Abstract
Background
Flavonoids can protect plants against extreme temperatures and ROS due to their antioxidant activities. We found that deep-purple seed coat color was controlled by two gene interaction (12:3:1) from the cross between yellow and deep-purple seed coat colored inbreds. F2:3 seeds were grouped in 3 by seed coat color and germinated under chilling (4 °C) and non-acclimated conditions (18 °C) for a week, followed by normal conditions (18 °C) for three weeks and a subsequent chilling stress (4 °C) induction. We analyzed mean daily germination in each group. Additionally, to study the acclimation in relationship to the different seed coat colors on the germination ability and seedling performances under the cold temperatures, we measured the chlorophyll content, ROS scavenging activity, and expression levels of genes involved in ROS scavenging, flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, and cold response in seedlings.
Results
The results of seed color segregation between yellow and deep purple suggested a two-gene model. In the germination study, normal environmental conditions induced the germination of yellow-seed, while under chilling conditions, the germination ratio of deep purple-seed was higher than that of yellow-colored seeds. We also found that the darker seed coat colors were highly responsive to cold acclimation based on the ROS scavenging enzymes activity and gene expression of ROS scavenging enzymes, flavonoid biosynthetic pathway and cold responsive genes.
Conclusions
We suggest that deep purple colored seed might be in a state of innate pre-acquired stress response state under normal conditions to counteract stresses in a more effective way. Whereas, after the acclimation, another stress should enhance the cold genes expression response, which might result in a more efficient chilling stress response in deep purple seed seedlings.
Low temperature has a large impact on the yield of crops. Thus, understanding the benefit of seed coat color response to chilling stress and the identification of limiting factors are useful for developing breeding strategies in order to improve the yield of wheat under chilling stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The increasing population and climate change are challenges for future agriculture production. To keep up with demands of the rising population, it has been estimated that agricultural production would have to double by 2050 [1]. Cold tolerant species are able to acclimate to low temperatures by an osmotic adjustment such as increasing sugars, organic acids, and amino acids [2, 3]. However, sudden changes in temperature can harm plants primarily from severe dehydration [4, 5]. Low temperatures, also called chilling temperatures, are low (0–15 °C) but not freezing temperatures (below 0 °C) [6]. Previous studies have reported that chilling temperatures can inhibit phloem export [7,8,9,10], decrease carbon fixation [7], interrupt the circadian rhythm by regulating the transcription of photosynthetic genes [11], and degrade damaged reaction PSII centers [12].
It is known that winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) requires vernalization, exposure of the plant to low temperatures as a mean of control of flower formation [13, 14]. It has been reported that the best vernalization response of winter wheat is between 7 and 8 °C as it shows slower responses at higher or lower temperatures [15]. Moreover, there is evidence suggesting that devernalization can occur when seedlings are placed under warm environmental conditions after a cold treatment [13].
Winter wheat can tolerate temperatures up to -20 °C through cold acclimation [16]. Cold-tolerant crops (winter wheat and winter rye, for example) can acquire maximum freezing tolerance after a prolonged seedling growth and development under low temperatures (0–5 °C) [7]. Since plants are exposed to low and subzero temperatures in the field during fall and winter [7], there is a need for plants to acclimate to sudden changes in temperature known to perturb their metabolic homeostasis and induce stress responses depending on the amplitude, frequency, and duration of the stress [17].
There have been studies comparing cold-hardened and nonhardened species between cultivars tolerant and non-tolerant to cold. Studies on cold-tolerant herbaceous plants after exposure to low temperatures have reported that reprogramming of carbon metabolism is involved in changes in gene expression, enzyme activity, and possibly changes of phosphate compartmentation [18]. Moreover, previous studies on winter rye leaves after growth at low temperatures have reported an increased in cell size, lower stomatal frequency, and an increase in chlorophyll content [19]. Plants can accumulate key metabolites [20] produced by enzymatic (e.g., CAT, POD, SOD) and non-enzymatic (e.g., ascorbic acid, carotenoids, tocopherols, and flavonoids) antioxidative components [21, 22] that work together to detoxify reactive oxygen species (ROS) [22] under biotic/abiotic stress conditions. Chlorophylls, carotenoids, and anthocyanins found in seed coats [23] are important antioxidants [24] known to be associated with seed germination behavior [25, 26] due to their antioxidant activities. Flavonoids is a group of natural substances consisting of variable phenolic structures and their subgroups, including flavones, flavanones, flavanonols, flavanols (catequins), anthocyanins, and chalcones [27]. They might be involved in the protective mechanism during freezing by scavenging ROS [28,29,30,31].
Transcriptions factors (TFs) can regulate gene expression by coordinating mechanisms involved in DNA methylation, chromatin organization, dimerization, and sequence-specific DNA binding. TFs can function as activators or repressors of genes [32]. The CBF/DREB1 family is the most studied transcription factor family responsible for cold hardening and frost tolerance. WSC120 is similarly induced by cold and freezing temperatures as well as after cold [33,34,35]. Recent studies have reported that TFs involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway are highly expressed in cold acclimated plants [36].
In this study, we hypothesized that the darker the seed coat color the better germination performance under low temperature conditions than those from other groups. Moreover, to study the acclimation in relationship to the different seed coat colors on the germination ability and seedling performances under the cold temperatures, two-group experimental designs were used to analyze how seed coat color and germination temperature could affect responses of seedlings to a chilling stress (CS). First, we performed inheritance analysis of deep purple seed coat color using F3 population obtained from the cross between yellow and deep purple seed inbreds. Second, segregating seeds were divided into three groups: yellow (Ye), medium purple (MP), and deep purple (DP). Seeds in each group were germinated under chilling-acclimated (CA) (4 °C) and non-acclimated (NA) conditions (18 °C) for a week, followed by normal growth for three weeks under control conditions. Finally, a second CS was induced for 6 h at 4 °C. This work aimed to evaluate the effects of chilling stress in different seed coat colors under non- acclimated and chilling-acclimated seeds and seedlings were evaluated in chlorophyll content, enzymatic activity, and gene expression of flavonoid related pathway, ROS scavenging enzyme genes and cold responsive genes in order to better characterize the seed coat color response to chilling stress and identify limiting factors useful for developing breeding strategies in order to improve the yield of wheat under chilling stress.
