Abstract
Background
Proteins with the jumonji (JMJ)-C domain belong to the histone demethylase family and contribute to reverse histone methylation. Although JMJ-C family genes have an essential role in regulating plant growth and development, the characterization of the JMJ-C family genes in melon has not been uncovered.
Results
In this study, a total of 17 JMJ-C proteins were identified in melon (Cucumis melo L.). CmJMJs were categorized into five subfamilies based on the specific conserved domain: KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1, JMJD6, KDM3/JHDM2, and JMJ-C domain-only. The chromosome localization analyses showed that 17 CmJMJs were distributed on nine chromosomes. Cis-acting element analyses of the 17 CmJMJ genes showed numerous hormone, light, and stress response elements distributed in the promoter region. Covariance analysis revealed one pair of replicated fragments (CmJMJ3a and CmJMJ3b) in 17 CmJMJ genes. We investigated the expression profile of 17 CmJMJ genes in different lateral organs and four developmental stages of fruit by RNA-seq transcriptome analysis and RT-qPCR. The results revealed that most CmJMJ genes were prominently expressed in female flowers, ovaries, and developing fruits, suggesting their active role in melon fruit development. Subcellular localization showed that the fruit-related CmJMJ5a protein is specifically localized in the cell nucleus.
Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive understanding of the gene structure, classification, and evolution of JMJ-C in melon and supports the clarification of the JMJ-C functions in further research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Epigenetics denotes the enzymatically reversible modifications of corresponding gene expression without any alteration of the DNA sequences, which can be stably inherited by the progeny [1]. Epigenetic processes include DNA methylation, nucleosome remodeling, covalent modification of histones, and noncoding RNA regulation [2,3,4,5,6]. The epigenetic mechanisms of histone modification activate or inhibit transcription by regulating the chromatin state or directly recruiting specific effector proteins, which in turn modulate chromatin accessibility or the activity of the underlying DNA [7,8,9]. The homeostasis of histone methylation is dynamically regulated by histone methyltransferases (HMTs) and histone demethylases (HDMs), which add or remove methyl groups on specific residues to make transcription factors facilitate or prevent access to genomic DNA [10, 11]. Jumonji-C (JMJ-C) family proteins belong to histone demethylases, which remove methylation marks by hydroxylation relying on Fe(II) and a-ketoglutarate (α-KG) with broader specificity [12]. JMJ-C protein function is involved in the epigenetic regulation of tumorigenesis and pathogen infection in animals [13], leaf senescence [14], floral transition [15, 16], the control of seed germination [17], the regulation of shoot regeneration [18], and rhythm-related processes in plants [19]. Genes encoding JMJ-C have been characterized in several plant species, including Arabidopsis thaliana [20], Zea mays [21], Citrus sinensis [22], Oryza sativa [23], Gossypium hirsutum [24], Solanum lycopersicum [25] and Jatropha curcas [26]. In Arabidopsis, 21 JMJ-C proteins were identified and categorized into different subfamilies based on sequence similarity and catalytic specificity, including KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1, JMJD6, KDM3/JHDM2, and JMJ-C domain-only [20]. KDM5/JARID subfamily proteins can remove the methylation of H3K4me1/2/3 [27]. AtJMJ16 gene negatively regulates leaf senescence by reducing the expression level of H3K4me3 and inhibiting the expression of the leaf maturation genes WRKY53 and SAG201 [28]. AtJMJ15 and AtJMJ18, which also belong to the KDM5/JARID subfamily, both can stimulate flowering by decreasing the methylation level of H3K4 at the FLC locus and subsequently suppressing FLC expression, thereby promoting FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) activity in the accompanying cells [29]. KDM4/JHDM3 subfamily genes eliminate the methylation of H3K9me2/3 and H3K36me2/3 [30], and KDM3/JHDM2 subfamily proteins have H3K9me1 and H3K9me2 demethylation activity [31]. JMJD6 subfamily can demethylate H3K27me2/3 [32], and JMJ-C domain-only subfamily proteins can remove the methylation of H3K27me3 [33].
JMJ-C proteins are involved in the expression of multiple genes, chromatin activity, and biological processes such as plant growth, metabolism and environmental responses. In Arabidopsis, AtJMJ27 negatively regulates the expression of the flowering regulatory factor CONSTANS (CO) and positively regulates FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) gene activity, leading to delayed flowering time [34]. At a suitable temperature, AtJMJ30 and AtJJMJ32 jointly remove H3K27me2/3 from FLC to prevent a premature flowering phenotype [35]. AtJMJ30 and AtJJMJ32 are also involved in mediating the abscisic acid (ABA) response during root development at the seedling stage by removing H3K27me3 from SnRK2.8 to activate its expression [36]. AtJMJ30 binds to LBD16 and LBD29 and promotes leaf callus transition by activating LBD expression [37]. AtJMJ27 is a histone H3K9 demethylase that directly associates with the drought stress positive regulators GOLS2 and RD20 to participate in drought stress [38]. In rice, OsJMJ706 has H3K4me1/2/3 demethylase activity, can affect rice flower morphology development [39] and OsJMJ703 participates in plant defense against drought stress [40]. In Medicago truncatula, MtJMJC5 undergoes cold-dependent alternative splicing and may be involved in the response to freezing tolerance [41]. In higher plants, fruit development is a vital biological process, which is regulated by gene regulatory network and epigenetic modification. In tomato, SlJMJ6 overexpression specifically demethylated H3K27 methylation and up-regulated the ripening-related genes, including SlRIN, SlACO1, SlACS4, SlPL, SlTBG4 and SlDML2, and thus accelerated the fruit development [25]. Overexpression of SlJMJ7 specifically demethylates the methylated H3K4me3 and inhibited the SlDML2 expression, which resulted in the delayed fruit ripening [42]. In banana, MaJMJ15 regulated the fruit maturation by removing H3K27me3 from their chromatin to activate the expression of several key RRGs [43].
