Abstract
Background
Cisplatin-based treatment has been considered the standard treatment regimen of HNSCC. Cetuximab is an emerging target therapy that has potential therapeutic benefits over cisplatin. Nevertheless, curative effects of cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy (CRT) versus cetuximab-based bioradiotherapy (BRT) are still controversial.
Methods
Potentially eligible studies were retrieved using PubMed, Embase and Medline. Basic characteristics of patients and statistical data were collected. A meta-analysis model was established to compare CRT and BRT.
Results
Thirty-one eligible studies and 4212 patients were found. The pooled HRs with 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) for OS and PFS were 0.32 [0.09, 0.55] and 0.51 [0.22, 0.80], respectively, and both were in favor of cisplatin. However, 3-year survival and recurrence analysis of the subgroups showed no differences between the two groups (p > 0.05). In subgroup analysis, oropharyngeal primary tumors exhibited improved results by cetuximab with a pooled HR of 1.56 [1.14, 2.13] for PFS. Additionally, the HPV+ status was a significant factor in positive outcomes with cetuximab with a pooled HR of 1.12 [0.46, 2.17] for OS.
Conclusion
Long-term use of BRT showed no significant difference compared with CRT, and both arms showed different aspects of toxicity. In subgroup analysis, taking the effects of treatment and adverse events into consideration, cetuximab plus radiation may show superior responses regarding OS and PFS in patients who have HPV+ or primary oropharyngeal HNSCC, respectively, but physicians should administer them with caution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) consists of cancers arising from the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx and comprises approximately 5 % of all cancers worldwide. The global incidence is increasing by half a million and causing more than 350,000 deaths every year [1, 2]. A limited number of patients with locally advanced disease are suitable for potentially curative surgery or definitive radiotherapy. Patients who are not candidates for surgery or definitive radiotherapy may receive chemotherapy plus radiation or systemic chemotherapy alone [3].
Cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy is now considered to be the established standard, first-line chemotherapy to treat patients with locally advanced HNSCC [69]. Many large randomized studies and meta-analyses have demonstrated that cisplatin-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy regimens provide significantly higher response rates than radiotherapy alone [4, 5].
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) seems to be critical to cancer cell growth and proliferation, and the function of EGFR in these two settings appears to be different [6, 7]. Head and neck cancer cells exhibit this difference compared to normal cells without exception [8]. In addition, EGFR expression was markedly increased or over-expressed in HNSCC compared to normal tissue, which has been shown to be an independent prognostic factor for poor survival [9]. Thus, EGFR inhibitors have become a burgeoning strategy in anti-tumor treatment. To date, several monoclonal antibodies targeting EGFR have been successfully used in clinical practice with significant effects. Improved loco-regional control and prolonged survival time have already been achieved in lung and gastro-intestinal cancers [10–12].
Cetuximab, an EGFR-targeting monoclonal antibody, is the first targeted therapy to show therapeutic benefit in head and neck cancer [13] and received FDA approval for use in treating HNSCC in 2006 [14, 15]. The Bonner trial showed impressively increased survival outcomes and loco-regional control rates when comparing cetuximab plus radiation versus radiation alone [16]. The Merlano trial exhibited a promising treatment response from adding cetuximab to standard chemotherapy, with limited toxicity [17]. Clinical trials have shown that the addition of cetuximab to traditional treatment regimens (e.g., cisplatin plus radiation) could improve survival outcomes [18, 19]. However, this combination may lead to increased treatment-related toxicity and increased cost, and the administration of multiple drugs may worsen quality of life.
Hence, we conducted a meta-analysis with the aims of gathering outcomes from clinical trials and obtaining a larger sample size to compare the curative effects between the administration of cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy (CRT) or cetuximab-based bioradiotherapy (BRT) with regards to survival results, loco-regional control or distant metastasis (failure), and treatment-related adverse effects in patients with HNSCC.
Methods
Search strategy
PubMed, Embase and Medline were searched on Mar 13, 2016. The following keywords were used to retrieve articles and abstracts: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), cancers of larynx, cancers of oral tongue, cancers of oropharynx, cancers of laryngopharynx, cetuximab, cisplatin and radiotherapy.
Study selection and inclusion/exclusion criteria
Titles and abstracts were reviewed in all of the searched studies, and full texts were reviewed in potentially eligible studies according to our inclusion criteria. To avoid duplicated data, when more than one trial was completed with crossed data in a single center, only the largest most updated trials were included.
