Abstract
Background
Pain-related fear-avoidance (FA) is a common problem affecting many patients with painful medical conditions. As there is great interest in the clinical importance of the relationship between FA and disability, several questionnaires have been developed to measure FA. The Fear-Avoidance Components Scale (FACS) is a recently developed patient-reported instrument that addresses critical issues not previously considered in previous FA-related questionnaires. The original English version of the FACS demonstrated good reliability, internal consistency, and construct, criterion, and predictive validity. Two factors were determined: General Fear Avoidance and Types of Activities That are Avoided. The aim of this study was to to translate the FACS into European-style Spanish (FACS-Sp), and validate its psychometric properties.
Methods
This two-stage psychometric study included 330 subjects with various chronic musculoskeletal pain disorders. An initial translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the FACS, from English to Spanish, was performed. Then, critical psychometric properties were analysed, including internal consistency by Cronbach’s α coefficients, structural validity from the Maximum Likelihood Extraction (MLE), and convergent validity by Pearson correlation with the Central Sensitization Inventory (CSI).
Results
This study reports for the first time the psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the FACS. Total scores ranged from 0 to 88 points, with a mean of 30.49 (±17.18). The FACS-Sp showed a high internal consistency for factor 1 (α = 0.902) and factor 2 (α = 0.88). Factor structure was two-dimensional and supported structural validity, accounting for 48.75% of the total variance. Convergent validity analysis found a significant Pearson correlation r = 0.414.
Conclusion
This study reports for the first time the psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the FACS-Sp. Psychometric properties supported the validation of FACS-Sp and ensured the conceptual equivalence with the original English version. In primary care and chronic pain rehabilitation, FA assessment is crucial for clinical decision-making and treatment guidance. The FACS-Sp offers a new measure of FA in Spanish speaking populations. Future research on the FACS-Sp should evaluate test-retest reliability, treatment responsiveness and psychometric comparisons with other translated versions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Primary care has traditionally functioned within a biomedical model, which only considers the physical components of illness, and has tended to disregard psychosocial components [1]. One of the most influential models to explain psychological factors of pain is the fear-avoidance model [2]. Pain-related fear-avoidance (FA) is a common problem affecting patients with painful medical conditions. The relationship between pain and fear was first introduced in 1983 by Lethem et al. [2]. According to this FA model, after an injury, patients can respond to fear by confrontation or avoidance. Fear of pain and avoidance of activities can result in desynchronization of the actual sensory component of pain. An updated FA model that incorporated cognitive behavioral components was introduced in 1995 by Vlaeyen et al. [3]. Since then, the FA model has been corroborated and refined, explaining that if an experienced pain (with or without associated injury) is understood as a threat, and the patient begins to catastrophize, then pain-related fear can evolve, leading to avoidance of activities, hypervigilance, depression, physical disuse, deconditioning, and disability [4,5,6].
As there is great interest in the clinical importance of the relationship between pain-related FA and disability, several questionnaires have been developed to measure FA [7]. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMS) [8, 9] are used to assess a patient’s symptoms and/or functional status at a specific time. Although PROMS data are subjective, they can help health care providers understand the patient’s subjective experiences, how a condition or disease influences a patient’s capabilities, and detect changes due to an intervention [10]. In the case of FA, several notable questionnaires have been published: the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK) [11], Pain Anxiety Symptoms Scale (PASS) [12], Pain Catastrophizing Scale (PCS) [13], and Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire (FABQ) [14] among them. However, their construct validity has been criticized and very little support has been provided for treatment responsiveness [2]. Until recently, only the PASS and the TSK have cut-off scores available for clinical interpretation [7, 15]. In addition, their original versions were developed before the current FA model was fully developed, so none of them assesses all cognitive, emotional, and behavioral components of the model.
Recently, the Fear-Avoidance Components Scale (FACS) was developed, which incorporates important components of previous FA-related measures, and includes components of the FA model not previously considered in the earlier-developed questionnaires, within a framework of the most current FA model of Vlaeyen [6, 16]. The FACS has demonstrated acceptable test/retest reliability (r = .90–.94) and internal consistency (Cronbach α = .92). The original English version, and other translated versions of the FACS, are available at https://www.pridedallas.com/questionnaires/.