Melon (Cucumis melo L.) is a widely cultivated horticultural crop with high nutritional and economic value. Melon fruits undergo dramatic changes in size, color, texture, nutrition, and aroma during development, and the fruit ripening has both climacteric and non-climacteric genotypes. Therefore, melon can be used as a good model plant to study the genetic mechanism of fruit development based on their diverse agronomic traits, such as sex determination, stress tolerance, fruit development and ripening processes. Although JMJ-C family proteins participate in varying aspects of plant growth in different species, their gene features and potential roles in melon have not been characterized. In this study, 17 CmJMJ genes were identified in melon. Then, we performed a comprehensive bioinformatic study of chromosomal location, phylogenetic relationships, genomic organization, conserved protein domains, cis-acting elements, gene duplication events, and synteny relationships. Additionally, the expression profiles of CmJMJs were analyzed in different tissues and four stages of fruit development. This study provides a molecular basis for further functional research on the JMJ-C domain-containing proteins in melon.
Results
Identification of JMJ-C genes in Cucumis melo L.
We performed genome-wide identification of CmJMJ proteins by a combinatorial approach of the domain characteristics, CDD, and InterPro database. A total of 17 JMJ-C genes were identified and then designated CmJMJ1 to CmJMJ15 (CmJMJ3a to CmJMJ3b and CmJMJ5a to CmJMJ5b) based on homology between the melon and Arabidopsis genes (Fig. 1). The basic information of CmJMJs, gene ID, molecular weight (Mw), isoelectric point (pI) and protein length are listed in Table 1. The protein length of CmJMJ showed various differences, which varied from 272 aa (CmJMJ7) to 1144 aa (CmJMJ6); the corresponding coding sequence length of the CmJMJ genes varied from 1242 bp (CmJMJ7) to 5454 bp (CmJMJ6); the molecular weights ranged from 46.68 kDa (CmJMJ7) to 208.73 kDa (CmJMJ6), and the predicted pI was between a minimum of 4.33 (CmJMJ8) and a maximum of 8.91 (CmJMJ10) (Table 1). The prediction of subcellular localization found that 17 melon JMJ-C gene family members were located in the nucleus, which was consistent with the occurrence of silencing redundant parts of the genome by histone demethylation to ensure the structural and functional integrity of the genome. The number of JMJ-C genes tends to be conserved in different species, with 21, 21, 20 and 20 JMJ-C genes in Arabidopsis thaliana [20], Vitis vinifera [44], rice (ChromDB database) [45] and Solanum lycopersicum [25], respectively. The reduced JMJ-C gene number in melon implied that several essential CmJMJ genes may undertake a comprehensive role in regulating plant growth during melon evolution.
Phylogenetic relationship of JMJ-C family proteins in melon (Cucumis melo), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), grape (Vitis vinifera), watermelon (Citrullus lanatus), and Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). The phylogenetic tree was constructed by MUSCLE and Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates in MEGA 7.0. JMJ-C proteins were clustered into five groups based on relative sequence homology. Blocks of subfamily KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1, JMJD6, KDM3/JHDM2, and JMJ-C domain-only were displayed in different color, as shown in the upper left corner of the figure
Phylogenetic Analysis of the JMJ-C genes
To explore the evolutionary relationship of CmJMJ genes, we constructed a phylogenetic tree using 96 JMJ-C protein sequences referenced from Cucumis melo, Vitis vinifera (21), Arabidopsis thaliana (21), Solanum lycopersicum (20), and Citrullus lanatus (17) (Fig. 1). According to the JMJ-C subfamilies in Arabidopsis, the phylogenetic tree was branched into five groups, KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1, JMJD6, KDM3/JHDM2, and JMJ-C domain-only, by blasting the sequence similarities and common conserved domains. Among them, KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1 and KDM3/JHDM2 are the three largest subfamilies, and JMJD6 subfamily has a minimum of members (Fig. 1). In melon, the member of subfamilies showed that there are four gene members in each of KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1 and KDM3/JHDM2 subfamilies, while the JMJD6 subfamily has two members (Fig. 2A).
