Abstract
Background
We aimed to propose a correction of the Lawton instrumental activity of daily living (IADL) score to take into account the possibility to have never done some activities, and measured its agreement and reliability with the usual IADL score.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted in outpatients attending French memory clinics between 2014 and 2017. Lawton IADL, cognitive performance, diagnosis, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and sociodemographics characteristics were collected. A corrected IADL was calculated and its agreement with the usual IADL was assessed.
Results
The study included of 2391 patients (79.9 years old, 61.7% female). Based on the usual IADL, 36.9% of patients had never carried out at least one of the activities. This proportion reached 68.8% for men and 17.7% for women. Women had a mean IADL higher than men: 4.72 vs 3.49, this difference decreased when considering the corrected IADL: 4.82 vs 4.26 respectively. Based on Bland-Altman method, 93.5% of observations lied within the limits agreement. The ICC between the 2 scores was 0.98. The relationships between patients’ characteristics and the IADL scores were similar, regardless the usual or corrected version.
Conclusions
This corrected IADL score had an excellent degree of agreement with the usual version based the ICC. This simple correction could benefit both for the clinical practice by providing a more accurate description of the real clinical state of the patients allowing to manage them more precisely, and for research involving the evaluation of the functional abilities of patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Alzheimer’s disease or related disorders are a main cause of functional decline, and the diagnosis of major neurocognitive stage is defined as a significant cognitive decline which interfere with independence in activities of daily living, as presented in the Diagnosis and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM-V) criteria [1]. Functional decline in older adults leads to institutionalization and increased health-care costs, as well as shifting many daily responsibilities to caregivers and increasing their burden [2,3,4,5]. The accuracy of the functional abilities assessment is therefore one of the key features in the diagnosis of neurocognitive disorders and their change, as well as in research studies which aim to assess the effect of interventions to delay functional decline [6, 7]. Among the several scales available to measure the level of functional abilities, and in the current lack of consensus, the Lawton Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL) scale has been widely adopted, and is usually part of the evaluation in clinical practice in the memory centers in France [8, 9]. The Lawton IADL scale was developed to assess more complex abilities of daily living necessary for living independently in the community, there are nevertheless a few information on its psychometric proprieties [8, 10]. Additionally, the original Lawton IADL scale displays some limits since it does not take into account the possibility to have never done one or several assessed activities, which lead to potentially underestimate the overall patient’s functional level. In this case, the total score could lack of precision because it does not capture the real abilities of the patient. This issue is particularly noticeable when comparing IADL scores between men and women, considering that some tasks are more representative of men or women activities, as previously mentioned [11, 12]. Consequently, previous studies have proposed to differentiate the calculation of the score between men and women, or to calculate the score by using only some items (3, 4 or 5 depending on the study) of the IADL questionnaire less dependent of gender or more related to the risk of dementia or cognitive disorders, nevertheless, the reliability of such new scales has not been formally tested, and the choice of item varies between studies making comparison difficult [8, 9, 12,13,14]. Conversely, others publications have recommended to rate all items without differentiation for both genders [15, 16]. Given the different situations, it still appears complicate to decide how the Lawton IADL should be used in clinical practice as well as in research studies.
In this study, we propose a corrected score for IADL on a 8-point scale which includes the possibility that an activity was never carried out by an individual. The objectives of this article were to assess the relevance of the proposed corrected score and to measure the degree of agreement between the usual IADL score and its corrected version.
Methods
Study population and setting
The study population was selected from the observational multicenter MEMORA cohort including successive outpatients visiting memory centers of the Clinical and Research Memory Centre of Lyon (CMRR) (Trial registration: NCT02302482, registered 27 November 2014) [17]. The study sample included patients having undergone a medical examination between 2014 and 2017. The inclusion criteria were a subjective cognitive complaint, either expressed by the patient or one of its relative, at all stage of cognitive impairment, with or without a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease or Related Diseases (ADRD), and having an evaluation of the IADL score. Non-inclusion criteria were an opposition to participate to the study, nursing home living, being under legal protection, or health conditions that do not allow carrying out clinical examinations based on questionnaires.
In terms of ethical and legal considerations, information has been individually provided to the patients and their informal caregivers at inclusion. They can oppose their participation in the research. The authorization for handling personal data has been granted by the national data protection commission.
