Abstract
Background
Nance-Horan syndrome (NHS) is an X-linked inheritance disorder characterized by bilateral congenital cataracts, and facial and dental dysmorphism. This disorder is caused by mutations in the NHS gene. However, NHS may be difficult to detect in individuals with subtle facial dysmorphism and dental abnormalities in whom congenital cataracts are the primary clinical manifestations.
Methods
In this study, we present a three-generation family with NHS. Whole exome sequencing was performed to determine the potential pathogenic variant in the proband. Further validation was explored with Sanger sequencing in 9 of the available individuals of the family and additional 200 controls.
Results
A novel truncation mutation in gene NHS (c.C4449G, p.Tyr1483Ter) was found in the proband, who presented with a long-narrow face, prominent nose and large anteverted pinnae ear, screw-driver like incisors, mild mulberry like molars, one missing maxillary second molar and malocclusion. We found this mutation was detected in 2 male patients and 4 female carriers in the family. However, the mutation was never detected in the control subjects.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we identified a novel truncation mutation in the NHS gene, which might associate with NHS. Our review on the NHS studies illustrated that NHS has significantly clinical heterogeneity. And NHS mutations in the NHS-affected individuals typically result in premature truncation of the protein. And the new mutation revealed in this study would highlight the understanding of the causative mutations of NHS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Nance-Horan syndrome (NHS) is a rare X-linked genetic disorder. According to the latest statistics of the National Organization for Rare Disorders shown that fewer than 50 families have been described in the medical literatures, and the exact incidence of the disorder remains unknown (https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/nance-horan-syndrome/). NHS is caused by a mutation in the NHS gene on chromosome Xp22. NHS is usually fully expressed in males only, with the affected males characterized by congenital cataracts and frequent microcornea, dental anomalies, and dysmorphic features [1, 2]. Approximately 20 to 30% of affected males may have varying levels of mental retardation [3]. Autism spectrum disorder symptoms have also been observed in a few patients [4]. Carrier females may show posterior Y-sutural cataracts with small corneas and slightly reduced vision only, they do not usually develop intellectual impairment [5, 6]. Since the symptoms of isolated microphthalmia with cataract; cataract-microcornea syndrome; X-linked congenital cataract and X-linked congenital cataract with microcornea are similar to those of NHS, making a definitive diagnosis without genetic information is difficult. Thus, to determine the potential disease-causing gene, we performed whole exome sequencing (WES) analysis in a proband.
Methods
Mutation screening
Peripheral blood was collected in potassium EDTA tubes from the three generations of family members. Genomic DNA was extracted with a QIAamp DNA blood kit (Qiagen, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Subsequent DNA quantification was performed with a NanoDrop ND-2000 spectrophotometer (https://www.labtech.com/nanodrop-nd2000-nd2000c-spectrophotometer) and analyzed with agarose gel electrophoresis. WES was explored with NimbleGen VCRome 2.1 capture reagents and sequenced by an Illumina HiSeq platform. The produced sequencing reads were aligned to the reference human genome (GRCh37/hg19) using the Burrows-Wheeler algorithm (version 0.7.5). Exome variants were identified with GATK workflows and annotated with the ANNOVAR pipeline.
In silico analyses and sanger sequencing
Variants were filtered for relevance to human disease based on a minor allele frequency greater than 0.01 in the 1000 Genomes, ExAC and ESP6500 databases: missense, nonsense, indel, and splice-site variants were identified. These candidate variants were further analyzed with SIFT, Polyphen 2, CADD and Mutation Taster (http://mutationtaster.org/) software to predict the probability of disease-causing mutations. Variant interpretation was explored with the InterVar pipeline [7]. The American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) standard was used as the final criterion to evaluate the pathogenicity of the variants. Sanger sequencing was performed to validate the variant sites in the proband as well as in 9 available family members using designed primers (forward primer 5’-TCAGACTGTGGGTGCTACAAGG-3′ and reverse primer 5’-AGCCTTCTGCATTAACTCGTGG-3′). In addition, candidate disease-causing mutations were examined in 200 control subjects, and all of the sequence traces were analyzed with Mutation Surveyor software [8].