It is estimated that 14% of Europeans speak Spanish, which is about 50 million people [17]. Spanish versions of the TSK [18], PCS [19] and FABQ [20] are currently available, and there has recently been great deal of interest in using these instruments to assess components of pain-related FA among Spanish-speaking populations with chronic pain conditions, such as chronic migraine, temporomandibular disorders [21], knee and hip osteoarthritis [22] and chronic pelvic pain [23]. However, there is no published Spanish version of FACS. Hence, the goal of the present study was to translate the FACS into European-style Spanish (FACS-Sp), and validate its psychometric properties for its clinical use with native Spanish-speakers in Spain.
Methods
Design
This cross-sectional study was conducted in two stages. First, an initial translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the FACS, from English to Spanish, was performed. Secondly, for evaluation of the FACS-Sp’s critical psychometric properties, patient volunteers from a physical therapy outpatient clinic were used.
Psychometric properties were assessed according to the “COnsensus-based Standards for the Selection of health status Measurement INstruments” COSMIN guidelines [24]. Reliability, internal consistency, construct validity (cross-cultural and structural validity), and construct validity, in terms of convergent validity, were evaluated.
Cross-cultural translation process
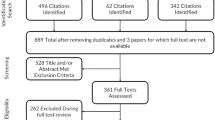
An English–to-Spanish translation was carried out to ensure conceptual equivalence of all of the test items, while maintaining appropriate Spanish cultural linguistic qualities. For this purpose, a direct- and reverse-translation methodology was utilized, with the help of a specialist in the field, as recommended in the literature [25]. For this purpose, two independent English-to-Spanish translations were made by two separate translators (CRJ and DPC authors). This process produced two Spanish versions of the FACS-Sp. After discussion among the two participants, a single FACS-Sp version was reached. Then, a backward Spanish-to-English translation was agreed-upon by two blinded and independent professional Spanish translators, who were not familiar with the concept of the questionnaire and who did not know the original document. This back translation was compared to the original version by a native English Speaker to ensure conceptual and semantic equivalence between the two versions. This pre-final version was evaluated by 25 patients for readability. This process is summarized in Fig. 1.
Participants, setting and procedure
A total of 330 volunteers with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Disorders (CMPDs) were recruited consecutively from the community-based Physiotherapy Program at the Malaga University. Demographic variables of the subject sample can be found in Table 1. Subjects suffering from back, joint pain, and musculoskeletal diseases were included. Medical diagnoses were made by a physician at once of two primary care centers in Torremolinos, Malaga, Spanish National Health Service. Patients were excluded if they were aged < 18 years old, had poor Spanish language comprehension as required for the completion of the questionnaire, or suffered from any cognitive impairment. All subjects signed an informed consent to participate. All eligible participants filled out the FACS-Sp and the Spanish version of the Central Sensitization Inventory (CSI-Sp) [26].
Patient-reported outcome measures
The FACS contains 20 separate items that are scored from 0 (“completely disagree”) to 5 (“completely agree”), with a total possible score of 100. Five severity levels are available for clinical interpretation: subclinical (0–20), mild (21–40), moderate (41–60), severe (61–80), and extreme (81–100) [16].
The CSI-Sp assesses 25 health-related symptoms common to Central Sensitization Syndromes (CSS). It contains 25 items that are scored from 0 (“never”) to 4 (“always”), with a total possible score of 100. The CSI-Sp has high internal consistency (α = 0.872) and test-retest reliability (r = 0.91) [27].
Statistical methods
Normality of the distribution of data was determined by one-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (significance < 0.05) for descriptive variables. Means and standard deviations of anthropometric variables were extracted for descriptive analyses.
Structural validity
Factor structure was calculated from the Maximum Likelihood Extraction (MLE) by varimax rotation. Requirements for factor extraction as proposed in the literature [28], included Eigen value > 1.0 and accounting for > 10% of variance. A cutoff point of 0.32 item loading was considered the minimum load per item, according to Tabachnick and Fidell [29]. A minimum ratio of five participants-per-item was required, as detailed in the literature [28].
Convergent validity
Convergent validity was calculated with Pearson correlation coefficients by P values (r,p) with the CSI-Sp. Along with FA, Central Sensitization is often present in individuals with CMPDs [30,31,32]. Therefore, the hypothesis was that the FACS-Sp would be positively correlated with CSI-Sp.
