Abstract
Background
Drought is a critical abiotic stress that influences maize yield and reduces grain yield when it occurs at the flowering or filling stage. To dissect the genetic architecture of grain yield under drought stress (DS), a genome-wide association analysis was conducted in a maize population composed of diverse inbred lines from five locations under well-watered and DS conditions at flowering in 2019 and 2020.
Results
Using a fixed and random model circulating probability unification model, a total of 147 loci associated with grain yield or the drought resistance index (DRI) were identified, of which 54 loci were associated with a DRI with an average phenotypic variation explanation of 4.03%. Further, 10 of these loci explained more than 10% of the phenotypic variation. By integrating two public transcriptome datasets, 22 differentially expressed genes were considered as candidate genes, including the cloned gene ZmNAC49, which responds to drought by regulating stomatal density. Enrichment and protein interaction network showed that signaling pathways responded to drought resistance, including jasmonic acid and salicylic acid, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and abscisic acid-activated. Additionally, several transcription factors involved in DS were identified, including basic leucine zipper (GRMZM2G370026), NAC (GRMZM2G347043), and ethylene-responsive element binding protein (GRMZM2G169654).
Conclusions
In this study, we nominated several genes as candidate genes for drought resistance by intergrating association maping and transcription analysis. These results provide valuable information for understanding the genetic basis of drought tolerance at the mature stage and for designing drought-tolerant maize breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Water scarcity and unpredictable droughts are posing a threat to corn production worldwide [1, 2]. As the Earth’s population increases, water pollution and climate change further aggravate the already declining water availability, which has caused many social problems and economic losses [3,4,5]. The water resource development report indicates that global water consumption has now increased threefold compared to that of the past 50 years, and the rising trend in agricultural water demand over the past few decades further confirms this situation [6, 7]. According to the data from the 2013 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the average surface temperature of the earth has increased by 0.85 ℃ over the past 130 years, resulting in frequent occurrences of extreme weather phenomena, such as droughts, floods, heat waves, strong winds, and thunderstorms, and drought is considered as the maximum limiting factor for crop yield [8, 9].
According to statistics from the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization ( www.FAO.org ), maize is not only the major crop in China since 2011, but also the major cereal crop in the world. In addition, it is widely used in animal husbandry and is known as the “king of feed” [10,11,12,13,14,15]. The Corn grain can serve as an important raw material and industrial base for the development of new energy sources worldwide, and its utilization has significant practical value [16]. Drought at different growth stages in maize will decrease maize production by affecting the growth and development through different regulatory mechanisms. Drought causes yield reductions ranging from 9.3% to 35.1% in China [17] and the 2012 drought in the U.S. led to decreased grain yield (GY) by 21% compared to that of the previous 5 years, with an average country-yield of 7.7 mg ha-1 [18]. The drought tolerance level of maize is mainly assessed by the performance of dry matter production under water stress [19]. Therefore, selecting maize germplasm resources with high drought resistance is an important strategy to improve yield.
Plant drought tolerance is a complex trait regulated by numerous quantitative trait loci (QTL), with relatively small effects [9]. A good variety with high drought tolerance contains an assembly of favorite alleles. Therefore, identification of functional genes or markers closely associated with the regulation of drought tolerance is a crucial step in genomics-assisted plant breeding. To reveal the genetic architecture of yield and secondary traits in maize, most linkage mapping studies have reported QTL associated with drought tolerance [20]. Many single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with drought resistance have been identified in genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of multiple associated populations. The association panel consists of 350 tropical and subtropical inbred maize lines, which revealed 33 candidate genes associated with GY and related secondary traits under well-watered (WW) and drought stress (DS) conditions [19]. In addition, a GWAS using 240 inbred lines detected 52 candidate genes associated with seven agronomic traits, including yield (GY) and related secondary traits, under both WW and DS conditions [21]. These genetic analyses provide abundant information on functional gene clones. There is a significant correlation between variation in the ZmVPP1 gene and drought tolerance in maize seedlings, and transgenic maize plants expressing ZmVPP1 exhibit enhanced drought tolerance [22]. Recently, a small inverted-repeat transposable element of 82 base pairs in length inserted in the ZmNAC111 promoter was shown to be associated with drought tolerance in maize seedlings [23]. ZmMPKL1 regulates homeostasis of abscisic acid (ABA) and mediates the response of maize seedlings to DS by encoding a functional kinase [24]. However, most genes cloned in previous studies were analyzed and cloned based on survival rates at the seedling stage, whereas few genes related to drought resistance were cloned at the maturity stage. A recent association study in maize using a natural-variation population demonstrated a significant correlation between the expression level of ZmEXPA4 and the increase in the anthesis and silking intervals (ASI) caused by drought. These results suggest that regulating the expression of ZmEXPA4 using drought-induced promoters can potentially reduce the negative effect of drought on ASI [25].
In addition, with the development of high-throughput phenotyping, metabolomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics, many relevant parameters have been utilized to assess drought response; these parameters are valuable resources for genetic analyses aimed at identifying genes involved in drought regulation [10,11,12,13,14,15]. However, most of these studies focused on the seedling stage and were rarely related to drought tolerance of mature plants. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct genetic analyses of DS during the mature stage in the field. Here, a GWAS of drought tolerance was conducted using GY and related indices under different water treatment (WW and DS) at flowering time. The aim of the study was to identify associated SNPs and candidate genes to understand the genetic basis of drought resistance for future research.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and growth conditions
For the 201 maize inbred lines adopted in this study, except for six public inbred lines (PH6WC, PH4CV, Zheng58, Chang7-2) that were regarded as controls, the rest were selected and bred by the institutions involved in this study (Table S1). Due to the collected materials were newly bred by breeders, some will be eliminated or added by comprehansive envaluated. The number of inbred lines were used in 2019 was 115 and 180 in 2020, with 94 common inbred lines termed AM201, AM115, and AM180, respectively. AM115 and AM180 were planted with two replications under WW and DS in five locations in China: including Yulin (YL; 109°45'N, 38°16'E) in Shaanxi, Yinchuan (YC; 10°06'N, 37°43'E) in Ningxia, ZhangYe (ZY; 100°48'N, 38°93'E) in GanSu, Urumqi (UR; 87°61'N, 43.79'E) in Xinjiang, and Taiyuan (TY; 87°61'N, 43°79'E) in Shanxi. There was a 2 m-wide isolation belt between the WW and DS treatments. At each location, all inbred lines for each treatment were planted in two-row plots using a split block design, with a 5 m row length and 0.6 m row intervals, and at plant density of 75,000 plants ha-1. Normal irrigation ensured sufficient water supply during the entire growth period. DS was performed using field water at vegetative stages V13 to VT; during these stages, irrigation was applied when the relative water content of soil reached 50–60%, while normal irrigation was provided during the other growth periods. All other field management practices followed local practices.
