Abstract
As one of the largest plant specific transcription factor families, NAC family members play an important role in plant growth, development and stress resistance. To investigate the function of NAC transcription factors during abiotic stress, as well as during somatic embryogenesis, we identified and characterized the NAC gene family in Liriodendron chinense. We found that most LcNAC members contain more than three exons, with a relatively conserved gene and motif structure, especially at the N-terminus. Interspecies collinearity analysis revealed a closer relationship between the L. chinense NACs and the P. trichocarpa NACs. We analyzed the expression of LcNAC in different tissues and under three abiotic stresses. We found that 12 genes were highly expressed during the ES3 and ES4 stages of somatic embryos, suggesting that they are involved in the development of somatic embryos. 6 LcNAC genes are highly expressed in flower organs. The expression pattern analysis of LcNACs based on transcriptome data and RT-qPCR obtained from L. chinense leaves indicated differential expression responses to drought, cold, and heat stress. Genes in the NAM subfamily expressed differently during abiotic stress, and LcNAC6/18/41/65 might be the key genes in response to abiotic stress. LcNAC6/18/41/65 were cloned and transiently transformed into Liriodendron protoplasts, where LcNAC18/65 was localized in cytoplasm and nucleus, and LcNAC6/41 was localized only in nucleus. Overall, our findings suggest a role of the NAC gene family during environmental stresses in L. chinense. This research provides a basis for further study of NAC genes in Liriodendron chinense.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Transcription factors (TFs) are a class of proteins that regulate the expression of target genes by binding to the specific cis-acting elements of their promoters. Plant TFs such as AP2, bHLH, ARF, MYC, WRKY and NAC, are essential regulators in many biological processes [1,2,3,4]. Among them, the NAC gene family is one of the largest families of transcription factors in plants. The NAC gene family name is composed of the initials of NAM (No Apical Meristem from Petunia hybrida), AF1/2 (transcriptional activator 1/2 from Arabidopsis thaliana) and CUC2 (cup-shaped cotyledon from Arabidopsis thaliana) transcription factors. So far, the NAC gene family has been characterized in a large number of plant species, including 117 NAC genes in Arabidopsis thaliana, 151 NAC genes in Oryza sativa L. subsp. japonica cv. [5], 72 NAC genes in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) [6], 93 NAC genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) [7], 73 NAC genes in Pineapple (Ananas comosus) [8], 180 NAC genes in apple (Malus domestica) [9] and 170 NAC genes in Populus trichocarpa [10].
NAC transcription factors usually have a highly conserved DNA-binding domain, a NAC domain, situated at the N-terminus, and a variable transcriptional regulatory region located at the C-terminus of the protein [11]. Generally, the N-terminal NAC domain is about 150 amino acid residues in length and consists of five (A-E) subdomains. The highly conserved subdomains C and D are predicted to bind to DNA, subdomain A is involved in homo- and heterodimerization, while the divergent subdomains B and E influence the functional diversity of NAC proteins [12, 13].
Many studies have shown that NAC genes play important roles in various biological processes, including in the regulation of flower and leaf development, secondary cell wall thickening, protein and lipid metabolism pathways, leaf senescence and fruit development, lateral root formation and seed germination. For example, in the cuc1; cuc2 double mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana, sepals, stamens and cotyledons fuse and apical meristem tissue has difficulty to form [14]. RhNAC100 in Rosa hybrida is post-transcriptionally regulated by ethylene through miR164, and overexpression of RhNAC100 significantly reduces petal size by inhibiting petal cell expansion [15]. In addition to the involvement of NAC in plant growth, some studies have shown that NAC family members play a role in somatic cell development. In the study of Dendrobium candidum, zhao et al. analyzed the RT-PCR and in situ hybridization of DcNAC and found that DcNAC was involved in the development and maturation of embryos [16]. Larsson et al. found that PaNAC01 of Picea abies was cloned into a cuc1cuc2 double mutant of A. thaliana, where PaNAC01 could functionally replace CUC2 and was associated with SAM differentiation and cotyledon formation [17]. Munir et al. identified Dimocarpus longan Lour and explored expression patterns during early somatic embryogenesis, and found that the expression of DlNACs at EC and GE stages was higher than that at ICpEC stages [18].
More and more reports have shown that NAC proteins play a major role in abiotic stress response [19]. The grape transcription factor VvNAC17, when overexpressed in A. thaliana, increases sensitivity to abscisic acid and improves salt, freezing and drought tolerance of the transgenic plant [20]. Overexpression of the SlNAC35 transcription factor improves cold tolerance of transgenic tomato plants [21]. The stress-responsive transcription factor SNAC3, when overexpressed in rice, increases heat and drought tolerance by regulating reactive oxygen species [22]. The transcription factors ANAC096 and bZIP act cooperatively in regulating dehydration and osmotic stress response in A. thaliana [23]. Overexpression of VvNAC08 from grapevine enhances drought tolerance in A. thaliana [24]. TaNAC29 from wheat, when overexpressed in A. thaliana, enhances its salt and drought tolerance [25]. Plants with ectopic expression of MlNAC12 have a higher rate of survival and experience reduced water loss, resulting in increased drought resistance [26].
L. chinense (Liriodendron chinense (Hemsl.) Sarg.) is a deciduous tree from the Magnoliaceous family, a rare species in China that often grows in mountainous forested areas at an altitude of 1000m [27]. Its flowers are shaped like tulips and its wood has a high commercial value. However, unfavorable environmental conditions such as heat, cold and drought affect the growth and development of L. chinense [28, 29]. As mentioned above, NAC transcription factors play an important role in response to abiotic stress, but NAC genes have rarely been studied in L. chinense. To investigate how L. chinense responds to abiotic stress, we focused on its endogenous NAC gene family. In this study, we performed genome wide identification of the NAC gene family members in L. chinense. We studied their subcellular localization, phylogenetic relationships and conserved motifs, and analyzed transcriptome data to study the expression of NAC genes at different developmental stages. This research provides a basis for further exploration of the function of NAC genes in L. chinense.