Results
Inheritance of purple seed color
Color segregation analysis was performed by bare eyes. Observers performed the analysis by dividing the whole set of seeds by plant into different color categories from 1 (yellow) to 9 (deep purple). After performing the analysis, the average score of three replicates was calculated and reported in Additional file 1: Table S1 and Additional file 2: Table S2.
Results from the genetic analysis showed that the best fit for our seeds was the ratio of 13 Ye: 3 DP with a χ2 of 3.413 and a p-value of 0.06 (Table 1). However, we followed our second best χ2 result based on seed color variations observed in Fig. 1b, classifying our seeds as from the average scored Ye-seed (from 1–5), MP-seed (above 5 to 7), and DP-seed (above 7 to 9) with 12:3:1 ratio, χ2 of 1.988, and a p value of 0.37 (Table 1). We suggested the two-gene model as shown in Table 2 where dominant allele A resulted in Ye-seed coat color phenotype and genotypes A_B or A_bb, regardless of the genotype at a second locus B. In the absence of the dominant A allele (the aa genotype), BB or Bb resulted in MP-seed coat color phenotype (aaB_), whereas bb resulted in DP-seed color coat (aabb).
Experimental design and crosses of RILs for color segregation. a Schematic representation of experimental design and treatments. NA: non-acclimated, chilling acclimated (CA), BCS: before chilling stress, ACS: after chilling stress; (b) crosses for the generation of the seed coat color segregation and seed coat color segregation groups based on our genetic analysis. Seed coat color segregation, bulked groups from average scores making each groups: yellow seeds from scores from 1 to 5; medium purple seeds, scores > 5 to 7, and deep purple seeds, scores > 7 to 9
Phenolics and anthocyanins quantification
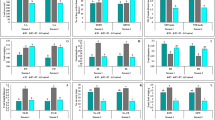
We bulked our seeds based on the bared eyes scores and the genetic analysis to generate groups (Ye-, MP- and DP-seed) and extracted free phenolics (FP), total phenolics (TP), and total anthocyanin (AC). Although DP-seed group had the highest amount of FP, DP-FP showed no significant difference between MP- and Ye-seed groups. For TP, the DP-seed group also showed the highest content. However, it was significantly different from TP in other groups (p ≤ 0.05) (Fig. 2a and b). Regarding anthocyanin content, it was significantly higher among all groups (p ≤ 0.05) with 1.974, 1.010, and 0.593 ppm in DP-, MP-, and Ye-seed groups, respectively (Fig. 2c). These results showed that TP, and AC contents increased with deepening purple seed coat color.
Phenolics and anthocyanins quantification in seeds. a Free phenolics, (b) total phenolics, and (c) anthocyanin quantification in yellow (Ye)-, medium purple (MP)- and deep purple (DP)- seed groups. Data are means ± SEM of three replicates. Significant differences, evaluated by t-test, are marked by asterisks: *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 when compared to Ye-seed
Germination rate of non- and chilling- acclimated conditions
Daily germination percentage was compared under NA and CA conditions among Ye-, MP-, and DP-seed groups. There were no visible differences in germination percentages on the first day (Additional file 3: Fig. S1). However, germination percentages started to show significant differences from the second day among the three groups. Daily germination percentage of the DP-seed group under CA condition was statistically similar to that of the DP-seed group under NA condition. Thus, germination performance of the DP-seed group was not affected by CS compared to other seed coat color groups. This was noted starting from day 2 when the DP-seed group under chilling germination already had germination rate of 53.33% compared to germination rates of 31.66% and 12.88% in MP- and Ye-seed groups, respectively. On day 3 under CA condition, DP-, MP-, and Ye-seed groups had germination rates of 83.33%, 65%, and 41.11%, respectively. This pattern was kept under the CA germination condition, with DP-seed germination percentage being higher compared than MP- and Ye-seed groups and the MP-seed group had higher germination rate until day 5 than the Ye-seed. However, on day 6, the MP-seed group did not show any more change in germination rate. Furthermore, after the fifth day, there was no significant difference in germination rate among Ye-, MP-, and DP-seed groups under NA or CA condition. Germination rates reached about 90% in all seed groups (Fig. 3).
Germination percentage under non-acclimated and chilling acclimated seeds. Germination percentage per day in yellow (Ye-seed), medium purple (MP-seed), and deep purple seed groups (DP-seed) under non-acclimated (NA) and chilling-acclimated (CA) conditions. Data are presented as means ± SEM of three replicates. Different letters indicate significant differences in each coordinate value between groups (p ≤ 0.05).”A” means no significant difference between Ye-, MP-, and DP- seed under non-acclimated and DP-seed groups under CA conditions
Chlorophyll contents in seedlings
Chlorophyll (Chl) has been used as an indicator for stress and chilling conditions of different crops [30, 37, 38]. We analyzed whether chlorophyll content was affected by seed coat color and acclimation by measuring chlorophyll contents in seedlings of seeds germinated under NA and CA conditions by measuring Chla, Chlb, total Chl and Chla/Chlb ratio.
Table 3 shows that there were no significant differences between the NA-BCS and CA-BCS seed seedlings between colors, moreover, there were also no significant differences after the chilling stress under NA- and CA- conditions between seed color groups.