Phenotype data collection and analyses
GY (kg hm-2) was adjusted to a 14% moisture content. The number of effective plants in each plot was determined before harvest and the ears of all inbred lines in each plot were harvested. A PM-8188 grain moisture tester (Kett Electric Laboratory, Japan) was used to determine the kernel water content at harvest and to convert the yield per unit area. The formula is as follows:
Where GY is the grain yield (kg hm-2); Wdry is the dry grain weight per ear (kg); N is the number of effective plants; A is the area of the two-row plot (m2); and M is the actual measurement of grain moisture content. Using the R package lme4 [26, 27], the best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) values were calculated for AM115, AM180, and AM201 and termed 2019DS, 2019WW, 2020DS, 2020WW, 201DS, and 201WS, respectively. The drought resistance index (DRI) was calculated according to the related BLUP values from each association panel and termed 2019DRI, 2020DRI, and 201DRI, respectively. The detailed formula for the DRI is as follows, according to [28]:
Where DC is the drought coefficient; GYS.T is the yield of the tested inbred lines under DS treatment, GYS.W is the yield of the tested inbred lines under WW treatment, and \(GYM.T\) is the average yield of all tested materials under DS. Basic descriptive analysis was performed using the SPSS v.22 software (IBM corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Phenotypic variation in yield traits was evaluated using analysis of variance. Genotype (G), environment (E), the interaction between genotype and environment (G \(\times\) E), and replication were fitted with a general linear model as follows:
Where \({y}_{ijk}\) is the phenotypic value of the ith inbred line from the kth replication in the jth environment; \(\mu\) is the overall mean of a trait; \({G}_{i}\) is the genetic effect of the ith inbred line; \({E}_{j}\) is the environmental effect of the jth environment; \({G}_{i}\times {E}_{j}\) is the interaction between genotype and environment for the ith inbred line and the jth environment; \(R{\left(E\right)}_{jk}\) is the kth replication within the jth environment; and \({\varepsilon }_{ijk}\) is the residual error. The formula for calculating broad-sense heritability (H2) is as follows:
Where \({\sigma }_{\mathrm{g}}^{2}\), \({\sigma }_{\mathrm{ge}}^{2}\), and \({\sigma }_{e}^{2}\) represent the genotypic variance, the G × E variance, and the residual error variance, respectively, and n and r are respectively the mean number of environments and replications that combine location and years as a random effect [29, 30].
DNA extraction and genotyping
At the five-leaf stage, 10 young leaves were mixed-sampled and frozen at -80 ℃ for DNA extraction using a modified cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) method [31, 32]. All DNA samples were submitted to the Beidahuang Company (Beidahuang Kenfeng Seed Industry Co., Ltd., Harbin, China) for genotype detection using the Maize 6H60K chip, which was independently developed by the Maize Research Center of the Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences. A total of 42,974 markers were considered sufficiently robust and consistent for use in this analysis and were screened for missing values > 0.25 and minor allele frequency (MAF) < 0.05. This led to further analysis using 42,003 SNPs.
Population structure and linkage disequilibrium (LD) analyses
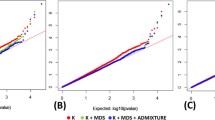
The population structure was inferred using the PuTTY Link (PLINK) version 1.90 [33] and ADMIXTURE version 1.3.0 software [34]. The subgroup parameter value K was set to 1–20, and the best cross-validation error was determined by running the ADMIXTURE software K value, which was best when the cross-validation error rate was closest to zero. The Q-matrix was used as a covariance matrix for the association analysis. For AM201, an unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean tree with 1000 bootstraps was constructed using the MEGA software (v7.0) [35] with a set of 42,003 high-quality SNPs. Principal component analysis (PCA) and kinship matrix analysis were performed using the LDAK5 [36] tool on the high-quality SNPs. The output of LDAK5 was fed as input into the RStudio software to graphically display the PCA and kinship matrix results, and the LD decay distance was calculated using the PopLDdecay software [37].
Genome-wide association study
GWAS was conducted for GY and DRI using a fixed and random model of circulating probability unification (FarmCPU) in the R software [38]. Manhattan plots were generated using the CMplot package in R. Due to the stringent threshold calculated by the Bonferroni correction, the GWAS threshold was set as -log(p) = 3.5 to declare significant associations, which were determined based on the Q-Q plots and distribution of p values. Candidate genes were predicted according to the LD decay distance, which was 150 kb (r2= 0.2) for AM201. Here, the MaizeGDB database based on the B73 RefGen_v3 genome (https://maizegdb.org/gbrowse/maize_v3) was used as a reference, because the SNP chip data were designed and the transcripptomic data used later were calculated using this verb.
Functional annotation of genes
Two public transcriptome datasets (Gene Expression Omnibus [GEO] accession numbers: GSE132113 and GSE71723), including three tissues (leaf, ear, and kernel) at four developmental stages (V12, V14, V18, and R1) and three tissues (leaf, ear, and tassel branch) at two stages (V9 and 5DAP) under DS were integrated using the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Genes were regarded as differentially expressed using the cutoff criterion of log2Fold change ≥2. Candidate genes were clustered and visualized using the R-package pheatmap (http://www.r-project.org/). To annotate the potential functions of candidate genes, Gene Ontology (GO) analysis was performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery website (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/tools.jsp). Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway [39,40,41] analysis was performed using the cluster Profile package in R [42]. The search tool for the retrieval of interacting genes/proteins (STRING, v11.0; https://string-preview.org/) was used to analyze the protein interaction network, whereas the Cytoscape software (V3.8.0; http://www.cytoscape.org/download.php) was used to visualize the protein interaction network [43].