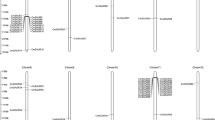
Comprehensive sequence analyses of the melon CmJMJ genes. A Phylogenetic relationship of CmJMJ proteins. The phylogenetic tree was performed using Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method and CmJMJ proteins were clustered into five groups. B Motif analysis. Ten motifs in CmJMJ proteins are indicated by different colored squares. C Schematic structure of conserved domains. The figure displays the position and size of the different conserved domain, which is indicated by colored triangle. D Gene structure analyses of the CmJMJ family genes. Green and yellow boxes represent UTR and exons, respectively. Black line represents the intron
Conserved motifs and gene structure analysis of CmJMJ-C genes
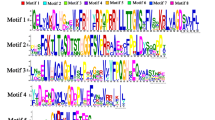
We analyzed the conserved motif and gene structure of all 17 CmJMJs and identified 10 motifs in melon (Fig. 2B). KDM3/JHDM2 subfamily genes have motif4, motif6, motif7, motif8, and motif10, which is unique in the KDM3/JHDM2 family (Fig. 2B). In the KDM4/JHDM3 and KDM5/JARID1 subfamilies, most CmJMJs contain motif1, motif2, motif3 and motif5, and align in the order of 3-1-2-5 (Fig. 2B). The JMJ-only subfamily only contains motif9, and the JMJD6 subfamily was equipped with motif9 and motif1 (Fig. 2B). Motifs in the KDM3/JHDM2 subfamily genes were aligned in the order of 7-10-6-8-4. The regular motif alignments in the different subfamilies indicated the sequence conservation within subfamilies and validated the reliability of the phylogenetic tree division. The conserved domain analyses showed that all melon JMJ-C proteins have JMJ-C domain, and some of KDM3/JHDM2 subfamily proteins have two JMJ-C domains (Fig. 2C). In KDM5/JARID1 and KDM4/JHDM3 subfamilies, the JMJ-N was always synchronized with JMJ-C domain (Fig. 2C). FYRC and FYRN domains appeared in the CmJMJ4 and CmJMJ5a proteins, and the longest protein CmJMJ6 had the most domains, containing ARID, PLU-1, and PHD (Fig. 2C). The gene structure analyses in CmJMJs exhibit tremendous variation in the exon number, which ranges from 2 to 35 (Fig. 2D). We assumed that the evolutionary diversification of JMJ-C family protein structures and functions may be conferred by the loss or gain of their conserved domains.
Chromosome distribution and collinear analysis of CmJMJ-C genes
Chromosomal localization analysis revealed that CmJMJ genes were evenly distributed on nine chromosomes (Chr1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 and 12), which displayed two genes on each chromosome (Fig. 3). Nevertheless, only CmJMJ14 is located on Chr08 (Fig. 3).
To reveal the evolutionary origin of the CmJMJ genes, a synteny analysis of interspecies collinearity between melon and two other species was conducted (Fig. 4). The gray lines show collinear blocks of different chromosomes, while the red line indicates the collinear JMJ-C gene pairs within melon and the two species (cucumber and Arabidopsis). We found 11 collinear gene pairs within the melon and Arabidopsis genomes when Arabidopsis Chr2 had no collinear gene with CmJMJ. A total of 17 pairs of putative JMJ-C genes were collinear between cucumber and melon. The increased number of orthologous genes in Cucurbitaceae may be attributed to their closer evolutionary relationship than Arabidopsis. Further covariance analysis found a pair of fragment replication (CmJMJ3a and CmJMJ3b) genes without tandem replication events within the CmJMJ family (Fig. 5). Combined with previous phylogenetic analyses, we found that both putative fragment replication genes belong to the same KDM3/JHDM2 subfamily and are on the same branch of the phylogenetic tree. We speculated that their replication events occurred late and functionally undifferentiated.
Synteny analysis of the melon genome and segmental duplications of CmJMJs. Gray lines denote the details of syntenic regions in the melon genome, and blue lines denote CmJMJ gene pairs with segmental duplication. The melon chromosomes arranged in the inner circle, and the scale numbers under the histograms indicate the chromosome size (Mb). The middle and outer circles indicate the gene density in the chromosomes
Cis-element analysis of the promoter regions of the CmJMJ genes
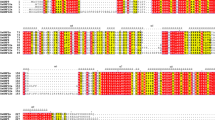
To further clarify the possible regulatory mechanisms of CmJMJ genes, we analyzed the cis-acting elements in the promoter regions (2000-bp upstream sequence from the translation start site) of CmJMJ genes by PlantCARE database (Fig. 6). We found the cis-acting elements involved in phytohormone (abscisic acid, gibberellin, MeJA, auxin and salicylic acid), light response, growth and development, and abiotic stress in CmJMJ genes. Light-responsive elements were found in all CmJMJ, and gibberellin-responsive, anaerobic induction, auxin-responsive element, MeJA-responsive and abscisic acid-responsive elements had the most common distribution. The hormone-related cis-acting elements were commonly presented in all subfamilies of CmJMJ: gibberellin-responsive elements were presented in the KDM3/JHDM2 and KDM4/JHDM3 subfamily genes, and MeJA-responsive elements were presented in all members of KDM5/JARID1. We also found that abiotic stress-related elements (low-temperature responsive, drought-inducible, defense and stress-responsive and anaerobic-inducible elements) were enriched in CmJMJs. The endosperm expression element was found only in JMJ-only subfamily genes.
