Abstract
Background
Cryptosporidiosis is a disease caused by infection with an intestinal coccidian parasite Cryptosporidium. Cryptosporidium species are the second leading cause of diarrheal disease and death in children in developing countries. Until now, no data have been available or published on its prevalence among children with diarrhea in Sudan. Therefore, this paper was designed to determine the prevalence rate of Cryptosporidium among children with diarrhea under 5 years who were admitted to Kosti Teaching Hospital.
Methods
A hospital-based cross-sectional study including children under 5 years old admitted to the pediatric section of the hospital between September 2020 and December 2020. A total of one-hundred and fifty stool samples were collected. All stool samples were examined using the modified Ziehl Neelsen (mZN) staining technique and then examined microscopically for Cryptosporidium infection.
Results
A total of 150 children were examined out of which 70 presented with diarrhea. A greater prevalence of 19/70 (27.1%) of Cryptosporidium was observed in children with diarrhea than children without diarrhea 7/80 (8.8%). There was a significant relationship between the prevalence of Cryptosporidium and the presence of diarrhea in children under 5 years in the Kosti Teaching Hospital(P < 0.05). It was found that a higher prevalence was registered among children using piped-water sources for drinking.
Conclusions
The overall prevalence of parasite detected was 17.3% among children admitted to Kosti Teaching Hospital. The prevalence rate of the infection among Children with diarrhoea was 27.1%. Studying the prevalence rate of cryptosporidiosis among diarrheic children may predict their health status, leading to a better diagnosis, treatment, and, therefore, patients’ status improvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cryptosporidium species are single-celled coccidian parasites that cause the diarrheal disease cryptosporidiosis [1,2,3,4]. They can be found in soil, food, water, and on surfaces that have been contaminated with fecal matter from infected humans or animals. Cryptosporidiosis may occur via contaminated water used for irrigation or application of agricultural chemicals, floodwater, contacting polluted dump tank or flume water used for post-harvest washing of infected workers [5,6,7,8,9].
Cryptosporidiosis is a worldwide illness caused by the coccidian parasite Cryptosporidium, which infects numerous species of vertebrates, including humans. Watery diarrhea is the most common symptom of the disease. Abdominal cramps, vomiting, nausea, dehydration, and weight loss are other symptoms associated with cryptosporidiosis. The onset of cryptosporidiosis is generally two to ten days after becoming infected with the parasite. Symptoms are usually self-limiting in healthy individuals. Diarrhoea and dehydration may be more severe and possibly life-threatening among individuals with weakened immune systems [10,11,12,13].
Cryptosporidiosis is usually diagnosed with microscopic detection of the parasite oocysts, oocyst antigens, or oocyst DNA in stool samples. For the detection of oocysts in stool, the sample must be concentrated using the formalin-ether sedimentation method before microscopic examination. The oocysts of Cryptosporidium in unconcentrated fecal smears can be easily observed by acid-fast or phenol–auramine staining methods [1, 2, 9, 14,15,16,17,18].
About 30–50% of cryptosporidiosis deaths in infants and children occur worldwide. It is the second after rotavirus as a leading cause of diarrhea and deaths among children [1, 9].
In developing countries or low-and-middle-income countries, the parasite was gradually associated with malnutrition and death caused by diarrhea in children [5, 6, 19,20,21,22,23]. Cryptosporidiosis, caused by the Cryptosporidium parvum, is of great concern because of its association with economic losses and the public health significance in humans. Over two-hundred water-borne, food-borne, and zoonotic cryptosporidiosis outbreaks have been registered. Cryptosporidium spp. in economically low resource countries are the second cause of diarrheal illness and death in children and remains the only member of the diarrheal diseases for which no consistent and effective therapy is available [7, 10, 11, 24,25,26,27,28,29,30].
Sudan is one of these countries, situated in Northeast Africa at the Nile Valley. Most epidemiological studies or surveys have reported and indicated that the infections caused by soil-transmitted helminths, Schistosoma spp., food- and water-borne protozoa, and Plasmodium spp., are endemic in Sudan [12,13,14, 17]. However, limited information is available on the prevalence of cryptosporidiosis among children in Sudan, especially children with diarrhea. This study aims to report on the prevalence of Cryptosporidiosis among children with diarrhea attending Kosti Teaching Hospital, White Nile State, Sudan.