Results
Evaluation of phenotypic variation
After evaluating the grain yield (GY) under well watered (WW) and drought stress (DS) in multiple environments over two years, GY was shown to follow a normal distribution (Fig. 1A-B). In 2019, the coefficient of variation(CV) of GY was significantly higher under DS than under WW conditions in the same environment (p < 0.01) (Fig. 1C). A similar trend was observed for GY in 2020 (Fig. 1D). In addition, analysis of variance based on GY at five locations over two years under the two water-management conditions showed that genotype effect, environment effect, and the interaction between genotype and environment were significantly different (p < 0.01); genotype, environment, and their interaction separately accounted for 34.96 34.48, and 24.84% of the total variation in AM115 and 41.34, 34.46, 33.07% of the total variation in AM180, respectively (Table S2). These results suggested that the difference in GY was mainly influenced by genotype, followed by environmental effects and the interaction between genotype and environment. The BLUP values of GY in 2019 and 2020 showed a similar trend; that is, GY under DS was significantly lower than that under WW (p < 0.01). GY declined to 29.96% in 2019 and to 24.17% in 2020, suggesting a moderate level of stress (Fig. 1E). In both populations, the coefficients of variation of GY at the five locations under DS were greater than those under normal irrigation in both years (Table 1). H2 of GY ranged from 71% in 2019DS to 82% in 2019WW, where the H2 was higher in WW than in DS (Table 1). This indicated that the drought treatment increased the difference in GY and decreased the genetic effect by inducing a stronger environmental effect.
Phenotypic performance of yield traits in different populations across multiple environments and treatments in 2019 and 2020. WW: well-watered; DS: drought stress; TY: Taiyuan; UR: Urumqi; YL: Yulin; ZY: Zhangye; YC: Yinchuan; BLUP: best linear unbiased prediction; Probability level: ** means significantly different for P <= 0.01. A Phenotypic description of yield traits under multiple environments and diffe rent water treatments in 2019; B Phenotypic description of yield traits under multiple environments and different water treatments in 2020; C Phenotypic performance of yield traits under multiple environments and different water treatments in 2019; D Phenotypic performance of yield traits under multiple environments and different water treatments in 2020. E Comparison of BLUP values of yield traits in 2019 and 2020 under different treatments
Analysis of genetic background for the AM201 panel
After detecting the genotype of the 201 germplasm (AM201) using the maize 6H60K SNP chip, 42,003 SNPs distributed on ten chromosomes were reserved by deleting those SNPs with missing values > 0.25 and MAF < 0.05. Among these, the number of SNPs was highest on chromosome 1 and lowest on chromosome 10, with 6,761 and 2,799 SNPs, respectively. Marker density ranged from 44.53 to 53.31 kb, with an average density of 48.36 kb (Fig. S1). Population structures were constructed using PLINK and the ADMIXTURE software, and the inbred lines were divided into eight groups according to the error rate of cross-verification and the optimal K value (Fig. 2A). The phylogenetic tree also showed eight distinct groups, in which six classical elite inbred lines (Zheng58, DK517M, DK517F, PH4CV, PH6WC, and Chang7-2) were distributed into six different subgroups (Fig. 2A-B), indicating that the groups were suitably divided. The heat map of the kinship matrix showed that most germplasms had no direct or close relationships, and several test materials were closely related to each other. The resulting matrix of kinship relationships was used to correct some of the related materials in the association analysis (Fig. 2C). In addition, the LD decay distance was 150 kb when R2 = 0.2 (Fig. 2D) and was used for candidate gene prediction during GWAS.
GWAS for DRI and GY in maize
To minimize the effect of environmental variation, BLUP values for GY across the five environments and drought resistance index (DRIs) were calculated for association studies using FarmCPU with a mixed linear model with kinship (K matrix) and population structure (Q matrix) to avoid spurious associations. A total of 147 associated SNPs were identified: 19, 16, 19, 12, 15, 28, 10, 8, and 20 SNPs in 2019DRI, 2020DRI, 201DRI, 2019DS, 2020DS, 201DS, 2019WW, 2020WW, and 201WW, respectively (Fig. 3). The phenotypic explained variation (PVE) at each associated site (R2) ranged from 0.01% to 22.19%, with an average of 3.84%. Among the 54 associated SNPs with DRIs, the PVE ranged from 0.04% to 22.19%, with an average of 4.03% and two of them were co-localized in traits 2020DRI and 201DRI, including Affx-291431276 and Affx-159033091, on chromosomes 1 and 2, respectively. In addition, six associated loci, Affx-291444080, Affx-88979175, Affx-291376326, Affx-291391165, Affx-291431276, and Affx-291405703, were co-localized in traits 2020DS and 201DS, and Affx-88980407 was co-localized in traits 2019DS and 201DS. For both conditions, the SNPs Affx-291423895, Affx-291405703, Affx-93144141, Affx-159071589, and Affx-291380961 were associated with WW, DS, and DRI (Fig. S2, Table S3). Furthermore, 18 SNPS associated with DS and DRI explained more than 10% of the phenotypic variation and were considered major effect genes (Table S3).
Genome-wide association results for yield and drought resistance index under different treatments in AM115, AM180, and AM201 populations. WW: well-watered; DS: drought stress; DRI: drought resistance index. A 2019DRI; B 2020DRI; C 201DRI; D 2019DS; E 2020DS; F 201DS; G 2019WW; H 2020WW; and (I) 201WW
Estimation of the distribution frequency of superior alleles in different populations revealed that the average percentage of superior alleles was 39.52% (variation: 8.70–87.83%) (Table 2). Among the 54 significant loci, only 14 loci had a superior allele frequency of > 50%. After examining the cumulative effect, DRI increased with an increasing number of superior alleles for 2019DRI, 2020DRI, and 201DRI, but the largest DRI did not exceed 1.2, even if nearly 20 superior alleles were assembled (Fig. 4A-C). These results suggested that drought resistance may be improved by accumulating superior alleles; however, a large gap in drought resistance remains owing to the low frequency and effects of the superior allele in the germplasm.
Identification of candidate genes by integrating the transcriptome
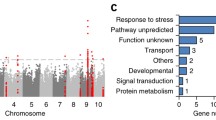
To recommend candidate genes for drought resistance, candidate genes in the confidence region were conferred according to the 150 kb LD decay distance. Herein, the genes located 150 kb around the significant sites were defined as candidate genes. Thus, 2092 candidate genes were obtained for GY under WW, GY under DS, and DRI. By integrating two public transcriptome datasets (GEO accession numbers: GSE132113 and GSE71723), including three tissues (leaf, ear, and kernel) at four developmental stages (V12, V14, V18, and R1) and three tissues (leaf, ear, and tassel branch) at two stages (V9 and 5DAP) under DS from NCBI (https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), 41 and 265 differentially expressed genes were acquired as candidates, respectively (Table S4 & S5, Fig. 5); of these, 22 differentially expressed genes were common and considered core candidate genes (Fig. S3, Table 3).