ROS scavenging enzymatic activity in seedlings
The activity of ROS scavenging enzyme of each seed coat color group was measured to analyze the relationship between seed coat color and antioxidant scavenging activity affected by CA during germination stage in seedlings. Table 4 shows total CAT, POD, and SOD levels in seedlings germinated under NA and CA conditions. CAT activity was highly increased in NA-ACS compared to CA-ACS in DP-seed seedlings ((p ≤ 0.01) from 0.53 U/gFW to 257.513 U/gFW), respectively. Whereas in MP-seed seedlings there was a significant increase from NA-ACS to CA-ACS (p ≤ 0.05), with 0.711 U/gFW to 222.428 U/gFW, respectively. Even though there was no significant differences in total POD between the groups, it can be noted that ACS, DP-seed seedlings had the highest total POD (7.638 U/gFW), compared to Ye- or MP-seed seedlings ACS. In case of total SOD BCS, MP-seed seedlings under NA conditions had the highest amount at 5.685 U/gFW, compared to Ye- and DP-seed seedlings. Moreover, ACS, DP-seed seedlings germinated under CA conditions had the highest total SOD ACS with 7.865 U/gFW, but these results are not statistically significant.
Expression of ROS scavenging genes, transcripts related to flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, and cold response genes
The heatmap of gene expression patterns related in ROS scavengers, flavonoid biosynthesis, and cold responses are shown in Fig. 4. Under NA condition, the highest gene expressions were found mostly in the NA-BCS DP-seed seedlings, with exception for CAT1, PAP1/MYB75, and TTG1/WD40. The expression of flavonoid biosynthesis genes, such as ANS, DFR, CHS, CHI and F3H, increased in the DP-seed seedlings under CA condition after the second chilling stress, whereas expression of the ROS scavenging related genes were reduced in DP-seed seedlings of CA-ACS. In case of transcription factors involved in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, PAP1/MYB75 showed highest expression in DP-seed seedlings of CA-ACS, however, expressions of TTG1/WD40, MYB11, and MYB111 were decreased in DP-seed seedlings of CA-ACS. Among the cold responsive genes, CBF3 and WCS120 in DP-seed seedlings showed high expression in DP-seed seedlings of CA-ACS.
Heatmap showing the effect of the second chilling stress in gene expression. ROS (reactive oxygen species) scavenging genes; flavonoid, anthocyanins, and transcription factors regulating the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway; and cold response genes were measured in yellow- (Ye-), medium purple- (MP-), and deep purple- (DP-) seed groups of seedlings germinated under non-acclimated (NA) (18 °C) and chilling acclimated (CA) (4 °C) conditions before chilling stress (BCS) (18 °C) and after chilling stress (ACS) (4 °C for 6 h). Ye BCS and Ye ACS sample were used for comparison within groups (NA and CA). Numbers represent the fold changes. Relative color values are based of the subtraction of the row median, divided by row standard deviation. Data are presented as means ± SD of three biological replicates
Discussion
Seed coat color scoring and genetic analysis
Seed color has been measured visually in several crops [39, 40]. For our experimental purposes, color was also evaluated by visual inspection, generating seeds scores from 1 to 9, where 1 represented yellow and 9 indicated deep purple of F3 seeds (Additional file 1: Table S1). Seed color is known to be determined by maternal genotype [41,42,43]. In the present study, F3 seeds (Fig. 1b) were analyzed for color segregation using Chi Square (χ2). χ2 results showed a 13: 3 (yellow: purple) ratio in this study (Table 1) that was previously reported in crosses between purple and blue wheat grains [42], with purple grains showing inhibiting effect on blue ones. Hence, in our materials, yellow grains had inhibiting effects on purple grains. It is well-known that this kind of ratio only two phenotypes segregate [44]. Therefore, we considered our second best χ2 result, identifying that the DP-seed color was controlled by a two gene interaction (12:3:1) from the cross between Ye-seed and DP-seed colored inbreds. F2:3 seeds were assigned into three groups based on seed coat color with a 12:3:1 ratio [yellow (Ye-seed), medium purple (MP-seed), deep purple (DP-seed), respectively] (Table 1), which has been demonstrated to be a characteristic of dominant epistasis usually having three phenotypes [44]. Our experiments and seed group color clusters were based on this segregation ratio. Therefore, we propose a dominant epistasis model of wheat seed color that Ye-seed color contained a dominant allele (A). In the presence of the dominant allele A, Ye-seed coat was produced as A allele was epistatic to both B_ and bb combination. In the absence of the dominant A allele (the aa genotype), BB or Bb resulted in MP-seed color, while bb resulted in DP-seed color (Table 2). This result is similar to a genetic model found for purple color deposition in rice pericarps [45].
Phenolics and anthocyanins in seeds
Phenolics have been studied in yellow and black Brassica napus [46] as well as in colored maize [47]. Both studies have shown that darker colored seeds (black and purple) have higher phenolic contents. Our study showed similar results, with DP-seed group having higher FP and TP contents, followed by MP- and Ye-seed groups, but just TP results were statistically significant (Fig. 2a and b). Similarly, contents of anthocyanins were higher in deeper colored seeds, showing higher antioxidant activities than lighter ones [47,48,49]. These results are in accordance with our data, with DP-seed group had higher contents of anthocyanins, followed by MP- and Ye-seed groups (Fig. 2c).
Germination
Under harsh conditions, it has been reported that seeds showing high antioxidant activity perform better due to scavenging of ROS [29, 36, 47]. We performed germination assay under chilling-acclimation (CA) (4 °C) and non-acclimated (NA) (18 °C) for a week. We hypothesized that darker colored seeds would show the fastest germination under low temperatures due to anthocyanins presented on their seed coats. As shown in Fig. 3, normal environmental conditions induced the germination of lighter-colored seeds (yellow seeds), whereas under chilling conditions, the germination ratio of darker-colored seeds (deep purple) was higher than that of yellow-colored seeds.