Usual and corrected IADL score
Functional abilities level was assessed using the Lawton IADL scale, which assesses 8 instrumental activities through 8 questions: ability to make telephone calls, to go grocery shopping, to prepare meals, to do housekeeping, to do laundry, to use transportation, to take medications, and to handle finances [8]. The IADL score corresponds to the sum of the binary answers at each question and varies from 0 (dependence) to 8 (autonomy). An additional answer “has never done” was added for each item of the IADL questionnaire to account for situation where a patient is not concerned by an activity.
A corrected IADL (C-IADL) was calculated in order to take into account the cases of patients who had never carried out one or more assessed abilities. C-IADL was given by the following formula:
where a corresponds to the number of activities never carried out in its life. Note that in the context of outpatient, it has been considered that everybody has used transport previously in its life. Consequently, a was only calculated on the 7 remaining activities, so that the denominator 8 − a could never be null. If a patient has never been concerned with laundry for instance, but presented autonomy on the 7 remaining activities, this patient had an usual IADL score equal to 7 on a 8-point scale and a C-IADL equal to 8 on a 8-point scale. This choice does not preclude measuring disability in this item since there is a possibility to answer “does not travel at all” or “Travel limited to taxi or automobile with assistance of another”.
Other covariates
The collection of sociodemographic characteristics included age, gender, marital status (single, married/in couple, divorced/separated, widowed, unspecified), educational level (nil, primary, secondary, tertiary) and lifestyle (at home with spouse, at home with relatives, at home alone with relatives in the neighborhood, at home alone without relatives in the neighborhood, other lifestyle). Global cognition was assessed using the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), a brief cognitive screening instrument [18]. The MMSE yields to a single cognitive function score ranging from 0 (severe cognitive impairment) to 30 (no impairment). The diagnosis stage and etiologies were established by specialists (neurologist, geriatrician, or psychiatrist). The diagnosis stage of mild or major neurocognitive disorders (NCD) was identified using the DSM-V nomenclature [1]. The etiologies were identified as follows: Alzheimer’s disease (AD), AD with cerebrovascular component, cognitive disorders of vascular origin, Lewy body disease, frontotemporal degeneration, Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s syndroma, psychiatric disorders, other disorders, and no trouble.
The neuropsychiatric symptoms were assessed using the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) [19]. The NPI assesses 12 psychiatric or behavioral disturbances i.e. delusions, hallucinations, depression, agitation, anxiety, apathy, disinhibition, irritability, euphoria, aberrant motor behaviors, sleep disorders, and eating disorders. The total score ranges from 1 to 144 (more severe symptoms).
Statistical analysis
Missing data were handled using the MICE method (Multivariate Imputations by Chained Equations) for marital status (5.6% of missing values), education (14.9%), lifestyle (0.1%), MMSE score (8.8%), and NPI score (17.8%) [20]. The IADL and C-IADL scores and all the above cited covariates were introduced in the imputation model.
Population characteristics were reported using the mean value and 95% CI for numeric variables, or counts and frequency for categorical variables. Mean values of usual IADL and C-IADL were described for each level of categorical covariates. The relationships between means of IADL or C-IADL and each variable were assessed using one-way ANOVA. The proportion of patients never concerned by one or several item of IADL was also reported overall and according to gender.
The Bland–Altman method was used to measure agreement between the usual IADL and C-IADL [21]. The first step of this method was to plot the difference between the two scores against their mean. The second step consisted in estimating the mean difference \( \overline{d} \) and the standard deviation of the differences s in order to calculate the 95% limits of agreement, \( \overline{d}-1.96\ s \) and \( \overline{d}+1.96\ s \). If the differences are normally distributed, 95% of differences will lie between these limits. The agreement rate, i.e. the proportion of differences between the 95% limits of agreement was also calculated. This analyze was carried out in the overall sample and was also stratified by gender and diagnosis stage. The intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) (“two-way mixed effects, absolute agreement, multiple raters/measurement”) was computed for the whole sample, by gender and diagnosis stage. The ICC was interpreted as poor agreement if ICC < 0.5: poor, moderate agreement if ICC is between 0.5 and 0.75, good agreement if ICC is between 75 and 0.9, and excellent agreement if ICC ≥0.9 [22, 23]. A multivariate logistic regression was performed to assess whether the characteristics of the patients i.e. age, gender, marital status, education, lifestyle, MMSE score, diagnosis stage, etiology stage, and NPI, may impact the agreement between the 2 scales. The outcome was a binary variable equal to 1 if the difference between the two scores lied between the 95% limits of agreement, 0 otherwise. A backward stepwise method was used to select significant variables. Adjusted Odds-ratios (OR), 95% CI and p value were reported.