Further annotation of these 22 candidate genes using GO and KEGG analyses revealed that they were enriched in plant hormone signal transduction and participated in several biological processes, including response to alcohol, shoot system development, reaction to oxygen-containing compounds, jasmonic acid (JA)- and salicylic acid (SA)-mediated signaling pathway regulation, response to carbohydrates, response to stress, and response to water shortage. In addition, molecular functions were enriched in transcription corepressor activity, metal ion binding, cation binding, and ion binding (Fig. 6, Table S6). These results suggested that hormone and transcriptional regulation play important roles to response DS.
Protein-protein interaction networks predicted by candidate genes
Based on the STRING (v11.0) database, an interaction network was predicted for the 22 core candidate genes. Of these, 18 were used to construct protein-protein networks that interacted with various functional proteins and with each other via an intermediate protein. The coding proteins participated in protein-protein network interactions. The protein interaction network, using the candidate genes as the core including GRMZM2G109130, GRMZM2G167220, GRMZM2G169654, GRMZM2G318220, GRMZM2G347043, GRMZM5G838098, GRMZM2G445634, GRMZM2G480954, and GRMZM2G370026, showed that these coding proteins belong to the lysyl oxidase, cytokinin oxidase (CKO), related to ABI3/VP1 (RAV), glutathione peroxidase, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), JAJZ1, OLE, and basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor families, respectively. These transcription factor families mainly respond to DS by regulating organic acid metabolism, oxygen-containing compound reactions, and JA and SA mediated signaling pathways.
Some protein-encoding candidate genes participated in responses to DS through common interacted genes between different interaction networks. For example, protein interaction networks with the core coding proteins of candidate genes GRMZM2G109130 (M5), GRMZM5G838098 (M11), GRMZM2G445634 (M12), and GRMZM5G872392 (M17) (Fig. 7) were mainly associated with biological processes involved in a network of signaling pathways, including the phytohormones JA/ethylene and SA, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone, and cellular response to organic substance. The interaction network of the coding proteins of candidate genes GRMZM2G177050 (M9), GRMZM2G459841 (M13), and GRMZM5G897067 (M18) was mainly involved in the response to hyperosmosis, cell response to hormone stimulation, monocarboxylic acid biosynthetic process, and root and flower development, which play an important role in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. These results provide a deeper understanding of the interactions between different drought response factors.
Protein–protein interaction networks of candidate genes. Nodes indicate proteins and lines indicate the interaction between proteins. The red circle indicates proteins encoded by the identified candidate genes and the interactive proteins in different networks are distinguished using different colors. M1–M18 are the candidate genes encoded proteins as Table 3
Discussion
Co-localization of associated loci with those from previous studies
Drought is an abiotic stress with great influence on the growth and development of maize [44]. In particular, subjection of maize to DS at the flowering stage leads to significant yield reduction [45, 46]. Therefore, understanding the phenotypic variation under drought and the genetic basis response to drought in maize is crucial for determining its drought sensitivity. Many studies have applied GWAS to elucidate the genetic mechanism of drought-resistant traits, and some results have been achieved [21, 47, 48]. In most published studies, the regulatory mechanism of drought resistance has been analyzed through physiological indicators such as chlorophyll content during the seedling stage [23, 24, 48, 49]. However, the Drought Resistance Index (DRI) calculated using yield (GY) under normal and stress conditions, which is an effective indicator for evaluating drought resistance of germplasm during breeding process [50,51,52], but is rarely used to understand the regulatory mechanism of drought resistance.
In this study, a GWAS was conducted for GY and DRI using an associated population consisting of 201 inbred maize lines that formed three sets of association panels according to actual plant information. In 2019 and 2020, 55 SNP markers were significantly associated with GY under DS conditions, 54 for DRI, and 38 for GY under WW conditions. Most of the associated SNPs indentified under WW and DS is different, which also happened for the comparison of the GWAS results under stressed and normal treatments [19]. These results indicate that the identified QTL may vary under different environmental conditions within the same population [44, 53]. In extreme cases, consensus loci were not detected for the same traits under different treatments, which is similar to the results of previous studies [54]. Here, 12 associated SNPs were shared between GY or DRIs from different years or treatments.
In addition, some associated SNPs were consistent with QTLs detected by multi-population linkage mapping or association analysis. On chromosome 1, a significant SNP (Affx-291414698) associated with 201DRI was located 45 kb from the nuclear NAC-transcription factor 49 (NAC49), which have been proved that ZmMPK5 phosphorylates the subdomain Thr-26 in NAC49 and enhances SOD activity to improve the oxidative stress tolerance of maize [55]. Affx-88980407 associated with 2019DS, Affx-291432872 for 2019DRI, Affx-291412215 for 201DRI, and other four SNPs (Affx-88980402, Affx-88980404, Affx-88980407 and Affx-291389339) for 201DS, were co-located in the MQTL10 interval with a size of 22.38-28.27Mb on chromosome 2 [53]. Affx-88984415 associated with 2019WW located on chromosome 3, was co-located in the QTL named qWW-GY7-1 interval with a size of 17.7-19.8Mb located using a doubled happy (DH) population consensus of 217 lines [56] . Affx-291377201 associated with 2020DS located on chromosome 1, was located in the region of mQTL_GY_1a with a interval of 161.07-183.29Mb by using three tropical maize populations [57], also shared the same QTL region on 1.06 for GY across WW and WS environments by using RFLP markers in a F3 population of tropical maize [58] and identified a cluster of QTL on bin 1.06 related to GY and other yield contributing traits under drought as well as WW conditions in Mexican and African environments [59]. The above significant SNP can provide a reference for further research and exploration of maize drought resistance molecular breeding.