Results
Patients and clinical characteristics
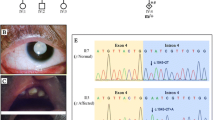
A 15-year-old boy was admitted to the laboratory of clinical genetics of Peking Union Medical College Hospital for genetic counseling due to congenital cataracts. In addition to the primary physical characteristic of congenital bilateral nuclear cataracts, the young patient had a long-narrow face, prominent nose and large anteverted pinnae, screw-driver like incisors, mild mulberry like molars, one missing maxillary second molar and malocclusion (Fig. 1). Available clinical information regarding the families is shown in Table 1, and the carrier females lens opacity and vision were unavailable here.
The proband (III:1) and another affected individual (II:5) underwent microincision cataract surgery at the ages of 15 and 21 years respectively. Available photos before the surgery revealed bilateral lens opacities that heavily affected the nucleus in the proband (Fig. 1; Fig. 2). Individual II: 5 presented with similar facial features including a long narrow face, mildly anteverted pinnae ear and screw-driver like incisors, mild mulberry like molars and malocclusion (Additional file 1). Individual II: 5 stated that he was affected by nystagmus, and at the time of recruitment in our study, which might associate with NHS. However, neither of these individuals had mental retardation or behavioral disturbances. Their family history revealed no obvious visual defects or dental abnormalities among the rest of the family members.
The pedigree and Sanger identification of the novel mutation. a The black-solid square represents the affected male patient. The black-shadow circle represents the female carrier. Unfilled squares and circles indicate normal males and females respectively. b The Sanger sequencing traces illustrated the NHS c.C4449G, p.Tyr1483Ter mutation in individualsI:2, II:2 and II:3 (hemizygous), and individuals II:5 and III:1 (homozygous)
A novel mutation associated with NHS
WES data were processed as described in the Methods section. Quality control parameters included an average coverage of 100× of the exome, and 97.6% of exonic regions sequenced at greater than 10× coverage. A total number of 63.6 million reads were mapped to the reference genome. After annotation 76,040 variants were detected in the proband. Variant isolation was performed with a strict workflow (Fig. 3), and 129 coding variants were selected with high priority, According to ACMG standards, 5 genes were identified and predicted to be pathogenic with very strong evidence [7], however, only the NHS gene was associated with cataract and NHS (Additional file 2). Thus, based on the family pathogenic segregation study and clinical manifestations, a novel stop-gain mutation c.C4449G, p.Tyr1483Ter in NHS was identified. We further validated this mutation in 9 available family members; it was detected in individual II: 5 and 4 female carriers, but not in the 200 controls (Fig. 2 and Additional file 3). Here, we predicted that this novel mutation was most likely associated with NHS.
Variant filter flow chart. To identify the underlying variant, we performed strict filter procedures. Benign*: variants occurred in the noncoding region and no prediction indicated pathogenic or likely pathogenic. Morderate^: variants occurred in the coding region, but no prediction implied pathogenic or likely pathogenic
ACMG standards: variants were classified with the rules of combining criteria of the ACMG guidelines, and 5 of the pathogenic variants were identified
Discussion
In this study, we revealed a novel truncation mutation (c.C4449G, p.Tyr1483Ter) in the NHS gene, which might associated with NHS in a three-generation Chinese family. The whole coding sequence of NHS gene is 4893 bp, and in our study the novel truncation occurred in c.4449 site, and the affected individuals in the family presented with relatively mild abnormality. Although the male affected individuals had the same variation, the phenotypic heterogeneity existed in the NHS family (Table 1). This implied that the underlying mechanism of clinical heterogeneity was still needed to be investigated.