Material and methods
NAC gene identification
The complete genome, protein sequences, and associated files of L. chinense were downloaded from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly/GCA_003013855.2). The A. thaliana genome data was downloaded from the TAIR (https://www.arabidopsis.org/) database. The NAM domain (PF02365) hidden Markov model file was retrieved from the Pfam website (https://pfam.xfam.org/). The NAM domain was utilized to search for LcNAC protein sequences using HMMER3.0 software with an E-value threshold of 1E-3. All candidate LcNAC proteins were aligned against AtNACs with BLASTp (v2.9.0) under an E-value cutoff of 1E-5. Finally, all candidate LcNAC genes were validated using the Conserved Domain Search tool (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi). The online website (http://web.expasy.org/Compute-pI/) was utilized for the prediction of molecular weight (MW) and isoelectric point (pI). The conserved NAC motifs of L. chinense were subjected to analysis using the MEME tool (https://meme-suite.org/meme/). Cis-acting elements of LcNAC genes were analyzed using Plantcare (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/).
Phylogenetic tree construction, chromosomal localization, collinearity analysis and protein interaction network prediction
The NAC protein sequences of A. thaliana and L. chinense were analyzed using Jalview software. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA7with the maximum likelihood method and 1000 bootstrap replicates [30]. We mapped the LcNAC gene chromosomal positions using TBtools software (TBtools.v1.09854). The collinearity and gene replication analysis were performed with the Dual Systeny Plot for MCscanX, Circle Gene View and Advanced Circos in TBtools. L. chinense NAC proteins were compared to their A. thaliana homologues using Blastp, referring to the known network relationship of A. thaliana NAC proteins on the String website (https://string-db.org/). The interaction of NAC proteins in L. chinense was predicted, and the NAC protein interaction network of L. chinense was constructed, with the default parameter settings.
Transcriptome sequencing of somatic embryos in L. chinense
Embryonic callus of L. chinense was induced to form somatic embryos in liquid suspension culture, and samples were collected at successive somatic embryo stages (11 stages) for RAN-seq (data not yet published). Stages were as follows: embryonic callus culture for 20 days (PEMs), liquid suspension culture for 10 days (ES1), single cell culture for 2 days (ES2), ABA induction for 1 day (ES3), ABA induction for 3 days (ES4), 7 days spherical embryo (ES5), 13-day heart-shaped embryo (ES6), 19-day torpedo embryo (ES7), 25-day immature cotyledon embryo (ES8), 31-day mature cotyledon embryo (ES9) and 37-day plantlet (PL). The Fragments Per Kilobase per million mapped fragments (FPKM) data of NAC genes at different stages of somatic embryos is shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Material culture, abiotic stress treatment, RNA-seq and RT-qPCR analysis of L. chinense
The conditions in the growth chamber were set as follows: 23 °C, 5000 Lux light intensity, 16 h light/8 h darkness, relative humidity 55% [31]. 36 seedlings with 3–4 true leaves were divided into three groups and subjected to 40℃ for heat treatment, 20% polyethylene glycol (PEG6000) for drought treatment and 4℃ for cold treatment, respectively. Leaf samples were collected at 0 h, 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h and 3d, respectively. Total RNA was isolated and followed by RNA-seq. Raw data was carried out quality control through FastQC (v0.12.1) and then were filtered by using Trimmomatic (v0.39) according to the quality control results, parameters as followed: remove adapters (ILLUMINACLIP: TruSeq3-PE.fa:2:30:10), remove leading low quality or N bases (LEADING:10), remove trailing low quality or N bases (TRAILING:10), scan the read with a 4-base wide sliding window, cutting when the average quality per base drops below 20 (SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20), drop reads below the 90 bases long (MINLEN:90). The clean reads were obtained from the Raw data by this step. The Q20, Q30, and GC content of the clean data were calculated simultaneously. High quality clean data can be used for analysis in the next step.
The paired-end clean reads were aligned to the Liriodendron genome that was built using Hisat2 (v2.2.1). Then we used DESeq2 (v1.16.1) to determine differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with the (ANOVA method: p.adjust < 0.05, |Log2FC|> 1). Then we selected the Kallisto (v0.46.2) to quantify gene expression by calculating all clean reads. The Fragments Per Kilobase per million mapped fragments (FPKM) values of individual genes were counted and FPKM values were used to calculate the transcript abundance of LcNACs. The transcriptome data can be downloaded from the NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA679089/) & (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA679101/). The transcriptional abundance of LcNAC genes at different time point of stress treatment was calculated based on transcriptome FPKM data, as shown in Supplementary Table S2 (cold and heat: PRJNA679089; drought: PRJNA679101). Phloem and xylem samples were obtained simply by separating the bark/phloem from the xylem core. A heat map was constructed (FPKM + 1, log base 2) using TBtools software [32].
Plant total RNA was extracted according to the KK Fast Plant Total RNA Kit (ZP405K) instructions and cDNA was synthesized using a reverse transcription kit. RT-qPCR-specific primers were designed using Primer (premier 6.0) software on the basis of the reference gene sequence, as shown in Supplementary Table S3. A LightCycler480 II (Roche, Switzerland) was used to detect expression of the gene of interest. SYBR Green Premix Pro Taq HS qPCR Kit (AG11701, ACCURATE BIOTECHNOLOGY, HUNAN, Co., Ltd.) was used for qPCR reactions. The RT-qPCR reaction procedure used was 95 °C for 2 min; 95 °C 5 s, 60 °C 30 s, 40 cycles, each reaction was performed in three biological triplicates and three technical replicates. LcActin and LcUBQ10 were used as dual internal reference genes [31, 33], and the gene expression calculation was analyzed via the 2−ΔΔCt method, visualized by Graphpad software.