In our meta-analysis, we used the following inclusion criteria: (1) studies containing patients with locally advanced HNSCC, including the following: cancers of the larynx, cancers of the oral tongue, cancers of the oropharynx, or cancers of the laryngopharynx; (2) studies comparing the administration of cisplatin-based chemotherapy versus cetuximab-based biotherapy; and (3) studies with available data regarding survival outcomes of patients included in the clinical trials. On the other hand, studies were excluded based on the following criteria: (1) articles that consisted of in vitro studies or were review articles; (2) studies with duplicated data, meaning that one analysis that had several articles reporting updated outcomes; and (3) studies containing metastatic and/or recurrent disease.
Data extraction
The following two investigators reviewed all of the articles independently: Huang JW and Shi CL. Any discrepancy was discussed until reaching a consensus. The data were independently extracted from eligible studies by two investigators (Huang JW and Shi CL), and then, the obtained data were integrated. The primary data consisted of HRs with a 95 % confidence interval (CI) or event/total patient numbers regarding survival outcomes, including OS and/or PFS and the recurrence rates, such as loco-regional and/or distant recurrence of disease in patients from cetuximab cohorts and cisplatin cohorts.
The additional data obtained from the studies included the first author, publication year, patient source (region), median age, percentage of each sex, TNM stage at diagnosis, treatment regimens, tumor site (%), survival outcomes, recurrence rates, type of study, toxicity N (G3 ~ 4) in CRT vs. BRT groups, and attitude of the original studies. The statistical data for acquiring logHR and SE were also obtained, including HR with a 95 % CI, Kaplan–Meier survival curves with p values, and response rates of the over-expression cohort compared to the normal/lower expression cohort [20].
Statistical methods
logHR and SE were required in our analysis. Some of the original papers provided logHR and SE directly, whereas other studies did not. As mentioned above, we utilized other data to calculate these values using methods developed by Parmar et al. (1998) [21], Williamson et al. (2002) [22], and Tierney et al. (2007) [23]. The logHRs and SEs were calculated with the methods described earlier when 1) there was a HR with 95 % CI or 2) there was a p value for the log-rank test with the Kaplan–Meier survival curve.
Hazard ratio (HR) was used as the measure index to describe the survival outcomes and disease control rates between the BRT arm and CRT arm (we considered the cisplatin regimen as the standard regimen). As a result of the analysis of survival in patients, a significant outcome was defined by a p value < 0.05, while a p value > 0.05 indicated no significant difference between the two comparison arms. Pooled HRs > 1 combined with p < 0.05 indicate a narrow difference between the two groups, and the cetuximab arm showed higher event incidences. In contrast, pooled HRs < 1 indicated a lower incidence of events in the cetuximab cohort. Furthermore, pooled HRs > 2 or <0.5 denote a significant result. We use the term “positive” to indicate a better outcome related to cetuximab treatment and “negative” to indicate an absence of correlation between the two comparison arms or better outcomes in the cisplatin arm.
In terms of heterogeneity, values of p < 0.10 or I2 > 50 % represent heterogeneity existing in the pooled HRs (Higgins et al., 2003) [24]. When homogeneity was minimal (p ≥ 0.10, I2 ≤ 50 %), a fixed-effects model was applied for secondary analysis; otherwise, a random-effects model was used. All of the earlier calculations and publication bias were measured using the Begg’s funnel plot, which was performed by STATA 11.0 (STATA Corporation, College Station, TX). This calculation for the current meta-analysis was performed using REVIEW MANAGER (version 5.0 for Windows; the Cochrane collaboration, Oxford, UK).
The sensitive analysis, which aims to test for the heterogeneity of all of the included studies and to determine if heterogeneity arose from any single study, was performed by STATA 11.0 (STATA Corporation, College Station, TX). In the analytic figure, an absence of heterogeneity is indicated by the containment of the studies within the constricted interval (defined between lower CI limit and Upper CI limit), while the existence of a single study far outside the confidence interval indicates that the heterogeneity is due to that individual study.
