Abstract
Background
Common carotid artery (CCA) occlusion (CCAO) is a rare condition. Owing to collateral circulation, ipsilateral internal carotid artery (ICA) and external carotid artery (ECA) are often patent.
Methods
This study included 16 patients with unilateral CCAO and patent ipsilateral ICA and ECA. The pathways which supplied ICA were investigated by digital subtraction angiography (DSA), transcranial Doppler (TCD), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA).
Results
In all 16 patients, TCD found antegrade blood flow in ipsilateral ICA, which was supplied by retrograde blood flow in ipsilateral ECA through carotid bifurcation. We call this phenomenon “ICA steal”. DSA and CTA discovered four pathways of ICA steal, including 1) ipsilateral vertebral artery – occipital artery – ECA – ICA, 2) ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk or costocervical trunk – ascending cervical artery or deep cervical artery – occipital artery – ECA – ICA, 3) contralateral ECA – contralateral superior thyroid artery – ipsilateral superior thyroid artery – ipsilateral ECA – ICA, and 4) ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk – inferior thyroid artery – superior thyroid artery – ECA – ICA.
Conclusions
ICA is possible to be patent and supplied by several collateral circulation pathways after CCAO.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
One of the risks of ischemic stroke is pathological changes of extracranial carotid circulation. Atherosclerotic occlusion of internal carotid artery (ICA) has been intensively studied for its clinical and imaging characteristics. However, common carotid artery (CCA) occlusion (CCAO) is rarely studied due to its low incidence [1, 2]. CCAO occurs in about 3% of symptomatic patients undergoing angiography [3]. Consensus has not been reached as for the indications, necessities and clinical benefits of invasive treatment of CCAO.
According to Riles et al’s classification, CCAO has four types: type 1A with patent ICA and external carotid artery (ECA), type 1B with occluded ICA and patent ECA, type 1C with patent ICA and occluded ECA, and type 2 with occluded ICA and ECA [4]. According to C. Klonaris et al’s review, most CCAO (61.5%) is type 1A, while type 1B and type 2 account for 26.6 and 11.9%, respectively. Type 1C account for none and may be just theoretical [5].
Since ipsilateral ICA and ECA are often patent after CCAO, there must be collateral circulation to supply them. This collateral circulation may relieve the ischemia of brain and symptoms of patients, thus affecting whether and how CCAO should be treated. So, it is important to discover the pathways of this collateral circulation and to evaluate their compensating abilities. This information, however, is available in few studies [6,7,8].
Our study was aimed to discover the collateral circulation pathways which could supply ICA after CCAO, and to investigate their hemodynamic and imaging characteristics.
Methods
We retrospectively examined the medical database of patients who had been admitted to the Department of Neurology or Neurointervention of the PLA Rocket Force General Hospital from January 2013 to December 2015. From the database we found 16 patients with unilateral CCAO but patent ipsilateral ICA and ECA (Riles type 1A). Among them, 9 were male and 7 were female. They were aged between 65 and 83 years old.
We summarized their examination results and images. Transcranial Doppler (TCD) detected the blood flow in CCA, ICA and ECA on both sides. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA), computed tomography angiography (CTA) and Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) offered dynamic and static images of intracranial and extracranial arteries and collateral circulation. All 16 patients had TCD examination. DSA, MRA and CTA were performed in 15, 5 and 7 patients, respectively (Table 1).
Results
TCD
No blood flow was detected in the occluded CCA (Fig. 1a), while the healthy CCA had normal blood flow (Fig. 1b). For all 16 patients, retrograde blood flow was detected in the ipsilateral ECA, the spectrum of which was similar to intracranial arteries (Fig. 1c). The contralateral ECA had normal blood flow (Fig. 1d). The ipsilateral ICA had lower but antegrade blood flow (Fig. 1e), while the contralateral ICA had normal blood flow (Fig. 1f). Eight patients had compensatory increased flow velocity in the V3 segment of ipsilateral vertebral artery (systolic velocity 120~150 cm/s, average velocity 80~100 cm/s). These patients also had reversed and increased flow velocity in the affected occipital artery.
TCD showed the blood flow in CCA, ECA and ICA on both sides of the 16 patients. a No blood flow in the occluded CCA. b Normal blood flow in the healthy CCA. c Retrograde blood flow in the ipsilateral ECA. d Normal blood flow in the contralateral ECA. e Lower but antegrade blood flow in the ipsilateral ICA. f Normal blood flow in the contralateral ICA
DSA
DSA was performed in 15 of the 16 cases. They all had retrograde blood flow in ipsilateral ECA and antegrade blood flow in ipsilateral ICA. DSA discovered three collateral circulation pathways that supplied ipsilateral ICA. Pathway 1: ipsilateral vertebral artery – occipital artery – ECA – ICA (Fig. 2). Pathway 2: ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk or costocervical trunk – ascending cervical artery or deep cervical artery – occipital artery – ECA – ICA (Fig. 3). Pathway 3: contralateral ECA – contralateral superior thyroid artery – ipsilateral superior thyroid artery – ipsilateral ECA – ICA (Fig. 4). These three pathways existed in 8, 4 and 1 patients, respectively. We failed to find any specific pathways in the remaining 2 patients.