Expression profiles of CmJMJs in melon
We explored the expression profile of all 17 CmJMJ genes in melon different tissues, roots, stems, leaves, female flowers, male flowers, ovaries, and flesh of fruits at four developmental stages (G stage: growing stage, R stage: ripening stage, C stage: climacteric stage, P stage: postclimacteric stage), using the released melon transcriptomic data on NCBI (Fig. 7A). The transcript abundance of CmJMJ genes in different tissues fluctuated widely, which indicates their comprehensive role in different aspects of melon growth and development (Fig. 7B). High expression of CmJMJs was mostly accumulated in the female flower, male flower, and young ovary. Then, we performed RT-qPCR to further verify the expression of CmJMJ genes and found that most of the gene expression had a similar trend to the transcriptome analysis (Fig. 8). The expression levels of the CmJMJ5a, CmJMJ6, CmJMJ9 and CmJMJ11 genes showed an increasing trend during the fruit ripening period from G to P (Fig. 7A), which may suggest their positive regulation in fruit ripening. CmJMJ5b and CmJMJ10 showed a decreasing trend in fruit developmental stages, suggesting that they may be associated with the inhibition of fruit ripening. The RT-qPCR results were consistent with the RNA-seq analysis (Fig. 8). CmJMJ1, CmJMJ3a, CmJMJ7, and CmJMJ15, showed high expression in the young ovary and reduced expression in the later G R C P developmental stages of fruit, implying their active role in regulating early fruit growth instead of ripening. CmJMJ2, CmJMJ11, CmJM12, and CmJMJ14 were highly accumulated in the female flower compared with other organs, while CmJMJ5a and CmJMJ13 had the highest expression in the male flower, showing their different transcription level in floral sex differentiation.
Expression profiles of CmJMJ genes in melon. A The heatmap and hierarchical cluster representing R (Root), S (Stem), L (Leaf), FF (Female Flower), MF (Male Flower), O (Ovary), and four different stages of fruit development: G (growing stage), R (ripening stage), C (climacteric stage), P (post-climacteric stage). B Schematic model of melon plant growth (left) and fruit development (right)
Relative expression of 17 CmJMJ genes in melon different tissues. L (leaf), R (root), S (stem), FF (female flower), MF (male flower), O (ovary), G stage (growing stage), R stage (ripening stage), C stage (climacteric stage), and P stage (post-climacteric stage). GAPDH was used as the reference gene, and gene expression in leaves was used as control “1”. Gene names are written under each histogram. The expression values were analyzed from three biological replicates and three technological replicates
To clarify the subcellular localization of CmJMJ protein, we cloned the CmJMJ5a coding sequence without stop codon fragment and constructed a gene-localizing vector. The young leaves of tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana) were transformed by the positive control 35S:GFP and the recombinant vector 35S:CmJMJ5a-GFP. The results showed that CmJMJ5a-GFP fusion protein was only expressed in the nucleus (Fig. 9), confirming the predicted subcellular localization in the Table 1.
Discussion
Plants have developed many biological capabilities to adapt the challenging environmental conditions during their evolution. Gene regulations and epigenetic modifications play vital roles in controlling plant biological processes, including root growth, gametophyte or embryo formation, floral organogenesis/senescence, and fruit development [46]. Histone methylation is an epigenetic modification that controls the dynamic balance by histone methyltransferases and demethylases [11]. JMJ-C domain–containing proteins are the largest family of histone demethylases in natural organisms. JMJ-C protein family have 21 members in model plant Arabidopsis thaliana [20], 20 members in rice [45], 20 members in Solanum lycopersicum [25], 21 members in Vitis vinifera [44], 20 members in Citrus sinensis [22], 18 members in Citrus grandis [47], 22 members in Phyllostachys edulis [48], and 28 JMJ-C members in Rosa chinensis [49]. We identified a total of 17 JMJ-C proteins in melon, showing a reduced member number compared to the other plants, which may because of the small genome size of melon and less gene duplication events during evolution. According to the sequence similarity and domain specification, the CmJMJ gene family in melon was classified into five subfamilies, KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1, JMJD6, KDM3/JHDM2, and JMJ-C domain-only (Fig. 1), which were consistent with the JMJ family classification in Arabidopsis and rice. JMJD6 subfamily has two members in the Arabidopsis, rice, tomato, banana and melon (Fig. 1), and KDM4/JHDM3, KDM5/JARID1, and KDM3/JHDM2 subfamilies showed the most protein member among the five plants, indicating the gene conservation of the subfamilies in different species.
Gene duplication events within the genome promote the generation of new genes, and gene family expansion or contraction ensure their essential function in life activities. In melon, two genes (CmJMJ3a and CmJMJ3b) displayed a syntenic relationship, suggesting one gene duplication with no tandem duplication events for gene family expansion. The collinearity analyses showed that melon had a better genomic collinearity with cucumber than Arabidopsis, which was due to the nearer evolutionary relationship among Cucurbitaceae plants. The coding sequences of 17 CmJMJ genes had no premature stop codons, meaning that these genes encode functional proteins. CmJMJ14 is located in chromosome 8, the remaining 16 genes are evenly distributed on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 12. All JMJ-C family members contain JMJ-C conserved domain, but this domain does not act alone in the histone demethylation process. Many conserved domains in JMJ-C proteins have DNA-binding functions, such as zf-4CXXC_R1, ARID, PLU-1, Zf-C5HC2, FYRN, and FYRC, and these DNA-binding domains contribute to the specific function of JMJ-C proteins [50]. The FYRN and FYRC conserved domains interact with the CTTGNNNNNNCAAG sequence of transcription factors NAC050 and NAC052 in Arabidopsis [51]. AtJMJ14 modulates plant defense against pathogens by regulating salicylic acid- and pipecolic acid-mediated defense pathway genes [52]. CmJMJ4, the homolog of AtJMJ14, had the same conserved FYRN and FYRC domains and salicylic acid response elements in gene sequence, which supposed to follow a similar gene regulation mechanism. The plant specific domains and motifs among the five CmJMJ subfamilies underlie their different activities in regulating biological processes.