Results
Eligible studies
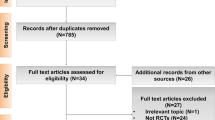
We initially obtained 794 studies from PubMed, Embase and Medline. After reviewing these abstracts, 73 potentially relevant studies were identified as candidates for a full-text review. We excluded 42 studies for the following reasons: twenty-one were clinical trials focused on CRT vs. CRT plus cetuximab, four were reviews, three were posters without follow-up statistics on the studies, and seven were in vitro studies (Fig. 1).
Finally, we enrolled 31 eligible articles containing survival outcomes [25–50]. These eligible studies were published from 2008 to 2016 and included a total of 4212 patients, ranging from 24 to 421 patients per study (median, 126). The basic clinical characteristics of patients and other useful information are shown in Table 1.
Comparison between cisplatin-based and cetuximab regarding overall survival
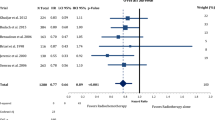
Twenty-three settings of accommodated data showed patients’ overall survival (OS). In these trials, patients were scheduled to receive cisplatin-based chemotherapy plus radiation or cetuximab single agent plus radiation. The pooled HRs to compare OS between the two groups showed better outcomes with cisplatin-based therapy and the mathematic value is 0.32 [0.09, 0.55], p = 0.006 (Table 2; Fig. 2).
Subgroup analysis
As survival outcomes were largely influenced by time of observation, we categorized OS outcomes by year of estimation: 2-years, 3-years, or 5-years and beyond. The pooled HR for 2-year estimation was 0.44 [0.13, 0.76], p = 0.006, which supports better survival achieved with cisplatin-based therapy, while the 3-year or 5-year and beyond time assessments showed no significant difference between the two groups, with pooled HRs of 0.21 [-0.14, 0.55], p = 0.241and 0.95 [0.51, 1.74], p = 0.86, respectively (Table 2; Fig. 2).
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection state might contribute to pathogenesis of HNSCC, and it has previously been demonstrated that HPV positive (HPV+) cases showed better prognosis and prolonged survival in the cetuximab single agent group. The pooled HR is 1.12 [0.46, 2.17], p = 0.015 (Table 2; Fig. 3).
The oropharynx was shown to be distinct in prognosis and therapy response compared with HNSCC in other locations. On this account, we analyzed this group separately, and the results showed that patients with primary tumors in the oropharynx exhibited similar values of OS with a pooled HR of 0.13 [-0.03, 0.89], p = 0.743 (Table 2; Fig. 4).
Comparison between cisplatin-based and cetuximab therapies regarding progression-free survival
Twenty-one studies published data including progression free survival (PFS). The PFS results displayed a similar tendency as the OS and the mathematic value for the pooled HR was 0.51 [0.22, 0.80], p = 0.001 (Table 2; Fig. 5).
Subgroup analysis
As assessed in the OS data, we categorized PFS outcomes by time intervals of estimation: 2-years, or 3-years and beyond. The pooled HRs were 0.56 [0.20, 0.92], p = 0.002, and 0.45 [-0.05, 0.95], p = 0.076 for the 2-year and 3-years and beyond time assessments, respectively, which indicate that better survival was achieved with cisplatin-based therapy (Table 2; Fig. 5).
For the HPV+ group, cetuximab-based therapy again showed outcomes superior to those of cisplatin-based therapy, and the pooled HR was 0.80 [0.38, 1.67], p = 0.55 (Table 2; Fig. 3).
We also analyzed PFS separately in patients with oropharynx tumors, and those patients who received cetuximab-based regimens showed prolonged PFS compared with administration of cisplatin-based therapy; the pooled HR was 1.56 [1.14, 2.13], p = 0.006 (Table 2; Fig. 4).
Comparison between cisplatin-based and cetuximab therapies regarding loco-regional containment
Nineteen studies reported loco-regional control or loco-regional failure in patients with HNSCC. The pooled HR to compare OS between the two groups showed better outcomes with cisplatin-based therapy, and the mathematic value was 0.49 [0.14, 0.85], p = 0.007 (Table 2; Fig. 6).
Subgroup analysis
Loco-regional control, like other recurrence rates and survival outcomes, directly correlated to the estimated time interval, and thus, we categorized the loco-regional control rates by the year of estimation: 2-years, 3-years, or 5-years and beyond. The pooled HR for the 2-year estimation was 0.63 [0.09, 1.17], p = 0.023, which supports better survival achieved with cisplatin-based therapy, while the 3-years or 5-years and beyond time assessments showed no significant difference between the two groups, and the pooled HRs were 0.34 [-0.12, 0.79], p = 0.15 and 2.67 [0.47, 8.73], p = 0.27, respectively (Table 2; Fig. 6).