Reliability
Internal consistency was obtained by Cronbach’s α coefficients at an anticipated value range of 0.80–0.95 [33, 34] for each factor, and ranges were expressed by Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC 95%).
All statistical analyses were conducted using the Statistical Package for Social Science version 21.0 (SPSS 21.0) for Windows. Ethical clearance was approved by the Tribunal of Review of Human Subjects at the University of Malaga.
Results
Cross-cultural translation
The final Spanish version of FACS is shown in Additional file 1. Though most of the FACS-Sp items were translated without language difficulties or other conceptual misunderstanding, some items led to difficulties in translation. For example, the term “bad” employed in item 6, could be traduced like “malo” in Spanish, which implies and negative connotation. Therefore, the term “intense” fitted better than “strong” when describing pain. This translation was used to facilitate understating for patients. Difficulties were solved easily by consensus between the translators. The pre-final version was tested in 25 patients without any difficulty, so the pre-final version format was finally kept as FACS-Sp final version, and sample recruitment continued.
Score distribution
No missing responses were found in the data collection. FACS-Sp scores ranged from 0 to 88 points, with a mean of 30.49 (±17.18). FACS severity level subgroups are displayed in Table 1.
Structural validity
It was determined that the correlation matrix was adequate for the Maximum Likelihood Extraction from the results observed in Kaiser–Meyer–Oklin values (0.900) and the Bartlett’s test of sphericity (Chi-squared value =3259.568 and df 190, p < 0.001). Maximum Likelihood Extraction detected four components with Eigenvalues above 1, explaining 39.68, 11.57, 7.25, and 5.12% of the variance, respectively. The last two factors, however, accounted for less than 10% of the total variance, so they did not completed requirements for factor extraction, according to established methodology. Hence, a two factor solution was extracted according to the established criteria, explaining 48.75% of total variance. Table 2 shows each item loading on both extracted factors. It can be observed as load index values in factor 1 ranged from 0.081 in item 17 to 0.816 in item 8. In factor 2, values ranged from 0.848 in item 18 to 0.064 in item 1. Items 10, 14 and 20 cross-loaded on both factors. The Goodness-of-fit test revealed a Chi square of 685.027 (p < 0.000) after analysis.
Convergent validity
The Pearson correlation for the FACS and CSI questionnaires was r = 0.414 (p < 0.001) in the total sample of 315 participants.
Reliability
The FACS-Sp showed a high degree of internal consistency, as illustrated by the high.
Cronbach value α = 0.902 (ICC = 0.850–0.95) in factor #1 and α = 0.808 (ICC = 0.775–0.837) in factor #2.
Discussion
The present study completed a cultural adaptation and validation of the FACS questionnaire to Spanish, resulting in a FACS-Sp version. In a first step, the translation process followed established guidelines explained in the literature, following a recommended direct- and reverse-translation- and back-translation methodology [25]. This process ensured the conceptual equivalence between terms employed in the original English version and the final version of FACS-Sp. In a second step, psychometric properties were evaluated in accordance with Costello and Osborne [28].
Structural validity
The two-factor solution that emerged in the factor analysis accounted for 48.75% of the total variance. The English [35] and Serbian [36] versions of FACS also found a two-factor solution, which provides support for the construct validity of the FACS-Sp. In the English version, the two factors accounted for a very similar percentage of the total variance (51.54%). Also, like the FACS-Sp, the English version factor analysis detected four initial factors with Eigenvalues above 1 [35]. The FACS was designed to include four primary constructs: cognitive (pain catastrophizing), affective (pain-related fear/anxiety), and behavioral (avoidance), as well as the reason of avoidance (pain without fear; fear of pain; or fear of injury or re-injury) [16]. The presence of these constructs could explain the presence of four factor having eigenvalues > 1.0 in both the Spanish and English versions. However, only two factors achieved an explanation of the variance more than 10% in both versions, so only two were retained, as has been recommended. It was determined that factor 1 represented general FA and factor 2 represented the types of activities that one is avoiding.