Candidate genes for drought resistance
By combining GWAS and two sets of transcriptome data, a total of 41 (Table S4 & Table S7) and 265 (Table S5 & Table S8) genes were mined and annotated, respectively. These genes participated in the regulation of the JA-mediated signaling pathway, response to oxygen-containing compounds, response to endogenous stimuli, response to ABA and JA metabolic process, and response to stress. In addition, some transcription factors, such as nuclear factor-YA, C2C2-DNA-binding one zinc finger, ethylene responsive factor (ERF), B3, bZIP, E2f-dp, OVATE family protein, NAC, myeloblastosis, and basic helix–loop–helix were associated with stress. Candidate genes, including GRMZM2G322672 (EREB37), GRMZM2G026926 (ERF), and GRMZM2G169654 (RAV), belong to the AP2/EREBP family, which has been cloned in crops, and performed important roles to response drought have been elucidated [53, 58]. In addition, the candidate genes GRMZM2G370026 (bZIP31), GRMZM2G140355 (bZIP80), and GRMZM2G006578 (bZIP7) belong to the bZIP family, which participates in various secondary metabolite synthesis pathways and protects plants from damage and stress by accumulating various metabolic substances [60,61,62,63,64].
Seven of these associated SNPs explained more than 10% of the phenotypic variation, and the related putative genes that showed significantly differential expression under DS conditions were GRMZM2G086430 (Affx-159033091), GRMZM2G167220 (Affx-291389086), and GRMZM2G050234 (Affx-291395613) (Table 3). GRMZM2G086430 (SPX8) is a membrane protein containing the domain SPX8, where the promoter region of ZmSPXs is rich in biological/abiotic stress elements [65]. GRMZM2G167220 is a cytokinin dehydrogenase involved in the synthesis of tolerance-related metabolites during deep sowing of maize, which is an important method to improve drought resistance [66]. GRMZM2G050234 is translated into an oxidoreductase that is involved in the REDOX process [67, 68]. Another candidate gene, GRMZM2G347043 (ZmNAC49), with a low PVE for 201DRI, has demonstrated that drought tolerance in maize can be improved by reducing stomatal density during the seedling stage, enhancing oxidative stress tolerance and responding to the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [55, 57, 69,70,71]. ZmNAC49 overexpression enhances drought tolerance of maize seedlings [72]. Thus, the above genes may be used for further research to understand drought resistance in maize.
A large gap for improving drought resistance in maize
Enhancing drought tolerance in plants is a multifaceted process. While genetic engineering is one approach, selecting and accumulating favorable alleles of crucial stress-tolerance genes can also be a promising strategy for crop improvement [22]. In this study, the assembly of superior alleles illustrated that the number of excellent alleles for DRI was positively correlated with the DRI value. Among the 54 significant loci, only 14 loci contained superior alleles in more than 50% of materials in AM201, and the largest DRI value still did not reach 1.2 (Fig. 4A-C). This indicates that enriching superior alleles in the existing drought-resistant germplasm is not sufficient, which is consistent with a previous study [46]. Sensitivity to drought increases concomitantly with increasing maize yield [73]. The synergy between drought resistance and yield may be one reason why extremely drought-resistant materials are not frequently used in breeding. In other words, some drought resistance-related superior alleles will be fixed and others will be lost during the breeding process. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the synergistic effect between drought resistance and yield and some progress has been made in plants.
For example, genetic engineering may be used to manipulate or delete genes, such as ZmMPKL1 and its homologs, to maintain yield stability by reducing the drought sensitivity of maize [24]. ZmGLK44 promotes tryptophan levels by activating the expression of tryptophan biosynthetic genes, which further enhances ABA signaling and water use efficiency to help plants resist drought [47]. The mechanisms driven by transposable element-inverted repeat structures pave the way for genome manipulation to design crops with high stress tolerance and high yields for the future [74]. These results indicated that drought resistance might be improved by filling the gap between drought resistance and yield with synergistic effects.
Conclusion
In this study, GY was investigated in associated panels under five environmental conditions with different moisture treatments for two years. A total of 147 significant SNP loci were identified using GWAS, of which 109 were associated with GY under DS and the DRI. There was a positive relationship between the number of superior alleles and DRI. Finally, 22 genes involved in cytokinin dehydrogenase activity, transcription factor activity, and ion binding were considered candidate genes by integrating transcriptome data. This study provides important reference information for exploring drought-resistance mechanisms and the application of molecular marker-assisted selection for drought-resistant breeding of maize.
Availability of data and materials
All reasonable requests for data and research materials should be addressed to the corresponding author (shutuxu@nwafu.edu.cn). Transcriptome data were obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE132113 and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE71723). The data have been uploaded to the National Agricultural Science Data Center (Project number: 2018YFD0100200). Genotype and phenotype data serial number A1C6936557C165AA6602839C316D1BCB and BF5CA18FD7F1AFF75CAFBEDEFE3D4525, respectively.
Abbreviations
- DS:
-
Drought stress
- WW:
-
Well-watered
- CK:
-
Control check
- TY:
-
Taiyuan
- UR:
-
Urumqi
- YL:
-
Yulin
- ZY:
-
ZhangYe
- YC:
-
Yinchuan
- DAP:
-
Days after pollination
- G:
-
Genotype
- E:
-
Environment
- G \(\times\) E:
-
Interaction between genotype and environment
- V9:
-
Ninth leaf
- V12:
-
Twelfth leaf
- V14:
-
Fourteenth leaf
- V16:
-
Sixteenth leaf
- VT:
-
Tasseling
- V:
-
Vegetative stages
- R:
-
Reproductive stages
- DRI:
-
Drought resistance index
- GY:
-
Grain yield
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association study
- ASI:
-
Anthesis and silking interval
- DC:
-
Drought coefficient
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- PVE:
-
Phenotypic variation explanation
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- REDOX:
-
Oxidation-reduction reaction
- NAC:
-
N-acetylcysteine
- ERF:
-
Ethylene-responsive factor
- RAV:
-
Related to ABI3/VP1
- BLUP:
-
Best linear unbiased prediction
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- H2 :
-
Broad-sense heritability
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
References
Daryanto S, Wang L, Jacinthe P. Global Synthesis of Drought Effects on Maize and Wheat Production. Plos One. 2016;11(5): e156362.
Gupta A, Rico-Medina A, Caño-Delgado AI. The physiology of plant responses to drought. Science (New York, NY). 2020;368(6488):266–9.
Hussain M, Mumtaz S. Climate change and managing water crisis: Pakistan’s perspective. Rev Environ Health. 2014;29(1–2):71–7.
Wallace JM, Held IM, Thompson DW, Trenberth KE, Walsh JE. Global warming and winter weather. Science. 2014;343(6172):729–30.
