Abstract
Nephrolithiasis is not common in children, but the incidence is gradually increased in these years. Urinary tract malformations, urinary infection, dietary habits, geographic region and genetic factor are involved in the etiology of nephrolithiasis. For the affected child, it is especially important to elucidate the etiology, which may provide an accurate diagnosis, a personalized therapy and effective follow-up strategy. Here to seek the etiology of a ten-year-old boy incidentally found with nephrolithiasis, next generation sequencing (NGS) including a panel with 248 genes involved in hereditary kidney diseases was performed for the boy and identified two mutations of KCNJ1, c.89G > A (p.C30Y) and c.65G > T (p.R22M), and the later was a novel missense mutation originated from his father. The child was confirmed with type II Bartter syndrome (BS) caused by KCNJ1 mutations. Our study suggests that BS may be difficult to get diagnosed at an early stage based on clinical manifestations or biochemical laboratory tests, and NGS is an efficient way to determine the etiology and provide further treatment and guide fertility counseling for the affected family.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Nephrolithiasis is not common in children compared to adults, but the incidence of pediatric nephrolithiasis is gradually increased in these years [1]. Urinary tract malformations, urinary infection, dietary habits, geographic region and genetic factor are involved in the etiology of nephrolithiasis [2, 3]. There are at least 30 genes shown to cause monogenic forms of nephrocalcinosis or nephrolithiasis in autosomal-dominant, autosomal-recessive, or X-linked transmission patterns [4]. For the affected child, it is especially important to detect the exact causative mutation of monogenic disease and know the etiology, which may provide an accurate diagnosis, personalized therapy and effective follow-up strategy.
In the present study, we described the clinic features of one 10-year old child who was incidentally found with nephrolithiasis and detected with the genetic mutation, which suggests that NGS is very important and efficient to identify the etiology of nephrolithiasis, which may not be easily diagnosed by manifestation or chemical laboratory tests.
Materials and methods
Enrollment of human subjects
This study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki and has been approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (ID: KS-2018-KY-36). Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient’s guardian for the release of the case report and any accompanying images. Copies with written consent are available for editorial review of this journal.
Next generation sequencing (NGS) and sanger sequencing
Targeted-NGS using inherited kidney disease panel including 248 disease-causing genes was performed by a commercial company (MyGenostics, Inc., Beijing, China). To validate the variants screened by NGS, the related fragments were performed PCR amplification for the proband and his parents, and the primers of the fragments were listed in Table 1. PCR products were bi-directionally sequenced using an ABI 3730XL sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) in the Center of Genetics and Prenatal Diagnosis of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Bioinformatics analysis
The harmful prediction was analyzed according to the scoring conditions using three kinds of software including SIFT, PolyPhen-2 and MutationTaster. The pathogenicity of the mutation site was annotated according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines.
Conservation analysis and molecular modeling of the protein encoded by KCNJ1
To evaluate the evolutionary conservation of the mutated site, the apical potassium inwardly-rectifying channel (ROMK) encoded by KCNJ1 from five animal species from fishes to mammals, including human (Homo sapiens: NP_722451.1), zebrafish (Danio rerio: NP_957329.1), mouse (Mus musculus: NP_062633.1), cattle (Bos taurus: NP_001179136.1), rat (Rattus norvegicus: P35560–2) were analyzed.
The initial mutant variant structures for ROMK (Residues1–372) were constructed using the automated protein-homology modeling server SWISS-MODEL, using the protein structure of an Inward rectifier potassium channel as a structural template (PDB: 3SPG). PROCHECK was employed to estimate the quality of our models. There are 98.6% residues located in the ‘core’ and ‘allowed’ regions, 1.3% in the ‘general’ region and only 0% in the ‘disallowed’ region. In the computational structure, 99.8% of the bond lengths for the main-chain residues and 99% of the bond angles for the main-chain residues are within the allowed limits. The sequence identity was 47.42%. Analysis of the 3-D structure of the proteins was carried out using Pymol.
