Abstract
Background
Person-centredness is considered as best practice for people living with dementia. A frequently used instrument to assess person-centredness of a care environment is the Person-centred Climate Questionnaire (PCQ). The questionnaire comprises of 14 items with the three subscales a climate of safety, a climate of everydayness and a climate of community.
Aim
The aim of the study is to describe the translation process of the English language Person-centred Climate Questionnaire (Staff version, Patient version, Family version) into German language (PCQ-G) and to evaluate the first psychometric properties of the German language Person-centred Climate Questionnaire– Staff version (PCQ-G-S).
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study. The three versions of the 14-item English PCQ were translated into German language (PCQ-G) based on the recommendations for cross-cultural adaption of measures. Item distribution, internal consistency and structural validity of the questionnaire were assessed among nursing home staff (PCQ-G-S). Item distribution was calculated using descriptive statistics. Structural validity was tested using principal component analysis (PCA), and internal consistency was assessed for the resulting subscales using Cronbach’s alpha. Data collection took place from May to September 2021.
Results
A total sample of 120 nurses was included in the data analysis. Nine out of 14 items of the PCQ-G-S demonstrated acceptable item difficulty, while five times showed a ceiling effect. The PCA analysis demonstrated a strong structural validity for a three-factor solution explaining 68.6% of the total variance. The three subscales demonstrated a good internal consistency with Cronbach’s alpha scores of 0.8 for each of the subscales.
Conclusion
The analysis of the 14-item German version (PCQ-G-S) showed first evidence for a strong internal consistency and structural validity for evaluating staff perceptions of the person-centredness in German nursing homes. Based on this, further investigations for scale validity of the PCQ-G versions should be carried out.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In Germany, 1.8 million people live with dementia [1] and one third of them live in a long-term care facility [2]. Worldwide, around 57.4 million people are affected, and this number will increase 152.8 million in 2050 [3]. Dementia is a clinical syndrome, characterised by cognitive, neuropsychiatric, and functional symptoms. Psychological and psychiatric changes finally lead to restrictions in daily life [4]. The care of people living with dementia is challenging for all people involved, i.e. the person living with dementia, their family members and health professionals, due to frequently occuring changed behaviour like aggression, agitation, sleep disturbances, wandering and restlessness [5].
In order to meet the complex care needs of people living with dementia, it is necessary to provide care based on patients’ individual needs [6]. Person-centredness is considered as best practice for people living with dementia and essential for high-quality long-term care for older people [7]. Person-centred care (PCC) was developed by Tom Kitwood, based on Roger’s social-psychological theory of personhood [8]. It is based on an established therapeutically relationship between the respective person and the health professional and means respect for the person, the individual’s right to self-determination, mutual respect and understanding [9]. To provide PCC, a supportive care environment is needed. This includes, for example, creating a PCC culture, implementing PCC educational programs for staff or designing health care facilities promoting PCC [10]. For this reason, some organisational conditions are necessary, e.g., PCC skills training for health professionals and creating a person-centred culture and environment. It is essential, that the organisation (e.g., the nursing home) creates conditions to enable person-centredness [11]. It becomes clear, that the implementation of PCC is very complex and this change process is time consuming [10]. In recent years, PCC has become a key indicator of quality in health care. In the course of this, numerous measurement instruments have been developed that capture person-centredness or related constructs [12].
An early developed, theoretically based and in research frequently used instrument is the Person-centred Climate Questionnaire (PCQ) [13,14,15]. The PCQ was developed based on a theoretical concept regarding supportive care settings [16], literature and a content validity analysis [13]. The original Swedish 14-item version for patients (PCQ-P) was developed and later on supplemented by another version for health care staff (PCQ-S) and family members (PCQ-F). Person-centred care concerns the patient, family and staff, why different scales are needed to address the different perspectives and to assess to what extent family members or health care staff perceive the care environment as person-centred.