Woodward A, Smith KR, Campbell-Lendrum D, Chadee DD, Honda Y, Liu Q, Olwoch J, Revich B, Sauerborn R, Chafe Z, Confalonieri U, Haines A. Climate change and health: on the latest IPCC report. Lancet. 2014;383(9924):1185–9.
Doell P, Bovolo CI, Parkin G, Sophocleous M. Vulnerability to the impact of climate change on renewable groundwater resources; a global-scale assessment. Environ Res Lett. 2009;4(3):35006.
Wada Y, van Beek LPH, Bierkens MFP. Modelling global water stress of the recent past: on the relative importance of trends in water demand and climate variability. Hydrol Earth Syst Sc. 2011;15(12):3785–808.
Farooq M, Basra SMA, Wahid A, Cheema ZA, Cheema MA, Khaliq A. Physiological Role of Exogenously Applied Glycinebetaine to Improve Drought Tolerance in Fine Grain Aromatic Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agron Crop Sci. 2008;194(5):325–33.
Hu H, Xiong L. Genetic engineering and breeding of drought-resistant crops. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2014;65:715–41.
Nakabayashi R, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Urano K, Suzuki M, Yamada Y, Nishizawa T, Matsuda F, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Shinozaki K, Michael AJ, Tohge T, Yamazaki M, Saito K. Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids. Plant J. 2014;77(3):367–79.
Zhang X, Warburton ML, Setter T, Liu H, Xue Y, Yang N, Yan J, Xiao Y. Genome-wide association studies of drought-related metabolic changes in maize using an enlarged SNP panel. Theor Appl Genet. 2016;129(8):1449–63.
Kim J, To TK, Matsui A, Tanoi K, Kobayashi NI, Matsuda F, Habu Y, Ogawa D, Sakamoto T, Matsunaga S, Bashir K, Rasheed S, Ando M, Takeda H, Kawaura K, Kusano M, Fukushima A, Endo TA, Kuromori T, Ishida J, Morosawa T, Tanaka M, Torii C, Takebayashi Y, Sakakibara H, Ogihara Y, Saito K, Shinozaki K, Devoto A, Seki M. Acetate-mediated novel survival strategy against drought in plants. Nat Plants. 2017;3(7):17097.
Todaka D, Zhao Y, Yoshida T, Kudo M, Kidokoro S, Mizoi J, Kodaira K, Takebayashi Y, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Toyooka K, Sato M, Fernie AR, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Temporal and spatial changes in gene expression, metabolite accumulation and phytohormone content in rice seedlings grown under drought stress conditions. Plant J. 2017;90(1):61–78.
Fabregas N, Lozano-Elena F, Blasco-Escamez D, Tohge T, Martinez-Andujar C, Albacete A, Osorio S, Bustamante M, Riechmann JL, Nomura T, Yokota T, Conesa A, Alfocea FP, Fernie AR, Cano-Delgado AI. Overexpression of the vascular brassinosteroid receptor BRL3 confers drought resistance without penalizing plant growth. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4680.
Wu X, Feng H, Wu D, Yan S, Zhang P, Wang W, Zhang J, Ye J, Dai G, Fan Y, Li W, Song B, Geng Z, Yang W, Chen G, Qin F, Terzaghi W, Stitzer M, Li L, Xiong L, Yan J, Buckler E, Yang W, Dai M. Using high-throughput multiple optical phenotyping to decipher the genetic architecture of maize drought tolerance. Genome Biol. 2021;22(1):185.
Lawrence CJ, Walbot V. Translational genomics for bioenergy production from fuelstock grasses: maize as the model species. Plant Cell. 2007;19(7):2091–4.
Wang C, Li S. Assessment of limiting factors and techniques prioritization for maizeproduction in China. Scientia Agricultrea Sinica. 2010;43:1136–46.
Boyer JS, Byrne P, Cassman KG, Cooper M, Delmer D, Greene T, Gruis F, Habben J, Hausmann N, Kenny N, Lafitte R, Paszkiewicz S, Porter D, Schlegel A, Schussler J, Setter T, Shanahan J, Sharp RE, Vyn TJ, Warner D, Gaffney J. The U.S. drought of 2012 in perspective: A call to action. Glob Food Sec. 2013;2(3):139–43.
Xue Y, Warburton ML, Sawkins M, Zhang X, Setter T, Xu Y, Grudloyma P, Gethi J, Ribaut JM, Li W, Zhang X, Zheng Y, Yan J. Genome-wide association analysis for nine agronomic traits in maize under well-watered and water-stressed conditions. Theor Appl Genet. 2013;126(10):2587–96.
Semagn K, Beyene Y, Warburton ML, Tarekegne A, Mugo S, Meisel B, Sehabiague P, Prasanna BM. Meta-analyses of QTL for grain yield and anthesis silking interval in 18 maize populations evaluated under water-stressed and well-watered environments. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:313.
Thirunavukkarasu N, Hossain F, Arora K, Sharma R, Shiriga K, Mittal S, Mohan S, Namratha PM, Dogga S, Rani TS, Katragadda S, Rathore A, Shah T, Mohapatra T, Gupta HS. Functional mechanisms of drought tolerance in subtropical maize (Zea mays L.) identified using genome-wide association mapping. Bmc Genomics. 2014;15(1):1182.
Wang X, Wang H, Liu S, Ferjani A, Li J, Yan J, Yang X, Qin F. Genetic variation in ZmVPP1 contributes to drought tolerance in maize seedlings. Nat Genet. 2016;48(10):1233–41.
Mao H, Wang H, Liu S, Li Z, Yang X, Yan J, Li J, Tran LP, Qin F. A transposable element in a NAC gene is associated with drought tolerance in maize seedlings. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8326.
Zhu D, Chang Y, Pei T, Zhang X, Liu L, Li Y, Zhuang J, Yang H, Qin F, Song C, Ren D. MAPK-like protein 1 positively regulates maize seedling drought sensitivity by suppressing ABA biosynthesis. Plant J. 2020;102(4):747–60.
Liu B, Zhang B, Yang Z, Liu Y, Yang S, Shi Y, Jiang C, Qin F. Manipulating ZmEXPA4 expression ameliorates the drought-induced prolonged anthesis and silking interval in maize. Plant Cell. 2021;33(6):2058–71.
Henderson CR. Best linear unbiased estimation and prediction under a selection model. Biometrics. 1975;31(2):423–47.