Other FA-related questionnaires have shown several factors. FABQ contains two dimensions: While FA beliefs about work explain a 43.7% of the total variance, FA beliefs related to physical activity explain 16.5% [14]. The Spanish version of FABQ maintained 2 dimensions [20], while the German version split work-related dimension in two: work as cause of pain, explaining a 43.4% of the variance, and patients’ assumptions of their probable return to work (11.8% of the variance). Physical activity dimension explained 8.9% of the variance [37]. In the case of PCS, the original version was composed of 3 dimensions: rumination, magnification, and helplessness, which account respectively for 41, 10 and 8% of the total variance [13], with similar percentages in the Spanish version (39, 11 and 10%) [19]. The original TSK questionnaire contains two dimensions, named Activity Avoidance and Harm, as maintained in a 11-items Spanish version [18]. However, other versions present different factor solutions: 5 factors in a fibromyalgia syndrome population [38], 4 factors in its Dutch version by Principal Component Analysis [39], and 2 different factors (Activity Avoidance and Pathological Somatic Focus) in 17-items English version [40], which provides inconsistent findings.
Regarding items loading from the present version items related to cognitive and affective pain tended to load higher on factor 1, while items related to reasons of avoidance loaded higher on factor 2. In the English version of FACS, factor 1 was composed of items 1–14, and factor 2 was composed by items 15–20; while item 6 was cross-loaded in both factors but finally included in factor 1 [35]. In the Spanish version, factor 1 was composed of items 1–15, and factor 2 was composed of items 16–20 (see Table 2); while items 20, 14 and 10 were cross-loaded. Although item 6 showed a low load (0.350), the minimum of 0.32 [29] was achieved for factor 1. Therefore, it was not eliminated, keeping the same items as its original English version [35].
Convergent validity
As expected, the FACS was positively correlated with the CSI, although this correlation was not strong (r = 0.414). This finding was expected as both questionnaires measure different construct. While the FACS measure FA, the CSI measures symptoms present in Central Sensitization Syndromes. However, the CSI was likely to converge (positive correlation) because both symptom dimensions often appear in CMPDs [30,31,32] and other chronic pain conditions [41, 42].
The convergent validity of CSI has previously been studied with questionnaires measuring FA, such as the PCS, showing similar results (r = .464; p < 0.001) in patients with chronic spinal pain [43]. Authors explained this association by the common variable of ‘Emotional distress’ which is assessed in both measures [44]. In patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain (LBP), CSI correlation with the PCS was higher (r = .518; p < 0.001), but lower and not significant with the TSK questionnaire (r = .348; p = 0.034) [45]. However, Pearson correlation was positive in both questionnaires, and patients with higher scores in pain catastrophizing and kinesiophobia showed higher degree of symptoms of CS measured by CSI. In addition to results from previous studies, It should be noted that FA is commonly identifies in patients with CSS [46], which would explain the correlation found between FACS and CSI.
Internal consistency
The FACS-Sp showed a high internal consistency illustrated by α = 0.902 for factor 1 and 0.808 for factor #2. Similar results were found in the Serbian version, with higher internal consistency in factor 1 (α =0.904) than 2 (α = 0.880) The original version of FACS showed similar results for the entire questionnaire (α = 0.92), but separate results for each of the two factors were not reported [16].. This high internal consistency is similar to the original version of PASS (α = 0.94) [12]. Lower values were found for the FABQ and PCS [13, 14]. Other Spanish versions of pain-related FA questionnaires have also shown similar values, like the FABQ (α = 0.9337) [20]. Others have shown lower internal consistency, like the Spanish PCS (α = 0.79) [19] and Spanish TSK (α = 0.92 for chronic, and 0.781 for acute populations) [18].
Clinical implications in primary care
According to the biopsychosocial model of chronic pain, psychological factors, like FA, contribute to the onset and progression of both pain and disability [47] and play a significant role in the transition between acute and chronic pain [48]. The sample from this study was suffering from CMPD, which represents a high cost in health care [49]. It should be noted that the mean FACS score in our study population was 30.49 ± 17.18, which corresponds to a mild severity level, according to recommended guideline from the original English version [16]. In the English version, two groups of patients with CMPD showed mean values of 67.90 ± 19.4 [16] and 68.2 ± 18.9 [35]. In the Serbian sample of subjects with CMPD, the mean value was 55.28 ± 22.53 [36]. Perhaps the Spanish subjects, with their lower FACS scores, were less chronic and/or less disabled than the English and Serbian populations. Or, perhaps cultural differences in self-report behaviour may have influenced the mean scores in these 3 subject populations.