The items of these versions are identical, they are answered using a six-point scale (1 = No, I disagree completely to 6 = Yes, I agree completely). Different versions only differ in their perspective. The instrument items operationalise the following subscales: a climate of safety (five items), a climate of everydayness (five items) and a climate of community (four items). All items are sum scored and scores can range from 14 (a climate not very person-centred) to 84 (a climate very person-centred) [17]. After the PCQ-S was translated into English [18], numerous further translations and psychometric evaluation studies were carried out for the Norwegian PCQ-S [19], the Chinese PCQ-S [20], and the Slovenian PCQ-S [21]. A German version of the instrument is not available so far. Therefore, we translated all three versions of the questionnaire into German language within the project “MoNoPol-Sleep - Multi-modal, non-pharmacological intervention to avoid sleep disturbances in people living in nursing home with dementia” [22] and piloted. We report the translation of the English language PCQ and the evaluation of the item distribution, internal consistency and structural validity of the translated German version based on staff ratings (PCQ-G-S) in a nursing home context.
Methods
Study design
A cross-sectional study was conducted to determine the item distribution, internal consistency and structural validity of the PCQ-G-S. The investigation of the structural validity was based on an exploratory factor analysis (principal component analysis). This methodical approach was based on the COSMIN standards for test theory studies [23]. The Ethical Committee of the German Society of Nursing Science approved the study protocol for all study centres (no. 20–016).
Setting and population
Participants were nurses and nursing assistants of the nursing homes enrolled in the MoNoPol-Sleep study (trial registration: ISRCTN36015309) during baseline assessment. Nursing homes were recruited by three regions in Germany (Lübeck: Northern Germany; Halle (Saale): Eastern Germany; Witten: Western Germany). Each region recruited eight nursing homes, first using already existing contacts. Additionally, nursing homes were recruited by means of nursing home registers, information folders, announcements in relevant nursing journals in Germany and the study website (www.monopol-sleep.de). Nursing homes were contacted via phone or email and verbally informed about the aim and content of the study. Nursing homes with at least 50 residents were eligible for inclusion. Nurses and nursing assistants were included if they were working at least three night shifts in the last three months and were contracted for at least part-time (half-a-day). Inclusion criteria and recruitment have been described in detail elsewhere [22].
Questionnaire translation
All three versions of the PCQ have been translated into German language (PCQ-G) based on four of the five steps recommended for cross-cultural adaption of measures [24] in the preparatory phase of the MoNoPol-sleep study [22]. Each step was documented in a comprehensible manner. The first stage was the forward translation, performing two independent translations from English to German by two different persons. Both translators were native German speakers with excellent English language skills. Next to the translation, it was possible to enter comments on difficulties in wording or other uncertainties. The second stage contained the synthesis of the translations. Translation results were discussed, inconsistencies were reviewed, and a final translation was agreed. Stage three comprised the back translation. The final version from stage two was back translated by two persons independently. The back-translators had English as mother tongue and excellent skills in German language. Both have been involved with translation issues in research before. Also, in this stage it was possible to enter comments on difficulties in wording or other uncertainties. In stage four an expert committee meeting was carried out. All four translators and the coordinator of the translation process (first author of this paper) were involved in this meeting. During the meeting, all versions of the questionnaire were reviewed, and discrepancies discussed until a consensus was reached. This stage was for validity checking to make sure that the translated version of the questionnaire was reflecting the same item content as the original version. After the fourth stage, the whole documentation of the translation process was sent to the author of the original PCQ, and we received permission for the accuracy of the translation. The final version of the PCQ-G is displayed in Table S1. In a final step, based on the available knowledge from the literature and the translation process, a user manual for the German language PCQ was created that is freely available to potential users [25]. We did not perform a pretest as a fifth step as recommended by Beaton et al. (2000) [24]. This was due to the restrictive protective measures for nursing homes and the enormous burden of nurses caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, which made it difficult to access nurses for a pretest at the time of the measurement translation.