Subcellular localization
LcNAC6/18/41/65 target fragments were obtained by PCR. The plasmid CaMV35S: GFP in pCAMBIA1302 was digested with NcoI enzyme, and the linear vector fragment was ligated with the target gene fragment to construct the CaMV35S: NACs-GFP fusion expression vector. Plasmids were extracted using an endotoxin-free plasmid extraction kit (DP117, TIANGEN). CaMV35S: NACs-GFP and CaMV35S: H2B-MCherry plasmids were transformed into protoplasts by PEG mediated transient transformation method. After 3 days of dark culture, GFP was observed using a laser confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM800).
Results
Identification and phylogenetic analysis of the L. chinense NAC gene family
The NAM domain was used as input to search for LcNAC protein sequences through HMMER3.0 software. 85 NAC gene family members were identified in L. chinense, 0.73 times the amount of NAC genes in the A. thaliana genome. We named the individual genes LCNAC01-LCNAC85, based on their position on the chromosome. The LcNAC genes are unequally distributed across the 17 L. chinense chromosomes, and a few genes could not be pinpointed to a definite chromosomal location, since they were present on genomic scaffolds (Fig. 1B). All LcNAC proteins contain either a conserved NAC domain (PF01849) or a NAM domain (PF02365). We analyzed the physicochemical properties of the 85 LcNAC genes, including amino acid number, molecular weight, isoelectric point and predicted subcellular localization (Supplementary Table S4). Amino acid length ranged from 102 (LcNAC36) to 842 (LcNAC66), the relative molecular weight ranged from 11337.81 Da (LcNAC36) to 93486.99 Da (LcNAC66), which is positively correlated with the amino acid number. 42 genes are basic proteins (pI > 7), and others are acidic proteins (pI < 7) among the NAC gene family and they have an isoelectric point between 4.19 (LcNAC27) and 9.85 (LcNAC63).
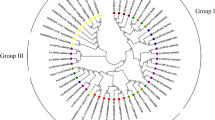
Phylogenetic tree analysis and Chromosomal location of the NAC gene family in L. chinense. A Phylogenetic tree analysis of the L. chinense and A. thaliana NAC genes. Blue stars represent A. thaliana and red circles represent L. chinense. B Distribution of LcNAC genes on L. chinense chromosomes and scaffolds. All named LcNAC genes are displayed on L. chinense chromosome, with the chromosome number marked at the top of each strip. The lines inside the chromosomes represent gene density
To explore the evolutionary interrelatedness of the LcNAC genes, we used the NAC protein sequences from A. thaliana and L. chinense to construct a phylogenetic tree. AtNACs can be subdivided into 17 subgroups [34], while LcNAC genes are divided into 16 subgroups (Fig. 1A). The ANAC063 subfamily contains 12 genes, making it the biggest subfamily. The ANAC001 subfamily contains 6 A. thaliana genes, but no LcNAC genes. The number of LcNAC members within each subfamily varies greatly.
Domain, motif and gene structure analysis of LcNACs
NAC proteins have a conserved NAM domain for DNA binding which is a key region for the biological functions of NAC proteins. Therefore, we focused on the differences between the domain sequences of L. chinense NAC members. We divided the NAC domain of L. chinense into five subdomains A-E. Most LcNAC proteins contain five conserved subdomains within their amino terminus (Fig. 2), indicating their strong sequence conservation during the evolutionary process. However, a few genes (LcNAC01, LcNAC22, LcNAC42, LcNAC61) have incomplete subdomains.
Multiple sequence alignment of the NAC domains from 85 LcNAC proteins. Some of the incomplete sequences or sequences which do not contain N-terminal domains were omitted from the above alignment. No color means that the similarity between amino acid residues of NAC gene family members at this site is less than 35%
To further explore LcNAC protein sequences, we analyzed the conserved motifs of LcNAC proteins. Ten conserved motifs were identified (Fig. 3A), ranging in length from 8 to 50aa (Supplementary Table S5). Motifs 1–5 correspond to the subdomains A-E. Motif 10 is only present in a small number of LcNAC genes. Further analysis of its evolutionary origin revealed that the protein sequences with motif 10 belong to subfamily ANAC063. LcNAC36 and LcNAC85 contain only one conserved motif (Motif3). In addition, some NAC family members, such as LcNAC10, LcNAC27, LcNAC42, LcNAC48, do not contain these motifs.
To further understand the structure of LcNAC genes, we analyzed their intron/exon compositions (Fig. 3B). The number of introns ranged from 1 to 7 and the number of exons ranged from 2 to 8, with LcNAC43 containing the largest number of introns (7) and exons (8). Most LcNAC genes contain three exons. Genes from the same subfamilies are similar in exon length, intron position and number, indicating that the NAC family gene structure is relatively conserved.
Gene duplication and collinearity analysis of LcNACs
To address to what extent gene duplication has contributed to LcNAC family expansion, we annotated and analyzed the intraspecific collinearity of LcNAC genes. The results showed that there are 20 collinearity pairs within the LcNAC gene family (Fig. 4). Chr2 and Chr4 contain the highest number of duplicated genes, while the other three paralogous gene pairs are located on Chr3 and Chr15 chromosomes. The remaining chromosomes contain either a single or two segmental duplications.