Cis-acting elements in the gene promoter region are involved in the regulation of gene expression. We analyzed the promoters [53] of CmJMJ genes and found many cis elements associated with plant hormones, abiotic stress, and plant growth and development. Light-responsive elements were found in the promoter of all 17 CmJMJs. Auxin-responsive elements, abscisic acid- responsive elements, gibberellin-responsive elements, and MeJA-responsive elements were found in more than ten CmJMJ genes, respectively. Notably, the duplication genes CmJMJ3a and CmJMJ3b had common drought stress-responsive elements and hormone cis-elements, implying that they might be co-induced under the hormones and drought stresses. The hormone signaling pathways regulate the fruit development by activating their downstream genes. For example, Auxin/IAA may operate synergistically with ethylene in peach fruit by using PpERF4 as a signaling component through auxin response factors PpIAA1 and promote ABA biosynthesis through binding to and activation of the PpNCED2 and PpNCED3 promoters [54]. Cis-elements analysis indicated that the expression levels of the CmJMJ genes may be modulated by diverse environmental factors, such as light, hormones and abiotic stress.
We characterized the expression profile of the 17 CmJMJ genes by RNA-seq transcriptome data analyses and further investigated by RT-qPCR. Several CmJMJ genes were significantly expressed in both female and male flowers, which may participate in the regulation of melon floral organ development. The expression levels of four genes, CmJMJ5a, CmJMJ9, CmJMJ5b and CmJMJ10, showed a significant change during different fruit developmental stages, suggesting their potential role in fruit development and ripening. In tomato, knockdown of the SlDML2 gene resulted in delayed fruit maturation and decreased 5-methylcytosine (5mC) DNA methylation levels at CNR locus [55, 56]. Tomato SlJMJ6 and SlJMJ7 genes were upregulated in early fruit development and downregulated in late fruit ripening [25, 42]. In banana (Musa acuminata), MaJMJ genes also showed specific expression during fruit development [43]. The correlated expression pattern of JMJs transcripts in the reproductive organs suggested their indispensable role in regulating fruit development in different plants. In conclusion, we identified 17 JMJ-C genes from Cucumis melo and characterized their sequence features, the protein characteristics, phylogenetic relationships, chromosomal localization, collinear synteny, and expression pattern analyses of CmJMJ genes, which will lay the foundation for further exploring their molecular functions.
Materials and Methods
Plant materials
The melon (Cucumis melo cv. Hetao) inbred line used in this study was cultivated in Dengkou County, Inner Mongolia. We have obtained permission to collect melon in Dengkou County. The original plants and planting materials were provided and authorized by Prof Hasi and his team. The Hetao melons were cultivated in the conventional cultivation method and bear one fruit per plant at the 3 or 4 sub-secondary node. Roots, stems, leaves, female and bisexual flowers and ovary at the day of anthesis were sampled from 60-day-old seedlings. The fruit pulp samples were collected 18 days (G stage) and 36 days (R stage) after pollination, as well as at the climacteric stage determined by a breathalyzer (C stage) and 48 h after the climacteric stage (P stage). All tissues were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C for quantitative real-time PCR.
Identification and analysis of physicochemical properties of CmJMJ
The HMM (Hidden Markov Model) files of the JumonjiC (JMJ-C) domain (PF02373) from the Pfam protein family database (http://pfam.xfam.org/) [57] were employed as the seed model to search predicted proteins of JMJ-C from the melon genome database (http://cucurbitgenomics.org/), with the default setting. All Arabidopsis JMJ-C protein sequences were used as query sequence to preform Basic Local Alignment Search to search the melon JMJ-C family members, with an E-value of 1e–5. After filtering redundant sequences from the HMM and the protein blast outcomes, all retrieved sequences obtained by the combinatorial method were examined with the NCBI Conserved Domain Database (CDD) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi) [58]. InterPro database (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/) [59] was used for accurate verification conserved protein domain (PF02373). The confirmed CmJMJ genes were named based on homology between the melon and Arabidopsis genes. The protein signatures, such as amino acids number (AAs), isoelectric point (pI) and molecular weight (Mw) of the CmJMJ proteins were acquired using prot-Param in ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/) [60]. The subcellular localization of CmJMJ genes was predicted with the Plant-mPLoe server (http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/Cell-PLoc-2/).
Classification and Phylogenetic Analysis of CmJMJ
MUSCLE was used to perform multiple sequence alignments of the full-length amino acid sequences of all predicted melon (Cucumis melo) JMJ-C proteins and the orthologs. JMJ-C proteins sequences from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), grape (Vitis vinifera), watermelon (Citrullus lanatus), and Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) were acquired. The protein data of 21 AtJMJ were extracted from the TAIR database (https://www.arabidopsis.org), and the protein data of other three species were downloaded from Phytozome database (http://www.phytozome.net/eucalyptus). The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the Neighbor Joining (NJ) method [61] in MEGA7.0 software [62], with 1000 bootstrap replicates.
Gene structure and conserved motif analysis of CmJMJ
The gene exon–intron structure information of the melon JMJ-C gene family was extracted from the melon genome database (http://cucurbitgenomics.org/) and visualized using the Redraw Gene Structure (From GFF/GTF3 File) function in TBtools. The conserved motifs and domains of the CmJMJ proteins were analyzed by the online software MEME (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) and TBtool software, respectively [63]. The visualized map of the motifs and conserved structural domains was performed by TBtool software.
