Abstract
Background
The ascomycetous heterothallic yeast Wickerhamomyces anomalus (WA) has received considerable attention and has been widely reported in the winemaking industry for its distinctive physiological traits and metabolic attributes. An increased concentration of ethanol during ethanol fermentation, however, causes ethanol stress (ES) on the yeast cells. Trehalose has been implicated in improving survival under various stress conditions in microorganisms. Herein, we determined the effects of trehalose supplementation on the survival, differentially expressed genes (DEGs), cellular morphology, and oxidative stress tolerance of WA in response to ES.
Results
The results indicated that trehalose improved the survival and anomalous surface and ultrastructural morphology of WA. Additionally, trehalose improved redox homeostasis by reducing the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inducing the activities of antioxidant enzymes. In addition, DEGs affected by the application of trehalose were enriched in these categories including in gene expression, protein synthesis, energy metabolism, and cell cycle pathways. Additionally, trehalose increased the content of intracellular malondialdehyde (MDA) and adenosine triphosphate.
Conclusions
These results reveal the protective role of trehalose in ES mitigation and strengthen the possible uses of WA in the wine fermentation sector.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The ascomycetous heterothallic yeast Wickerhamomyces anomalus (WA), or known as Candida pelliculosa, Pichia anomala, and Hansenula anomala, has gained considerable attention in recent years for its tolerance to diverse extreme environmental conditions [1]. This yeast has been reported in many different natural habitats, and it exhibits remarkable physiological robustness toward environmental stresses [2]. It can grow at a very low or very high pH (2.0–12.4) and at a temperature range of 3–37 °C, and it also has a high tolerance to osmotic stress (salt) and heavy metals [3, 4]. Moreover, WA shows wide-ranging antimicrobial activity against a variety of microorganisms as a result of the biosynthesis of volatile compounds or killer proteins, and it could be used for biopreservation [5].
Reportedly, WA has a broad carbon source capability and can produce ethanol from sucrose or xylose except for glucose [1]. Furthermore, WA secretes several kinds of glycosidases that can hydrolyze substrates containing glucosidic bonds and releases free glycoside ligands with aromatic characteristics. It has been widely used for food aroma improvement, especially in various winemaking processes [6]. Application of WA along with Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a mixed starter can positively influence the chemical composition and sensory features of produced cider [7]. Additionally, this mixed fermentation enriches the types and concentrations of the volatiles of kiwi wines and has better sensory properties when using WA along with S. cerevisiae [8]. The increased content of ethanol during ethanol fermentation introduces ethanol stress (ES) to the yeast cells, inhibits growth, increases death, and decreases the survival of the yeast cells [9, 10]. To date, the exact response mechanisms of WA to ES has remained obscure.
Trehalose, a nonreducing disaccharide, is commonly found in plants, microorganisms (yeast, bacteria, and fungi), and invertebrate animals [11,12,13]. Trehalose plays crucial physiological roles in organisms not only as a reserve carbohydrate but also as a protectant against different stresses [14]. Rehman et al. found that externally supplemented trehalose improves cadmium stress tolerance and mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) yield in both soil and hydroponic growth methods by attenuating cadmium uptake and improving photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant activity [15]. In addition, trehalose confers protection to maize plants against salt stress and phosphorus deficiency [16]. Moreover, evidence has demonstrated that trehalose is involved in regulating the response of S. cerevisiae against osmotic stress, ES, dehydration stress, oxidative stress, thermal stress, and glucose starvation by preventing proteins from denaturing and that it suppresses the aggregation of denatured proteins [17,18,19,20].
In our previous research, we found that a high concentration of ethanol strongly suppressed the growth of WA and influenced nucleic acid metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and energy metabolism [21]. To reduce the adverse effects of ES on WA, we selected trehalose for application in this study. We investigated the survival, surface and ultrastructural morphology, antioxidant enzyme activities, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and gene expressions of WA to explore the roles of trehalose in the ES tolerance of WA. These findings provide a theoretical basis for further understanding the molecular basis of trehalose-induced ES tolerance in WA.
Results
Trehalose improves the survival of WA under ES
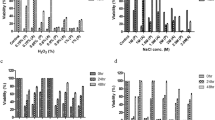
As displayed in Fig. 1A, the growth of WA was markedly suppressed with lower OD values compared to the control group when they were exposed to 9% ethanol. In contrast, trehalose could alleviate the suppressive effects of ES on the growth of WA by increasing the OD values.