Patients with HPV+ infection states showed a non-significantly better prognosis and prolonged survival in the cetuximab single agent group, and the pooled HR was 0.06 [-0.40, 0.52], p = 0.808 (Table 2; Fig. 3).
Analysis of patients with primary tumors in the oropharynx showed no significant difference between the cisplatin and cetuximab groups with a pooled HR of -0.05 [-1.34, 0.35], p = 0.248 (Table 2; Fig. 4).
Comparison between cisplatin-based and cetuximab therapies regarding distant metastasis
Five studies reported incidences of distant metastases. The pooled HR was 0.25 [0-0.06, 0.56], p = 0.118, indicating no significant difference between cisplatin and cetuximab administration (Table 2; Fig. 7).
Assessment of adverse events
Twenty-one types of acute toxicity or late toxicity in patients treated with cisplatin plus radiotherapy or cetuximab plus radiotherapy were assessed. The pooled HRs of all toxicities, including acute and late toxicities, showed no difference for patients who received cisplatin-based or cetuximab-based therapy, and the mathematic value was -0.34 [-0.72, 0.04], p = 0.079 (Fig. 8).
Subgroup analysis
We estimated individual toxicities separately, which is shown in Fig. 9. We found that incidence of toxicities, such as leukopenia (p = 0.00), acute kidney injury (p = 0.002), and neutropenia (p = 0.002), were significantly higher in the cisplatin plus radiotherapy regimen, while some dermatitis-related toxicities, such as acneiform rash (p = 0.002), displayed a higher incidence in the cetuximab plus radiotherapy regimen. Other toxicities showed no statistical significance between the two groups (Table 3; Fig. 9).
Results from sensitive tests
As shown in Fig. 10, all of the scattered points were restricted within the interval of the lower CI and upper CI limitations, which indicated that the heterogeneity was acceptable and constrained (Fig. 10).
Assessment of publication bias
On the basis of Begg’s funnel plot, the p value was greater than 0.10, which indicates that the publication bias was acceptable in the analysis. According to Begg’s funnel plot analysis, the publication bias arising in the OS cohort (p = 0.758), the PFS cohort (p = 0.90), the loco-regional control cohort (p = 0.83) or the distant metastasis cohort (p = 0.854) was acceptable (Fig. 11).
Discussion
In this systemic review, we conducted a meta-analysis to compare the effect of cisplatin-based chemotherapy plus radiotherapy versus cetuximab plus radiotherapy in controlling the overall survival, progression-free survival, loco-regional recurrence and distant metastasis of locally advanced HNSCC. Meanwhile, different time periods of estimation, primary tumor sites in the oropharynx and HPV infection status were also taken into consideration. Our study demonstrated that in all settings of the estimated OS time duration, the outcomes were found to be better with cisplatin treatment; however, specifically observing the longer follow-up time intervals, patients between the two groups shared similar overall survival rates, as there was no statistical significance between the two groups with a follow-up time duration equal to or longer than 3 years. Progression-free survival and loco-regional control rates displayed similar tendencies as the OS rates. In subgroup analysis, tumors with a primary site in the oropharynx and tumors with HPV+ infection status showed non significantly better PFS and OS, respectively, with cetuximab single agent treatment plus radiotherapy, while no remarkable difference was observed between the remaining survival outcomes and loco-regional control in the two subgroups, indicating that equivalent effects of the two treatment regimens were achieved in these categories.
Concurrent cisplatin-based therapy has been regarded as the standard treatment regimen for patients with HNSCC [51]; however, cisplatin has been reported to cause immediate treatment-related adverse events and delayed toxicity. Cetuximab, an emerging monoclonal antibody therapeutic, targeting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), seemed promising to provide patients with an effective alternative treatment [52]. Whether cetuximab could replace cisplatin in definitive chemoradiotherapy for HNSCC remains controversial because cetuximab has a reasonably good toxicity profile [53] but the tumor control effect and survival benefit present inconsistent results.