Chromosome location and collinearity analysis of CmJMJ
The chromosomal locations information of the CmJMJs were acquired from annotated gff3 files in the melon genome database (DHL92) and then analyzed by TBtools software. MCScanX with the default parameters was used to identify gene duplication events of CmJMJs in melon and their synchronous relationship with the homologous JMJs in Arabidopsis and cucumber. All the above results were drawn by the TBtool software.
Cis-regulatory element analysis of CmJMJ
The upstream sequences of CmJMJs (defined as 2 kb away from the transcription start site) were downloaded and submitted to PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) [64] for the promoter cis-element analysis, and visualization was performed using TBtool software.
Transcriptomic resources
To explore the expression pattern of the CmJMJs, the transcriptomic data of ‘Hetao’ melon JMJ-C genes in different tissues (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, male flowers, and ovaries) were used the NCBI sequence read archive (SRA) with accession number PRJNA803327. The RNA-seq data for melon different fruit development stages, including the growing stage (G stage), ripening stage (R stage), climacteric stage (C stage) and post climacteric stage (P stage), were downloaded from the NCBI sequence read archive (SRA) with accession numbers PRJNA543288. The heatmap was constructed from the FPKM normalized log-transformed values of the different samples and visualized via TBtool software.
RNA extraction and quantitative RT-PCR
Different tissue samples of melon were extracted, and 1 μg of RNA was extracted from each sample. First-strand cDNA was synthesized by the PrimeScript® RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The obtained cDNA was diluted tenfold as the template for quantitative real-time PCR, and CmGAPDH was used as the internal reference gene. The CmJMJ gene-specific primers were designed by Primer BLAST of NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/). RT-qPCR was performed using a 96-well Chromo4 Real-Time PCR system with SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™II (Takara RR820A). The RT-q PCR conditions were as follows: predenaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles at 60 °C for 30 s. The relative gene expression values of CmJMJ were calculated with the 2−ΔΔCt method. Three independent biological replicates and three technical replicates were used for each sample. The data analyses with the mean ± standard deviation of three replications were visualized in GraphPad Prism 8.
Subcellular localization analysis of CmJMJ5a
To determine the subcellular localization pattern of CmJMJ5a, the coding sequence without the stop codon was amplified and inserted into the pCAMBIA1300-GFP vector with XmaI I and BamH I restriction enzymes to form the construct 35S:CmJMJ5a-GFP. The fusion construct (35S:CmJMJ5a-GFP) and control vector (35S:GFP) were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101. The fusion expression vectors were transformed into tobacco (N. benthamiana) leaves for agroinfiltration as described previously [65]. The GFP fluorescence was visualized by a Nikon AX/AX R Confocal Microscope System. DAPI (40-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) was used to stain the nuclei.
Availability of data and materials
Raw reads for RNA-Seq were downloaded from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) under accession number PRJNA803327 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/view/PRJNA803327) and PRJNA543288 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/view/PRJNA543288). The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akimoto K, Katakami H, Kim HJ, Ogawa E, Sano CM, Wada Y, Sano H. Epigenetic inheritance in rice plants. Ann Bot. 2007;100(2):205–17.
Allis CD, Jenuwein T. The molecular hallmarks of epigenetic control. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(8):487–500.
Ziegler-Birling C, Daujat S, Schneider R, Torres-Padilla ME. Dynamics of histone h3 acetylation in the nucleosome core during mouse preimplantation development. Epigenetics. 2016;11(8):553–62.
Dudakovic A, Camilleri ET, Xu F, Riester SM, McGee-Lawrence ME, Bradley EW, Paradise CR, Lewallen EA, Thaler R, Deyle DR, et al. Epigenetic control of skeletal development by the histone methyltransferase ezh2. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(46):27604–17.
Huang F, Ramakrishnan S, Pokhrel S, Pflueger C, Parnell TJ, Kasten MM, Currie SL, Bhachech N, Horikoshi M, Graves BJ, et al. Interaction of the jhd2 histone H3 lys-4 demethylase with chromatin is controlled by histone H2A surfaces and restricted by H2B ubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(48):28760–77.
Dowling JE, Wald G. "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America." Nutr Rev. 1981;39(3):135–8.
Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447(7143):407–12.
Jayani RS, Ramanujam PL, Galande S. Studying histone modifications and their genomic functions by employing chromatin immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. Methods Cell Biol. 2010;98:35–56.
Stricker SH, Köferle A, Beck S. From profiles to function in epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18(1):51–66.
Klose RJ, Zhang Y. Regulation of histone methylation by demethylimination and demethylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(4):307–18.
Liu C, Lu F, Cui X, Cao X. Histone methylation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:395–420.
Qian S, Wang Y, Ma H. Expansion and functional divergence of Jumonji C-containing histone demethylases: significance of duplications in ancestral angiosperms and vertebrates. Plant Physiol. 2015;168(4):1321–37.
Holla S, Prakhar P, Singh V, Karnam A, Mukherjee T, Mahadik K, Parikh P, Singh A, Rajmani RS, Ramachandra SG, et al. Musashi-mediated expression of JMJD3, a H3K27me3 demethylase, is involved in foamy macrophage generation during mycobacterial infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(8): e1005814.