NHS manifestations appear in multiple organ systems especially the features of facial, teeth, skeleton, heart and neurologic system features, and even encompass behavior. And heterozygous females commonly had posterior Y-sutural cataracts. In this study we had no chance to perform the professional ophthalmologic examination for the carrier females, since they do not think they have vision impairment, and their lens opacity and vision was not quite clear. However, X-linked cataract merely involves the eyes. Heterozygous females had posterior stellate or suture cataracts, or a combination of the two, with normal vision or a slight reduction (Table 2). However, the facial dysmorphology and dental abnormalities might be subtle and easily missed in NHS patients in whom congenital cataracts are the primary clinical concern. Additionally, there was not enough evidence to identify the two disorders that might be allelic [9].
The NHS gene is alternatively spliced and composed of 10 coding exons, which encode a protein containing 4 conserved nuclear localization signals, The encoded protein can regulate actin remodeling and cell morphology. Expression studies in mice showed that the NHS gene plays critical roles in regulating eye, tooth, brain, and craniofacial development. Additionally, the complex pattern of temporally and spatially regulated expression of NHS was consistent with the pleiotropic features of NHS [3].
Previous studies illustrated that variations in the NHS gene could induce X-linked cataracts and NHS [10,11,12]. However, the identical association between the genotype and phenotype was unclear. One study predicted that a lack of functional NHS protein might cause NHS, whereas aberrant transcription of the NHS gene might lead to a milder X-linked cataract phenotype [10]. To determine whether NHS and X-linked cataract were the two distinguishing phenotypes of NHS gene mutations, we reviewed the pathogenic/likely pathogenic mutations, which were recorded in the ClinVar and Cat-Map databases [13]. Here, more than 50 mutations of the NHS gene accounted for pathogenic clinical conditions. Variants including missense, frame-shift (InDel) and stop-gain mutations were identified as contributors to NHS; and a 4.8 kb deletion and a 500 kb triplication were associated with X-linked cataract 40 (Additional file 4); Considering the genotypes and phenotypes of NHS and X-linked cataracts, we found that NHS was mostly resulted from the point mutation and micro InDel [14,15,16], while the X-linked cataract was caused by large-scale recombination of the NHS gene, which was predicted to result in altered transcriptional regulation of the NHS gene. However, this difference could not be used to define NHS and X-linked cataract [9], since a microdeletion of 170,6 kb at Xp22.13 was detected in an Italian boy with NHS syndrome [15]. The latest cytogenetic and molecular analyses in two patients, a mother and daughter, who presented with NHS, demonstrated a 46, X, t(X;1) (p22.13;q22) karyotype in each patient. No copy-number genomic imbalances were detected. The mother had a preferential inactivation of the normal X chromosome and no mRNA isoform of NHS was detected. This study implied that NHS could be due to the disruption of NHS gene expression [12].
NHS-affected individuals have mutations in the NHS gene that typically result in premature truncation of the protein (Additional file 4). The mutant proteins failed to localize to the cellular periphery in epithelial cells and instead were found in the cytoplasm. The mislocalization of the mutant NHS-A protein is expected to adversely affect cell-cell junctions in epithelial cells such as the lens epithelium, which may explain the cataractogenesis in NHS patients [10, 17, 18], and NHS proteins localized to the cellular periphery. In the developing of mammalian lens, researchers discovered continuous expression of NHS that became restricted to the lens epithelium in prenatal and postnatal lenses; this finding suggested that disturbances in intercellular contacts were the underlying mechanisms of cataractogenesis in NHS [19]. Additionally, the NHS gene appears to have multiple isoforms as a result of alternative transcription. The N-terminus of isoforms NHS-A and NHS-1A, which are implicated in the pathogenesis of NHS, have a functional WAVE homology domain that interacts with the Abi protein family, haematopoietic stem/progenitor cell protein 300 (HSPC300), Nap1 and Sra1. NHS knockdown resulted in the disruption of the actin cytoskeleton, and led to a striking increase in cell spreading. Conversely, ectopic over expression of NHS inhibited lamellipod formation. The NHS gene was demonstrated to be a novel regulator of actin remodeling and cell morphology, and may orchestrate actin regulatory protein function in response to signaling events during development [20]. Therefore, we speculate that X-linked cataract might represent differences in the expression of NHS.