To further explore the evolutionary interrelationships of the NAC genes in different species, we performed interspecies collinearity analysis between L. chinense and A. trichopoda, A. thaliana, O. sativa, V. vinifera and P. trichocarpa (Fig. 5). The NAC family members of L. chinense have the most collinear pairs with P. trichocarpa, with a total of 82 collinear pairs, indicating a close evolutionary relationship between the NAC genes from L. chinense and P. trichocarpa. Furthermore, LcNAC14, LcNAC28 and LcNAC50 genes in L. chinense have homologous relationships with A. thaliana, V. vinifera, and P. trichocarpa. In addition, there were 28 NAC collinear gene pairs between L. chinense and A. thaliana. The protein sequences were compared between L. chinense and A. thaliana, revealing that LcNAC49 is highly homologous with AT1G32770, AT2G46770 and AT3G61910 genes of A. thaliana. AT3G61910 is specifically expressed in both interfascicular fibers and xylem, and acts as a negative regulator in the thickening process of the secondary wall, suggesting the LcNAC49 gene may have a similar function in fiber biosynthesis.
Protein interaction prediction of LcNACs
The interactive relationship of the NAC proteins in L. chinense was predicted by using the interaction of A. thaliana NAC proteins as a reference. We found that a single A. thaliana NAC protein corresponded to one or more NAC proteins of L. chinense. 9 LcNAC proteins (LcNAC12, LcNAC57, LcNAC24, LcNAC80, LcNAC06, LcNAC01, LcNAC67, LcNAC39 and LcNAC03) may be key nodes in the network (Fig. 6). In addition, there is the interaction between NAC and other transcription factors. It is hypothesized that the regulatory cascade of NAC083-CUC2-CUC3 and NAC083-NAC102-ATAF1/2 may be important to perform their functions, suggesting that NACs may be involved in organ growth, development and stress response.
Predicted protein–protein interaction network for the L. chinense NACs. Different line colors represent different types of protein–protein interactions. colored nodes: query proteins and first shell of interactors, white nodes: second shell of interactors, filled nodes: some 3D structure is known or predicted
Analysis of LcNACs Cis-acting elements
To predict the upstream regulators of LcNAC genes, we analyzed the 2000 bp upstream of the LcNAC genes’ transcription start site through the PlantCARE database (Fig. 7). We identified 310 ABRE elements (abscisic acid response elements) indicating possible ABA-dependent regulation, 63 LTR elements (cold temperature response), 361 MYB binding sites (drought response), 48 CAT-box elements (meristem expression associated) and 30 WUN-motif elements (defense and stress response). In addition, response elements for light, circadian rhythm, auxin and methyl jasmonate were identified. Cis-elements are enriched especially in the NAM subfamily. The results suggest that LcNAC genes might be involved in environmental stresses, growth regulation and hormonal regulation, and play important roles in physiological and developmental processes.
Cis-acting elements within the promoter region of L. chinense NAC genes. It represents the number of various cis-acting elements in the promoter region of each LcNAC gene on the right, and squares with different colors on the left represent different types of cis-acting elements and their positions in the promoter region
Expression patterns of LcNAC genes during somatic embryogenesis
NAC genes are involved in somatic embryo development [35]. Consistently, our analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoter region of LcNAC genes showed that it contains regulatory elements associated with embryogenesis. To explore the specific roles of NAC genes during somatic embryogenesis, we analyzed RNA-seq expression data of 11 successive somatic embryo developmental stages (PEMs, ES1, ES2, ES3, ES4, ES5, ES6, ES7, ES8, ES9, PL, see methods) (Fig. 8). More than half of the LcNAC genes are not present during somatic embryogenesis. There are three expression patterns in general; 1) some LcNAC genes are highly expressed during all 11 stages, such as LcNAC01, LcNAC42, LcNAC10, LcNAC47, LcNAC12, LcNAC27 and LcNAC48. 2) some LcNAC genes are specifically expressed during certain specific stages. For example, the expression level of LcNAC58, LcNAC59 and LcNAC40 genes during the ES3 and ES4 stage is a hundred times higher than that of PEMs. The LcNAC41 gene was expressed more than twenty times more strongly in the PL than in the PEMs. 3) some genes are expressed in waves during embryo development; the expression of LcNAC62 in PEMs-ES1 and ES6-8 stages was very high, but its expression decreased during the remaining stages of embryo development. These results suggest that some LcNAC genes are involved in somatic embryo development, especially in regulating certain developmental stages.
Expression patterns of NAC genes in L. chinense at different stages of somatic embryonic development. Embryonic callus culture for 20 days (PEMs), liquid suspension culture for 10 days (ES1), single cell culture for 2 days (ES2), ABA induction for 1 day (ES3), ABA induction for 3 days (ES4), 7 days spherical embryo (ES5), 13-day heart-shaped embryo (ES6), 19-day torpedo embryo (ES7), 25-day immature cotyledon embryo (ES8), 31-day mature cotyledon embryo (ES9) and 37-day plantlet (PL). The color key indicates the range of log 2 transformed FPKM + 1 values. The blue represents high expression level and gray represents low expression level
Expression profiling of LcNAC genes across different tissues
To further investigate LcNAC gene function, 10 NAC genes were selected for expression level analysis in 11 different tissues, including root, xylem, phloem, petiole, mature leaf, young leaf, bud, petal, sepal, stamen and pistil (Fig. 9). 3 genes (LcNAC7, LcNAC65, LcNAC80) are highly expressed in both petals and sepals and 3 genes (LcNAC16, LcNAC18, LcNAC70) are highly expressed in stamens, suggesting that these 6 genes play a role in the L. chinense reproductive organs. Some LcNAC genes are highly expressed in the vegetative organs. For example, LcNAC41 is expressed in both young and mature leaves. LcNAC23 is expressed especially high in roots and phloem. The genes highly expressed in the xylem are LcNAC7, LcNAC16, LcNAC59 and LcNAC80.