Finally, multivariate linear regressions were performed to determine whether the same covariates explained the IADL and C-IADL scores, with similar effects. Two models were performed using alternatively the usual IADL and the C-IADL as dependent variable. Regression coefficients (b), standard error (SE) and p-value were reported.
A p-value < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant and all tests were bilateral. Analyses were performed using R software (version 3.5.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
Characteristics of the study sample
The study population included 2391 patients, with a mean age of 79.9 (95% CI [79.6–80.2]) (Table 1). There was a majority of women (61.7%), 54.2% of the patients were married or in couple, while 31% were widowed; 53% of the patients lived at home with spouse, while 28.6% lived at home alone with their relatives in the neighborhood. Regarding medical conditions, the mean MMSE was 20.2 (95%CI = [19.2–20.4]) and 41.1% of the patients had a MMSE score inferior to 20. Patients with major neurocognitive disorders represented 40.8% of the population study and 42.2% of patients were concerned with ADRD. The mean NPI score was 17.4 (95%CI = [16.7–18.0]).
Distribution of IADL and C-IADL according other covariates
Overall, the mean IADL and the mean C-IADL were 4.25 and 4.61, respectively. Women had a mean IADL higher than men: 4.72 vs 3.49. This difference between women and men decreased when considering the mean C-IADL: 4.82 vs 4.26. The mean IADL was also higher for single or widowed compared to married/in couple patients: 5.39 and 5.17 respectively, vs 3.87. This difference between single, widowed and married patients decreased when considering the mean C-IADL: 5.47, 5.26, and 4.45, respectively. The usual IADL and the C-IADL scores increased with the educational level. The functional autonomy increased with the MMSE score, and the two mean scores IADL and C-IADL were lower for patients with major cognitive disorders and/or with ADRD.
Gender disparities on instrumental daily living activities
On the overall study population, 36.9% of patients had never carried out at least one activity (Table 2). This proportion was different according to gender: more men had never carried out at least one activity (68.8%) compared to women (17%). Regarding the detailed item of IADL, the higher differences between men and women were for the item “has never done their laundry”, with a large difference between men (61.4%) and women (0.6%), “has never prepared meals” (33.1% vs. 0.3% respectively), and “has never done housekeeping” (25.9% vs. 0.2% respectively). Disparities were less pronounced for the other activities.
Agreement measurement between the two scores
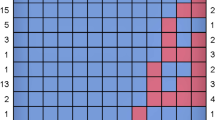
With the Bland-Altman analysis, the mean difference between the two scores (IADL and C-IADL) was − 0.35 (SD = 0.7) (Table 3). Overall, 93.5% of observations lied within the 95% limits of agreement [− 1.72–1.01]. The observations which were outside the limits interval had a mean ranging from 3 to 7 (Fig. 1). The difference between the two scores tended to get larger as the mean increased. In the stratified analysis by gender, the mean difference was larger in women (− 0.77, SD = 0.9) than women (− 0.1, SD = 0.3). Almost 95% of the observations for male lied within the 95% limits of agreement compared to 93% of the observations for women, nevertheless the limits of agreement for men were larger than those for women. In the stratified analysis by diagnosis stages, the difference between the two methods also increased with the mean increase, and proportion from 93 to 100% of observations lied within the 95% limits of agreement depending of the diagnosis stages.
The ICC analysis showed a coefficient at 0.98 indicating an excellent agreement between the 2 scores. In the stratified analyses by gender and diagnosis staged, the ICC ranged from 0.93 to 0.99 depending on the groups.
Sensitivity of agreement to patients’ characteristics
In the multivariate logistic regression model, female gender, living at home with spouse or at home alone with their relatives in the neighborhood, as well as major neurocognitive disorders were mutually associated with increased chance to be within the limits agreement (Table 4). The variables of age, marital status, educational level, MMSE, NPI and etiology did not contribute significantly and were excluded of the model.