When assessing the survival of WA cells, we found that the survival was inhibited, and the death increased after treatment with ethanol for 6 h (Fig. 1B). The decreased survival of WA cells was partially mitigated by the addition of trehalose. Furthermore, the addition of exogenous trehalose partially mitigated the heightened cell death rate induced by ES (Fig. 1C). In addition, the application of exogenous trehalose enhanced the compromised biomass caused by ES (Fig. S1).
Ethanol induces trehalose accumulation in WA
As demonstrated in Fig. 2, the level of trehalose in each group was the same at the begining of the treatment. In contrast, the level of trehalose was remarkably elevated compared with the control group when exposed to ethanol for 6 h. These results indicated that ethanol induced trehalose accumulation, and trehalose might have played a role in the response to ES in WA. Moreover, exogenous application of trehalose led to a higher intracellular level of trehalose in WA during the entire ES period than that in cells without trehalose addition.
Trehalose ameliorates the anomalous morphology of WA under ES
We first examined the surface morphology of WA using a SEM. The external morphology of WA in the control group was ellipsoidal, full, and smooth (Fig. 3A). The surface of some WA cells became uneven and deformed, and the fullness decreased when exposed to ethanol (Fig. 3B). The anomalous external morphology of many WA cells, however, was restored to normal morphology after trehalose addition (Fig. 3C).
We further verified the cellular ultrastructure of WA after replenishment of trehalose. Figure 4A shows that the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum of WA in the control group could be clearly observed, and the structures of the cell membrane, nucleus, and mitochondria were normal and had integrity. For the cells of the ethanol group, swelling of cytoplasmic organelles, especially for mitochondria, and a decline of cristae were the major characteristics of the ultrastructural morphology. The cell membrane was also destroyed by ethanol and became incomplete (Fig. 4B). Exogenous trehalose application alleviated the swelling of mitochondria and nucleus, which indicated that their function may have improved (Fig. 4C).
Trehalose attenuates the oxidative stress and enhanced activities of antioxidant enzymes under ES
As shown in Fig. 5A, the production of ROS was higher in ethanol group than in control group, indicating that the burst of ROS and the oxidative stress were induced by ES. The production of ROS, however, was reduced after trehalose intervention. Furthermore, the activities of antioxidant enzymes (e.g., CAT and SOD) were markedly influenced by ES in WA. As demonstrated in Fig. 5B and C, the activities of CAT and SOD were remarkably higher in ethanol group than in control group. Trehalose intervention also enhanced CAT and SOD activities, which were higher than in the ethanol and control groups. Clearly, exogenous trehalose application diminished oxidative stress by strengthening the activities of the antioxidant enzymes.
Trehalose regulates the relative contents of malondialdehyde and adenosine triphosphate in WA
We determined the relative content of MDA, and the result showed that the MDA level was markedly increased in the ethanol group compared with the control group. In contrast, the relative content of MDA remarkably decreased after the addition of trehalose, suggesting that ethanol induced the oxidation of cell membranes and trehalose could reduce the degree of this oxidation (Fig. 6A). In addition, the results of ATP measurement (Fig. 6B) showed that the level of ATP was remarkably lower in ethanol group than in control group, suggesting that ES could decrease energy production because of the damaged mitochondria. The ATP level of ethanol + Tre group was dramatically higher than that of ethanol group, but was lower than that of control group. These findings indicated that ES could decrease the intracellular level of ATP, while trehalose exhibited an opposite trend.
Trehalose regulated the transcriptome of WA under ES
Identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs)
In total, we obtained 44,347,105.33, 43,247,100.67, and 43,713,072.67 raw reads in the control, ethanol, and ethanol + Tre groups, respectively. After data quality control, 43,022,481.33, 41,698,653.33, and 42,324,616.67 clean reads were acquired from these three sequencing groups, respectively. For all groups, the error rate was 0.03%, and both Q20 (%) and Q30 (%) values exceeded 95% (Table S1). The GC content was about 37%. Additionally, the results of principal component analysis (PCA) showed that the samples of the sequencing group were well separated from those of the other groups (Fig. S2). These data indicated that the sequencing samples' quality was deemed acceptable.