Data collection procedures
The PCQ-G staff version (PCQ-G-S) was part of a 7-page questionnaire measuring nurses’ attitudes regarding the implementation of change processes, person-centredness in care and inter-professional cooperation, as part of the process evaluation in the MoNoPol-Sleep study [22]. Beside the PCQ-G-S, the questionnaire consisted demographic variables. The questionnaire was handed out by the supervising nurse. Participating nurses and nursing assistants received information about the aim and content of the study at the first page of the questionnaire. Furthermore, they received information that informed consent was provided by filling in the questionnaire. Questionnaires were returned by postal mail or personally collected by one researcher in the nursing home. In general, the application of the PCQ-G-S was based on the recommendations by the authors of the original instrument as documented in the German user manual [25].
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics were calculated for demographic characteristics and item distribution of the PCQ-G-S items. For the item distribution, the cut-off values were set at < 0.8 and > 3.2, based on the recommendations of Bortz & Döring (2006) [26].
In a second step, an explorative factor analysis was performed based on a principal component analysis (PCA). Reasons for conducting the exploratory factor analysis were: no previous knowledge of the factor structure of the PCQ-G S version and the limited sample of nurses available in the Monopol-Sleep study. In addition, the chosen procedure also corresponds to the procedures for the first psychometric evaluation in other countries ( [19,20,21].
The prerequisites for conducting a PCA were tested [27]: Measure of sample adequacy was performed with the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) criterion. The KMO should be ≥ 0.5. Additionally, the Bartlett’s test for sphericity was conducted. The common significance level of < 0.05 was used for verification of a non-existent item correlation assumed before conducted the component analysis [27]. After, the factor analysis was performed, based on a PCA using an orthogonal rotational procedure (varimax). The factor extraction followed the criteria: (1) eigenvalues > 1 for a factor (Kaiser-Guttman criterion), and (2) scree plot. Missing values were pairwise excluded. The internal consistency of the scale was evaluated by calculating Cronbach’s α coefficients [28]. Data were entered into SPSS v. 22 [29]. Plausibility checks were carried out during data entry. To ensure data quality, all data were checked by a second person.
Results
Characteristics of the sample
A total sample of 120 nurses was included in data analysis. The mean age of participants was 40.7 (SD 11.7), with an average working experience in the care of people living with dementia of 14.6 years (SD 10.1). Participants’ demographic characteristics are displayed in Table 1.
Item distribution
The descriptive investigation of the PCQ-G-S showed a balanced distribution (Table 2). The response option “yes, I agree” was used most often whereas the response option “no, I disagree completely” was used least frequently. Distributions of the other response options also varied. Based on the mean values, five items (item 4, item 11, item 12, item 13, item 14) showed a ceiling effect (> 0.8). Missing value analyses demonstrated very low percentages of missing values in general. Only item 3, 5 and 9 of the PCQ-G-S showed a percentage of missing values of 1.7% and items 2, 4, 7 and 11 a percentage of missing values of 0.8%. The reason for this was nurses’ and nursing assistants’ denial to rate.
Structural validity
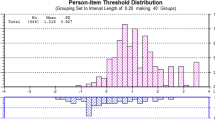
PCA was used to evaluate scale dimensionality and structural validity since Bartlett’s test of sphericity yielded X2 = 1048,911, was significant (P < 0.01) and Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin was satisfactory (0.863). This indicates the appropriateness of the factor analysis of the data. Kaiser’s eigenvalue > 1 criterion was used to decide on the number of components to extract and a component loading cut-off of 0.5 was used to conclude if an item loaded on a specific component. Based on a first exploratory PCA, three factors with a Kaiser’s eigenvalue > 1 were determined. The scree plot illustrates the result (see Fig. 1). Thus, the analysis resulted in a 3-component solution, where all 14 items could be assigned with 68.6% of the total variance. The results of the analysis including factor loads of each item are presented in Table 3.