Materials and methods
Study area
The research was conducted at the pediatric section and clinical laboratory department of Kosti Teaching Hospital, Kosti, Sudan. This Hospital serves customers from Kosti city and its surrounding cities in the State. Kosti city is one of the major cities in Sudan that lies south of Khartoum, the capital of Sudan, and sits at the western bank of the White Nile river opposite Rabak (the capital of the White Nile state) where there is a bridge. The locality is composed of five administrative units. It has been bordered by Eldewiem locality in the north, Rabak locality in the east, Al salam locality in the south, and Tendalty locality in the west. The most essential water resource is rainwater and the White Nile. Most activities are grazing, agriculture, trade, and fishing.
Study design
This study is a hospital-based cross-sectional study conducted at Kosti Teaching Hospital Laboratory between the first of September and 30th of December, 2020. All participants who were consulted for or hospitalized in the pediatric section were included in the study. A consecutive sampling method was performed and those who met our inclusion criteria and consented to the research were directly included and selected.
Study population
The participants of this study were children who were 5 years and below and presented at Kosti Teaching Hospital.
Inclusion criteria
The study was restricted to children who were of the age 5 years and below. They involved those that had diarrhea or without diarrhea and parents/guardians agreed for their children to be part of the study after explaining to them in English and Arabic the objectives of our study.
Exclusion criteria
Children above 5 years were excluded as well as those children 5 years or below whose parents/guardians did not agree to be part of the study. Additionally, we excluded children whose parents could not give the exact age of their children.
Ethical considerations
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, University of El Imam El Mahdi.
Data collection
Questionnaires were administered to collect demographic data that included; name, age, sex, clinical symptoms including diarrhea, patient’s residence, presence of toilet facility, and sources of drinking water. This questionnaire was appropriated or adapted from the research of Tombang A N et al. in Cameroon [1].
Stool sample collection
Parents/guardians of children with gastrointestinal symptoms (with diarrhea or without diarrhea) were given labeled stool containers to collect one stool sample at the time of collection. They were guided on how to collect a suitable amount of stool in the containers and send them to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Stool sample handling and storage
Suitable gloves were worn to take or handle the containers. The samples were checked for stool quantity and also their physical appearance was recorded. The labels of the containers were also checked and matched to their corresponding questionnaires. Fresh stool samples were kept and preserved at − 20 °C in the freezer of the fridge at the clinical laboratory for investigations at the end of each working day.
Modified Ziehl Neelsen (mZN) staining technique
The stool samples were taken from the laboratory fridge and put at room temperature before fecal smears were prepared on microscope slides using wooden stick applicators. Then the smears were left on racks to air dry.
Staining
The slides were put in staining racks for fixation in absolute methanol for 3 min followed by a strong carbol fuchsin stain for 15 min. Then, the slides were rinsed in tap water. A decolorization was made by adding 1% hydrochloric acid alcohol for 15 s and rinsed with tap water. Then, a counterstain of 1% methylene blue was added for 30 s, rinsed well, and left to air dry. The stained slides were investigated and examined microscopically using 40x and 100x objectives and the presence or absence of oocysts was recorded.
Oocyst determination
Oocysts are round to ovoid, and the size usually ~ 4–6 μm in diameter. They are acid-fast staining. Oocyst is variable in staining. Some oocysts may appear unstained and fully sporulated structures can be found in which a red color staining, crescentic shapes or bodies. The sporozoites can appear within an unstained wall of the oocyst. The quantity of oocysts was determined as 1+ (1-10oocysts/preparation); 2 + (11-50oocysts/preparation); and 3 + (>50oocysts/preparation).
Statistical analysis
Data was recorded and analyzed using the Chi-square test by a statistical package for social science (SPSS version 21) program. P values < 0.05 was considered significant for all statistical analyses.
Results
Socio-demographic characteristics of participants
A total of 150 children with ages 5 years old and below were enrolled in this study. The mean age of the children was 46.8 (SD = 17.7) months, and the median age was 60 months. More than half i.e. 85 (56.7%) of the children were males. Also, a total of 137 (91.3%) or 13(8.7%) have latrines or without latrines in their homes respectively (Table 1).
Diarrhea and stool consistency from children ages 5 years and below in Kosti (n = 150)
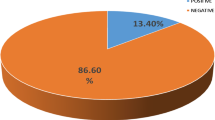
A total of 70/150 (46.7%) participants were presented with diarrhea (watery/mucoid stool) whereas the remaining 80/150 (53.3%) children were presented with formed/semi-formed stool.
