obtaining ethics approval from five respective in-country universities’ Ethics Committees. The participants were invited to complete the questionnaire after voluntarily signing an online informed consent form.
Measures of variables
Postpartum depression was measured by self-reported major depressive symptoms using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS), which screens for symptoms of perinatal depression and anxiety. The self-report instrument assesses emotional experiences over the past seven days using a 10-item Likert scale. Each item uses a four-point scale (from zero to three) and has a total range of 0–30 [16]. A score of 13 or more was considered a postpartum depression “case.” We used validated EPDS versions from each country [17,18,19,20].
We also collected data on age, educational level, working status, marital status, local residence, parity, planned pregnancy, delivery mode, birth weight, health problems of mother during pregnancy/delivery or postpartum number of postnatal care visits, and food insecurity (if it changed from before and during the COVID-19 pandemic), if women were tested as COVID-19 positive, received COVID-19 vaccinations, and social support. To identify the variable “health problems of mother” women responded “Yes” or “No” for each question: “Do you have any health problems during pregnancy?”, “Do you have any health problems during delivery?” and “Do you have any health problems during postpartum?”.
Infant feeding information was collected using the question: “How was your youngest baby fed in the last 24 hours?” Women responded “Yes” or “No” for each item pertaining to the previous 24 h: breastfeeding (baby only fed directly from the breast), expressed human milk, infant formula feed, and solid/semi-solid or soft foods (including non-breast milk liquids). Further, beliefs towards breastfeeding scores (from 6 to 18) were obtained using a 3-point Likert scale (1 = agree, 2 = uncertain, 3 = disagree) in response to the following questionnaire statements:1) “COVID-19 can be passed on to the baby through human milk and breastfeeding;” 2) “If the mother is confirmed or suspected to have the COVID-19 infection, the mother should not breastfeed;” 3) “If the mother is confirmed or suspected to have the COVID-19 infection, the baby should still be immediately be placed skin-to-skin and breastfed following delivery;” 4) “If the mother is confirmed or suspected of having the COVID-19 infection, it is safer to give the baby infant formula milk compared to human milk or practice breastfeeding at the breast;” 5) “A breastfeeding mother who is confirmed or suspected of having the COVID-19 infection should always wear a face mask when breastfeeding;” and 6) “A mother who is confirmed or suspected to have the COVID-19 infection can touch and hold her newborn baby without wearing a face mask.” Questions 3 and 5 were coded before being summed up in reverse. A higher score indicated a more positive breastfeeding belief [21].
Social support was measured using the Maternal Social Support Scale (MSSS). It is a six-item self-report measure of maternal perceptions of social support: (1) “I have good friends who support me,” (2) “My family is always there for me,” (3) “My husband/partner helps me a lot,” (4) “There is conflict with husband/partner,” (5) “I feel controlled by my husband/partner,” and (6) “I feel loved by my husband/partner.” Each item was rated on a 5-point Likert scale from 1 (never) to 5 (always), scoring up to 30 points. Items 4 and 5 were reverse-scored [22]. We considered low social support scores to be < 19, medium social support scores to be 19–24, and high social support scores to be 25–30 [22].
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SAS 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Descriptive statistics were used to calculate frequencies and percentages for categorical variables and means and standard deviations for continuous variables. The chi-square test or Student’s t-test was used to examine the association between the independent variables and PPD symptoms (13 or higher scores), as appropriate. Co-variates with p-value < 0.05 in univariate analysis were entered into final multiple logistic regression. A binary logistic regression model was used to identify explanatory factors associated with PPD symptoms, and crude and adjusted odds ratios (COR and AOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. Statistical significance was set at a p-value < 0.05. For multiple linear regression, independent variables which showed p-value less than 0.05 in simple linear regression were employed in multiple linear regression.
Results
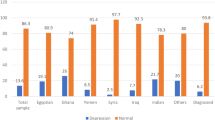
A total of 3,253 women participated in the survey (Brazil: 560; Taiwan: 614; Thailand: 840; South Korea: 381; UK: 858). Participants were mostly 30–39 years old (61.6%), only 24.2% had a college or secondary education level, more than half were on maternity leave (59.2%), mostly married (95.5%), and lived in an urban area residence (72.6%). Regarding obstetric data, 57% had one child, most had a planned pregnancy (80.4%), 39% had a C-section delivery mode, only 32.9% chose 4 or more postnatal care factors, only 12.3% had a preterm delivery, and 43.7% experienced maternal health problems (during pregnancy, delivery, or postpartum period) (Table 1).