Definition of DEGs
To further identify DEGs after trehalose intervention under ES, we used the following screening criteria: P < 0.05 and |log2(FC)|> 2. As shown in Fig. 7A, 2512 DEGs were significantly changed under stress for 6 h, including 1118 upregulated DEGs and 1394 downregulated DEGs. We found 2384 significantly changed DEGs, including 1415 upregulated DEGs and 969 downregulated DEGs, following exogenous supplementation with trehalose for 6 h under the ES condition (Fig. 7B).
Classification analysis of DEGs
To examine the potential function of these DEGs induced by trehalose intervention under ES, we performed Gene Ontology (GO) classification analysis and categorized the DEGs into 20 functional subcategories. The DEGs were classified according to 3 categories: molecular function, biological process, and cellular component. When WA cells were exposed to ethanol, most of the DEGs distributed in the categories of “molecular function”, “biological process”, and “cellular component” were annotated to “catalytic activity”, “cellular process” and “cell part”, respectively (Fig. 8A). These data suggested that the structure of the cells was destroyed and the intracellular metabolic reactions were disturbed when WA was stressed by ethanol. Note that the regulated targets of trehalose in WA cells have also been annotated to “cell part,” “cellular process,” and “catalytic activity” (Fig. 8B).
GO classification analysis and KEGG classification analysis of DEGs in WA after trehalose intervention under ES. A GO analysis of DEGs between the ethanol and control groups. B GO analysis of DEGs between the ethanol + Tre and ethanol groups. C KEGG analysis of DEGs between the ethanol and control groups. D KEGG analysis of DEGs between the ethanol + Tre and ethanol groups
We further conducted KEGG analysis to check the potential functions of these DEGs induced by trehalose intervention under ES. We classified these DEGs into 5 categories: genetic information processing, metabolism, cellular processes, environmental information processing, and organismal systems. When analyzing the DEGs regulated by ES in WA, we found that “aging” was the sole term of the organismal systems, “signal transduction” accounted for most of the DEGs distributed in environmental information processing, and “transport and catabolism” accounted for most of the DEGs distributed in cellular processes (Fig. 8C). Amino acid metabolism was the most identified DEG in the term of “metabolism.” For the “genetic information processing” term, the most distributed DEGs were annotated to “translation.” When probing the DEGs induced by trehalose addition under ES in WA, the following terms also were annotated: “aging” in organismal systems, “transport and catabolism” in cellular processes, “signal transduction” in environmental information processing, and “translation” in genetic information processing (Fig. 8D).
KEGG analysis of differentially expressed genes
We further performed a KEGG analysis to explore the potential pathways in which the DEGs were involved. As shown in Fig. 9A, most of the DEGs induced by ethanol treatment were related to the following pathways: oxidative phosphorylation, meiosis-yeast, cell cycle-yeast, pyruvate metabolism, ribosome biogenesis, and biosynthesis of cofactors. These data indicated that ethanol influenced energy metabolism, protein synthesis, metabolic reactions, cell meiosis, and the cell cycle of WA cells.
After trehalose supplementation, these pathways, including ribosome, DNA replication, RNA polymerase, oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, and cell cycle-yeast pathways, were abundantly enriched, suggesting that gene expression, protein synthesis, energy metabolism, and cell cycle were affected by trehalose addition (Fig. 9B).
Discussion
In recent years, it has generally been accepted that non-Saccharomyces yeasts significantly affect the characteristics and aroma of wines. Among these yeasts, WA has attracted special attention in the wine industry because of its unique physiological and metabolic characteristics. It has been reported that WA is an interesting source of different enzymes, such as β-glucosidase, α-arabinofuranosidase, α-rhamnosidase, and β-xylosidase, which are involved in the release of aromatic compounds from the precursors and could be used in the winemaking industry [1]. Many authors have explored the application of this species along with S. cerevisiae in the fermentation of Baijiu [22], beer [23], rice wine [24], and fruit wines [25]. Fan et al. [26] proposed that the co-culture of WA and S. cerevisiae exhibited a favorable impact on ethyl-acetate formation, presenting potential opportunities to modify the aroma and flavor profile of Baijiu. In another study conducted by Zha et al. [27], the presence of WA in a mixed culture enhanced the flavor metabolism of S. cerevisiae during Baijiu production. The accumulated ethanol during ethanol fermentation, especially in the middle and late stages, exerted stress responses on the yeast cells, including reduced cell vitality, induction of yeast cell death, disruption of cell structure and function, modulation of gene expression, and subsequent decline in fermentation performance and efficiency [9, 10].