Therefore, to achieve better quality of life and avoid these aggressive treatment regimens, concurrent cetuximab plus radiation versus cisplatin plus radiation therapies have been compared. A recent meta-analysis including 15 studies comparing CCRT and concurrent cetuximab with radiotherapy, with various estimation time intervals, suggested that cisplatin usage improved OS and PFS [54], consistent with our results. Nevertheless, it seems that these drug responses and effects will benefit patients in certain circumstances. In our analysis, we showed that patients from selected subgroups of HNSCC might benefit from concurrent cetuximab plus radiotherapy.
In our analysis, we found that both the oropharyngeal primary tumor and HPV+ subgroups showed differences regarding survival outcomes, possibly supporting the utility of cetuximab to a large extent.
We focused on HPV+ patients, as the biological behavior of these tumors showed particularity. HPV is now considered to be an independent and important risk factor in HNSCC [55, 56]. Recently, Dayyani et al. published a meta-analysis, which showed that HPV infection has a critical impact on survival and response to therapy, and they also demonstrated that HPV+ status was not rare (HPV+ 22 %, with 86.7 % exhibiting HPV16+ genotype) [57]. However, some negative outcomes also exist, and no significant difference was shown between cisplatin and cetuximab with radiation in LAHNC [58]. One major obstacle in this work was the lack of information regarding the HPV/p16 status; thus, we suggest that patients should undergo HPV testing for this unique and separate biologic entity. In our analysis, patients in the HPV+ group achieved better OS due to the highly selective and biologic characteristics, which made the HPV+ group more suitable for the concurrent BRT treatment regimen than the whole HNSCC group.
We also observed unique responses in patients who had primary lesions in the oropharynx. One comprehensive study estimated chemotherapy effects via tumor sites, and the results showed increased benefits only for oropharyngeal and laryngeal tumors [59, 60]. There are well-established patient risk factors associated with HPV infection in oropharyngeal cancer, and a higher incidence of HPV infection was found in cancers of the oropharynx [61, 62]. In our analysis, better PFS was observed in the oropharyngeal group rather than all cases of HNSCC, which could support the administration of cetuximab as a single agent plus radiation in this specific subgroup.
Adverse effects are important additional parameters to be taken into consideration when comparing treatment regimens. In our analysis, we found that there were no significant differences between the two groups for all toxicity data. The cisplatin regimen resulted in adverse events, including high-grade neutropenia, leukopenia and acute kidney injury, while adverse events due to BRT included grade 3-4 acne-like rash and oral mucositis. We found that the incidence of adverse events was elevated in advanced cases. One recent study published by Lawrence D. Koutcher et al, showed serious grade radiation dermatitis with spontaneous bleeding in patients undergoing the BRT regimen [63], which could further decrease quality of life [64] and have a negative impact on cosmetic outcomes [65]. As the total incidence of adverse events did not show significance between cisplatin and cetuximab and the two regimens cause different adverse events in different aspects, doctors need to take toxicity into consideration and choose regimens according to each patient’s condition.
To further confirm the quantity of evidence of the analyzed the data, heterogeneity and sensitive analysis were examined, and no obvious heterogeneity was detected; as shown in every group estimation, I2 was <50 %, with no exception. In addition, the further sensitive analysis assessed heterogeneity in detail and revealed only limited heterogeneity. In addition, as this is a meta-analysis, some limitations still exist. Primarily, only published data from prospective or retrospective studies were included in our meta-analysis, without individual data. Therefore, we could only use these integrated data, which may lead to patient selection bias as patient selection and reporting processes could not be controlled by us. In addition, we combined both retrospective and randomized trials in our meta-analysis, which could also contribute to the bias of this meta-analysis as the inclusion criteria of these two types of studies may not be the same and result in mixed data bias. Additionally, in pooled-data calculation processes, we chose multivariate data, if they were available. Otherwise, our calculated data consisted of univariate data without adjusting for some other influencing factors, such as age, sex, and histologic grade. This would represent a source of bias because multivariate studies examine the prognostic value independently, while univariate studies consider single factor.
Conclusion
In spite of all of the limitations and biases of our meta-analysis, we conclude that long-term use of cetuximab plus radiation showed no significant difference compared with cisplatin plus radiation for all of the survival and toxicity data examined. In subgroup analysis, cetuximab plus radiation may show superior responses regarding OS and PFS in patients who have HPV+ or primary oropharyngeal HNSCC, respectively, but physicians should administer them with caution.