Relationships between patients’ characteristics and functional level assessed with both scores
Results of the two multivariate linear regressions showed similar relationships between patients’ characteristics and the functional level measured either with the usual IADL or C-IADL, excepted for the gender i.e. the estimated effect associated to women was lower in comparison to male when modelling C-IADL (b = 0.55, SE = 0.02) than the estimated effect when modelling the usual IADL score (b = 1.09 SE = 0.09) (Table 5).
Discussion
In this large study population, we found that the corrected IADL score had an excellent degree of agreement with the usual IADL score based on an ICC equal to 0.98, while Bland and Altman method showed that 93.5% of observations lied within the 95% limits of agreement. The level of agreement between the usual IADL and the corrected IADL varies little according to gender and diagnosis stage. This study also showed that 36.9% of patients had never carried out at least one of the seven abilities evaluated in the IADL questionnaire (transportation being always at least carried out once), and large disparities were observable between gender, justifying the need to adjust the IADL score calculation to ensure its clinical relevance. Analyses by item of the IADL scores also highlighted that, in this study population, men were less frequently concerned by some abilities such as doing laundry, preparing meals and doing housekeeping compared to men. The proposed correction of the IADL score showed a reduction to the difference of the global score between men and women and provides a more accurate reflection of reality: a patient who has never carried out an ability being count has if he/she did not have this ability in the usual IADL score, which leads to a possible underestimation of the level of overall functional autonomy. Another interesting finding is that the same factors were related to the two IADL scores, the direction and the magnitude of the estimated effects being quite similar.
Strengths and weaknesses of the study
To our knowledge, this study is the first to provide a simple and intuitive correction of the usual IADL that ensures the real clinical state of the patient. This correction scored is easy to calculate in clinical setting and for research purpose and would simply imply the adding of the answer “has never done” at each item of the IADL questionnaire. As the corrected IADL score is scored on 8 points for all the patients, as the usual score, this facilitates its interpretation from a patient to another for both physicians and research: patients with an identical IADL score might not be at the same functional level depending on whether this score was calculated with the answer to the 8 questions or less. Another strength of the study is the evaluation of the corrected score in the context of current practice in a large population of patients at all stages of NCD or with subjective cognitive complaint which allows to expand the scope of these results. This analysis was able to take into account a wide range of patients’ characteristics which could be related with the degree of agreement between the two scores.
In this study, the proportion of observations within the limits agreement was slightly inferior to 95% which is the threshold that was recommended by Bland and Altman to consider that two measures are commutable. The Bland and Altman plot also shows a negative bias. The question that may arise is whether this correction could not overestimate the functional abilities if we consider that patients who have never done some of the activities could have lower functional level compared to those who have already done them. There is no evidence that a patient who has never done an activity would be able to do it if he/she had to do it. Thus, we hypothesize that the fact to have never done some of the activities could be related to individual preferences or living habits (a person living in couple with another person who accomplishes the task). This hypothesis is supported by additional analyses of our data. For example, proportions of men who had never done these activities were higher when they lived with someone compared to when they lived alone: 40.3% of men living with someone had never prepared meals vs. 6.8% in men living alone, respectively 30.3% vs. 8.3% for having never done housekeeping. Furthermore, the comparison of the cognitive performance (MMSE) between patients who had never prepared meals or who had never done housekeeping with patients who had already done these activities showed that both groups had similar cognitive performance (respective p values for difference p = 0.2 and p = 0.5) (detailed results now shown). In contrast, patients who were unable to perform these tasks were much more cognitively impaired than those who had never done it (p values for difference p < 0.0001 for meals preparation and housekeeping). Thus, one possible explanation of the negative bias observed in the Bland and Altman plot is that the estimation of the functional abilities level with the usual IADL is precisely affected by a systematic bias measurement due to gender difference. The corrected IADL could then allow correcting this bias.
The present study was conducted in a population of older adults attending a memory center; their characteristics are different from the general population with higher proportion of patients with neurocognitive disorders and functional limitations, studies conducted in others populations would therefore be needed to assess the relevance of the proposed corrected score in different contexts.