Hence, the application of exogenous chemicals becomes essential to mitigate the damage inflicted by ES on yeast. Prior research has demonstrated that engineering the trehalose synthesis pathway offers a means to modulate yeast ES tolerance [28]. The ethanol yield of the engineered S. cerevisiae strain surpassed that of the wild-type strain, primarily attributable to the elevated intracellular trehalose accumulation resulting from TPS1(Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase) overexpression and NTH1 (Neutral trehalase) deletion [29]. In addition, exogenous application of trehalose also promoted survival under ES condition [30]. In this study, the contribution of trehalose to ES tolerance of WA was investigated by exogenous trehalose supplementation, and our results clearly showed that trehalose served as a protectant against ES and that the exogenous supply of trehalose improved the survival of WA under ES (Figs. 1, 10).
Evidence shows that the increased concentrations of ethanol during fermentation prompt the generation of ROS [9, 10]. Excess ROS result in the occurrence of oxidative stress, which is cytotoxic to the cells, especially for cell organelles like DNA, proteins, and lipids [31]. In this research, we observed a higher level of ROS when WA was exposed to ethanol (Fig. 5A). In contrast, trehalose inhibited the generation of ROS. RNA-seq data showed that trehalose significantly regulated the DEGs annotated to DNA replication, ribosome, and RNA polymerase (Fig. 8B, D). The antioxidant enzymes SOD and CAT have been shown to work synergistically to combat oxidative stress by scavenging excess ROS [32]. We also detected higher activities of SOD and CAT in WA after exogenous application of trehalose under ES (Fig. 5B, C), which was consistent with a study on S. cerevisiae [33, 34].
The main targets of ethanol in yeast cells are thought to be plasma membranes [35]. An increased amount of ethanol during fermentation leads to lipid peroxidation, thereby affecting the permeability and fluidity properties of the plasma membranes [9, 10]. In this study, we found that the cell membrane was destroyed by ethanol when checking the ultrastructure of WA (Fig. 4A). Moreover, a higher level of MDA (lipid peroxidation product) was detected in ethanol group compared with control group (Fig. 6A), suggesting the lipid peroxidation by ethanol treatment in WA. In contrast, trehalose could mitigate this lipid peroxidation and stabilize the structural integrity of cell membranes. In addition, trehalose intervention also protected mitochondria against ES by ameliorating the swelling of mitochondria (Fig. 4C) and improving the structure of cristae, thus increasing the production of ATP (Fig. 6B).
The destroyed integrity of cell membranes may further disrupt the transport of amino acids into the cell [36]. Several amino acids have been found to have positive effects on ethanol tolerance in yeast, such as proline [37], arginine [38], and tryptophan [35]. In our previous study, we found that aspartate, glutamate, and arginine exhibited protective roles in WA cells against ES [21]. In this study, we also annotated alanine, aspartate, glutamate, proline, lysine, and phenylalanine metabolism from the transcriptomic data after the addition of trehalose (Fig. 9B). Thus, further studies on the mechanisms underlying the relationship between trehalose metabolism and the metabolism of these amino acids in the ethanol response of WA is warranted.