Results
Clinical examinations
The proband was 10-year old, and the weight was 28 kg (−1standard deviation [SD] for age), with the height 130 cm (− 2 SD). The other general physical examinations of the proband were normal, with a normal blood pressure of 123/65 mmHg. Biochemical laboratory tests showed blood routine, electrolyte, liver function, renal function, urinary routine were normal. The urinary ultrasound showed enhanced echo of bilateral renal collecting system, several echogenic foci with posterior shadow, the largest one on the left kidney 8 mm × 6 mm, on the right side 9 mm × 6 mm (Fig. 1), the blood perfusion was normal, and multiple high echo spots in the prostate with posterior shadow, the largest one 6.4 mm × 4.6 mm. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) showed multiple high density shadows in bilateral renal medulla and left high density nodules of urethra prostate. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the left kidney was 34.07 ml/min shown by SPECT-CT, indicating mild impairment of left renal function (normal range: 40–50 ml/min), and GFR in the right kidney was 51.11 ml/min. Traced back to the previous history of the proband, he was born prematurely at 31 weeks of gestation with low birth weights about 1.7 kg following polyhydramnios. No obvious abnormality was seen until 4 years ago, and he presented intermittent cramps, fatigue and muscle weakness and these symptoms were released after taking oral potassium chloride.
Mutation analysis
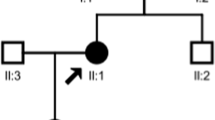
Two heterozygous mutation sites of KCNJ1 gene (NM_153767) were found in the proband by NGS and convinced by PCR and Sanger sequencing, which were originated from his father and mother (Fig. 2). Both mutations were located at exon 4. One site c.89G > A (p.C30Y) was a known pathogenic mutation of KCNJ1 [5]. The other one c.65G > T (p.R22M) was a novel missense mutation, leading to the arginine being substituted by methionine at codon 22. This missense mutation was absent from the HGMD, Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) database (dbSNP), 1000 Genomes Project (TGP) database and ClinVar database. Additionally, to our knowledge, this mutation has not been described in the Universal Mutation Database KCNJ1 database or reported in any published literature. This missense mutation was predicted to be deleterious by SIFT, Polyphen-2 and MutationTaster (Table 1), which might be responsible for this family. Based on the ACMG guidelines, the c.65G > T (p.R22M) variant of KCNJ1 was predicted to be Variant of Uncertain Significance (VUS)(PM2 + PP2 + PP3). Clinical reports indicated that the c.89G > A (p.C30Y) mutation was pathogenic [6].
Functional analysis
An alignment of ROMK revealed that p.R22 and p.C30 are highly conserved among many different species (Fig. 3). Homology modelings of wild-type and mutant KCNJ1 variants are shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. The mutation results in a change from a basic amino acid (Arg) to a neutral amino acid (Met) at residue 22. The predicted model showed that the hydrogen bonds decreased. p.R22M could change the conformation of an arginine/lysine/arginine triad (KRR) and produce steric clashes with spatially adjacent residues, causing structural destabilization. The p.C30Y mutation caused a side-chain change of residue, which may affect protein structure and function.
Homology modeling of wild-type and mutant KCNJ 1 variants. A Modeled structure of the ROMK protein; B Neighboring residues of Arg22 in the wild type of KCNJ1. Arg22 is shown in green; C Neighboring residues of Met22 in mutant KCNJ 1. Met22 is shown in yellow. D Neighboring residues of Cys30 in the wild type of KCNJ1. Cys30 is shown in white; E Neighboring residues of Tyr30 in mutant KCNJ1. Tyr30 is shown in magenta. Predicted H bonds are indicated by yellow dashed lines
Structural model of ROMK1 channel protein and the position of the two variants identified in this study shown in red, the variants of ROMK1 detected in ref. [7]
in green
Discussion
In the present study, the proband, a ten-year old boy primarily incidentally detected with bilateral nephrolithiasis was found with compound heterozygous mutations of KCNJ1 gene by NGS. KCNJ1 gene is one of the five types of genes involved in the etiology of Bartter syndrome type II (BS II) which is a group of rare tubulopathies. Patients with different type of BS present with overlapping clinical phenotypes as polyuria, polydipsia, volume contraction, muscle weakness and growth retardation induced from hypokalaemia, hyperreninism and hyperaldosteronism. According to the onset and severity of BS, it can be grouped into three types: the hypocalciuric-hypomagnesemic variant described by Gitelman et al., the classic syndrome originally described by Bartter et al., and the antenatal hypercalciuric variant associated with severe systemic manifestations classical type [8]. KCNJ1 gene encodes the apical potassium inwardly-rectifying channel (ROMK) in the thick ascending limb of the Henle’s loop (TALH) in the distal nephron to ensure adequate luminal potassium available for the efficient function of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter which is involved in salt reabsorption. Effective chloride reabsorption in the TALH prevents renal salt wasting and is an essential mechanism to maintain tubular concentrating capability. Loss-of-functional mutations in the KCNJ1 gene cause antenatal/neonatal BS II in autosomal recessive pattern [9].