Chlorophyll contents in seedlings after CS under NA and CA conditions
Chlorophyll (Chl) has been used as an indicator for stress and chilling conditions in different crops [30, 37, 38]. Our results showed that Chl contents in wheat leaves under BCS were different between germination under NA and CA conditions. Under NA conditions, contents of Chla, Chlb, total Chl, and Chla/Chlb ratio were higher (Table 3). On the other hand, when seeds were germinated under CA condition, results showed that Chl contents (a, b, total, and a/b ratio) decreased than those under NA condition in Ye- and MP-seed seedlings before CS. However, there was an increase of Chl contents in DP-seed seedlings. However, these results show no significant difference. We speculate these results are due to the short period of chilling temperature exposure.
ROS scavenging enzymes
Stress induces the plant defense mechanisms and production of secondary metabolites [50]. ROS scavenging enzymes were quantified to verify effects of antioxidants on seedlings acclimation. Under the condition of ACS, the highest amount of ROS scavenging enzymes was detected in DP-seedling (CAT, POD, and SOD levels of 257.513, 7.638, and 7.865 U/gFW, respectively), higher than that under other conditions (Table 4). It has been described that the presence of ROS scavenging enzymes such as CAT, POD and SOD plays an important role in ROS detoxification as a defense mechanism against various stresses [51, 52]. However, these results were not in accordance with gene expression results by qRT-PCR when comparing NA-BCS and CA-BCS conditions. qRT-PCR results showed that under NA conditions BCS, with exception of CAT1, the rest of ROS related genes showed the highest expression in DP-seed seedlings (Fig. 4). In Table 4 it is shown that the CA-ACS in MP- and DP-seed seedlings that the CAT enzyme activity was dramatically increased compared to the Ye-seed seedlings and the NA condition. Prasad et al. [53] reported in acclimated and non-acclimated maize seedlings, that the CAT activity increased after treatment of maize seedlings for 7 days with temperature of 4 °C, concluding that for an unknown reason, there was no increase of CAT3 expression in non-acclimated seedlings, suggesting that CAT3 expression is post-transcriptionally or post-translationally controlled.
Based on these results, we can conclude that DP-seed seedlings have high ROS enzyme activities under normal conditions. A high ROS scavenging activity in DP-seed could maintain redox homeostasis to protect cell damage caused by various stresses.
Our results of NA and CA conditions after CS showed that exposure to low temperatures promoted the accumulation of POD and SOD related genes in MP- and DP-seed seedlings germinated under NA conditions. For POD related genes, PER2 and RCl3 were highly expressed in MP-seed seedlings. For SOD genes, CSD2 and CSD3 were also highly expressed in MP-seed seedlings, whereas CSD1 was highly expressed in DP-seed seedlings. A previous study has shown that cold-primed plants possess more effective reactive oxygen scavenging systems than non-primed plants due to increased activities of SOD, APX and CAT, resulting in a better maintenance in homeostasis of ROS production [54]. Similarly, it has been reported that exposure to low temperatures can lead to accumulation of ROS [33]. Based on these results, we can assume that DP-seed seedlings under normal conditions already have a better maintenance of ROS. Therefore, under chilling conditions, DP-seed seedlings were not as affected as lighter colored seed seedlings under low temperatures stresses.
Flavonoid biosynthetic pathway and cold responsive genes
According to previous reports [29, 36], anthocyanin biosynthetic genes are strongly down-regulated in more freezing-sensitive accessions but are more induced in more freezing-tolerant accessions. Our results (Fig. 4) showed that most of flavonoid biosynthesis gene transcripts were highly expressed in DP-seed seedlings under NA-BCS condition. Under CA-ACS condition, DP-seed seedlings showed the highest expression levels of flavonoid biosynthetic genes. Additionally, we found that CHI, UG78D1/F3RT, and OMT were induced by low temperatures, showing increases of their transcript levels in seedlings under NA-ACS.
The MBW, MYB-bHLH-WD40 complex, is associated with the regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanins biosynthesis. These transcription factors are key for activation of genes related to the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway [55, 56]. Previous reports have demonstrated that R2R3-MYB, PAP1/MYB75, and MYB111 can control anthocyanin-specific biosynthetic steps [55, 57]. The present study showed that there was an increase in transcript level of MYB11 but not MYB111. MYB11 is known to regulate early steps of the flavonoid pathway by activating promoters of early genes such as CHS, CHI, and F3H [55]. We can conclude that MYB111 in wheat might be a regulator of the anthocyanin pathway, whereas MYB11 can act as a regulator for CHI in NA-ACS in DP-seed seedlings. [36] have also shown that anthocyanin biosynthesis transcripts are induced by low temperatures. They are also induced in more acclimated plants. Likewise, our results showed high expression levels of anthocyanin related genes (ANS and DFR) after cold acclimation in DP-seed seedlings germinated under CA condition after CS. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that TTG1/WD40 can interact with PAP1/MYB75 for anthocyanin biosynthesis [57]. However, in our results under CA-ACS condition, PAP1/MYB75, but not TTG1/WD40, was highly expressed in DP-seed seedlings, similar to results reported by [36]. We can conclude that the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway might not be regulated by a MBW complex in wheat seedlings. Probably PAP1/MYB75 is a key transcription factor of anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation in wheat seedlings. Our results indicate that there might be an upstream regulator unidentified in DP-seed seedlings for the anthocyanin pathway in response to CS.