Although avoidance behaviors may be adaptive in the context of acute pain, long-term avoidance can impair daily functioning and lead to physical disability [50]. As it is know that FA is associated with disability, FA is likely an important treatment target for reducing pain-related disability [50]. However, the translation of the guiding principles relating psychological factors to the clinic field have remained a challenge [47]. In this line, in 2011 the Institute of Medicine published a report on pain care, highlighting that a biopsychosocially-oriented approach, promoting patients’ self-management skills, was required for effectiveness of chronic pain treatment [51]. This paradigm promotes a multi-modal strategy including non-pharmacological pain treatment modalities [52]. Early intervention strategies, including screening and appropriate referrals, may help prevent patients with chronic illnesses from becoming disabled [53].
Approximately 55% of our sample was suffering from LBP. Evidence suggests that fear avoidance beliefs are prognostic for poor outcomes in subacute LBP, so early treatment, including interventions to reduce fear avoidance beliefs, may avoid delayed recovery and chronicity [54]. A recent systematic review concluded that targeting psychosocial predictors through clinical guidelines and a national strategy are need to support a cultural change in pain care [55]. Due to the new paradigm of pain, a biomechanical analysis is not comprehensive enough to identify subgroups [47] and credibility of subgroup claims in LBP trials is slow [56]. Therefore, LBP assessment should include the emotional and behavioral consequences of pain, which can contribute to the treatment outcomes [47]. Following this line, in primary care there are clinical prediction rules to identify patient prognosis to certain type of treatment [57]. Also, subgroup classification of patient with chronic LBP are available, based on a multifactorial approach, including psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, functional disability, pain, and FA beliefs [58]. Even clinical prediction models to inform clinical decision-making after some type of surgery are being developed, which includes FA [59]. Hence, FA assessment is crucial to guide treatment in primary care. Results from the present study offer a new screening tool for Spanish-speaking health providers in Spain and throughout Europe who wish to evaluate pain-related FA. It has demonstrated good psychometric properties, offers easy-to-interpret severity levels, and incorporates the important components of the most current FA model of Vlaeyen [6, 16].
Study strengths
One of the strengths of the present study was the good psychometric results of the FACS-Sp, supporting previous research on the original English [35] and Serbian [36] versions. Our results suggest that reliable score comparisons can be made between different language-speaking populations in different areas of the world and that the FACS-Sp is appropriate for Spanish-speaking populations in Europe.
Limitations
As a limitation, there was a lack of longitudinal data, so it did not include test-retest reliability, responsiveness and error scores or provide information on minimal clinically important difference values.
Conclusion
This study reports for the first time the psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the FACS (FACS-Sp). The reliability, in terms of internal consistency, and structural validity were comparable to the original English version [16], ensuring conceptual equivalence. The FACS-Sp provides a reliable and potentially useful FA measures for European-style Spanish-speaking populations. The fact that Spanish is the second largest geographical language [60] makes this new FACS-Sp especially important for more wide-spread international use. Finally, future research on the FACS-Sp should evaluate test-re-test reliability, treatment responsiveness and psychometric comparisons with other translated versions. In primary care, FA assessment is crucial in clinical decision-making and treatment planning. The FACS-Sp allows a quick and easy patient-reported measure of FA in Spanish speaker populations.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body Mass Index
- CSI-Sp:
-
Spanish version of the Central Sensitization Inventory
- CSS:
-
Central Sensitization Syndromes
- FA:
-
Pain-related Fear Avoidance
- FABQ:
-
Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire
- FACS:
-
Fear-Avoidance Components Scale (FACS)
- FACS-Sp:
-
Fear-Avoidance Components Scale European-style Spanish
- MLE:
-
Maximum Likelihood Extraction
- PASS:
-
Pain Anxiety Symptoms Scale
- PCS:
-
Pain Catastrophizing Scale
- PROMS:
-
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
- TSK:
-
Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia
References
Williams N, Wilkinson C, Stott N, Menkes DB. Functional illness in primary care: dysfunction versus disease. BMC Fam Pract. 2008;9:30.
Lethem J, Slade PD, Troup JD, Bentley G. Outline of a fear-avoidance model of exaggerated pain perception--I. Behav Res Ther. 1983;21(4):401–8.
Vlaeyen JW, Kole-Snijders AM, Boeren RG, van Eek H. Fear of movement/(re)injury in chronic low back pain and its relation to behavioral performance. Pain. 1995;62(3):363–72.