Expression analysis of LcNAC genes in different tissues based on RT-qPCR. A Diagram showing the different tissues of L. chinense. The first figure indicates the annotation of different tissues of the plant, the color is only for the convenience of distinguishing different tissues, not the color of the plant itself. The remaining 10 plants represent the cartoon heat map of different tissues expression, with red representing high level of gene expression and green representing low expression level. B The heatmap were drew by TBtools using mean values. Red represents high expression level and green represents low expression level. The expression levels are shown using the log2 transform. Three biological replicates were used
Expression analysis of LcNAC gene under abiotic stress
The NAC gene family has been reported to be widely involved in response to abiotic stress [36]. Therefore, we were interested to know whether this is the case for LcNAC genes in L. chinense. We treated seedlings with three types of abiotic stresses (heat, drought and cold) for 0 h, 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h and 3d. Plant materials were collected, and total RNA was isolated, followed by RNA-Seq analysis. After heat treatment, the expression of 11 LcNAC genes is continuously up-regulated during the treatment (Fig. 10). By contrast, the expression of 6 LcNAC genes is continuously down-regulated during the treatment. The expression of the other 11 genes decreased first, then increased again. After cold treatment, 15 LcNAC genes are continuously up-regulated, while 9 LcNAC genes were persistently down-regulated. The expression level of 16 LcNAC genes increased first, then decreased only to increase again, in a wave-like manner. After drought treatment, there were 10 LcNAC genes with the same trend and double peak expression trend increased twice. Another seven genes went down and then up. Only 6 LcNAC genes are consistently up-expressed and 4 LcNAC genes were consistently down-expressed (Supplementary Figure S1). These various types of expression indicate that there are likely to be functional differences between LcNAC genes in response to abiotic stress.
Transcriptional expression patterns of NAC genes in L. chinense under (A) heat, (B) drought and (C) cold stress. The LcNACs were subjected to three different stress factors: Cold-, Heat-, and Drought stress. Heat_0h, Heat_1h, Heat_3h, Heat_6h, Heat_12h, Heat_1d, Heat_3d represent three biological repetitions of each time point (0 h, 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 1d, 3d). Transcript abundance levels are shown using the log2(FPKM + 1) transform. The values on the right panel of the heatmap indicate the level of expression
To validate our RNA-Seq results, we selected 10 NAC genes from the NAM subfamily for RT-qPCR analysis, since the NAM subfamily members is known to be involved in plant growth and development [36]. We harvested the leaves of L. chinense that were treated with cold, heat and drought stress for the analysis, and the expression of these LcNAC genes are upregulated and downregulated to variable degrees after the treatment. 40% of LcNAC genes (LcNAC06, LcNAC23, LcNAC59, LcNAC65) were down-regulated after 40℃ high temperature treatment compared with the control group (Fig. 11A). Besides, there were some genes that responded dramatically to high temperature treatment (LcNAC16, LcNAC18, LcNAC41, LcNAC80). The representative gene was LcNAC18, its expression level did not change significantly during the period of 0-6 h after high temperature treatment, but showed a leap at the time point of 24 h, and was enhanced many times compared with the control group, LcNAC18 also peaked at the time point of 24 h in the transcriptome (Fig. 11D). The changes in gene expression levels after drought treatment were obviously different from the previous two stresses, and the changes in gene expression trends were more diverse (Fig. 11B). Only LcNAC18 expression was consistently up-regulated, with trends for most genes fluctuated at the 3-day drought treatment time point. The LcNAC16 and LcNAC23 genes increased by 15 and 2 times of the control at 6 h, and the expression trends of these two genes were consistent with those of the RNA-Seq (Fig. 11E). It is possible that osmotic stress due to drought enhanced transcription levels in the short term. In addition, 50% of the genes (LcNAC07, LcNAC41, LcNAC59, LcNAC65, LcNAC70) expression peaked at 24 h after drought treatment, and 20% of the genes (LcNAC06, LcNAC80) expressed with peak expression at 3-day after drought treatment. The peak expression of the LcNAC gene at different epochs indicated a temporal discrepancy in the response to drought stress in members of the LcNAC gene family. The expression levels of three genes (LcNAC16, LcNAC18 and LcNAC41) were continuously increased with increasing time after cold treatment (Fig. 11C). On the contrary, the expression levels of two genes (LcNAC65 and LcNAC80) were continuously down-regulated within 3 days of treatment. The RNA-Seq results showed that the expression of LcNAC16, LcNAC18 and LcNAC41 also increased (Fig. 11F). Overall, our RNA-seq data were consistent with our RT-qPCR results, indicating that our transcriptome data were reproducible.
NAC gene expression in L. chinense under multiple abiotic stresses. A-C RT-qPCR; D-F RNA-Seq. The relative mRNA levels are depicted in the y-axis over time in the x-axis. Red, brown, and blue represent heat, drought, and low temperature stresses, respectively. The area of the circle represents the gene expression level. The bar at the top of the heat map indicates the level of expression. The error line of the bar graph represents the mean ± SD (n = 3)
Subcellular localization of LcNAC genes
Subcellular localization provides important insight into a protein’s function. In order to determine the subcellular localization of LcNAC genes, LcNAC6, LcNAC18, LcNAC41 and LcNAC65 were selected for subcellular localization analysis. The plasmids CaMV35S:LcNAC6-GFP, CaMV35S:LcNAC18-GFP CaMV35S:LcNAC41-GFP, CaMV35S:LcNAC65-GFP, CaMV35S:GFP, and CaMV35S:H2B-mCherry were transformed into L. chinense protoplasts by PEG mediated transformation (Fig. 12). The signal could be detected in the whole cell when CaMV35S:GFP was transformed. The results showed that CaMV35S:LcNAC6-GFP and CaMV35S:LcNAC41-GFP were typical transcription factors localized only in the nucleus. CaMV35S:LcNAC18-GFP and CaMV35S:LcNAC65-GFP not only emit strong fluorescence signals mainly in the nucleus, but also weak signals are detected in the cytoplasm. It is speculated that these two genes may play a role in cytoplasm in addition to the nuclear regulation of transcription factors, and the specific cytoplasm functions remain to be explored in the next step.