Internal consistency
The reliability analysis using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the 14-item PCQ-G-S showed a strong internal consistency based on Cronbach’s alpha scores for each of the three subscales: “a climate of safety”: alpha = 0.845, “a climate of everydayness”: alpha = 0.877 and “a climate of community”: alpha = 0.867 (Table 3).
Discussion
The investigation of the item distribution of the PCQ-G-S demonstrated a balanced distribution of the six response options. Nine out of 14 items showed an acceptable item difficulty, but five items (item 4, 11, 12, 13, 14) showed a ceiling effect (> 0.8). However, it should not be generally indicated to cancel these items of the PCQ-G-S. Instead, it must be considered that this is an exploratory study and further evaluation of the scale validity are needed including a larger sample. Since the item distribution has not yet been examined in other studies, no comparison of the results is possible. Further research is justified needed here, because the identified ceiling effects affect all items of the subscale climate of community and 36% of all PCQ-G-S items.
The results for structural validity show that the original factor structure of the PCQ-G is robust. Similar to the original Swedish version [13], the 14 items of the PCQ-G-S could be assigned to the three subscales a climate of safety, a climate of everydayness, and a climate of community. The same instrument structure was found for the Swedish (Edvardsson et al., 2009), Norwegian [19], Slovenian [21], and Chinese [20] versions. Thus, Cai et al. (2017) found a stable three-factor solution explaining 73.3% of the total variance for the Chinese version (“a climate of safety”: 0.58 to 0.84; “a climate of everydayness”: 0.68 to 0.82”; “a climate of community”: 0.64 to 0.66), Bergland et al. (2012) reported the three-factor solution that explained nearly 68% of the variance in the data for the Norwegian version (“a climate of safety”: 0.55 to 0.84; “a climate of everydayness”: 0.49 to 0.83”; “a climate of community”: 0.62 to 0.80) and Vrbnjak et al. (2017) found a three-factor solution that explained 71.22% of the variance in the data of the Slovenian version (“a climate of safety”: 0.59 to 0.87; “a climate of everydayness”: 0.77 to 0.84”; “a climate of community”: 0.54 to 0.86). The analysis of the original Swedish version resulted in a three-factor solution explaining 60.0% of the total variance (“a climate of safety”: 0.64 to 0.79; “a climate of everydayness”: 0.57 to 0.78, “a climate of community”: 0.58–0.82) [17]. Therefore, scale dimensionality could be seen as confirmed.
Psychometric evaluation of the English PCQ-S resulted in a four-component rotated solution (a climate of safety, a climate of everydayness, a climate of community and a climate of comprehensibility) explaining 71,8% of the total variance [18]. The fourth subscale “a climate of comprehensibility” included four items, relating to the extent staff provided understandable information to patients, patients felt safe, staff were easy to talk to and where patients also had others to talk about their experiences [18]. In the original version, these four items belonged to the subscales a climate of safety and climate of community [17]. Edvardsson et al. (2010) explained the deviation from the original version with three subscales by the fact that the study evaluating the original Swedish version included a sample working on an elective surgery ward with a short length of stay. Because of limited possibility for interactions between staff and patients, the sample in this study may felt prioritising that patients understand implemented medical procedures instead of focusing on proving PCC [18].
Based on a Rasch analysis of the English PCQ-S, residual correlations greater than 0.29 than the mean correlation in the matrix were found. This indicated some evidence of local dependence between two items (item 13 “a place where it is easy for patients to talk to staff”; item 14 “a place where patients have someone to talk”) of subscale three. Since removing or combining item 13 and 14 caused other difficulties, according to Wilberforce et al. (2019) the two items were kept.