This analysis is a combination of current data. Previously, it was thought that cetuximab could cause fewer side effects and may be preferable to cisplatin, as they showed similar survival outcomes. However, we showed that the two regimens caused toxicity without significant differences, while cisplatin treatments exhibited better survival outcomes. Thus, with all of the limitations, we recommend further RCTs to determine the utility of cetuximab in HNSCC, especially in the oropharyngeal and/or HPV+ specific subgroups.
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74–108.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Bar-Ad V, Palmer J, Yang H, Cognetti D, Curry J. Current management of locally advanced head and neck cancer: the combination of chemotherapy with locoregional treatments. Semin Oncol. 2014;41(6):798–806.
Pignon JP, le Maitre A, Maillard E, et al. MACH-NC Collaborative Group: meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): An update on 93 randomized trials and 17,346 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:4–14.
Cooper JS, PAJAK TF, Forestiere AA, et al. Postoperative irradiation with or without concomitant chemotherapy for high-risk squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1937–44.
Rubin GJ, Chakraborty A, Melhem MF, Zeng Q, Tweardy DJ. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression and function decreases proliferation of head and neck squamous carcinoma but not normal mucosal epithelial cells. Oncogene. 1997;15(4):409–16.
Kalyankrishna S, Grandis JR. Epidermal growth factor receptor biology in head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(17):2666–72.
Ozanne B, Richards CS, Hendler F, Burns D, Gusterson B. Over-expression of the EGF receptor is a hallmark of squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 1986;149(1):9–14.
Ma X, Huang J, Wu X, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor could play a prognostic role to predict the outcome of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Cancer Biomark. 2014;14(4):267–77.
Keedy VL, Temin S, Somerfield MR, et al. American society of clinical oncology provisional clinical opinion: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Mutation testing for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer considering first-line EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):2121–7.
Sequist LV, von PJ, Garmey EG, et al. Randomized phase II study of erlotinib plus tivantinib versus erlotinib plus placebo in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(24):3307–15.
Shah MA, Jhawer M, Ilson DH, et al. Phase II study of modified docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil with bevacizumab in patients with metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(7):868–74.
Mehra R, Cohen RB, Burtness BA.The role of cetuximab for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2008;6(10):742–50
Kono SA, Haigentz Jr M, Yom SS, Saba N. EGFR Monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a view beyond cetuximab. Chemother Res Pract. 2012;2012:901320.
Cohen MH, Chen H, Shord S, et al. Approval summary: Cetuximab in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin and 5-fluorouracil for the first-line treatment of patients with recurrent locoregional or metastatic squamous cell head and neck cancer. Oncologist. 2013;18(4):460–6.
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(1):21–8.
Merlano M, Russi E, Benasso M, Corvò R, Colantonio I, et al. Cisplatin-based chemoradiation plus cetuximab in locally advanced head and neck cancer: a phase II clinical study. Ann Oncol. 2007;22(3):712–7.
Ang KK, Zhang Q, Rosenthal DI, et al. Randomized phase III trial of concurrent accelerated radiation plus cisplatin with or without cetuximab for stage III to IV head and neck carcinoma: RTOG 0522. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(27):2940–50.
Burtness B, Goldwasser MA, Flood W, Mattar B, Forastiere AA. Phase III randomized trial of cisplatin plus placebo compared with cisplatin plus cetuximab in metastatic/recurrent head and neck cancer: an Eastern cooperative oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(34):8646–54.
JPT Higgins SG. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Library. 2005
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998;17(24):2815–34.
Williamson PR, Smith CT, Hutton JL, Marson AG. Aggregate data meta-analysis with time-to-event outcomes. Stat Med. 2002;21(22):3337–51.
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 2007;8:16.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
Walsh L, et al. Toxicity of cetuximab versus cisplatin concurrent with radiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell cancer (LAHNSCC). Radiother Oncol. 2011;98(1):38–41.
Caudell JJ, Sawrie SM, Spencer SA, et al. Locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer treated with primary radiotherapy: a comparison of the addition of cetuximab or chemotherapy and the impact of protocol treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71(3):676–81.