Conclusion
In this study, we found a novel truncation mutation in the NHS gene, which was predicted to be likely associated with NHS. Moreover, we reviewed the characteristics of the NHS gene mutations in NHS and X-linked cataract, this review illustrated that NHS mutations in the NHS-affected individuals typically result in premature truncation of the protein or disruption of NHS gene expression; and the X-linked cataract might due to the protein expression aberration. Additionally, NHS has significantly clinical heterogeneity, and the manifestations of mild NHS could be similar to those of X-linked cataract, which suggested that the combination of genome detection and the manifestations could improve the clinical diagnosis. And, the novel mutation in the NHS gene might highlight the understanding of the causative mutations of Nance-Horan syndrome.
Abbreviations
- CADD:
-
Combined annotation dependent depletion
- Chr:
-
Chromosome
- EDTA:
-
Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid
- ExAc:
-
The exome aggregation consortium
- GATK:
-
Genome analysis toolkit
- InDel:
-
Insertions and deletions
- NHS:
-
Nance-Horan syndrome
- NHS :
-
NHS gene
- OMIM:
-
Online Mendelian inheritance in man
- PolyPhen:
-
Polymorphism phenotyping
- SIFT:
-
Sorting intolerant from tolerant
- WES:
-
Whole exome sequencing
References
Kammoun M, Brady P, De Catte L, Deprest J, Devriendt K, Vermeesch JR. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia as a part of Nance-Horan syndrome? Eur J Hum Genet. 2018;26:359–66.
Tian Q, Li YP, Kousar R, Guo H, Peng FL, Zheng Y, et al. A novel NHS 339 mutation causes Nance-Horan syndrome in a Chinese family. Bmc Med Genet. 2017;18(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-016-0360-9.
Burdon KP, McKay JD, Sale MM, Russell-Eggitt IM, Mackey DA, Wirth MG, et al. Mutations in a novel gene, NHS, cause the pleiotropic effects of Nance-Horan syndrome, including severe congenital cataract, dental anomalies, and mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73:1120–30.
Liao HM, Niu DM, Chen YJ, Fang JS, Chen SJ, Chen CH. Identification of a microdeletion at Xp22.13 in a Taiwanese family presenting with Nance-Horan syndrome. J Hum Genet. 2011;56:8–11.
Nance WE, Warburg M, Bixler D, Helveston EM. Congenital X-linked cataract dental anomalies and brachymetacarpalia. Birth defects original article series. 1974;10:285–91.
Li A, Li B, Wu L, Yang L, Chen N, Ma Z. Identification of a novel NHS mutation in a Chinese family with Nance-Horan syndrome. Curr Eye Res. 2015;40:434–8.
Li Q, Wang K. InterVar: clinical interpretation of genetic variants by the 2015 ACMG-AMP guidelines. Am J Hum Genet. 2017;100:267–80.
Minton JA, Flanagan SE, Ellard S. Mutation surveyor: software for DNA sequence analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;688:143–53.
Ramprasad VL, Thool A, Murugan S, Nancarrow D, Vyas P, Rao SK, Vidhya A, Ravishankar K, Kumaramanickavel G. Truncating mutation in the NHS gene: phenotypic heterogeneity of Nance-Horan syndrome in an asian Indian family. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:17–23.
Coccia M, Brooks SP, Webb TR, Christodoulou K, Wozniak IO, Murday V, et al. X-linked cataract and Nance-Horan syndrome are allelic disorders. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:2643–55.
Brooks S, Ebenezer N, Poopalasundaram S, Maher E, Francis P, Moore A, Hardcastle A. Refinement of the X-linked cataract locus (CXN) and gene analysis for CXN and Nance-Horan syndrome (NHS). Ophthalmic Genet. 2004;25:121–31.