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Usinglme4. J Stat Softw. 2015;67(1):1–48.
Lan JS. Comparison of evaluating methods for agronomic drought resistance in crops. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica. 1998;7:85–7.
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM. Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis1. Crop Sci. 1985;25(1):i1985–11183.
Ding J, Zhang L, Chen J, Li X, Li Y, Cheng H, Huang R, Zhou B, Li Z, Wang J, Wu J. Genomic Dissection of Leaf Angle in Maize (Zea mays L.) Using a Four-Way Cross Mapping Population. Plos One. 2015;10(10):e141619.
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81(24):8014–8.
Stewart CNJ, Via LE. A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique useful for RAPD fingerprinting and other PCR applications. Biotechniques. 1993;14(5):748–50.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MAR, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PIW, Daly MJ, Sham PC. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81(3):559–75.
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009;19(9):1655–64.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–4.
Myles S, Boyko AR, Owens CL, Brown PJ, Grassi F, Aradhya MK, Prins B, Reynolds A, Chia JM, Ware D, Bustamante CD, Buckler ES. Genetic structure and domestication history of the grape. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(9):3530–5.
Zhang C, Dong S, Xu J, He W, Yang T. PopLDdecay: a fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics. 2019;35(10):1786–8.
Liu X, Huang M, Fan B, Buckler ES, Zhang Z. Iterative usage of fixed and random effect models for powerful and efficient genome-wide association studies. Plos Genet. 2016;12(2):e1005767.
Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):27–30.
Kanehisa M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 2019;28(11):1947–51.
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Ishiguro-Watanabe M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D587–92.
Yu G, Wang L, Han Y, He Q. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics. 2012;16(5):284–7.
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498–504.
Tuberosa R, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Giuliani MM, Salvi S, Conti S. Identification of QTLs for root characteristics in maize grown in hydroponics and analysis of their overlap with QTLs for grain yield in the field at two water regimes. Plant Mol Biol. 2002;48(5–6):697–712.
Bänziger M, Araus J. Recent Advances in Breeding Maize for Drought and Salinity Stress Tolerance. In.: Springer Netherlands; 2007; 587-601.
Setter TL, Flannigan BA, Melkonian J. Loss of Kernel Set Due to Water Deficit and Shade in Maize. Crop Sci. 2001;41(5):1530–40.
Yuan Y, Cairns JE, Babu R, Gowda M, Makumbi D, Magorokosho C, Zhang A, Liu Y, Wang N, Hao Z, San VF, Olsen MS, Prasanna BM, Lu Y, Zhang X. Genome-wide association mapping and genomic prediction analyses reveal the genetic architecture of grain yield and flowering time under drought and heat stress conditions in maize. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:1919.
Zhang F, Wu J, Sade N, Wu S, Egbaria A, Fernie AR, Yan J, Qin F, Chen W, Brotman Y, Dai M. Genomic basis underlying the metabolome-mediated drought adaptation of maize. Genome Biol. 2021;22(1):260.
Zhang X, Mi Y, Mao H, Liu S, Chen L, Qin F. Genetic variation in ZmTIP1 contributes to root hair elongation and drought tolerance in maize. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020;18(5):1271–83.
Zhang T, Yu L, Zheng P, Li Y, Rivera M, Main D, Greene SL. Identification of Loci Associatedwith Drought Resistance Traits in Heterozygous Autotetraploid Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Using Genome-Wide Association Studies with Genotyping by Sequencing. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138931.
Sun F, Chen Q, Chen Q, Jiang M, Qu Y. Yield-based drought tolerance index evaluates the drought tolerance of cotton germplasm lines in the interaction of genotype-by-environment. PeerJ. 2023;11:e14367.
Khatibi A, Omrani S, Omrani A, Shojaei SH, Mousavi S, Illés Á, Bojtor C, Nagy J. Response of maize hybrids in drought-stress using drought tolerance indices. Water. 2022;14(7):1012.
Messmer R, Fracheboud Y, Banziger M, Vargas M, Stamp P, Ribaut JM. Drought stress and tropical maize: QTL-by-environment interactions and stability of QTLs across environments for yield components and secondary traits. Theor Appl Genet. 2009;119(5):913–30.
Morosini JS, Mendonça LD, Lyra DH, Galli G, Vidotti MS, Fritsche-Neto R. Association mappingfor traits related to nitrogen use efficiency in tropical maize lines under field conditions. Plant Soil. 2017;421(1):453–63.
Xiang Y, Bian X, Wei T, Yan J, Sun X, Han T, Dong B, Zhang G, Li J, Zhang A. ZmMPK5 phosphorylates ZmNAC49 to enhance oxidative stress tolerance in maize. New Phytol. 2021;232(6):2400–17.
Li W, Liu Z, Shi Y, Song Y, Wang T, Xu C, Li Y. Detection of Consensus Genomic Region of QTLs Relevant to Drought-Tolerance in Maize by QTL Meta-Analysis and Bioinformatics Approach. Acta Agronomica Sinica. 2010;36(9):1457–67.
Wang N, Cheng M, Chen Y, Liu B, Wang X, Li G, Zhou Y, Luo P, Xi Z, Yong H, Zhang D, Li M, Zhang X, Vicente FS, Hao Z, Li X. Natural variations in the non-coding region of ZmNAC080308 contributes maintaining grain yield under drought stress in maize. Bmc Plant Biol. 2021;21(1):305.
Almeida GD, Makumbi D, Magorokosho C, Nair S, Borém A, Ribaut JM, Bänziger M, Prasanna BM, Crossa J, Babu R. QTL mapping in three tropical maize populations reveals a set of constitutive and adaptive genomic regions for drought tolerance. Theor Appl Genet. 2013;126(3):583–600.
Ribaut JM, Jiang C, Gonza´lez-de-Leo´n D, Edmeades GO, Hoisington DA. Identification of quantitative trait loci under drought conditions in tropical maize. 1. Yield components and marker-assisted selection strategies. Theor Appl Genet. 1997;94:887–96.
Zhang G, Chen M, Li L, Xu Z, Chen X, Guo J, Ma Y. Overexpression of the soybean GmERF3 gene, an AP2/ERF type transcription factor for increased tolerances to salt, drought, and diseases in transgenic tobacco. J Exp Bot. 2009;60(13):3781–96.