L. D. Koutcher ES, D. Carlson NK, M. Fury SW, Z. Zhang QM, D. Pfister. Cisplatin (CDDP) and Radiation (RT) versus Cetuximab (C) and RT in the Context ofHuman Papillomavirus (HPV) and P16 in the Treatment of Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer (LAHNC). 2012. Annual ASTRO Meeting.
Jensen AD, Krauss J, Weichert W, et al. Disease control and functional outcome in three modern combined organ preserving regimens for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN). Radiat Oncol. 2011;6:122.
Koutcher L, Sherman E, Fury M, et al. Concurrent cisplatin and radiation versus cetuximab and radiation for locally advanced head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(4):915–22.
Beijer YJ, Koopman M, Terhaard CH, Braunius WW, van Es RJ, de Graeff A. Outcome and toxicity of radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy or cetuximab for head and neck cancer: our experience in one hundred and twenty-five patients. Clin Otolaryngol. 2013;38(1):69–74.
Ley J, Mehan P, Wildes TM, et al. Cisplatin versus cetuximab given concurrently with definitive radiation therapy for locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology. 2013;85(5):290–6.
Ye AY, Hay JH, Laskin JJ, Wu JS, Ho CC. Toxicity and outcomes in combined modality treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: cisplatin versus cetuximab. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9(4):607–12.
Pajares B, Trigo JM, Toledo MD, et al. Differential outcome of concurrent radiotherapy plus epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors versus radiotherapy plus cisplatin in patients with human papillomavirus-related head and neck cancer. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:26.
Lefebvre JL, Pointreau Y, Rolland F, et al. Induction chemotherapy followed by either chemoradiotherapy or bioradiotherapy for larynx preservation: the TREMPLIN randomized phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(7):853–9.
M. Ghi AP, R. Orecchia SP, F. Bertoni NM. A Phase 2-3 Study Comparing Concomitant Chemoradiation Therapy (CRT) Versus Cetuximab/RT (CET/RT) With or Without Induction Docetaxel/Cisplatin/5-Fluorouracil (TPF) in Locally-Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (LASCCHN) e Efficacy Results of the GSTTC Italian Study (NCT01086826). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 [eAbstract] .
N. Riaz AB, D. Adkins SR, J. Huang PC, J. Ley DK, W. Thorstad NL. Multi-institution Analysis of Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy With Cisplatin (CDDP) Versus Cetuximab (C225) in Locally-Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (LA-HNSCC): Can HPV Help Decide Which Agent. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008 [eAbstract].
Hu MH, Wang LW, Lu HJ, et al. Cisplatin-based chemotherapy versus cetuximab in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:904341.
Levy A, Blanchard P, Bellefqih S, et al. Concurrent use of cisplatin or cetuximab with definitive radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Strahlenther Onkol. 2014;190(9):823–31.
Tang C, Chan C, Jiang W, et al. Concurrent cetuximab versus platinum-based chemoradiation for the definitive treatment of locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 2015;37(3):386–92.
Fayette J, Bonnin N, Ferlay C, et al. Neoadjuvant TPF in locally advanced head and neck cancer can be followed by radiotherapy combined with cisplatin or cetuximab: a study of 157 patients. Anticancer Drugs. 2013;24(6):623–9.
Huang J, Baschnagel AM, Chen P, et al. A matched-pair comparison of intensity-modulated radiation therapy with cetuximab versus intensity-modulated radiation therapy with platinum-based chemotherapy for locally advanced head neck cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014;19(2):240–6.
Shapiro LQ, Sherman EJ, Riaz N, et al. Efficacy of concurrent cetuximab vs. 5-fluorouracil/carboplatin or high-dose cisplatin with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for locally-advanced head and neck cancer (LAHNSCC). Oral Oncol. 2014;50(10):947–55.
Kanakamedala MR SPG, Abraham RS AAA, Vijayakumar S aRDH. Comparison of Cisplatin Versus Cetuximab With Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy in Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinomas of Head and Neck: Toxicity, Patterns of Failure, and Survival Analysis. Radiat Oncol. 2014;90(15). Annual ASTRO Meeting.
N. Riaz AB, D. Adkins SR, J. Huang PC, J. Ley DK, W. Thorstad NL. Multi-institution Analysis of Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy With Cisplatin (CDDP) Versus Cetuximab (C225) in Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (LAHNSCC): Can HPV Help Decide Which Agent. Int J Radiat Oncol Supplement 2014 [eAbstract].