NAC subcellular localization in L. chinense. H2B-mCherry (first panel) indicates red fluorescence photography. GFP indicates (second panel) green fluorescence photography. The merged third panel indicates the fusion of red fluorescence, green fluorescence and bright field, the rightmost panel shows the bright field images. Bar = 5 μm
Discussion
The NAC transcription factor family is one of the largest families of transcription factors in plants and has been identified and characterized in a variety of species such as Medicago truncatula [37], Cleistogenes songorica [38], Arachis hypogaea [39], Musa Acuminata [40]. The NAC gene family in Liriodendron chinense remains so far undescribed however. In this study, a total of 85 NAC gene family members of L. chinense were identified genome wide, localized on 17 chromosomes. LcNAC transcription factors could be divided into 16 subfamilies, of which the ANAC063 subfamily contains the most members in L. chinense.
In the evolutionary process of many gene families, there is a diversity of gene structure, which is beneficial to create new functions to adapt to environmental changes. The gene structure of LcNAC genes is similar to that of Fagopyrum tataricum [41]. The N-terminus of NAC transcription factors is highly conserved, and members of different subfamilies contain non-identical motifs, but all contain the DNA binding domain.
Increasing the number of genes in a species depends on gene duplication events, which occur at non-regular frequencies across different lineages. A total of 20 fragment duplication genes occurred in L. chinense, and LcNAC gene duplication occurred on 11 chromosomes (Fig. 4). In addition, the KA/KS value was less than 1, indicating that LcNAC genes received purification selection during evolution (Supplementary Table S6). These results are similar to those of previous studies on L. chinense. Collinearity analysis showed that there are more orthologous genes between L. chinense and P. trichocarpa than between L. chinense and A. thaliana, which may be due to the separate evolution of herbaceous and woody plants. In accordance with the results of previous articles in our laboratory [42], the collinearity between P. trichocarpa and other woody plants is stronger, which may be related to the change of the different environment between woody plants and herbaceous plants.
Predicting the regulatory network of unknown proteins from the regulatory network of known proteins is a common method to study the regulatory network of unknown proteins in different species. In this study, using A. thaliana proteins as the reference, it was predicted that nine LcNAC proteins play key roles in the protein regulatory network of L. chinense. Nine LcNAC proteins have regulatory relationships with other proteins, and the ATAF subfamily plays a key role in the protein regulatory network. In addition, there is an interaction between BABY BOOM (BBM) family related proteins and NAC proteins, which is consistent with previous studies that there is a mutual regulatory relationship between NAC proteins and BBM proteins [43]. There is also an interaction between the xylem development related factor VND1 and NAC proteins. The genes regulating the formation and differentiation of L. chinense flower organs also play a key role in the network. The promoters of LcNACs mainly contain stress response elements (low temperature, high temperature and drought response elements) and growth and development related elements (light response, auxin response elements), suggesting that LcNAC genes are involved in the growth and development of L. chinense and the process of coping with abiotic stress.
One way to uncover gene function is to analyze the gene expression pattern. There is obvious diversity in the expression patterns of LcNAC genes across the 11 stages of somatic embryogenesis. The members of NAP and NAM subfamilies are significantly higher expressed during the ES3 and ES4 stages of embryogenesis. The results of this study are similar to those of Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz, both of which indicate that NAC family members are involved in somatic embryogenesis, especially in early development [44]. In addition, most of the LcNAC genes show tissue specific expression, especially the high expression abundance of NAM subfamily members in the reproductive organs of L. chinense, suggesting that they may play an important role in L. chinense reproduction.
In this study, RNA-Seq and RT-qPCR were combined to examine the expression patterns of NAC gene members in L. chinense under three abiotic stresses. The lowest expression of most LcNAC genes was at 6 h after low temperature stress, which may be due to the sudden stimulation of low temperature, leading to enzymatic activity in the plant being reduced, the metabolism slowing down, and the defense system not being ready. The expression characteristics of the LcNAC genes are similar to those of the homologous gene SlNAC10 [45]. The gene expression level is generally higher after 24 h of low temperature, compared to 6 h of cold treatment. We speculate that the plant has fully activated their defense system after a period of abiotic stress and enhanced the expression level of genes related to low temperature response through signal transmission, including the expression of NAC gene family members. In particular, the expression of LcNAC18 and LcNAC65 from the NAM subfamily changed dramatically with the three types of abiotic stress response we applied, suggesting that these two genes play a key role in response to multiple abiotic stresses. Furthermore, most NAC transcription factors have been shown to localize to the nucleus, and we found that LcNAC18 and LcNAC65 are present both in the cytoplasm and nucleus, which is not consistent with our predictions.
Conclusion
This study performed a comprehensive genomic characterization of the L. chinense NAC transcription factors. We identified a total of 85 LcNACs, distributed across 17 chromosomes. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that LcNACs can be classified into 17 distinct subfamilies. The expression patterns of LcNAC genes across different tissues and somatic embryos were explored, and the expression patterns of LcNAC genes under abiotic stress were analyzed. Investigation of the expression profiles revealed that LcNACs respond to external stimuli (cold, drought and heat stress), among which LcNAC6/18/41/65 responded to all three stresses investigated. This study provides the basis for further investigating the function of LcNACs under abiotic stresses.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available in the manuscript and its additional files. The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. Genome and gene model annotations files are available on the NCBI website (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly/GCA_003013855.2). RNA-seq data can be found here: NCBI, accession numbers: PRJNA679089 and PRJNA679101. All materials were obtained with permission, and are available by contacting the corresponding authors (jshi@njfu.edu.cn and chengtl@njfu.edu.cn).