DSA discovered a collateral circulation pathway that supplied ipsilateral ICA after CCAO. This was a right (ipsilateral) subclavian artery angiography (lateral position, arterial phase). Right CCA was occluded. The collateral circulation pathway was: right vertebral artery (arrow①) – right occipital artery (arrow②) – right ECA (retrograde, arrow③) – right ICA (arrow④)
DSA discovered another collateral circulation pathway that supplied ipsilateral ICA after CCAO. This was a left (ipsilateral) subclavian artery angiography (front position (a) and lateral position (b), arterial phase). Left CCA was occluded. The original part of left subclavian artery had moderate stenosis. The V1 segment of left vertebral artery had severe stenosis. The V4 segment of left vertebral artery became undeveloped after it gave out the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The collateral circulation pathway was: ascending cervical artery from left thyrocervical trunk (arrow①) and deep cervical artery from left costocervical trunk (arrow②) – occipital artery (retrograde, arrow③) – ECA (retrograde, arrow④) – carotid bifurcation – ICA (arrow⑤)
DSA discovered a third collateral circulation pathway that supplied ipsilateral ICA after CCAO. This was a left (contralateral) CCA angiography (front position, arterial phase (a) and parenchymal phase (b)). Right CCA was occluded. The collateral circulation pathway was: left ECA – left superior thyroid artery – thyroid anastomosis (arrow①) – right superior thyroid artery – right ECA – right ICA (arrow②)
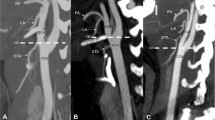
MRA and CTA
MRA (Fig. 5) and CTA (Fig. 6) showed occluded CCA but patent ipsilateral ICA, ECA and carotid bifurcation. Vertebral artery and thyrocervical trunk which participated in collateral circulation could also be shown.
CTA results. CTA showed the occlusion of left CCA. Left ICA, ECA and carotid bifurcation (arrow①(a,b)) were well developed. No abnormality was found in the development of distal arteries. Vertebral artery and thyrocervical trunk (arrow② (a)) which participated in collateral circulation were also developed
In particular, in the one patient who did not had DSA examination, CTA showed coexistence of the pathways 1 and 2 mentioned above, and a fourth pathway: ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk – inferior thyroid artery – superior thyroid artery – ECA – ICA (Fig. 7).
CTA discovered a fourth collateral circulation pathway that supplied ipsilateral ICA after CCAO. CTA showed coexistence of several collateral circulation pathways in one patient. Pathway 1: ipsilateral vertebral artery – occipital artery (arrow ①) – ECA – ICA. Pathway 2a: ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk – ascending cervical artery (arrow②) – occipital artery – ECA – ICA. Pathway 2b: ipsilateral costocervical trunk – deep cervical artery (arrow ③) – occipital artery – ECA – ICA. Pathway 4: ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk – inferior thyroid artery – superior thyroid artery (arrow ④) – ECA – ICA
Discussion
CCAO is a rare condition that may be associated with ischemic cerebral diseases. There is no clear consensus on the role of invasive treatment of CCAO. Owing to collateral circulation, about 61.5% of patients with CCAO have patent ipsilateral ICA and ECA [5]. For patients with ischemic cerebrovascular diseases, collateral circulation evaluation has great clinical significance, such as in explaining clinical manifestations, developing therapeutic schedule, evaluating the efficacy of treatments and estimating prognosis [9,10,11].
The basic driving force that leads to the formation of collateral circulation is the change in blood pressure. When a main artery from aortic arch is occluded, the blood pressure in the distal segment can be much lower than adjacent arteries. As a result, blood flow in adjacent arteries may be drawn reversely to the distal segment. This phenomenon is called “steal”, with subclavian steal syndrome as an example. When CCA is occluded, the blood pressure in ipsilateral ICA can be obviously lower than ipsilateral ECA. As a result, ICA “steals” blood from ECA. This phenomenon was defined as “carotid artery steal” by Anne G. Osborn [12]. However, we think this definition is not clear enough. Since ECA supplies blood and ICA receives blood, we propose a new definition here – “ICA steal”.