As a nonreducing disaccharide, trehalose acts as a stress protectant against various adverse environmental conditions, such as freezing, salinity, water, heat, and pinene, as well as oxidative and osmotic stress, but not limited to ES in microorganisms [11,12,13]. Most of the research on the protective roles of trehalose against these stresses has been performed using the baker’s yeast S. cerevisiae as a model. This approach, however, has several notable drawbacks. For example, some mutants were unable to synthesize trehalose for the disrupted metabolic pathway of trehalose, could not grow on readily fermentable sugars, and lost many regulatory responses. Several species of non-Saccharomyces yeasts have been used to explore the mechanism of yeast response to unlivable conditions. Péter and co-workers found that lipids and trehalose synergistically collaborated to manage heat stress in Schizosaccharomyces pombe [39]. This species of yeast also has been reported by Soto et al. [40], and they observed that the overexpression of tps1 in S. pombe, leading to trehalose accumulation, resulted in enhanced resistance to multiple stresses, including osmotic stress and dehydration, freezing, and ES. In Dhanasekaran’s study, the results showed that trehalose supplementation improved the biocontrol efficiency of Sporidiobolus pararoseus via increased oxidative stress tolerance and altered transcriptome [41]. Additionally, Ma and co-workers [42] assessed the effects of trehalose and ergosterol on pinene stress of Candida glycerinogenes, and they found that overexpression of genes that encoded trehalose and ergosterol was related to tolerance to higher concentrations of pinene. In this study, we demonstrated the protective roles of trehalose in relieving ES to the yeast cells in WA because of the great potential for wine production. Moreover, the genomic sequence of WA had been finished and reported, which is convenient for research on the gene modification of this yeast species [2, 3]. In addition, WA could tolerate multiple adverse environmental conditions, such as extreme pH, high osmotic stress, and anaerobic conditions [2,3,4,5]. Therefore, this species of yeast also may be used as a model to probe the molecular mechanism of various stresses alongside ES [43, 44].
Conclusions
To our knowledge, this study represents the first comprehensive analysis of the role of trehalose in contributing to ES tolerance in WA. Under ES, trehalose improved the survival and anomalous surface and ultrastructural morphology of WA. In addition, trehalose improved redox homeostasis by reducing the production of ROS and increasing the activities of antioxidant enzymes. In addition, the RNA-seq analysis provided evidence that trehalose altered the gene expression, protein synthesis, energy metabolism, and the cell cycle in WA, contributing to the proliferation and biological activities of yeast cells. These results revealed the protective role of trehalose in ES mitigation and strengthened the possible uses of WA in the wine fermentation sector.
Materials and methods
Yeast strains, media, and culture conditions
In this study, we usedstrain of WA C11, which was isolated from the spontaneous fermentation broth of Rosa roxburghii Tratt [45]. The yeast strain was cultured in YEPD medium for 72 h at 28 °C, and subsequently preserved at 4 °C for future use.
ES conditions
WA C11 was cultured in YEPD broth medium for 8 h at 28 °C. We then assigned it into 3 groups: control group, ethanol group, and ethanol + Tre group. For the ethanol group, the cells were directly exposed to ES (9% v/v). The cells in the ethanol + Tre group were exposed to 9% ethanol and 10 mmol/L of trehalose. For the control group, the cells received neither ethanol nor trehalose treatment. The beginning of treatment was regarded as 0 h. After incubation for 6 h, we collected the cells from each group for the experiments of this study.
Survival analysis of WA
We first determined the growth curve. The optical density (OD) values of the control, ethanol, and ethanol + Tre groups were determined at 600 nm every 4 h. We repeated each experiment in triplicate.
We conducted a spot analysis to further analyze the survival of yeast cells. After treatment, the cells were collected, washed, resuspended, and spotted onto YEPD solid plates according to the method of Liu and colleagues. Each colony was captured using a microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
We then performed methylene blue staining to monitor the dead cells based on the method of Sami and co-workers [46]. The death rate was determined by counting the blue-stained cells, indicating dead cells, while the live cells remained unstained.
Transcriptomic analysis of WA
We extracted total RNA from the yeast cells of the control, ethanol, and ethanol + Tre groups using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocols. We removed genomic DNA by digesting total RNA with DNase I (TaKara, Shiga, Japan). RNA-seq transcriptome library was established using a TruSeqTM RNA sample preparation kit (San Diego, CA, USA). cDNA target fragments of 300 bp were selected from the libraries using 2% Low Range Ultra Agarose, followed by PCR amplification with Phusion DNA polymerase (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) for 15 PCR cycles. The resulting paired-end RNA-seq sequencing library was then sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq xten/NovaSeq 6000 sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). We conducted the identification of DEGs, classification analysis of DEGs, and KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs using the Majorbio Cloud Platform (https://cloud.majorbio.com) according to the method of Li and colleagues [47].