Liu P, Zhang S. The Histone H3K4 Demethylase JMJ16 represses leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2019;31(2):430–43.
Yang H, Mo H, Fan D, Cao Y, Cui S, Ma L. Overexpression of a histone H3K4 demethylase, JMJ15, accelerates flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2012;31(7):1297–308.
Zheng S, Hu H, Ren H, Yang Z, Qiu Q, Qi W, Liu X, Chen X, Cui X, Li S, et al. The Arabidopsis H3K27me3 demethylase JUMONJI 13 is a temperature and photoperiod dependent flowering repressor. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1303.
Cho JN, Ryu JY, Jeong YM, Park J, Song JJ, Amasino RM, Noh B, Noh YS. Control of seed germination by light-induced histone arginine demethylation activity. Dev Cell. 2012;22(4):736–48.
Cheng K, Xu Y, Yang C, Ouellette L, Niu L, Zhou X, Chu L, Zhuang F, Liu J, Wu H, et al. Histone tales: lysine methylation, a protagonist in Arabidopsis development. J Exp Bot. 2020;71(3):793–807.
Accari SL, Fisher PR. Emerging Roles of JmjC domain-containing proteins. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015;319:165–220.
Lu F, Li G, Cui X, Liu C, Wang XJ, Cao X. Comparative analysis of JmjC domain-containing proteins reveals the potential histone demethylases in Arabidopsis and rice. J Integr Plant Biol. 2008;50(7):886–96.
Qian Y, Chen C, Jiang L, Zhang J, Ren Q. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase gene family in maize. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):256.
Xu J, Xu H, Liu Y, Wang X, Xu Q, Deng X. Genome-wide identification of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) histone modification gene families and their expression analysis during the fruit development and fruit-blue mold infection process. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:607.
Chowrasia S, Panda AK, Rawal HC, Kaur H, Mondal TK. Identification of jumonjiC domain containing gene family among the Oryza species and their expression analysis in FL478, a salt tolerant rice genotype. Plant physiology and biochemistry : PPB. 2018;130:43–53.
Sun Z, Wang X, Qiao K, Fan S, Ma Q. Genome-wide analysis of JMJ-C histone demethylase family involved in salt-tolerance in Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant physiology and biochemistry : PPB. 2021;158:420–33.
Li Z, Jiang G, Liu X. Histone demethylase SlJMJ6 promotes fruit ripening by removing H3K27 methylation of ripening-related genes in tomato. New Phytol. 2020;227(4):1138–56.
Wang J, Jiang X, Bai H, Liu C. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase gene family in Jatropha curcas L. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):6543.
Tahiliani M, Mei P, Fang R, Leonor T, Rutenberg M, Shimizu F, Li J, Rao A, Shi Y. The histone H3K4 demethylase SMCX links REST target genes to X-linked mental retardation. Nature. 2007;447(7144):601–5.
Liu C, Cheng J, Zhuang Y, Ye L, Li Z, Wang Y, Qi M, Xu L, Zhang Y. Polycomb repressive complex 2 attenuates ABA-induced senescence in Arabidopsis. The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology. 2019;97(2):368–77.
Yang H, Han Z, Cao Y, Fan D, Li H, Mo H, Feng Y, Liu L, Wang Z, Yue Y, et al. A companion cell-dominant and developmentally regulated H3K4 demethylase controls flowering time in Arabidopsis via the repression of FLC expression. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(4): e1002664.
Klose RJ, Kallin EM, Zhang Y. JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(9):715–27.
Yamane K, Toumazou C, Tsukada Y, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Wong J, Zhang Y. JHDM2A, a JmjC-containing H3K9 demethylase, facilitates transcription activation by androgen receptor. Cell. 2006;125(3):483–95.
Allis CD, Berger SL, Cote J, Dent S, Jenuwien T, Kouzarides T, Pillus L, Reinberg D, Shi Y, Shiekhattar R, et al. New nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes. Cell. 2007;131(4):633–6.
Jones MA, Morohashi K, Grotewold E, Harmer SL. Arabidopsis JMJD5/JMJ30 acts independently of LUX ARRHYTHMO within the plant circadian clock to enable temperature compensation. Front Plant Sci. 2019;10:57.
Dutta A, Choudhary P, Caruana J, Raina R. JMJ27, an Arabidopsis H3K9 histone demethylase, modulates defense against Pseudomonas syringae and flowering time. The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology. 2017;91(6):1015–28.
Gan ES, Xu Y, Wong JY, Goh JG, Sun B, Wee WY, Huang J, Ito T. Jumonji demethylases moderate precocious flowering at elevated temperature via regulation of FLC in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5098.
Wu J, Yamaguchi N. Histone demethylases control root elongation in response to stress-signaling hormone abscisic acid. Plant Signal Behavior. 2019;14(7):1604019.
Lee K, Park OS, Seo PJ. JMJ30-mediated demethylation of H3K9me3 drives tissue identity changes to promote callus formation in Arabidopsis. The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology. 2018;95(6):961–75.
Wang Q, Liu P, Jing H, Zhou XF, Zhao B, Li Y, Jin JB. JMJ27-mediated histone H3K9 demethylation positively regulates drought-stress responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2021;232(1):221–36.
Sun Q, Zhou DX. Rice jmjC domain-containing gene JMJ706 encodes H3K9 demethylase required for floral organ development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(36):13679–84.