References
Erpen L, Devi HS, Grosser JW, Dutt M. Potential use of the DREB/ERF, MYB, NAC and WRKY transcription factors to improve abiotic and biotic stress in transgenic plants. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2018;132(1):1–25.
Ohta M, Sato A, Renhu N, Yamamoto T, Oka N, Zhu J, et al. MYC-type transcription factors, MYC67 and MYC70, interact with ICE1 and negatively regulate cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep. 2018;8:11622.
Luo P, Li Z, Chen W, Xing W, Yang J, Cui Y. Overexpression of RmICE1, a bHLH transcription factor from Rosa multiflora, enhances cold tolerance via modulating ROS levels and activating the expression of stress-responsive genes. Environ Exp Bot. 2020;178:104160.
Yao S, Wu F, Hao Q, Ji K. Transcriptome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors and their expression profiles under different types of biological and abiotic stress in Pinus massoniana Lamb. Genes-Basel. 2020;11(11):1386.
Nuruzzaman M, Manimekalai R, Sharoni AM, Satoh K, Kondoh H, Ooka H, et al. Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Gene. 2010;465(1):30–44.
Nie G, Yang X, Yang Z, Zhong M, Zhu Y, Zhou J, et al. Genome-wide investigation of the NAC transcript factor family in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and expression analysis under various abiotic stressor. Genomics. 2020;112(6):4224–31.
Jin JF, Wang ZQ, He QY, Wang JY, Li PF, Xu JM, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) during aluminum stress. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):288.
He Q, Liu Y, Zhang M, Bai M, Priyadarshani SVGN, Chai M, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in pineapple. Trop Plant Biol. 2019;12(4):255–67.
Su H, Zhang S, Yuan X, Chen C, Wang X, Hao Y. Genome-wide analysis and identification of stress-responsive genes of the NAM-ATAF1,2-CUC2 transcription factor family in apple. Plant Physiol Bioch. 2013;71:11–21.
Meng L, Chen S, Li D, Huang M, Zhu S. Genome-wide characterization and evolutionary expansion of poplar NAC transcription factors and their tissue-specific expression profiles under drought. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):253.
Wen S, Li J, Hao Z, Wei L, Ma J, Zong Y, Li H. Overexpression of the LcCUC2-like gene in Arabidopsis thaliana alters the cotyledon morphology and increases rosette leaf number. PeerJ. 2022;10:e12615.
Chen Q, Wang Q, Xiong L, Lou Z. A structural view of the conserved domain of rice stress-responsive NAC1. Protein Cell. 2011;2(1):55–63.
Su H, Zhang S, Yin Y, Zhu D, Han L. Genome-wide analysis of NAM-ATAF1,2-CUC2 transcription factor family in Solanum lycopersicum. J Plant Biochem Biot. 2015;24(2):176–83.
Aida M, Ishida T, Fukaki H, Fujisawa H, Tasaka M. Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: an analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant. Plant Cell. 1997;9(6):841–57.
Pei H, Ma N, Tian J, Luo J, Chen J, Li J, et al. An NAC transcription factor controls ethylene-regulated cell expansion in flower petals. Plant Physiol. 2013;163(2):775–91.
Zhao P, Wang W, Sun M. Characterization and expression pattern analysis of DcNAC gene in somatic embryos of Dendrobium candidum Wall Ex Lindl. Plant Cell Tiss Org. 2011;107(1):151–9.
Larsson E, Sundstrom JF, Sitbon F, von Arnold S. Expression of PaNAC01, a Picea abies CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON orthologue, is regulated by polar auxin transport and associated with differentiation of the shoot apical meristem and formation of separated cotyledons. Ann Bot-London. 2012;110(4):923–34.
Munir N, Yukun C, Xiaohui C, Nawaz MA, Iftikhar J, Rizwan HM, et al. Genome-wide identification and comprehensive analyses of NAC transcription factor gene family and expression patterns during somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan Lour. Plant Physiol Bioch. 2020;157:169–84.
Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819(2):97–103.
Ju Y, Yue X, Min Z, Wang X, Fang Y, Zhang J. VvNAC17, a novel stress-responsive grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) NAC transcription factor, increases sensitivity to abscisic acid and enhances salinity, freezing, and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Bioch. 2020;146:98–111.
Wang GD, Liu Q, Shang XT, Chen C, Xu N, Guan J, et al. Overexpression of transcription factor SlNAC35 enhances the chilling tolerance of transgenic tomato. Biol Plantarum. 2018;62(3):479–88.
Fang Y, Liao K, Du H, Xu Y, Song H, Li X, et al. A stress-responsive NAC transcription factor SNAC3 confers heat and drought tolerance through modulation of reactive oxygen species in rice. J Exp Bot. 2015;66(21):6803–17.
Xu Z, Kim SY, Hyeon DY, Kim DH, Dong T, Park Y, et al. The Arabidopsis NAC Transcription Factor ANAC096 Cooperates with bZIP-Type Transcription Factors in Dehydration and Osmotic Stress Responses. Plant Cell. 2013;25(11):4708–24.
Ju Y, Min Z, Yue X, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Zhang Z, et al. Overexpression of grapevine VvNAC08 enhances drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Bioch. 2020;151:214–22.