Morphological analysis of WA
We assessed the surface morphological characteristics of WA using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and observed the cellular ultrastructure using a transmission electron microscope (TEM). We collected the WA cells of the control, ethanol, and ethanol + Tre groups by centrifugation (4000 × g, 10 min), which were then rinsed 3 times with physiological saline. The cells were then suspended in 2.5% glutaraldehyde and underwent three washes with 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4). Subsequently, the cells were dehydrated with 0%, 50%, 70%, 85%, 95%, and 100% ethanol solutions. After drying with in a critical point dryer (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan), WA cells were coated with a gold/palladium alloy, and then examined using an FEI Quanta FEG 450 SEM system (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA). The dehydrated WA cells were embedded in an epoxy resin and sectioned with a diamond knife (LKB-Nova, Elkin, NC, USA). The ultrathin sections were stained with lead citrate, viewed, and photographed with an FEI Tecnai spirit 120 kV (FEI).
ROS determination
We measured the ROS levels of WA cells using the fluorescent dye dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) [48]. After treatment, we collected the cells of each group by centrifugation (10,000 rpm, 10 min). The cells were rinsed with PBS (pH 7.4) three times and then stained with DCFH-DA (25 mM/L). We observed the ROS accumulation using a stereoscopic fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss Axio Zoom v16; Zeiss International, Oberkochen, Germany).
Catalase and superoxide dismutase activity assay
We collected the cells by centrifugation (5000 rpm, 5 min) and rinsed them twice with PBS (pH 7.4). We determined the catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities using the CAT and total SOD assay kits (Jiancheng Bioengineering, Jiangsu, China), respectively, following the manufacturer’s protocols. We calculated the activities of CAT and SOD according to the value of ethanol group or ethanol + Tre group divided by the that of control group.
Measurement of trehalose, malondialdehyde, and adenosine triphosphate levels
We measured the levels of trehalose, malondialdehyde (MDA), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using the trehalose content detection (Jiancheng), MDA assay (Jiancheng), and ATP assay kits (Beyotime, Shanghai, China), respectively, following the manufacturer’s protocols. We calculated the levels of trehalose, MDA, and ATP based on the value of Eth group or ethanol + Tre group divided by that of control group.
Statistics
All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. We used SPSS 21.0 software (IBM-SPSS Inc., IL, USA) for the univariate analysis of variance (ANOVA) and determined the significance of the difference. P < 0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- W. anomalus :
-
Wickerhamomyces anomalus
- S. cerevisiae :
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- RNA-seq:
-
RNA-sequencing
- PBS:
-
Phosphatic buffer solution
- OD:
-
Optical density
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
Padilla B, Gil JV, Manzanares P. Challenges of the non-conventional yeast Wickerhamomyces anomalus in winemaking. Fermentation. 2018;4:68.
Schneider J, Rupp O, Trost E, Jaenicke S, Passoth V, Goesmann A, et al. Genome sequence of Wickerhamomyces anomalus DSM 6766 reveals genetic basis of biotechnologically important antimicrobial activities. FEMS Yeast Res. 2012;12:382–6.
Cunha AC, Santos RA, Riaño-Pachon DM, Squina FM, Oliveira JVC, Goldman GH, et al. Draft genome sequence of Wickerhamomyces anomalus LBCM1105, isolated from cachaça fermentation. Genet Mol Biol. 2020;43:e20190122.
Asri M, Elabed S, Elabed A, Bahafid W, Koraichi SI, Ghachtouli NE. Effect of putrescine on cell surface properties of Wickerhamomyces anomalus: Performance on Cr (VI) biosorption. Environ Eng Sci. 2019;36:396–404.
Raynaldo FA, Dhanasekaran S, Ngea GLN, Yang Q, Zhang X, Zhang H. Investigating the biocontrol potentiality of Wickerhamomyces anomalus against postharvest gray mold decay in cherry tomatoes. Sci Horti. 2021;285:110137.
Sabel A, Martens S, Petri A, König H, Claus H. Wickerhamomyces anomalus AS1: a new strain with potential to improve wine aroma. Ann Microbiol. 2014;64:483–91.
Satora P, Tarko T, Sroka P, Blaszczyk U. The influence of Wickerhamomyces anomalus killer yeast on the fermentation and chemical composition of apple wines. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014;14:729–40.
Sun N, Gao Z, Li S, Chen X, Guo J. Assessment of chemical constitution and aroma properties of kiwi wines obtained from pure and mixed fermentation with Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Sci Food Agr. 2022;102:175–84.
Auesukaree C. Molecular mechanisms of the yeast adaptive response and tolerance to stresses encountered during ethanol fermentation. J Biosci Bioeng. 2017;124:133–42.