A previous research [36] has shown that TTG1/WD40 and OMT are highly expressed under warm conditions but with minor changes in cold conditions. Contrary to that, OMT was only highly expressed in DP-seed seedlings germinated under NA before CS, but was induced after CS. Therefore, OMT and TTG1/WD40 might be affected by cold in wheat.
CBF and WSC120 are genes that encode transcriptional activators which are similarly induced by cold and freezing temperatures [33,34,35]. We analyzed CBF3, CBF12, and WSC120 transcripts to observe low temperature responses of our NA and CA seedlings. Similarly, of cold responsive genes under BCS condition in NA plants, the highest transcripts of those genes were detected in DP-seed seedlings, whereas CBF3 and WCS120 showed high transcript levels in DP-seed seedlings germinated under CA condition in NA-ACS plants. CBF12 was highly expressed in ACS condition of Ye-seed seedlings germinated under CA. Our results show that DP-seed seedlings NA-BCS had higher expression than CA-BCS, suggesting that the DP-seed seedlings might be in a state of innate pre-acquired stress response state under normal conditions. This data supports the results from DP-seed seedlings under CA-BCS where results showed that the gene expression was reduced in the cold responsive genes studied, showing that the chilling acclimation in DP-seed could endow the potence to meet with the stress resulting in reduce gene expressions. After the acclimation, another stress should enhance the cold genes expression response, which might result in a more efficient chilling stress response, as reported by [34] where the spring wheat cultivars have low tolerance to cold temperature compared to winter cultivars due to the inability to maintain low-temperature genes in an up-regulated state. Although CBF12 and WCS120 are known to be responsive to cold, the mode of expression might be different depending on the circumstances. As seen in Fig. 4, CBF12 and WCS120 gene expressions are higher in NA-BCS than CA-ACS for DP-seed seedlings, this may be due to the reasons stated above that the DP-seed seedlings are in a defensive state in NA-BCS. On the other hand, when comparing the gene expression level between CA-BCS and CA-ACS, there was an increase after the chilling stress, suggesting that the cold responsive genes in DP-seed seedlings were more responsive which could provide an effective tolerance ability of DP-seed. Also, based on these results, we suggest that CBF3 could be the largely responsive gene in DP-seed seedlings in this study.
Conclusions
Winter wheat is frequently exposed to a combination of low and subzero temperatures during early seedling stages. When the temperature is decreased gradually, wheat plants can acclimate to cold temperatures. However, sudden temperature changes can harm plants. Our results show that seed coat color has an impact on germination. Moreover, darker seed color seedlings can response better to lower temperatures. Seedlings from DP seeds under non-acclimated stated had increased of ROS scavenging enzymes, and transcription levels of genes involved in ROS scavenging, flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, and cold response suggesting that deep purple colored seed might be in a state of innate pre-acquired stress response state under normal conditions to counteract stresses in a more effective way. Whereas, after the acclimation, another stress should enhance the cold genes expression response, which might result in a more efficient chilling stress response in deep purple seed seedlings.
Low temperature conditions typically reduce physiological and biochemical processes. However, the present study showed that the darkest seed-color seedlings had better performances than lighter colored ones under chilling stress. Globally, low temperatures have a large impact on yields of crops. Thus, understanding seed coat colors and their benefits would be useful for generating crops with desired acclimation traits.
Materials and methods
Plant materials
Recombinant Inbred Lines (RILs) with different seed coat phenotypes, Yellow (accession no. 10DS1673, Korea University wheat sub-gene bank) and Deep Purple (accession no. 10DS1674), were used [58]. Seeds were germinated on moistened filter paper at room temperature for 24 h and vernalized at 4 °C in a dark chamber for 4 weeks. Each seedling was then transplanted to a pot (5 × 5 × 16 cm) filled with soil (Sunshine mix #1, Sun Gro Horticulture, Canada) in a well-controlled glasshouse at Korea University with a photoperiod of 16:8 h and temperatures between 20–25 °C. F3 seeds from 141 F2 plants were used for the analysis of seed coat color segregation. A detailed description of the material is shown in Additional file 1: Table S1.
Genetic analysis of color segregation and germination assay
Color segregation analysis of the F3 population was performed by bare eye. F3 seeds from each 141 F2 plant were analyzed in nine different color categories (1: light yellow and 9: deep purple). Genetic analysis was performed using Chi Square (χ2) test in Microsoft Excel. Seeds were washed with commercial sodium hypochlorite (4%) for 3 min, rinsed with distilled water, and germinated in magenta boxes (6.5 × 6.5 × 20 cm; Greenpia Technology Inc., Yeoju, Korea) on a polypropylene mesh, keeping distilled water beneath the mesh. Non-acclimated (NA) conditions were performed in a chamber with a photoperiod of 16 h light: 8 h dark, temperature of 18 °C, humidity of 60%, and luminous power of 17,000 FLUX. Chilling-acclimation (CA) was performed in a fridge with a temperature of 4 °C for a week. Three replicates were performed for both NA and CA conditions.
Germination percentages [Germination Percentage = (Seeds germinated / Total seeds) * 100%] [59] were recorded daily for 7 days using radicle extrusion as a criterion [60, 61]. After 7 days of germination test, both NA and CA seedlings were transferred to a chamber with controlled photoperiod of 16 h light: 8 h dark, temperature of 18 °C, and humidity of 60% for three weeks. Both NA and CA groups were then exposed to a chilling stress (CS) for 6 h at 4 °C. Samplings for determining chlorophyll content, ROS, and RNA extraction for the gene expression were performed before and after CS as shown in Fig. 1a. Germination results are expressed as average germination of each color score bulked in yellow (Ye-seed, scores: 1–5), medium purple (MP-seed, scores: >5–7), and deep purple (DP-seed, scores: >7–9) groups based on genetic analysis.