Crombez G, Eccleston C, Van Damme S, Vlaeyen JWS, Karoly P. Fear-avoidance model of chronic pain: the next generation. Clin J Pain. 2012;28(6):475–83.
Vlaeyen JW, Linton SJ. Fear-avoidance and its consequences in chronic musculoskeletal pain: a state of the art. Pain. 2000;85(3):317–32.
Vlaeyen JWS, Linton SJ. Fear-avoidance model of chronic musculoskeletal pain: 12 years on. Pain. 2012;153(6):1144–7.
Lundberg M, Grimby-Ekman A, Verbunt J, Simmonds MJ. Pain-related fear: a critical review of the related measures. Pain Res Treat. 2011;2011:494196.
Garratt A. Patient reported outcome measures in trials. BMJ. 2009;338:a2597.
Cella D, Yount S, Rothrock N, Gershon R, Cook K, Reeve B, et al. The patient-reported outcomes measurement information system (PROMIS): progress of an NIH roadmap cooperative group during its first two years. Med Care. 2007;45(5 Suppl 1):S3–11.
Fayers PM, Machin D. Quality of Life: The Assessment, Analysis and Interpretation of Patient-reported Outcomes. John Wiley & Sons; 2013. 579 p.
Miller RP, Kori SH, Todd D. The Tampa scale: a measure of kinesiophobia. Clin J Pain. 1991;7(1):51–2.
McCracken LM, Zayfert C, Gross RT. The pain anxiety symptoms scale: development and validation of a scale to measure fear of pain. Pain. 1992;50(1):67–73.
Sullivan MJL, Bishop SR, Pivik J. The pain Catastrophizing scale: development and validation. Psychol Assess. 1995;7(4):524–32.
Waddell G, Newton M, Henderson I, Somerville D, Main CJ. A fear-avoidance beliefs questionnaire (FABQ) and the role of fear-avoidance beliefs in chronic low back pain and disability. Pain. 1993;52(2):157–68.
Neblett R, Hartzell MM, Mayer TG, Bradford EM, Gatchel RJ. Establishing clinically meaningful severity levels for the Tampa scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK-13). Eur J Pain Lond Engl. 2016;20(5):701–10.
Neblett R, Mayer TG, Hartzell MM, Williams MJ, Gatchel RJ. The fear-avoidance components scale (FACS): development and psychometric evaluation of a new measure of pain-related fear avoidance. Pain Pract Off J World Inst Pain. 2016;16(4):435–50.
European Commission. Europeans and their Languages. In: Eurobarometer nº243. 2016. http://ec.europa.eu/commfrontoffice/publicopinion/archives/ebs/ebs_243_en.pdf. Accessed 11 Nov 2018.
Gómez-Pérez L, López-Martínez AE, Ruiz-Párraga GT. Psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Tampa scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK). J Pain Off J Am Pain Soc. 2011;12(4):425–35.
García Campayo J, Rodero B, Alda M, Sobradiel N, Montero J, Moreno S. Validación de la versión española de la escala de la catastrofización ante el dolor (Pain Catastrophizing Scale) en la fibromialgia. Med Clínica:487–93.
Kovacs FM, Muriel A, Medina JM, Abraira V, Sánchez MDC, Jaúregui JO, et al. Psychometric characteristics of the Spanish version of the FAB questionnaire. Spine. 2006;31(1):104–10.
Gil-Martínez A, Navarro-Fernández G, Mangas-Guijarro MÁ, Lara-Lara M, López-López A, Fernández-Carnero J, et al. Comparison between chronic migraine and Temporomandibular disorders in pain-related disability and fear-avoidance behaviors. Pain Med Malden Mass. 2017;18(11):2214–23.
Sánchez-Herán Á, Agudo-Carmona D, Ferrer-Peña R, López-de-Uralde-Villanueva I, Gil-Martínez A, Paris-Alemany A, et al. Postural stability in osteoarthritis of the knee and hip: analysis of association with pain Catastrophizing and fear-avoidance beliefs. PM R. 2016;8(7):618–28.
Ariza-Mateos MJ, Cabrera-Martos I, Ortiz-Rubio A, Torres-Sánchez I, Rodríguez-Torres J, Valenza MC. Effects of a patient-centered graded exposure intervention added to manual therapy for women with chronic pelvic pain: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;9.