Saini P, Beniwal A, Kokkiligadda A, Vij S. Response and tolerance of yeast to changing environmental stress during ethanol fermentation. Process Biochem. 2018;72:1–12.
Feofilova EP, Usov AI, Mysyakina IS, Kochkina GA. Trehalose: chemical structure, biological functions, and practical application. Microbiology. 2014;83:184–94.
Chen A, Tapia H, Goddard JM, Gibney PA. Trehalose and its applications in the food industry. Compr Rev Food Sci F. 2022;21:5004–37.
Eleutherio E, Panek A, De Mesquita JF, Trevisol E, Magalhães R. Revisiting yeast trehalose metabolism. Curr Genet. 2015;61:263–74.
Kosar F, Akram NA, Sadiq M, Al-Qurainy F, Ashraf M. Trehalose: a key organic osmolyte effectively involved in plant abiotic stress tolerance. J Plant Growth Regul. 2019;38:606–18.
Rehman S, Chattha MU, Khan I, Mahmood A, Hassan MU, Al-Huqail AA, et al. Exogenously applied trehalose augments cadmium stress tolerance and yield of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) grown in soil and hydroponic systems through reducing cd uptake and enhancing photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant defense systems. Plants. 2022;11:822.
Rohman MM, Islam MR, Monsur MB, Amiruzzaman M, Fujita M, Hasanuzzaman M. Trehalose protects maize plants from salt stress and phosphorus deficiency. Plants. 2019;8:568.
Mahmud SA, Nagahisa K, Hirasawa T, Yoshikawa K, Ashitani K, Shimizu H. Effect of trehalose accumulation on response to saline stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 2009;26:17–30.
Herdeiro RS, Pereira MD, Panek AD, Eleutherio ECA. Trehalose protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae from lipid peroxidation during oxidative stress. BBA-Gen Subjects. 2006;1760:340–6.
Asada R, Watanabe T, Tanaka Y, Kishida M, Furuta M. Trehalose accumulation and radiation resistance due to prior heat stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol. 2022;204:1–8.
Li L, Ye Y, Pan L, Zhu Y, Zheng S, Lin Y. The induction of trehalose and glycerol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in response to various stresses. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2009;387:778–83.
Li Y, Long H, Jiang G, Yu Z, Huang M, Guan T, et al. Analysis of the ethanol stress response mechanism in Wickerhamomyces anomalus based on transcriptomics and metabolomics approaches. BMC Microbiol. 2022;22:1–13.
Wang W, Fan G, Li X, Fu Z, Liang X, Sun B. Application of Wickerhamomyces anomalus in simulated solid-state fermentation for Baijiu production: changes of microbial community structure and flavor metabolism. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:598758.
Canonico L, Galli E, Ciani E, Comitini F, Ciani M. Exploitation of three non-conventional yeast species in the brewing process. Microorganisms. 2019;7:11.
Tian S, Liang X, Chen J, Zeng W, Zhou J, Du G. Enhancement of 2-phenylethanol production by a wild-type Wickerhamomyces anomalus strain isolated from rice wine. Bioresource Technol. 2020;318: 124257.
Cai W, Li B, Chen Y, Fu G, Fan H, Deng M, et al. Increase the content of ester compounds in blueberry wine fermentation with the ester-producing yeast: Candida glabrata, Pichia anomala, and Wickerhamomyces anomalus. Foods. 2022;11:3655.
Fan G, Teng C, Xu D, Fu Z, Minhazul KAH, Wu Q, et al. Enhanced production of ethyl acetate using co-culture of Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng. 2019;128:564–70.
Zha M, Sun B, Wu Y, Yin S, Wang C. Improving flavor metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mixed culture with Wickerhamomyces anomalus for Chinese Baijiu making. J Biosci Bioeng. 2018;126:189–95.
Divate NR, Chen GH, Wang PM, Ou B, Chung Y. Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improvement in ethanol tolerance by accumulation of trehalose. Bioengineered. 2016;7:445–58.
Trevisol ETV, Panek AD, Mannarino SC, Eleutherio CA. The effect of trehalose on the fermentation performance of aged cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biot. 2011;90:697–704.
Lucero P, Penalver E, Moreno E, Lagunas R. Internal trehalose protects endocytosis from inhibition by ethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environn Microb. 2000;66:4456–61.