Xiong H, Yu J, Miao J, Li J, Zhang H, Wang X, Liu P, Zhao Y, Jiang C, Yin Z, Li Y, Guo Y, Fu B, Wang W, Li Z, Ali J, Li Z. Natural Variation in OsLG3 Increases Drought Tolerance in Rice by Inducing ROS Scavenging. Plant Physiol. 2018;178(1):451–67.
Hsieh T, Li C, Su R, Cheng C, Sanjaya, Tsai Y, Chan M. A tomato bZIP transcription factor, SlAREB, is involved in water deficit and salt stress response. Planta. 2010;231(6):1459–73.
Liu C, Mao B, Ou S, Wang W, Liu L, Wu Y, Chu C, Wang X. OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol. 2014;84(1–2):19–36.
Hartmann L, Pedrotti L, Weiste C, Fekete A, Schierstaedt J, Göttler J, Kempa S, Krischke M, Dietrich K, Mueller MJ, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Hanson J, Dröge-Laser W. Crosstalk between Two bZIP Signaling Pathways Orchestrates Salt-Induced Metabolic Reprogramming in Arabidopsis Roots. Plant Cell. 2015;27(8):2244–60.
Xiao J, Xie X, Li C, Xing G, Cheng K, Li H, Liu N, Tan J, Zheng W. Identification of SPX family genes in the maize genome and their expression under different phosphate regimes. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021;168:211–20.
Zhao X, Zhong Y, Zhou W. Molecular mechanisms of mesocotyl elongation induced by brassinosteroid in maize under deep-seeding stress by RNA-sequencing, microstructure observation, and physiological metabolism. Genomics. 2021;113(6):3565–81.
Knauer S, Javelle M, Li L, Li X, Ma X, Wimalanathan K, Kumari S, Johnston R, Leiboff S, Meeley R, Schnable PS, Ware D, Lawrence-Dill C, Yu J, Muehlbauer GJ, Scanlon MJ, Timmermans M. A high-resolution gene expression atlas links dedicated meristem genes to key architectural traits. Genome Res. 2019;29(12):1962–73.
Wang Y, Xu J, Yu J, Zhu D, Zhao Q. Maize GSK3-like kinase ZmSK2 is involved in embryonic development. Plant Sci. 2022;318: 111221.
Vilela B, Moreno-Cortes A, Rabissi A, Leung J, Pages M, Lumbreras V. The maize OST1 kinase homolog phosphorylates and regulates the maize SNAC1-type transcription factor. Plos One. 2013;8(2):e58105.
Estermann MA, Ugarte A, Pretini N, Vega CRC, Olmos SE. Allele mining in the Argentine public maize inbred line collection of two paralogous genes encoding NAC domains. Mol Breed. 2017;37(2):12.
Wang G, Yuan Z, Zhang P, Liu Z, Wang T, Wei L. Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in maize under drought stress and rewatering. Physiol Mol Biol Pla. 2020;26(4):705–17.
Xiang Y, Sun X, Bian X, Wei T, Han T, Yan J, Zhang A. The transcription factor ZmNAC49 reduces stomatal density and improves drought tolerance in maize. J Exp Bot. 2021;72(4):1399–410.
Lobell DB, Roberts MJ, Schlenker W, Braun N, Little BB, Rejesus RM, Hammer GL. Greater sensitivity to drought accompanies maize yield increase in the U.S. Midwest. Science. 2014;344(6183):516–9.
Sun X, Xiang Y, Dou N, Zhang H, Pei S, Franco AV, Menon M, Monier B, Ferebee T, Liu T, Liu S, Gao Y, Wang J, Terzaghi W, Yan J, Hearne S, Li L, Li F, Dai M. The role of transposon inverted repeats in balancing drought tolerance and yield-related traits in maize. Nat Biotechnol. 2023;41(1):120–7.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Maize in the Arid Area of the Northwest Region for their help and support with field material planting and phenotype collection. Also, we would like to thank High-Performance Computing of Northwest A&F University (HPC of NWAFU) for providing computing resources.
Funding
This study was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (CARS-02-77 and 2023-YBNY-027) and the Innovation Project of the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0100200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xu Shutu and Xue Jiquan conceived the study and designed the experiments. Zhang Ningning, Liu Binbin, Ye Fan, Hu Die, Wu Ying, Chang Jianzhong, Zhou Yuqian, Wang Yejian, Zhang Wenjie, and Zhang Xinghua performed field experiments and collected phenotypes. Zhang Ningning, Liu Binbin, and Ye Fan performed data analysis and wrote the manuscript. Shutu Xu and Jiquan Xue edited the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Figure S1. The distribution density of 42,003 SNPs on different chromosomes.
Additional file 2:
Figure S2. Significant SNPs co-located in different traits. 2019DS, 2020DS, 201DS represented the results grain yield under drought stress in AM115,AM180 and AM201 respectively. And 2019WW, 2020WW and 201WS represented the results of grain yield under well water in AM115, AM180 and AM201 respectively.
Additional file 3:
Figure S3. Transcriptome data 1 and 2 co-locate candidate genes.
Additional file 4:
Table S1. List of 201 inbred lines.
Additional file 5:
Table S2. Joint analysis of variance of yield under different treatment conditions. SS: sum of squares; SS(%): Percent of SS; MS: mean squares; *, and ** means significantly different for P <= 0.05, P <= 0.01.
Additional file 6:
Table S3. Phenotypic interpretation rate of significant SNP loci in different traits. WW: well-watered, DS: drought stress; DRI: drought resistance index; Percentage (%) : estimated by the ratio of the number of superior alleles for each stable loci within different group with the number of all inbred lines; The red-marked SNP is co-located with 201DRI and 2020DRI; The blue-marked SNP is co-located with 201DS and 2020DS; The purple-marked SNP is co-located with 201DS and 2019DS; The green-marked SNP is co-located with all traits.
Additional file 7:
Table S4. 41 Key differentially expressed genes in different periods and tissues under drought stress.
Additional file 8: Table S5.
265 key differentially expressed genes in different tissues and different periods under drought stress.
Additional file 9:
Table S6. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of 22 candidate genes.
Additional file 10:
Table S7. GO enrichment for 41 differentially expressed genes.
Additional file 11:
Table S8. GO enrichment for 265 differentially expressed genes.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ningning, Z., Binbin, L., Fan, Y. et al. Molecular mechanisms of drought resistance using genome-wide association mapping in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Plant Biol 23, 468 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04489-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04489-0