Peddi P, Shi R, Nair B, Ampil F, Mills GM, Jafri SH. Cisplatin, cetuximab, and radiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell cancer: a retrospective review. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2015;9:1–7.
S. L. Galper HD, Decker MGRaRH. Cetuximab versus cisplatin concurrent with IMRT in locally advanced head and neck cancer (LAHNC). J Clin Oncol ASCO Annual Meeting. 2009. 27(e17030).
Delphine Borchiellini CD, Jocelyn Gal BL, Marc Alfonsi KB, Christian Righini BG, Beltran M. Induction TPF followed by chemoradiation or radiotherapy-cetuximab in nonresectable advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study in 164 patients . Int J Radiat Oncol. 2012;30(e16044).
Strom TJ, et al. Comparison of every 3 week cisplatin or weekly cetuximab with concurrent radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2015;51(7):704–8.
Riaz N, et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with cisplatin versus cetuximab for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Am J Clin Oncol. 2016;39(1):27–31.
Magrini SM, et al. Cetuximab and radiotherapy versus cisplatin and radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer: a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(5):427–35.
Network NCC. NCCN head and neck cancers guidelines (Version 1, 2016). America: NCCN; 2016.
Robert F, Ezekiel MP, Spencer SA, Meredith RF, et al. Phase I study of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab in combination with radiationtherapy in patients with advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(13):3234–43.
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(6):567–78.
Petrelli F, Coinu A, Riboldi V, et al. Concomitant platinum-based chemotherapy or cetuximab with radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies. Oral Oncol. 2014;50(11):1041–8.
Fakhry C, Westra WH, Li S, et al. Improved survival of patients with human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in a prospective clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100(4):261–9.
Gillison ML, Harris J, Westra W, et al. Survival outcomes bytumor human papillomavirus (HPV) in stage III-IV oropharyngeal cancer (OPC) in RTOG 0129 [Abstract]. Proc Am SocClinOncol 2009;27(Suppl.):15 s .
Dayyani F, Etzel CJ, Liu M, Ho CH, Lippman SM, Tsao AS. Meta-analysis of the impact of human papillomavirus (HPV) on cancer risk and overall survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC). Head Neck Oncol. 2010;2:15.
Riaz N, Sherman E, Koutcher L, et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with cisplatin versus cetuximab for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014.
Blanchard P, Baujat B, Holostenco V, et al. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): a comprehensive analysis by tumour site. Radiother Oncol. 2011;100(1):33–40.
Lill C, Kornek G, Bachtiary B, Selzer E, et al. Survival of patients with HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer after radiochemotherapy is significantly enhanced.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2011;123(7–8):215–21.
Kreimer AR, Clifford GM, Boyle P, Franceschi S. Human papillomavirus types in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas worldwide: a systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14(2):467–75.
Termine N, Panzarella V, Falaschini S, et al. HPV in oral squamous cell carcinoma vs head and neck squamous cell carcinoma biopsies: a meta-analysis (1988-2007). Ann Oncol. 2008;19(10):1681–90.
Koutcher LD, Wolden S, Lee N. Severe radiation dermatitis in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer treated with concurrent radiation and cetuximab. Am J Clin Oncol. 2009;32(5):472–6.
Elliott EA, et al. Phase III Trial of an emulsion containing trolamine for the prevention of radiation dermatitis in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Trial 99-13. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(13):2092–7.
Dorr W, Hendry JH. Consequential late effects in normal tissues. Radiother Oncol. 2001;61(3):223–31.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the study participants in each of the individual studies for their involvement.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Beijing, China (Grant No. 81101991) and Research Award Fund for New Young Teachers in Higher Education Institutions, China (Grant No. 20120181120024). The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the article.
Availability of data and materials
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Authors’ contribution
This study was designed by LL and WYQ, and the manuscript was written by HJW. Data were collected by HJW and SCL. Statistical process was done by SCL and ZJ. Figures and tables were made by HJW and SCL. All authors have read and approved the manuscript, and ensure that this is the case.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Zhang, J., Shi, C. et al. Survival, recurrence and toxicity of HNSCC in comparison of a radiotherapy combination with cisplatin versus cetuximab: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 16, 689 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2706-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2706-2