Mokkink LB, Terwee CB, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Stratford PW, Knol DL, et al. The COSMIN study reached international consensus on taxonomy, terminology, and definitions of measurement properties for health-related patient-reported outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2010;63(7):737–45.
Muñiz J, Elosua P, Hambleton RK. International test commission. [international test commission guidelines for test translation and adaptation: second edition]. Psicothema. 2013;25(2):151–7.
Cuesta-Vargas AI, Roldan-Jimenez C, Neblett R, Gatchel RJ. Cross-cultural adaptation and validity of the Spanish central sensitization inventory. SpringerPlus. 2016;5(1).
Cuesta-Vargas AI, Roldan-Jimenez C, Neblett R, Gatchel RJ. Cross-cultural adaptation and validity of the Spanish central sensitization inventory. SpringerPlus. 2016;5(1):1837.
Costello AB, Osborne JW. Best practices in exploratory factor analysis: four recommendations for getting the Most from your analysis. Pract Assess Res Eval. 2005;10(7):1–9.
Tabachnick BG, Linda S Fidell. Using Multivariate Statistics. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon; 2001.
Noten S, Struyf F, Lluch E, D’Hoore M, Van Looveren E, Meeus M. Central pain processing in patients with shoulder pain: a review of the literature. Pain Pract Off J World Inst Pain. 2017;17(2):267–80.
Van Oosterwijck J, Nijs J, Meeus M, Paul L. Evidence for central sensitization in chronic whiplash: a systematic literature review. Eur J Pain Lond Engl. 2013;17(3):299–312.
Lluch E, Nijs J, Courtney CA, Rebbeck T, Wylde V, Baert I, et al. Clinical descriptors for the recognition of central sensitization pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Disabil Rehabil. 2017;2:1–10.
Terwee CB, Bot SDM, de Boer MR, van der Windt DAWM, Knol DL, Dekker J, et al. Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(1):34–42.
Cronbach LJ. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika. 1951;16(3):297–334.
Neblett R, Mayer TG, Williams MJ, Asih S, Cuesta-Vargas AI, Hartzell MM, et al. The fear-avoidance components scale (FACS): responsiveness to functional restoration treatment in a chronic musculoskeletal pain disorder (CMPD) population. Clin J Pain. 2017 Mar;21.
Knezevic A, Neblett R, Gatchel RJ, Jeremic-Knezevic M, Bugarski-Ignjatovic V, Tomasevic-Todorovic S, et al. Psychometric validation of the Serbian version of the fear avoidance component scale (FACS). PLoS One. 2018;13(9).
Pfingsten M, Kröner-Herwig B, Leibing E, Kronshage U, Hildebrandt J. Validation of the German version of the fear-avoidance beliefs questionnaire (FABQ). Eur J Pain. 2000;4(3):259–66.
Burwinkle T, Robinson JP, Turk DC. Fear of movement: factor structure of the Tampa scale of kinesiophobia in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. J Pain Off J Am Pain Soc. 2005;6(6):384–91.
Vlaeyen JW, Kole-Snijders AM, Rotteveel AM, Ruesink R, Heuts PH. The role of fear of movement/(re)injury in pain disability. J Occup Rehabil. 1995;5(4):235–52.
Clark ME, Kori SH, Brockel J. Kinesiophobia and chronic pain: psychometrics characteristics and factor analysis of the Tampa Scale. In American Pain Society; 1996. p. 77.
Gatchel RJ, Neblett R, Kishino N, Ray CT. Fear-avoidance beliefs and chronic pain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2016;46(2):38–43.
Cuesta-Vargas AI, Neblett R, Chiarotto A, Kregel J, Nijs J, van Wilgen CP, et al. Dimensionality and reliability of the central sensitization inventory (CSI) in a pooled multi-country sample. J Pain Off J Am Pain Soc. 2017;30.
Kregel J, Schumacher C, Dolphens M, Malfliet A, Goubert D, Lenoir D, et al. Convergent validity of the Dutch central sensitization inventory: associations with psychophysical pain measures, quality of life, disability, and pain cognitions in patients with chronic spinal pain. Pain Pract Off J World Inst Pain. 2018;18(6):777–87.
van Wilgen CP, Vuijk PJ, Kregel J, Voogt L, Meeus M, Descheemaker F, et al. Psychological distress and widespread pain contribute to the variance of the central sensitization inventory: a cross-sectional study in patients with chronic pain. Pain Pract Off J World Inst Pain. 2017;27.