Quantification of phenolics and anthocyanins in seeds
Free phenolics (FP) and total phenolics (TP) were measured using the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent following the protocol of [62]. F3 bulked seeds from each group, Ye-, MP-, and DP-seed, were ground with liquid nitrogen and 20 mg grain powder was measured. Total anthocyanin content was determined according to the protocol of [63]. Absorbance was read at 765 nm for FP and TP whereas it was read at 530 nm and 657 nm for anthocyanins using a microplate reader (HIDEX-Sense 425–301, Finland). Results are expressed as the average of three biological replicates of phenolics or anthocyanin of each color score seeds bulked in Ye-, MP- or DP-seed groups based on genetic analysis.
Chlorophyll content analysis for seedlings
Chlorophyll content was measured in triplicate using leave samples collected before and after the second CS from each color seed group, Ye-, MP-, and DP-seed. Samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C until further use. Chlorophyll content was performed using the method of [64] by measuring the absorbance at 652 and 665 nm with a microplate reader (HIDEX-Sense 425–301, Finland). Results are presented as the average of chlorophyll content of each color score seeds bulked in Ye-, MP- or DP-seed groups based on genetic analysis.
ROS scavenging enzyme
Germination was performed in triplicate using RILs (accession no. 10DS1673 and 10DS1674), and the MP-seed group (F3 seeds generated from MP-seed scored seeds). Samples were taken before and after the second CS, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80 °C until further use. Fresh tissue (0.5 g) was ground with liquid nitrogen and homogenized in 0.5 mL protein extraction buffer [0.2 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) and 0.1 mM EDTA]. The Bradford method was used for total protein quantification followed by quantification of total superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) using the protocol of [58].
RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, and real-time PCR
Total RNA extraction was performed in triplicate from samples taken before and after the second CS from RILs (accession no. 10DS1673 and 10DS1674) and the MP-seed group (F3 seeds generated from MP scored seeds). Samples were ground in liquid nitrogen. TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, USA) was used for RNA extraction. cDNA synthesis was performed using the cDNA Takara PrimeScript™ 1st strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Takara, Japan). Gene-specific primers were designed using Primer-BLAST (NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/tools /prime r-blast /) or from previous publications as described in Additional file 4: Table S3. Quantitative PCR was performed in triplicate using EvaGreen 2X qPCR MasterMix (ABM, Canada) on a CFX-96 RT-PCR machine (Bio-Rad, USA). β-actin (accession no. AB181991) was used as an internal control. Ct values for each gene were then normalized against actin expression. The 2−ΔΔCT method was used to calculate expression levels in fold changes as previously described [65]. Heatmaps were created using Gene-E (https://software.broadinstitute.org/GENE-E/).
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as means from three replicates. Significant differences were subjected to ANOVA, Duncan or t-test using R Studio version 1.2.5033 (http://www.rstudio.com/) or IBM® SPSS® Statistics for MAC version 25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). All tests were performed with 95%, 99% and 99.9% of confidence.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated during this study are included within the article and in its supplementary information files or are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Anthocyanin
- ACS:
-
After chilling stress
- BCS:
-
Before chilling stress
- CA:
-
Chilling-acclimated
- Chl:
-
Chlorophyll
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DP:
-
Deep purple
- FP:
-
Free phenolics
- MP:
-
Medium purple
- NA:
-
Non-acclimated
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TP:
-
Total phenolics
- Ye:
-
Yellow
References
Mall RK, Gupta A, Sonkar G. 2 - Effect of Climate Change on Agricultural Crops. Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering. Elsevier. 2017; 23–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63661-4.00002-5
Parkin KL, Marangoni A, Jackman RL, Yada RY, Stanley DW. Chilling Injury. A Review of Possible Mechanisms. Journal of Food Biochemistry. 1989;13(2):127–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4514.1989.tb00389.x
van Buer J, Prescher A, Baier M. Cold-priming of chloroplast ROS signalling is developmentally regulated and is locally controlled at the thylakoid membrane. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):3022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39838-3.
Huner NP, Oquist G, Hurry VM, Krol M, Falk S, Griffith M. Photosynthesis, photoinhibition and low temperature acclimation in cold tolerant plants. Photosynth Res. 1993;37(1):19–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02185436.
Thomashow MF. PLANT COLD ACCLIMATION: Freezing Tolerance Genes and Regulatory Mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1999;50:571–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.571.
Theocharis A, Clément C, Barka EA. Physiological and molecular changes in plants grown at low temperatures. Planta. 2012;235(6):1091–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1641-y.
Hurry VM, Huner NP. Effect of cold hardening on sensitivity of winter and spring wheat leaves to short-term photoinhibition and recovery of photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1992;100(3):1283–90. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.100.3.1283.
Hurry VM, Malmberg G, Gardestrom P, Oquist G. Effects of a Short-Term Shift to Low Temperature and of Long-Term Cold Hardening on Photosynthesis and Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase and Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Activity in Leaves of Winter Rye (Secale cereale L.). Plant Physiol. 1994;106(3):983–990. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.3.983
Klotke J, Kopka J, Gatzke N, Heyer AG. Impact of soluble sugar concentrations on the acquisition of freezing tolerance in accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana with contrasting cold adaptation – evidence for a role of raffinose in cold acclimation. Plant, Cell & Environ. 2004;27(11):1395–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01242.x.
Strand A, Hurry V, Gustafsson P, Gardeström P. Development of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves at low temperatures releases the suppression of photosynthesis and photosynthetic gene expression despite the accumulation of soluble carbohydrates. Plant J. 1997;12(3):605–14. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1997.00605.x.