In this study, two mutations of KCNJ1 c.89G > A (p.C30Y) and c.65G > T (p.R22M) were detected in the proband. The distribution of the identified variations in KCNJ1 is shown in Fig. 5. ROMK is responsible for K+ secretion and control of NaCl absorption in the kidney. The channel is gated by intracellular pH in the neutral range and reach half-maximal activation at a pH of 6.8. The gating is driven by the protonation of lysine within KRR [10], which is assembled by amino acid residues at positions 22, 61, and 292 in the transmembrane region [7]. Structural disturbance of KRR shifts the pKa of the lysine residue away from the neutral pH range and leads to channel inactivation. The predicted model of p.R22M revealed that the distance to Arg292 (11.8 Å) and Lys61 (30.3 Å) changed into 13.1 Å, and 31.2 Å, respectively, when the mutation replaced Arg22 with Met22. The p.R22M mutation could disrupt the conformation of KRR and produce steric clashes with spatially adjacent residues, causing structural destabilization. A three-dimensional structural analysis also revealed that Arg22 formed H bonds with Glu299, Ser294, and Val24. When the mutation replaced Arg22 with Met22, these H bonds were destroyed. In summary, the p.R22M mutation was able to influence KRR in two ways, either shifting the pKa of the lysine residue off the neutral pH range or influencing the tertiary geometry to further change the integrity of the structure and function of ROMK. The p.C30Y mutation caused a side-chain change of residue, which may affect protein structure and function. Clinical reports indicated that the p.C30Y mutation was pathogenic. Through the symptoms and genetic test, the proband was confirmed with type II Bartter syndrome (BS-II).
The Phenotype in most of patients with BS II can begin in utero with marked fetal polyuria presenting polyhydramnios from 24 weeks of gestation and premature delivery. During neonatal period, patients may have life-threatening volume depletion caused by severe renal salt wasting or failure to thrive. During childhood, other secondary symptoms including developmental retardation, fever, vomitting, occasional diarrhea may present. All the symptoms resulted from metabolic alkalosis, hyposthenuria, hyperreninaemic, hyperaldosteronism which was stimulated by elevated plasma concentration of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The basic deficiency of antenatal BS is the malfunction of mTAL chloride transport, which involves an interaction among the apical Na-K-2Cl cotransporter (NKCC2), the luminal ATP-sensitive potassium channel ROMK, the basolateral chloride channel (ClC), a basolateral K-CL cotransporter and the Na-K-ATPase. Therefore, any gene encoding or involving in these channels or transporters will result in defective chloride transport. NKCC2, KCNJ1, CLCNKB for chloride channel and BSND gene encoding barttin, a subunit for ClC-Ka and ClC-Kb have been confirmed with antenatal BS [11, 12]. Rare disease shall also be differentiated from Rabson-Medndenhall syndrome caused by INSR [13].
The other equally important feature in antenatal BS is hypercalciuria. Continuous loss of calcium results in nephrocalcinosis, nephrolithiasis and osteopenia [14, 15], usually medullary nephrocalcinosis is seen [16, 17]. Hypercalciuria and associated nephrocalcinosis are present in approximately 85% of infants with this neonatal BS [18]. The prevalence of nephrolithiasis is high, but the prevalence secondary to BS is not known very well, and may be lower than the prevalence of nephrocalcinosis. Both nephrocalcinosis and nephrolithiasis share a well-recognized heritability [19, 20], and around 15% of the patients were detected with causative genes [4]. Although low plasma potassium concentration, secondary low urinary citrate, tubulointerstitial damage, chloride deficiency, and increased intracellular chloride activity were also suggested to contribute to the hypercalciuria, the exact pathogenesis of nephrocalcinosis or nephrolithiasis in BS remains unclear [21]. Renal function is generally well preserved. In the present study, GFR of the proband was lower than the normal population. According to the ten-year outcome study by Puricelli E et al. [22], 25% of the patients with type I or type II BS had GFR lower than the normal range, which may be resulted from nephrocalcinosis. More than 30 genes have been reported to be with the etiology of nephrolithiasis [4]. Two-thirds of the genes currently known to be associated with nephrolithiasis coding for membrane proteins or enzymes involved in renal tubular transport [23]. The TALH and connecting tubules (CNT) have a central role in maintenance of fluid, electrolytes and acid-base homeostasis. Therefore, mutations of genes involved in TALH and CNT function can result in phenotypically severe disease. 14 of all genes are of paramount importance accounting for 15% of nephrolithiasis or nephrocalcinosis [24]. Recessive causes were more frequent among children, whereas dominant disease occurred more abundantly in adults. Therefore, NGS panel including genes involved in functions of TALH, connecting tubules, systemic disorders such as chromic hypercalcemia from vitamin D, primary hyperoxaluria, ARPT deficiency, distal renal tubular acidosis, Dent’s disease, cystinuria and family hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria shall be applied [25, 26]. In this study, 248 genes associated with hereditary kidney diseases were all included in the panel, and no other suspicious gene mutations were found except KCNJ1 gene.