Table 1 shows 29.3% of women with postpartum depression symptoms based on the cut-off score (13 or more) and was associated with women being younger (p < .0001), with college or lower educational levels (p = .001), unemployed (p < .0001), unplanned pregnancies (p < .0001), health problems during pregnancy, delivery, or postpartum (p < .0001), and not receiving postnatal care support (p < .0001). Women whose food insecurity did not change or worsen during the COVID-19 pandemic were associated with PPD symptoms (p < .0001), and women with PPD symptoms tended not to receive the vaccination (p = .0177).
Table 2 shows that most infants were breastfed at the breast in the 24 h prior to the survey (73.5%), 38.3% received expressed human milk, and 40.6% received formula feeding. Most postpartum women received professional healthcare support (67.1%), 51.6% also received support from a spouse/partner, friend, or relative, and 6.24% expressed high social support.
Women who expressed human milk (p = .0288) and gave complementary food to infants (p < .0001) were associated with PPD symptoms. Women who presented with PPD symptoms had lower mean scores on beliefs about breastfeeding (7.10; vs. 7.48; p = .0003). In addition, no support received for infant feeding (p < .0001), less health professional care postpartum feeding support (p = .0004), and less spouse/partner/friend or relative support (p < .0001) were associated with PPD symptoms. Low and middle social support were associated with postpartum depression (p < .0001) (Table 2).
The results of the logistic regression analysis are presented in Table 3. Women living in Taiwan and Thailand have a lower likelihood of PPD symptoms than those in Brazil. In addition, women who planned their pregnancies had a lower likelihood of PPD symptoms. Younger women who experienced health issues during pregnancy, delivery, or postpartum and experienced no change or worse food insecurity had a higher likelihood of PPD in the five countries. Feeding babies with expressed human milk and complementary food was associated with PPD symptoms. Women who received low or moderate support had a higher likelihood of having PPD symptoms. In Table 4 multiple linear regression confirm the results presented above.
Discussion
Pooled samples from Brazil, the UK, Taiwan, Thailand, and South Korea presented 29.3% of women with postpartum depression symptoms. We found that women who were 18–29 years old; experienced health problems during pregnancy, delivery, or postpartum; had worse or no change in food insecurity; low or middle social support; who fed their babies expressed human milk and/or complementary food; and had low or medium social support were factors associated with PPD symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic among postpartum women in the five countries. Women who had PPD symptoms had lower belief towards breastfeeding. Women who planned their pregnancies had a low risk of developing PPD symptoms during the study period.
Our research supports studies reporting the prevalence of mental health issues during the COVID-19 pandemic [6, 23, 24], despite the difference in cut-off value between studies. We used the EPDS cut-off value 13, which, according to a systematic review, is more specific and could be used for postpartum women with higher symptom levels [25]. Considering that, rates of prevalence of PPD could be higher than studies using a cut-off value lower than 13. In clinical practice, health professionals may use a lower cut-off value to PPD screening.
Primiparous, women younger than 35 years, employed full-time, and middle-income categories increased the risk of depressive and anxiety symptoms during the outbreak [23]. A study in Japan identified a correlation between PPD and primiparity, premature delivery, difficult labor, concern about baby care, and experience of life events [26]. Similar results were found in the five countries in which PPD symptoms were associated with women being younger and who had health problems during pregnancy, delivery, or postpartum. Younger age and first baby experience may bring more anxiety about delivery and motherhood. Supporting these women might be effective to prevent and identify PPD earlier [26]. Healthcare professionals should discuss women’s mental health when caring for the health problems during pregnancy, delivery or postpartum [27].
Regarding food insecurity, a study identified an associated 253% higher risk of depression [28], results congruent with our findings that women who experienced worse or no change in food insecurity were associated with a higher risk of PPD symptoms. The COVID-19 pandemic has increased insecurity in women in many aspects. A scoping review conducted between 2020 and 2021 indicated an increased prevalence of food insecurity due to negative changes in food accessibility and availability [29]. Food insecurity compromises health because of its association with poor diet quality, obesity, depression, and high mortality rates [30]. It increases the risk of eating disorders, depression, and anxiety 1.19 times [31]. Maternal depression increases the risk of delayed early childhood development when associated with household food insecurity [32]. Therefore, it is important to identify and support households experiencing food insecurity to prevent and address maternal mental health problems.
Our study identified a higher likelihood of PPD symptoms in women who fed their baby human milk and/or complementary food. Another study conducted in the United States found that women who fed their children infant formula had 92% greater odds of PPD symptoms compared to breast or bottle feed with expressed human milk [33]. In addition, a recent systematic review showed that women who did not exclusively breastfeed had an 89% higher PPD rate [34].
Despite the pandemic giving mothers the opportunity to be at home to breastfeed their babies, first-time mothers may be at higher risk of breastfeeding cessation because of a lack of support [35]. Postpartum women need support to grow their babies, and the COVID-19 pandemic has negatively influenced their support. Mothers reported increased stress and isolation and had an immense desire for social and professional support [35]. Poor social support could be a reason for the increase in PPD symptoms found in our study.