Gomez-Laguna L, Martinez-Herrera A, Reyes-de la Rosa ADP, Garcia-Delgado C, Nieto-Martinez K, Fernandez-Ramirez F, et al. Nance-Horan syndrome in females due to a balanced X;1 translocation that disrupts the NHS gene: familial case report and review of the literature. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018;39:56–62.
Shiels A, Bennett TM, Hejtmancik JF. Cat-map: putting cataract on the map. Mol Vis. 2010;16:2007–15.
Li H, Yang L, Sun Z, Yuan Z, Wu S, Sui R. A novel small deletion in the NHS gene associated with Nance-Horan syndrome. Sci Rep. 2018;8:2398.
Accogli A, Traverso M, Madia F, Bellini T, Vari MS, Pinto F, Capra V. A novel Xp22.13 microdeletion in Nance-Horan syndrome. Birth defects research. 2017;109:866–8.
Shoshany N, Avni I, Morad Y, Weiner C, Einan-Lifshitz A, Pras ENHS. Gene mutations in Ashkenazi Jewish families with Nance-Horan syndrome. Curr Eye Res. 2017;42:1240–4.
Sharma S, Burdon KP, Dave A, Jamieson RV, Yaron Y, Billson F, et al. Novel causative mutations in patients with Nance-Horan syndrome and altered localization of the mutant NHS-A protein isoform. Mol Vis. 2008;14:1856–64.
Brooks SP, Ebenezer ND, Poopalasundaram S, Lehmann OJ, Moore AT, Hardcastle AJ. Identification of the gene for Nance-Horan syndrome (NHS). J Med Genet. 2004;41:768–71.
Sharma S, Ang SL, Shaw M, Mackey DA, Gecz J, McAvoy JW, Craig JE. Nance-Horan syndrome protein, NHS, associates with epithelial cell junctions. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1972–83.
Brooks SP, Coccia M, Tang HR, Kanuga N, Machesky LM, Bailly M, Cheetham ME, Hardcastle AJ. The Nance-Horan syndrome protein encodes a functional WAVE homology domain (WHD) and is important for co-ordinating actin remodelling and maintaining cell morphology. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:2421–32.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient and the families for participating in the genetic study, donating blood samples and providing detailed medical history.
Funding
This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. The funding number is: 2016RC310006.
Availability of data and materials
The whole exome sequencing data were submitted to the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database, and the access number is: SRR6872897.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL carried out the genetic studies and performed the data analysis and wrote the manuscript; RS performed the clinical diagnosis and the manifestations analysis; and FY performed the genetic data analysis and assisted the revision. ZW advised and conducted this study. XZ and SZ designed and conducted the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the duly constituted ethics committee of Peking Union Medical College Hospital. Written consent was obtained from all family members to participate in this study, and consent was obtained from the parent on behalf of the proband as they are a minor.
Consent for publication
Written consent was obtained from all family members for the publication of this study and the clinical images, and consent was obtained from the parent on behalf of the proband as they are a minor.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Dental dysmorphism of II: 5. A&B. Screwdriver blade-shaped incisors and mulberry-like molars are shown. C. Dental X-ray showing the overview of the tooth formation. (TIF 8647 kb)
Additional file 2:
Detailed annotation of the retained 129 variants. ACMG standards were used for variant classification, and the OMIM database was used for priority analysis of the phenotype matching. (XLSX 47 kb)
Additional file 3:
Mutation verification. The novel mutation was further verified in 200 control subjects by Sanger sequencing, and the NHS c.C4449G mutation was not detected in any individual. (DOC 1807 kb)
Additional file 4:
Variants in gene NHS accounted for pathogenic clinical conditions. Pathogenic mutation revealed in this study and those reported in ClinVar and Cat Map databases were reviewed in the table. (XLSX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, C., Sui, R., Yao, F. et al. Whole exome sequencing identified a novel truncation mutation in the NHS gene associated with Nance-Horan syndrome. BMC Med Genet 20, 14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-018-0725-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-018-0725-3