KCNJ1 gene mutation associated antenatal BS is phenotypically distinct from the other disease because of prominent polyhydramnios with preterm delivery together with discontinuous fatigue, still phenotypic variability presents in patients with KCNJ1 mutation and absence of enough recognition for this type of disease may exist. The patient in the present study was not gotten accurate diagnosis until he was ten-years old and incidentally found bilateral nephrolithiasis, although he had the previous infant history with polyhydramnios and preterm delivery, and the intermittent cramps, fatigue and muscle weakness during childhood.
There are other causes which could also induce either of these symptoms. The clinicians or parents may ignore the real etiology beneath the manifestations and the clinical misdiagnosis of BS was nearly 25%, especially in developing countries [27]. Also the onset of BS type may be late. One adult male patient initially presented with an incidental finding of nephrocalcinosis was diagnosed as a late-onset BS due to detection of a homozygous KCNJ1 missense mutation [28].
Our case showed that the presentations in patients with BS may not be unusual, and specific disorders within the spectrum of BS or nephrolithiasis may not easily be diagnosed or differentiated by rigorous clinical manifestations. Genetic test, especially NGS is a very efficient tool to distinguish specific disorder from multiple confusing spectrums.
Availability of data and materials
Datasets used in this article are available from corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kusumi K, Becknell B, Schwaderer A. Trends in pediatric urolithiasis: patient characteristics, associated diagnoses, and financial burden. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30(5):805–10.
Edvardsson VO, Ingvarsdottir SE, Palsson R, Indridason OS. Incidence of kidney stone disease in Icelandic children and adolescents from 1985 to 2013: results of a nationwide study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018;33(8):1375–84.
Sharma AP, Filler G, Dwight P, Clark WF. Chronic renal disease is more prevalent in patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome who had a positive history of diarrhea. Kidney Int. 2010;78(6):598–604.
Halbritter J, Seidel A, Muller L, Schonauer R, Hoppe B. Update on hereditary kidney stone disease and introduction of a new clinical patient registry in Germany. Front Pediatr. 2018;6:47.
Schulte MD, Shock EL, Obsil M, Majer V. Volumes of aqueous alcohols, ethers, and ketones to T = 523 K and p = 28 MPa. J Chem Thermodyn. 1999;31(9):1195–229.
Schulte U, Hahn H, Konrad M, Jeck N, Derst C, Wild K, et al. pH gating of ROMK (K (ir)1.1) channels: control by an Arg-Lys-Arg triad disrupted in antenatal Bartter syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(26):15298–303.
Zuo J, Guo W, Wang S, Lang Y, Wang S, Shi X, et al. Eight novel KCNJ1 variants and parathyroid hormone overaction or resistance in 5 probands with Bartter syndrome type 2. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2020;511:248-254.
Simon DB, Karet FE, Hamdan JM, DiPietro A, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP. Bartter's syndrome, hypokalaemic alkalosis with hypercalciuria, is caused by mutations in the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter NKCC2. Nat Genet. 1996;13(2):183–8.
Simon DB, Karet FE, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Hamdan JH, DiPietro A, Trachtman H, et al. Genetic heterogeneity of Bartter's syndrome revealed by mutations in the K+ channel, ROMK. Nat Genet. 1996;14(2):152–6.
Khandelwal P, Sabanadesan J, Sinha A, Hari P, Bagga A. Isolated nephrocalcinosis due to compound heterozygous mutations in renal outer medullary potassium channel. CEN Case Rep. 2020;9(3):232–6.
Birkenhager R, Otto E, Schurmann MJ, Vollmer M, Ruf EM, Maier-Lutz I, et al. Mutation of BSND causes Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness and kidney failure. Nat Genet. 2001;29(3):310–4.