Comparison with the literature
Our findings are consistent with previous studies which have observed item response bias and in particular gender bias in the Lawton IADL scale, the overall score could reflect in some cases more a living context than real functional limitations [8, 11, 24,25,26]. Besides, in Hesseberg et al. the difference between gender was only found for the item “laundry” [27]. Though, there is still a lack of a standard way of measurement of the IADL, and while some tasks appear more specific for women, they can also concern men and excluding some of them in routine care could constitute an a priori subjective judgment that could interfere with the results. Our findings highlighting similar relationships between the patients’ characteristics and the usual IADL score, and the corrected IADL score confirm and extend the results of previous studies conducted in community-dwelling study population, or which used only a limited selection of items included in the IADL questionnaire [14, 28, 29]. In terms of patient’s characteristics, our study sample differed slightly to the larger sample of the French National Alzheimer (BNA) database registers in memory centers in France (mean age 79.9 years old vs. 77.4 to 81.3 in the BNA depending on the selection; 62% of women vs. 63.2 to 70.6% in the BNA; 29.6% of patients with probable AD vs. 27.3 to 29.9% in the BNA, mean MMSE 20.2 vs. 16.8 to 25.7 in the BNA) [28, 30].
Conclusions
This study proposes a simple correction of the usual IADL score which has an excellent reliability, and allows to take into account the possibility that patients have never done one or several assessed activities. As the Lawton IADL is often used to evaluate the diagnosis stage of the neurocognitive disorders of patients in memory centers, this corrected version could benefit both for the clinical practice by providing a more accurate description of the real clinical state of the patients allowing to manage them more precisely, and for research involving the evaluation of the functional abilities of patients such as those assessing the efficacy of interventions on the limitation of functional loss. Additional researches should be performed to confirm these results in others populations and to assess the sensibility to change of the corrected score.
Availability of data and materials
The study dataset cannot be publicly available due to regulations and agreements obtained to perform the MEMORA study. Data requests can be submitted to the researchers at the Memory Research Centre of Lyon (CMRR of Lyon, Charpennes Hospital, University Hospital of Lyon, Villeurbanne, France).
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ADRD:
-
Alzheimer’s Disease or Related Diseases
- DSM-V:
-
Diagnosis and Statistical Manual of mental disorders criteria
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- IADL:
-
instrumental activity of daily living
- MICE:
-
Multivariate Imputations by Chained Equations
- MMSE:
-
Mini-Mental State Examination
- NCD:
-
Neurocognitive disorders
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Dufournet M, Dauphinot V, Moutet C, Verdurand M, Delphin-Combe F, Krolak-Salmon P. Impact of cognitive, functional, behavioral disorders, and caregiver burden on the risk of nursing home placement. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;S1525-8610:30322–6.
Dauphinot V, Delphin-Combe F, Mouchoux C, et al. Risk factors of caregiver burden among patients with Alzheimer’s disease or related disorders: a cross-sectional study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;44:907–16.
Eska K, Graessel E, Donath C, Schwarzkopf L, Lauterberg J, Holle R. Predictors of institutionalization of dementia patients in mild and moderate stages: a 4-year prospective analysis. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord Extra. 2013;3:426–45.
Gustavsson A, Brinck P, Bergvall N, et al. Predictors of costs of care in Alzheimer’s disease: a multinational sample of 1222 patients. Alzheimer Dement. 2011;7:318–27.
Callahan CM, Boustani MA, Schmid AA, et al. Targeting functional decline in Alzheimer disease: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:164–71.
Vellas B, Andrieu S, Sampaio C, Caley N, Wilcock G. Endpoints for trials in Alzheimer’s disease: a European task force consensus. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:436–50.
Lawton M, Brody E. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9:179–86.
Barberger-Gateau P, Commenges D, Gagnon M, Letenneur L, Sauvel C, Dartigues JF. Instrumental activities of daily living as a screening tool for cognitive impairment and dementia in elderly community dwellers. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992;40:1129–34.
Graf C. The Lawton instrumental activities of daily living scale. Am J Nurs. 2008;108:52–62.
Niti M, Nq TP, Chiam PC, Kua EH. Item response bias was present in instrumental activity of daily living scale in Asian older adults. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:366–74.
Cromwell DA, Eager K, Poulos RG. The performance of instrumental activities of daily living scale in screening for cognitive impairment in elderly community residents. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56:131–7.