Prevalence of Cryptosporidium and the presence/absence of diarrhea
Table 2 shows that the age group less than 30 months old recorded a 10/63 (15.8%) and a 16/87 (18.4%) prevalence for the age group equal to 60 months. The participants that presented with diarrhea recorded a 19/70 (27.1%) prevalence while those that did not present with diarrhea recorded a 7/80 (8.8%) prevalence (Table 2).
Prevalence of Cryptosporidium among children under or equal the ages 5 years in Kosti that presented with diarrhea
Overall, the prevalence of Cryptosporidium among children admitted to Kosti Teaching Hospital was 26/150 (17.3%). A high prevalence of Cryptosporidium (19/70, 27.1%) was observed among children who have diarrhea than in children without diarrhea (7/80, 8.8%). There was a significant relationship (p = 0.003) between the prevalence of Cryptosporidium and the presence of diarrhea among children of 5 years and below presented to the Kosti Teaching Hospital (Table 3).
Discussion
Cryptosporidium is among the four major pathogens causing diarrheal diseases in low-and-middle-income countries, especially in children. This parasite is recognized as a highly infectious enteric pathogen and is transmitted mainly by the fecal-oral route [1, 2]. This current study aimed to determine the prevalence rate of Cryptosporidiosis among children with diarrhea admitted to Kosti Teaching hospital, Kosti city, White Nile state in Sudan. One-hundred and fifty diarrhoeic stool samples were examined using first, direct wet preparation and formal ether concentration technique and second, examined using modified ZN staining technique.
In our present findings, the overall prevalence rate of cryptosporidiosis was 26 (17.3%) among children with diarrhea admitted to the pediatrics emergency section at Kosti Teaching Hospital using the modified ziehl neelsen technique. This result shows a higher prevalence compared to the results reported in Tanzania, Cameroon, Rwanda, and Benin [1,2,3, 6] with the prevalence of 10.4, 8.93, 9.4, and 5.8% respectively. A higher prevalence rate has also been found in low-and-middle-income countries with high average rainfall such as Nigeria [5], with 38.3%. Our result is in line with the result obtained in residents in rural areas of the White Nile state in Sudan (13.3%) and near to that result obtained in Iraq (21.92%) [4, 7]. This prevalence rate is probably justified by fact that Kosti is a city with improved access to drinkable water, latrine use, less fecal contamination rates, thus limiting the occurrence of parasitosis in general and cryptosporidiosis in particular. Also, this low prevalence may be explained by the methodology, i.e. using microscopy can be less sensitive than PCR.
Our relevant analysis explained that the prevalence of cryptosporidiosis among diarrhoeic children was a higher increase in males 18 (12%) than in females 8 (5%). But there was no significant difference (p > 0.05). The reason for these differences is not clear since they have the same exposure at the crawling stage but probably be due to the fact that females show less activity level and are mostly home. This result is comparable to the results obtained in Iraq [4].
In the current findings, a high detection or recovery of cryptosporidium parasite was found among the age group of five years 16 (10.7%) than the age under five years old 10 (6.7%). This finding is in agreement with research carried out in Germany, and Cameroon [1, 8] and by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) in 2020 [9] where a greater prevalence rate was observed among children of the ages of 5 years than those under 5 years. In this age, the high prevalence is maybe related to the fact that this age group is usually in danger of diarrhea, for the reason that those basal hygiene activities are unknown or not respected and paired with the fact that the immune system of their body is not sophisticated [9]. This high prevalence rate of children with ages equal to 5 years could be because schooling ages in Sudan are usually around five years old. Also, in this age group, this prevalence can be inferred from the fact that the crest of parasitism occurs at the ages of kindergarten and primary schools when community games involve touching contaminated and dirty soil. Perhaps, it is for this reason, that this current research was conducted in Kosti, an urban and mostly civilian area with a multiracial population, where children find better care than children in rural areas where the rates of malnutrition are greater.
Further investigations expressed the prevalence was high among children who consumed pipeline water 18 (12%) than the other sources of water. Despite pipeline water with a purification system which is the main source of water for most populations in Kosti city, this high prevalence rate may be related sometimes to the stopping of water purification system and it may be associated with economic improvement. The risk of using contaminated bare hands for feeding children may enable the transmission of foodborne diseases like Cryptosporidiosis from infected adults to children. These practices can generate big chances for the ingestion of contaminated food and water with oocysts shed from Cryptosporidium-infected individuals. This elaborates why Cryptosporidium is ranked 5th among the most important foodborne parasites globally [2, 5, 7, 30].