Martino-Catt S, Ort DR. Low temperature interrupts circadian regulation of transcriptional activity in chilling-sensitive plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(9):3731–5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.9.3731.
Krupa Z, Oquist G, Gustafsson P. Photoinhibition and Recovery of Photosynthesis in psbA Gene-Inactivated Strains of Cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Plant Physiol. 1990;93(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.93.1.1.
Lang A. Physiology of flower initiation. Differenzierung Und Entwicklung / Differentiation and Development. 1965;1380–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-50088-6_39
Yan L, Li G, Yu M, Fang T, Cao S, Carver BF. Genetic Mechanisms of Vernalization Requirement Duration in Winter Wheat Cultivars. Advances in Wheat Genetics: From Genome to Field. 2015;117–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55675-6
Rawson HM, Zajac M, Penrose LDJ. Effect of seedling temperature and its duration on development of wheat cultivars differing in vernalization response. F Crop Res. 1998;57(3):289–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(98)00073-2.
Frederiks TM, Christopher JT, Borrell AK. Low temperature adaption of wheat post head-emergence in northern Australia. The 11th International Wheat Genetics Symposium. 2008;(1):1–3.
Ensminger I, Busch F, Huner NPA. Photostasis and cold acclimation: sensing low temperature through photosynthesis. Physiol Plant. 2006;126:28–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00627.x.
Strand A, Hurry V, Henkes S, et al. Acclimation of Arabidopsis leaves developing at low temperatures. Increasing cytoplasmic volume accompanies increased activities of enzymes in the Calvin cycle and in the sucrose-biosynthesis pathway. Plant Physiol. 1999;119(4):1387–1398. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.119.4.1387
Huner N, Palta J, Li P, Carter J. Anatomical Changes in Leaves of Puma Rye in Response to Growth at Cold-Hardening Temperatures. Botanical Gazette. 1981;142(1):55–62. Retrieved March 22, 2021, from http://www.jstor.org/stable/2474787
Porter JR, Semenov MA. Crop responses to climatic variation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005;360(1463):2021–35. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1752.
Gill SS, Tuteja N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010;48(12):909–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016.
You J, Chan Z. ROS Regulation During Abiotic Stress Responses in Crop Plants. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:1092. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01092.
Stintzing FC, Carle R. Functional properties of anthocyanins and betalains in plants, food, and in human nutrition. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2004;15(1):19–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2003.07.004
Delgado-Vargas F, Jiménez AR, Paredes-López O. Natural pigments: carotenoids, anthocyanins, and betalains–characteristics, biosynthesis, processing, and stability. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2000;40(3):173–289. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690091189257.
Bajji M, MʼHamdi M, Gastiny F, Rojas-Beltran, JA, du Jardin, P. Catalase inhibition accelerates dormancy release and sprouting in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers. Final Jordan Cochabamba. 2007; 11(22):121–131.
Hendricks SB, Taylorson RB. Breaking of seed dormancy by catalase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975;72(1):306–9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.72.1.306.
Panche AN, Diwan AD, Chandra SR. Flavonoids: an overview. J Nutr Sci. 2016;5:e47. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2016.41.
Nakabayashi R, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Urano K, et al. Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids. Plant J. 2014;77(3):367–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12388.
Schulz E, Tohge T, Zuther, E. et al. Flavonoids are determinants of freezing tolerance and cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34027. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34027
Zhu H, Li X, Zhai W, et al. Effects of low light on photosynthetic properties, antioxidant enzyme activity, and anthocyanin accumulation in purple pak-choi (Brassica campestris ssp. Chinensis Makino). PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0179305. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179305
Zong Y, Xi X, Li S, et al. Allelic Variation and Transcriptional Isoforms of Wheat TaMYC1Gene Regulating Anthocyanin Synthesis in Pericarp. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1645. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01645.
Feller A, Machemer K, Braun EL, Grotewold E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011;66(1):94–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04459.x.
Achard P, Gong F, Cheminant S, Alioua M, Hedden P, Genschik P. The cold-inducible CBF1 factor-dependent signaling pathway modulates the accumulation of the growth-repressing DELLA proteins via its effect on gibberellin metabolism. Plant Cell. 2008;20(8):2117–29. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058941.
Fowler DB, Chauvin LP, Limin AE, Sarhan F. The regulatory role of vernalization in the expression of low-temperature-induced genes in wheat and rye. Theor Appl Genet. 1996;93(4):554–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417947.
Houde M, Dhindsa RS, Sarhan F. A molecular marker to select for freezing tolerance in Gramineae. Mol Gen Genet. 1992;234(1):43–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272343.
Schulz E, Tohge T, Zuther E, Fernie AR, Hincha DK. Natural variation in flavonol and anthocyanin metabolism during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana accessions. Plant Cell Environ. 2015;38(8):1658–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12518.
Kalisz A, Jezdinský A, Pokluda R, Sękara A, Grabowska A, Gil J. Impacts of chilling on photosynthesis and chlorophyll pigment content in juvenile basil cultivars. Hortic Environ Biotechnol. 2016;57(4):330–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-016-0095-8.
Liu A, Gao F, Kanno Y, et al. Regulation of wheat seed dormancy by after-ripening is mediated by specific transcriptional switches that induce changes in seed hormone metabolism and signaling. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e56570. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056570.
Nandy S, Chen Q, Cheng S, Faiz S, Graf R, Kereliuk G. Nutritional Analyses and Their Inheritance Properties in Colored Wheat Seed lines from Different Origins Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. The Americas Journal of Plant Science and Biotechnology. 2008;2(2):74–9.
Van Deynze AE, Pauls KP. Seed colour assessment in Brassica napus using a Near Infrared Reflectance spectrometer adapted for visible light measurements. Euphytica. 1994;76(1–2):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024019.