The 14-item PCQ-G-S consists of three subscales. It showed strong internal consistency for each of the three subscales a climate of safety (alpha = 0.845), a climate of everydayness (alpha = 0.877), and a climate of community (alpha = 0.867). These results are in line with the results of previous psychometric evaluations. Also, the Swedish [17], English [18], Norwegian [19], Slovenian [21] and Chinese [20] version of the PCQ-S showed internal consistency scores of at least 0.77 for each subscale. Sample sizes in previous studies were comparable to our study. Only in the study of Cai et al. (2017) included more participants (n = 1237).
Although further evaluations in other settings and with lager sample sizes are necessary, e.g. studies evaluation reliability, the PCG-G already contribute to gain a deeper understanding of the extent of person-centred care provided in German-language countries. Additionally, the psychometric properties of the family and patient version should be tested. After that, it would be possible to identify similarities and differences about person-centredness is perceived through patients, families, and staff.
Strengths and limitations
A major strength of this study is that additionally to the German version of the PCQ, a user manual for the questionnaire (PCQ-G) was developed which is now available online. Thus, an internationally proven questionnaire for the assessment of person-centredness is available for research and practice in the German-speaking countries. Moreover, this is the first study evaluating the psychometric properties of the staff version of the PCQ-G.
This study has some limitations. First, only the staff version of the PCQ-G was evaluated. This means that an evaluation of the patient and family versions is pending and recommended. Second, given the relatively small number of nurses and nursing assistants included in the study, results must be interpreted with caution and have to be proven in a larger study with a confirmatory approach for the PCQ-G-S. Third, the PCQ-G-S was only applied in nursing homes participating in the MoNoPol-Sleep study [22]. Further psychometric validation in different settings is needed to ensure generalisability and to help for further comparisons in different contexts. Fourth, we were unable to perform a pretest of the translated PCG-G-S as recommend by Beaton et al. (2000) [24], because of the restrictions and enormous burden in nursing homes during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, it is crucial to state that no relevant uncertainties regarding the understanding of the items arose in the translation process. Consequently, the decision not to pretest was pragmatic and appropriate considering the context. Moreover, the development of cut-off scores for interpretation purposes is a future goal for the PCQ-G versions.
Conclusions
The aim of this study was the translation and examination of first psychometric properties of the PCQ-G-S in a nursing home context. The results of this study indicate first evidence for the internal consistency and structural validity for the use of the PCQ-G-S to assess the degree of person-centeredness. Based on these results the questionnaire should be used in further studies to measure person-centredness in nursing homes. Therefore, the item distribution, reliability and especially the construct validity of the PCQ-G-S should be further investigated.
Data Availability
Data is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
DAlzG. Informationsblatt 1. Die Häufigkeit von Demenzerkrankungen 2020 14.12.2021]; Available from: https://www.deutsche-alzheimer.de/fileadmin/Alz/pdf/factsheets/infoblatt1_haeufigkeit_demenzerkrankungen_dalzg.pdf.
DAlzG. Zahlen zu Häufigkeit, Pflegebedarf und Versorgung Demenzkranker in Deutschland 2016 14.12.2021]; Available from: https://www.pflegeversicherung-direkt.de/_Resources/Persistent/5cd8c700bdeb89e0795b2480b1a9d99c8c1523c1/Daten-Zahlen_2016-10-von-DALZG.pdf.
GBD. 2019 Dementia Forecasting Collaborators, Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 Lancet Public Health, 2022. 7(2): p. e105-e125.
Gale SA, Acar D, Daffner KR. Dement Am J Med. 2018;131(10):1161–9.
Kales HC, Gitlin LN, Lyketsos CG. Assessment and management of behavioral and psychological symptoms of Dementia. BMJ. 2015;350:h369.
Fazio S, et al. The fundamentals of person-centered care for individuals with Dementia. Gerontologist. 2018;58(suppl1):S10–9.
Edvardsson D, Winblad B, Sandman O. Person-centred care of people with severe Alzheimer’s Disease: current status and ways forward. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(4):362–7.
Kitwood T. Dementia reconsidered: the person comes first. Berkshire, UK.: Open University Press; 1997.