Schieber M, Chandel NS. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 2014;24:R453–62.
Kapoor D, Singh S, Kumar V, Romero R, Prasad R, Singh J. Antioxidant enzymes regulation in plants in reference to reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Plant Gene. 2019;19:100182.
Jing H, Liu H, Zhang L, Gao J, Song H, Tan X. Ethanol induces autophagy regulated by mitochondrial ROS in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Microbiol Biotechn. 2018;28:1982–91.
Ribeiro MJS, Leão LSC, Morais PB, Rosa CA, Panek AD. Trehalose accumulation by tropical yeast strains submitted to stress conditions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1999;75:245–51.
Hirasawa T, Yoshikawa K, Nakakura Y, Nagahisa K, Furusawa C, Katakura Y, et al. Identification of target genes conferring ethanol stress tolerance to Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on DNA microarray data analysis. J Biotechnol. 2007;131:34–44.
Chakrabarti AC. Permeability of membranes to amino acids and modified amino acids: Mechanisms involved in translocation. Amino Acids. 1994;6:213–29.
Takagi H, Taguchi J, Kaino T. Proline accumulation protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells in stationary phase from ethanol stress by reducing reactive oxygen species levels. Yeast. 2016;33:355–63.
Cheng Y, Du Z, Zhu H, Guo X, He X. Protective effects of arginine on Saccharomyces cerevisiae against ethanol stress. Sci Rep. 2016;6:1–12.
Soto T, Fernández J, Vicente-Soler J, Cansado J, Gacto M. Accumulation of trehalose by overexpression of tps1, coding for trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, causes increased resistance to multiple stresses in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Appl Environ Microb. 1999;65:2020–4.
Péter M, Gudmann P, Kóta Z, Török Z, Vígh L, Glatz A, et al. Lipids and trehalose actively cooperate in heat stress management of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:13272.
Dhanasekaran S, Yang Q, Godana EA, Liu J, Li J, Zhang H. Trehalose supplementation enhanced the biocontrol efficiency of Sporidiobolus pararoseus Y16 through increased oxidative stress tolerance and altered transcriptome. Pest Manag Sci. 2021;77:4425–36.
Ma T, Cai H, Zong H, Lu X, Zhuge B. Effects of trehalose and ergosterol on pinene stress of Candida glycerinogenes. Biotechnol. Appl Biochem. 2022; 70:1–12.
Ojha N, Das N. Effects of various stress conditions to enhance polyhydroxyalkanoates accumulation in Wickerhamomyces anomalus VIT-NN01. Curr Biotechnol. 2020;9:143–57.
Luo Y, Liu W, Guo W, Fu X, Xu L, Hu Z, et al. Effect of cold stress on the metabolome of Wickerhamomyces anomalus with cold resistance. Food Sci. 2019;40:190–5.
Liu X, Li Y, Zhao H, Yu Z, Hardie WJ, Huang M. Identification and fermentative properties of an indigenous strain of Wickerhamomyces anomalus isolated from Rosa roxburghii Tratt. Brit Food J. 2021;123:4069–81.
Sami M, Ikeda M, Yabuuchi S. Evaluation of the alkaline methylene blue staining method for yeast activity determination. J Fermentation Bioeng. 1994;78:212–6.
Li Y, Long H, Jiang G, Yu Z, Huang M, Zou S, et al. Protective effects of thiamine on Wickerhamomyces anomalus against ethanol stress. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:1057284.
Allen SA, Clark W, McCaffery JM, Cai Z, Lanctot A, Slininger PJ, et al. Furfural induces reactive oxygen species accumulation and cellular damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2010;3:1–10.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32160557).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. L (Yinfeng Li) and X. L wrote the original draft manuscript; G. J, H. L, Y. L (Yifa Liao), and L. W conducted the experiments; W. H helped to analyze the data of transcriptomics; X. L conceive and designed the experiments. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Figure S1. Trehalose increased biomass of W. anomalus under ethanol stress. Figure S2. Principal component analysis (PCA) results of the samples used in this study. Table S1. Quality analysis of transcriptome sequencing data of different groups.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Jiang, G., Long, H. et al. Contribution of trehalose to ethanol stress tolerance of Wickerhamomyces anomalus. BMC Microbiol 23, 239 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-023-02982-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-023-02982-y