Conclusion
The overall prevalence of Cryptosporidiosis among children who are 5 years and below who were admitted at Kosti Teaching Hospital was 17.3%. The Prevalence rate among children that have diarrhea was 27.1%. Children whose parents were using pipe water for drinking registered a higher prevalence. Additionally, there is an association between Cryptosporidium and diarrhea among children who are 5 years and below admitted with diarrhea in Kosti. Our findings clearly explained that Cryptosporidium is an essential causative agent of diarrhea for children in Kosti. It is necessary to build or improve more water purification systems and sanitation facilities to help the population of this area to access clean drinking water for preventing cryptosporidium infection. Health education and personal hygiene programs should be held to teach people how to avoid the infection.
Limitation of the study
Freezing and thawing of stool samples may lead to fragmentation of oocysts and undercounting. Staining of Spores and artifacts with mZN stain may lead to false-positive results for untrained eyes. Additionally, a too thick smear prepared may not adequately destain and therefore, false-negative results may occur.
Availability of data and materials
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Tombang AN, Ambe NF, Bobga TP, Nkfusai CN, Collins NM, Ngwa SB, et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with cryptosporidiosis among children within the ages 0–5 years attending the Limbe regional hospital, southwest region, Cameroon. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):1144. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7484-8.
Razzolini MTP, Breternitz BS, Kuchkarian B, Bastos VK. Cryptosporidium and Giardia in urban wastewater: a challenge to overcome. Environ Pollut. 2020;257:113545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113545.
Kabayiza JC, Andersson ME, Nilsson S, Bergström T, Muhirwa G, Lindh M. Real-time PCR identification of agents causing diarrhea in Rwandan children less than 5 years of age. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33(10):1037–42. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000448.
Salman YJ, Sadek WS, Rasheed ZK. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium parvum among Iraqi displaced people in Kirkuk city using direct microscopy, flotation technique and ELISA-copro antigen test. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2015;4(11):559–72.
Aniesona AT, Bamaiyi PH. Retrospective study of cryptosporidiosis among Diarrhoeic children in the arid region of North-Eastern Nigeria. Zoonoses Public Health. 2014;61(6):420–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/zph.12088.
Ogouyèmi-Hounto A, Alihonou F, Aholoukpe IE, et al. Prevalence of cryptosporidiosis infection among children under 5-years in Cotonou, Benin. J Parasitol Vector Biol. 2017;9(6):89–94.
Sim S, Yu JR, Lee YH, Lee JS, Jeong HG, Mohamed AAWS, et al. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection among inhabitants of 2 rural areas in White Nile state, Sudan. Korean J Parasitol. 2015;53(6):745–7. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2015.53.6.745.
Chalmers RM, Cacciò S. Towards a consensus on genotyping schemes for surveillance and outbreak investigations of Cryptosporidium, Berlin, June 2016. Eurosurveillance. 2016;21(37):30338.
www.cdc.gov/parasite; Last updated 5, 2019, Accessed 13,11,2020.
Khalil IA, Troeger C, Rao PC, Blacker BF, Brown A, Brewer TG, et al. Morbidity, mortality, and long-term consequences associated with diarrhoea from Cryptosporidium infection in children younger than 5 years: a meta-analyses study. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(7):e758–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30283-3.
Tamomh AG, Suliman MA, Cedric KK, et al. The role of two parasitological staining techniques in diagnosis of cryptosporidiosis among diarrheic patient’s admitted to Kosti teaching hospital. White Nile state, Sudan. MOJ Public Health. 2018;7(2):54–7.
Tamomh AG, Yousfi SR, Abakar AD, Nour BY. Prevalence of intestinal Schistosomiasis among basic school children in White Nile sugar scheme a new irrigated project, White Nile state, Sudan. Biol Med (Aligarh). 2018;10(425):2.
Tamomh AG, Elamin E, Suliman MA, et al. Intestinal parasitic infections among hemodialysis Sudanese patients. Microbes Infect Dis. 2020; https://doi.org/10.21608/MID.2020.45454.1070.