Huysmans E, Ickmans K, Van Dyck D, Nijs J, Gidron Y, Roussel N, et al. Association between symptoms of central sensitization and cognitive behavioral factors in people with chronic nonspecific low Back pain: a cross-sectional study. J Manip Physiol Ther. 2018;41(2):92–101.
Adams LM, Turk DC. Psychosocial factors and central sensitivity syndromes. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2015;11(2):96–108.
Linton SJ, Shaw WS. Impact of psychological factors in the experience of pain. Phys Ther. 2011;91(5):700–11.
Hasenbring MI, Chehadi O, Titze C, Kreddig N. Fear and anxiety in the transition from acute to chronic pain: there is evidence for endurance besides avoidance. Pain Manag. 2014;4(5):363–74.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Advancing Pain Research C. Pain as a Public Health Challenge. In: Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press (US); 2011. p. 91–5.
Zale EL, Lange KL, Fields SA, Ditre JW. The relation between pain-related fear and disability: a meta-analysis. J Pain Off J Am Pain Soc. 2013;14(10):1019–30.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Advancing Pain Research, Care, and Education. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011. (The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health).
Becker WC, Dorflinger L, Edmond SN, Islam L, Heapy AA, Fraenkel L. Barriers and facilitators to use of non-pharmacological treatments in chronic pain. BMC Fam Pract. 2017;18:41.
Keeley P, Creed F, Tomenson B, Todd C, Borglin G, Dickens C. Psychosocial predictors of health-related quality of life and health service utilisation in people with chronic low back pain. Pain 2008;135(1–2):142–50.
Wertli MM, Rasmussen-Barr E, Weiser S, Bachmann LM, Brunner F. The role of fear avoidance beliefs as a prognostic factor for outcome in patients with nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review. Spine J Off J North Am Spine Soc. 2014;14(5):816–836.e4.
Hruschak V, Cochran G. Psychosocial predictors in the transition from acute to chronic pain: a systematic review. Psychol Health Med. 2018;28:1–17.
Saragiotto BT, Maher CG, Moseley AM, Yamato TP, Koes BW, Sun X, et al. A systematic review reveals that the credibility of subgroup claims in low back pain trials was low. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;79:3–9.
Fritz JM, Childs JD, Flynn TW. Pragmatic application of a clinical prediction rule in primary care to identify patients with low back pain with a good prognosis following a brief spinal manipulation intervention. BMC Fam Pract. 2005;6:29.
Rose-Dulcina K, Vuillerme N, Tabard-Fougère A, Dayer R, Dominguez DE, Armand S, et al. Identifying subgroups of patients with chronic nonspecific low Back pain based on a multifactorial approach: protocol for a prospective study. JMIR Res Protoc. 2018;7(4):e104.
Rushton AB, Verra ML, Emms A, Heneghan NR, Falla D, Reddington M, et al. Development and validation of two clinical prediction models to inform clinical decision-making for lumbar spinal fusion surgery for degenerative disorders and rehabilitation following surgery: protocol for a prospective observational study. BMJ Open. 2018;8(5):e021078.
Lewis PM, Simons GF, Fennig CD. Ethnologue: languages of the world [internet]. 19th ed. Dallas: SIL International; 2016. Available from: http://www.ethnologue.com.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the volunteers for their participation.
Funding
Authors, their immediate family, and any research foundation with which they are affiliated have not received any financial payments or other benefits from any commercial entity related to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AC, RN, RG have contributed to the conception of this study. CR and AC drafted the protocol and manuscript. AC, RN, RG and CR participated in the analysis and interpretation of data and were involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors have given final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval for the study was granted by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Malaga. The study complied with the principles laid out in the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants in this study signed an informed written consent form prior to inclusion, and their participation was voluntary.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or financial involvement in any organization or entity with a direct financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in the article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Cuesta-Vargas, A.I., Neblett, R., Gatchel, R.J. et al. Cross-cultural adaptation and validity of the Spanish fear-avoidance components scale and clinical implications in primary care. BMC Fam Pract 21, 44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-020-01116-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-020-01116-x