A study of postpartum women in Canada showed that the COVID-19 pandemic interfered with access to formal and informal breastfeeding social support, which facilitated feelings of less protection and connectedness [36]. Supporting mothers during breastfeeding is important to clarify their doubts and discuss problems. Breastfeeding professional support increases the degree of mother’s satisfaction and helps them network, protecting breastfeeding rates for more than six months [37].
Health professional workers should screen for mental health issues and support women and their babies to protect them from negative consequences, especially in a pandemic such as COVID-19.
The limitations of the study are as follows: women completed the EPDS by themselves on an online survey form, which may impact the PPD symptom score. Only women who could access the internet participated in the study and might not be representative of different social classes. Non-probability samples may not be representative of all countries and cannot be generalized to other settings. Due to the study design, causation cannot be established in the cross-sectional.
Conclusion
Postpartum depression symptoms were high and were associated with being younger, having health problems during pregnancy, delivery, and/or postpartum, worse and/or no change in food insecurity, low or middle social support, less professional care postpartum feeding support, and feeding babies with expressed human milk and complementary food during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study highlights that professionals should be trained to identify potential postpartum women with PPD and provide personal or virtual support to guarantee adequate support during the COVID-19 pandemic. Supporting postpartum women’s mental health may protect the practice of breastfeeding and the well-being of newborns.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed for this study are presented in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- PPD:
-
Postpartum depression
- BF:
-
Breastfeeding
- EBF:
-
Exclusive breastfeeding
- UK:
-
United Kingdom
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Robinson E, Sutin AR, Daly M, Jones A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies comparing mental health before versus during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. J Affect Disord. 2022;296:567–76.
Holmes EA, O’Connor RC, Perry VH, Tracey I, Wessely S, Arseneault L, et al. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7:547–60.
Ceulemans M, Foulon V, Ngo E, Panchaud A, Winterfeld U, Pomar L, et al. Mental health status of pregnant and breastfeeding women during the COVID-19 pandemic - A multinational cross-sectional study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021;100:1219–29.
Wang Z, Liu J, Shuai H, et al. Mapping global prevalence of depression among postpartum women. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:543.
Goodman JH. Postpartum depression beyond the early postpartum period. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2004;33:410–206.
Wang Z, Liu J, Shuai H, Cai Z, Fu X, Liu Y, et al. Mapping global prevalence of depression among postpartum women. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:543.
Halbreich U, Karkun S. Cross-cultural and social diversity of prevalence of postpartum depression and depressive symptoms. J Affect Disord. 2006;91:97–111.
Hahn-Holbrook J, Cornwell-Hinrichs T, Anaya I. Economic and health predictors of national postpartum depression prevalence: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of 291 studies from 56 countries. Front Psychiatry. 2017;8:248.
O’Hara MW, Swain AM. Rates and risk of postpartum depression—A meta-analysis. Int Rev Psychiatry. 1996;8:37–54.
Murray L, Fiori-Cowley A, Hooper R, Cooper P. The impact of postnatal depression and associated adversity on early mother-infant interactions and later infant outcome. Child Dev. 1996;67:2512–26.
Pacheco F, Sobral M, Guiomar R, de la Torre-Luque A, Caparros-Gonzalez RA. Ganho-Ávila A. Breastfeeding during COVID-19: A narrative review of the psychological impact on mothers.Behav Sci (Basel).2021;11.
Gonçalves-Ferri WA, Pereira-Cellini FM, Coca K, Aragon DC, Nader P, Lyra JC, et al. The impact of coronavirus outbreak on breastfeeding guidelines among brazilian hospitals and maternity services: a cross-sectional study. Int Breastfeed J. 2021;16:30.
Ongeri L, Wanga V, Otieno P, Mbui J, Juma E, Stoep AV, et al. Demographic, psychosocial and clinical factors associated with postpartum depression in kenyan women. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18:318.
Gelaye B, Rondon MB, Araya R, Williams MA. Epidemiology of maternal depression, risk factors, and child outcomes in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3:973–82.
O’Connor DB, Aggleton JP, Chakrabarti B, Cooper CL, Creswell C, Dunsmuir S, et al. Research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond: a call to action for psychological science. Br J Psychol. 2020;111:603–29.
Cox JL, Holden JM, Sagovsky R. Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the 10-item Edinburgh postnatal depression scale. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:782–6.
Santos IS, Matijasevich A, Tavares BF, Barros AJ, Botelho IP, Lapolli C, et al. Validation of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale (EPDS) in a sample of mothers from the 2004 Pelotas Birth Cohort Study. Cad Saude Publica. 2007;23:2577–88.