Tamomh AG, Abakr AD, Nour BY. Urinary Schistosomiasis among basic school children in a new irrigated sugar scheme area, White Nile state. Sudan J Microbiol Exp. 2018;6(2):93–6.
Majeed QA, El-Azazy OM, Abdou NE, et al. Epidemiological observations on cryptosporidiosis and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in sheep and goats in Kuwait. Parasitol Res. 2018;117(5):1631–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-5847-1.
Tamomh AG, Yousif SR, Weldegiorgis TZ, et al. Prevalence of cryptosporidiosis among diarrhoeic patient’s attending to kosti teaching hospital, White Nile state. Sudan Wjpmr. 2018;4(2):25–30.
Wang ZD, Liu Q, Liu HH, Li S, Zhang L, Zhao YK, et al. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium, microsporidia and Isospora infection in HIV-infected people: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11(1):28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2558-x.
Florescu DF, Sandkovsky U. Cryptosporidium infection in solid organ transplantation. World J Transplant. 2016;6(3):460–71. https://doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v6.i3.460.
Sannella AR, Suputtamongkol Y, Wongsawat E, Cacciò SM. A retrospective molecular study of Cryptosporidium species and genotypes in HIV-infected patients from Thailand. Parasit Vectors. 2019;12(1):1–6.
Arora DR, Arora BB. Medical parasitology, 3rd edition. New Delhi: CBS publishers and distributers pVT. LTD; 2010.
Cheesbrough M. District laboratory practice in tropical countries part 1. 2nd edition. Norfolk: Tropical Health Technology; 2005.
Zahedi A, Paparini A, Jian F, Robertson I, Ryan U. Public health significance of zoonotic Cryptosporidium species in wildlife: critical insights into better drinking water management. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2016;5(1):88–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2015.12.001.
Ehsan MA, Akter M, Ahammed M, Ali MA, Ahmed MU. Prevalence and clinical importance of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in human and animals. Bangladesh J Vet Med. 2016;14(2):109–22.
Squire SA, Ryan U. Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Africa: current and future challenges. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10(1):195. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2111-y.
Saeed AS, Abd Alla AB, Abdullah HS, et al. Prevalence of cryptosporidiosis and intestinal parasites among Immunocompromised patients in Khartoum state-Sudan. Global Adv Res J Microbiol. 2018;7(5):098–103.
Wang RJ, Li JQ, Chen YC, Zhang LX, Xiao LH. Widespread occurrence of Cryptosporidium infections in patients with HIV/AIDS: epidemiology, clinical feature, diagnosis, and therapy. Acta Trop. 2018;187:257–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.08.018.
Gunasekera S, Zahedi A, O’Dea M, King B, Monis P, Thierry B, et al. Organoids and bioengineered intestinal models: potential solutions to the Cryptosporidium culturing dilemma. Microorganisms. 2020;8(5):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050715.
Yimer M, Hailu T, Mulu W, Abera B. Evaluation performance of diagnostic methods of intestinal parasitosis in school age children in Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8(1):1–5.
Mengist HM, Demeke G, Zewdie O, Belew A. Diagnostic performance of direct wet mount microscopy in detecting intestinal helminths among pregnant women attending ante-natal care (ANC) in east Wollega, Oromia, Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2018;11(1):276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3380-z.
Zheng H, He J, Wang L, Zhang R, Ding Z, Hu W. Risk factors and spatial clusters of Cryptosporidium infection among school-age children in a rural region of eastern China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(5):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050924.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AGT, AMA, EE, MAS, ME, ABO and SAM conceived and designed the study: AGT and AMA implement the study: AGT supervised the study: EE and MAS conducted data analysis: AGT, AMA, EE, MAS, ME, ABO and SAM interpreted study results: AGT wrote the first draft of the manuscript, while AMA, EE, MAS, and ME reviewed and corrected the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Institutional Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, University of El Imam El Mahdi approved the study. As children who are 5 years and below are involved in the study and their parents were involved in the questionnaire, and the informed consent was obtained from their parents or legal guardians for themselves and on behalf of their children. All participants were adequately informed about their rights, responsibilities, and all the relevant guidelines or aspects of the research. Also, all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations/declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tamomh, A.G., Agena, A.M., Elamin, E. et al. Prevalence of cryptosporidiosis among children with diarrhoea under five years admitted to Kosti teaching hospital, Kosti City, Sudan. BMC Infect Dis 21, 349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06047-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06047-1