Song T, Zhang Q, Wang H, Han J, Xu Z, Yan S, Zhu Z. OsJMJ703, a rice histone demethylase gene, plays key roles in plant development and responds to drought stress. Plant physiology and biochemistry : PPB. 2018;132:183–8.
Shen Y, Wu X, Liu D, Song S, Liu D, Wang H. Cold-dependent alternative splicing of a Jumonji C domain-containing gene MtJMJC5 in Medicago truncatula. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;474(2):271–6.
Ding X, Liu X. SlJMJ7 orchestrates tomato fruit ripening via crosstalk between H3K4me3 and DML2-mediated DNA demethylation. New Phytol. 2022;233(3):1202–19.
Zeng J, Jiang G, Liang H, Yan H, Kong X, Duan X, Li Z. Histone demethylase MaJMJ15 is involved in the regulation of postharvest banana fruit ripening. Food Chem. 2023;407: 135102.
Cheng YZ, He GQ, Yang SD, Ma SH, Ma JP, Shang FH, Li XF, Jin HY, Guo DL. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of JmjC domain-containing genes in grape under MTA treatment. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022;22(5):783–95.
Zong W, Zhong X, You J, Xiong L. Genome-wide profiling of histone H3K4-tri-methylation and gene expression in rice under drought stress. Plant Mol Biol. 2013;81(1–2):175–88.
Berr A, Shafiq S, Shen WH. Histone modifications in transcriptional activation during plant development. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2011;1809(10):567–76.
Zeng J. Comprehensive analysis of jumonji domain C family from Citrus grandis and expression profilings in the exocarps of “Huajuhong” (Citrus grandis “Tomentosa”) during various development stages. Horticulturae. 2021;7:592.
Shi W, Li Z, Dong K, Ge B, Lu C, Chen Y. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase gene family in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). S Afr J Bot. 2023;157:335–45.
Dong Y, Lu J, Liu J, Jalal A, Wang C. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of JmjC domain-containing genes in flower development of Rosa chinensi. Plant Mol Biol. 2020;102(4–5):417–30.
Staiger D, Brown JW. Alternative splicing at the intersection of biological timing, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell. 2013;25(10):3640–56.
Zhang S, Zhou B, Kang Y, Cui X, Liu A, Deleris A, Greenberg MV, Cui X, Qiu Q, Lu F. C-terminal domains of a histone demethylase interact with a pair of transcription factors and mediate specific chromatin association. Cell Discovery. 2015;1:15003.
Li D, Liu R. JMJ14 encoded H3K4 demethylase modulates immune responses by regulating defence gene expression and pipecolic acid levels. New Phytol. 2020;225(5):2108–21.
Shang FH, Liu HN, Wan YT, Yu YH, Guo DL. Identification of grape H3K4 genes and their expression profiles during grape fruit ripening and postharvest ROS treatment. Genomics. 2021;113(6):3793–803.
Wang X, Pan L, Wang Y, Meng J, Deng L, Niu L, et al. PpIAA1 and PpERF4 form a positive feedback loop to regulate peach fruit ripening by integrating auxin and ethylene signals. Plant science : an international journal of experimental plant biology. 2021;313:111084.
Liu R, How-Kit A, Stammitti L, Teyssier E, Rolin D, Mortain-Bertrand A, Halle S, Liu M, Kong J, Wu C, et al. A DEMETER-like DNA demethylase governs tomato fruit ripening. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:10804–9.
Lang Z, Wang Y, Tang K, Tang D, Datsenka T, Cheng J, Zhang Y, Handa AK, Zhu J-K. Critical roles of DNA demethylation in the activation of ripening-induced genes and inhibition of ripening-repressed genes in tomato fruit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:E4511–9.
Eddy S, Sonnhammer ELL, Howe DK, et al. The Pfam protein families database[J]. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):263–6.
Aron MB, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales NR, et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database[J]. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;D1:D222.
Mitchell A, Chang HY, Daugherty L, et al. The InterPro protein families database: The classification resource after 15 years[J]. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;43:D213–21.
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(13):3784–8.
Saitou N. The neighbor-joining method : a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4:406–25.
Sudhir K, Glen S, Koichiro T. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 70 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–4.
Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW. MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Research. 2006;34:W369–73.
Lescot M. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences[J]. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(1):325–7.
Walter M, Chaban C, Schütze K, Batistic O, Weckermann K, Näke C, Blazevic D, Grefen C, Schumacher K, Oecking C, et al. Visualization of protein interactions in living plant cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. The Plant journal : for cell and molecular biology. 2004;40(3):428–38.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32202513 and 31860563), the Applied Technology Research and Development Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2021PT0001), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2021BS03002), and the Inner Mongolia University High-Level Talent Research Program (10000–21311201/056). The work was also supported by the Key Laboratory of Herbage and Endemic Crop Biotechnology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Agula Hasi and Gen Che supervised the work and acquired funding. Wuyun Jin designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Wei Yan performed the bioinformatic analyses. Ming Ma performed RT-qPCR validation. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The plant material in this study does not involve endangered or protected species, and the collection and experimentation of plant material in this study complies with institutional, national and international guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primer sequence and application
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, W., Yan, W., Ma, M. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the JMJ-C gene family in melon (Cucumis melo L.) reveals their potential role in fruit development. BMC Genomics 24, 771 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09868-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09868-3