Heh SS. Validation of the chinese version of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale: detecting postnatal depression in taiwanese women. Hu Li Yan Jiu. 2001;9:105–13.
Pitanupong J, Liabsuetrakul T, Vittayanont A. Validation of the Thai Edinburgh postnatal depression scale for screening postpartum depression. Psychiatry Res. 2007;149:253–9.
Kim JI. A Validation Study on the Translated Korean Version of the Edinbergh Postnatal Depression Scale. 2013;12:204–9.
Coronavirus disease. (COVID-10): Breastfeeding.
Webster J, Linnane JW, Dibley LM, Hinson JK, Starrenburg SE, Roberts JA. Measuring social support in pregnancy: can it be simple and meaningful? Birth. 2000;27:97–101.
Wu Y, Zhang C, Liu H, Duan C, Li C, Fan J, et al. Perinatal depressive and anxiety symptoms of pregnant women during the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:240e1–9.
Galletta MAK, Oliveira AMDSS, Albertini JGL, Benute GG, Peres SV, Brizot MdL, et al. Postpartum depressive symptoms of brazilian women during the COVID-19 pandemic measured by the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale. J Affect Disord. 2022;296:577–86.
Levis B, Negeri Z, Sun Y, Benedetti A, Thombs BD, DEPRESsion Screening Data (DEPRESSD) EPDS Group. Accuracy of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale (EPDS) for screening to detect major depression among pregnant and postpartum women: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ. 2020;371:m4022.
Tamaki R, Murata M, Okano T. Risk factors for postpartum depression in Japan. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997;51:93–827.
Liu X, Wang S, Wang G. Prevalence and risk factors of postpartum depression in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Nurs. 2022;31(19–20):2665–77.
Fang D, Thomsen MR, Nayga RM. The association between food insecurity and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Public Health. 2021;21:607.
Louie S, Shi Y, Allman-Farinelli M. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on food security in Australia: a scoping review. Nutr Diet. 2022;79:28–47.
Ramsey R, Giskes K, Turrell G, Gallegos D. Food insecurity among adults residing in disadvantaged urban areas: potential health and dietary consequences. Public Health Nutr. 2012;15:227–37.
Zickgraf HF, Hazzard VM, O’Connor SM. Food insecurity is associated with eating disorders independent of depression and anxiety: findings from the 2020–2021 healthy minds study. Int J Eat Disord. 2022;55:354–61.
Pedroso J, Buccini G, Venancio SI, Pérez-Escamilla R, Gubert MB. Maternal mental health modifies the association of food insecurity and early child development. Matern Child Nutr. 2020;16:e12997.
Shuman CJ, Peahl AF, Pareddy N, Morgan ME, Chiangong J, Veliz PT, et al. Postpartum depression and associated risk factors during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Res Notes. 2022;15:102.
Alimi R, Azmoude E, Moradi M, Zamani M. The association of breastfeeding with a reduced risk of postpartum depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breastfeed Med. 2022;17:290–6.
Snyder K, Worlton G. Social support during COVID-19: perspectives of breastfeeding mothers. Breastfeed Med. 2021;16:39–45.
Siwik E, Larose S, Peres D, Jackson KT, Burke SM, Mantler T. Experiences of at-risk women in accessing breastfeeding social support during the Covid-19 pandemic. J Hum Lact. 2022;8903344221091808:38:422–32.
Baño-Piñero I, Martínez-Roche ME, Canteras-Jordana M, Carrillo-García C, Orenes-Piñero E. Impact of support networks for breastfeeding: a multicentre study. Women Birth. 2018;31:e239–44.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Associate Professor Dr. Seung Chun Paek, Mahidol University, for.
the provision of data analysis support.
Funding
This research project was supported by Mahidol University, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors met the authorship criteria. SAH and YSC initiated and designed this study. SAH, YSC, KPC, LYC, EYL, and ACPS were involved in the data collection. KPC created a preliminary draft. SAH and YSC interpreted the results and revised the manuscript accordingly. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval was obtained from the Ethical Committee of Universidade Federal de São Paulo in Brazil (No. 4.858.900), the Psychiatry Nursing and Midwifery Research Ethics Subcommittee at King’s College London in the UK (HR/DP-20/21-22651, RESCM-20/21-22651), the Institutional Review Board of the National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University in Taiwan (No. YM110060E), the Institutional Review Board of the Institute for Population and Social Research at Mahidol University in Thailand (No. 2021/03–042), and the institutional review board of Catholic Kkottongnae University in South Korea (No. 2-7008080-A-N-01-202103-HR-003). All methods were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Coca, K.P., Chien, LY., Lee, E.Y. et al. Factors associated with postpartum depression symptoms among postpartum women in five countries during the COVID-19 pandemic: an online cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 23, 171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-023-04607-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-023-04607-0