Peters M, Jeck N, Reinalter S, Leonhardt A, Tonshoff B, Klaus GG, et al. Clinical presentation of genetically defined patients with hypokalemic salt-losing tubulopathies. Am J Med. 2002;112(3):183–90.
Abe Y, Sato T, Takagi M, Watanabe T, Nagayama Y, Hasegawa T, et al. A case of Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome with a novel mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor gene complicated by medullary sponge kidney. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2012;25(5–6):587–90.
Bertoncello R, Bettinelli M, Casarin M, Maccato C, Pandolfo L, Vittadini A. An experimental and theoretical study of the electronic structure of zinc Thiophenolate-capped clusters. Inorg Chem. 1997;36(21):4707–16.
Leonhardt H, Page AW, Weier HU, Bestor TH. A targeting sequence directs DNA methyltransferase to sites of DNA replication in mammalian nuclei. Cell. 1992;71(5):865–73.
Kurtz DB, White TL. Metrics of odorant dissimilarity. Labeled magnitude scale vs magnitude estimation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;855:638–40.
Garel L, Filiatrault D, Robitaille P. Nephrocalcinosis in Bartter's syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 1988;2(3):315–7.
Seys E, Andrini O, Keck M, Mansour-Hendili L, Courand PY, Simian C, et al. Clinical and genetic Spectrum of Bartter syndrome type 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(8):2540–52.
Stechman MJ, Loh NY, Thakker RV. Genetics of hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis: renal stone disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1116:461–84.
Goldfarb DS, Fischer ME, Keich Y, Goldberg J. A twin study of genetic and dietary influences on nephrolithiasis: a report from the Vietnam era twin (VET) registry. Kidney Int. 2005;67(3):1053–61.
Naesens M, Steels P, Verberckmoes R, Vanrenterghem Y, Kuypers D. Bartter's and Gitelman's syndromes: from gene to clinic. Nephron Physiol. 2004;96(3):p65–78.
Puricelli E, Bettinelli A, Borsa N, Sironi F, Mattiello C, Tammaro F, et al. Italian collaborative Group for Bartter S: long-term follow-up of patients with Bartter syndrome type I and II. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(9):2976–81.
Faller N, Dhayat NA, Fuster DG. Nephrolithiasis secondary to inherited defects in the thick ascending loop of henle and connecting tubules. Urolithiasis. 2019;47(1):43–56.
Halbritter J, Baum M, Hynes AM, Rice SJ, Thwaites DT, Gucev ZS, et al. Fourteen monogenic genes account for 15% of nephrolithiasis/nephrocalcinosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26(3):543–51.
Marra G, Taroni F, Berrettini A, Montanari E, Manzoni G, Montini G. Pediatric nephrolithiasis: a systematic approach from diagnosis to treatment. J Nephrol. 2019;32(2):199–210.
Mohebbi N, Ferraro PM, Gambaro G, Unwin R. Tubular and genetic disorders associated with kidney stones. Urolithiasis. 2017;45(1):127–37.
Najafi M, Kordi-Tamandani DM, Behjati F, Sadeghi-Bojd S, Bakey Z, Karimiani EG, et al. Mimicry and well known genetic friends: molecular diagnosis in an Iranian cohort of suspected Bartter syndrome and proposition of an algorithm for clinical differential diagnosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019;14(1):41.
Huang L, Luiken GP, van Riemsdijk IC, Petrij F, Zandbergen AA, Dees A. Nephrocalcinosis as adult presentation of Bartter syndrome type II. Neth J Med. 2014;72(2):91–3.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the patient and his family for participation in the study.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China for Young Scholars (No.81701497) to QH.W. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qinghua Wu and Saisai Yang conceived the ideas and wrote the manuscript; Guanghui Yao revised the draft and participated the draft’s drawing and modeling; Xin Chen helped to collect the clinical information of this study and gave us lots of pertinent suggestions during the writing; Huirong Shi, Chihong Lou analyzed the data and revised the draft; Shumin Ren, Zhihui Jiao, Cong Wang and Xiangdong Kong gave good suggestions during the study. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by The Human Ethics Committees of The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (ID: KS-2018-KY-36). Written informed consent was obtained from the guardians of the patient for publication of this Case Report and any accompanying images. The copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Yao, G., Chen, X. et al. A novel mutation of KCNJ1 identified in an affected child with nephrolithiasis. BMC Nephrol 23, 227 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-022-02783-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-022-02783-x