Pérès K, Chrysostome V, Fabrigoule C, Orgogozo JM, Dartigues JF, Barberger-Gateau P. Restriction in complex activities of daily living in MCI: impact on outcome. Neurology. 2006;67:461–6.
Barberger-Gateau P, Dartigues JF, Letenneur L. Four instrumental activities of daily living score as a predictor of one-year incident dementia. Age Ageing. 1993;22:457–63.
Lawton MP, Moss M, Fulcomer M, Kleban MH. Multi-level assessment instrument manual for full-lenght MAI. North Wales: Polisher Research Institute, Madlyn and Leonard Abramson Center for Jewish Life; 2003.
Lawton MP, Moss M, Fulcomer M, Kleban MH. A research and service oriented multilevel assessment instrument. J Gerontol. 1982;37:91–9.
Dauphinot V, Moutet C, Rouch I, et al. A multicenter cohort study to investigate the factors associated with functional autonomy change in patients with cognitive complaint or neurocognitive disorders: the MEMORA study protocol. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19:191.
Folstein M, Folstein S. Mini-mental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive stade of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12:189–98.
Cummings JL, Mega M, Geay K, Rosenberg-Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J. The neuropsychiatric inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology. 1994;44:2308–14.
Zhang Z. Multiple imputation with multivariate imputation by chained equation (MICE) package. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4:30.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–10.
Koo TK, Li MY. A guideline of selecting and reporting Intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15:155–63.
McGraw KO, Wong SP. Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychol Methods. 1996;1:30–46.
Ward G, Jagger C, Harper W. A review of instrumental ADL assessments for use with elderly people. Rev Clin Gerontol. 1998;8:65–71.
Allen SM, Mor V, Raveis V, Houts P. Measurement of need for assistance with daily activities: quantifying the influence of gender role. J Gerontol. 1993;48:S204–11.
Scheel-Hincke L, Möller S, Lindhal-Jacobsen R, Jeune B, Ahrenfeldt LJ. Cross-national comparison of sex differences in ADL and IADL in Europe: findings from SHARE. Eur J Ageing. 2019;17:69–79.
Hesseberg K, Bentzen H, Ranhoff AH, Engedal K, Bergland A. Disability in instrumental activities of daily living in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2013;36:146–53.
Le Duff F, Develay AE, Quetel J, et al. The 2008-2012 French Alzheimer plan: description of the National Alzheimer Information System. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;29:891–902.
Connolly D, Garvey J, McKee G. Factors associated with ADL/IADL disability in community dwelling older adults in the Irish longitudinal study on ageing (TILDA). Disabil Rehabil. 2017;39:809–16.
Tifratene K, Duff F, Pradier C, et al. Use of drug treatments for Alzheimer’s disease in France: a study on a national level based on the National Alzheimer’s data Bank (Banque Nationale Alzheimer). Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21:1005–12.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the specialist physicians of the geriatric and memory centers who contribute to inclusion of patients in the study, and the memory center of Charpennes Hospital and the Dugougon Hospital for their contribution to data collection.
Funding
The MEMORA study is supported by a grant of the MSD Avenir fund. This funding body enabled the funding of a researcher and nurses to carry out the research and the questionnaires; it had no role in the design of the study, the collection, the analysis, the interpretation and the writing in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
All authors have read and approved the manuscript. The corresponding and senior authors had full access to all the data and shared final responsibility for the decision to submit the paper for publication. MD, VD and PKS participated to the conception and the design of the study. CM, FDC, PKS, VD participated to the inclusion of the patients and the data collection. MD, VD and SA conducted data management and data analysis. MD, PKS, VD interpreted the results and drafted this manuscript. MD, CM, FDC, PKS, SA, VD critically revised this manuscript. PKS and VD conceived the research idea and are responsible for the data.
Authors’ information
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approvals were obtained with three committees as required in France: the Committee for the protection of persons concerned (CPP) on July 29, 2014, the Advisory Committee on Information Processing in Material Research in the Field of Health, and the National Commission for Data Protection and Liberties (CNIL). Witten information was provided to participants and oral consent had to be obtained to participate, as required by the French committee for this type of non-interventional study. The study enrolment began in November 2014. The study enrolment began in November 2014.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Dufournet, M., Moutet, C., Achi, S. et al. Proposition of a corrected measure of the Lawton instrumental activities of daily living score. BMC Geriatr 21, 39 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01995-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01995-w