Huang Q, Wang Y, Li B, Chang J, Chen M, Li K, et al. TaNAC29, a NAC transcription factor from wheat, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15:268.
Yang X, He K, Chi X, Chai G, Wang Y, Jia C, et al. Miscanthus NAC transcription factor MlNAC12 positively mediates abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2018;277:229–41.
Chen J, Hao Z, Guang X, Zhao C, Wang P, Xue L, et al. Liriodendron genome sheds light on angiosperm phylogeny and species-pair differentiation. Nat Plants. 2019;5(1):18–25.
Wu W, Zhu S, Zhu L, Wang D, Liu Y, Liu S, et al. Characterization of the Liriodendron chinense MYB gene family and its role in abiotic stress response. Front Plant Sci. 2021;12:641280.
Wu W, Zhu S, Xu L, Zhu L, Wang D, Liu Y, et al. Genome-wide identification of the Liriodendron chinense WRKY gene family and its diverse roles in response to multiple abiotic stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2022;22(1):25.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–4.
Guan Y, Liu S, Wu W, Hong K, Li R, Zhu L, et al. Genome-wide identification and cold stress-induced expression analysis of the CBF gene family in Liriodendron chinense. J Forestry Res. 2021;32(6):2531–43.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13(8):1194–202.
Sheng Y, Hao Z, Peng Y, Liu S, Hu L, Shen Y, et al. Morphological, phenological, and transcriptional analyses provide insight into the diverse flowering traits of a mutant of the relic woody plant Liriodendron chinense. Hortic Res-England. 2021;8(1):174.
Ooka H, Satoh K, Doi K, Nagata T, Otomo Y, Murakami K, et al. Comprehensive analysis of NAC family genes in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res. 2003;10(6):239–47.
Kunieda T, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M, Takeda S, Aida M, Tasaka M, et al. NAC Family Proteins NARS1/NAC2 and NARS2/NAM in the Outer Integument Regulate Embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2008;20(10):2631–42.
Kusano H, Asano T, Shimada H, Kadowaki K. Molecular characterization of ONAC300, a novel NAC gene specifically expressed at early stages in various developing tissues of rice. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005;272(6):616–26.
Ling L, Song L, Wang Y, Guo C. Genome-wide analysis and expression patterns of the NAC transcription factor family in Medicago truncatula. Physiol Mol Biol Pla. 2017;23(2):343–56.
Zong X, Yan Q, Wu F, Ma Q, Zhang J. Genome-wide analysis of the role of NAC family in flower development and abiotic stress responses in Cleistogenes songorica. Genes-Basel. 2020;11(8):927.
Li P, Peng Z, Xu P, Tang G, Ma C, Zhu J, et al. Genome-wide identification of NAC transcription factors and their functional prediction of abiotic stress response in peanut. Front Genet. 2021;12:630292.
Li B, Fan R, Yang Q, Hu C, Sheng O, Deng G, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the NAC transcription factor family in Musa Acuminata and Expression Analysis during Fruit Ripening. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):634.
Liu M, Ma Z, Sun W, Huang L, Wu Q, Tang Z, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):113.
Hwarari D, Guan Y, Li R, Movahedi A, Chen J, Yang L. Comprehensive bioinformatics and expression analysis of TCP transcription factors in Liriodendron chinense reveals putative abiotic stress regulatory roles. Forests. 2022;13(9):23.
Mendez-Hernandez HA, Ledezma-Rodriguez M, Avilez-Montalvo RN, Juarez-Gomez YL, Skeete A, Avilez-Montalvo J, et al. Signaling overview of plant somatic embryogenesis. Front Plant Sci. 2019;10:77.
Liu H, Chen S, Wu X, Li J, Xu C, Huang M, et al. Identification of the NAC transcription factor family during early seed development in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. Plants-Basel. 2023;12(7):22.
Du X, Su M, Jiao Y, Xu S, Song J, Wang H, et al. A Transcription factor SlNAC10 gene of Suaeda liaotungensis regulates proline synthesis and enhances salt and drought tolerance. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):9625.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the funders of this research, the editors, and reviewers for the effort and time spent giving helpful comments to improve our work.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China during the 14th Five-year Plan Period (2021YFD2200103), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32071784, 32101546) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S. and T.C.; methodology, T.C.; software, S.L.; validation, S.L. and Y.G.; investigation, Y.W. and B.L.; resources, J.S.; data curation, S.L., Y.G. and L.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, S.L. and Y.G.; visualization, S.L., J.C. and Z.H.; supervision, T.C.; project administration, J.S. and T.C. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Liriodendron seedlings were derived via somatic embryogenesis, cultured and collected in the laboratory of Nanjing Forestry University (Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China). All plant materials used in the experiments did not include any wild species at risk of extinction. No specific permit was required for sample collection for this experiment. We comply with the IUCN Policy Statement on Research Involving Species at Risk of Extinction and the Convention on the Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Table S1. The Fragments Per Kilobase per million mapped fragments (FPKM) data of NAC genes at different stages of somatic embryos.
Additional file 2:
Table S2. FPKM values of LcNACs under heat, drought and cold stress.
Additional file 3:
Table S3. The specific primers used in the qRT-PCR analysis for the selected LcNACs.
Additional file 4:
Table S4. Characteristics of NAC in L. chinense.
Additional file 5:
Table S5. The conserved motifs of the genes in the LcNAC gene family are determined by MEME.
Additional file 6:
Table S6. The Ka/Ks values of LcNAC linked genes.
Additional file 7:
Figure S1. Clustering analysis of RNA-seq expression trends for LcNAC genes by gene number.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Guan, Y., Weng, Y. et al. Genome-wide identification of the NAC gene family and its functional analysis in Liriodendron. BMC Plant Biol 23, 415 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04415-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04415-4