McCormack B, McCance TV. Person-centred practice in nursing and Healthcare: theory and practice. London: Wiley-Blackwell; 2017.
Santana MJ et al. How to practice person-centred care: A conceptual framework 2018(1369–7625 (Electronic)).
Dichter MN et al. Organizational interventions for promoting person-centred care for people with dementia (Protocol) Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2019(7).
DeSilva D. Helping measure person-centred care: a review of evidence about commonly used approaches and tools used to help measure person-centred care. London.: The Health Foundation; 2014.
Edvardsson D, Sandman PO, Rasmussen B. Swedish language person-centred climate questionnaire - patient version: construction and psychometric evaluation. J Adv Nurs. 2008;63(3):302–9.
Xu L et al. Person-centered climate, Garden Greenery and Well-being among nursing home residents: a cross-sectional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022. 20(1).
Yang Y, et al. Resident and staff perspectives of person-centered climate in nursing homes: a cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19(1):292.
Edvardsson J, Sandman P, Rasmussen B. Sensing an atmosphere of ease: a tentative theory of supportive care settings. Scand J Caring Sci. 2005;19(4):344–53.
Edvardsson D, Sandman PO, Rasmussen B. Construction and psychometric evaluation of the Swedish language person-centred climate questionnaire - staff version. J Nurs Manag. 2009;17(7):790–5.
Edvardsson D, Koch S, Nay R. Psychometric evaluation of the English language person-centred climate questionnaire–staff version. J Nurs Manag. 2010;18(1):54–60.
Bergland Å, Kirkevold M, Edvardsson D. Psychometric properties of the Norwegian person-centred climate questionnaire from a nursing home context. Scand J Caring Sci. 2012;26(4):820–8.
Cai L, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the person-centred climate questionnaire - staff version (PCQ-S). BMJ Open. 2017;7(8):e017250.
Vrbnjak D, et al. Psychometric testing of the Slovenian person-centred climate questionnaire - staff version. J Nurs Manag. 2017;25(6):421–9.
Dichter MN, et al. Evaluation of a multi-component, non-pharmacological intervention to prevent and reduce sleep disturbances in people with Dementia living in nursing homes (MoNoPol-sleep): study protocol for a cluster-randomized exploratory trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):40.
Mokkink LB, et al. COSMIN Risk of Bias tool to assess the quality of studies on reliability or measurement error of outcome measurement instruments: a Delphi study. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20(1):293.
Beaton DE, et al. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(24):3186–91.
Wilfling D et al. Person-Centered Climate Questionnaire – German version (PCQ-G). Benutzerhandbuch für die deutschsprachige Version 2022, Köln.
Bortz J, Döring N. Forschungsmethoden und Evaluation: für Human- und Sozialwissenschaftler Vol. 4. überarb. Auflage. 2006, Heidelberg.: Springer.
Field A, Miles J, Field Z. Discovering Statistics Using R 2012, London: SAGE Publication Ltd.
Polit DF. Statistics and Data Analysis for Nursing Research. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall; 2014.
IBM. IBM SPSS statistics for windows. Armonk: IBM Corp; 2013.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all staff nurses, nursing assistants and nursing home managers who participated in the study.
Funding
This study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF grants 01GL1802A-C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study Concept and Design: DW, RM, AB, JD, NB, TK, GM, MH, SK, MND. Data Analysis and Interpretation: DW, RM, AB, JD, NB, TK, GM, MH, SK, MND. Drafting the Manuscript: DW, RM, AB, JD, NB, TK, GM, MH, SK, MND.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was received from the ethics committee of the German Society of Nursing Science (no. 20–016). This study was performed in accordance with the relevant regulations and guidelines. All participants provided informed consent.
Consent of publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wilfling, D., Möhler, R., Berg, A. et al. Item distribution, internal consistency and structural validity of the German language person-centred climate questionnaire - staff version (PCQ-G-S): a cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr 24, 57 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04528-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04528-3