Our study discovered four collateral circulation pathways of “ICA steal” by DSA and CTA: 1) ipsilateral vertebral artery – occipital artery – ECA – ICA, 2) ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk or costocervical trunk – ascending cervical artery or deep cervical artery – occipital artery – ECA – ICA, 3) contralateral ECA – contralateral superior thyroid artery – ipsilateral superior thyroid artery – ipsilateral ECA – ICA, and 4) ipsilateral thyrocervical trunk – inferior thyroid artery – superior thyroid artery – ECA – ICA. Pathway 4 was previously reported by Lie TA et al. [6]. This collateral circulation may also involve other branches of ECA theoretically, such as facial artery, maxillary artery and superficial temporal artery; but this has not been reported yet.
The imaging characteristics of ICA steal under CTA and MRA include: 1) disappearance of the original segment of CCA, 2) normal development of ICA, ECA and carotid bifurcation, and 3) development of thyrocervical trunk in some patients. The hemodynamic characteristics of ICA steal under TCD include: 1) no blood signal in the occluded CCA; 2) retrograde blood flow in ipsilateral ECA with similar spectrum to intracranial arteries; 3) lower but antegrade blood flow in ipsilateral ICA. These phenomena indicate the possibility of ICA steal.
Our study has some limitations. We did not quantitatively evaluate the influence of these collateral circulation pathways on brain perfusion. In fact, this is crucial since it may affect whether a patient with CCAO needs further invasive treatment. Further studies are needed to evaluate the brain perfusion of different Riles types and different collateral circulation pathways, and to analyse how compensation affects patients’ neurological symptoms, benefits from invasive treatment, and prognosis.
Conclusion
ICA is possible to be patent and supplied by several collateral circulation pathways after CCAO.
Availability of data and materials
The data and images used in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CCA:
-
Common carotid artery
- CCAO:
-
Common carotid artery occlusion
- CTA:
-
Computed tomography angiography.
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- ECA:
-
External carotid artery
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- TCD:
-
Transcranial Doppler
References
Barnett HJ. Delayed cerebral ischemic episodes distal to occlusion of major cerebral arteries. Neurology. 1978;28(8):769–74.
Barnett HJ, Peerless SJ, Kaufmann JC. “Stump” on internal carotid artery--a source for further cerebral embolic ischemia. Stroke. 1978;9(5):448–56.
Belczak S, Mulatti GC, Abrao SR, da Silva ES, Aun R, Puech-Leao P, de Luccia N. Common carotid artery occlusion: a single-center experience in 40 cases. Int J Angiol. 2016;25(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1547340.
Riles TS, Imparato AM, Posner MP, Eikelboom BC. Common carotid occlusion. Assessment of the distal vessels. Ann Surg. 1984;199(3):363–6.
Klonaris C, Kouvelos GN, Kafeza M, Koutsoumpelis A, Katsargyris A, Tsigris C. Common carotid artery occlusion treatment: revealing a gap in the current guidelines. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2013;46(3):291–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2013.06.006.
Lie TA, Op de Coul AA. Collateral circulation through thyroid arteries after occlusion of the common carotid artery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1977;80(2):83–5.
Bacci D, Valecchi D, Sgambati E, Gulisano M, Conti AA, Molino-Lova R, Macchi C. Compensatory collateral circles in vertebral and carotid artery occlusion. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2008;113(4):265–71.
Terao S, Sobue G, Miura N, Yokoi Y, Mitsuma T. A case of asymptomatic common carotid artery occlusion with the persistent proatlantal intersegmental artery. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1993;33(8):901–4.
Chuang YM, Chan L, Lai YJ, Kuo KH, Chiou YH, Huang LW, Kwok YT, Lai TH, Lee SP, Wu HM, Yeh YC. Configuration of the circle of Willis is associated with less symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage in ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. J Crit Care. 2013;28(2):166–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.08.018.
Omura-Matsuoka E, Yagita Y, Sasaki T, Terasaki Y, Oyama N, Sugiyama Y, Todo K, Sakoda S, Kitagawa K. Hypertension impairs leptomeningeal collateral growth after common carotid artery occlusion: restoration by antihypertensive treatment. J Neurosci Res. 2011;89(1):108–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22522.
Bang OY, Saver JL, Kim SJ, Kim GM, Chung CS, Ovbiagele B, Lee KH, Liebeskind DS. Collateral flow predicts response to endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2011;42(3):693–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.595256.
Osborn AG. Diagnostic cerebral angiography. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: LWW Press; 1998.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW - study design, data acquisition, interpretations of results, manuscript preparation and revisions; CZ - interpretations of results, manuscript preparation and revisions; BH and AH - data acquisition, manuscript revision; XZ and BD - study design, manuscript revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the General Hospital of the PLA Rocket Force (Beijing, 100088, China). Oral informed consent was achieved from each patient through telephone interview.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zheng, C., Hou, B. et al. Four collateral circulation pathways were observed after common carotid artery occlusion. BMC Neurol 19, 201 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1425-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1425-0