Griffin WB. Outcrossing in New Zealand wheats measured by occurrence of purple grain. N Z J Agric Res. 1987;30:287–90.
Guo Z, Xu P, Zhang Z, Guo Y. Segregation ratios of colored grains in F1 hybrid wheat. Crop Breeding and Applied Biotechnology. 2012;12(2):126–31.
Guo Z, Xu P, Zhang Z, Wang D. Segregation ratios of colored grains in crossed wheat. Aust J Crop Sci. 2011;5:589–94. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-70332012000200005.
Griffiths AJF, Miller JH, Suzuki DT, et al. An Introduction to Genetic Analysis. 7th edition. New York: W. H. Freeman; 2000. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21766/
Rahman MM, Lee KE, Lee ES, et al. The genetic constitutions of complementary genes Pp and Pb determine the purple color variation in pericarps with cyanidin-3-O-glucoside depositions in black rice. J Plant Biol. 2013;56(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-012-0043-9.
Qu C, Fu F, Lu K, et al. Differential accumulation of phenolic compounds and expression of related genes in black- and yellow-seeded Brassica napus. J Exp Bot. 2013;64(10):2885–98. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert148.
Deng B, Yang K, Zhang Y, et al. The effects of temperature on the germination behavior of white, yellow, red and purple maize plant seeds. Acta Physiol Plant. 2015;37:174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1937-1.
Furuta S, Takahashi M, et al. Radical Scavenging Activities of Soybean Cultivars with Black Seed Coats. Food Sci Technol Res. 2003;9(1):73–5. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.9.73.
Slavin M, Kenworthy W, Yu LL. Antioxidant properties, phytochemical composition, and antiproliferative activity of Maryland-grown soybeans with colored seed coats. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57(23):11174–85. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf902609n.
Rezaie R, Abdollahi Mandoulakani B, Fattahi M. Cold stress changes antioxidant defense system, phenylpropanoid contents and expression of genes involved in their biosynthesis in Ocimum basilicum L.. Sci Rep. 2020;10(5290). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62090-z
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010;33(4):453–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02041.x.
Zoz T, Steiner F, et al. Peroxidase activity as an indicator of water deficit tolerance in soybean cultivars. Biosci J. 2013;29(5):1664–71.
Prasad TK, Anderson MD, Martin BA, Stewart CR. Evidence for Chilling-Induced Oxidative Stress in Maize Seedlings and a Regulatory Role for Hydrogen Peroxide. Plant Cell. 1994;6(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.1.65.
Li X, Cai J, et al. Cold priming drives the sub-cellular antioxidant systems to protect photosynthetic electron transport against subsequent low temperature stress in winter wheat. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014;82:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.05.005.
Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Leavitt JM, Lloyd AM. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2008;53(5):814–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03373.x.
Xu W, Grain D, Le Gourrierec J, et al. Regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis involves an unexpected complex transcriptional regulation of TT8 expression. Arabidopsis New Phytol. 2013;198(1):59–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12142.
Teng S, Keurentjes J, Bentsink L, Koornneef M, Smeekens S. Sucrose-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis requires the MYB75/PAP1 gene. Plant Physiol. 2005;139(4):1840–52. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.066688.
Shin OH, Kim DY, Seo YW. Effects of different depth of grain colour on antioxidant capacity during water imbibition in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Sci Food Agric. 2017;97(9):2750–2758. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8102
Manmathan H, Lapitan N. Measuring Germination Percentage in Wheat. Bio-Protocol. 2013; 3(16), 3–5. https://doi.org/10.21769/bioprotoc.866
Bewley JD. Seed Germination and Dormancy. Plant Cell. 1997;9(7):1055–66. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.9.7.1055.
Schopfer P, Plachy C. Control of Seed Germination by Abscisic Acid : III. Effect on Embryo Growth Potential (Minimum Turgor Pressure) and Growth Coefficient (Cell Wall Extensibility) in Brassica napus L. Plant Physiol. 1985;77(3):676–686. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.77.3.676
Galicia L, Miranda A, et al. Laboratorio de calidad nutricional de maíz y análisis de tejido vegetal: protocolos de laboratorio 2012. CIMMYT. 2012
Hong MJ, Kim DY, Ahn JW, Kang SY, Seo YW, Kim JB. Comparison of radiosensitivity response to acute and chronic gamma irradiation in colored wheat. Genet Mol Biol. 2018;41(3):611–23. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2017-0189.
Warren C. Rapid measurement of chlorophylls with a microplate reader. J Plant Nutr. 2008;31:1321–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160802135092.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Acknowledgements
PCF acknowledges CONACYT for the scholarship granted.
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of the “Next-Generation BioGreen21 Program for Agriculture & Technology Development (Project No. PJ015666)” Rural Development Administration. Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PCF and YWS conceived and designed the experiments. PCF performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript with support from DYK and YWS. JSY helped with the antioxidant enzymatic expression and the gene expression analysis. DYK and YWS contributed with valuable discussions. All authors have discussed the results and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Table S1. Description of the seed materials used for the study of the seed coat color segregation.
Additional file 2:
Table S2. Summary of statistical analysis of seed coat color scoring by observers.
Additional file 3:
Fig. S1. Germination and recovery pictures. a) Germination under Non-Acclimated (NA) and Chilling-acclimated (CA) conditions; b) Images of the NA and CA seedlings after the 3 weeks of Normal condition before the chilling stress (BCS).
Additional file 4:
Table S3. List of primers used in this study for the qrt-PCR of the flavonoid related, ROS scavenging and cold responsive genes.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Calderon Flores, P., Yoon, J.S., Kim, D.Y. et al. Effect of chilling acclimation on germination and seedlings response to cold in different seed coat colored wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 21, 252 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03036-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03036-z